Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 159
April 21, 2021
How Does GitLab Make Money? The GitLab Business Model In A Nutshell

GitLab was created in 2013 by Ukrainian developers Dmitriy Zaporozhets, Valery Sizov, and Sytse Sijbrandij as a source code management solution for collaborative software teams. GitLab is a web-based, open-source DevOps tool providing issue-tracking and continuous integration and deployment pipeline features. It makes money via its main two paid plans (Premium & Ultimate) and via its subscription add-ons.
Origin StoryGitLab is a web-based, open-source DevOps tool providing issue-tracking and continuous integration and deployment pipeline features.
GitLab was created by Ukrainian developers Dmitriy Zaporozhets, Valery Sizov, and Sytse Sijbrandij as a source code management solution for collaborative software teams. Later iterations saw GitLab evolve to a more integrated solution, covering the entire DevOps lifecycle. Teams can now automate every aspect of this cycle, from planning to creation, build verification, security testing, deployment, and monitoring.
Today, the software incorporates an open-core development model. The core functionality is released under an open-source MIT license, but any additional functionality is subject to a proprietary license.
Gitlab has expanded aggressively since its founding in 2014, employing over 1300 team members across 67 countries. Last year, company revenue topped $150 million.
GitLab revenue generationGitlab follows the freemium model that is supported by a paid subscription service.
The free option is touted as providing a complete DevOps platform, but it does require that users provide their own CI runners and production environment.
For those desiring more functionality, there are two paid options:
Premium ($19/user/month, billed at $228 annually) – the premium plan provides DevOps with added features including code integrity controls, productivity data, and project management. Disaster recovery and 24/7 support are also offered.Ultimate ($99/user/month, billed at $1188 annually) – the Ultimate plan offers full DevSecOps with advanced security testing, compliance, and portfolio management. Teams can also utilize vulnerability management, free guest users, dependency scanning, and 50,000 CI/CD minutes per month.Add-on subscriptionsFor users who exceed their CI/CD minutes usage, additional CI minutes can be purchased for $10 per 1,000 minutes. Aside from this one-time payment, Gitlab also allows users to simply upgrade their plan to receive a greater allowance.
For those desiring more storage space, Gitlab offers 10GB for an additional $60. It should be noted that this charge is an annual, recurring subscription regardless of the data used.
Special projectsGitLab also offers special pricing in the form of a free Ultimate license to eligible:
Start-ups.Educational institutions, andOpen-source projects.Additional usersGitLab allows its customers to add more users mid-subscription by contacting the company for a customized quote.
The cost of adding extra users is pro-rated from the date of the quote or purchase through to the end of the subscription period.
Alternatively, customers can use the GitLab True-Up model to add additional users. In this case, a company that has grown from 100 to 300 users can renew on a 300-user plan while also paying a full annual fee for the 200 extra users it added.
Key takeaways:GitLab is a web-based, open-source tool that allows full automation of the entire DevOps lifecycle. It was created by Ukrainian developers Dmitriy Zaporozhets, Valery Sizov, and Sytse Sijbrandij.GitLab works on a freemium model backed by two paid subscription plans with greater functionality: Premium and Ultimate.Gitlab also makes money through add-on subscriptions, enabling users to purchase additional CI minutes and storage space. Additional users can also be accommodated on a prorated basis or by using the proprietary True-Up system.Read Next: How Does GitHub Make Money?
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does GitLab Make Money? The GitLab Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Lemonade Make Money? The Lemonade Business Model In A Nutshell

Lemonade is an insurance tech company using behavioral economics and artificial intelligence to process claims efficiently. The company leverages technology to streamline onboarding customers while also applying a financial model to reduce conflicts of interest with customers (perhaps by donating the variable premiums to charity). The company makes money by selling its core insurance products, and via its tech platform, it tries to enhance its sales.
Origin StoryLemonade is an insurance company using behavioral economics and artificial intelligence to process claims efficiently.
Founded in 2015 by Daniel Schreiber, Shai Wininger, and Ty Sagalow, the company quickly made a positive impact in the typically bureaucratic and exploitative insurance industry.
To that end, Lemonade uses artificial intelligence to promise zero paperwork and near-instantaneous claim processing for its customers. With so much of the claim process automated, the company can offer extremely competitive pricing.
It is also changing the stigma of insurance companies by sending a portion of its underwriting profits to a non-profit organization of the customer’s choosing.
Understanding Lemonade business modelMarketing Flywheel Trifecta: delightful experience, aligned values, and great prices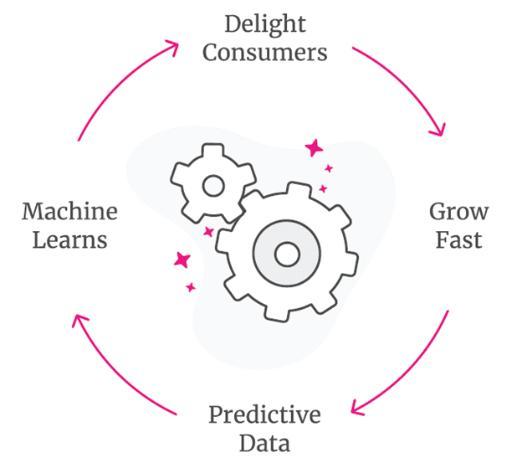 Lemonade Marketing Flywheel is driven by what Lemonade defines its trifecta, delightful experience, aligned values, and great prices
Lemonade Marketing Flywheel is driven by what Lemonade defines its trifecta, delightful experience, aligned values, and great prices (Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus).
