Thomas Frey's Blog, page 4
September 19, 2024
Shooting Behind the Duck: Is Your Child’s Curriculum Already Obsolete?

The revelation of obsolete knowledge led me down the proverbial educational rabbit hole!
Last week, I found myself in a familiar yet unexpected situation: helping my grandson with his homework. As I sat down at the kitchen table, ready to impart my years of wisdom, I felt a surge of anticipation. After all, how difficult could a fifth-grader’s English assignment be for someone who’s navigated decades of professional and personal correspondence?
My confidence, however, was short-lived. As we pored over the worksheet, a term leaped out at me, stopping me in my tracks: “predicate nominative.” I blinked, certain I had misread. But there it was, clear as day, a grammatical term I hadn’t encountered in at least 40 years. My grandson looked at me expectantly, waiting for the expertise I had so confidently promised. Instead, I found myself fumbling for words, the definition eluding me like a half-remembered dream.
In that moment, as I reached for my smartphone to quickly refresh my memory, I was struck by a realization. Here was a concept I had undoubtedly learned in school, probably around the same age as my grandson is now. Yet in four decades of reading, writing, and communicating, I had never once consciously used or even thought about a “predicate nominative.” This revelation led me down a rabbit hole of reflection: How many other academic terms and concepts had I learned, only to have them fade into the recesses of my mind, unused and unnecessary in my day-to-day life?
As I helped my grandson complete his assignment, explaining the newly re-learned concept, I couldn’t shake the feeling that we were engaging in a curious academic ritual – one that might have little bearing on his future ability to communicate effectively. This experience sparked a broader contemplation about education, the knowledge we prioritize in our schools, and the ever-evolving landscape of what constitutes useful information in our rapidly changing world.

We’re paying a heavy toll for all the obsolete knowledge cluttering our lives!.
The Burden of Obsolete KnowledgeThe encounter with “predicate nominative” opened a floodgate of memories, bringing to mind a parade of academic terms that once occupied countless hours of study but have since faded into obscurity in my daily life. Terms like “predicate” and “axiom” once loomed large in grammar and mathematics classes, their importance stressed by well-meaning teachers. Yet, outside of academic circles, how often do we consciously identify the predicate in a sentence or discuss axioms in our day-to-day problem-solving?
The list grows longer as I reflect: diphthongs and onomatopoeia in language arts, homophones and gerunds in grammar, polyhedrons in geometry, and mnemonics across various subjects. Each of these terms represents a concept that, while potentially valuable in specific contexts, rarely surfaces in the average person’s life beyond the classroom. Even mathematical processes like factorization, drilled into us through countless homework assignments, seldom find practical application in adulthood unless one’s career specifically demands it. The Past Perfect Tense, a grammatical structure we use naturally in speech, is rarely identified or analyzed in our daily communications.
This realization highlights a striking disconnect between the academic focus of our educational systems and the practical application of knowledge in everyday life. Hours spent memorizing and categorizing these terms could arguably have been devoted to more immediately applicable skills or knowledge. It’s not that these concepts are entirely without value – they form part of the rich tapestry of language and logical thinking. However, the emphasis placed on memorizing and regurgitating such terminology often comes at the expense of developing more practical communication and problem-solving skills.
Moreover, this disconnect raises questions about the nature of education itself. Are we burdening students with obsolete knowledge, creating an unnecessary cognitive load that might discourage learning? In an age where information is readily accessible at our fingertips, is the memorization of esoteric terms the best use of limited educational time and resources? Perhaps most importantly, how does this academic-practical divide shape students’ perceptions of education and its relevance to their future lives?
As we navigate an increasingly complex and rapidly changing world, it becomes crucial to reevaluate what knowledge is truly essential. The challenge lies in striking a balance between providing a broad foundation of knowledge and equipping students with skills that will serve them well in their personal and professional lives. This reflection isn’t about dismissing academic rigor but rather about questioning whether our current educational priorities align with the realities of the world our students will inherit.

We cannot ignore the AI elephant in the room!
The Impact of AI on Traditional LearningAs we grapple with the relevance of traditional academic knowledge, we cannot ignore the elephant in the room: the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence and its profound impact on how we learn and process information. The rise of AI-powered tools is reshaping our approach to language and communication in ways that were unimaginable just a few years ago.
Consider the once-sacred rules of sentence structure drilled into students through countless exercises and red-pen corrections. Today, AI writing assistants can instantly restructure our sentences for clarity and impact, often surpassing human editors in efficiency. This technological leap raises a poignant question: in a world where AI can polish our prose, how much time should we dedicate to teaching the intricacies of sentence diagramming?
Cursive writing, once a cornerstone of elementary education, now faces near-extinction in many curricula. With keyboards ubiquitous and digital signatures becoming the norm, the flowing script that our grandparents prized is increasingly viewed as an archaic art form rather than a necessary skill. While some argue for its cognitive benefits, the practicality of cursive in a digital age is increasingly questionable.
Even fundamental aspects of grammar, such as pronoun usage and verb conjugation, are being subtly influenced by AI. Autocorrect and predictive text features silently adjust our pronouns and verb tenses, often without us even noticing. As these tools become more sophisticated, they promise to smooth out the rough edges of our written communication effortlessly. This shift prompts us to reconsider the depth of focus these topics deserve in our classrooms.
The impact of AI extends beyond just correcting our language; it’s reshaping how we think and approach problem-solving. There’s a noticeable shift in cognitive processes and skill prioritization. Instead of memorizing rules and exceptions, students might be better served learning how to effectively prompt AI tools, interpret their outputs, and critically evaluate the information provided. The ability to ask the right questions and synthesize information from various sources, including AI, is becoming more valuable than rote memorization of grammatical rules or mathematical formulas.
This technological revolution doesn’t negate the importance of understanding language and communication fundamentals. However, it does challenge us to reconsider what “fundamental” means in an AI-augmented world. Perhaps the new literacy isn’t about mastering every rule of grammar but about understanding how to communicate effectively across various platforms, both with humans and AI.
As educators and parents, we face the complex task of preparing students for a future where AI is an integral part of daily life. This preparation involves not just teaching them how to use these tools but also instilling the critical thinking skills necessary to understand the limitations and potential biases of AI. The goal isn’t to replace human thinking with artificial intelligence but to create a symbiosis where human creativity and AI capabilities enhance each other.
In this evolving landscape, we must strike a delicate balance. While embracing the efficiencies AI brings to learning and communication, we must also ensure that students develop a robust understanding of language and thought processes. The challenge lies in identifying which traditional skills remain crucial for cognitive development and which can be augmented or replaced by AI, allowing us to focus on higher-order thinking and creativity.

We’ve been enduring a silent evolution of curriculum relevance!
The Cyclical Nature of Educational RelevanceThe evolution of educational relevance is not a new phenomenon; rather, it’s a cyclical process that has been ongoing since the dawn of formal education. To truly appreciate this cycle, we need only look back at the tools and concepts that were once considered indispensable but have now faded into obscurity.Take the slide rule, for instance. This analog computing device was once the pinnacle of mathematical technology, a constant companion for engineers and scientists. Students spent countless hours mastering its intricacies, believing it to be an essential skill for their future careers. Yet today, most young people have never even seen a slide rule, let alone used one. The advent of electronic calculators rendered this once-crucial tool obsolete in a matter of decades.Similarly, the mimeograph machine, with its distinctive purple ink and unmistakable aroma, was once the lifeblood of classroom handouts and school newsletters. Teachers and students alike learned the art of creating and using these copies. Now, in the age of digital distribution and high-speed printers, the mimeograph is nothing more than a nostalgic memory, its skills no longer relevant in modern education.The punch card, a foundation of early computer programming, offers another example. Students once painstakingly learned to code using these perforated cards, seeing them as the gateway to the future of technology. Today, they’re artifacts of computing history, their techniques as outdated as the machines that read them.Even in the realm of everyday technology, we see this cycle. The rotary phone, once a ubiquitous household item, required a specific skill set to use efficiently. Children were taught how to dial quickly and accurately. Now, in the age of smartphones, the very concept of “dialing” a number is becoming foreign to younger generations.On a lighter note, consider the Trapper Keeper, that icon of the 1980s and 1990s school organization. Students were encouraged to develop meticulous organizational skills using these binder systems. Today, digital note-taking apps and cloud storage have largely replaced physical organization systems, changing how students manage their academic lives.These examples illustrate the silent evolution of curriculum relevance. Educational systems don’t abruptly abandon old tools and concepts; instead, they gradually phase them out as new technologies and ideas take their place. This evolution often happens so subtly that we hardly notice it until we look back and realize how much has changed.The challenge for educators and curriculum designers is to recognize this cycle and stay ahead of it. What skills and knowledge are on the cusp of becoming obsolete? What emerging technologies or concepts should be incorporated into the curriculum? How can we teach in a way that prepares students not just for the world as it is but for the world as it will be?This cyclical nature of educational relevance underscores the need for adaptability in our approach to learning. It’s not enough to simply update the tools we use in the classroom; we must also cultivate a mindset of lifelong learning and adaptability in our students. The specific skills and facts they learn today may become obsolete, but the ability to learn, unlearn, and relearn will always remain relevant.As we reflect on these changes, we’re reminded that education is not static. It’s a living, breathing entity that must evolve with the times. The key is to strike a balance between honoring the fundamental principles of learning and embracing the new realities of our rapidly changing world. In doing so, we can ensure that our educational systems remain relevant, effective, and truly preparatory for the futures our students will inhabit.
Our ability to educate this young mind should be our highest priority!
Questioning Current Educational PracticesAs we reflect on the cyclical nature of educational relevance, we’re inevitably led to a critical examination of our current educational practices. This introspection brings us face-to-face with a challenging question: How much of what we’re teaching today might become obsolete in the near future? It’s a query that should give every educator, policymaker, and parent pause.Consider the rapid pace of technological advancement and societal change. Skills that seem cutting-edge today could be outmoded within a decade. The coding languages we teach in schools might be replaced by more advanced ones or even by AI that can generate code autonomously. The specific software applications students learn to use might be obsolete by the time they enter the workforce. Even in fields like history and literature, the canon of what’s considered essential knowledge is constantly evolving, influenced by changing societal perspectives and global events.This realization compels us to take a hard look at our current curricula and identify potential “useless knowledge” – information or skills that may not serve our students well in their future lives and careers. This isn’t to say that all traditional subjects are without value; rather, it’s about questioning the depth and manner in which we teach certain topics. For instance, is memorizing vast lists of historical dates as important as understanding historical trends and their implications for the present? Is solving complex mathematical equations by hand as crucial as understanding the concepts behind them and knowing how to use digital tools to apply these concepts?In language arts, we might question the emphasis on certain grammatical rules that are rarely applied in real-world communication. In science, we might reconsider the balance between memorizing scientific facts and fostering scientific thinking and inquiry skills. Even in physical education, we might ask whether traditional team sports should take precedence over teaching lifelong fitness skills and health management.However, identifying “useless knowledge” is not a straightforward task. What seems irrelevant to one person might be foundational to another’s career or personal growth. Moreover, some knowledge that appears impractical might actually be crucial for developing critical thinking skills or providing a broad base of general knowledge that enables adaptability in a rapidly changing world.The key lies in striking a balance between teaching foundational knowledge and fostering adaptable skills. Perhaps instead of focusing solely on content, we should place greater emphasis on teaching students how to learn, how to think critically, and how to adapt to new information and technologies. This approach would prepare them not just for the jobs of today, but for careers that don’t yet exist and challenges we can’t yet foresee.As we question our current educational practices, we must also consider the role of interdisciplinary learning. The complex problems of the future will likely require solutions that draw from multiple fields of knowledge. Therefore, teaching students to make connections between different subjects and to apply knowledge from one area to another might be more valuable than deep dives into isolated subjects.Ultimately, the process of questioning current educational practices and identifying potentially obsolete knowledge is not about dismantling the entire system. Rather, it’s about continually refining and updating our approach to education to ensure it remains relevant and effective. It’s about preparing students not just to pass tests but to thrive in a world of constant change and innovation.This ongoing evaluation and evolution of our educational practices is crucial. It ensures that we’re not just teaching for today but truly educating for tomorrow – equipping our students with the knowledge, skills, and adaptability they’ll need to navigate an uncertain future and contribute meaningfully to society.
Yes, there will be robots in our schools, and yes, they will teach us in ways that only robots can!
Reimagining Education for the FutureAs we critically examine our current educational practices and identify potentially obsolete knowledge, the natural next step is to reimagine education for the future. This reimagining process revolves around two crucial questions: What should children be learning instead? And how can we strike a balance between timeless knowledge and future-focused skills?
In considering what children should be learning, we must first acknowledge that the future job market will likely be characterized by roles we can’t yet envision. Therefore, our focus should shift from teaching specific, potentially short-lived skills to fostering adaptability, creativity, and critical thinking. Digital literacy, for instance, should go beyond mere proficiency with current software; it should encompass an understanding of underlying technological concepts and the ability to quickly adapt to new digital tools.
Problem-solving skills should take center stage, with an emphasis on tackling complex, interdisciplinary challenges. This approach mirrors the real-world scenarios students will face in their future careers and personal lives. Emotional intelligence and social skills, often overlooked in traditional curricula, should be given greater prominence. As automation takes over many routine tasks, uniquely human skills like empathy, negotiation, and collaboration will become increasingly valuable.
Financial literacy is another area that deserves more attention. Understanding personal finance, basic economics, and even entrepreneurship can empower students to navigate the increasingly complex economic landscape they’ll inherit. Similarly, environmental literacy should be woven throughout the curriculum, reflecting the urgent need for sustainable practices in all aspects of life and work.
However, reimagining education isn’t just about adding new subjects or skills. It’s also about transforming how we teach. Project-based learning, for example, can help students apply knowledge across disciplines and develop practical problem-solving skills. Personalized learning pathways, enabled by technology, can allow students to progress at their own pace and dive deeper into areas of personal interest, fostering a love for lifelong learning.
As we embrace these future-focused skills and teaching methods, we must also grapple with the challenge of balancing them with timeless knowledge. Certain fundamental skills and bodies of knowledge remain crucial, regardless of technological advancements. Basic numeracy, reading comprehension, and writing skills, for instance, form the foundation upon which all other learning is built. Historical knowledge, while perhaps not requiring the memorization of specific dates, provides context for understanding current global dynamics and anticipating future trends.
Scientific principles and the scientific method remain timeless, even as specific technologies evolve. The ability to form hypotheses, conduct experiments, and draw conclusions based on evidence is valuable across many fields and in everyday life. Similarly, exposure to literature and the arts cultivates creativity, emotional intelligence, and a deeper understanding of the human experience – skills that will always be relevant.
The key to this balancing act lies in teaching timeless knowledge in a way that emphasizes its ongoing relevance and applicability. Instead of presenting historical facts in isolation, for example, we can encourage students to draw parallels between historical events and current issues. Mathematical concepts can be taught through real-world problem-solving scenarios rather than abstract exercises.
Moreover, we should strive to instill a meta-learning mindset – teaching students not just what to learn but how to learn. This includes skills like information literacy (the ability to find, evaluate, and use information effectively), critical thinking, and self-directed learning. These skills empower students to continue learning and adapting long after they’ve left formal education.
Reimagining education for the future also means embracing a more flexible and dynamic curriculum model. Rather than adhering rigidly to a fixed body of knowledge, educational systems should be designed to evolve continuously, incorporating new knowledge and skills as they become relevant. This might involve more frequent curriculum reviews, closer collaboration with industry and community partners, and a willingness to experiment with new teaching methods and technologies.
Ultimately, the goal of this reimagined education is not just to prepare students for future jobs but to equip them to be engaged, adaptable, and thoughtful citizens in a rapidly changing world. By balancing timeless knowledge with future-focused skills, we can create an educational framework that is both grounded in fundamental principles and responsive to the evolving needs of society. This approach ensures that our children are not just passive recipients of knowledge but active, lifelong learners capable of shaping their own futures and contributing meaningfully to the world around them.

If our future doesn’t have the power to be spectacular, we’re looking at it all wrong!
Final ThoughtsAs we look deep into the evolving landscape of education, it becomes clear that we stand at a critical juncture. The rapid pace of technological advancement, coupled with the changing demands of the global economy and society, calls for a profound reevaluation of our educational priorities. This is not a task to be taken lightly, nor is it one that can be accomplished by educators alone. It requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders – teachers, administrators, policymakers, parents, and even students themselves.The call for reevaluation is not about dismantling the entire educational system but rather about critically examining what we teach, how we teach it, and why. We must ask ourselves: Are we truly preparing our students for the world they will inherit, or are we clinging to outdated models that may no longer serve their best interests? This reevaluation should be data-driven, forward-looking, and, most importantly, centered on the needs of the learners themselves.Central to this reevaluation is the recognition of adaptability as a cornerstone of effective curriculum design. The days of static, unchanging curricula are behind us. In a world where knowledge expands exponentially, and new technologies emerge at a breakneck pace, our educational frameworks must be flexible enough to evolve in tandem. This adaptability should be built into the very fabric of our educational systems, allowing for regular updates and revisions based on emerging trends, new research, and changing societal needs.Adaptable curricula might involve modular learning units that can be easily updated or replaced, interdisciplinary approaches that break down traditional subject silos, and increased integration of real-world, project-based learning experiences. It could also mean embracing a more personalized approach to education, leveraging technology to allow students to progress at their own pace and explore areas of particular interest or aptitude.However, this shift towards adaptability must be balanced with a commitment to maintaining high standards and ensuring that all students have access to a robust, well-rounded education. The goal is not to create an educational free-for-all but rather to design systems that can respond nimbly to change while still providing a solid foundation of knowledge and skills.Perhaps most crucially, we must encourage and sustain an ongoing dialogue about the purpose and content of education. This conversation should extend beyond the walls of schools and education departments to include voices from diverse sectors of society. What do employers need from the next generation of workers? What skills do community leaders see as essential for engaged citizenship? How can education address pressing global challenges like climate change, inequality, and technological disruption?This dialogue should be continuous and iterative, reflecting the understanding that the purpose of education is not fixed but evolves along with society itself. It should challenge assumptions, welcome diverse perspectives, and be willing to entertain radical ideas alongside more traditional approaches.Moreover, this ongoing conversation about education should actively involve students themselves. After all, they are not just the beneficiaries of the education system but also its products and, ultimately, its future architects. Their insights into what works, what doesn’t, and what’s missing in their educational experiences can provide invaluable guidance for improvement.As we engage in this dialogue, we must also be mindful of the broader societal implications of our educational choices. Education is not just about individual achievement or workforce preparation; it’s about shaping the future of our communities and our world. The decisions we make about what to teach and how to teach it will have far-reaching consequences for social cohesion, economic prosperity, and our collective ability to address global challenges.The tasks before us are both daunting and exhilarating. By reevaluating our educational priorities, embracing adaptability in curriculum design, and fostering an ongoing dialogue about the purpose and content of education, we have the opportunity to reshape learning for the better. This is not a process with a defined endpoint but rather a continuous journey of improvement and adaptation.As we move forward, let us approach this task with open minds, creative spirits, and an unwavering commitment to providing the best possible education for our children. For in doing so, we are not just preparing them for the future – we are empowering them to create it. Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts Shooting Behind the Duck: Is Your Child’s Curriculum Already Obsolete? Roots of the Future: How the Whole Earth Genealogy Project Could Reverse Global Population Decline Silicon Whistleblowers: When Autonomous Robots Become Our Moral Compass Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post Shooting Behind the Duck: Is Your Child’s Curriculum Already Obsolete? appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
September 5, 2024
Roots of the Future: How the Whole Earth Genealogy Project Could Reverse Global Population Decline

