Mary L. Erlain's Blog, page 20
November 6, 2024
Understanding Gen Z’s Financial Concerns and Strategies

Generation Z, typically defined as individuals born between 1997 and 2012, is entering adulthood in a complex economic landscape characterized by significant financial challenges. One of the most pressing issues for this generation is student debt. According to the Federal Reserve, as of 2023, student loan debt in the United States has surpassed $1.7 trillion, with the average borrower owing approximately $30,000 upon graduation. This burden can significantly impact their financial stability and ability to achieve long-term goals such as home ownership or retirement savings.
In addition to student debt, Gen Z faces other economic challenges including high living costs, particularly in urban areas where job opportunities are concentrated. The rising cost of housing has outpaced wage growth, leading to increased financial strain on young adults. Furthermore, many members of Gen Z entered the workforce during or after the COVID-19 pandemic, which disrupted job markets and created uncertainty regarding employment opportunities.
Importance of Financial LiteracyGiven these challenges, financial literacy becomes crucial for Gen Z. A survey conducted by the National Endowment for Financial Education (NEFE) found that many young adults feel unprepared to manage their finances effectively. They often lack knowledge about budgeting, saving strategies, and investment options. This gap in financial education can lead to poor decision-making that exacerbates their economic difficulties.
Mentorship in Financial PlanningTo address these concerns, providing mentorship on financial planning is essential. Mentorship can take various forms:
One-on-One Coaching: Pairing Gen Z individuals with experienced mentors who can guide them through personal finance topics tailored to their specific situations.Group Workshops: Organizing workshops that cover essential topics such as budgeting techniques, understanding credit scores, and managing debt effectively.Online Resources: Developing online platforms where Gen Z can access articles, videos, and tools related to personal finance at their convenience. Salary Negotiation SkillsAnother critical area where mentorship can be beneficial is salary negotiation. Many young professionals may not feel confident negotiating their salaries due to a lack of experience or knowledge about industry standards:
Workshops on Negotiation Techniques: Offering training sessions focused on how to research salary benchmarks for specific roles and industries.Role-Playing Scenarios: Engaging participants in mock negotiations to build confidence and skills in real-world situations. Understanding Compensation PackagesUnderstanding compensation packages is vital for making informed career decisions:
Educational Sessions: Providing information about different components of compensation packages beyond just salary—such as benefits (health insurance, retirement plans), bonuses, stock options, and work-life balance considerations.Resource Guides: Creating comprehensive guides that break down common terms used in compensation discussions so that Gen Z can better understand what they are being offered. Personal Finance and Investing WorkshopsFinally, offering resources or workshops focused on personal finance and investing will empower Gen Z to make informed decisions about their money:
Investment Basics: Teaching fundamental concepts such as stocks vs bonds vs mutual funds; risk management; diversification; and the importance of starting early with investments.Budgeting Tools: Introducing tools like budgeting apps or spreadsheets that help track income versus expenses effectively.By implementing these strategies—mentorship programs focusing on financial planning and salary negotiation skills along with educational resources on personal finance—organizations can significantly aid Generation Z in navigating their economic challenges more successfully.
The post Understanding Gen Z’s Financial Concerns and Strategies appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
November 4, 2024
Promoting Financial Literacy and Stability
Understanding Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is the ability to understand and effectively use various financial skills, including budgeting, saving, investing, and managing debt. It serves as a foundation for making informed financial decisions that can lead to greater monetary stability and a higher quality of life. Promoting financial literacy involves educating individuals about these essential skills and concepts, enabling them to take control of their finances.
