Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 157
April 26, 2021
How Does Kickstarter Make Money? The Kickstarter Business Model In A Nutshell
Founded in 2009 by Perry Chen, Yancey Strickler, and Charles Adler with a mission to help bring creative projects to life, Kickstarter uses an all-or-nothing model funding model (if a project does not meet its financial goal, no money changes hands between the creator and the backers funding the project). The company primarily makes money via transaction fees.
Origin StoryKickstarter is a Brooklyn-based public benefit corporation and is best known for its crowdsourcing platform.
It was founded in 2009 by Perry Chen, Yancey Strickler, and Charles Adler with a mission to help bring creative projects to life. This means the platform is frequented by a diverse range of creatives, including musicians, filmmakers, comedians, journalists, and gamers.
From 2012 to 2017, Kickstarter embarked on an expansion strategy that saw it establish a presence in the UK, New Zealand, Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Mexico, Japan, and most of western Europe.
As of November 2020, the platform has launched over 500,000 projects worth $5.4 billion.
Kickstarter in numbersKickstarter has become one of the largest crowdfunding platforms, and the place where many business ideas have been validated and launched. To gain a bit of context it’s worth looking at some of its key statistics.


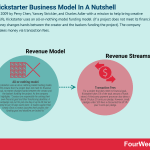
 Source: kickstarter.com/help/statsKickstarter revenue generation
Source: kickstarter.com/help/statsKickstarter revenue generationKickstarter uses an all-or-nothing model funding model. This means that if a project does not meet its financial goal, no money changes hands between the creator and the backers funding the project.
As the company highlights:
We established the all-or-nothing model when we launched in 2009 as a measure to protect creators, and to minimize risk for everyone. By not releasing funds unless a project meets its goal, this ensures that creators have enough money to do what they promised and they’re not expected to complete a project without the funds necessary to do so. This also assures backers that they’re only funding creative ideas that are set to succeed.
Thus, the company argues that this model increases revenue generation for both Kickstarter and the creator. Financial goals encourage creators and backers to rally together and create a sense of urgency. A sense of community is then created when both parties cross the finish line together and successfully fund a project.
For projects that are ultimately unsuccessful, Kickstarter does not collect a fee and the money is returned to the backers.
Transaction feesFor a project that does meet its financial goal, Kickstarter takes 5% of the total amount of funds raised.
A third-party payment processor also takes a fee of 3% plus 20 cents per pledge. However, small pledges under $10 have a discounted fee of 5% plus 5 cents per pledge.
For users in the United States, this third-party processor is usually Stripe.
In the case of $10,000 raised by 100 pledges, the creators will receive $9000. Kickstarter then takes a $500 commission and the payment processor another $500. Given its relatively low operating costs, the commission Kickstarter receives is relatively profitable.
Kickstarter maintains that its fee structure has set the industry standard for crowdfunded creator projects. In other words, the company believes in paying the creator as much as possible by eliminating the numerous intermediaries in a traditional funding process.
These include agents, distributors, dealers, record labels, publishers, and fiscal sponsors.
Benefit Corporation certificationIn 2015, Kickstarter was reincorporated as a Benefit Corporation in the United States. This means the company gauges success according to how well it delivers on its mission. While profits are important, they are no more important than socially responsible decision-making and goals.
Key takeawaysKickstarter is an American crowdfunding platform that was reincorporated as a Benefit Corporation in 2015. Its mission is to help bring creative projects to life for a diverse range of creators.For successfully funded projects, Kickstarter charges a commission of 5% of the total amount raised. A third-party payment processor – usually Stripe – also takes a cut for facilitating the transaction.Kickstarter encourages projects to become fully funded by creating a sense of camaraderie between backers and creators. Ultimately, this financially benefits both the creators and the company itself.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does Kickstarter Make Money? The Kickstarter Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Kayak Make Money? The Kayak Business Model In A Nutshell
Kayak is an online travel agency and search engine founded in 2004 by Steve Hafner and Paul M. English as a Travel Search Company and acquired by Booking Holdings in 2013 for $2.1 billion. The company makes money via an advertising model based on cost per click, cost per acquisition, and advertising placements.
Origin StoryKayak is an American online travel agency and search engine. The platform was founded in 2004 by Steve Hafner and Paul M. English as Travel Search Company, Inc. Through a mobile app and website, users can search Kayak to compare rates between car rentals, flights, and hotels.
After changing its name to Kayak in 2005, the company received $196 million in financing and went on to make a series of acquisitions. These included German travel search platform Swoodoo and online travel agency SideStep.
In 2013, Kayak was acquired by Booking Holdings – which at the time was known as Priceline.com – for $2.1 billion.