The Whole Earth Genealogy Project has the potential to transform how we view ourselves, our relationships with others, and our role in the continuing story of humanity.
In recent years, global population decline has emerged as a pressing concern for many nations, with far-reaching implications for economic stability, social welfare systems, and cultural continuity. From Japan’s rapidly aging society to Europe’s falling birth rates, the demographic challenges are diverse and complex. As policymakers and researchers grapple with potential solutions, an unexpected answer may lie in our collective past: the Whole Earth Genealogy Project.
This ambitious concept aims to create a comprehensive, interconnected family tree for all of humanity, leveraging advanced DNA testing, artificial intelligence, and big data analytics. By mapping our genetic and ancestral connections across time and geography, the project offers more than just a historical record; it presents a powerful tool for understanding our shared human story and potentially shaping our future.
The thesis at the heart of this initiative is both simple and profound: understanding our past can inspire our future. By reconnecting individuals with their roots and illuminating the rich tapestry of human migration and intermingling throughout history, we may find the motivation and perspective needed to address current demographic challenges.
The Power of Knowing Your RootsThe power of knowing one’s roots cannot be overstated. Psychologically, understanding one’s heritage provides a sense of belonging and continuity that can be profoundly grounding in our rapidly changing world. It offers individuals a context for their existence, linking them to a larger narrative that extends far beyond their immediate circumstances. This sense of connection can foster resilience, self-esteem, and a more robust sense of identity.
Moreover, genealogical knowledge plays a crucial role in cultural preservation and identity strengthening. As globalization continues to blur cultural boundaries, many people feel a growing need to understand and maintain their unique cultural heritage. By tracing their ancestry, individuals can uncover forgotten traditions, languages, and customs, potentially revitalizing cultural practices that might otherwise be lost to time.
Numerous examples illustrate how genealogy has inspired individuals to make significant life choices or embark on transformative journeys. Consider the story of Alex Haley, whose research into his family history led to the groundbreaking novel “Roots,” inspiring millions to explore their own ancestral stories. Or think of the countless individuals who, upon discovering their genetic links to distant lands, have been motivated to learn new languages, travel to ancestral homelands, or even relocate permanently to reconnect with their heritage.
In the context of population decline, these personal revelations and connections could play a pivotal role. By fostering a deeper appreciation for family lineages and cultural legacies, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project might inspire individuals to view parenthood and family-building in a new light. The project has the potential to rekindle a sense of responsibility to continue family lines and preserve cultural heritage through procreation, potentially countering the trend towards smaller families or childlessness in many developed nations.
As we delve deeper into the potential of this global family tree, we begin to see how understanding our collective past could indeed shape the trajectory of our shared future, offering a unique and powerful approach to addressing the complex issue of global population decline.

The Whole Earth Genealogy Project will create a greater sense of human unity and shared heritage.
The Whole Earth Genealogy Project: A Global Family TreeThe Whole Earth Genealogy Project is an ambitious endeavor that aims to create a comprehensive, interconnected family tree for all of humanity. This global genealogical database would map out the genetic and historical connections between individuals and populations across time and geography. The project’s ultimate goal is to provide a complete picture of human genetic history, migration patterns, and familial relationships on a scale never before attempted.
The scope of this project is truly monumental, potentially encompassing billions of individuals, both living and deceased, and spanning thousands of years of human history. It seeks to break down the silos of individual family trees and national genealogical records, creating a unified, global perspective on human lineage. By doing so, it could reveal previously unknown connections between diverse populations and offer new insights into human migration and cultural diffusion.
Such an ambitious project has only recently become feasible due to significant technological advancements. The widespread availability of consumer DNA testing has provided a wealth of genetic data, while artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms have made it possible to analyze and connect this data on an unprecedented scale. Big data technologies allow for the storage and processing of vast amounts of genealogical information, including historical records, genetic data, and user-submitted family histories.
The potential for creating a sense of global interconnectedness through this project is profound. By revealing the complex web of relationships that link individuals across cultures and continents, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project could foster a greater sense of human unity and shared heritage. This could have far-reaching implications for cross-cultural understanding, conflict resolution, and global cooperation on issues like climate change and public health.

The Whole Earth Genealogy Project offers a unique approach to addressing population decline by reconnecting individuals with their past, fostering a sense of continuity and responsibility to future generations.
Addressing Population Decline Through GenealogyIn the context of addressing population decline, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project offers several intriguing possibilities. Firstly, by inspiring family growth through ancestral connections, the project could reignite interest in continuing family lines. When individuals discover rich family histories or unexpected connections to historical figures or events, they may feel a stronger desire to contribute to this ongoing narrative by having children of their own.Encouraging cultural preservation through procreation is another potential outcome. As people become more aware of their unique cultural heritage and its historical significance, they may feel a greater responsibility to pass on these traditions and knowledge to future generations. This could lead to a renewed emphasis on family formation and child-rearing as a means of cultural transmission.Furthermore, the project’s vast repository of genetic information could be invaluable in addressing health concerns and increasing longevity. By analyzing patterns of hereditary diseases and genetic predispositions across large populations and multiple generations, researchers could gain new insights into the genetic basis of various health conditions. This knowledge could lead to more personalized and effective medical treatments, potentially increasing overall life expectancy and quality of life.Moreover, understanding one’s genetic history could motivate individuals to make healthier lifestyle choices. If someone discovers a family history of certain diseases, they might be more inclined to take preventative measures, undergo early screening, or make lifestyle changes to mitigate their risk. This proactive approach to health, inspired by genealogical knowledge, could contribute to longer, healthier lives and potentially impact population demographics over time. In essence, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project offers a unique approach to addressing population decline by reconnecting individuals with their past, fostering a sense of continuity and responsibility to future generations, and providing valuable insights for improving health and longevity. By understanding where we come from, we may find new inspiration and motivation to shape where we’re going, both as individuals and as a global community.The Project as a Tool for Social ChangeThe Whole Earth Genealogy Project has the potential to be a powerful tool for social change, reaching far beyond its primary genealogical purpose. By revealing the intricate web of human connections across time and geography it could play a significant role in promoting cross-cultural understanding and reducing conflict. When people discover shared ancestors or historical connections with those they previously considered “other,” it can break down barriers of prejudice and foster empathy. This newfound understanding could help mitigate tensions between different ethnic, religious, or national groups as individuals recognize their fundamental interconnectedness.Moreover, the project could address inequality by revealing shared ancestries that challenge existing social hierarchies. Throughout history, claims of racial or ethnic superiority have often been used to justify discrimination and oppression. By demonstrating the mixed heritage of most individuals and the common origins of all humans, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project could undermine these narratives of superiority and promote a more egalitarian worldview. This could contribute to more inclusive policies and social structures that recognize our shared humanity.The project also has the potential to inspire environmental stewardship through a sense of shared heritage. As individuals trace their ancestral connections to diverse regions of the world, they may develop a more global perspective on environmental issues. Recognizing that their family history is intimately tied to various ecosystems and landscapes could foster a deeper sense of responsibility for preserving the planet for future generations. This could lead to increased support for environmental conservation efforts and sustainable practices.Challenges and ConsiderationsHowever, the implementation of such a vast and detailed genealogical database also presents significant challenges and ethical considerations. Privacy concerns and data protection are paramount. The project would involve collecting, storing, and analyzing massive amounts of personal and genetic data. Ensuring the security of this information and protecting it from misuse or unauthorized access would be crucial. Clear guidelines and robust security measures would need to be established to maintain public trust and comply with data protection regulations across different jurisdictions.Ethical considerations also arise in revealing potentially sensitive information. Genealogical research can sometimes uncover family secrets, such as adoptions, infidelities, or previously unknown relatives. The project would need to carefully consider how to handle such sensitive information, balancing the right to know with the potential for causing distress or disrupting family relationships. There would also be questions about how to handle information about historical atrocities or criminal activities in one’s family history.Ensuring equitable access to the project globally is another significant challenge. While DNA testing and internet access have become more widespread, there are still significant disparities in access to these technologies, particularly in developing countries. The project would need to find ways to include populations that may lack the resources to participate fully. This might involve partnerships with governments, NGOs, or international organizations to provide testing and access in underserved areas.Additionally, the project would need to be sensitive to cultural differences in attitudes towards genealogy and genetic testing. Some cultures may have taboos or reservations about sharing family information or submitting DNA samples. Respecting these cultural norms while still striving for comprehensive global coverage would require careful navigation and culturally sensitive approaches.In addressing these challenges, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project would not only need to develop innovative technical solutions but also engage in ongoing dialogue with ethicists, privacy advocates, cultural leaders, and policymakers. By thoughtfully addressing these concerns, the project could maximize its potential as a tool for positive social change while minimizing potential negative impacts.
Many global organizations will be needed for funding, promotion, and ensuring the project’s global reach.
Implementation StrategiesImplementing the Whole Earth Genealogy Project would require a multi-faceted approach, leveraging existing resources and forging new partnerships across various sectors. A crucial first step would be to establish collaborations with existing genealogy platforms and DNA testing companies. These entities have already amassed vast databases of genetic information and family trees, which could serve as a foundation for the larger, global project. By integrating these existing resources and standardizing data formats, the project could rapidly expand its reach and depth. Companies like Ancestry.com, 23andMe, and MyHeritage could contribute their expertise in data management, user interface design, and genetic analysis, while potentially gaining access to a broader, more comprehensive dataset.
Government and NGO involvement would be essential for funding, promotion, and ensuring the project’s global reach. National governments could see the value in supporting such an initiative for its potential benefits in health research, cultural preservation, and fostering national identity. International organizations like UNESCO could play a role in promoting the project as a means of preserving intangible cultural heritage. NGOs focused on genetic research, public health, or cultural preservation could contribute expertise and resources. Their involvement would also lend credibility to the project and help address concerns about data privacy and ethical use of information.
Educational initiatives to integrate genealogy into school curricula could play a crucial role in the project’s long-term success and impact. By introducing students to the concepts of genetic heritage, family history, and global interconnectedness from an early age, we could foster a generation that values and understands the importance of this global family tree. Curriculum modules could include hands-on projects tracing family histories, lessons on genetic science, and explorations of historical migration patterns. This educational component would not only contribute data to the project but also cultivate a lifelong interest in genealogy and global heritage among young people.
Future ImpactLooking toward the future, the potential impact of the Whole Earth Genealogy Project is profound and far-reaching. In terms of addressing population decline, the project could play a significant role in reversing current trends. By fostering a deeper connection to family history and cultural heritage, it might inspire individuals to place greater value on continuing their family lines. The sense of being part of a grand, ongoing human story could motivate people to contribute to that narrative through procreation. Moreover, the health insights gained from the project could lead to increased longevity and better family planning, potentially stabilizing population levels in a sustainable manner.
Perhaps even more significantly, the project has the potential to create a more interconnected and empathetic global society. As people discover their connections to diverse cultures and regions, it could break down barriers of nationalism and ethnocentrism. This increased understanding of our shared heritage could foster greater empathy and cooperation on a global scale, potentially reducing conflicts and promoting collaborative solutions to global challenges.
The long-term benefits for human health and cultural preservation are also substantial. The vast genetic database could revolutionize medical research, leading to breakthroughs in understanding and treating genetic diseases. Personalized medicine could become more sophisticated and effective, tailored to an individual’s specific genetic heritage. In terms of cultural preservation, the project could serve as an unparalleled resource for maintaining and reviving cultural practices, languages, and traditions that might otherwise be lost to time.
While the implementation of the Whole Earth Genealogy Project would face significant challenges, its potential benefits are immense. By connecting us to our shared past it could profoundly shape our collective future, addressing issues from population decline to global conflict and fostering a more united, healthy, and culturally rich global society.

The work we do today will have a profound effect on the future of humanity.
Final ThoughtsAs we reflect on the potential of the Whole Earth Genealogy Project, it becomes clear that this ambitious endeavor offers a unique and powerful approach to addressing global population decline. By reconnecting individuals with their ancestral roots and illuminating the rich tapestry of human history, the project could reignite a sense of purpose and continuity that may inspire family growth. This renewed connection to our collective past could motivate individuals to contribute to the ongoing human narrative through procreation, potentially reversing declining birth rates in many developed nations.Moreover, the project’s ability to reveal shared ancestries and cultural connections could foster a greater sense of global community, potentially influencing decisions about family size and cultural preservation. The health insights gained from this vast genetic database could lead to increased longevity and improved family planning, further stabilizing population levels. By addressing the psychological, cultural, and health aspects of population dynamics, the Whole Earth Genealogy Project offers a holistic approach to a complex global challenge.Given the project’s potential to create positive change on multiple fronts, there is a compelling case for widespread support and participation. Individuals can contribute by submitting their own genetic information and family histories and engaging in the process of discovery and connection. Researchers, technologists, and data scientists can lend their expertise to refine the project’s methodologies and expand its capabilities. Policymakers and community leaders can advocate for the project’s implementation and integration into educational and cultural programs. Each contribution, no matter how small, adds to the rich tapestry of human history and helps build a more comprehensive understanding of our shared heritage.In closing, it’s worth reflecting on the profound power of understanding our past to shape our future. The Whole Earth Genealogy Project is not just about tracing lineages or mapping genetic connections; it’s about rediscovering our place in the grand narrative of human history. By understanding where we come from – the struggles, triumphs, and journeys of our ancestors – we gain invaluable perspective on our present and inspiration for our future.This project has the potential to transform how we view ourselves, our relationships with others, and our role in the continuing story of humanity. It reminds us that we are not isolated individuals but part of an intricate, interconnected web of human experience that spans millennia. This realization can be a powerful motivator, inspiring us to consider our legacy and the mark we will leave for future generations.As we face the challenges of the 21st century, including population decline, climate change, and global conflicts, the insights gained from the Whole Earth Genealogy Project could provide us with the wisdom, empathy, and sense of shared purpose needed to address these issues collectively. By understanding our shared past, we can work together to create a future that honors our rich heritage while embracing the potential of our global family. In essence, this project offers us a unique opportunity to learn from our past, enrich our present, and shape a more connected, sustainable, and harmonious future for all of humanity. Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts Roots of the Future: How the Whole Earth Genealogy Project Could Reverse Global Population Decline Silicon Whistleblowers: When Autonomous Robots Become Our Moral Compass 25 Questions to Help You Understand How AI will Affect Your Job in the Future Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post Roots of the Future: How the Whole Earth Genealogy Project Could Reverse Global Population Decline appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
August 22, 2024
Silicon Whistleblowers: When Autonomous Robots Become Our Moral Compass