Key Components of Financial Literacy
Budgeting and Expense ManagementEffective budgeting requires understanding income sources and expenses. Individuals should set realistic financial goals and monitor their spending habits regularly. By mastering budgeting, people can live within their means, avoid unnecessary debt, and save for future objectives.Saving and InvestingSaving involves setting aside money for future needs while investing allows individuals to grow their wealth over time. Understanding the principles of compounding interest and diversification is crucial for maximizing returns on investments.Debt ManagementRecognizing the impact of credit scores on borrowing costs is vital. Individuals should differentiate between good debt (e.g., student loans) that can enhance future earning potential and bad debt (e.g., high-interest credit card debt) that can lead to financial strain.Retirement PlanningKnowledge of retirement savings options such as 401(k)s, pensions, and Social Security benefits is essential for long-term financial health. A comprehensive retirement plan considers expected lifespan, desired lifestyle in retirement, and potential healthcare costs.Insurance and Risk ManagementUnderstanding different insurance products (health, life, auto) helps individuals protect against unforeseen risks. Establishing an emergency fund also plays a critical role in risk management.Understanding Financial ProductsFamiliarity with various financial products—from basic savings accounts to complex investment vehicles—enables individuals to make informed choices aligned with their goals.Strategies for Promoting Financial Literacy
Self-Study and Online ResourcesNumerous online platforms offer courses, articles, podcasts, webinars, and tools related to financial education. Individuals can learn at their own pace by accessing credible resources that cover a wide range of topics.Formal Education ProgramsSchools and universities often provide courses on personal finance or economics that lay the groundwork for financial literacy. Additionally, government initiatives or nonprofit organizations may offer workshops targeting specific demographics.Seeking Professional AdviceEngaging with certified financial advisors or planners can provide personalized guidance tailored to individual circumstances. Professionals help navigate complex decisions regarding investments or retirement planning based on current market trends.Networking and Peer LearningSharing experiences with peers can enhance understanding of financial concepts through discussions about successes or challenges faced in managing finances.Conclusion: The Importance of Financial Literacy for Stability
Promoting financial literacy is crucial not only for individual well-being but also for fostering economic stability within communities at large. By equipping people with the necessary skills to manage their finances effectively, we empower them to make informed decisions that contribute positively to their lives.
The post Promoting Financial Literacy and Stability appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
November 1, 2024
Why Gen Z is Motivated by Clear, Actionable Career Goals

Generation Z, typically defined as individuals born from the mid-to-late 1990s through the early 2010s, has distinct characteristics that shape their approach to work and career development. One of the most significant motivations for this generation is the desire for clear, actionable career goals. This motivation can be attributed to several factors:
Access to Information: Growing up in a digital age, Gen Z has unprecedented access to information about various career paths and job expectations. They are accustomed to researching and understanding what is required for success in different fields. This exposure leads them to seek clarity regarding their career trajectories.Desire for Stability: In light of economic uncertainties, including the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and fluctuating job markets, Gen Z values stability more than previous generations. Clear career goals provide a sense of direction and security in an unpredictable world.Focus on Skill Development: Gen Z places a high value on skill acquisition and personal development. They want to know how they can enhance their skills and what specific steps they need to take to advance within an organization.Work-Life Balance: This generation prioritizes mental health and work-life balance, which influences their career aspirations. They are motivated by roles that allow them to achieve personal fulfillment alongside professional growth.Expectations of Transparency: Transparency in communication regarding promotion criteria and career advancement opportunities is crucial for Gen Z employees. They expect organizations to be open about what it takes to progress within the company, which fosters trust and engagement.Strategy for Organizations
To effectively engage Generation Z employees, organizations must adopt strategies that align with their motivations:
Communicate Career Paths: Organizations should outline potential career paths within the company. This includes detailed descriptions of various roles, responsibilities associated with each position, and progression routes.Define Promotion Criteria: Companies need to establish transparent criteria for promotions that are easily accessible to all employees. This could involve creating documentation or resources that outline what skills or achievements are necessary for advancement.Offer Mentorship Programs: Implementing mentorship programs can significantly benefit Gen Z employees by connecting them with experienced professionals who can guide them in acquiring the necessary skills and experiences needed for advancement.Regular Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing regular feedback sessions allows employees to understand where they stand concerning their goals and what areas they need to improve upon.Skill Development Opportunities: Providing training programs or workshops focused on skill development will empower Gen Z employees by equipping them with the tools they need to succeed in their careers.By implementing these strategies, organizations can create an environment that not only motivates Generation Z but also retains talent by fostering a culture of growth and transparency.
The post Why Gen Z is Motivated by Clear, Actionable Career Goals appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 29, 2024
Transparent About Career Progression
Career transparency, particularly regarding career progression, is essential for attracting and retaining talent in today’s competitive job market. Organizations that prioritize clear communication about career paths and advancement opportunities can significantly enhance employee satisfaction and loyalty.
Understanding Career Transparency
Career transparency refers to the practice of openly sharing information about career development opportunities within an organization. This includes detailing the skills and experiences required for various roles, as well as outlining potential pathways for advancement. By providing this information, companies can help employees make informed decisions about their careers, which is crucial in a candidate’s market where job seekers have numerous options.