 Booking Holdings is the company the controls six main brands that comprise Booking.com, priceline.com, KAYAK, agoda.com, Rentalcars.com, and OpenTable. Over 76% of the company revenues in 2017 came primarily via travel reservations commissions and travel insurance fees. Almost 17% came from merchant fees, and the remaining revenues came from advertising earned via KAYAK. As a distribution strategy, the company spent over $4.5 billion in performance-based and brand advertising.
Booking Holdings is the company the controls six main brands that comprise Booking.com, priceline.com, KAYAK, agoda.com, Rentalcars.com, and OpenTable. Over 76% of the company revenues in 2017 came primarily via travel reservations commissions and travel insurance fees. Almost 17% came from merchant fees, and the remaining revenues came from advertising earned via KAYAK. As a distribution strategy, the company spent over $4.5 billion in performance-based and brand advertising. Through a mobile app and website, users can search Kayak to compare rates between car rentals, flights, and hotels. The company also recently launched a corporate travel management platform, allowing business travelers to plan trips more efficiently.
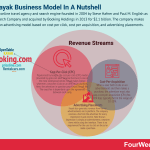
Kayak revenue generationKayak operates on a CPC model. Let’s expand on this model below.
Cost-per-clickPopularized by Google, the cost-per-click (CPC) model (invented by goto.com later became Overture) is one of the most widespread online.
 Google generated over $116 billion from advertising revenues in 2018, which represented 85% of its total revenues. Of those revenues over 70% came from traffic via Google’s main properties (Google search engine, YouTube, Gmail, and others). Google’s main properties are monetized primarily via a cost-per-click mechanism. Network member sites are primarily monetized on a cost-per-impression basis. Google also spent over $26 billion in 2018 to sustain its traffic on both its properties and as a revenue-share mechanism with its network members (AdSense and AdMob).
Google generated over $116 billion from advertising revenues in 2018, which represented 85% of its total revenues. Of those revenues over 70% came from traffic via Google’s main properties (Google search engine, YouTube, Gmail, and others). Google’s main properties are monetized primarily via a cost-per-click mechanism. Network member sites are primarily monetized on a cost-per-impression basis. Google also spent over $26 billion in 2018 to sustain its traffic on both its properties and as a revenue-share mechanism with its network members (AdSense and AdMob). Kayak makes money whenever a searcher clicks on an offer on its platform. Here, the advertiser in question pays Kayak a small fee. The exact fee is dependent upon the agreement between each party.
Cost-per-acquisitionWhen a user both clicks on an advertisement and then makes a purchase, the advertiser must also pay a cost-per-acquisition (CPA) fee. CPA fees typically fall in the range of 10-20%.
This so-called distribution revenue is paid by travel companies, including airlines such as JetBlue and car rental agencies such as Hertz. The airline industry is particularly profitable for Kayak, with estimates suggesting it derives a third of its total revenue from the source.
Advertising placementsKayak also generates revenue from banner advertisements on its platform. It can charge a premium rate for ad placement because of its proven ability to generate high numbers of leads.
The company receives a fee from the advertiser for every impression its ads receive. Note that an impression is simply an advertisement a searcher views while using the interface. There is no requirement for the user to click on the ad or make a purchase.
ExpansionKayak now operates in dozens of countries and continues to acquire hotel aggregation businesses in significant European and Asian markets.
This allows it to increase revenue by maintaining its status as a trusted and comprehensive travel service. With more consumers flocking to the platform, travel companies become incentivized to use the platform to remain competitive.
Key takeaways:Kayak is an online travel aggregation service. Founded in 2004 by Steve Hafner and Paul M. English, the platform is now available in more than 60 countries.Kayak operates on a CPC and CPA model to drive the bulk of its revenue. Advertisers pay the company a fee whenever a user clicks on an ad or makes a direct purchase.Kayak is also able to charge a premium for ad placements. This is because of its popularity with users and aggressive acquisition strategy to corner areas of the travel market.Read Next: Booking Business Model, How Does Opentable Make Money, How Does Trivago Make Money, How Does Airbnb Make Money, How Does RedFin Make Money.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does Kayak Make Money? The Kayak Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does HubSpot Make Money? The HubSpot Business Model In A Nutshell
HubSpot is a CRM (customer relationship management) solution, providing various levels of its B2B and Enterprise subscription plans. Beyond subscriptions, the company monetizes via professional services. However, these carry a negative marginality as the company uses professional services (in the form of onboarding and implementation) to increase its tools, which help companies leverage digital marketing channels to generate leads.
Origin StoryHubSpot is an American software developer and marketer with a focus on sales, customer service, and inbound marketing.
It was founded in 2006 at MIT by Brian Halligan and Dharmesh Shah. Just four years later, the company reached $15.6 million in revenue and acquired Twitter app store Oneforty. It also progressed from serving small companies to serving larger businesses with as many as 1,000 employees. It soon acquired competitor GroupSharp and debuted on the NYSE in 2014.
