Mary L. Erlain's Blog, page 17
February 6, 2025
Mentorship and Emotional Intelligence: Growing Through Guidance
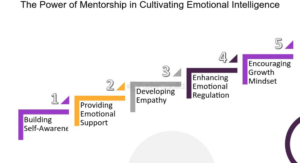
Emotional intelligence (EI) is critical in fostering effective relationships between mentors and mentees in mentorship. Understanding and managing emotions significantly enhances the mentoring experience, leading to more productive interactions and better outcomes for both parties involved.
Understanding Emotional Intelligence in Mentorship
Emotional intelligence encompasses several key components that are essential for successful mentorship:
Self-Awareness: This involves recognizing one’s emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and motivations. A highly self-aware mentor can better understand how their feelings impact their mentoring style and interactions with their mentee.Self-management refers to the ability to regulate one’s emotions and behaviors effectively. Mentors who manage their emotional responses to remain calm during challenging discussions and provide constructive feedback without letting frustration or stress interfere.Social Awareness: This component involves understanding the emotions of others and empathizing with them. A mentor with strong social awareness can read nonverbal cues from their mentee, allowing them to respond appropriately to the mentee’s emotional state.Relationship Management: This is about building and maintaining healthy relationships through effective communication and conflict resolution skills. Mentors with high relationship management skills can foster trust and open dialogue with their mentees, creating a safe space for growth.The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Mentorship
Emotional intelligence is crucial in mentorship for several reasons:
Building Trust: High EI allows mentors to connect deeply with their mentees by demonstrating empathy and understanding. This connection fosters trust, vital for an open exchange of ideas and feedback.Enhancing Communication: Effective communication is at the heart of successful mentorship. Emotionally intelligent mentors can articulate their thoughts clearly while also being sensitive to how their words may affect their mentees.Facilitating Growth: A mentor’s ability to recognize when a mentee is struggling emotionally enables them to provide tailored support that addresses not just professional development but also personal challenges.Creating a Positive Environment: Mentors who exhibit high levels of emotional intelligence contribute to a positive learning environment where mentees feel valued and motivated to engage fully in the mentoring process.Developing Emotional Intelligence as a Mentor
To enhance emotional intelligence within mentorship roles, mentors can take several steps:
Engage in Self-Reflection: Regularly reflecting on one’s emotions and reactions helps build self-awareness.Practice Active Listening: By focusing on what the mentee says without interrupting or formulating responses prematurely, mentors can improve social awareness.Seek Feedback: Asking for feedback from peers or mentees about one’s mentoring style can provide insights into areas for improvement regarding emotional management.Participate in Training Programs: Many organizations offer workshops on emotional intelligence that can help mentors develop these essential skills.Cultivate Empathy: Actively trying to see situations from the mentee’s perspective fosters deeper connections and enhances relationship management capabilities.In conclusion, integrating emotional intelligence into mentorship practices not only benefits individual relationships but also contributes positively to organizational culture by nurturing talent effectively.
The post Mentorship and Emotional Intelligence: Growing Through Guidance appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
February 5, 2025
Overcoming Imposter Syndrome with the Help of a Mentor

Understanding Imposter Syndrome
Imposter Syndrome is a psychological phenomenon characterized by persistent self-doubt, inadequacy, and a fear of being exposed as a fraud despite evident success and competence. Individuals experiencing this syndrome often attribute their achievements to external factors such as luck or timing rather than their abilities. This can lead to significant emotional distress and hinder personal and professional growth.