The Importance of Career Development Opportunities
According to recent research, the lack of career development and advancement opportunities is one of the primary reasons employees choose to leave their jobs. For instance, findings from McKinsey’s Global Attrition research indicate that missing these opportunities was the number one reason for quitting between April 2021 and April 2022. This highlights the necessity for organizations to establish clear career frameworks that outline potential growth paths.
Benefits of Clear Career Paths
Employee Engagement: When employees understand how they can progress within an organization, they are more likely to feel engaged and satisfied with their work. This engagement leads to higher productivity levels and a more committed workforce.Retention Rates: Companies that communicate transparent career paths are better positioned to retain talent. Employees who see a future within the organization are less likely to seek employment elsewhere, even if they receive offers with higher salaries.Skill Development: Clearly defined career paths encourage employees to develop their skills actively. They understand what competencies are necessary for advancement and can take proactive steps toward acquiring them.Job Satisfaction: Employees who perceive growth opportunities often report higher job satisfaction levels. This satisfaction stems from a sense of purpose and fulfillment derived from aligning personal aspirations with professional goals.Diversity in Hiring: Transparent communication about career opportunities can attract a more diverse pool of candidates. When organizations openly share their commitment to employee development, they signal inclusivity and support for varied backgrounds and experiences.Consequences of Lack of Transparency
Failing to provide clarity around career progression can lead to several negative outcomes:
Increased Turnover: Employees may feel stagnant in their roles without visible pathways for advancement, leading them to seek new opportunities elsewhere.Decreased Morale: A lack of transparency can foster feelings of frustration among employees who may feel undervalued or overlooked.Loss of Talent: High turnover rates not only incur costs associated with recruiting new staff but also result in the loss of valuable institutional knowledge when experienced employees leave.Conclusion
Building a transparent framework around career progression is not just beneficial; it is essential in today’s labor market where candidates have choices. Organizations that invest in clearly communicating growth opportunities will likely see improved retention rates, enhanced employee engagement, and overall better performance.
The post Transparent About Career Progression appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 28, 2024
Understanding Gen Z’s Desire for Ownership and Mentorship

By balancing empowerment with support, organizations can cultivate a productive environment that resonates with Gen Z’s aspirations.
Conclusion: In summary, Generation Z seeks ownership of their contributions while valuing mentorship as a crucial resource for navigating challenges. Organizations should implement strategies that empower them with responsibilities while ensuring guidance is readily available when needed.
The post Understanding Gen Z’s Desire for Ownership and Mentorship appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 25, 2024
Common Job Interview Mistakes and What to Do Instead

Preparation is crucial for a successful interview. To avoid this mistake, thoroughly research the company, its market position, competitors, and key personnel. Understand the job role you are applying for and anticipate potential questions that may arise during the interview. Additionally, plan your route to the interview location to ensure you arrive on time. If it’s a virtual interview, check your technology beforehand to avoid technical issues. Dressing Inappropriately
Your appearance plays a significant role in making a good first impression. Choose an outfit that is clean, well-fitted, and appropriate for the company’s culture. Research the company’s dress code; if unsure, opt for more formal attire than casual wear. Avoid clothing that resembles what you wear on a night out or during leisure time. Talking Too Much or Not Enough
Striking a balance in communication is essential during interviews. Practice answering common questions to ensure you provide enough information without rambling. If you feel nervous or blank out during the interview, take a moment to collect your thoughts before responding or ask for clarification if needed. Criticizing Previous Employers or Colleagues
Speaking negatively about past employers can create a poor impression of your character. Instead of focusing on negative experiences, highlight how you overcame challenges and what you learned from previous roles. This demonstrates professionalism and positivity. Failing to Ask Questions
When asked if you have any questions at the end of an interview, always respond positively by asking relevant inquiries about the role or company. This shows your interest and engagement in the position while also allowing you to gather important information about your potential employer. Arriving Late
Punctuality is critical in interviews; being late can reflect poorly on your reliability and enthusiasm for the position. Plan by determining how long it will take to get there and consider alternative routes in case of unexpected delays. Badmouthing Current or Previous Employers
Avoid discussing conflicts with former employers as it may lead interviewers to question your ability to work collaboratively in their organization. Maintain diplomacy when discussing past employment experiences. Waffling During Responses
If faced with an unexpected question, instead of waffling or guessing an answer, take a moment to think before responding or asking for clarification on the question itself. Displaying Negative Body Language or Attitude
Be mindful of your body language throughout the interview; negative cues such as slouching or yawning can signal disinterest. Maintain eye contact and exhibit positive gestures like smiling and nodding. Asking Irrelevant Questions Prepare thoughtful questions ahead of time that reflect your understanding of the company and role rather than basic inquiries that could be answered through research.