In 2017, the company strengthened its product offering by acquiring Kemvi – a service for sales teams incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence.
HubSpot recently eclipsed 100,000 paying customers with over $1 billion in annual recurring revenue.
Understanding the CRM solutionAs HubSpot highlighted in its financials:
At the core of our CRM Platform is our CRM that our customers use which creates a single view of all interactions a prospective or existing customer has with their marketing, sales and customer service teams. The CRM shares data across every application in the CRM Platform, automatically informing more personalized emails, website content, ads, and conversations, and enables more accurate timing cues for our customer’s internal teams. In addition, the CRM Platform was built to easily and seamlessly integrate third party applications to further customize to an individual company’s industry or needs. We designed and built our CRM Platform to serve a broad range of customers globally. Our CRM Platform starts completely free and grows with our customers to meet their needs at different stages in their life-cycles. It supports multiple languages and currencies and offers an array of sophisticated features, including content partitioning at the enterprise level for companies operating in or serving multiple countries.

By 2020, HubSpot counted almost 104k customers, that counted an average $9,582 subscription revenue.
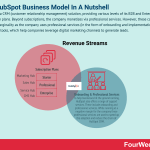
HubSpot revenue generation
HubSpot shows two primary revenue streams: subscriptions (with various B2B to Enterprise) plans and professional services. Subscriptions make up most of the company’s revenues (over $853 million in 2020), while professional services represent a more marginal part of its revenues ($30 million by 2020).
While the revenues grew over the years, the HubSpot business model never turned into profitability. The balance between offered a high-priced B2B subscription, even though coupled (as we’ll see) with onboarding professional services, it hasn’t yet struck a balance for the company’s profitability. The company does spend a good chunk of its revenues on sales and marketing. However, it leverages a lot on stock-based compensations.
It’s important to notice that professional services carry a negative marginality. In short, HubSpot loses money on them. So why does it offer these?
It does so that to further prompt the sales of its subscription services, as professional services help various level of customers to better understand HubSpot’s solutions.
In fact, HubSpot highlights that professional services and other revenue are derived primarily from customer on-boarding and training services. Those on-boarding services usually involve an implementation specialist working directly with the customers to make them understand how to attract leads and convert them into customers through search engine optimization, social media, blogging, and other content.
Indeed, the primary means of revenue generation for HubSpot is the selling of software via paid subscriptions.
Let’s take a look at these subscriptions in more detail.
Marketing HubMarketing Hub contains everything a business needs to turn leads into customers. There are three options:
Starter – $50/month or $45/month if paid annually. Features include landing pages, ad management, conversational bots, list segmentation, email marketing, and ad targeting.Professional – $890/month or $800/month if paid annually for businesses that need to market to at least 2,000 contacts. Extra features include A/B testing, multi-language content, and Salesforce integration.Enterprise – $3,200/month for enterprises with at least 10,000 marketing contacts. Features unique to this plan include partitioning, user roles, adaptive testing, and predictive lead scoring.Sales HubSales Hub encompasses HubSpot CRM software, helping teams organize data and close deals.
There are also three options here:
Starter – $50/month or $45/month if paid annually. This option provides simple automation, quotes, calling, live chat, and a reporting dashboard.Professional – $500/month or $450/month if paid annually. Extra features include sales analytics, custom reporting and forecasting, 1:1 video creation, calculated properties, and eSignatures.Enterprise – $1,200/month for at least 10 paid users. Hierarchical teams, advanced permissions, playbooks, and call transcription are all Enterprise-level features.Service HubService Hub is a customer service solution, helping businesses turn their customers into fans.
There are three different plans under this hub:
Starter – $50/month or $45/month paid annually and including features such as conversational bots, team email, canned snippets, and rep productivity reports.Professional – $400/month or $360/month paid annually. Teams selecting this plan can utilize ticket status and routing, video hosting, and surveys focused on NPS, customer experience, and customer support.Enterprise – $1,200/month for at least 10 paid users. Enterprise features include customer objects, calculated properties, field-level permissions, and webhooks.CMS HubFor those wishing to build or scale an optimized website, HubSpot also makes money via two plans:
Professional – $300/month or $270/month if paid annually. These plans are feature-rich and include a drag-and-drop editor, SEO optimization, and a contact attribution report builder. Uptime of 99.99% and 24/7 security monitoring is also providedEnterprise – $900/month for extra features including serverless functions, memberships, custom CDN integration, code alerts, and an additional brand domain.Onboarding and professional servicesTo help businesses hit the ground running, HubSpot also offers a range of support services. These include:
Onboarding – providing technical advice for each of the Hub plans mentioned above. There are also specific onboarding services for partners and start-ups. Prices are based on the plan chosen from a specific Hub.Professional services – encompassing inbound consulting, technical consulting, migration services, and classroom training. Prices are based on the length and nature of the training provided.Key takeawaysHubSpot is a software marketer and developer platform. It was founded in 2006 at MIT by Brian Halligan and Dharmesh Shah.HubSpot makes money by offering a diverse range of subscription plans. Each plan is categorized according to the size of an organization, with options in sales, marketing, customer service, and CMS.HubSpot also charges for various onboarding and professional services to help businesses with product implementation and training.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does HubSpot Make Money? The HubSpot Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does ClassPass Make Money? The ClassPass Business Model In A Nutshell
ClassPass is a North American fitness class provider using a flat-rate monthly subscription model. ClassPass primarily makes money via a subscription model leveraging five main plans, ranging from $15/month to $199/month. It also provides enterprise services to large companies like Under Armour, Morgan Stanley, and Google. Besides, ClassPass charges a cancellation fee of $15 if a cancellation is made within 12 hours of the class start time.
