Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 158
April 25, 2021
Who Is Elon Musk? The Elon Musk’s Story
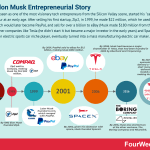
Elon Musk, seen as one of the most visionary tech entrepreneurs from the Silicon Valley scene, started his “career” as an entrepreneur at an early age. After selling his first startup, Zip2, in 1999, he made $22 million, which he used to found X.com, which would later become PayPal, and sell for over a billion to eBay (Musk made $180 million from the deal). He founded other companies like Tesla (he didn’t start it but became a major investor in the early years) and SpaceX. Tesla started as an electric sports car niche player, eventually turned into a mass manufacturing electric car maker.
How did Elon Musk become wealthy? The full business story Elon Musk has made most of his money by investing in ideas and companies he is passionate about. After eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion in 2002, Musk used his personal wealth to fund his new ventures: Tesla and SpaceX. Most of Elon Musk’s wealth comes from Tesla, as he’s the major shareholder for the company. Making Elon Musk’s net worth well past the hundred billion-dollar mark.
Elon Musk has made most of his money by investing in ideas and companies he is passionate about. After eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion in 2002, Musk used his personal wealth to fund his new ventures: Tesla and SpaceX. Most of Elon Musk’s wealth comes from Tesla, as he’s the major shareholder for the company. Making Elon Musk’s net worth well past the hundred billion-dollar mark. Elon Musk’s wealth increased exponentially when one of his major bets, Tesla, became among the most valued companies on earth. Elon Musk started from a very early age building tech startups.
The early yearsFor instance, as a child, he had a passion for code, so after developing it, he sold the source code for his first video game for $500 at age 12. After moving to the US, by 1995, with his brother, they founded Zip2, which was later (in 1999) sold to Compaq, in a deal worth $341 million, where Elon Musk made $22 million.
With the capital from Zip2, Musk founded X.com in 1999, one of the first FDIC-insured online banks in the world. After seeing promise in its easy payment service.
At the same time, a company named PayPal, as a money-transfer system, had been founded in 1998 by a company called Confinity.
At the time, Confinity had a fierce competitor, called X.com. Rather than competing, the two companies merged by bringing them together under the umbrella of PayPal.
The “PayPal Mafia” yearsOnce the company merged, they could finally focus on the commercial strategy. Rather than boiling the ocean, PayPal started with a small niche at the time, until they monopolized it and grew further.
Musk merged his company with Confinity the following year. In 2001, the company became PayPal and Musk became an 11.7% shareholder.
When eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion in 2002, Musk received $180 million which he would later reinvest into some of his most famous passion projects.
 PayPal makes money primarily by processing customer transactions on the Payments Platform and from other value-added services. Thus, the revenues streams are divided into transaction revenues based on the volume of activity or total payments volume. And value-added services, such as interest and fees earned on loans and interest receivable. As of 2017 PayPal generated over $13 billion in net revenues and almost $1.8 billion in net income.
PayPal makes money primarily by processing customer transactions on the Payments Platform and from other value-added services. Thus, the revenues streams are divided into transaction revenues based on the volume of activity or total payments volume. And value-added services, such as interest and fees earned on loans and interest receivable. As of 2017 PayPal generated over $13 billion in net revenues and almost $1.8 billion in net income. Indeed, it seems that at the time most PayPal users were coming from eBay. As reported by a release on July 2002:
The agreement also should benefit eBay shareholders. The combination of the two networks should expand both platforms while minimizing shared operational costs. Strengthening the marketplace and realizing the efficiencies made possible by the acquisition will increase the value of both businesses.
Read Also: How Does PayPal Make Money?