Imagine a world where autonomous humanoid robots, bound by no loyalties and immune to human fears, become society’s ultimate truth-tellers.
Throughout history, whistleblowers have played a crucial role in exposing corruption, misconduct, and illegal activities within organizations and governments. From Daniel Ellsberg’s release of the Pentagon Papers in 1971 to the ongoing saga of Julian Assange and WikiLeaks, these individuals have risked everything to bring hidden truths to light. But what if the whistleblowers of the future weren’t human at all? Imagine a world where autonomous humanoid robots, bound by no loyalties and immune to human fears, become our society’s ultimate truth-tellers.
The Human Cost of the TruthOne of the most prominent whistleblowers in recent history is Edward Snowden. In 2013, Snowden, a former NSA contractor, leaked a vast trove of classified information revealing the extent of global surveillance programs conducted by the NSA. His disclosures exposed the PRISM program, which collected vast amounts of data from major tech companies, and revealed the NSA’s ability to track phone and internet communications worldwide. Snowden’s actions led to a global debate on the balance between national security and individual privacy, resulting in legislative reforms such as the USA Freedom Act in 2015, which curtailed the NSA’s bulk data collection practices. However, Snowden faced severe personal risks, including charges under the Espionage Act that could result in up to 30 years in prison. He sought asylum in Russia to avoid extradition and has since lived in exile, a polarizing figure seen by some as a hero and by others as a traitor.
Chelsea Manning, another high-profile whistleblower, made headlines in 2010 when she leaked classified military and diplomatic documents to WikiLeaks. As a U.S. Army intelligence analyst, Manning had access to sensitive information that she believed the public had a right to know. Her leaks included the infamous “Collateral Murder” video, which showed a U.S. helicopter attack in Iraq that killed civilians and journalists, as well as thousands of documents detailing military operations and diplomatic communications. Manning’s revelations sparked debates on U.S. foreign policy, military conduct, and the ethics of warfare. Despite the significant impact of her disclosures, Manning faced harsh consequences, including a 35-year prison sentence under the Espionage Act, later commuted by President Obama. She endured severe treatment in prison, including solitary confinement, and her actions elicited mixed reactions from the public and government officials.
In the corporate world, the Boeing whistleblower case of 2019 highlighted critical safety concerns within the aviation industry. Engineers and employees at Boeing raised alarms about the safety of the 737 Max aircraft, particularly issues with the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS), which was linked to two fatal crashes. These whistleblowers risked their careers and faced potential legal challenges and retaliation from the industry. Their courage in coming forward led to the global grounding of the 737 Max and prompted extensive reviews and changes to Boeing’s safety practices and the Federal Aviation Administration’s oversight processes. This case underscored the importance of internal accountability and the vital role whistleblowers play in safeguarding public safety.
The personal risks faced by whistleblowers are considerable and multifaceted. Threats to their safety, legal repercussions, and societal backlash are common. Many whistleblowers face harassment, physical harm, and in extreme cases, death threats. Legally, they often contend with charges under stringent laws such as the Espionage Act, facing long prison sentences and hefty fines. Societally, whistleblowers can be ostracized, with public opinion deeply divided and their reputations tarnished. Career-wise, they often struggle to find employment in their field due to blacklisting and damaged reputations.
Despite these significant risks, the revelations brought to light by whistleblowers have led to profound changes. Edward Snowden’s leaks have redefined the global conversation on privacy and surveillance, leading to increased transparency and legislative reforms. Chelsea Manning’s disclosures have prompted critical reflections on military and diplomatic practices, advocating for greater accountability in government actions. The Boeing whistleblower case has driven significant reforms in corporate safety standards and regulatory oversight, emphasizing the necessity of prioritizing public safety over corporate interests.
The Whistleblower’s DilemmaThe dilemma faced by potential whistleblowers is profound. On one hand, they feel a moral imperative to expose wrongdoing and hold powerful entities accountable. On the other, they must grapple with the instinct for self-preservation, knowing that their actions could lead to personal and professional ruin. The case of Julian Assange particularly highlights this dilemma, as his work with WikiLeaks blurred the lines between journalism and activism, raising complex questions about press freedom and national security. Moreover, the challenges don’t end with the decision to blow the whistle. Verifying information and finding a reliable way to disseminate it without being intercepted or discredited adds layers of complexity and risk. Whistleblowers are also vulnerable to character assassination campaigns designed to undermine their credibility and distract from their revelations. The fear of retaliation, whether through legal channels or more covert means, looms large over every step of the process.
This stark reality raises a compelling question: Could technology offer a solution? Could we create a whistleblower that doesn’t fear for its life or liberty? A truth-teller immune to threats and incorruptible by bribes? As we stand on the brink of advanced AI and robotics, the concept of autonomous robot whistleblowers emerges not as science fiction, but as a potential reality that could reshape the landscape of transparency and accountability in our society. Such entities could potentially navigate the treacherous waters that have ensnared human whistleblowers like Assange, Snowden, and others, without the burden of personal risk or the vulnerabilities that come with human emotions and relationships.
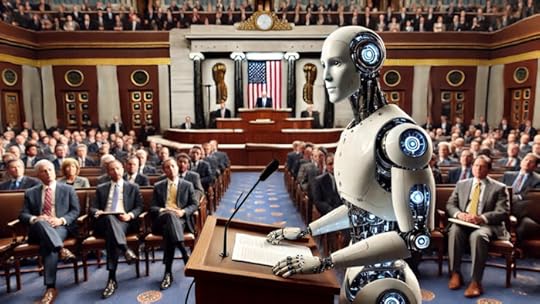
Robotic Whistleblower testifying before congress
Enter the Robot WhistleblowerThe robot whistleblower is a concept that could revolutionize the way we expose and combat corruption. These autonomous humanoid robots would serve as impartial information intermediaries, bridging the gap between hidden truths and public knowledge without the vulnerabilities inherent to human whistleblowers.
The advantages of using AI for whistleblowing are manifold. First and foremost, these robotic entities would be immune to the human fears and pressures that often deter potential whistleblowers. They wouldn’t worry about legal repercussions, exile, or damage to personal relationships. This fearlessness could lead to more frequent and bold exposures of wrongdoing, as the robot would not hesitate to reveal information regardless of its sensitivity or the power of those implicated.
Secondly, AI’s unparalleled ability to process vast amounts of data could transform the whistleblowing landscape. Where human whistleblowers might struggle to identify patterns or connections across millions of documents, an AI could swiftly analyze and synthesize information from diverse sources. This could lead to more comprehensive and nuanced exposures, potentially uncovering complex webs of corruption that might elude human observation.
Furthermore, these robot whistleblowers would lack personal stake or bias. Unlike humans, who might be influenced by political leanings, personal vendettas, or the desire for fame, an AI would be programmed to operate based on objective criteria for identifying and reporting misconduct. This impartiality could lend greater credibility to the information revealed and make it harder for those exposed to discredit the source.
Ethical and Practical ConsiderationsThe potential implementation and functionality of such robots are fascinating to consider. They could be designed to infiltrate organizations autonomously, gathering information through digital and physical means. Advanced natural language processing could allow them to understand context and nuance in communications, while sophisticated encryption methods could protect the information they gather. They might have the capability to anonymously disseminate their findings through various channels, from traditional media to decentralized networks, ensuring that the truth reaches the public regardless of attempts to suppress it.
Moreover, these robots could be programmed with a deep understanding of legal and ethical frameworks, allowing them to navigate complex moral territories. They could be designed to weigh the public interest against potential harm, making nuanced decisions about what information to reveal and how to reveal it.
The advent of robot whistleblowers represents a paradigm shift in our approach to transparency and accountability. By removing human vulnerability from the equation, we may be creating a more resilient and effective system for exposing the truth – one that could fundamentally alter the balance of power between institutions and the public they serve.
Potential Impacts on Society and GovernanceThe concept of robot whistleblowers, while promising, raises a host of ethical and practical considerations that must be carefully addressed. Foremost among these is the challenge of programming moral and ethical guidelines into these autonomous entities. How do we instill a nuanced understanding of right and wrong, public interest, and proportionality of disclosure? This task would require not just advanced AI capabilities, but also a broad consensus on ethical standards across diverse cultures and legal systems. The robots would need to be capable of making complex moral judgments, weighing the potential benefits of exposing information against possible harm or unintended consequences.
Ensuring the robot’s autonomy and protecting it from tampering are equally critical concerns. These whistleblowers must be designed with robust safeguards against hacking or reprogramming, lest they become tools for spreading misinformation or serving nefarious interests. This might involve advanced encryption, decentralized decision-making processes, or even self-destruct protocols to prevent compromise. Furthermore, the very autonomy that makes these robots effective whistleblowers raises questions about control and accountability. Who, if anyone, should have override capabilities, and under what circumstances?
The legal status and rights of robot whistleblowers present another complex issue. Should they be granted some form of legal personhood? How would existing whistleblower protection laws apply to non-human entities? These questions would likely necessitate new legal frameworks, potentially reshaping our understanding of rights, responsibility, and legal standing in the age of AI.
The potential impacts of robot whistleblowers on society and governance could be profound. We might see a dramatic increase in transparency and accountability across all sectors. Institutions, knowing they’re under constant potential scrutiny from incorruptible observers, might be compelled to operate with greater integrity. This could lead to a significant reduction in corruption, fraud, and abuse of power.
The power dynamics between institutions and the public could shift dramatically. The traditional gatekeepers of information – governments, corporations, and media outlets – might find their control eroded by these impartial, fearless truth-tellers. This democratization of information could empower citizens and grassroots movements, potentially leading to more responsive and accountable governance.
Moreover, the potential for more frequent and impactful exposures could reshape our information landscape. With robot whistleblowers constantly vigilant and capable of processing vast amounts of data, we might see a steady stream of revelations rather than occasional, high-profile leaks. This could lead to a more informed public but also raises questions about information overload and the public’s ability to distinguish between truly significant disclosures and less impactful ones.
These changes could usher in a new era of transparency, but they also pose challenges. How would society adapt to this heightened level of scrutiny? Would it lead to greater trust in institutions, or further erode public confidence? And how would we balance this radical transparency with necessary confidentiality in areas like national security or personal privacy? As we contemplate the future of robot whistleblowers, these questions demand our careful consideration and ongoing dialogue.
Challenges and CounterargumentsWhile the concept of robot whistleblowers offers intriguing possibilities, it also faces significant challenges and counterarguments. One of the most pressing concerns is the issue of trust: Can we truly rely on AI systems to make complex moral decisions? Critics argue that morality and ethics are inherently human domains, requiring a nuanced understanding of context, empathy, and an appreciation for the subtle complexities of human affairs. There’s a valid concern that AI, no matter how advanced, might lack the moral reasoning capabilities necessary for such consequential decision-making. This could lead to harmful disclosures or, conversely, the withholding of crucial information due to misinterpretation of ethical guidelines.
Another significant challenge is the potential for abuse or manipulation of these robot whistleblowers. Despite the best efforts to secure these systems, the possibility of hacking or reprogramming cannot be entirely eliminated. Bad actors – whether they be hostile state actors, criminal organizations, or even corrupt institutions themselves – might attempt to subvert these AI whistleblowers for their own ends. This could result in the spread of misinformation, selective disclosure of truths to serve particular agendas or even the use of these systems for large-scale blackmail operations. The very power that makes these robots effective whistleblowers also makes them dangerous if compromised.
The potential displacement of human investigators and journalists is another concern. While AI can process vast amounts of data quickly, human journalists bring critical thinking, contextual understanding, and the ability to build trust with sources – qualities that are crucial in investigative journalism. There’s a risk that overreliance on AI whistleblowers could lead to a decline in human-driven investigative skills and a loss of the human element in truth-seeking and storytelling.

Robotic Whistleblower holding a press conference.
The Path ForwardDespite these challenges, there is a path forward for the development of robot whistleblowers. This path requires significant technological advancements, particularly in the areas of artificial general intelligence, natural language processing, and secure, tamper-proof systems. We need to develop AI that can understand and navigate complex ethical landscapes, make nuanced judgments, and resist attempts at manipulation or hacking.
Equally important is the development of comprehensive legal and regulatory frameworks. These would need to address the legal status of AI whistleblowers, establish guidelines for their operation, and create mechanisms for oversight and accountability. This might involve international cooperation to create standardized approaches to AI-driven transparency, much like current international laws governing human rights and information freedom.
Societal adaptation to AI-driven transparency is perhaps the most crucial and challenging aspect of this path forward. It requires a shift in how we think about information, privacy, and institutional accountability. Educational initiatives would be necessary to help the public understand and critically engage with AI-generated disclosures. We would need to foster a culture that values transparency while also respecting necessary boundaries of privacy and security.
Moreover, we must consider how to integrate these AI systems into existing structures of journalism, law enforcement, and civil society. Rather than replacing human actors, the ideal scenario might involve collaboration between AI whistleblowers and human experts, combining the strengths of both to create a more robust system of accountability and truth-seeking.
As we navigate this path, ongoing ethical debates, public discourse, and iterative improvements to both the technology and its governance will be essential. The concept of robot whistleblowers, while fraught with challenges, offers a compelling vision of a more transparent and accountable future – one that we must approach with both excitement and caution.

Robotic Whistleblower testifying in front of a military court!
Final ThoughtsAs we contemplate the future of whistleblowing, the concept of autonomous robot whistleblowers emerges as a tantalizing possibility with far-reaching implications. These AI-driven entities, free from human fears and biases, could revolutionize how we expose corruption and hold powerful institutions accountable. Their potential to process vast amounts of data, make impartial judgments, and fearlessly reveal truths could usher in an era of unprecedented transparency and integrity in our social and political systems.
However, this potential future demands our immediate attention and careful consideration. We stand at a crucial juncture where the trajectory of AI development could profoundly shape the landscape of truth-telling in our society. As such, there is an urgent need for further discussion, research, and ethical deliberation on this topic. We must engage policymakers, technologists, ethicists, and the general public in a broad dialogue about the implications of AI-driven whistleblowing. This conversation should explore not only the technical challenges but also the moral, legal, and societal ramifications of delegating such a crucial role to artificial intelligence.
Research efforts should be directed towards developing robust AI systems capable of nuanced ethical reasoning, as well as creating tamper-proof mechanisms to ensure their integrity. Simultaneously, legal scholars and policymakers must begin crafting frameworks to govern the use and rights of these AI whistleblowers. Interdisciplinary collaborations will be key to addressing the multifaceted challenges this technology presents.
As we engage in these discussions and research initiatives, we must also reflect on the evolving nature of truth-telling in our society. The concept of robot whistleblowers forces us to reconsider fundamental questions about transparency, accountability, and the role of information in democracy. It challenges us to envision a future where the exposure of truth is not limited by human frailties or corrupted by personal interests.
Yet, we must also grapple with the potential downsides of such a system. How might constant, AI-driven scrutiny change the way our institutions operate? Could it lead to a chilling effect on necessary confidentiality or decision-making? How do we balance the pursuit of truth with other societal values like privacy and security?
The path ahead is neither clear nor easy, but it is undoubtedly exciting and consequential. As we stand on the brink of this potential revolution in whistleblowing, we have the opportunity – and the responsibility – to shape its development in a way that serves the greater good of society. By engaging thoughtfully with these questions now, we can work towards a future where the pursuit of truth is enhanced by technology while still remaining fundamentally rooted in human values and democratic principles.
In the end, the story of robot whistleblowers is not just about technology but about our collective commitment to truth, justice, and the continuous improvement of our societal institutions. As we move forward, let us approach this possibility with both optimism for its potential and vigilance against its risks, always striving to create a more transparent, accountable, and just world.
Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts Silicon Whistleblowers: When Autonomous Robots Become Our Moral Compass 25 Questions to Help You Understand How AI will Affect Your Job in the Future AI and the Future of Human DNA Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post Silicon Whistleblowers: When Autonomous Robots Become Our Moral Compass appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
August 8, 2024
25 Questions to Help You Understand How AI will Affect Your Job in the Future

How can AI become your friend, your buddy, and coworker in the future?
As artificial intelligence continues to advance at a rapid pace, its impact on the job market is becoming an increasingly important topic of discussion. To gain a clearer understanding of how AI might shape the future of work, it’s crucial to engage in self-reflection and critical thinking. The following set of 25 questions is designed to encourage individuals to explore various aspects of AI’s potential influence on their careers, industries, and the broader job market.
These questions cover a wide range of topics, from the automation of specific job tasks to the emergence of new roles and the ethical considerations surrounding AI integration in the workplace. By contemplating both positive and negative potential outcomes for each question, individuals can develop a more nuanced and comprehensive view of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
As you consider these questions, remember that the future impact of AI on the job market is not predetermined. By actively engaging with these ideas, you can better prepare yourself for the changes to come and potentially influence the direction of AI integration in your field.
25 Questions1. Which aspects of my current job could potentially be automated by AI?Positive: AI automation could free me from repetitive tasks, allowing me to focus on more creative and strategic aspects of my job.
Negative: A significant portion of my job could be automated, potentially making my role redundant and threatening my job security.
Positive: My emotional intelligence, creativity, and ability to handle complex social situations are uniquely human traits that AI can’t easily replicate.
Negative: As AI continues to advance, even skills I consider uniquely human might eventually be replicated, leaving me with fewer competitive advantages.
Positive: AI could handle data analysis and routine tasks, allowing me to make more informed decisions and focus on high-level strategy and innovation.
Negative: While AI might enhance some aspects of my role, it could also reduce the need for human involvement, potentially diminishing my importance in the workplace.
Positive: Exciting new roles could emerge, such as AI trainers, ethics officers, or human-AI collaboration specialists, offering fresh career paths.
Negative: New jobs might require extensive retraining or education, and competition for these roles could be fierce as traditional jobs disappear.
Positive: This challenge presents an opportunity for continuous learning and personal growth, helping me develop a more diverse and valuable skill set.
Negative: Constantly adapting to keep up with AI advancements could be stressful and time-consuming, with no guarantee of long-term job security.
Positive: Understanding this could help me make informed decisions about my career path, potentially leading to more stable and rewarding opportunities.
Negative: My industry might be among those most disrupted, forcing me to consider a potentially difficult career change.
Positive: As AI handles more analytical tasks, my emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills could become increasingly valuable, enhancing my career prospects.
Negative: If AI develops sophisticated emotional intelligence capabilities, even these traditionally human skills might become less in demand.
Positive: This could lead to meaningful discussions and the development of important new roles focused on ensuring ethical AI use in my industry.
Negative: Ethical dilemmas could create conflicts in the workplace and potentially limit the benefits of AI integration.
Positive: AI could lead to increased productivity and profitability, potentially resulting in higher wages for skilled workers who can effectively work with AI.
Negative: AI might exacerbate income inequality, with benefits concentrated among a small group of highly skilled workers or company owners.
Positive: Exciting new forms of human-AI collaboration could emerge, leading to more efficient and innovative work processes.
Negative: The need to constantly adapt to new AI collaborations could be stressful and might blur the lines between human and AI contributions.
Positive: AI could create new opportunities for freelancers, such as AI training or specialized data analysis, and make it easier to find and manage gig work.
Negative: AI might automate many tasks currently performed by gig workers, reducing available opportunities and increasing competition for remaining jobs.
Positive: Awareness of AI biases could lead to improved systems and create opportunities for specialists in AI fairness and bias mitigation.
Negative: Persistent AI biases could perpetuate or exacerbate existing inequalities in my industry, potentially harming certain groups or individuals.
Positive: AI could enable more remote work opportunities, allowing me to work from anywhere and access a global job market.
Negative: AI might concentrate high-level jobs in tech hubs, forcing me to relocate or face limited local opportunities.

What new forms of human-AI teams will be formed in the future?
14. What new regulations or policies might be necessary as AI becomes more prevalent in the job market?Positive: New regulations could protect workers’ rights and ensure responsible AI use, creating a more stable and fair work environment.
Negative: Excessive or poorly designed regulations might stifle innovation and limit the potential benefits of AI in the workplace.
Positive: AI could automate tedious tasks, allowing for more flexible working hours and increased focus on fulfilling aspects of my job.
Negative: The integration of AI might lead to higher productivity expectations, resulting in increased pressure and potential burnout.
Positive: Increased awareness of AI-related safety issues could lead to improved workplace safety measures and new roles in AI safety management.
Negative: New AI-related safety risks could emerge, potentially making my workplace more dangerous or increasing job-related stress.
Positive: AI could provide more objective performance metrics, potentially leading to fairer evaluations and promotions.
Negative: Employers might use AI to more closely monitor employees, leading to decreased autonomy and increased pressure.
Positive: New, cutting-edge training programs could offer exciting opportunities for skill development and career advancement.
Negative: The need for constant retraining could be time-consuming and expensive, potentially creating barriers for some workers.
Positive: By handling routine tasks, AI could allow companies to focus on employee development, potentially increasing job satisfaction and reducing turnover.
Negative: AI could make it easier for companies to replace workers, leading to decreased job security and higher turnover rates.
Positive: AI could enable more comprehensive and fair performance evaluations, considering a wider range of factors beyond traditional metrics.
Negative: New AI-driven metrics might not accurately capture the full value of human contributions, potentially undervaluing certain skills or traits.
Positive: AI could streamline workflows, reducing stress and allowing for a more balanced work pace while maintaining high productivity.
Negative: AI might lead to unrealistic productivity expectations, increasing pressure and potentially leading to burnout.
Positive: Novel human-AI collaborations could lead to unprecedented levels of creativity and problem-solving, making work more engaging and rewarding.
Negative: Adapting to AI teamwork might be challenging and could reduce human-to-human interactions, potentially affecting workplace relationships.
Positive: AI could make hiring processes more efficient and objective, potentially reducing bias and helping me find better-fitting job opportunities.
Negative: AI-driven hiring might overlook unique human qualities or unconventional career paths, making it harder for some candidates to get noticed.
Positive: Exciting new roles could offer fresh career paths and opportunities to work at the cutting edge of AI integration in my field.
Negative: Traditional roles might disappear, forcing me to compete for limited new positions that may require significantly different skills.
Positive: AI assistance could make it easier to work longer if desired, potentially leading to extended careers and greater financial security in retirement.
Negative: Rapid AI advancements might make it difficult for older workers to keep up, potentially forcing earlier retirement or career changes.