Origin StoryClassPass is a North American fitness class provider using a flat-rate monthly subscription model.
The company was founded in 2013 by Indian-American MIT graduate Payal Kadakia. Years earlier, Kadakia had lamented searching for an open ballet class in New York City for over an hour.
This led to the release of Classtivity in 2012, a search engine with a built-in reservation system for fitness classes. After being renamed ClassPass in 2014, the idea for the service pivoted to a Groupon-style system where users could pay a fixed amount for 10 classes every year.
Incorporating detailed feedback, this was increased to 10 classes per month. In 2016, ClassPass had already booked 17 million reservations and added tiered pricing to its business model. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, ClassPass lost 95% of its revenue – despite online classes increasing in popularity.
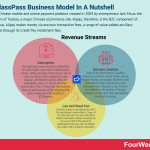
ClassPass revenue generationAs hinted at earlier, ClassPass makes money through a subscription-based model.
Each plan gives users access to credits they can use to book virtual and in-studio fitness classes, salons, and spas. These classes vary in value according to their popularity, type, location, and whether special offers are redeemable.
Users can try the ClassPass service with a free, 14-day trial. Alternatively, they can purchase one of the following five plans:
$15/month – including 7 credits to book up to 2 classes.$49/month – 23 credits to book up to 8 classes.$79/month – 38 credits to book up to 13 classes.$139/month – 68 credits to book up to 24 classes.$199/month – 100 credits to book up to 35 classes.It’s important to note that ClassPass is only providing the subscription system – it does not run the fitness classes themselves.
When a user attends a class, the company takes a 5% commission from the total price the fitness provider would ordinarily charge. This arrangement ultimately benefits both the consumer and ClassPass, with a certain number of unused credits able to be rolled over to the next month.
Enterprise solutionsSome of the more famous ClassPass enterprise customers include Under Armour, Morgan Stanley, and Google.
Bundled access is provided to large enterprises to give employees near-complete access to every class offered on the platform. Pricing is contingent on the size of the organization and also its location.
Late and missed feesClassPass charges a cancellation fee of $15 if a cancellation is made within 12 hours of the class start time.
For users who fail to attend a reservation without canceling, the fee is up to $20. In the case of an unattended virtual class, the user forfeits the credits used to make the reservation.
Key takeawaysClassPass is a subscription-based, North American fitness provider. It was created after founder Payal Kadakia experienced difficulty in finding a ballet class in New York City.ClassPass allows users to purchase fitness classes using credits that can be bought across five subscription plans. The company then takes a 5% commission for each fitness class a user attends.ClassPass also offers enterprise solutions, with prices tailored to suit specific needs. It also charges cancellation and missed class fees.Read Also: Peloton Business Model, Subscription Business Models.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does ClassPass Make Money? The ClassPass Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is A Super App And Why It Matters To Understand Mobile-Based Business Models
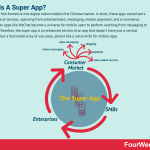
Super Apps first formed on the digital native mobile-first Chinese market. In short, these apps comprised a whole range of services, spanning from entertainment, messaging, mobile payments, and e-commerce. Indeed, super apps like WeChat became a universe for mobile users to perform anything from messaging to payments. Therefore, the super app is an enhanced version of an app that doesn’t have just a vertical application but a horizontal array of use cases, almost like a swiss-knife for mobile apps.
The Chinese Mobile-First Internet EcosystemThe Internet ecosystem in China really scaled around the years 2000s, and most of the population started to join in around the 2010s.
This has made the Chinese market extremely well versed for mobile-based applications. Therefore, in a western market, that evolved and scaled primarily through desktop computing, and where the transition to mobile is still going on. China was a native mobile digital player. That made it much easier for the Chinese market to become the hotbed to various mobile-based business models.