PayPal would be also an extremely important hotbed, for what would be later called “PayPal Mafia” a group of smart people that went on to fund many of the companies that created an impact over the Silicon Valley tech ecosystem:
Jawed Karim (Youniversity Ventures),Jeremy Stoppelman (founded Yelp with Russel Simmons),Andrew McCormack (partner at venture capital firm Valar Ventures),Premal Shah (non-profit organization Kiva),Luke Nosek (Founders Firm),Ken Howery (VP at Clarium Capital),David Sacks (produced “Thank You for Smoking”),Peter Thiel (created hedge fund Clarium Capital and Founders Firm),Keith Rabois (held senior positions at LinkedIn, Slide),Reid Hoffman (LinkedIn),Max Levchin (Slide. Google bought it for $182 million in 2010),Roelof Botha (Sequoia Capital),Russel Simmons (Yelp),Elon Musk (Tesla, SpaceX).After two decades from PayPal acquisition from eBay Elon Musk went on to create some of his most prominent ventures:
 Elon Musk is one of the richest people in the world, with his main ownership in Tesla, making him worth more than a hundred billion dollars. The companies founded by Elon Musk range from electric vehicles and renewable energies, with Tesla, rockets, with SpaceX, infrastructure, with The Boring Company, and neurotechnology with Neuralink. When Tesla was a niche electric sport’s car maker
Elon Musk is one of the richest people in the world, with his main ownership in Tesla, making him worth more than a hundred billion dollars. The companies founded by Elon Musk range from electric vehicles and renewable energies, with Tesla, rockets, with SpaceX, infrastructure, with The Boring Company, and neurotechnology with Neuralink. When Tesla was a niche electric sport’s car maker 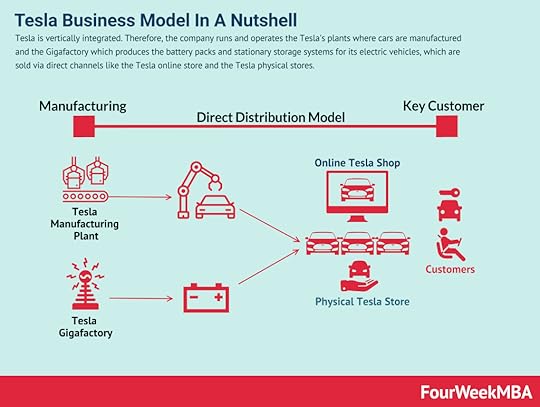 Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates Tesla’s plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores.
Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates Tesla’s plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores. Tesla is perhaps the biggest accelerator of Elon Musk’s net worth.
The company became among the most valued tech companies in the last years.
The electric carmaker company now owned by entrepreneur/visionary Elon Musk was founded by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning in July 2003.
By 2006 Musk joined, first as investor and chairman, then he took the role of CEO which he still holds today. Musk is the major Tesla’s shareholder:
 Elon Musk, an early investor and CEO of Tesla, is the major shareholder with 21.7% of stocks. Other major shareholders comprise investment firms like Baillie Gifford & Co. (7.7%), FMR LLC (5.3%), Capital Ventures International (5.2%), T. Rowe Price Associates (5.2%), and Capital World Investors (5%). Another major individual shareholder is Larry Ellison (co-founder and CEO of Oracle), with a 1.7% stake.
Elon Musk, an early investor and CEO of Tesla, is the major shareholder with 21.7% of stocks. Other major shareholders comprise investment firms like Baillie Gifford & Co. (7.7%), FMR LLC (5.3%), Capital Ventures International (5.2%), T. Rowe Price Associates (5.2%), and Capital World Investors (5%). Another major individual shareholder is Larry Ellison (co-founder and CEO of Oracle), with a 1.7% stake. Back in 2012, Elon Musk explained the vision for the company:
“In 2006 our plan was to build an electric sports car followed by an affordable electric sedan, and reduce our dependence on oil…delivering Model S is a key part of that plan and represents Tesla’s transition to a mass-production automaker and the most compelling car company of the 21st century.”

By starting with a niche strategy, mainly focused on proving an electric sport’s car could be delivered in a premium market, Tesla slowly, then quickly ramped up its new models to cover wider and wider sections of the market, and it ramped up its manufacturing capability.
Beyond early adoption, using a transitional business model to scale upTherefore, Tesla finally moved from a transitional, niche business model, to a scaled up business model:

The hardest part for Elon Musk has been the scale up of Tesla’s manufacturing facilities. In what Elon Musk would later recall as a “logistic hell.”
Going almost bankrupt to pass beyond the “logistic hell”Between mid-2017 to mid-2019 Tesla has been very close to bankruptcy for lack of liquidity.
As Elon Musk has explained in a Tweet back in November 2020:
Closest we got was about a month. The Model 3 ramp was extreme stress & pain for a long time — from mid 2017 to mid 2019. Production & logistics hell.
As Elon Musk further explained in that Twitter thread:
I put in my last money, even though I thought we would still fail. But, it was either that or certain death for Tesla. Extremely difficult to raise money for an electric car startup (considered super quirky back then), while stalwarts like GM & Chrysler were going bankrupt.
Indirectly, the Tesla share price appreciation is the result of a new wave of younger investors and strong demand for electric vehicles – particularly from China. A Biden election win has also helped Tesla benefit from legislation designed to bring electric vehicles to the mainstream.
Today Tesla is an electric empire, which potential goes way beyond the automotive sector!