Lemonade follows a customer-centric experience approach with a financial model that leverages technology while trying to minimize conflict of interest with customers:
Leveraging technology: every process on the platform, from marketing to onboarding leverages technology to both improve customer experience and mitigate risk.Alignment of our interests: in the Lemonade model, the company gives away variable premiums, and as the customer purchases a policy, they can designate a charitable cause which is where Lemonade gives the residual premiums from their policy. Subscription-based model : Lemonade follows a subscription-based model to smooth out its revenue generation. Technology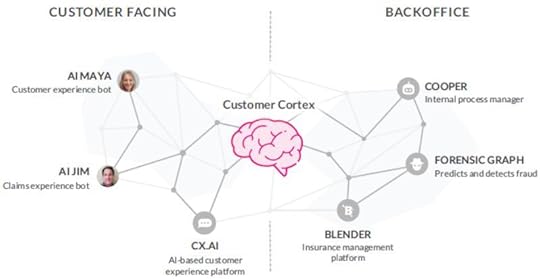 As a technology company, the business model is powered up by a set of bots and platforms to enhance the customer experience and build what Lemonade calls a “customer cortex (Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus).
As a technology company, the business model is powered up by a set of bots and platforms to enhance the customer experience and build what Lemonade calls a “customer cortex (Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus). AI Maya: The Lemonade onboarding and customer experience bot sells policies and handles everything from collecting information and personalizing coverage to creating quotes and facilitating payments.
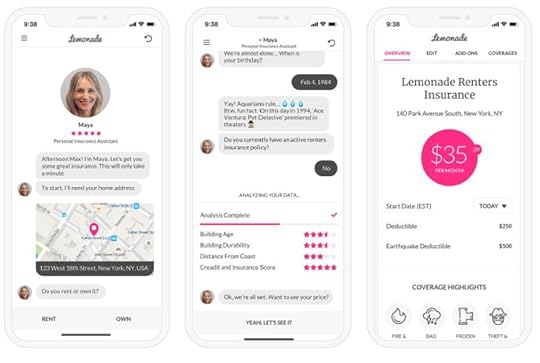 Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus.AI Jim: handling the “first notice of loss” for 96% of claims (as of September 30, 2020).
Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus.AI Jim: handling the “first notice of loss” for 96% of claims (as of September 30, 2020).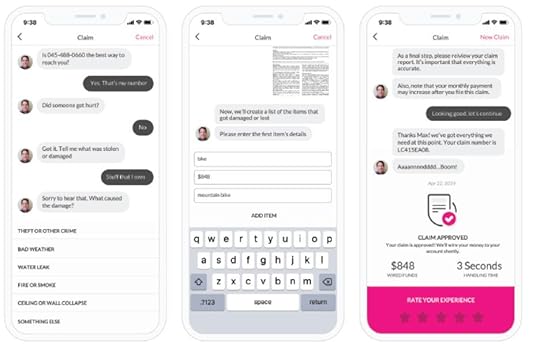 Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus.CX.AI: the bot platform is built to resolve customer requests without human intervention.Forensic Graph: to predict, deter, detect, and block fraud throughout the customer engagement.Blender: to facilitateing collaboration among customer experience, underwriting, claims, growth, marketing, finance, and risk teams.Cooper: hancling complex and repetitive internal tasks.Product Offering & Upselling Strategy
Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus.CX.AI: the bot platform is built to resolve customer requests without human intervention.Forensic Graph: to predict, deter, detect, and block fraud throughout the customer engagement.Blender: to facilitateing collaboration among customer experience, underwriting, claims, growth, marketing, finance, and risk teams.Cooper: hancling complex and repetitive internal tasks.Product Offering & Upselling Strategy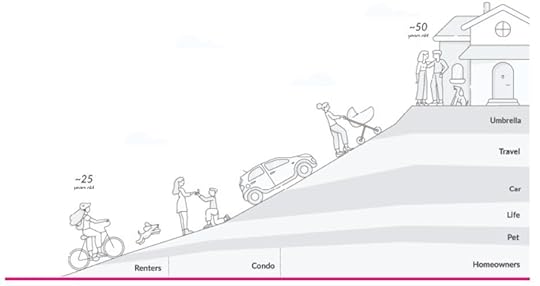 The wide variety of products on the platform enables a potential up-sell strategy, where customers can be re-engaged and provided additional services, based on their preferences (Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus).
The wide variety of products on the platform enables a potential up-sell strategy, where customers can be re-engaged and provided additional services, based on their preferences (Image Source: Lemonade Financial Prospectus).Products:
Renters and Homeowners Insurance : Pet Insurance . Giveback Feature : Lemonade donates leftover money to causes our customers care about.Reinsurance service through which the “reinsurer,” agrees to cover a portion of the claims of another insurer, the “primary insurer,” in return for a portion of their premiums.Lemonade revenue generation This Lemonade trifecta, delightful experience, aligned values, and great prices, is used to move three key metrics
This Lemonade trifecta, delightful experience, aligned values, and great prices, is used to move three key metrics (Image Source Lemonade Financial Prospectus).
Lemonade makes money by selling a range of insurance options.
These include:
Renters insurance – starting from $5/month.Condo insurance – starting from $25/month with the exact price depending upon the deductible, the age of the building, the desired coverage amount, and the location of the condo. The average cost of condo insurance in Massachusetts is $46/month. In Illinois, it is $31/month.Pet insurance – starting at $10/month. Lemonade also offers a 10% discount to customers if their home is also insured with the company.Term life insurance – starting at $9/month with a five-minute application process that saves customers from having to schedule a medical exam.Homeowners insurance – starting from $25/month.Co-op insurance – ideal for those living in a co-op arrangement. This policy covers the individual and their personal belongings and excludes physical structures, facilities, or grounds. Prices are available on request.Of the premiums collected by Lemonade, 25% is used to cover administrative costs and any surplus amount becomes profit.