In the FourWeekMBA interview, professor Jeffrey Towson, author of The 1-Hour China book highlighted:
Mobile apps take off like crazy and they spend more time online than other consumers in other countries. They contribute more. They post more. They add content more. So it just turns out they are some of the world’s most enthusiastic netizens are Chinese. That wasn’t necessarily predictable but it’s true.
The Chinese digital market then is so different from the Western counterpart, which is hard to imagine. Indeed, as Jeffrey Towson highlighted in the same interview:
One of the things that were different early on was people don’t use email. I mean you send an email to someone in China, you better wait a week because they’re probably not going to check their email. It was all about messaging. So it started out with messaging with QQ (an instant messaging software part of Tencent) and that led to WeChat.
Therefore, instant messaging, like WeChat really started early own as powerful commercial use cases for the consumer Chinese market. From there, as those apps quickly scaled up, more and more features got added. From, mobile payments, to e-commerce, these apps really became a Universe of possibilities for people.
Thus, the name Super App.
Horizontal vs. Vertical AppsAnother key difference to appreciate why in the Western world we didn’t see before Super Apps are also, and again peculiar to the Chinese market. Indeed, where US companies, like Facebook had to move very fast in conquering their vertical markets (in Facebook and its other products like Instangram and WhatsApp these were social media and instant messaging), thus they remained constrained to a fewer, more restricted markets.
Thus, Facebook and Google perhaps took respectively a decade and two to move to other markets. For Chinese companies, as outside competition was reduced by the Government intervention, and massive tech monopolies were incentivised, it was possible to move the expansion of these application horizontally.
Therefore, not just entertainment but also shoppiong and payments.
Indeed, in the US, as the same companies that just a few years ago managed to monopolize their markets only there they started to use the “Super App” strategy. In fact, as a monopolist it was now possible to scale horizontally.
That is why Western tech companies took notice and started to emulate this model, as Towson highlighted:
What’s the next Super App? WhatsApp vs. WeChat case studyFacebook is basically copying WeChat right now. They’re consolidating their messengers, which is WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook Messenger first, and then they’re going to try and add mobile payment, which is Calibra, and then they’re going to try and add E-commerce. They’re basically trying to copy WeChat, but I doubt it will work.
As we say, the features of the Chinese digital market (the Internet really scaled to the Chinese population in the 2010s, so the Chinese people were native mobile users) and given the features of the Chinese’s economy (discouraging outside competition and favouring the rise of a few tech monopolies in a shorter span of time) Super Apps really were something that could easily form as a result of this context.
A great example of that is WeChat, part of Taobao, within the tech conglomerate Tencent.
 Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees.
Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees. WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it.
WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it.  Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in.
Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in.In the western world, tech companies like Facebook are trying to emulate this strategy. Facebook perhaps is trying to transform WhatsApp into a Super App:
 Founded in 2009 by Brian Acton, Jan Koum WhatsApp is a messaging app acquired by Facebook in 2014 for $19B. In 2018 WhatsApp rolled out customers’ interaction services. WhatsApp might be transitioning toward a set of features from video chats to social commerce that might transform WhatsApp into a Super App.
Founded in 2009 by Brian Acton, Jan Koum WhatsApp is a messaging app acquired by Facebook in 2014 for $19B. In 2018 WhatsApp rolled out customers’ interaction services. WhatsApp might be transitioning toward a set of features from video chats to social commerce that might transform WhatsApp into a Super App.Read Next: Alibaba Business Model, What Does Tencent Own, WeChat Business Model, WhatsApp Business Model, Facebook Business model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post What Is A Super App And Why It Matters To Understand Mobile-Based Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Chinese Tech Companies

Baidu makes money primarily via online marketing services (advertising). In fact, in 2017 Baidu made about $11.24 in online marketing services and a remaining almost $1.8 billion through other sources. According to Statista, Baidu has an overall search market share of 73.8% of the Chinese market. Other sources of revenues comprise membership services of iQIYI (an innovative market-leading online entertainment service provider in China) and financial services.
Read Next: Baidu Business Model
TikTok: The Sticky App From The Bytedance Empire TikTok makes money through advertising. It is estimated that ByteDance, its owner, made over $17 billion in revenues, for 2019. While we don’t know the exact figure for TikTok ads revenues, given it counted over 800 million users by 2020, it is a multi-billion company, worth anywhere between $50-100 billion and among the most valuable social media platforms of the latest years.
TikTok makes money through advertising. It is estimated that ByteDance, its owner, made over $17 billion in revenues, for 2019. While we don’t know the exact figure for TikTok ads revenues, given it counted over 800 million users by 2020, it is a multi-billion company, worth anywhere between $50-100 billion and among the most valuable social media platforms of the latest years. Read Next: TikTok Business Model
Alibaba: Inside The Jack Ma’s Empire
 Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees.
Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees. Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.
Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.Read Next: Alibaba Business Model, Taobao Business model, Alipay Business Model.
Tencent: The Fater of The Super App Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in.
Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in. WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it.
WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it. Read Next: Tencent Business Model, WeChat Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post Chinese Tech Companies appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Taobao Make Money? The Taobao Business Model In A Nutshell
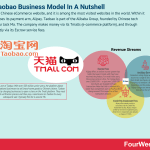
Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees.
Origin StoryTaobao is a Chinese eCommerce website and it is among the most visited websites in the world.
The platform was founded by Alibaba Group in 2003 as a marketplace to facilitate consumer-to-consumer (C2C) transactions for small businesses and entrepreneurs.

Initially, Taobao offered free listings to sellers and increased buyer-seller trust by incorporating Alipay – an escrow-based payment facilitation service. This saw the platform gain significant market share from eBay which was seen as a major competitor at the time.
In 2008, Taobao introduced the B2C platform Taobao Mall (Tmall) to complement its existing C2C offering. Two years later, the online shopping search engine eTao was introduced.
Taobao reacheda a billion product listings by 2016 and on the platform, most products are new and sold at a fixed price, but it does offer eBay-style auctions for some listings.
Taobao revenue generationConsidering how many transactions Taobao handles on an annual basis, the platform does not charge sellers or buyers a transaction fee.
Instead, it makes money by offering SEO-like advertising to sellers in much the same way that Google does. With more than 1 billion product listings spread across 8 million sellers, there is high competition between merchants to get the attention of buyers.
Merchants can choose between pay-for-performance or display marketing ads.
TmallAs noted earlier, Tmall is the B2C arm of Taobao. With over 500 million active users, the platform allows Chinese and international businesses to sell brand-name goods to Chinese citizens.
Taobao makes money here by charging businesses to open a store on the Tmall platform. They must pass a stringent verification process and then pay a commission to Taobao for every subsequent sale. Typically this fee is around 5%.
As a real-world example, sunglasses retailer Lemon Optics paid a fee of around $25,000 to become verified and establish a shopfront on Tmall.
Alipay Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.
Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.Escrow provider Alipay also charges for its services on Taobao. Merchants are charged a 0.55% fee for every successful sale. The system is free to use for withdrawals under RMB 20,000 – or approximately 3,000 USD. Above this threshold, users are charged a 0.1% fee.
Compared to rates offered by traditional credit card companies and payment facilitators, Alipay is an extremely attractive option for merchants. At least theoretically, this increases ad revenue for Taobao as sellers compete for that buyer visibility.
Key takeaways:Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce site founded by the Alibaba Group in 2003. It was initially created to counter the dominance of eBay in the Chinese market and increase trust between the buyer and the seller.Taobao sells advertising placements to more than 8 million sellers on its platform. With high competition for visibility, advertising represents a lucrative source of income.Taobao also charges Chinese and international businesses to open on B2C arm Tmall. After the initial setup fee, Taobao also charges a commission for every sale. Usually, this commission is around 5%. Escrow provider Alipay also charges users for its service. Here, low service fees are in part compensated by the huge volume of transactions on the Taobao platform.Read Next: Alibaba Business Model ,What Does Tencent Own, WeChat Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does Taobao Make Money? The Taobao Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Alipay Make Money? The Alipay Business Model In A Nutshell
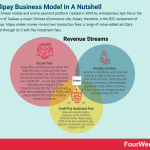
Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.
Origin StoryAlipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform.
It was created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. In this capacity, Alipay also served as the B2C component of Alibaba Group.

After eBay acquired Chinese eCommerce company EachNet, Taobao made moves to secure competitive advantage by increasing the trust between the buyer and seller. At the time, this was the most pressing issue in the Chinese eCommerce market.
Alipay is one of just three central digital payment providers in China, serving as the brand of parent company Ant’s consumer finance app. There are reported to be approximately 1.3 billion annual active users of Alipay globally, with the vast majority being Chinese citizens. The company also has customers in e-wallet partner countries, including Malaysia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Thailand, and South Korea.
Alipay revenue generationAs noted earlier, Alipay revenue generation is focused on increasing trust between the buyer and seller. In many countries this would not be profitable, but commerce in China traditionally involved cash purchases in brick-and-mortar stores.
Such was the lack of trust in other forms of payment that a merchant would not ship a product until it was paid for. A buyer, on the other hand, would only pay once they had the product in their hands.
With all of that said, let’s look at how Alipay makes money and has revolutionized Chinese commerce in the process.
EscrowAlipay offers an online escrow system that holds the buyer’s funds until they have received the product.
Information concerning real-time payment and delivery is tracked and shared with both the consumer and merchant.
For small-time users, the escrow service is free. For transactions over 20,000 CNY – or just over 3,000 USD – merchants are charged 0.1% per transaction. Note that this is substantially lower than competitors such as PayPal, who charge around 3% irrespective of the transaction amount.