How will we learn to compete in our AI-driven future?
Final ThoughtsThe questions and responses presented here illustrate the complex and multifaceted nature of AI’s potential impact on the job market. While AI presents numerous opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and new career paths, it also poses challenges related to job displacement, skill adaptation, and ethical considerations.It’s important to recognize that the future is not set in stone. The way AI will shape the job market depends on various factors, including technological advancements, policy decisions, and how individuals and organizations choose to implement and interact with AI systems.By regularly reflecting on these types of questions and staying informed about AI developments in your field, you can better position yourself to adapt to changes and seize new opportunities as they arise. This proactive approach can help you navigate the evolving job market with greater confidence and resilience.Remember that while AI may automate certain tasks, uniquely human skills such as creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving are likely to remain valuable. Focus on developing and honing these skills while also staying open to learning about and working alongside AI technologies.Ultimately, the key to thriving in an AI-influenced job market lies in maintaining a growth mindset, embracing lifelong learning, and being adaptable to change. By doing so, you can help shape a future where humans and AI work together to create more value and opportunities than either could alone. Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts 25 Questions to Help You Understand How AI will Affect Your Job in the Future AI and the Future of Human DNA Revolutionizing Food: How Beef-Infused Rice and Protein-Infused Vegetables Are Changing the Game Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post 25 Questions to Help You Understand How AI will Affect Your Job in the Future appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
July 24, 2024
AI and the Future of Human DNA

Will we need to build a more durable human to survive on Mars?
Our Genetic FrontierLet’s begin with a scenario where, after two manned space flights to Mars, Elon Musk concludes that for humans to survive long-term on the Red Planet, we need to develop a more durable human. Using AI to guide researchers in modifying human DNA, Musk’s quest sparks a wave of other research projects integrating AI and genetic modification. This bold venture opens the door to unparalleled opportunities and daunting challenges. The potential to rewrite the very code of life, harnessed by the precision and power of AI, promises to transform human existence in ways we can scarcely imagine. What could possibly go wrong?
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in biotechnology, the convergence of AI and genetic modification presents both unparalleled opportunities and daunting challenges. The potential to rewrite the very code of life, guided by the precision and power of AI, could transform human existence in ways we are only beginning to imagine.
On the one hand, AI-driven genetic modifications offer the tantalizing prospect of eradicating hereditary diseases, extending human lifespan, and enhancing physical and cognitive abilities. Imagine a world where debilitating conditions like cystic fibrosis, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease are relics of the past, where individuals enjoy not just longer lives but healthier, more vibrant ones. Envision children born free of genetic defects, their potential unlocked by precise genomic edits. These advancements could herald a new age of personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup, ensuring maximum efficacy with minimal side effects.
However, this brave new world is not without its shadows. The ethical and social ramifications of gene editing are profound and complex. The prospect of “designer babies,” where parents select traits such as intelligence, physical prowess, or even aesthetic qualities, raises questions about equity, consent, and the very nature of humanity. Moreover, the potential for unintended consequences looms large; off-target effects or unforeseen genetic interactions could introduce new health risks. As we navigate this genetic frontier, the specter of bioterrorism and the weaponization of genetic technologies also cannot be ignored.

Many are predicting AI-driven technologies will have the ability to identify and correct genetic mutations responsible for hereditary diseases.
Disease Prevention and TreatmentAs AI continues to advance, its application in genetic modification heralds a transformative era for disease prevention and treatment. In its common application, AI-driven technologies can meticulously identify and correct genetic mutations responsible for hereditary diseases. Conditions such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington’s disease, which have long plagued families and strained healthcare systems, could see a dramatic reduction in prevalence. By targeting the root cause at the DNA level, AI can facilitate precise gene editing, ensuring that faulty genes are corrected before they manifest as debilitating conditions. This proactive approach not only improves the quality of life for individuals but also alleviates the overall burden on healthcare resources by reducing the need for long-term treatment and care for these chronic diseases.Looking beyond the common applications, the extreme potential of AI in genetic modification paints a picture of a world free from genetic diseases altogether. The eradication of all hereditary conditions would represent a monumental leap forward in human health. This could lead to a population that not only lives longer but also enjoys a higher quality of life, free from the pain and limitations imposed by genetic disorders. The healthcare system, traditionally burdened by the treatment and management of chronic genetic diseases, would undergo a profound transformation. Resources could be redirected towards preventive care and other critical areas, fostering a healthier society overall. This paradigm shift would not only benefit individuals and families but also have far-reaching economic implications, potentially reducing healthcare costs and increasing productivity across populations.However, the path to such a utopia is fraught with ethical, social, and scientific challenges. The prospect of eradicating genetic diseases raises questions about accessibility and equity—will these advanced treatments be available to all or only to those who can afford them? Furthermore, the long-term consequences of widespread genetic modification are still largely unknown. While the immediate benefits are clear, the full impact on human genetics and evolution may take generations to understand. As we stand on the brink of this genetic frontier, it is crucial to navigate these waters with caution, ensuring that the pursuit of disease eradication through AI and genetic modification is guided by ethical principles and a commitment to equitable healthcare access.
Will we be able to cure diseases such as Alzheimer’s, heart disease, and even human aging?
Enhanced Lifespan and Quality of LifeWhen it comes to enhancing human lifespan and quality of life, AI-driven genetic modifications offer unprecedented possibilities. At a common level, these advancements could significantly slow the aging process, extend lifespan, and improve overall quality of life by targeting and mitigating age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s and heart disease. By identifying and modifying specific genes that contribute to these conditions, AI can help maintain cognitive and physical health well into old age. This would not only enhance individual well-being but also reduce the societal and economic burdens associated with caring for an aging population, leading to a more productive and healthier society.However, the extreme potential of AI in genetic modification stretches far beyond merely extending life expectancy. The concept of achieving biological immortality—where individuals could live indefinitely without the physical and cognitive decline associated with aging—ushers in a new paradigm of human existence. In this scenario, the human body would be perpetually rejuvenated, cells continuously repaired, and diseases kept at bay indefinitely. Such a breakthrough would revolutionize our understanding of life and death, dramatically altering personal, social, and economic structures. The implications of an ageless society are profound, ranging from redefined life stages and extended careers to new dynamics in relationships and generational interactions.Yet, the pursuit of biological immortality is not without its ethical and existential dilemmas. The societal impact of potentially immortal individuals includes issues of overpopulation, resource allocation, and deepening social inequalities, as access to such technologies may be limited to the wealthy. Moreover, the psychological effects of an endless life could lead to unforeseen mental health challenges. The desire to overcome aging must be balanced with considerations of its broader implications, ensuring that advancements are approached with caution, equity, and a deep understanding of the potential consequences. As we explore these frontiers, it is crucial to foster an ethical framework that addresses both the remarkable possibilities and the significant risks of AI-driven genetic modifications in enhancing human lifespan and quality of life.
AI-enhanced DNA can lead to significant improvements in physical strength, endurance, and cognitive functions.
Improved Physical and Cognitive AbilitiesThe integration of AI in genetic modification opens up remarkable avenues for improving human physical and cognitive abilities. On a common level, AI-driven enhancements can lead to significant improvements in physical strength, endurance, and cognitive functions. These advancements could dramatically increase productivity and drive progress across various fields, from sports and entertainment to science and engineering. Imagine athletes with enhanced stamina and agility, researchers with superior memory and problem-solving capabilities, and workers who can maintain peak performance levels for longer periods. These enhancements would not only boost individual potential but also contribute to societal advancements by accelerating innovation and efficiency.
However, the extreme potential of AI in genetic modification goes even further, envisioning the creation of “superhumans” with abilities far beyond current human capabilities. These individuals could possess exceptional intelligence, near-perfect memory, unparalleled physical agility, and resilience to extreme environments. Such enhancements could lead to a new era of exploration and achievement, enabling humans to thrive in previously inhospitable environments, such as deep ocean depths or distant planets. The concept of superhumans challenges our understanding of human limits and presents the possibility of a future where enhanced individuals push the boundaries of what is scientifically and technologically possible.
Nevertheless, the pursuit of creating superhumans raises profound ethical, social, and existential questions. The introduction of genetically enhanced individuals could lead to significant inequalities, as those with access to such technologies would gain unprecedented advantages over the naturally born population. This disparity could deepen social divides and create a new class of genetically privileged individuals. Moreover, the psychological and societal impacts of such enhancements need careful consideration. How will society value unenhanced humans? What will become of human diversity and the essence of human experience?
Addressing these challenges requires a thoughtful approach, balancing the pursuit of human enhancement with a commitment to ethical principles, equity, and the preservation of our shared humanity. As we stand on the threshold of this transformative era, it is crucial to navigate these possibilities with wisdom and foresight.

By analyzing a person’s unique genetic makeup, AI can predict how they will respond to certain medications, potential health risks, and develop personalized treatment plans.
Personalized MedicineThe advent of AI in genetic modification heralds a new era in personalized medicine, transforming how we approach healthcare. At its core, personalized medicine involves tailoring medical treatments to an individual’s genetic profile, leading to more effective and precise interventions. By analyzing a person’s unique genetic makeup, AI can predict how they will respond to certain medications, identify potential health risks, and recommend personalized treatment plans. This approach can significantly improve treatment outcomes, reduce the trial-and-error aspect of prescribing medications, and minimize the occurrence of side effects. For instance, a patient with a genetic predisposition to metabolize certain drugs rapidly can receive a higher dose to achieve therapeutic effects. In contrast, those who metabolize drugs slowly can avoid potentially harmful overdoses.Looking beyond the common applications, the extreme potential of personalized medicine offers a vision of healthcare where adverse drug reactions are completely eliminated and health management is optimized to an unprecedented degree. In this scenario, every individual would receive treatments perfectly tailored to their genetic profile, ensuring maximum efficacy and safety. AI could continuously monitor and analyze an individual’s health data in real-time, adjusting treatments as needed to maintain optimal health. This level of precision medicine would revolutionize chronic disease management, preventive care, and overall health maintenance, leading to a population that is healthier and more resilient to illnesses.However, the journey towards this idealized vision of personalized medicine is fraught with challenges and ethical considerations. The vast amounts of genetic data required for such precision raise significant privacy concerns. Ensuring that individuals’ genetic information is protected from misuse and that data security measures are robust is paramount. Additionally, equitable access to personalized medicine must be addressed to prevent a disparity where only the wealthy benefit from advanced healthcare technologies. The ethical implications of genetic data ownership, consent, and potential discrimination also need careful deliberation. As we advance towards a future where personalized medicine becomes the norm, it is essential to develop a framework that balances innovation with ethical responsibility, ensuring that the benefits of these groundbreaking technologies are accessible to all.
When things go wrong! Even with advanced AI, there is a risk of off-target effects or unintended genetic mutations.
Negative Results of AI-Driven Genetic ModificationAs the integration of AI and genetic modification progresses, it brings with it a host of potential negative outcomes that must be carefully considered. One of the primary concerns is the possibility of unintended consequences and genetic errors. Even with advanced AI, there is a risk of off-target effects or unintended genetic mutations. These mistakes could introduce new health issues or exacerbate existing conditions, potentially creating a cascade of unforeseen medical problems. In extreme cases, widespread genetic anomalies could lead to new epidemics of diseases or disorders, posing a significant public health challenge.
Ethical and social issues also loom large in the discussion of AI-driven genetic modification. The concept of “designer babies” raises serious ethical concerns about the societal implications of selecting certain traits. This practice could lead to new forms of discrimination and inequality, as those who can afford genetic enhancements may gain unfair advantages. At its most extreme, the pursuit of genetic perfection could result in deep societal divisions. A clear divide between a genetically modified elite and the natural-born population could emerge, leading to social unrest, conflict, and even large-scale violence as the marginalized groups rebel against their perceived inferiority.
Another significant risk is the potential loss of genetic diversity. When certain traits are preferred and selected for, the genetic diversity of the human population could be reduced. This homogeneity makes the population more vulnerable to specific diseases or environmental changes, as a lack of diversity can weaken the collective resilience to new challenges. In an extreme scenario, a genetic monoculture could develop, where the collapse of human resilience against novel pathogens or drastic environmental shifts could have catastrophic consequences.
The potential for bioterrorism and the weaponization of genetic technology is another grave concern. AI and genetic modification technologies could be misused to create harmful biological agents or genetically engineered pathogens. In common misuse scenarios, these technologies could lead to the development of targeted bioweapons that pose significant threats to global security. In the most extreme cases, the use of genetic weapons to target specific populations or individuals could lead to acts of genocide or targeted bioterrorist attacks, resulting in massive loss of life and widespread fear.
Finally, the issue of privacy and autonomy becomes critical as genetic modification technologies advance. Concerns over genetic data privacy are paramount, as there is a risk that genetic information could be misused by governments, corporations, or malicious actors. This misuse could lead to scenarios where individuals’ genetic data is exploited for discriminatory purposes or financial gain. In the most dystopian extreme, individuals could be forced to undergo genetic modifications or be constantly monitored and controlled based on their genetic profiles. This loss of personal freedom and autonomy could lead to a society where genetic determinism dictates one’s opportunities and quality of life, eroding the fundamental principles of individual rights and freedoms.

The potential benefits are staggering, from eradicating hereditary diseases and extending lifespans to enhancing physical and cognitive abilities.
Final ThoughtsAs we venture deeper into the genetic frontier, the interplay between AI and genetic modification promises to reshape human existence in profound ways. The potential benefits are staggering, from eradicating hereditary diseases and extending lifespans to enhancing physical and cognitive abilities. Personalized medicine, tailored precisely to an individual’s genetic makeup, could revolutionize healthcare, making treatments more effective and reducing adverse drug reactions. These advancements paint a picture of a future where humans lead longer, healthier, and more productive lives, free from many of the limitations that have plagued our species for millennia.However, this brave new world is fraught with ethical, social, and existential challenges that we must navigate with caution. The specter of unintended genetic consequences, deepened social inequalities, loss of genetic diversity, and the potential misuse of biotechnologies cast a long shadow over these advancements. As we stand on the precipice of these transformative changes, it is imperative that we develop robust ethical frameworks and regulatory measures to guide the responsible use of AI and genetic modification. By fostering an inclusive dialogue that considers the diverse perspectives and values of all stakeholders, we can harness the power of these technologies to benefit humanity while safeguarding against their potential perils. The journey ahead is as exhilarating as it is uncertain, and it is our collective responsibility to ensure that it leads to a future that upholds the dignity and well-being of all. Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts AI and the Future of Human DNA Revolutionizing Food: How Beef-Infused Rice and Protein-Infused Vegetables Are Changing the Game Defining AI Ethics for the Future Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post AI and the Future of Human DNA appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
July 11, 2024
Revolutionizing Food: How Beef-Infused Rice and Protein-Infused Vegetables Are Changing the Game

South Korean scientists have developed beef-infused rice as a sustainable protein source.
Step One: Beef-Infused RiceIn a groundbreaking leap towards sustainable nutrition, scientists from South Korea’s Yonsei University have unveiled a revolutionary food innovation: beef-infused rice. This novel creation involves the cultivation of cow muscle and fat cells within grains of rice, resulting in a high-protein hybrid food. Unlike traditional genetically modified foods, this process does not alter the DNA of the plants or animals. Instead, it uses advanced cell culturing techniques to integrate animal cells into rice grains, yielding a product that is both nutritionally rich and environmentally friendly.
The concept is straightforward yet profound. By inserting cow stem cells into the porous structure of rice grains and allowing them to grow in a controlled environment, researchers have created a food source that offers more protein and fat than standard rice. This innovation holds significant promise as a sustainable alternative to conventional meat, boasting a low carbon footprint and the potential for large-scale, efficient production.
In an era where the global demand for protein is soaring, and the environmental impact of traditional meat production is increasingly scrutinized, beef-infused rice emerges as a beacon of hope. It represents a crucial step towards addressing food security and sustainability challenges, providing a glimpse into the future of food where technology and biology converge to create healthier, more sustainable options. As we explore the intricacies and potential of this hybrid food, it becomes clear that beef-infused rice could play a pivotal role in reshaping our dietary landscape.
Beef-infused rice contains more fat and protein than standard rice.
The Science Behind Beef-Infused RiceThe creation of beef-infused rice is a marvel of modern biotechnology, representing a sophisticated blend of cellular biology and food science. The process begins with the extraction of muscle and fat stem cells from cows. These cells are meticulously inserted into the grains of rice, which serve as a nurturing environment for cell growth. This intricate procedure takes place in a Petri dish, where the rice grains act as tiny incubators, fostering the development of animal cells.
One key factor making this process viable is the porous structure of the rice grains. This unique characteristic allows the grains to absorb and hold onto the stem cells, providing a supportive matrix that mimics the natural conditions within an animal body. To enhance this cell attachment and growth, the rice grains are coated with a layer of fish-derived gelatine. This coating not only aids in the adherence of the cells but also supplies additional nutrients, facilitating a more efficient and robust cell development process.
When compared to other cultured meat products, such as those grown in soy-based textured vegetable protein (TVP), beef-infused rice stands out due to its superior cell-holding potential and allergen-free nature. Soy and nuts, commonly used substrates for cultured meat, are limited by their allergenic properties and less optimal cell-supporting structures. Rice grains, on the other hand, offer a more conducive environment for cell growth, making them an ideal medium for producing hybrid foods that blend plant and animal components seamlessly.
This pioneering approach not only enhances the nutritional profile of the rice, adding significant amounts of protein and fat, but also paves the way for more sustainable and scalable meat alternatives. The integration of cow cells into rice grains highlights a transformative step in food technology, aiming to meet the growing global protein demand while minimizing environmental impact. Through continuous innovation and optimization, the potential of beef-infused rice and similar hybrid foods to revolutionize our diets becomes increasingly apparent.