The remaining 75% is used to buy reinsurance, cover taxes and fees, and fund claims. Any surplus of the remaining 75% goes to a charity chosen by the customer.
Artificial intelligence and behavioral economicsUsing the vast amount of data it collects, Lemonade can give more accurate quotes to prospective customers. It also uses anti-fraud algorithms to process simple claims more quickly, saving money on employee wages.
Furthermore, the company uses behavioral economics to minimize insurance fraud which erodes profits. By allowing each customer to donate to charity, they become less motivated to make unreasonable claims.
It should also be noted that Lemonade is a B-Corporation. In the United States, this denotes a for-profit organization that also meets rigorous social and environmental performance, accountability, and transparency standards.
Ultimately, this means that making a profit and being a force for public good are of equal importance to Lemonade.
Key takeaways:Lemonade is an American insurance company using artificial intelligence to disrupt the bureaucratic and somewhat inefficient insurance industry.Lemonade makes money by selling a host of insurance products for a monthly fee. Customers can opt for renders, condo, pet, co-op, homeowners, or life insurance.Lemonade also uses behavioral economics to reduce insurance fraud and champion social causes. The latter is particularly important to Lemonade as an organization that prioritizes profit-making alongside public service.Read Also: How Does Compass Make Money? The Compass Business model In A Nutshell
Read Next: PropTech Business Models, Affirm Business Model , Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Lemonade Make Money? The Lemonade Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Offerpad Make Money? The Offerpad Business Model In A Nutshell

Offerpad is a tech-enabled real estate platform enabling users to buy and sell homes. The company makes money via service fees. Indeed, whenever a home is sold through the Offerpad platform, the company collects a service fee. And it also makes money via sales profits As a seller and buyer of homes, Offerpad is in a position to make a profit on homes they sell to members of the general public.
Origin StoryOfferpad is a tech-enabled real estate platform enabling users to buy and sell homes.
The company was founded by Brian Bair in 2015, a former real estate professional with a deep understanding of the difficulties people encountered when selling their homes.
Bair noted that the selling process was highly stressful – sellers had to prepare for open inspections and there was a high degree of uncertainty over the final sale price. They also had to deal with removalists and then wait patiently for the settlement date.
Offerpad had a clear goal from the start: reinvent the home sale process and give sellers the convenience, control, and certainty they desired.
The platform itself offers a unique blend of industry experience and technological integration. Headquartered in Chandler, Arizona, the company now operates in nearly 1,000 cities and towns across the United States.
Offerpad revenue generationThere are two central components to the Offerpad revenue generation model.
Service feesWhenever a home is sold through the Offerpad platform, the company collects a service fee.
On average, the service fee is 7% of the total sale price – though it can range from anywhere between 6-10%.
If the property in question requires renovations before on-selling, Offerpad will charge a further maintenance fee. This cost varies according to the level of work required.
Sales profitsAs a seller and buyer of homes, Offerpad is in a position to make a profit on homes they sell to members of the general public.
The company is one of a host of so-called “iBuyers” – or real estate companies that use algorithmic technology to make near-instant cash offers to homeowners.
This technology allows Offerpad to make an offer it believes will be profitable for the company once the time comes to sell. To assist in this process, the algorithm pulls data from public databases detailing previous home sales in the area. Data is supplemented by user surveys and certified real estate agents who inspect the homes in person.
Ultimately, this technology gives Offerpad the confidence to make a rapid offer that is usually below the market rate. This increases the likelihood of making a profit once the property is sold back to the market.
Like many iBuyers, Offerpad concentrate on middle-class homes in the $100,000-500,000 price range. The company notes that luxury homes above half a million dollars are harder to value and thus make a profit on.
Key takeaways:Offerpad is a technology real estate company founded by former real estate agent Brian Bair. It is one of several iBuyers operating in the real estate industry or companies that use algorithmic technology to make near-instant cash offers to sellers.Offerpad charges a service fee for every house sold on its platform. Typically this is around 7%, though it can be anywhere from 6-10%. Additional charges are incurred for homes needing renovation before on-selling.Offerpad also makes money on homes they sell for a profit. The odds of the company making a profit are increased by its technological valuation method and its ability to make cash offers below the market rate.Read Also: How Does Compass Make Money? The Compass Business model In A Nutshell
Read Next: PropTech Business Models, Affirm Business Model , Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Offerpad Make Money? The Offerpad Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Compass Make Money? The Compass Business model In A Nutshell
Compass is a licensed American real-estate broker incorporating online real estate technology as a marketing medium. The company makes money via sales commissions (collected whenever a sale is facilitated or tenants are found for a rental property) and bridge loans (a service allowing the seller to purchase a home before the revenue from the sale of their previous home is available).
Origin StoryCompass is a licensed American real-estate broker incorporating online real estate technology as a marketing medium.
The company began as Urban Compass in 2012 and was founded by entrepreneurs Robert Reffkin and Ori Allon – a former engineer at Twitter. In the early days of Compass, users could schedule online appointments with salaried real estate brokers after searching listings on the company desktop or mobile app.
In 2014, the company pivoted from employing brokers full-time to collecting a commission from contracted (but independent) brokers.
Originally focused on the rental market, Compass now specializes in luxury, high-margin homes in affluent areas. After its IPO on the NYSE in 2021 the company passed the ten billion market capitalization.