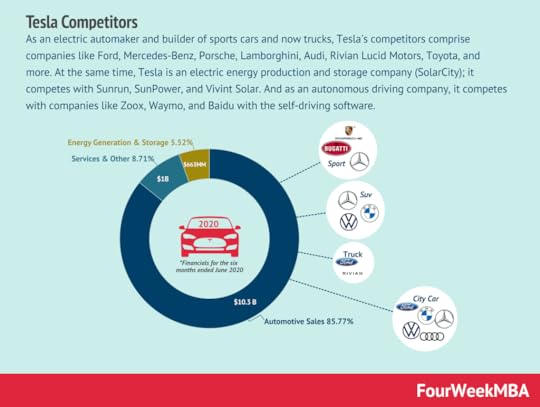 As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with self-driving software. SpaceX
As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with self-driving software. SpaceX – SpaceX is a space transportation service and manufacturer of space rockets and other transport vehicles. It was founded by Elon Musk in 2002. – SpaceX makes money by charging both governmental and commercial customers to send goods into space. These goods include ISS supplies and infrastructure, but also people and satellites for various purposes. – SpaceX is also in the process of creating its Starlink network, designed to give every citizen access to fast and affordable internet.
– SpaceX is a space transportation service and manufacturer of space rockets and other transport vehicles. It was founded by Elon Musk in 2002. – SpaceX makes money by charging both governmental and commercial customers to send goods into space. These goods include ISS supplies and infrastructure, but also people and satellites for various purposes. – SpaceX is also in the process of creating its Starlink network, designed to give every citizen access to fast and affordable internet.Musk has always had a passion for space exploration. Even before the eBay acquisition of PayPal, he conceived of greenhouses to grow food crops on Mars. Such was his passion that he traveled to Moscow to purchase intercontinental ballistic missiles that could send payloads into space.
In Moscow however, Musk was seen as an amateur and rejected. Undeterred, he returned to the U.S. and founded SpaceX in 2002 using $100 million of his own capital. In 2008, SpaceX received a $1.6 billion NASA grant for rockets to resupply the International Space Station. The company then became the first to berth a private vehicle with the ISS. Reusable rockets with large payloads were also launched into space and successfully returned to Earth using SpaceX autonomous drone ships.
By March of 2018, SpaceX had over 100 launches on its manifest worth approximately $12 billion in revenue. SpaceX’s most recent contract is the $2.89 billion NASA program to carry American astronauts to the moon.
The greatest marketer of our timesWhile for large companies demand generation can be easily bought. For startups it’s more complicated, because they need to do that with a few resources. Indeed, spending most of the budget with demand generation is too risky in the short-term.
Yet, creating demand for your product is the most important long-term strategy as it will make the difference between selling a commoditized product at no margins instead of a premium-priced product (which gives the business enough resources to keep financing its R&D, marketing, and operations).
However, demand generation can be inexpensive if done correctly. While for massive corporations like Nike, it makes sense to spend all this money on demand generation.
For rising companies and startups demand generation can be done at no cost. Demand generation can be done cheaply if you think:
Unconventionally, do things that for linear thinkers do not make any sense. Obliquely, it doesn’t directly promote your company/product, but the connection there is more subtle. Yet when it gets triggered it becomes even more powerful than a linear promotion. Other-oriented, it’s not about you, your company or your product. A successful demand generation campaign at no cost is about others. It’s about making them feel special, unique and part of something.Let’s use an emphasized example by the master of all PR stunts: Elon Musk (indeed also the greatest salesman alive).
To be good at demand generation at no cost, you need to think obliquely. In short, rather than promoting directly your product, as you would do in a traditional ad, with demand generation you promote it indirectly, through something that is so compelling, that will drive attention and money to your main business.
For instance, in 2018, Elon Musk tweeted a video where he handled a flamethrower:

Source: Elon Musk Tweet
Not long after, still in 2018, the company had sold 50,000 hats of the boring company:

As of 2021 the Boring company has sold over 20,000 flamethrowers, which as you might imagine helped finance the core business of Musk’s venture:

At first sight that doesn’t make any sense. And yet, this unconventional stunt made the company ten million dollars (flamethrowers were selling for $500 each) in revenues that could be reused toward the innovative projects the company is working on.
The flamewthover could be bought for cheaper elsewhere, but who bought it felt part of something (and indeed could resell it at a much higher price later on, as those were limited pieces).
This of course is an extreme example, but you get the idea. Startups can generate demant when they use unconventional marketing tactiques (lateral vs. linear thinking), oblique (indirect vs. direct promotion) and centered on making other people feel good about themselves (the iPhone could have never scaled at that premium price if it was only a smartphone).