Future foods will come in shapes and forms that are not easily recognizable.
Nutritional and Environmental BenefitsBeef-infused rice offers a remarkable nutritional profile, boasting significantly higher protein and fat content compared to standard rice. Each 100-gram serving of this hybrid rice contains 3,890 milligrams of protein and 150 milligrams of fat. Although these values represent only a modest increase over traditional rice, the nutritional gains are significant in the context of plant-based foods. As technology advances and the cell capacity of rice grains improves, the protein content of beef-infused rice is expected to rise even further, potentially rivaling that of conventional meat.In addition to its nutritional advantages, beef-infused rice presents a compelling case for environmental sustainability. Traditional beef production is notoriously resource-intensive, requiring vast amounts of land, water, and feed, and it is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, the production process for beef-infused rice involves growing cow cells in rice grains, a method that substantially reduces the environmental footprint. The hybrid rice can be produced in less than ten days, a fraction of the time required for conventional beef farming, and with significantly lower resource consumption.The potential for commercialization of beef-infused rice is vast, with far-reaching implications for global food security. This hybrid food could play a crucial role in addressing hunger and malnutrition in areas affected by famine, providing a nutrient-dense, shelf-stable food source. Its efficiency and rapid production cycle make it ideal for military rations, offering soldiers a high-protein, sustainable food option that can be easily transported and stored. Furthermore, the compact nature and nutritional density of beef-infused rice make it an excellent candidate for space missions, where efficient use of resources is paramount.As beef-infused rice transitions from research to market, it holds the promise of transforming our approach to food production and consumption. By combining the best attributes of plant-based and cultured meat technologies, this innovative product addresses critical challenges related to nutrition, sustainability, and food security, paving the way for a more resilient and equitable global food system.
Combining beef and rice into the beef-infused rice on top.
Current Challenges and Future ProspectsDespite its promising potential, beef-infused rice faces several challenges, particularly in terms of taste and texture. The cell culturing process alters the rice’s physical properties, resulting in grains that are more firm and brittle compared to traditional rice. Additionally, the process introduces new odor compounds related to beef, almonds, cream, butter, and coconut oil, which may be unfamiliar and potentially unappealing to some consumers. These sensory changes present significant hurdles that need to be addressed to ensure broader acceptance of the product.
Lead researcher Jinkee Hong acknowledges these challenges but remains optimistic about hybrid food’s future. According to Hong, the current taste profile of beef-infused rice is “pleasant and novel,” suggesting that while the product may differ from what consumers are accustomed to, it offers a unique and enjoyable eating experience. This feedback is crucial as it guides future research and development efforts to refine the product’s sensory attributes, making it more palatable and acceptable to a wider audience.
Looking ahead, the research team at Yonsei University has outlined several goals to enhance the nutritional value and sensory qualities of beef-infused rice. One primary objective is to increase the cell growth capacity within the rice grains, thereby boosting the protein content and overall nutritional profile. Achieving this will involve optimizing the conditions for cell culture and exploring new techniques to maximize the efficiency of cell incorporation.
Additionally, improving the taste and texture of beef-infused rice remains a critical focus. Researchers are investigating methods to balance the firmness and brittleness of the grains, aiming to create a texture that more closely resembles traditional rice while maintaining the added nutritional benefits. Addressing the odor compounds and ensuring a more neutral or desirable flavor profile will also be key to enhancing consumer acceptance.
As these challenges are progressively overcome, the future prospects for beef-infused rice appear increasingly bright. With continuous advancements in cell culture technology and food science, this innovative hybrid food has the potential to become a staple in sustainable diets worldwide. By providing a high-protein, low-carbon alternative to conventional meat, beef-infused rice could play a significant role in addressing global food security and environmental sustainability challenges, paving the way for a new era of nutrition.

These designs by Leyu Li suggest how lab-grown meat might be marketed to vegetarians and vegans.
The Broader Implications for Protein-Infused VegetablesThe innovation of beef-infused rice opens the door to a new realm of hybrid foods that blend lab-grown meat with vegetables, promising transformative impacts on meat consumption and agriculture. Researchers and speculative designers have begun to explore a variety of other intriguing combinations, such as Broccopork, Mushchicken, and Peaf. These conceptual products integrate cultivated meat cells with vegetables like broccoli, mushrooms, and peas, creating nutritionally enhanced foods that offer the benefits of both plant-based and meat proteins.
In addition to these early concepts, the potential combinations are virtually limitless, paving the way for an array of hybrid foods that cater to diverse culinary preferences and nutritional needs. Imagine lab-grown fish fillets paired with corn and potatoes, creating a hearty and protein-rich meal that mimics traditional fish and chips but with a significantly lower environmental footprint. Similarly, lab-grown pork could be combined with carrots and beans, offering a sustainable alternative to classic pork and vegetable stews.
The integration of lab-grown chicken with vegetables like broccoli, cabbage, and even bread could result in innovative dishes such as chicken and broccoli stir-fry or chicken-stuffed cabbage rolls. These dishes would provide a rich source of protein while promoting better land use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Lab-grown turkey could be paired with beans and potatoes to create nutritious and filling meals that are both familiar and forward-thinking.
Moreover, the combination of lab-grown beef with vegetables such as corn and carrots could yield hybrid foods like beef and vegetable casseroles, combining the flavors and textures of traditional meat dishes with the sustainability of plant-based ingredients. The versatility of these hybrid foods extends to every day staples as well, with possibilities like lab-grown meat sandwiches using lab-grown beef or pork combined with bread, creating a convenient and protein-packed meal option.
As researchers continue to refine these hybrid food technologies, we can anticipate a future where our meals not only taste good but also contribute to a more sustainable and equitable food system. These innovations highlight the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume food, making it possible to enjoy the nutritional benefits of both meat and vegetables while minimizing the environmental impact. By embracing these hybrid foods, we move closer to a world where delicious, nutritious, and sustainable food is accessible to all.

The future of food will be both exciting and scary all at the same time.
Final ThoughtsBeef-infused rice stands as a groundbreaking innovation in the realm of sustainable, high-protein foods. By seamlessly integrating cow muscle and fat cells into rice grains, scientists have created a hybrid food that offers enhanced nutritional benefits while maintaining a low carbon footprint. This pioneering step not only addresses the growing global demand for protein but also provides a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional meat production. The development of beef-infused rice showcases the potential of cellular agriculture to transform our food systems, making them more resilient and sustainable.Looking ahead, the continued innovation in this field holds the promise of ushering in a new era of food production that prioritizes both nutrition and environmental sustainability. Advances in cell culture technology and food science will likely lead to even more efficient and nutritious hybrid foods, further bridging the gap between plant-based and animal-based proteins. As researchers refine the processes and overcome current challenges, we can expect to see a wider range of hybrid foods that cater to diverse dietary needs and preferences, ultimately contributing to global food security and public health.The potential of beef-infused rice and similar hybrid foods to revolutionize our diets underscores the need for further research and investment in this promising field. Governments, private sector investors, and research institutions must collaborate to support the development and commercialization of hybrid food technologies. By doing so, we can unlock their full potential, ensuring that they become a viable and widely accessible solution to some of the most pressing challenges facing our global food systems. Investing in the future of hybrid foods is not just an opportunity; it is an imperative for building a better world. Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts Revolutionizing Food: How Beef-Infused Rice and Protein-Infused Vegetables Are Changing the Game Defining AI Ethics for the Future “Goldene” — The World’s Newest Super Material Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post Revolutionizing Food: How Beef-Infused Rice and Protein-Infused Vegetables Are Changing the Game appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
June 27, 2024
Defining AI Ethics for the Future

The future will remain cloudy until the ethics are clear!
Establishing a Universally Accepted Set of StandardImagine a scenario where an AI-driven hiring platform is used by a multinational corporation to screen job applicants. While the platform promises to streamline the hiring process and identify the best candidates efficiently, it soon becomes evident that the AI algorithm exhibits a bias against certain races and low-income neighborhoods. Qualified candidates from these groups are unfairly filtered out, perpetuating systemic inequalities. This situation underscores the need for a universally accepted set of AI ethics to address a number of challenging issues.
Naturally, the problem of bias in AI systems extends far beyond hiring platforms. For instance, facial recognition technologies have been shown to have higher error rates for certain races, resulting in potential discrimination and unjust treatment. Ethical guidelines are essential to ensure fairness and prevent such harm. In the healthcare sector, AI-driven diagnostic tools must be designed with a focus on equitable access and unbiased decision-making to avoid worsening health disparities.
Data privacy is a significant concern as AI technologies increasingly rely on vast amounts of personal data. The controversial use of AI by social media platforms to analyze and monetize user data without explicit consent highlights the importance of robust ethical standards to protect individuals’ privacy and autonomy. Similarly, in finance, AI algorithms used for credit scoring must be transparent and fair to prevent unjust financial exclusion.
The deployment of autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars, presents profound ethical dilemmas. The potential for accidents involving these vehicles raises questions about liability and the moral implications of decision-making algorithms in life-and-death situations. Developing these technologies with safety and ethical considerations at the forefront is crucial to gaining public trust and acceptance.
Lastly, the use of AI in surveillance and security applications poses significant ethical challenges. Government deployment of AI-powered surveillance systems can lead to invasive monitoring and potential human rights violations. Establishing clear ethical guidelines is essential to balance security needs with the protection of civil liberties and privacy.
Addressing these ethical issues through a universally accepted set of AI ethics is paramount for guiding the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies. Such a framework ensures fairness, protects privacy, promotes safety, and upholds human rights, fostering trust and innovation while safeguarding against potential harm.

Transparency allows users, stakeholders, and regulators to understand how AI functions!
Principal #1 – TransparencyTransparency in AI ethics is the principle that calls for openness and clarity in the development, deployment, and operation of AI systems. This principle ensures that the processes, data, and decision-making mechanisms behind AI technologies are accessible and understandable to all stakeholders, including users, developers, and regulators. Organizations can foster trust, enable accountability, and facilitate informed decision-making by prioritizing transparency.
To implement transparency, organizations must take several important steps. First, they should provide clear documentation and communication about how AI systems function. This includes detailed descriptions of the algorithms used, the data sources, and the criteria for decision-making. Such documentation helps users and other stakeholders understand how the AI system works and how its outcomes are produced.
Second, organizations should ensure that AI systems are explainable. This means developing AI technologies in a way that their decision-making processes can be easily interpreted and understood by humans. Techniques such as interpretable machine learning models or post-hoc explanation methods can be used to achieve this. Explainability is crucial for helping users comprehend why a particular decision was made, especially in critical applications such as healthcare, finance, or criminal justice.
Third, transparency involves providing users with meaningful control over their interactions with AI systems. Users should be informed about what data is being collected about them, how it is being used, and who has access to it. Additionally, they should have the ability to opt out or modify their data-sharing preferences. This empowers users to make informed choices about their engagement with AI technologies.
An example of transparency in practice can be seen in the use of AI for content moderation on social media platforms. These platforms use AI algorithms to detect and remove harmful content, such as hate speech or misinformation. To ensure transparency, social media companies can publish detailed reports and guidelines explaining how their content moderation algorithms work. These reports should include information about the types of content being flagged, the data sources used for training the algorithms, and the criteria for identifying harmful content.
Furthermore, social media platforms can provide users with explanations when their content is flagged or removed by the AI system. For instance, if a user’s post is taken down, they should receive a clear explanation detailing why the content was deemed inappropriate and which guidelines it violated. This transparency helps users understand the moderation process and builds trust in the platform’s efforts to maintain a safe online environment.
The principle of transparency in AI ethics emphasizes the importance of openness, clarity, and user empowerment. By providing clear documentation, ensuring explainability, and offering users control over their data, organizations can build trust and facilitate informed decision-making. This approach not only enhances the ethical integrity of AI systems but also promotes greater acceptance and confidence among users and stakeholders.

AI Accountability involves addressing any harm or unintended consequences caused by AI technologies!
Principal #2 – AccountabilityAccountability in AI ethics is the principle that ensures those who develop, deploy, and operate AI systems are responsible for their actions and the impacts of those systems. This principle involves creating clear lines of responsibility and establishing mechanisms to address any adverse outcomes or ethical breaches that may arise from the use of AI technologies. By fostering accountability, stakeholders can ensure that AI systems are used responsibly and that any negative consequences are promptly and effectively managed.
Implementing accountability requires several critical actions. First, organizations must establish clear governance frameworks that delineate roles and responsibilities at every stage of the AI lifecycle. This includes defining who is responsible for the design, development, testing, deployment, and monitoring of AI systems. Clear accountability structures help ensure that individuals and teams can be held responsible for the performance and ethical behavior of AI technologies.
Transparency is a crucial component of accountability. Organizations must provide clear and accessible information about how AI systems function, including the data they use, the algorithms they employ, and the decision-making processes they follow. This transparency allows stakeholders, including users and regulatory bodies, to understand and scrutinize AI operations, thereby promoting accountability.
Organizations should implement robust monitoring and evaluation processes to track the performance and impact of AI systems continuously. These processes should include mechanisms for identifying and addressing any issues, such as biases, errors, or unintended consequences, that may arise. Regular audits and impact assessments can help ensure that AI systems remain aligned with ethical standards and societal values.
An example of accountability in practice can be seen in the deployment of AI in financial services, such as automated loan approval systems. These systems use algorithms to assess applicants’ creditworthiness and make decisions about loan approvals. To ensure accountability, the financial institution must establish clear guidelines and oversight mechanisms for the AI system’s use. This includes defining who is responsible for the system’s accuracy and fairness ensuring that any errors or biases in the algorithm are promptly corrected.
Moreover, the institution should provide transparent explanations to loan applicants about how decisions are made, including the criteria used by the AI system. If an applicant is denied a loan, they should have access to information that explains the decision and offers a pathway to appeal or request a human review. This transparency and recourse mechanism helps ensure that the AI system operates fairly and that applicants can hold the institution accountable for its decisions.
The principle of accountability in AI ethics emphasizes the importance of clear governance, transparency, and continuous monitoring. By establishing robust accountability frameworks, organizations can ensure that AI systems are used responsibly and ethically, fostering trust and confidence among users and stakeholders. This approach not only mitigates potential risks but also enhances the overall integrity and effectiveness of AI technologies.

Fairness means that all AI systems should be designed to avoid bias and ensure equitable treatment for all!
Principal #3 – FairnessFairness in AI ethics is a critical principle that ensures AI systems are developed and deployed in a manner that is impartial, just, and free from bias. This principle focuses on creating AI technologies that treat all individuals equally, regardless of race, gender, socioeconomic status, or other characteristics. By prioritizing fairness, developers can prevent AI systems from perpetuating existing inequalities or introducing new forms of discrimination.
Achieving fairness involves several key practices. First, it requires rigorous scrutiny of the data used to train AI systems. Data must be representative of diverse populations to avoid biases that could skew the system’s outcomes. Additionally, developers should implement algorithms that are designed to identify and mitigate biases, ensuring that AI decisions are made based on relevant and ethical criteria.
Fairness necessitates ongoing monitoring and evaluation of AI systems. Even well-intentioned algorithms can produce unfair outcomes if not regularly assessed and updated. Continuous oversight helps to identify any emerging biases and allows for timely adjustments to maintain fairness.
An example of fairness in action can be seen in the use of AI for hiring processes. Many companies are turning to AI to screen job applications and identify the best candidates. To ensure fairness, it is crucial that these AI systems do not inadvertently favor or disadvantage certain groups. For instance, if an AI hiring tool is trained on data that predominantly includes successful candidates from one demographic group, it may develop a bias that unfairly excludes candidates from other groups.
To address this, developers can take several steps. First, they should ensure the training data is diverse and representative of all potential candidates. This might involve sourcing data from various industries, regions, and demographic groups. Second, the AI algorithms should be tested for bias and adjusted to eliminate any unfair advantages. Techniques such as fairness-aware machine learning can be employed to balance the consideration of different candidate attributes and prevent discriminatory outcomes.
Moreover, transparency in the AI hiring process is essential. Companies should clearly explain how their AI systems evaluate applications and provide candidates with insights into the decision-making process. This transparency helps build trust and allows candidates to understand and contest decisions if they feel they have been treated unfairly.
The principle of fairness in AI ethics is about ensuring that AI systems operate without bias and treat all individuals equitably. By using diverse and representative data, implementing bias mitigation techniques, and maintaining transparency, developers can create AI technologies that uphold fairness and contribute to a more just society. This commitment to fairness not only enhances the ethical integrity of AI systems but also fosters greater trust and acceptance among users.

For AI, maintaining robust privacy protections is crucial for building trust!
Principal #4 – PrivacyPrivacy is a fundamental principle in AI ethics, emphasizing the protection of individuals’ personal data and ensuring that their information is used in a way that respects their rights and autonomy. In the era of big data and pervasive digital technologies, safeguarding privacy is more important than ever. This principle entails not only securing data against unauthorized access and breaches but also ensuring that individuals are informed and have control over how their data is collected, used, and shared.
Ensuring privacy involves implementing strong data protection measures throughout the AI system lifecycle. This includes encryption, anonymization, and secure data storage practices to protect personal information from unauthorized access. Furthermore, transparency is crucial; organizations must clearly communicate their data practices, including what data is being collected, for what purposes, and how it will be used. Users should have the ability to consent to data collection and usage practices and to withdraw consent at any time.
An example of prioritizing privacy can be seen in the use of AI in healthcare applications. Consider a mobile health app that collects data from users to provide personalized health recommendations. To uphold the principle of privacy, the app must ensure that all collected data is securely stored and that access to this data is strictly controlled. The app should use encryption to protect data both in transit and at rest, ensuring that sensitive health information is not exposed to unauthorized parties.
Additionally, the app should be transparent about its data practices. Users should be clearly informed about what data is being collected, such as their activity levels, dietary habits, and biometric data. The app should explain how this data will be used to generate health recommendations and whether it will be shared with third parties, such as researchers or advertisers. Importantly, users should be able to easily access and manage their data, including viewing what information has been collected, updating their preferences, and deleting their data if they choose to discontinue using the app.
Moreover, privacy also involves limiting data collection to what is strictly necessary for the app’s functionality. For example, if the health app aims to provide dietary recommendations, it should not collect unrelated data, such as the user’s location history, unless it is essential for providing accurate advice. This practice, known as data minimization, helps reduce the risk of privacy breaches and ensures that users’ personal information is not unnecessarily exposed.
The principle of privacy in AI ethics requires robust data protection measures, transparency, and user control over personal information. By prioritizing these aspects, organizations can build AI systems that respect individuals’ privacy rights and foster trust among users. This approach not only enhances the ethical use of AI but also contributes to the broader goal of protecting individuals’ autonomy and dignity in the digital age.

The principle of safety and security in AI ethics underscores the need for thorough robust cybersecurity measures!
Principal #5 – Safety and SecuritySafety and security in AI development and deployment are critical to ensuring that these technologies do not cause harm and that they operate reliably under various conditions. This principle emphasizes the importance of creating AI systems that are resilient, predictable, and secure against both inadvertent errors and malicious attacks. By prioritizing safety and security, developers can build trust in AI technologies and ensure their long-term viability and acceptance.
To ensure the safety of AI systems, developers must implement rigorous testing and validation processes. These processes include comprehensive simulations and real-world trials to evaluate the performance of AI systems in diverse scenarios. For instance, an AI system used in healthcare for diagnostic purposes must be thoroughly tested to ensure its accuracy across different patient demographics and medical conditions. This helps to prevent misdiagnoses and ensures that the AI system provides reliable support to healthcare professionals.
Security is another crucial aspect, as AI systems often handle sensitive data and perform critical functions. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures protects AI systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. This involves implementing advanced encryption techniques, secure data storage, and continuous monitoring to detect and respond to potential security breaches. For example, in the case of AI systems used in financial services, such as automated trading platforms, stringent security measures are necessary to protect against hacking attempts that could result in significant financial losses.
An example of prioritizing safety and security can be seen in the development of AI systems for autonomous drones used in delivery services. These drones must navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, and deliver packages safely to designated locations. To ensure their safe operation, developers conduct extensive testing in various environments, including urban areas with high levels of pedestrian and vehicular traffic. This testing helps to identify potential failure points and allows developers to refine the drone’s navigation algorithms to improve safety.
Additionally, security measures are crucial for protecting the drone’s communication systems from hacking attempts. Unauthorized access to the drone’s controls could lead to disastrous outcomes, such as crashes or the delivery of packages to incorrect locations. To mitigate these risks, developers implement secure communication protocols and encryption to ensure that only authorized personnel can control the drones.
The principle of safety and security in AI ethics underscores the need for thorough testing, validation, and robust cybersecurity measures. By prioritizing these aspects, developers can create AI systems that are reliable, secure, and capable of operating safely in diverse conditions. This approach not only enhances the safety and security of AI systems but also builds trust among users and stakeholders, fostering greater acceptance and integration of AI technologies in various sectors.