Analyzing Compass strategyAs the company highlighted in its financial prospectus, “we envision a world where the experience of selling or buying a home is simple and pleasant for everyone. Our strategy is to replace today’s complex, paper-driven, antiquated workflow with a seamless, all-digital, end-to-end platform that empowers real estate agents to deliver an exceptional experience to every seller and buyer. Our agent-centric platform is at the heart of our mission to help everyone find their place in the world.”
The company executes that by providing an “end-to-end platform that empowers our residential real estate agents to deliver exceptional service to seller and buyer clients.”
 The Compass platform consists of three primary user journeys: advising sellers, attracting and retaining clients, advising buyers.
The Compass platform consists of three primary user journeys: advising sellers, attracting and retaining clients, advising buyers. (Image Source: Compass Financial Prospectus).Understanding the Compass value proposition
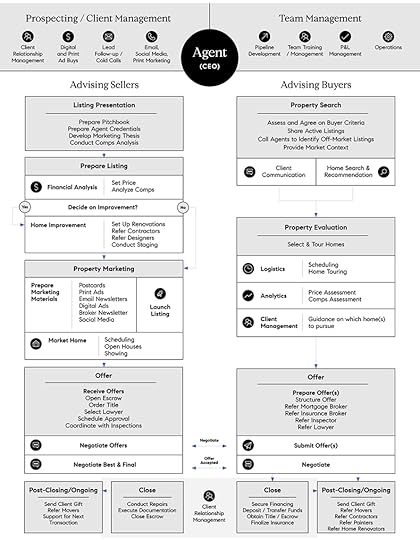 An example of the workflows, tasks, and complexity that agents need to go through to perform well at their jobs as “CEOs.” The primary value proposition for Compass is to cut through that complexity to help them streamline most of its workflows
An example of the workflows, tasks, and complexity that agents need to go through to perform well at their jobs as “CEOs.” The primary value proposition for Compass is to cut through that complexity to help them streamline most of its workflows(Image Source: Compass Financial Prospectus).
Differently from other PropTech companies, Compass doesn’t try to remove the human from the loop. Instead, it tries to empower the agent to facilitate the transactions’ closing. In fact, Compass highlights how most buyers still want to deal with agents.
Understanding the Compass marketing flywheel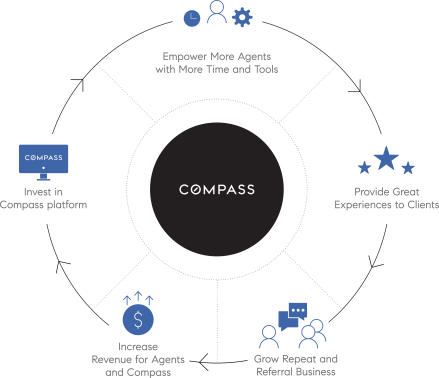 The Compass marketing flywheel starts from a key stakeholder: the agent. As more agents are empowered through the platform, they attract, engage and delight buyers. This creates a reputation for the platform, and repeat purchases, that lead to revenue growth, invested back to the development of the technological platform to provide more and more empowering tools for agents. (Image Source: Compass Financial Prospectus).Compass revenue generation
The Compass marketing flywheel starts from a key stakeholder: the agent. As more agents are empowered through the platform, they attract, engage and delight buyers. This creates a reputation for the platform, and repeat purchases, that lead to revenue growth, invested back to the development of the technological platform to provide more and more empowering tools for agents. (Image Source: Compass Financial Prospectus).Compass revenue generationLike many real estate brokers, Compass makes money from commissions and referral fees. Following is a more detailed look at each revenue stream.
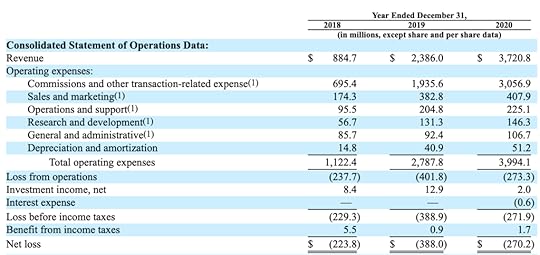
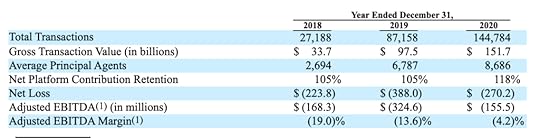 Compass revenue generation and some KPIs.Sales commissions
Compass revenue generation and some KPIs.Sales commissionsThe bulk of Compass revenue generation comes from sales commissions. These are collected whenever a sale is facilitated or tenants are found for a rental property.
These fees are split between Compass and the real estate agent. The exact nature of the split is unclear, but it might be assumed that more experienced agents can command a higher share of the commission.
The company also seeks to maximize commission fees by focusing exclusively on higher-end properties. Sellers can also opt to use the Compass concierge service which increases the fee the company can charge.
Through the Compass Private Exclusives facility, homes are privately listed before they hit the market. This creates hype and urgency among buyers which in turn increases the odds of a successful sale. It also allows property owners to get an idea of how much their home is worth using a host of marketing insights.
Lastly, the company endeavors to increase revenue by making its platform attractive to agents. To that end, Compass offers a range of curated learning resources to help real estate entrepreneurs grow their businesses. Topics offer assistance in marketing, financial planning, and comparative market analysis (CMA) reporting.
Bridge loansIn 2019, Compass began to offer a bride loan service in conjunction with mortgage partners Freedom Mortgage and Better Mortgage.
Essentially, the service allows the seller to purchase a home before the revenue from the sale of their previous home is available.
It should be noted that Compass cannot collect revenue on loan interest because it does not issue the loans. Having said that, it does receive a referral fee from the aforementioned partners for sending business their way.