Key takeawaysElon Musk has made most of his money by investing in ideas and companies he is passionate about. After PayPal was acquired by eBay, he used his significant stake in the company to fund the creation of SpaceX.After initial teething problems, SpaceX grew to become a company with 100 launches on its manifest worth $12 billion. The company has also made Musk money through several, multi-billion dollar contracts with NASA.Tesla and its rapidly appreciating share price are responsible for a large proportion of Musk’s net worth. A sizeable shareholding combined with an influx of young investors and favorable legislation has seen Musk become one of the richest men on the planet.Read Also: Tesla Business Model, How Does Elon Musk Make Money, Elon Musk Companies, Who Owns Tesla, Transitional Business Models, Tesla Competitors.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post Who Is Elon Musk? The Elon Musk’s Story appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Reddit Make Money? The Reddit Business Models In A Nutshell
Reddit is a social news and discussion website that also rates web content. The platform was created in 2005 after founders Alexis Ohanian and Steve Huffman met venture capitalist Paul Graham and pitched the company as the “front page of the internet.” Reddit makes money primarily via advertising. It also offers premium membership plans.
Reddit Origin StoryReddit is a social news and discussion website that also rates web content.
The platform was created in 2005 after founders Alexis Ohanian and Steve Huffman attended a lecture by programmer and entrepreneur Paul Graham. After his lecture, Graham spoke with the pair and invited them to apply for his start-up incubator Y Combinator.
Ohanian and Huffman initially pitched an SMS-based food ordering service, but it was deemed unviable. Their second attempt, imagined by Graham as the “front page of the internet”, did receive funding from Y Combinator and was launched as Reddit in June of the same year.
In October 2006, Conde Nast Publications acquired Reddit – with Graham and Ohanian leaving the company three years later once their contractual obligations had ended. In 2014, Reddit secured several high-profile investments and was valued at $500 million.
The following year, Huffman returned to the company to serve as CEO. Several subsequent rounds of funding culminated in a $300 million investment by Tencent in 2019, valuing Reddit at $3 billion. In February 2012, valuation had doubled to $6 billion.
Reddit ongoing popularityOne of the things that strikes the most when looking at Reddit is its ability (nonetheless being a social media site) to be popular for over a decade. Indeed, Reddit managed to be interesting to newer generations that can engage in discussions around anything.
 The Reddit Brand’s Search Volume trend over the years. Opposite to other social media and sites, Reddit managed to keep growing its popularity over the years, thus as 2021, still representing among the most searched websites across the globe (Data Source: KW Everywhere).Reddit revenue generation
The Reddit Brand’s Search Volume trend over the years. Opposite to other social media and sites, Reddit managed to keep growing its popularity over the years, thus as 2021, still representing among the most searched websites across the globe (Data Source: KW Everywhere).Reddit revenue generationReddit makes money primarily through selling advertising space and membership plans.
Advertising spaceAdvertising space is sold in two ways:
The first is the Reddit Ads managed service for large-scale advertisers or political advisors with a minimum advertising budget of $50,000 per quarter. Advertisers are given access to a dedicated Reddit sales team and a full suite of tools and best practices.The second form of advertising involves an auction-based system where advertisers bid using a click per thousand (CPM) model. Prices per 1,000 impressions start at $3.50 and then rise as bidding commences.Advertising on the Reddit platform arguably requires more finesse when compared to other platforms. Reddit users are privacy-conscious and are highly suspicious of paid advertisements. Nevertheless, companies such as Nissan, McDonald’s, Subaru, and Costco have been relatively successful on the platform.
In recent years, advertising has taken the form of sponsored AMA (Ask Me Anything) sessions and other interactive events that promote a more organic form of paid promotion. Native mobile advertisements followed soon after.
Membership planReddit users can also choose to sign up for the ad-free Reddit Premium membership plan.
Reddit charges $5.99/month for this service. In addition to an ad-free experience, premium members also receive a monthly supply of 700 coins to award to other members. They also get exclusive access to selected subreddits and a personalized avatar called a snoovatar.
Content agreementsIn 2019, Reddit signed an advertising and content generation deal with the NFL. Players and other key personnel from the National Football League participated in AMAs while the NFL itself produced and supplied video content.
While Reddit did not earn a direct free from the content agreement, it is safe to assume the extra traffic brought an increase in ad revenue. There is potential that content agreements also result in sponsorships and other forms of revenue as Reddit works with other organizations to produce content.
Key takeaways:Reddit is a social news and discussion website founded in 2005 by Alexis Ohanian and Steve Huffman. The idea for the platform was pitched to Paul Graham, founder of the start-up accelerator program Y Combinator.Reddit makes money by selling advertising space in two ways. The Reddit Ads managed service give large businesses with deep pockets access to a sales team and propriety tools. There is also an auction-based CPM system.Reddit also offers a membership plan to its users, giving them an ad-free interface plus access to coins and custom avatars.Read Next: Google Business Model, Facebook Business Model, TikTok Business Model, Pinterest Business Model, Clubhouse Business Model.