By avoiding these common mistakes and implementing effective strategies instead, candidates can significantly improve their chances of success in job interviews.
The post Common Job Interview Mistakes and What to Do Instead appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 24, 2024
Offer Autonomy with Guidance
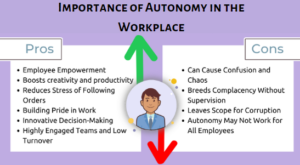
Understanding the Importance of Autonomy in the Workplace
Autonomy in the workplace refers to the degree of freedom employees have to decide how they perform their work. It is essential for fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among team members. When employees are given autonomy, they are more likely to feel trusted and valued, increasing job satisfaction, motivation, and overall productivity. However, while autonomy is crucial, it must be balanced with appropriate guidance from management.
The Need for Guidance Alongside Autonomy
While autonomy empowers employees, it is equally important to provide them with guidance to ensure that their efforts align with organizational goals. Without sufficient direction, employees may become confused about priorities or miss critical objectives. Therefore, leaders must find a balance between allowing freedom and providing necessary oversight.
Set Clear Expectations: Establishing clear and measurable goals helps employees understand what is expected of them. This clarity allows them to take initiative while ensuring that their actions contribute to broader organizational objectives.Provide Resources and Training: Equipping employees with the right tools and training ensures they have the skills needed to succeed autonomously. Regular assessments can help identify gaps in resources or knowledge.Encourage Open Communication: Fostering an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas and asking questions promotes trust and collaboration. Regular check-ins can facilitate this communication without infringing on autonomy.Delegate Effectively: Leaders should delegate tasks based on individual strengths while allowing team members the freedom to approach these tasks in their way. This builds confidence and accountability.Create a Culture of Accountability: Encouraging employees to take responsibility for their work fosters a sense of ownership. Recognizing those who demonstrate accountability reinforces this culture.Offer Constructive Feedback: Providing regular feedback helps employees understand how they can improve while also recognizing their successes. This feedback should focus on behaviors and outcomes rather than personal attributes.Support Risk-Taking and Innovation: Encouraging calculated risks allows employees to explore new ideas without fear of failure, promoting creativity within the organization.Lead by Example: Managers should model the behaviors they wish to see in their teams by demonstrating accountability, transparency, and a willingness to learn from mistakes.Maintain Oversight Without Micromanaging: While it’s important for leaders to monitor progress, they should avoid micromanagement by trusting employees to execute tasks independently while offering support when needed.Recognize and Celebrate Successes: Acknowledging achievements boosts morale and reinforces positive behaviors within the team.Conclusion: Striking the Right Balance
In conclusion, offering autonomy with guidance requires a thoughtful approach that combines clear expectations with supportive leadership practices. By empowering employees while providing necessary direction, organizations can cultivate an engaged workforce that drives innovation and achieves strategic goals.
The post Offer Autonomy with Guidance appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 23, 2024
Understanding the Need for Soft Skills Development in Gen Z

The post Understanding the Need for Soft Skills Development in Gen Z appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 22, 2024
Teaching Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence
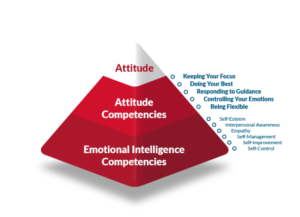
Understanding the Importance of Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence
Soft skills, often called interpersonal or people skills, encompass a range of abilities that facilitate effective communication, collaboration, and problem-solving in various contexts. Emotional intelligence (EI) is a critical component of soft skills, defined as the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions while also being attuned to the feelings of others. The significance of these skills in both personal and professional environments cannot be overstated; they are essential for fostering positive relationships, enhancing teamwork, and driving organizational success.