In addition to referral fees, the company also charges for title and escrow-related services.
Key takeaways:Compass is an American property technology company founded by Robert Reffkin and Ori Allon. The company has a focus on providing services for real estate buyers and sellers in lucrative, high-margin markets.Compass collects a sales commission for each property sold and shares it with the agent. Since these professionals are independent contractors, Compass offers professional development resources around marketing and finance to name a couple.Compass also earns money through bridging loan referral fees, which are underwritten by partnering lenders.Read Next: PropTech Business Models, Affirm Business Model , Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Compass Make Money? The Compass Business model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
April 20, 2021
How Does GitHub Make Money? The GitHub Business Model In A Nutshell

GitHub provides web-based hosting for software development and version control using Git, which facilitates collaborative source code development among programmers. GitHub was founded by Chris Wanstrath, P. J. Hyett, Tom Preston-Werner, and Scott Chacon in 2008. Microsoft acquired the company for $7.5 billion in 2018, and it was integrated as part of Microsoft’s enterprise offering. On top of its free repository, GitHub also offers plans for teams and enterprise customers. And the GitHub marketplace also monetizes on some of the apps developed on top of it.
Origin StoryGitHub provides web-based hosting for software development and version control using Git, a program that facilitates collaborative source code development among programmers.
GitHub was founded by Chris Wanstrath, P. J. Hyett, Tom Preston-Werner, and Scott Chacon in 2008. In the following year, Github amassed over 100,000 users and hosted over 90,000 unique public source file repositories. It quickly earned a reputation as a popular resource, with tech companies such as Apple, Google, and Amazon known to frequent it.
In 2012, the company raised $350 million in funding and opened its first office outside of the United States in Japan. Six years later, GitHub was acquired by Microsoft for $7.5 billion.
GitHub revenue generationGitHub work on a freemium model of revenue generation. Indeed, their value proposition is such that “anybody can host their software code on GitHub’s servers, and collaborate on it by multiple developers, teams, and organizations.”
As such, access to public repositories is both free and unlimited. For private repositories with a high feature set and customization level, a subscription fee is charged.
Subscription plansGithub offers four subscription plans for both individuals and teams:
Free – a free-of-charge option for individuals and small businesses who require a minimal number of features and storage space. While the company does not make any money from this option directly, it uses the freemium concept to allow consumers to try before they buy, so to speak.Team ($4/month)Enterprise ($21/month)GitHub One – pricing available on request.The latter three paid plans exist for those who want to scale projects with added features. Such features include more storage, secured sign-ins, and dedicated support. Many also opt for a paid plan to utilize Actions, or higher workflow automation minutes.
It’s also important to note that GitHub makes money whenever its customers exceed the limitations of their plan. For example, repository storage is charged at an extra $0.25 for every gigabyte over the stated limit.
MarketplaceGitHub Marketplace allows developers to enhance the functionality of the GitHub platform through third-party apps.
Apps are categorized according to code quality, continuous integration, monitoring, and project management. Some apps are free, while the company charges a flat or per-unit-used fee for others.
Given that these apps are provided by a third party, it is safe to assume that Github takes a percentage of whatever fee is charged.
Key takeaways:GitHub provides a platform for software development and version control called Git. It was founded by four tech entrepreneurs in 2008 and quickly grew its user base in the succeeding years.GitHub uses a freemium model supported by three paid subscription plans. Each plan offers a different feature set and level of functionality according to the needs of the user.GitHub Marketplace allows third-party app creators to sell their products on the platform. The exact fee the company collects is likely a pre-determined percentage amount and is charged as a flat or per-unit-used amount.Read Next:
Open-Source Business ModelMicrosoft Business ModelFreemium Business ModelMain Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does GitHub Make Money? The GitHub Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Wealthfront vs. Betterment Business Model
Wealthfront and Betterment are major players in the Robo-advising space. Both companies make money via advisory fees. And Betterment has additional revenue streams like the service for advisors, the cash reserves, and the checking accounts.
 Wealthfront is an automated Fintech investment platform providing investment, retirement, and cash management products to retail investors, mostly making money on the annual 0.25% advisory fee the company charges for assets under management. It also makes money via a line of credits and interests on the cash accounts.
Wealthfront is an automated Fintech investment platform providing investment, retirement, and cash management products to retail investors, mostly making money on the annual 0.25% advisory fee the company charges for assets under management. It also makes money via a line of credits and interests on the cash accounts.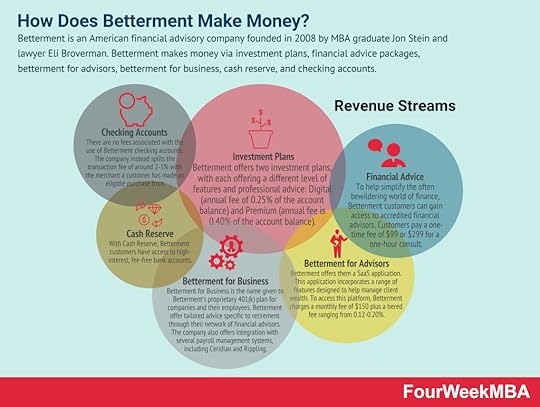 Betterment is an American financial advisory company founded in 2008 by MBA graduate Jon Stein and lawyer Eli Broverman. Betterment makes money via investment plans, financial advice packages, betterment for advisors, betterment for business, cash reserve, and checking accounts.