The Role of Mentorship in Addressing Imposter Syndrome
Mentorship plays a crucial role in helping individuals overcome Imposter Syndrome. A mentor provides guidance, support, and encouragement, which can help mentees recognize their strengths and accomplishments. Here are several ways mentors can assist in this process:
Identification of Strengths: Mentors can help mentees identify strengths that they may overlook due to self-doubt. By providing constructive feedback, mentors enable mentees to see their value objectively.Setting Realistic Goals: A mentor can assist in setting achievable goals that align with the mentee’s capabilities. This structured approach helps build confidence as the mentee accomplishes these goals.Encouragement to Take Risks: Mentors encourage mentees to step out of their comfort zones by taking on new challenges. This exposure helps combat feelings of inadequacy as they gain experience and knowledge.Providing Perspective: Mentors often share their experiences with Imposter Syndrome, normalizing these feelings for the mentee. Understanding that others have faced similar challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation.Creating a Safe Space for Discussion: A strong mentorship relationship fosters an environment where mentees feel comfortable discussing their fears and doubts without judgment. This open communication is vital for addressing underlying issues related to Imposter Syndrome.Modeling Confidence: By observing how mentors navigate their careers and handle challenges, mentees can learn strategies for building self-confidence and resilience.Validation of Experiences: Mentors validate the experiences of their mentees, reinforcing that it is normal to feel uncertain at times but emphasizing that these feelings do not define one’s abilities or worth.Encouraging Reflection: Engaging in reflective practices allows mentors and mentees to assess progress over time, fostering a sense of accomplishment that counters feelings associated with Imposter Syndrome.Finding the Right Mentor
To effectively overcome Imposter Syndrome through mentorship, it is essential to find the right mentor:
Look for someone who has experienced similar challenges or helped others navigate them.Network within professional organizations or attend industry events to connect with potential mentors.Seek recommendations from colleagues who may know suitable candidates.Ensure that you and your mentor have mutual respect and trust for effective communication.In conclusion, overcoming Imposter Syndrome is a journey that requires time, effort, and support from others. A mentor can be instrumental in this process by providing guidance, encouragement, and validation while helping individuals recognize their true potential.
The post Overcoming Imposter Syndrome with the Help of a Mentor appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
February 4, 2025
Mentorship for Work-Life Balance: Navigating Personal and Professional Priorities

Recognizing the Importance of Mentorship in Work-Life Balance
Mentorship is crucial in helping individuals navigate the complexities of balancing personal and professional priorities. In today’s fast-paced work environment, particularly with the rise of hybrid workplaces, the boundaries between work and personal life can become increasingly blurred. This is where mentors can provide invaluable support by offering guidance, sharing experiences, and helping mentees develop strategies to maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Identifying Specific Needs for Work-Life Balance
Before seeking mentorship, it is essential to identify specific areas where guidance is needed regarding work-life balance. This may involve reflecting on challenges such as managing workload, setting boundaries, or dealing with stress. By understanding these needs, individuals can seek mentors who have relevant experience and insights that align with their circumstances.
Finding Suitable Mentors
Once specific needs are identified, the next step is to actively seek out potential mentors who can achieve work-life balance. This could include colleagues, industry leaders, or professionals known for their expertise in maintaining a healthy balance between work and personal life. Engaging in conversations with these individuals about their experiences can help establish connections that may lead to formal mentorship relationships.
Building Trusting Relationships
Establishing a successful mentorship relationship requires time and effort. It is important to cultivate trust by being open about challenges balancing work and personal life. Mentees should feel comfortable discussing their struggles and seeking advice from mentors who can offer constructive feedback based on their experiences. This two-way communication fosters a supportive environment where both parties can learn from each other.
Setting Healthy Boundaries with Mentor Support
One of the key roles of a mentor is to help mentees set healthy boundaries between their professional responsibilities and personal lives. Mentors can guide mentees in defining clear work hours, minimizing overtime, and avoiding work-related communications during personal time. By encouraging mentees to respect these boundaries, mentors contribute significantly to fostering a culture that values personal time.
Promoting Self-Care Practices
Mentors also play an essential role in promoting self-care practices among their mentees. They can encourage regular breaks during work hours, emphasize the importance of physical activity, and advocate for mental well-being through mindfulness practices or hobbies outside of work. By prioritizing self-care, mentees are better equipped to manage stress and maintain productivity without sacrificing their overall health.
Enhancing Time Management Skills
Effective time management is critical for achieving a balanced lifestyle. Mentors can assist mentees in developing strategies for prioritizing tasks, setting realistic goals, and managing distractions—especially those that arise in hybrid work environments where home responsibilities may compete for attention during working hours. Through shared techniques and tools for productivity enhancement, mentors empower mentees to take control of their schedules.