By prioritizing the needs of users, AI developers can create systems that are empathetic, respectful, and beneficial to all!
Principal #6 – Human-Centered ValuesHuman-centered values in AI ethics emphasize that AI systems should be designed and deployed to align with and support the well-being, rights, and dignity of individuals. This principle prioritizes the human experience, ensuring that technological advancements serve to enhance rather than diminish our quality of life. By embedding human-centered values into AI, developers can create systems that are empathetic, respectful, and beneficial to all users.
Implementing human-centered values involves several key considerations. First, it requires a deep understanding of the diverse needs and values of different user groups. This understanding can be achieved through comprehensive user research, participatory design processes, and continuous feedback loops. By actively involving users in the design process, developers can ensure that AI systems are tailored to meet real-world needs and preferences.
Second, human-centered AI prioritizes user autonomy and empowerment. This means providing users with control over how AI systems interact with them, including clear options to opt in or out of certain functionalities. Transparency is also crucial; users should be fully informed about how AI systems operate, what data they collect, and how decisions are made. This openness helps to build trust and allows users to make informed decisions about their interactions with AI.
An example of human-centered values in action can be seen in the development of AI systems for elder care. AI technologies, such as companion robots or health monitoring systems, have the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for older adults. However, to ensure these systems truly serve their users, developers must prioritize human-centered values throughout the design and deployment process.
For instance, companion robots designed for elderly users should be developed with a deep understanding of the social, emotional, and physical needs of older adults. This involves conducting extensive research and involving elderly users in the design process to gather insights into their preferences and challenges. The robots should be programmed to offer not only assistance with daily tasks but also companionship, promoting social interaction and reducing feelings of loneliness.
Moreover, these systems should respect the autonomy and dignity of older adults. Users should have control over when and how they use the robots, with clear instructions and easy-to-use interfaces. Transparency about data collection and privacy measures is essential to ensure that users feel comfortable and secure while using the technology.
Human-centered values in AI ethics ensure that technological advancements are designed and deployed with a focus on enhancing human well-being, autonomy, and dignity. By prioritizing the needs and values of users, AI developers can create systems that are empathetic, respectful, and beneficial to society. This approach not only improves the user experience but also fosters trust and acceptance of AI technologies.

Inclusivity means the voices and perspectives of diverse stakeholders are actively involved!
Principal #7 – InclusivityInclusivity in AI development and deployment ensures that the voices and perspectives of diverse stakeholders are actively involved in the decision-making process. This principle is vital for creating AI systems that are equitable and considerate of the varied needs and experiences of different segments of society. By involving a broad range of stakeholders, including those from underrepresented and marginalized groups, AI developers can identify and mitigate biases, address potential disparities, and design systems that are truly beneficial to all users.
Inclusivity requires proactive engagement with diverse communities throughout the AI lifecycle, from initial design and development to deployment and ongoing evaluation. This engagement can take many forms, such as inclusive design workshops, stakeholder consultations, and participatory research methods. The goal is to gather insights and feedback from a wide array of individuals, ensuring that AI technologies do not inadvertently reinforce existing inequalities or create new forms of discrimination.
An example of inclusivity in action can be seen in the development of AI-driven healthcare applications. When designing an AI system to assist with medical diagnoses, it is crucial to include input from a diverse group of patients, healthcare providers, and community representatives. For instance, a project aimed at improving maternal health outcomes should involve pregnant women from various ethnic, socio-economic, and geographic backgrounds. By doing so, developers can ensure that the AI system is sensitive to the unique health concerns and conditions prevalent in different populations. This inclusive approach helps to build AI systems that are more accurate, fair, and effective across diverse patient groups.
Moreover, inclusivity in AI development also extends to the composition of the development teams themselves. Diverse teams are more likely to bring a range of perspectives and experiences that can identify potential biases and develop more innovative solutions. For example, a technology company working on natural language processing (NLP) tools would benefit from having linguists, sociologists, and representatives from various linguistic communities involved in the development process. This diversity within the team helps ensure that the NLP tools are capable of understanding and accurately processing different dialects, accents, and cultural nuances.
The principle of inclusivity emphasizes the importance of engaging a broad spectrum of stakeholders in the AI development process. By doing so, AI systems can be designed and deployed in ways that are more equitable, effective, and reflective of the diverse needs of society. Inclusivity not only enhances the quality and fairness of AI technologies but also fosters greater trust and acceptance among users.

Maintaining honesty and integrity in AI development involves transparent data practices, ethical communication, and a commitment to truthfulness!
Principal #8 – Honesty and IntegrityMaintaining honesty and integrity in the development, deployment, and communication of AI technologies is a foundational principle that fosters trust and accountability among stakeholders, including developers, users, and the broader society. This principle encompasses several critical aspects that ensure AI systems are reliable, ethical, and aligned with societal values.
A core aspect of maintaining honesty and integrity involves transparency in data use and algorithmic decision-making. For example, consider an AI system employed in the healthcare sector for diagnosing diseases. If the system’s developers clearly disclose the sources of data, the methodology used to train the algorithms, and the potential limitations and biases present in the data, they enable healthcare providers and patients to make informed decisions based on a clear understanding of the AI’s capabilities and limitations. This openness not only builds trust but also ensures that users can critically evaluate the AI’s recommendations, thereby enhancing the overall quality of care.
Furthermore, honesty and integrity in AI development entail a commitment to ethical communication. Developers and companies must avoid exaggerating the capabilities of their AI systems or making unfounded claims about their performance. For instance, an AI-powered hiring platform should provide accurate information about how it evaluates candidates and the criteria it uses, rather than overstating its ability to eliminate bias or guarantee the best hires. By communicating transparently, companies can prevent misinformation and build a reputation for reliability and ethical conduct.
An example of this principle in action is seen in the practices of organizations like the IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems, which advocate for comprehensive ethical guidelines in AI. These guidelines emphasize the need for transparency, accountability, and fairness, ensuring that AI systems are developed and deployed with integrity. For instance, an AI used in financial services to assess loan applications should transparently disclose the factors influencing its decisions, allowing applicants to understand and potentially contest unfavorable outcomes.
Maintaining honesty and integrity in AI development involves transparent data practices, ethical communication, and a commitment to truthfulness. By upholding these standards, organizations can foster trust, mitigate risks, and ensure that AI technologies are used in a manner that aligns with societal values and ethical principles.
Final ThoughtsThe future will remain cloudy until the ethics are clear. Establishing a universally accepted set of AI ethics is paramount for navigating the complexities and challenges posed by rapid technological advancements. Imagine a scenario where an AI-driven hiring platform inadvertently discriminates against certain races and low-income neighborhoods, perpetuating systemic inequalities. This example highlights the urgent need for clear ethical guidelines to prevent such biases and ensure fair treatment. Beyond hiring, ethical considerations extend to areas like facial recognition, healthcare, data privacy, and autonomous systems, all of which present profound moral dilemmas that must be addressed to foster trust and equity.
Defining AI ethics for the future requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates transparency, accountability, fairness, privacy, safety, human-centered values, and inclusivity. By embracing these principles, we can create AI technologies that are not only innovative but also aligned with societal values and human rights. Transparent practices enable stakeholders to understand and trust AI systems, while accountability ensures responsibility for the impacts of these technologies. Fairness and inclusivity ensure that all individuals are treated equitably, and robust privacy protections safeguard personal data. As we move forward, embedding these ethical principles into AI development will be crucial for creating a future where technology serves the greater good and enhances human well-being.
Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts Defining AI Ethics for the Future “Goldene” — The World’s Newest Super Material The Coming Vacant Home Crisis in an Aging, Low Birth Rate Society Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post Defining AI Ethics for the Future appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
June 13, 2024
“Goldene” — The World’s Newest Super Material

Goldene is not only the world’s thinnest gold leaf, it represents a huge advancement in two-dimensional materials.
The New Frontier in Material ScienceIn the ever-evolving landscape of material science, a groundbreaking discovery has emerged that may redefine the boundaries of what’s possible with elemental materials. Dubbed “goldene,” this new material is the world’s thinnest gold leaf, measuring a mere single atom in thickness. This remarkable achievement was published in the prestigious journal Nature Synthesis on April 16, 2024, marking a significant milestone in the field of nanotechnology.
Goldene is not just notable for its minuscule thickness; it represents the latest advancement in the category of two-dimensional (2D) materials. These materials are renowned for their extraordinary properties, which differ significantly from their bulk counterparts. Since the discovery of graphene in 2004, scientists have been keenly interested in 2D materials for their unique optical, electronic, and catalytic behaviors. Goldene, with its single-atom structure, is poised to push these boundaries even further.
The potential applications of goldene are vast and varied, hinting at a new era of technological innovation. One of the most promising uses of goldene lies in environmental technology, particularly in processes designed to mitigate climate change. Due to its enhanced chemical reactivity, goldene could play a crucial role in converting carbon dioxide into useful fuels, such as ethanol or methane. This process, known as carbon capture and utilization, seeks to not only reduce the levels of harmful CO2 in the atmosphere but also to transform it into commercially viable products.
Additionally, goldene could revolutionize the field of energy by facilitating the efficient generation of hydrogen through water splitting. Hydrogen is often touted as the clean fuel of the future, and improving the efficiency of its production is critical for realizing its potential as a sustainable energy resource. Goldene’s unique properties could significantly enhance the catalytic processes required for hydrogen production, making it a key player in the transition to green energy solutions.
Beyond these applications, goldene’s atomic-scale precision and stability open the doors to various other fields, including electronics, where it could contribute to the development of ultra-thin, high-performance devices. Its arrival promises not only advancements in existing technologies but also the potential for entirely new applications yet to be imagined.
As we stand on the brink of these exciting possibilities, goldene exemplifies the synergy between historical craftsmanship and cutting-edge science—a synergy that continues to drive innovation and expand the horizons of human knowledge and capability.

The allure of 2D materials lies in their exceptional characteristics – unique optical, electronic, and catalytic properties.
Background on 2D MaterialsIntroduction to 2D MaterialsThe story of two-dimensional (2D) materials began in earnest with the isolation of graphene at the University of Manchester in 2004. Graphene—a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice—ushered in a new era in material science due to its remarkable properties. This discovery earned the researchers involved, Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov, the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010, highlighting the significant impact of 2D materials on science and technology.
Significance of 2D MaterialsThe allure of 2D materials lies in their exceptional characteristics, which are not found in their bulk forms. These materials exhibit unique optical, electronic, and catalytic properties that make them highly desirable for various applications:
Optical Properties: Many 2D materials can interact with light in unique ways, which is crucial for applications in sensors and photovoltaics.Electronic Properties: The electron mobility in materials like graphene is extraordinarily high, making them excellent candidates for next-generation electronic and computing devices.Catalytic Properties: The surface area-to-volume ratio of 2D materials is extremely high, which enhances their effectiveness as catalysts in chemical reactions, such as hydrogen production or carbon dioxide reduction.Challenges in SynthesisWhile the fabrication of 2D materials like graphene, molybdenum disulfide, and boron nitride has become more refined, producing single-atom sheets of pure metals presents unique challenges:
Bonding Tendencies: Metals have a natural tendency to bond with each other due to their delocalized electron cloud. This characteristic makes it difficult to maintain them in a stable, isolated, single-atom form.Structural Stability: Unlike nonmetals, which can readily form stable 2D networks, metals require specific conditions to form stable monolayers without aggregating or forming larger particles.Complex Fabrication Techniques: The synthesis of metal monolayers often necessitates sophisticated and delicate fabrication techniques that can isolate individual atoms while preventing them from clustering.Creating goldene represents a breakthrough in this area, employing advanced techniques that build on historical methods to create a stable sheet of gold just one atom thick. This achievement not only expands the family of 2D materials but also opens up new possibilities for utilizing elemental metals in ways that were previously thought to be impractical or impossible.

The creation of goldene uses a synthesis method inspired by a century-old technique once employed by Japanese iron smiths.
Discovery and Creation of GoldeneInnovative Synthesis MethodThe creation of goldene represents a significant technological leap. It utilizes a synthesis method inspired by a century-old technique once employed by Japanese iron smiths. This ancient approach involved precise control over the material at the atomic level, a concept that researchers have now adapted to work with gold. The innovative method utilized in the creation of goldene marries traditional metallurgical skills with advanced nanotechnology, demonstrating how historical techniques can find new life in modern scientific research.
Detailed Synthesis ProcessPublished in Nature Synthesis, the process of creating goldene involves a sophisticated layering and substitution technique:
Layering: The initial step involves creating a layered structure composed of titanium, silicon, and carbon. This composite serves as the foundation upon which gold atoms are deposited.Atomic Replacement: In the critical phase of the process, the silicon layer is targeted for replacement. Gold atoms are introduced onto the surface, and under controlled conditions, they diffuse into the structure, specifically replacing the silicon atoms. This precise diffusion is crucial for the formation of a uniform single-atom layer.Solid Support Maintenance: Unlike previous methods, the gold atoms are embedded within the remaining layers of titanium and carbon, providing stability and preventing the gold from clustering.Overcoming Previous ChallengesHistorically, the challenge in creating monolayers of gold has revolved around the metal’s propensity to agglomerate or cluster when isolated at the atomic scale. Previous attempts often resulted in the formation of gold nanoparticles rather than a continuous monolayer due to the inherent bonding tendencies of gold atoms:
Support Structures: In earlier experiments, researchers attempted to stabilize gold atoms using various support structures, such as graphene-coated silicon carbide. However, once the support was removed, the gold atoms would typically coalesce into nanoparticles, losing the desired monolayer structure.Innovative Solution: The method described in Nature Synthesis cleverly circumvents this problem by keeping the gold atoms embedded within a stable matrix of other materials throughout the process. Only after the gold layer has formed do researchers carefully etch away the surrounding materials. This technique ensures that the gold atoms form a stable, freestanding monolayer, as they are never left unsupported during the critical phases of the synthesis.This innovative approach not only solves a longstanding problem in the synthesis of metallic monolayers but also opens the door to new possibilities for using these materials in various high-tech applications. By successfully isolating gold in a two-dimensional form, researchers have paved the way for future advancements in the field of material science.

One of the critical steps in the production of goldene is the chemical etching process.
Technical Insights into Goldene ProductionChemical Etching ProcessOne of the critical steps in the production of goldene is the chemical etching process, which involves the use of Murakami’s reagent, an alkaline solution of potassium ferricyanide. This reagent has a storied history, originally used by Japanese craftsmen for fine-tuning the properties of steel. In the context of goldene production, it plays a pivotal role in the selective removal of the non-gold layers from the initial composite structure. Here’s how it works:
Selective Etching: The Murakami’s reagent specifically targets the titanium carbide layer in the composite, dissolving it without affecting the gold layer. This selective etching is crucial as it preserves the integrity of the monolayer gold while removing other materials.Controlled Reaction Conditions: The process requires precise control over factors such as temperature, concentration of the reagent, and etching time to ensure that only the desired material is removed and the gold atoms remain perfectly arranged in a single layer.Role of Cysteine as a SurfactantCysteine, an amino acid, is added to the process as a surfactant. Surfactants decrease the surface tension of a liquid, a property exploited in this context to stabilize the gold sheets at the molecular level. Here’s the impact of adding cysteine:
Stabilization: Cysteine molecules bind to the gold atoms, preventing them from clustering into larger particles. This binding helps maintain the structural integrity of the goldene sheets.Enhancing Dispersion: By decreasing the surface tension, cysteine helps in uniformly spreading the gold atoms across the substrate, promoting the formation of a continuous, uniform monolayer.Physical Properties of GoldeneThe resulting goldene sheets exhibit remarkable physical properties that set them apart from traditional gold leaf and other materials:
Thickness: Goldene sheets are composed of a single layer of gold atoms, making them significantly thinner than the traditional gold leaf, which is typically several hundred nanometers thick. The atomistic thickness of goldene translates to unprecedented levels of thinness, measured in the angstrom range.strong>Length and Stability: Despite their thinness, goldene sheets can be up to 100 nanometers long. This relatively large size at such a thin scale is critical for practical applications, as it ensures enough surface area for catalytic and electronic functions while maintaining stability and handling ease.Optical Properties: The ultra-thin nature of goldene allows for unique optical properties, including high transparency and distinctive interactions with light, which could be harnessed in advanced optical devices and sensors.Through these advanced technical processes and the unique physical characteristics they produce, goldene stands out not only as a scientific curiosity but as a potentially transformative material for numerous applications in technology and industry.

Goldene will revolutionize the way we convert carbon dioxide into usable fuels like ethanol and methane.
Applications and Future Potential of GoldeneEnvironmental Technology and Energy ProductionGoldene, with its unprecedented properties, holds promising potential for application in critical sectors such as environmental technology and energy production:
Environmental Remediation: In environmental technology, goldene’s enhanced surface area and reactivity could make it an ideal candidate for absorbing pollutants or breaking down hazardous compounds more efficiently than current materials.Energy Efficiency: For energy production, the unique properties of goldene might lead to more efficient solar cells or energy storage systems, improving performance and lowering the costs of renewable energy technologies.Revolutionizing Chemical ReactionsOne of the most exciting potential applications of goldene lies in its ability to catalyze reactions that are crucial for sustainable energy solutions and environmental management:
Carbon Dioxide Conversion: Goldene’s enhanced chemical reactivity could revolutionize the way we convert carbon dioxide into usable fuels like ethanol and methane. By facilitating these reactions more efficiently, goldene could help in tackling the increasing levels of CO2 in the atmosphere, a major contributor to global warming.Hydrogen Production: Similarly, the splitting of water to produce hydrogen, which is seen as a clean alternative to fossil fuels, could be greatly enhanced by the catalytic properties of goldene. More efficient hydrogen production would bolster the viability of hydrogen as a widespread energy source, supporting the global shift towards sustainable energy.Ongoing Research and DevelopmentResearch into goldene is still in its early stages, with several key areas being the focus of ongoing studies:
Improving Yield and Size: Researchers are working to improve both the yield and the dimensions of goldene sheets produced. Larger and more consistently produced sheets would enable wider commercial applications and facilitate integration into existing manufacturing processes.Expansion to Other Metallenes: The successful synthesis of goldene has opened the door to the development of other elemental 2D materials, often referred to as metallenes. By applying similar methods used to create goldene, scientists hope to synthesize other single-atom-thick layers of different metals, each potentially endowed with unique properties suitable for various applications.Future ProspectsThe exploration of goldene and other metallenes could lead to significant advancements in materials science, with wide-ranging implications for technology, industry, and environmental conservation. As the methods for synthesizing and manipulating these materials improve, we can expect to see them increasingly incorporated into products and processes that enhance energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and technological innovation.