Betterment is an American financial advisory company founded in 2008 by MBA graduate Jon Stein and lawyer Eli Broverman. Betterment makes money via investment plans, financial advice packages, betterment for advisors, betterment for business, cash reserve, and checking accounts. Read Next: Affirm Business Model , Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
 Fintech business models leverage tech and digital to enhance the financial service industry. Fintech business models, therefore, apply tech to various financial service use cases. Fintech business model examples comprise Affirm, Chime, Coinbase, Klarna, Paypal, Stripe, Robinhood, and many others whose mission is to digitize the financial services industry.
Fintech business models leverage tech and digital to enhance the financial service industry. Fintech business models, therefore, apply tech to various financial service use cases. Fintech business model examples comprise Affirm, Chime, Coinbase, Klarna, Paypal, Stripe, Robinhood, and many others whose mission is to digitize the financial services industry. Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Wealthfront vs. Betterment Business Model appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Betterment Make Money? The Betterment Business Model In A Nutshell
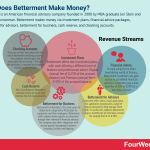
Betterment is an American financial advisory company founded in 2008 by MBA graduate Jon Stein and lawyer Eli Broverman. Betterment makes money via investment plans, financial advice packages, betterment for advisors, betterment for business, cash reserve, and checking accounts.
Origin StoryBetterment is an American financial advisory company. Based in New York City, it was founded in 2008 by MBA graduate Jon Stein and lawyer Eli Broverman.
Initially, Stein and Broverman wanted to create an investment and broker-dealer advice service for customers. After securing the relevant regularly approvals, the Betterment platform was launched in 2010.
The company quickly expanded its product range to include goal-based investment advice, auto-deposit and rebalancing, checking and savings accounts, and individual retirement accounts (IRAs).
As of 2012, Betterment has more than $29 billion in assets under management across 600,000 customers.
Betterment revenue generationBetterment generates revenue via multiple channels.
Let’s take a look at them in more detail.
Investment plansBetterment offers two investment plans, with each offering a different level of features and professional advice:
Digital – where the company charges an annual fee of 0.25% of the account balance.Premium – where the annual fee is 0.40% of the account balance.Financial advice packagesTo help simplify the often bewildering world of finance, Betterment customers can gain access to accredited financial advisors.
For the privilege, customers pay a one-time fee of $99 or $299 for a one-hour consult. However, it should be noted that these advisors do not work for Betterment directly. It must be assumed the company only receives a portion of the total fee.
Betterment for AdvisorsTo strengthen the relationship between the company and its financial advisors, Betterment offers them a SaaS application. This application incorporates a range of features designed to help manage client wealth.
To access this platform, Betterment charges a monthly fee of $150 plus a tiered fee ranging from 0.12-0.20%.
The exact fee is dependent upon the aggregate assets of the advisor in question.
Betterment for BusinessBetterment for Business is the name given to Betterment’s proprietary 401(k) plan for companies and their employees.
Betterment offer tailored advice specific to retirement through their network of financial advisors. The company also offers integration with several payroll management systems, including Ceridian and Rippling.
Pricing for this service depends on the number of employees and the monetary assets deployed. Add-on features and the payroll system chosen also influence the total price.
Cash ReserveWith Cash Reserve, Betterment customers have access to high-interest, fee-free bank accounts.
Since the company does not derive revenue from fees, it instead receives compensation from partnering banks such as Citi and Barclays.
Checking accountsFor those who prefer a simple checking account with an attached debit card, Betterment has them covered also.
Like the Cash Reserve facility, there are no fees associated with the use of Betterment checking accounts. The company instead splits the transaction fee of around 2-3% with the merchant a customer has made an eligible purchase from.
Key takeaways:Betterment is an American financial advisory company founded in 2008 by Jon Stein and Eli Broverman. It offers a range of investment, banking, and retirement services and advice.Betterment drive revenue from two investment plans, charging a flat fee based on the total investment balance.The company also makes money in an advisory capacity, offering individuals and businesses sound financial advice and access to a host of tools. Betterment also makes a less significant amount of money via fee-free checking and high-interest bank accounts.Read Next: Affirm Business Model , Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Betterment Make Money? The Betterment Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Indeed Make Money? The Indeed Business Model In A Nutshell
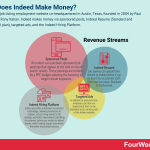
Indeed is a job listing employment website co-headquartered in Austin, Texas, founded in 2004 by Paul Forster and Rony Kahan. Indeed makes money via sponsored posts, Indeed Resume (Standard and Professional plan), targeted ads, and the Indeed Hiring Platform.
Origin StoryIndeed is a job listing employment website co-headquartered in Austin, Texas, and Stamford, Connecticut.
The company was founded in 2004 by Paul Forster and Rony Kahan. In 2005, the pair released a beta version of the platform and described it as a pay-per-click (PPC) job advertising network. Indeed also tracks the popularity of words over time to identify new trends in the job market.
In recent years, the company has made several acquisitions. In 2019 it acquired Syft – a major recruitment platform in the UK for the industrial, event, and hospitality sectors. In the same year, Indeed also acquired the automated job advertisement platform ClickIQ.
Indeed is now the most popular job website in the world, attracting 250 million unique monthly visitors with 10 new jobs posted every second.
Indeed revenue generationThe Indeed platform of free of charge for job searchers, so the company instead charges businesses for the privilege of listing vacant positions.
With so many jobs posted daily, an individual listing can quickly become buried among thousands of similar search results. Therefore, Indeed allows recruiters to increase their visibility via several paid tools.
We will have a look at these tools and some other revenue streams below.
Sponsored postsFirstly, recruiters can purchase sponsored job postings that appear at the side or top of search results. These postings are funded by a PPC budget allowing the business to target certain keywords.