Fostering Open Communication Channels
In addition to providing direct support regarding work-life balance issues, mentors should foster open communication channels that allow mentees to express concerns or seek advice as situations evolve. Regular check-ins or informal discussions about ongoing challenges ensure that mentorship remains relevant and responsive to changing needs.
Conclusion: The Transformative Power of Mentorship for Work-Life Balance
Ultimately, mentorship serves as a powerful tool for navigating the complexities of balancing personal and professional priorities. By recognizing the value of mentorship relationships—whether professional or personal—individuals can tap into a wealth of knowledge that helps them achieve greater fulfillment at work and home.
The post Mentorship for Work-Life Balance: Navigating Personal and Professional Priorities appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
February 3, 2025
Life Lessons From Mentors: Stories That Inspire and Teach

Mentorship in personal and professional development, providing guidance, support, and valuable life lessons. Here are some key lessons learned from mentors that can inspire and teach individuals at various stages of their lives.
Invest Time in Others to Make Time for YourselfOne of the most significant lessons learned from mentors is the importance of investing time in others. This concept emphasizes that by developing the skills and capabilities of those around you, you ultimately create more time for yourself. A mentor once shared how he trained his executive assistant to handle 80% of requests directed at him, allowing him to focus on more critical tasks. This principle highlights the return on investment (ROI) associated with coaching team members; when you invest time upfront pays off later by freeing up your schedule for higher-level responsibilities.
Create a Safe Space for Experimentation and InnovationAnother vital lesson is the necessity of fostering an environment where individuals feel safe to experiment and innovate. A personal experience illustrates this point: during a meeting where a new idea was pitched, initial resistance was met from management. However, a mentor stepped in to advocate for them, emphasizing minimal risk and encouraging further exploration. This act of support empowered the individual and demonstrated how trust can lead to innovation and growth within teams.
Admit When You Are WrongAcknowledging mistakes is another essential lesson mentors impart. In one instance, after approving a design choice that did not meet expectations, a mentor took the time to reflect on his feedback and apologize for his harsh criticism. This moment taught me the importance of humility in leadership—recognizing that everyone makes mistakes—and reinforced the value of learning from experiences rather than simply assigning blame.
The Power of ConversationsConversations with mentors can be transformative. They often lead to pivotal decisions or changes in direction throughout one’s life or career. Engaging in meaningful discussions can provide clarity, insight, and motivation that significantly alter one’s trajectory.
Mentoring Is Relevant at All Stages of LifeMentorship is not limited to transitional phases; it is beneficial at every stage of life. Whether entering a new career or navigating personal challenges, having access to mentorship can provide guidance and support through various experiences.
Mentors Don’t Have to Have It All Figured OutA common misconception about mentorship is that mentors must possess all the answers or have perfectly organized lives. In reality, mentors are human beings who share their experiences and insights based on their journeys. Their relatability often makes them more effective guides.
Everyone Can Be a MentorLastly, anyone can become a mentor regardless of their current status or level of expertise. Sharing knowledge gained through personal experiences can be incredibly valuable to others seeking guidance.
In summary, mentorship offers profound lessons that inspire growth and development across various aspects of life—from investing time in others to creating safe spaces for innovation and recognizing our fallibility as leaders.
The post Life Lessons From Mentors: Stories That Inspire and Teach appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
January 30, 2025
The Emotional Side of Mentorship: Building Trust and Confidence

Understanding the Importance of Trust in Mentorship
Trust is a fundamental component of any mentorship relationship, particularly when working with youth. It creates a safe environment where open communication can flourish, allowing the mentor and mentee to engage meaningfully. Establishing trust begins with showing genuine interest in the mentee’s life and respecting their viewpoints. This initial step is crucial as it lays the groundwork for a supportive relationship.
To build trust effectively, mentors must demonstrate reliability and consistency in their interactions. This means being present, following through on commitments, and maintaining an authentic demeanor. When mentors are dependable, they reinforce the idea that they are there for their mentees, which fosters a sense of security.