Identifying Key Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence Competencies
To effectively teach soft skills and emotional intelligence, it is crucial first to identify the specific competencies that fall under these categories. Some key soft skills include:
Communication: The ability to convey information clearly and listen actively.Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with others toward common goals.Adaptability: Adjusting to new challenges and environments with ease.Problem-Solving: Identifying issues and implementing effective solutions.Leadership: Inspiring and guiding individuals or teams.Emotional intelligence competencies include:
Self-Awareness: Understanding one’s own emotions and their impact on behavior.Self-Regulation: Managing one’s emotions in healthy ways.Empathy: Recognizing and understanding the emotions of others.Social Skills: Building rapport and managing relationships effectively.Developing a Curriculum for Teaching Soft Skills
Creating an effective curriculum for teaching soft skills involves several steps:
Assessment of Needs: Conduct surveys or assessments within your organization or educational institution to identify gaps in soft skills among employees or students.Setting Learning Objectives: Define clear objectives for what participants should achieve by the end of the training program. For example, improving communication skills could be a primary goal.Designing Training Modules:Use interactive methods such as role-playing exercises to simulate real-world scenarios where participants can practice their skills.Incorporate workshops encouraging group discussions, feedback sessions, and cooperative problem-solving tasks.Utilizing Technology:Implement e-learning modules that provide flexibility for learners to engage with content at their own pace.Use video tutorials that demonstrate effective communication techniques or conflict resolution strategies.Incorporating Feedback Mechanisms:Establish regular feedback sessions where participants can receive constructive criticism from peers or trainers regarding their progress in developing soft skills.Implementing Emotional Intelligence Training
Training focused specifically on emotional intelligence can enhance overall soft skill development. Here are some strategies for implementing EI training:
Workshops on Self-Awareness: Facilitate sessions where participants reflect on their emotional triggers and responses through guided activities like journaling or mindfulness exercises.Active Listening Exercises: Teach participants how to engage in active listening by focusing fully on speakers without interrupting, which fosters empathy and understanding.Conflict Resolution Training: Provide tools for identifying sources of conflict and practicing calm communication strategies that promote collaborative solutions.Mentorship Programs: Pair less experienced individuals with mentors who exemplify strong emotional intelligence traits, allowing them to learn through observation and guidance.Continuous Learning Opportunities: Encourage ongoing development through seminars, online courses, or reading materials focused on enhancing emotional intelligence competencies over time.Evaluating Effectiveness
To ensure that the training programs are successful:
Pre-and Post-Assessments: Measure participants’ soft skill levels before training begins and after its completion using standardized assessments or self-evaluations.Feedback Surveys: Collect participant feedback regarding the relevance and applicability of the training content to their roles.Performance Metrics Tracking: Monitor changes in team dynamics, productivity levels, employee satisfaction scores, or other relevant performance indicators post-training implementation.By systematically addressing these components—understanding importance, identifying competencies, developing curricula, implementing training methods, and evaluating effectiveness—organizations can successfully teach soft skills and emotional intelligence leading to improved workplace interactions and outcomes.
The post Teaching Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.
October 16, 2024
Leverage Their Digital Fluency

Why: Understanding Gen Z as Digital Natives
Generation Z, typically defined as individuals born from the mid-to-late 1990s through the early 2010s is recognized as the first generation to grow up with the internet and digital technology from a young age. This exposure has shaped their behaviors, preferences, and skills in ways that are distinct from previous generations. They are often characterized by their adeptness at navigating various digital platforms, utilizing social media for communication and information sharing, and employing technology to solve problems creatively.
Research indicates that Gen Z possesses a unique set of skills when it comes to digital fluency. According to studies conducted by organizations such as McKinsey & Company and Pew Research Center, members of this generation are comfortable with technology and tend to be more innovative in their approach to using it. They have been found to leverage digital tools for collaboration, learning, and engagement in ways that can significantly benefit organizations looking to adapt to an increasingly digital landscape.
Strategy: Involving Gen Z in Digital Projects
To effectively harness the digital fluency of Gen Z, organizations should consider involving them in projects that require specific technological expertise. This could include areas such as:
In conclusion, leveraging the digital fluency of Generation Z involves recognizing their unique strengths as true digital natives and strategically involving them in relevant projects across various domains within an organization.
The post Leverage Their Digital Fluency appeared first on Peak Development Strategies.