Indeed charge for keyword targeting based on how popular it is as a search term. Ads can be run for a minimum of $5 per day, with no upper limit on how much an employer can spend.
Indeed ResumeJob seekers can upload their résumé to Indeed where it can be found by recruitment staff.
However, Indeed charge a monthly subscription fee for the privilege. There are two plans:
Standard – for businesses making a few hires, Indeed charges $100/month for 30 contacts. Here, contacts are defined as interactions between an employer and a job seeker.Professional – for larger businesses who require more interaction, Indeed charges $250/month for 100 contacts. There are also additional tools such as bulk messaging and Indeed’s Hiring Insights analytics.Targeted adsIn addition to sponsored ads, employers can also use targeted ads that can be displayed across various parts of the Indeed website.
While Indeed does not publicly disclose the prices for targeted ads, it is likely to be based on the location the ad occupies and how long it runs for.
Indeed Hiring PlatformIndeed also offer automated recruitment technology, allowing businesses to conduct virtual hiring events to fill multiple positions. Interviewees satisfying the relevant criteria are invited to attend events, which Indeed argues streamlines the entire recruitment process.
Again, prices for this holistic service are undisclosed. But they are based on the geographic location, job demand, and the number of job seekers targeted. There is also likely to be a one-time fee for hosting the event itself.
Key takeaways:Indeed is a job listing employment website founded by Paul Forster and Rony Kahan. The platform borrows aspects of Google PPC advertising and search-based ad placement.Indeed is free to use for job seekers. Instead, revenue generation is primarily focused on an increasing job listing visibility for employers.Indeed also offer a range of ancillary services. Indeed Resume allows businesses to access a database of job seeker résumés. The Indeed Hiring Platform gives employers an automated, all-in-one solution to attracting, interviewing, and then hiring suitable candidates.Read Next:
LinkedIn Business ModelB2B Business ModelsHow Does Glassdoor Make MoneyHow Does Craigslist Make MoneyGoogle Business ModelMain Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Indeed Make Money? The Indeed Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Mint Make Money? The Mint Business Model In A Nutshell
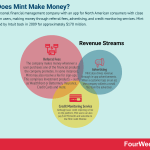
Mint is a personal financial management company with an app for North American consumers with close to 20 million users, making money through referral fees, advertising, and credit monitoring services. Mint was acquired by Intuit back in 2009 for approximately $170 million.
Origin StoryMint is a personal financial management company with an app for North American consumers.
The company was created by Aaron Patzer in 2006 through a deal with software firm Yodlee to provide account aggregation services. Three years later, Mint was acquired by Intuit and shifted to using its account connecting system.
Using the Mint platform, users can track bank, credit card, investment, and loan balances using a single interface. Customers can also set financial goals through smart budgeting, receive a free credit score, and use a bill tracker for recurring payments or subscriptions.
At last count, Mint claimed to have northwards of 20 million users.
Mint revenue generationMint operates under a freemium model. Full access to the Mint app is free for all users.
So how does it make money?
Referral feesThe company makes money whenever a user purchases one of the financial products the company promotes. In some instances, Mint may also receive a fee for sign-ups.
Since Mint is an aggregation service, it can promote a vast swathe of products and services.
These include (but are not limited to):
Investment products – such as Wealthfront or Betterment.Insurance – whether that be life, home, or vehicular insurance.Personal and student loans.Credit cards.Personal banking services from participating financial institutions, including American Express and Bank of America.The exact fee structure is dependent upon the nature of the agreement between Mint and its partners.
Given Mint’s access to the complete financial history of its customers, referral fees should be a lucrative source of income for the company. By analyzing spending habits, targeted offers can be sent to consumers.
Many have speculated that this valuable data might have been sold to other companies as a further revenue stream. However, there has been no indication that Mint has made modes to sell customer data.
AdvertisingMint also drives revenue through in-app advertisements. When a customer taps on an ad, the company collects a small fee from the advertiser.
Again, the ads are likely to be highly targeted given Mint’s access to detailed customer data.
Credit monitoring serviceAlthough basic credit reporting is free on the platform, Mint users can also pay $16.99/month and subscribe to the Mint Credit Monitor.
This premium reporting service incorporates data from three credit agencies: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. The service also monitors for (and reports on) possible instances of identity theft.
Key takeaways:Mint is a personal financial services company founded in 2006 by Aaron Patzer. The platform is an aggregation tool, allowing users to track all of their financial products in a single app.Mint operates on the freemium model. But as a data aggregator, it has access to vast amounts of valuable consumer data regarding spending and saving habits among other things. As a result, it derives the bulk of its revenue via targeted referral fees.Mint also offers in-app advertising and a premium credit monitoring service that gives users the credit score across three different agencies.Read Next:
How Does Venmo Make Money?How Does Zoom Make Money?How Does Discord Make Money? How Does Zelle Make Money? How Does Affirm Make Money?Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does Mint Make Money? The Mint Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Twitch Make Money? Twitch Business Model In A Nutshell
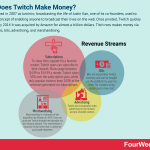
Twitch started in 2007 as Justin.tv, broadcasting the life of Justin Kan, one of its co-founders, used to prove the concept of enabling anyone to broadcast their lives on the web. Once pivoted, Twitch quickly grew, and by 2014 it was acquired by Amazon for almost a billion dollars. Titch now makes money via subscriptions, bits, advertising, and merchandising.
Origin StoryHow Twitch pivoted from Justin.tv, to become among the most successful streaming services, bought for a billion by Amazon.Twitch is a North American live streaming service with a focus on esports broadcasting and video game streaming. Twitch was founded as a spin-off to Justin.tv. Founders Justin Kan and Emmett Shear noted that the gaming category on Justin.tv was the most-watched category on the site.