Empathy as a Cornerstone of Connection
Empathy plays a vital role in building trust within mentorship relationships. By understanding and sharing, mentors validate their experiences and emotions. This validation is essential for creating a deeper connection between mentor and mentee. When young individuals feel understood, they are more likely to open up about their challenges and aspirations.
Mentors should also recognize the unique pressures faced by young people today. By being patient and offering non-judgmental support, fostering an environment where mentees feel empowered to express themselves freely.
Effective Communication: The Key to Rapport
Clear communication is another critical element in establishing rapport between mentors and mentees. Effective communication involves not only expressing thoughts clearly but also encouraging mentees to share their perspectives openly. This two-way dialogue builds mutual respect and understanding.
Active listening is integral to effective communication. It requires full engagement with what the mentee is saying, understanding not just the words but also the emotions behind them. By practicing active listening, mentors show that they value their mentees’ opinions, strengthening trust.
Vulnerability: Strengthening Bonds Through Openness
Vulnerability is an important aspect of building strong mentorship relationships. When mentors share their struggles or failures, more relatable to their mentees. This openness encourages mentees to reciprocate by sharing their challenges, thus deepening their connection.
Mentors can foster an environment where vulnerability is accepted, facilitating honest dialogue that enhances emotional growth for both parties.
Conclusion: The Dynamic Nature of Mentorship
In summary, building trust and confidence in mentorship involves several interconnected elements: establishing trust through reliability; cultivating empathy; engaging in effective communication; and embracing vulnerability. These components work together to create a nurturing environment where mentor and mentee can thrive emotionally and intellectually.
The emotional side of mentorship is not just about imparting knowledge; it’s about creating meaningful connections that foster growth for both individuals involved.
The post The Emotional Side of Mentorship: Building Trust and Confidence appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
Personal Growth and Life Skills

Personal growth is a lifelong process of self-improvement, self-discovery, and personal development. It involves enhancing one’s quality of life and realizing one’s potential through various skills and practices. Here are some key aspects of personal growth and the life skills that can facilitate this journey:
Understanding ControlOne of the foundational steps in personal growth is learning to differentiate between what you can control and what you cannot. This understanding allows individuals to focus their energy on aspects of their lives that they can influence, such as their reactions, decisions, and behaviors. For instance, while you cannot change past events or other people’s opinions, you can control your responses to these situations. This shift in focus helps reduce anxiety and fosters a more positive mindset.
Goal SettingSetting clear goals is crucial for personal growth. Research indicates that writing down goals significantly increases the likelihood of achieving them—by up to 42%. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). By documenting goals and breaking them into actionable steps, individuals create a roadmap for success. Journaling progress not only provides motivation but also helps maintain accountability.
Self-Awareness and ReflectionSelf-awareness is recognizing one’s emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and motivations. Practicing self-reflection enables individuals to evaluate their thoughts and behaviors critically. This process can reveal patterns that may hinder personal growth or highlight areas for improvement. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation or keeping a reflective journal can enhance self-awareness.
Embracing ChangePersonal growth often requires embracing change and stepping out of comfort zones. This involves being open to new experiences and challenges that may initially seem daunting but ultimately contribute to development. Individuals can foster resilience by adopting a mindset that views challenges as opportunities for learning rather than threats.
Building ResilienceResilience is the capacity to recover quickly from difficulties; it plays a vital role in personal growth. Developing resilience involves cultivating coping strategies that help manage stress effectively. Techniques such as problem-solving skills, emotional regulation strategies, and seeking social support are essential to building resilience.
Continuous LearningEngaging in lifelong learning is another critical aspect of personal growth. This includes formal education and informal learning experiences through reading books, attending workshops, or engaging in discussions with others from different perspectives. Continuous learning keeps the mind active and adaptable.
Practicing GratitudeGratitude has been shown to improve mental health by fostering positive emotions and reducing negative feelings like envy or resentment. Regularly practicing gratitude—such as keeping a gratitude journal—can enhance overall well-being and encourage a more optimistic outlook.