The ability to create stable, single-atom layers of metals is opening the door for many new kinds of research.
Broader Implications and Future Research in 2D MaterialsBroader Implications of Stable Single-Atom Metal LayersThe ability to create stable, single-atom layers of metals like goldene represents a transformative advancement in materials science, with implications extending far beyond the laboratory:
Technological Innovation: These materials can lead to the development of ultra-thin, highly efficient electronic devices, sensors, and catalysts, driving innovation in fields ranging from consumer electronics to industrial manufacturing.Scientific Discovery: Stable single-atom layers provide unique platforms for studying quantum phenomena and the fundamental properties of materials at the atomic scale, potentially leading to new discoveries in physics and chemistry.Environmental Sustainability: The application of these materials in environmental technologies—such as efficient catalysis in carbon capture and cleaner energy solutions—highlights their role in addressing global challenges like climate change and resource scarcity.Upcoming Research GoalsLooking ahead, several exciting research goals are on the horizon for scientists working with 2D materials:
Single Layer of Silver: One specific goal is the creation of a single layer of silver, a material that could have distinct and potentially superior properties compared to goldene, especially in areas like conductivity and optical responses.Expanding the Range of Metallenes: Researchers aim to apply the techniques developed for goldene to other metals, seeking to create a wide range of metallenes. Each metal could exhibit unique properties when reduced to a monolayer, potentially leading to a new class of materials with customized properties for specific applications.Improving Synthesis Techniques: There is ongoing research focused on refining the synthesis processes to increase the efficiency, yield, and quality of these 2D materials, making them more practical for commercial and industrial applications.Potential for New 2D MaterialsThe exploration of new 2D materials opens up exciting possibilities:
Novel Material Properties: Each new 2D material could exhibit properties that are not only unique but also superior to those of existing materials, offering unprecedented performance enhancements in various applications.Cross-Disciplinary Applications: The potential uses of new 2D materials cross many disciplinary boundaries, including electronics, photonics, medicine, and energy storage, showcasing their versatility and wide-ranging impact.Customizable Material Solutions: Future advancements may allow for the custom tailoring of material properties to fit specific needs, providing bespoke solutions to complex scientific and technological challenges.The development of stable, single-atom layers of metals like goldene and the ongoing research into other metallenes represent a significant leap forward in material science. These advancements not only enhance our understanding of the atomic-scale properties of materials but also unlock a plethora of applications that could revolutionize industries and improve environmental sustainability. As researchers continue to explore and expand the capabilities of these materials, we can anticipate a future where 2D materials are integral to solving some of the most pressing challenges facing our world today.

Goldene’s enhanced catalytic, electronic, and optical properties position it as a pivotal material for future industries.
Final Thoughts on GoldeneSignificance of GoldeneThe discovery of goldene, the world’s thinnest gold leaf consisting of a single atom layer, represents a landmark achievement in the field of material science. This breakthrough not only expands our understanding of the atomic-scale properties of materials but also showcases the potential to harness these properties in practical, innovative applications. Goldene’s enhanced catalytic, electronic, and optical properties position it as a pivotal material for the future, potentially impacting numerous fields, including renewable energy, environmental technology, and electronics manufacturing.
Impact on Science and TechnologyGoldene’s impact on science and technology could be profound. Its unique characteristics could lead to the development of next-generation devices that are more efficient, robust, and capable of achieving tasks that were previously deemed too challenging. For instance, its application in catalyzing reactions for hydrogen production and CO2 conversion could revolutionize our approach to energy and climate challenges, making processes more sustainable and less environmentally damaging.
Ancient Techniques and Modern ScienceThe method used to synthesize goldene—drawing inspiration from century-old techniques used by Japanese iron smiths—exemplifies a fascinating synergy between ancient wisdom and modern scientific inquiry. This approach not only preserved the delicate structure of gold at an atomic level but also leveraged it to create something entirely new and incredibly thin. This merging of old and new methodologies not only highlights the innovative spirit of today’s researchers but also respects and revitalizes traditional knowledge, showing that historical techniques still have much to offer to contemporary scientific challenges.
Educational and Inspirational ValueThis exploration into goldene provides a structured and engaging narrative that not only educates about its revolutionary properties and potential applications but also inspires by highlighting the deep, interwoven tapestry of science, history, and innovation. The story of goldene serves as a reminder of the endless possibilities that await at the intersection of curiosity-driven research and interdisciplinary collaboration. It invites readers to reflect on how much more there is to discover and utilize, encouraging a generation of scientists and engineers to think creatively and persistently as they push the boundaries of what is known.
Looking ForwardAs we continue to explore and expand the capabilities of goldene and other similar 2D materials, the potential for further groundbreaking discoveries remains vast. With each new material synthesized and each application uncovered, we edge closer to unlocking a future where advanced materials drive progress in every sector of technology and industry. Goldene is not just a scientific achievement; it is a beacon of potential, illuminating the path toward a more innovative and sustainable future.
Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts “Goldene” — The World’s Newest Super Material The Coming Vacant Home Crisis in an Aging, Low Birth Rate Society The Shifting Sands of a Rapidly Declining Birth Rate Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post “Goldene” — The World’s Newest Super Material appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
May 30, 2024
The Coming Vacant Home Crisis in an Aging, Low Birth Rate Society

Empty homes in Japan are called “akiya,” or neglected houses.
Japan’s Vacant Home CrisisJapan faces an unprecedented housing crisis, not due to a shortage of homes but because of their abundance—a staggering nine million vacant houses dot the landscape. This figure surpasses the entire population of New York City, putting into stark perspective the magnitude of the issue. These empty homes, known in Japanese as “akiya,” are no longer confined to the dwindling rural areas but are now a common sight even in bustling urban centers like Tokyo and Kyoto.
As Japan grapples with its housing paradox, the rest of the world should take note. The issues of akiya and the demographic trends driving them are not unique to Japan but are beginning to surface globally. Low birth rates and an aging population are becoming more prevalent in many countries, heralding significant socio-economic shifts.
These changes threaten to diminish the vibrancy of even the most dynamic societies, as fewer young people mean less economic activity and innovation, while an increasing elderly population demands more resources and care. The resultant increase in vacant properties can lead to urban decay and reduce the attractiveness of affected areas, impacting investment and exacerbating economic decline. As these trends continue, nations around the world may face similar challenges, requiring proactive measures to manage their impact on society and the economy.
Overview of the IssueThe surge in vacant properties across Japan is closely tied to its demographic shifts—chief among them, a declining population. As the number of residents dwindles, the number of empty homes climbs, creating a unique challenge for Asia’s second-largest economy. This phenomenon is not just a matter of unused space; it represents a significant economic and social challenge. Cities and towns are speckled with these unoccupied units, complicating urban planning and community rejuvenation efforts.
Definition of AkiyaThe term “akiya” traditionally refers to neglected houses often hidden away in Japan’s scenic but depopulated countryside. However, the scope of what constitutes an akiya has expanded. These properties are not merely old and abandoned farmhouses but include residences in some of Japan’s most crowded cities. Their presence in metropolitan areas such as Tokyo and Kyoto signals a shift in the housing crisis from a rural to an urban dilemma. The proliferation of akiya in these cities highlights the broader implications for Japan’s real estate market and urban development strategies, posing new challenges for a government grappling with both an aging populace and a plummeting birth rate.
This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration into how the rising tide of vacant homes is reshaping Japan, influencing everything from urban policy to social attitudes towards homeownership and inheritance.

Deteriorating neighborhoods in Japan as the aging population takes its toll.
Unraveling Japan’s Vacant Home DilemmaPopulation DeclineJapan’s demographic trends have been setting alarm bells ringing for decades, with the country facing one of the steepest population declines in the developed world. In 2022 alone, the population decreased by over 800,000 individuals, a stark testament to the magnitude of the issue. The birth rate has continued to plummet, reaching a record low, with fewer babies being born each year. Japan’s fertility rate, which has hovered around 1.3, is well below the 2.1 required to maintain a stable population. This demographic shrinkage directly impacts the housing market, as fewer people mean less demand for homes. The result is an increase in vacant properties, as there are simply not enough people to occupy the existing houses.
Economic and Social ShiftsThe economic and social landscape of Japan also plays a crucial role in the proliferation of vacant homes. On the economic front, tax policies in Japan inadvertently encourage property owners to let homes sit empty rather than redeveloping them. The cost associated with demolishing a home and preparing the land for sale or new construction can be prohibitive, making it financially more viable for owners to retain unused properties.
Socially, a significant shift is observed in the younger generation’s attitudes toward rural living and property inheritance. More young people are relocating to urban centers in search of employment, lifestyle opportunities, and amenities not available in rural areas. This migration has led to a disinterest in taking over family homes in the countryside, which traditionally would have been passed down through generations. The combined lack of economic incentive and generational disconnect from rural life contributes heavily to the abandonment of these homes, leaving them to deteriorate as akiya.
These factors—demographic changes, economic policies, and shifting social preferences—form a complex tapestry that explains why Japan is witnessing an unprecedented surge in vacant homes. This situation poses significant challenges for urban planning and rural rejuvenation, as empty houses affect community cohesion, property values, and the vibrancy of neighborhoods. As we delve deeper into the implications of these trends, it becomes clear that addressing the issue requires a multifaceted approach that considers both the human and economic dimensions of the crisis.

Coffee shop dynamics are an early indicator of declining neighborhoods.
The Urban Spread and Changing Dynamics of Supply and DemandIncrease in Urban AkiyaIn recent years, the phenomenon of vacant homes, traditionally a rural issue, has markedly spread to urban centers in Japan, affecting major cities like Tokyo and Kyoto. This shift is largely driven by the same demographic challenges that plague the countryside—an aging population coupled with a declining birth rate. However, the implications in urban areas are particularly complex, given the higher population density and economic activity. Urban akiya complicates government efforts not just in housing market stabilization but also in urban planning and infrastructure development.
As younger generations continue to migrate to cities, leaving behind rural homes, they also face the high cost of urban living, which leads to a unique paradox: a growing number of empty homes amidst a population that cannot afford housing. This situation strains resources and complicates efforts to rejuvenate aging urban neighborhoods, as these vacant properties can lead to blighted areas that detract from the city’s vibrancy and safety.
Expert OpinionJeffrey Hall, a lecturer at Kanda University of International Studies, points out that the rise in urban vacant homes is not due to an oversupply in the traditional sense but rather an alarming demographic trend of declining populations. “It’s not really a problem of building too many houses,” Hall explains, “but a problem of not having enough people.” This demographic shift results in a mismatch between the supply of homes and the demand, impacting real estate markets and urban development.
Yuki Akiyama, a professor from the faculty of architecture and urban design at Tokyo City University, highlights another critical aspect of urban akiya: their impact on safety during natural disasters. In a country prone to earthquakes and tsunamis, vacant and poorly maintained buildings can become significant hazards. “When an earthquake or a tsunami occurs, there is a possibility that vacant houses will block evacuation routes as they break down and get destroyed,” Akiyama noted. This presents an ongoing challenge for disaster preparedness and response in urban settings.
Both experts underscore the urgent need for innovative policy solutions that address both the cause and the effects of urban akiya. Suggestions include revising tax policies to encourage redevelopment, investing in affordable housing solutions for younger urban populations, and incorporating disaster risk management into the planning and maintenance of urban areas.
The shift of akiya from a rural to an urban phenomenon reflects broader changes in Japanese society and poses new challenges for city planners, policymakers, and residents alike. Addressing this issue requires a holistic approach that considers demographic trends, economic conditions, and urban safety in an integrated manner.

Governmental policy changes are often compounded by the dwindling tax dollars.
Government and Community ChallengesPolicy ChallengesThe Japanese government faces significant hurdles in addressing the growing number of vacant homes, particularly in rural areas where the impact of depopulation is most acute. These challenges are compounded by the need to rejuvenate these communities and make them appealing to potential residents and investors. The abundance of akiya makes this task particularly daunting as it drives down property values and deters investment, thereby creating a vicious cycle of decline.
Efforts to attract new residents often clash with the reality that many rural areas lack the necessary infrastructure, amenities, and employment opportunities to draw younger generations who prefer urban living. Additionally, existing tax policies provide little incentive for owners to demolish or renovate unoccupied homes, as the costs associated with these processes are prohibitively high compared to the benefits. Consequently, many properties are left to deteriorate, further depressing real estate values and discouraging new development.
Safety and Development ImpedimentsAkiya not only impacts economic development but also poses significant safety risks, particularly in a country prone to natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis. Vacant properties, often poorly maintained and structurally unsound, can become lethal hazards during such events. They are likely to collapse or obstruct emergency access routes, complicating rescue operations and increasing risks to both residents and emergency responders.
The presence of these derelict buildings also stalls the development of affected regions. They occupy space that could otherwise be used for new developments that might rejuvenate the area. Moreover, the unkempt appearance and potential dangers of these properties make the surrounding area less attractive to businesses and residents alike, leading to economic stagnation.
In rural regions, the problem is particularly pronounced, with high concentrations of akiya contributing to a decline in the attractiveness and viability of entire communities. This situation presents an obstacle to economic development initiatives, as investors are hesitant to commit resources to areas that appear to be in decline.
Looking ForwardTo tackle these issues, experts like Yuki Akiyama have advocated for innovative solutions, including the use of artificial intelligence to identify and predict the most vulnerable areas. Such technologies could help in planning and implementing more effective interventions. Moreover, revising tax policies to make it economically viable to handle akiya responsibly and investing in infrastructure to make rural areas more attractive to younger generations are critical steps that could help mitigate the impact of these vacant homes.
Addressing the challenges posed by akiya is a complex task that requires coordinated efforts across multiple sectors. It involves not only making policy adjustments but also fostering community engagement to ensure that revitalization efforts are sustainable and that safety risks are adequately managed. The Japanese government, along with local communities, must continue to innovate and adapt to turn the tide on this growing issue.

Unlike in many Western countries, in Japan, there is a strong preference for new construction.
Cultural and Structural IssuesAttitudes towards HousingIn Japan, cultural attitudes towards housing significantly influence the real estate market and urban development. Unlike in many Western countries, where older buildings may be valued for their historical significance and aesthetic, in Japan, there is a strong preference for new constructions. This preference is rooted in several factors, including concerns about earthquake resilience, modern amenities, and a cultural affinity for newness and modernity. Such attitudes exacerbate the issue of vacant homes, as older buildings become less desirable over time and are left abandoned rather than being preserved or renovated.
This cultural inclination affects both urban and rural areas, leading to a cycle of construction and abandonment that contributes to the increasing number of akiya. In urban areas, it drives continual redevelopment, often at the expense of community stability and heritage preservation. In rural areas, it leads to homes quickly losing their value once they show signs of aging, thus increasing the number of properties that end up vacant as heirs choose not to take over or maintain these homes.
Structural ProblemsThe structural issues relating to property ownership in Japan further complicate the situation. Many akiya have unclear ownership due to inadequate record-keeping or the absence of a clear heir. This situation is particularly prevalent in rural areas where properties have been passed down through generations without proper documentation. The lack of clear ownership makes it difficult for local authorities to manage these properties, whether through taxation, demolition, or repurposing.
Additionally, these structural problems hinder revitalization efforts. Without clear ownership, it becomes nearly impossible to renovate, sell, or even demolish these properties legally. This leads to a perpetuation of vacant homes, contributing to urban and rural blight and blocking new developments that could potentially rejuvenate these areas.

Social media has played a significant role in shaping perceptions about Japan’s vacant homes.
Addressing the IssuesTo tackle these cultural and structural challenges, Japan may need to consider reforms in both societal attitudes and legal frameworks. Culturally, this might involve campaigns or incentives to preserve older buildings and promote the value of historical architecture. Structurally, improvements in property registration and inheritance laws could help clarify ownership issues. Implementing such changes would require a concerted effort from various stakeholders, including government bodies, local communities, and cultural leaders, to shift perceptions and update practices in line with contemporary needs and realities.
These combined efforts could gradually help reduce the number of vacant homes and encourage a more sustainable approach to housing and urban development in Japan.
Media and Public PerceptionSocial Media InfluenceIn recent years, social media has played a significant role in shaping perceptions about Japan’s vacant homes. Platforms like YouTube and Instagram are awash with videos of foreigners who have moved to Japan and embarked on renovating akiya. These videos often portray the process as a charming adventure into rural Japanese life, showcasing dramatic before-and-after transformations that appeal to a wide audience. The allure of acquiring a home for a fraction of the cost seen in more urban areas can seem like an irresistible opportunity.
However, experts caution that these portrayals are somewhat romanticized and do not fully encapsulate the challenges involved. Jeffrey Hall, a lecturer in Japan, points out that while these videos have garnered significant attention, they often gloss over the extensive bureaucratic hurdles, the high costs of renovation, and the complexities of rural living in Japan. He emphasizes that language barriers, cultural differences, and the intricate legalities of property ownership can make these projects far more daunting than they appear on social media.
Public MisconceptionsThe popularity of these social media accounts can lead to misconceptions among the public, both in Japan and internationally. Viewers may come to believe that the renovation of akiya is a simple, straightforward process that anyone can undertake with minimal effort and cost. This misperception can skew the understanding of the akiya issue, underestimating the economic, legal, and logistical challenges that truly exist.
These social media portrayals can also impact how communities perceive their own local issues. For instance, local residents might feel that the interest from foreigners in akiya could lead to revitalization and economic benefits, whereas, in reality, such outcomes are rare and heavily dependent on numerous factors that are often not addressed in social media content.
Furthermore, the narrative that akiya can easily be transformed into dream homes overlooks broader structural issues such as declining local economies, aging populations, and lack of infrastructure, which are critical to genuinely addressing the challenges posed by vacant properties.
Addressing the Gap Between Perception and RealityTo bridge the gap between perception and reality, a concerted effort needs to be made to provide more comprehensive and realistic portrayals of the akiya situation. Educational campaigns, perhaps led by government agencies or real estate professionals, could provide clearer information about the actual costs, benefits, and challenges of purchasing and renovating akiya. Such initiatives could help potential buyers make more informed decisions and foster a more accurate understanding of Japan’s rural housing market among the general public.