Three years after Twitch was founded, it was identified as the fourth-largest source of peak internet traffic in the United States. As a result, the parent company of Justin.tv was rebranded as Twitch Interactive and Justin.tv was shut down.
Twitch Interactive was then acquired by Amazon for $970 million, enabling the platform to become integrated with Amazon Prime.
Twitch continues to dominate the gaming and esports streaming market, boasting over a hundred million actively monthly users. The platform has since expanded to offer creative content, music broadcasts, and affiliate programs for streamers.
The Amazon acquisition explained by Twitch co-founderJustin Kan, co-founder of Twitch explains how he sold the company to Amazon for almost a billion dollars!Now Twitch is part of the Amazon’s empire:
 In 2014, Twitch was bought by Amazon for $970 million. Therefore Twitch is part of Amazon, comprising other subsidiaries bought over the years, like Audible, Whole Foods, and Zappos (in total, Amazon has 12 subsidiaries). Therefore, as of 2020, Twitch is a multi-billion dollar company, making money primarily via advertising through its video streaming platform (creators use Twitch today across many other verticals).
In 2014, Twitch was bought by Amazon for $970 million. Therefore Twitch is part of Amazon, comprising other subsidiaries bought over the years, like Audible, Whole Foods, and Zappos (in total, Amazon has 12 subsidiaries). Therefore, as of 2020, Twitch is a multi-billion dollar company, making money primarily via advertising through its video streaming platform (creators use Twitch today across many other verticals). 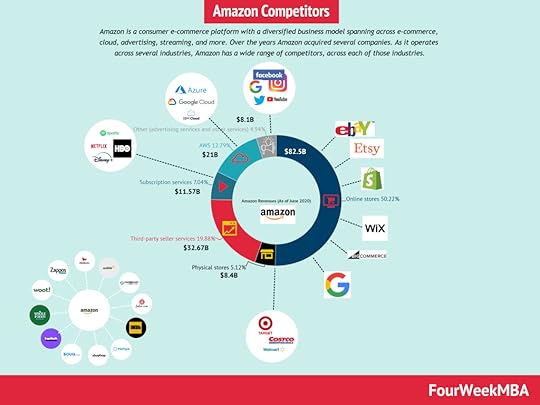 Amazon is a consumer e-commerce platform with a diversified business model spanning e-commerce, cloud, advertising, streaming, and more. Over the years, Amazon acquired several companies. As it operates across several industries, Amazon has a wide range of competitors across each of those industries. For instance, Amazon’s E-commerce competes with Shopify, Wix, Google, Etsy, eBay, BigCommerce.Twitch revenue generation
Amazon is a consumer e-commerce platform with a diversified business model spanning e-commerce, cloud, advertising, streaming, and more. Over the years, Amazon acquired several companies. As it operates across several industries, Amazon has a wide range of competitors across each of those industries. For instance, Amazon’s E-commerce competes with Shopify, Wix, Google, Etsy, eBay, BigCommerce.Twitch revenue generationTwitch has an extensive revenue generation model – despite being predominantly a freemium product. Without further ado, let’s delve into the finer details.
SubscriptionsTo show their support for a favorite creator, Twitch users can subscribe to their channel.
There are three, tiered options, with the latter two accommodating those who generally wish to provide more support:
$4.99/month is the minimum amount, giving subscribers access to creator emotes (Twitch-specific emoticons) and other benefits which each creator can define.$9.99/month – offering one extra emote.$24.99/month – offering two extra emotes.Irrespective of the plan chosen, Twitch takes 50% of the total revenue. In limited scenarios, Twitch allows popular creators to keep 100% of the subscription revenue as an incentive to keep them on the platform.
BitsBits are essentially Twitch currency and can be bought on the platform by users to cheer for creators using emoticons in live chat.
100 bits can be purchased for $1.40, with 25,000 bits available for $308. The creators themselves receive $0.01 for each bit that is used in their chat.
AdvertisingTwitch also incorporates video advertising on live streams and pre-recorded content.
The company first negotiates with an advertiser and then the creator receives a portion of the advertising revenue. The total amount a creator receives is dependent on their CPM (Cost Per Mile), or a fixed price per one thousand views.
Twitch works with each creator to agree on a unique CPM. Confidentiality clauses mean that exact CPM rates are hard to quantify.
MerchandiseMerchandising is a hallmark of the acquisition by Amazon in 2014.
Fans can purchase Twitch-branded merchandise via the Amazon website. This merchandise is exclusive in the sense that it cannot be purchased elsewhere. Clothing is the most popular form of merchandise, but Twitch fans can also purchase gift cards and pet accessories.
Amazon Prime integration makes these purchases exceedingly easy. Such is the popularity of Twitch that profit margins are also high.
Key takeaways:Twitch is a live streaming video platform founded by Justin Kan and Emmett Shear. The platform was created after Kan and Shear noted the surge in video game streaming popularity on Justin.tv.After becoming the fourth largest source of peak internet traffic in 2014, Twitch was acquired by Amazon. Its product range quickly expanded to include music broadcasting, affiliate programs, and other creative content.Twitch makes money by offering creator subscription plans. Fans can also purchase in-house currency to show their support using proprietary emoticons. Twitch also makes money on exclusive, high-margin merchandise.Read Next:
Amazon Business ModelAmazon CompetitorsHow Does Discord Make MoneyNetflix Business ModelSpotify Business ModelMain Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Twitch Make Money? Twitch Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