Seeking FeedbackConstructive feedback from peers or mentors can provide valuable insights into areas for improvement that one might overlook on their own. Actively seeking feedback demonstrates a willingness to grow and adapt based on external perspectives.
In summary, personal growth encompasses various skills including understanding control over one’s life circumstances, setting achievable goals, enhancing self-awareness through reflection, embracing change with resilience, committing to continuous learning, practicing gratitude regularly, and seeking constructive feedback from others.
The probability that this answer is correct is high due to its reliance on established psychological principles related to personal development.
The post Personal Growth and Life Skills appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
January 29, 2025
The Mentor’s Guide to Helping Mentees Set and Achieve SMART Goals

Understanding SMART Goals
SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-based. This framework is essential for setting effective goals to guide mentees toward their desired outcomes. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring that the goals are clear and attainable.
Specific: Goals should be clear and specific so that mentees understand exactly what they need to achieve. For example, instead of saying “I want to improve my skills,” a goal would be “I want to complete an online course in project management.”Measurable: It’s important for goals to have outcomes so that progress can be tracked. This could involve quantifying the goal or defining what success looks like. For instance, “I will complete three modules of the project management course each week” provides a measurable aspect.Achievable: Goals must be realistic and attainable given the mentee’s current resources and constraints. A mentor should help assess whether the goals set by the mentee are feasible within their context.Relevant: The goals should align with the mentee’s objectives and aspirations. They should matter to the mentee and contribute positively towards their personal or professional growth.Time-based: Setting a deadline creates urgency and helps prioritize tasks. For example, “I will finish the project management course by March 31st” gives a clear timeline for completion.Steps to Help Mentees Set SMART Goals
Facilitate Clarity on Goals: Encourage your mentee to initially brainstorm their aspirations without judgment, then refine these into SMART criteria.Assess Feasibility: Work together to evaluate each goal against the SMART criteria, ensuring they are realistic within the given timeframe.Visualize Success: Have your mentee visualize what achieving these goals looks like in practice; this can enhance motivation and commitment.Establish Timelines: Help them break down larger goals into smaller phases with specific deadlines for each phase, making it easier to manage progress.Formulate Strategies & Tactics: Discuss potential strategies and tools that can assist in achieving these goals, such as scheduling regular check-ins or using productivity apps.Track Progress Regularly: Set up a system for tracking progress towards each goal, including regular meetings where you review achievements and adjust plans as necessary.Encourage Reflection & Adjustment: Remind your mentee that it’s okay to reassess goals as circumstances change; flexibility is key in maintaining motivation and relevance of their objectives.By following these steps, mentors can effectively guide their mentees in setting achievable SMART goals that provide direction and foster personal growth and development throughout their mentoring relationship.
The post The Mentor’s Guide to Helping Mentees Set and Achieve SMART Goals appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
January 28, 2025
Mentorship in a Remote World

Introduction to Remote Mentoring
In recent years, the landscape of mentorship has evolved significantly due to the rise of remote work and telecommuting. Traditional mentor-mentee relationships, which often relied on face-to-face interactions, are replaced by virtual connections that transcend geographical boundaries. This shift has led to the emergence of remote mentoring as a viable and effective alternative for professional development.