Value-added servicesConsumers using Alipay wallet also have access to a range of ancillary services, including:
Train ticket purchasing.The ability to check balances on connected bank accounts.Utility bill payments.Insurance.Mobile phone credit purchasing.The ability to make offline payments in affiliated Chinese shops and websites.The ability to split restaurant bills with friends or family.Credit card servicing payments. In this case, Alipay charges a 0.1% fee for all monthly credit card payments exceeding $299.Depending on the product or service, Alipay charges an average merchant transaction fee of 0.55%.
It also collects interest from the funds sitting in customer accounts.
Credit Pay InstalmentAlipay also extends credit to consumers via the Credit Pay Instalment facility.
Similar to a BNPL service, consumers can pay for goods and services over 3, 6, or 12 installments. Alipay charges 2.30% for the three-installment plan, while the 12-installment plan attracts a charge of 7.50%.
Key takeawaysAlipay is a Chinese third-party transaction facilitator. It was created by Jack Ma to establish trust between the buyer and the seller in the cash-dominated Chinese market.Alipay is primarily an Escrow service that holds payments until goods are delivered. It charges a flat 0.1% for transactions over a certain amount. Smaller, less frequent transactions are free of charge.Alipay also offers an extensive range of value-added services, including insurance, utility payments, and credit cards. The platform also enables consumers to purchase on credit and pay back over a predetermined period.Read Next: Alibaba Business Model ,What Does Tencent Own, WeChat Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does Alipay Make Money? The Alipay Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Does Tencent Own? Inside The Tencent Business Model
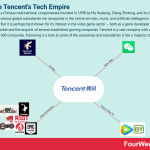
Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in.
Tencent GamesTencent Games is the video game publishing division of Tencent Interactive Entertainment.
The Tencent division operates game development studios in China and the United States. It produces mostly mobile and browser-friendly games for the Chinese marketplace.
Tencent launched its own gaming platform called WeGame in 2017, allowing gamers to host global games and get access to purchases, downloads, live streaming, and community services.
Established game developersTencent has also acquired several game developers over the years. In 2015, it gained total ownership over Riot Games – developer of League of Legends.
The company also has majority ownership of Funcom (100%), Leyou (100%), Sharkmob (100%), Supercell (84%), and Grinding Gear Games (80%).
Epic Games – the creator of Fortnite – is also 40% owned by Tencent.
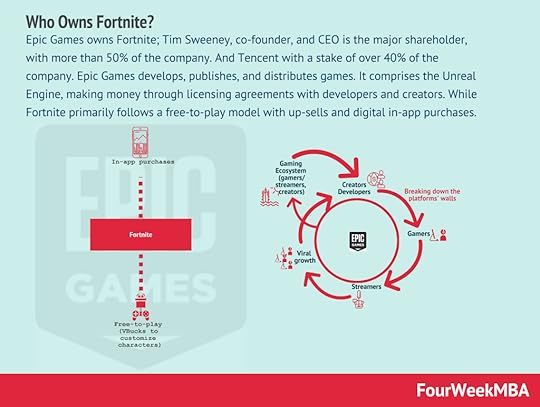 Epic Games owns Fortnite; Tim Sweeney, co-founder, and CEO is the major shareholder, with more than 50% of the company. And Tencent with a stake of over 40% of the company. Epic Games develops, publishes, and distributes games. It comprises the Unreal Engine, making money through licensing agreements with developers and creators. While Fortnite primarily follows a free-to-play model with up-sells and digital in-app purchases.
Epic Games owns Fortnite; Tim Sweeney, co-founder, and CEO is the major shareholder, with more than 50% of the company. And Tencent with a stake of over 40% of the company. Epic Games develops, publishes, and distributes games. It comprises the Unreal Engine, making money through licensing agreements with developers and creators. While Fortnite primarily follows a free-to-play model with up-sells and digital in-app purchases.  Epic Games is a gaming company, that develops, publishes, and distributes games. It comprises the Unreal Engine, making money through licensing agreements with developers and creators. Its games (like Fortnite) mostly follow a free-to-play model on PC and an in-app purchase model on the digital marketplace. And its storefront Epic Games Store, taking a 12% cut on games’ sales. WeChat
Epic Games is a gaming company, that develops, publishes, and distributes games. It comprises the Unreal Engine, making money through licensing agreements with developers and creators. Its games (like Fortnite) mostly follow a free-to-play model on PC and an in-app purchase model on the digital marketplace. And its storefront Epic Games Store, taking a 12% cut on games’ sales. WeChat WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it.
WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it. WeChat is a multi-purpose messaging, mobile payment, and social media app developed by the company in 2011. Seven years after its release, it became the largest standalone app in the world by total users.