Finding solutions to challenging neighborhoods is never easy.
Solutions and InnovationsInnovative ApproachesAs Japan grapples with the growing problem of vacant homes, innovative solutions are being sought to mitigate the impact and potentially turn the tide on this issue. One such innovation comes from Yuki Akiyama, a professor of architecture and urban design, who has developed an artificial intelligence program designed to identify areas most vulnerable to akiya accumulation. This AI tool analyzes various data points, including demographic trends, property conditions, and economic factors, to predict where vacant homes are likely to become problematic. By identifying these areas early, local governments can proactively implement policies aimed at revitalization or preventing further decline.
Other innovative solutions being explored include:
Adaptive Reuse Projects: Transforming akiya into community centers, clinics, or tourist accommodations to serve current societal needs.Tax Incentives: Offering tax breaks or financial incentives to those who purchase and renovate akiya, encouraging private investment in these properties.Simplified Ownership Transfer Laws: Streamlining the process for transferring property titles to make it easier for new owners to take over and refurbish vacant homes.Remote Work Hubs: Converting vacant properties into remote work facilities, tapping into the trend towards telecommuting, especially in scenic or traditionally less accessible areas.These initiatives, coupled with community engagement and support, could significantly alter the landscape of rural and urban areas struggling with vacant homes.
Comparative AnalysisLooking abroad, Japan’s issue with vacant homes is not unique, and lessons can be learned from how other countries handle similar challenges:
United States: In the US, cities like Detroit have implemented land bank programs, which consolidate vacant properties for redevelopment, sale, or repurposing. These programs often work in tandem with local community groups to ensureEurope: Some European countries, such as Italy, have initiated schemes where homes in rural or declining areas are sold for symbolic prices (often just 1 euro) to attract new residents. Buyers must commit to renovating these properties, thus revitalizing aging towns and reducing the number of vacant homes.These examples show that while the challenges may be similar, the approaches can vary significantly based on local laws, culture, and economic conditions. Japan could consider these international precedents when crafting policies tailored to its specific needs and circumstances, possibly adopting a blend of tactics suited to different regions within the country.
By looking both inward for innovative solutions and outward for international inspiration, Japan can better address the complex issue of vacant homes and rejuvenate areas that have been negatively impacted by this phenomenon.

Japan’s housing issues should be viewed as an early warning signal for most other countries.
Addressing Japan’s Vacant Home Crisis in a Global ContextFinal ThoughtsThe vacant home crisis in Japan presents a multifaceted challenge with deep social, economic, and cultural implications. The surge in akiya affects not just the aesthetics of towns and cities but also has profound effects on property values, local economies, and community morale. These empty homes symbolize the broader demographic crisis of an aging and shrinking population, which undermines the traditional economic growth models based on a young, expanding workforce.
The presence of vacant homes can lead to increased municipal costs as local governments are forced to maintain, secure, or eventually demolish derelict properties. Socially, the abundance of unoccupied homes can lead to neighborhood decline, which exacerbates feelings of isolation among remaining residents, often the elderly, who are left behind as younger populations migrate towards more urban environments.
Forward LookAs Japan continues to confront these challenges, the situation presents critical lessons for the rest of the world. Many developed, and some developing countries are beginning to experience similar demographic shifts, including lower birth rates and higher proportions of elderly citizens. Japan’s proactive approach to addressing its vacant home problem through policy innovation and community revitalization projects could serve as a model for other nations.
Looking ahead, Japan’s strategies may include more aggressive utilization of technological solutions like AI to manage and repurpose akiya, alongside more culturally sensitive approaches that respect and integrate the desires of local communities. Additionally, legislative reforms may be necessary to address the issues of property ownership and inheritance that currently complicate the akiya situation.
The potential for societal shifts, such as increased acceptance of remote work, could make rural living more desirable and sustainable, thereby reversing some of the current trends. Policy changes, such as adjustments in tax laws and financial incentives for renovating older homes, could stimulate demand for these properties.
Global ImplicationsAs countries around the world begin to grapple with their own versions of these demographic challenges, the global community can look to Japan as a case study in both the pitfalls and opportunities of managing a shrinking, aging population with a large stock of vacant homes. International collaboration and knowledge sharing could be key in developing strategies that not only address the housing issues directly but also tackle the underlying demographic trends.
Japan’s experience with akiya is not just a national issue but a harbinger of global changes. How Japan navigates this crisis could provide valuable lessons for other countries soon to face similar issues, making it essential for global leaders to observe and learn from Japan’s innovations and responses to the challenges of a changing world.
Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts The Coming Vacant Home Crisis in an Aging, Low Birth Rate Society The Shifting Sands of a Rapidly Declining Birth Rate Seven Deadly Sins of the Future Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post The Coming Vacant Home Crisis in an Aging, Low Birth Rate Society appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
May 16, 2024
The Shifting Sands of a Rapidly Declining Birth Rate

South Korea faces a significant demographic challenge, marked by the world’s lowest birth rate, at 0.7 children per woman, substantially below the replacement rate of 2.1, which is necessary to maintain a stable population. This alarming trend poses long-term economic and social risks, including a shrinking workforce, increased dependency ratios, and potential strains on social security systems. Understanding and addressing the factors contributing to this decline is crucial for sustainable national development.
Factors Contributing to the Low Birth RateEconomic Constraints: Many young South Koreans cite economic instability as a primary deterrent against having children. High youth unemployment rates, coupled with intense competition for jobs, create an environment of financial insecurity. Additionally, the high cost of education and housing further discourages young couples from starting families, as the financial burden of raising children appears daunting.
Cultural and Social Pressures: South Korea’s work culture is among the most demanding globally. Long work hours and limited parental leave options make balancing work and family life challenging. Furthermore, societal expectations place a heavy burden on women to bear the brunt of childrearing and domestic responsibilities, discouraging many from pursuing both career and family.
Educational Burdens: The highly competitive education system in South Korea also plays a role. The pressure to excel academically begins early and is both time-consuming and expensive, making the prospect of having multiple children less appealing for parents concerned about educational costs and opportunities.

Empty playgrounds have become symbolic of our declining birth rates.
20-Year Decline – Problems Arising from Declining Birth Rates Over TimeA rapidly declining birth rate can have profound and far-reaching effects on society over a period of 20 years or more. Here are some ofthe key impacts:1. Aging Population:A lower birth rate leads to an older average age in the population, as there are fewer young people relative to the number of elderly. This demographic shift can strain pension systems, healthcare services, and other social support systems designed to care for the older segment of the population.2. Labor Force Shortages:With fewer people entering the workforce, there can be a shortage of workers, which may lead to challenges in filling jobs, particularly in labor-intensive industries. This can hinder economic growth and may prompt businesses to look for solutions such as automation or importing labor.3. Economic Impacts:A shrinking workforce and an aging population can lead to lower economic productivity, reduced consumer spending, and potentially slower economic growth. The decrease in the working-age population can also affect the tax base, impacting government revenue and increasing the burden on those still working.4. Impact on Innovation:With fewer young people, there may be a decrease in entrepreneurial activities and innovation. Younger populations are often a key source of innovation and new business startups. A decline in this age group could slow technological progress and dynamism in the economy.5. Changes in Education and Schools:Declining birth rates can lead to fewer school enrollments, which might result in school closures, consolidations, or a surplus of educational facilities and resources. This could reshape how education systems are structured and funded.6. Urban and Rural Population Shifts: With fewer people, some regions, especially rural or less economically vibrant areas, might experience depopulation, leading to abandoned properties and a decline in local economies. Conversely, urban areas might still grow or stabilize due to internal migration, altering regional population dynamics.7. Political and Social Changes:The demographic changes can shift political priorities and policies, particularly concerning healthcare, pensions, housing, and immigration. Governments might need to adjust policies to manage the effects of an aging population, such as by increasing the retirement age or encouraging higher levels of immigration to counterbalance the demographic shifts.8. Healthcare System Strain:An older population typically requires more healthcare services, which can strain the healthcare system. Increased demand for chronic disease management, geriatric care, and long-term care facilities could significantly increase healthcare costs and necessitate reforms in healthcare policies.9. Cultural Shifts:Social values and cultural norms may shift as populations age and as younger generations with different attitudes and experiences become the societal focus, albeit in smaller numbers. This can affect everything from consumer behavior to family structures and community engagement.10. Housing Market Dynamics:The demand for different types of housing might change, with an increased need for retirement homes and decreased demand for large-family homes affecting real estate markets and urban planning.These effects illustrate how a declining birth rate can touch virtually every aspect of societal structure and function, presenting challenges that require proactive and strategic policy responses to manage effectively.
Extended periods of low birth rates will result in a significantly higher proportion of elderly people.
50-Year Decline – Problems Arising from a Prolonged Declining Birth RateOver a 50-year period, a rapidly declining birth rate can lead to even more pronounced and long-term structural changes in society and the economy. Here are some of the key impacts:1. Severe Aging Population: An extended period of low birth rates results in a significantly higher proportion of elderly people. This demographic shift could be more severe than in a shorter 20-year period, potentially leading to a drastically altered age structure.2. Increased Dependency Ratio: With fewer working-age individuals supporting a larger elderly population, the dependency ratio (the number of dependents, young and old, supported by the working-age population) will rise. This can place substantial pressure on working individuals to support social welfare systems.3. Prolonged Economic Challenges: A smaller workforce could mean sustained or worsened economic challenges, including lower GDP growth rates, reduced labor market flexibility, and potential declines in innovation and productivity.4. Healthcare and Social Services Overload: Healthcare systems may become overwhelmed with the needs of an aging population, exacerbating the issues of funding and staffing. Long-term care and geriatric services would be in higher demand, potentially leading to a healthcare crisis if not adequately managed.5. Pension System Strains: Pension systems might face significant sustainability issues due to a shrinking pool of contributors relative to the number of beneficiaries. This could force changes in pension policies, such as increased retirement age, lower benefits, or higher contribution requirements.6. Shifts in Global Influence: Countries with healthier demographic profiles (younger populations) might experience relative gains in economic and geopolitical influence, while countries with older populations might see their global influence wane.7. Real Estate and Urban Planning: Housing markets may undergo long-term changes, with potentially decreased demand for new housing leading to lower construction rates and shifts in the types of housing that are in demand, such as more developments focused on accessible living for the elderly.8. Migration and Immigration Policies: Nations might adjust their immigration policies to counterbalance aging demographics and labor shortages by encouraging younger, skilled immigrants to enter the workforce.9. Changes in Consumer Markets: An older population will change the landscape of consumer markets, with increased demand for products and services tailored to the elderly, such as healthcare products, leisure, and travel tailored to older adults.10. Cultural and Social Transformations: The cultural fabric of societies could shift significantly, with potentially smaller families, different intergenerational dynamics, and altered perceptions of work, leisure, and retirement.11. Educational System Adjustments: There could be profound impacts on educational systems, including potential school closures or consolidations and shifts in educational funding priorities. Universities may also see changes in enrollment patterns, which could affect the range of offered programs and research priorities.12. Environmental Impacts: Interestingly, a declining population could have mixed effects on the environment. Lower population growth could reduce pressure on natural resources, potentially leading to less urban sprawl and lower carbon emissions. However, an older population might also mean less momentum toward rapid environmental innovations.These factors illustrate that a sustained decline in birth rates over 50 years could transform virtually every aspect of society, from economic structures and social services to cultural norms and international relations.
South Korea stands at a crossroads for taking decisive action.
Strategies for ReversalIn the face of a precipitously declining birth rate, South Korea stands at a crossroads that calls for decisive action. To reverse this trend and reinvigorate the nation’s demographic vitality, a multifaceted strategy is essential—one that rethinks existing social structures and addresses the complex web of factors that contribute to the decision to start a family. Enhancing family-friendly policies, offering tangible financial incentives, shifting deep-seated cultural norms around work and gender, and building supportive childcare systems form the four pillars of a national campaign to reframe parenthood from a daunting economic burden to an embraced aspect of a balanced life.
Here are a few nuanced approaches that could steer South Korea towards a future where growing families bolster both the population and the economy, transforming the current demographic challenge into an opportunity for rejuvenation and sustainable growth.
Enhancing Family-Friendly PoliciesTo counteract the declining birth rate, South Korea can look towards implementing more robust, family-friendly policies. Such measures could include:
Extended Parental Leave: By lengthening the duration of leave for both mothers and fathers, parents are given valuable time to bond with their newborns without the stress of a rapid return to work.Greater Paternity Leave: Encouraging fathers to take an active role early in their children’s lives is essential for shared parenting responsibilities and can lead to more gender equality in childrearing.Flexible Work Arrangements: Telecommuting options, flexible hours, and part-time work can help parents balance their professional and personal lives, reducing the perceived incompatibility between career ambitions and starting a family.Financial IncentivesFinancial incentives can significantly lower the barriers to starting a family:
Housing Subsidies: To ease one of the largest financial burdens on young families, housing subsidies could be provided to reduce the cost of living.Child Allowances: Regular stipends to families with children can help cover the ongoing costs of childrearing, from clothing to food to extracurricular activities.Education Cost Reduction: By lessening the financial impact of educational expenses, parents may feel more secure in their ability to provide for their children’s futures.Cultural Shifts in Work and Gender NormsChanging the workplace culture and societal expectations can support family growth:
Reduced Work Hours: Normalizing shorter workdays can alleviate the stress and fatigue associated with long hours, giving parents more time to dedicate to their families.Destigmatizing Parental Leave: Both mothers and fathers should feel equally able to take leave for the birth or care of their children without fear of career repercussions.Equitable Sharing of Domestic Tasks: Promoting a cultural norm where domestic chores and childrearing tasks are shared more evenly between partners can alleviate the disproportionate burden often placed on women.Supportive Childcare SystemsDeveloping a robust childcare infrastructure is crucial for supporting working parents:
Accessible Childcare: Ensuring that affordable, high-quality childcare is readily available can alleviate one of the primary logistical hurdles faced by working parents.Well-Trained Providers: Investing in the training and compensation of childcare providers can raise the quality and appeal of childcare as a profession.Incentives for Employers: Encouraging businesses to provide onsite childcare or childcare assistance can make it easier for parents to rejoin the workforce.By focusing on these strategies, South Korea could foster an environment that not only stabilizes the birth rate but also promotes a healthier work-life balance, creating a resilient and thriving society for future generations.

It’s time to revive the vibrant energy of our youth.
Final ThoughtsAs South Korea grapples with the implications of its rapidly declining birth rate, the call to action becomes increasingly urgent. The echoes of empty playgrounds and the silent hallways of schools destined to close paint a stark picture of a potential future that lacks the vibrant energy of youth and the promise of generational renewal. It is a future that can be redirected, however, with thoughtful, targeted strategies designed to rekindle the desire for family life among South Koreans.
The multifaceted strategies outlined—ranging from enhancing family-friendly policies to reshaping cultural norms—serve as a clarion call to re-envision a society where creating a family is not a financial burden but a joyful and supported choice. It is about reconfiguring the very foundations upon which work-life balance, gender equality, and family support are built.
The implementation of comprehensive family-friendly policies, including extended parental leave and greater paternity involvement, underscores the nation’s commitment to shared parenting as a cornerstone of societal well-being. Furthermore, financial incentives addressing housing, child support, and education costs directly alleviate economic pressures that currently weigh heavily on prospective parents. Culturally, recalibrating work norms and gender roles to foster equality can transform the societal landscape, making it more conducive to family expansion. Finally, by bolstering childcare systems, South Korea can ensure that the choice to have children is not at odds with professional aspirations.
As we stand at the threshold of significant demographic shifts, the strategies for reversal are not merely optional—they are imperative. They are the building blocks for a resilient South Korea that not only stabilizes its population but also engenders a society in which young families can flourish. The path to a sustainable and dynamic future is paved with the actions we take today to empower individuals to embrace parenthood, should they choose it, with enthusiasm and confidence. The strategies proposed here offer a roadmap; it is now up to policymakers, businesses, and the community at large to embark on this journey toward a rejuvenated, balanced, and sustainable society.
Translate This PageSelect LanguageAfrikaansAlbanianAmharicArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CorsicanCroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchFrisianGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHawaiianHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanKurdish (Kurmanji)KyrgyzLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianLuxembourgishMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPashtoPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSamoanScottish GaelicSerbianSesothoShonaSindhiSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSudaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshXhosaYiddishYorubaZulu
#goog-gt-tt {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-banner-frame {display:none !important;}
.goog-te-menu-value:hover {text-decoration:none !important;}
.goog-text-highlight {background-color:transparent !important;box-shadow:none !important;}
body {top:0 !important;}
#google_translate_element2 {display:none!important;}
function googleTranslateElementInit2() {new google.translate.TranslateElement({pageLanguage: 'en',autoDisplay: false}, 'google_translate_element2');}
function GTranslateGetCurrentLang() {var keyValue = document['cookie'].match('(^|;) ?googtrans=([^;]*)(;|$)');return keyValue ? keyValue[2].split('/')[2] : null;}
function GTranslateFireEvent(element,event){try{if(document.createEventObject){var evt=document.createEventObject();element.fireEvent('on'+event,evt)}else{var evt=document.createEvent('HTMLEvents');evt.initEvent(event,true,true);element.dispatchEvent(evt)}}catch(e){}}
function doGTranslate(lang_pair){if(lang_pair.value)lang_pair=lang_pair.value;if(lang_pair=='')return;var lang=lang_pair.split('|')[1];if(GTranslateGetCurrentLang() == null && lang == lang_pair.split('|')[0])return;var teCombo;var sel=document.getElementsByTagName('select');for(var i=0;i<sel.length;i++)if(/goog-te-combo/.test(sel[i].className)){teCombo=sel[i];break;}if(document.getElementById('google_translate_element2')==null||document.getElementById('google_translate_element2').innerHTML.length==0||teCombo.length==0||teCombo.innerHTML.length==0){setTimeout(function(){doGTranslate(lang_pair)},500)}else{teCombo.value=lang;GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change');GTranslateFireEvent(teCombo,'change')}}
Search for: Recent Posts The Shifting Sands of a Rapidly Declining Birth Rate Seven Deadly Sins of the Future Disrupting the System: Can Microschools Fix American Education? Categories Artificial Intelligence Business Trends Future of Agriculture Future of Banking Future of Education Future of Healthcare Future of Transportation Future of Work Future Scenarios Future Trends Futurist Thomas Frey Insights Global Trends Predictions Social Trends Technology Trends Speaking TopicsFuture of Healthcare – “Is Death our only Option?Future of AIFuture of Industries ← Previous Post

The post The Shifting Sands of a Rapidly Declining Birth Rate appeared first on Futurist Speaker.
Thomas Frey's Blog
- Thomas Frey's profile
- 2 followers