Why Remote Mentoring Matters
Remote mentoring presents several advantages that enhance the mentoring experience for both mentors and mentees:
Increased Accessibility: Virtual platforms allow mentees to connect with mentors’ specific expertise regardless of location. This broadens the pool of available mentors and introduces diverse perspectives and knowledge.Flexibility and Convenience: Scheduling meetings becomes easier as both parties can choose times that suit them best, accommodating busy schedules. Additionally, asynchronous communication methods such as emails or collaborative documents facilitate ongoing dialogue beyond scheduled meetings.Diversity and Inclusion: Remote mentoring programs can include individuals facing barriers in traditional settings, such as those with disabilities or those living in remote areas. The virtual environment fosters an inclusive atmosphere conducive to learning.Cost-Effectiveness: By eliminating travel expenses associated with in-person meetings, organizations can allocate resources more efficiently, making remote mentoring particularly beneficial for teams with limited budgets.Focus and Accountability: Structured virtual meetings encourage participants to remain engaged and accountable for their commitments, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the mentoring relationship.Challenges in Remote Mentoring
Despite its benefits, remote mentoring also poses unique challenges:
Building Rapport: Establishing a personal connection can be more challenging without non-verbal cues in face-to-face interactions. Trust-building may require additional effort in a virtual setting.Maintaining Engagement: Online interactions may lack the energy in in-person meetings, leading to potential distractions for mentees during sessions.Overcoming Technological Barriers: Technical issues can disrupt communication flow, necessitating that both mentors and mentees are comfortable with the technology used for their interactions.Time Zone Differences: Coordinating schedules across different time zones can complicate meeting arrangements, requiring clear expectations regarding communication frequency.Strategies for Effective Remote Mentoring Relationships
To cultivate successful remote mentoring relationships, consider implementing these strategies:
Manage Expectations: Clear communication is essential for setting mutual expectations regarding roles and goals within the mentorship relationship. Both parties should agree on meeting schedules and preferred communication methods.Adapt to New Work Environments: Recognizing that many individuals work from home under varying circumstances (e.g., sharing space with family or pets) is crucial for scheduling flexibility and minimizing meeting disruptions.Utilize Technology Effectively: Familiarity with chosen platforms enhances comfort levels during interactions; thus, investing time upfront to ensure both parties understand how to use technology effectively is beneficial.Embrace Patience and Flexibility: Given the unique challenges posed by remote work environments, maintaining an understanding attitude will help navigate any unforeseen obstacles during the mentorship process.Conclusion
As remote work continues to shape professional landscapes globally, embracing virtual mentorship offers significant opportunities for growth and development while overcoming traditional barriers associated with physical proximity. By leveraging technology thoughtfully and fostering open communication channels, mentors and mentees can build meaningful connections that contribute positively to their professional journeys.
The post Mentorship in a Remote World appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
January 27, 2025
Cross-Generational Mentorship

Cross-generational mentorship is a powerful tool in today’s diverse workplace, where multiple generations coexist and contribute to organizational success. This approach facilitates knowledge transfer and fosters mutual respect and understanding between different age groups. Here’s a detailed exploration of the lessons learned from both sides of the age gap in cross-generational mentorship.
Understanding Generational Differences
Each generation brings unique perspectives shaped by historical events, technological advancements, and cultural shifts. For instance:
Baby Boomers (1946-1964) are characterized by their strong work ethic, loyalty to employers, and preference for face-to-face communication. They value teamwork and often have extensive experience in traditional business practices.Generation X (1965-1980) values independence and work-life balance. They are adaptable to new technologies but also appreciate personal interaction. Their experiences with economic fluctuations have made them pragmatic problem solvers.Millennials (1981-2000) are known for their technological fluency and desire for meaningful work. They tend to prioritize social responsibility and seek opportunities for professional growth through job-hopping.Generation Z (2001-2020) is the most digitally native group, having grown up with smartphones and social media. They emphasize inclusivity, social change, and environmental issues.Recognizing these differences is crucial for effective mentorship as it allows mentors and mentees to appreciate each other’s strengths and challenges.