WeChat also offers an extensive digital payment service in line with Chinese government initiatives to support eCommerce development in the country.
Tencent Music EntertainmentThe primary function of Tencent Music Entertainment (TME) is the creation of music streaming services specifically for the Chinese market.
In collaboration with Swedish audio streaming service Spotify, TME has created several apps including Kugou, Kuwo, WeSing, QQ Music, and Ultimate Music. Collectively, these apps represent 800 million active users, 15% of which are subscribed to a paid plan.
Tencent VideoTencent Video is a Chinese video streaming website. The website is complemented by WeTV, the international version of Tencent Video.
It also offers a video-on-demand service and supports television broadcasts by providing video volume amplification, color quality management, and other functional services.
In terms of the content itself, Tencent has a strategic focus on original content in the form of micro movies and homemade dramas. It also offers short-film contests and support plans.
Tencent PicturesTencent Pictures is the film production and distribution arm of Tencent. Through subsidiary Tencent Penguin Pictures, the company has a focus on online content and feature film investment.
Tencent Pictures has been involved in several notable films, including Men In Black: International and the upcoming Top Gun sequel.
Key takeawaysTencent is a vast Chinese conglomerate founded in 1998. It has a stake in over 600 companies.Tencent is perhaps best known for video gaming. It owns and operates a gaming production facility to develop games for the Chinese market. It also has majority ownership of established game developers responsible for titles such as Fortnite and League of Legends.Tencent also owns the instant messaging app WeChat and has a significant investment in the production of movies, short films, and dramas for Chinese and international markets.Read Next: Google Business Model, Facebook Business Model, TikTok Business Model, Pinterest Business Model, Clubhouse Business Model.
Other Business Models: Quora Business Model, Twitter Business Model, Amazon Business Model, GitHub Business Model, Medium Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post What Does Tencent Own? Inside The Tencent Business Model appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does WeChat Make Money? The WeChat Business Model In A Nutshell
WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it.
Origin StoryDeveloped by Chinese conglomerate Tencent in 2011, WeChat is a messaging, mobile payment, and social media app. The platform was originally called Weixin by creator Allen Zhang and only became WeChat after it passed 100 million users in 2012.
WeChat is often described as the Chinese “app for everything” because of its high level of functionality. Far from being a simple messaging app, users can play video games, hold video conferences, and share photographs or their location if desired.
As part of the Chinese government initiative to support eCommerce in China, the platform also incorporates digital payment services under the name WeChat Pay. This allows users to pay bills, transfer money to others, and order goods or services.
In 2018, WeChat became the world’s largest standalone app with over 1 billion active users.
WeChat revenue generationTraditional instant messaging apps have proven difficult to monetize, but WeChat has developed several revenue streams by becoming an essential part of daily life. WeChat average revenue per user (ARPU) is $7, or seven times that of similar service WhatsApp.
Here is a look at each revenue stream in more detail.
Value-added servicesWeChat sells many value-added services to consumers:
Moments – this is the name given to the WeChat social feed, giving users an interactive platform to post images and messages and share articles and music. So-called stickers (emoticons) can also be used while messaging, with an average price of $0.99 for a set.Public accounts – WeChat users or businesses can create a public account to interact socially with subscribers or provide them with services. Official organizations must be verified beforehand for approximately US $45, with many using public accounts to offer hospital pre-registration, credit card services, or visa renewals. Users can opt to receive tips from readers who deem their content valuable, and it is safe to assume WeChat takes a percentage of this amount.Gaming – mobile gaming is extremely popular in China, with most citizens never having grown up with desktop gaming. Once they became addicted to a particular game, WeChat offers value-added services that enhance gameplay. These include better weapons, avatar costumes, and virtual VIP rooms.AdvertisingWeChat also makes money by advertising, which has been progressively added to most WeChat functions over the years.
Advertising has been particularly successful on the WeChat Moments platform. Small and large businesses can target a user based on their physical location.
WeChat also makes advertising revenue from the blogs associated with public accounts. Recent figures suggest there are over 15 million individual and business blogs inside the WeChat app.
WeChat paymentsAs a digital payment provider, WeChat charges users a 0.01% fee to withdraw funds from their WeChat Wallet when the transfer sum exceeds 1,000 yuan. Transfers within the app ecosystem are free of charge.
Key takeawaysWeChat is a messaging, mobile payment, and social media app developed by Chinese conglomerate Tencent. With high functionality, it is often called the Chinese “app for everything”.WeChat makes money by selling a range of value-added services. These include stickers to enhance the instant messaging experience, video game upgrades, and public account verification for organizations.WeChat also drives revenue through advertising, with implementation most successful on the Moments platform. As a digital payment provider, the platform also charges a small fee to withdraw funds from a digital wallet.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does WeChat Make Money? The WeChat Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