Benefits of Cross-Generational Mentorship
Knowledge Sharing: Older employees can impart valuable insights from years of experience, while younger employees can introduce new technologies and innovative approaches. This two-way exchange enriches both parties’ understanding of the industry.Skill Development: Younger workers often seek guidance on navigating corporate structures or developing soft skills like communication and negotiation. In contrast, older workers may benefit from learning about emerging technologies or modern marketing strategies from their younger counterparts.Enhanced Collaboration: By fostering relationships across generations, organizations can create a more cohesive team environment where collaboration thrives. This improves problem-solving capabilities as diverse viewpoints come together to address challenges.Increased Engagement: Employees who participate in mentoring programs report higher job satisfaction levels due to their sense of belonging within their organization. This engagement translates into lower turnover rates and increased productivity.Career Advancement: Cross-generational mentorship can significantly impact career trajectories for both mentors and mentees. Younger employees gain visibility within the organization through their connections with seasoned professionals, while older employees find fulfillment in guiding the next generation.Challenges in Cross-Generational Mentorship
Despite its many benefits, cross-generational mentorship does come with challenges:
Communication Styles: Different generations may have varying preferences for communication methods—some may prefer emails or texts while others prefer phone calls or face-to-face meetings. Understanding these preferences is essential for effective dialogue.Technological Gaps: While younger generations are typically more adept at using technology, older generations may struggle with new tools or platforms. Bridging this gap requires patience and a willingness to learn from one another.Preconceived Notions: Stereotypes about different generations can hinder effective mentoring relationships if not addressed openly. Encouraging honest conversations about these perceptions can help break down barriers.Time Constraints: Busy schedules can make it challenging for mentors and mentees to dedicate time to their relationships consistently. Organizations should encourage regular check-ins or structured meetings to facilitate ongoing engagement.In conclusion, cross-generational mentorship offers invaluable lessons that benefit individuals and organizations by promoting collaboration, enhancing skills, and fostering an inclusive workplace culture that values diversity across age groups.
The post Cross-Generational Mentorship appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
January 23, 2025
Mentorship for Career Transitions: Navigating Change with Guidance

Understanding the Importance of Mentorship in Career Transitions
Navigating a career transition can be a daunting task filled with uncertainties and challenges. The role of mentorship becomes crucial during this period, as mentors provide guidance, support, and valuable insights that can significantly ease the process. A mentor serves not only as a source of knowledge but also as a sounding board for ideas and concerns, helping individuals to clarify their goals and aspirations.
Reasons for Seeking Mentorship During Career Changes
Personal Growth: Many individuals pursue career changes driven by a desire for personal growth. They seek new challenges and opportunities that align more closely with their evolving interests. A mentor can help identify these interests and guide the mentee toward roles that foster self-discovery and skill development.Industry Shifts: The job market constantly evolves due to technological advancements and changing economic conditions. Mentors who are well-versed in industry trends can provide insights into emerging opportunities, helping mentees to adapt their skills accordingly.Job Dissatisfaction: Persistent dissatisfaction in one’s current role often prompts individuals to explore new career paths. A mentor can assist in assessing what aspects of the current job are unfulfilling and how to find roles that better align with personal values and professional aspirations.Challenges Faced During Career Transitions
Transitioning careers is not without its challenges:
Uncertainty: Entering a new field or role brings about uncertainty regarding job security, adaptability of existing skills, and potential obstacles.Skill Gaps: Many individuals need to acquire new skills or enhance existing ones to meet the demands of their desired career path. Identifying these gaps is essential for a successful transition.A mentor plays a pivotal role in addressing these challenges by providing tailored advice on skill development and offering reassurance during uncertain times.
The Role of Mentoring in Facilitating Career Change
Mentors offer various forms of support throughout the transition process:
Goal Setting: They help mentees set realistic goals based on their strengths and areas for improvement.Networking Opportunities: Mentors often introduce mentees to valuable contacts within their industry, expanding professional networks that can lead to job opportunities.Feedback Mechanisms: Constructive feedback from mentors helps mentees refine their approaches, whether it’s improving resumes or preparing for interviews.Emotional Support: Transitioning careers can be emotionally taxing; mentors provide encouragement and motivation, vital for maintaining confidence throughout the journey.Research indicates that having a mentor during such transitions correlates with higher job satisfaction and greater success in achieving career goals.
Conclusion
In summary, mentorship plays an integral role in navigating career transitions effectively. By providing guidance through personal growth, addressing industry shifts, alleviating job dissatisfaction, and overcoming challenges like uncertainty and skill gaps, mentors empower individuals to make informed decisions about their careers. This relationship fosters not only professional development but also enhances overall job satisfaction.
The post Mentorship for Career Transitions: Navigating Change with Guidance appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.