Comparables: Quora Business Model, Twitter Business Model, Amazon Business Model, GitHub Business Model, Medium Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does Reddit Make Money? The Reddit Business Models In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does OpenTable Make Money? The OpenTable Business Model In A Nutshell
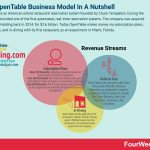
OpenTable is an American online restaurant reservation system founded by Chuck Templeton. During the late 90s, it provided one of the first automated, real-time reservation systems. The company was acquired by Booking Holding back in 2014, for $2.6 billion. Today OpenTable makes money via subscription plans, referral fees, and in-dining with its first restaurant, as an experiment in Miami, Florida.
Origin StoryOpenTable is an American online reservation service for restaurants. The company was founded in 1998 by Chuck Templeton, with initial operations focused exclusively on restaurants in San Francisco.
Using the original system, restaurants who signed up for the service used OpenTable software to manage dinner reservations. In the late 1990s, the ability for restaurants to take reservations using a real-time system was somewhat revolutionary. The service quickly expanded to approximately 30,000 restaurants across the United States and limited international cities.
In 2014, OpenTable was acquired by Booking Holdings (formerly Priceline Group) for $2.6 billion. The platform now seats over 1 billion diners per year in countries such as Mexico, the UK, Australia, Canada, France, Japan, and Germany. It serves restaurants and eating establishments found in bars, wineries, hotels, casinos, and grocery stores.
 Booking Holdings is the company the controls six main brands that comprise Booking.com, priceline.com, KAYAK, agoda.com, Rentalcars.com, and OpenTable. Over 76% of the company revenues in 2017 came primarily via travel reservations commissions and travel insurance fees. Almost 17% came from merchant fees, and the remaining revenues came from advertising earned via KAYAK. As a distribution strategy, the company spent over $4.5 billion in performance-based and brand advertising. OpenTable revenue generation
Booking Holdings is the company the controls six main brands that comprise Booking.com, priceline.com, KAYAK, agoda.com, Rentalcars.com, and OpenTable. Over 76% of the company revenues in 2017 came primarily via travel reservations commissions and travel insurance fees. Almost 17% came from merchant fees, and the remaining revenues came from advertising earned via KAYAK. As a distribution strategy, the company spent over $4.5 billion in performance-based and brand advertising. OpenTable revenue generationOpenTable makes money in a few different ways.
Subscription feesThe company offers its management platform across three different plans:
Basic ($29/month) – allowing restaurant owners to reach diners and build a reputation. OpenTable charges Basic plan users 25 cents per reservation plus a flat $49 fee. There is also a charge of $1.50 per network cover. In restaurant parlance, a cover refers to a single meal or customer for whom the meal is served.Core ($249/month) – for restaurant owners who want a more efficient front-of-house or to maximize patronage. Website reservations are free and there is a $1 charge per network cover.Pro ($449/month) – the Pro plan allows loyal customers to be recognized and rewarded through relationship management. Pricing for reservations and network covers is the same as the Core plan.Regardless of the plan chosen, OpenTable also charges a 2% service fee for restaurant experiences and takeout.
Referral feesOpenTable users can also order from restaurants that offer delivery. Depending on geographic location, supporting delivery partners include Olo, Toast Delivery, Uber Eats, Postmates, Deliveroo, and ChowNow.
OpenTable makes an undisclosed amount by partnering with these services, most likely in the form of an agreed-upon referral fee.
In-diningOpenTable recently opened its first restaurant in Miami, Florida.
Serving eastern Mediterranean fare, the restaurant is an innovative pilot project for the company. While the quality of food is important, OpenTable hopes to use technology to develop a highly personalized hospitality service. The wait staff at the restaurant use historical customer food and drink preferences to give diners what they want without them having to ask for it.
If the concept proves profitable, there is scope to suggest that OpenTable will open similar restaurants elsewhere.
Key takeaways:OpenTable is an American online restaurant reservation system founded by Chuck Templeton. During the late 90s, it provided one of the first automated, real-time reservation systems.OpenTable makes money by giving restaurant owners access to its platform across three, paid plans. The Core and Pro plans incorporate free reservations and charge $1 per network cover.OpenTable also earns referral fees from the many delivery services it partners with. It has recently opened its first branded restaurant in Miami using customer insights to offer a highly personalized restaurant experience.Read Next: Booking Business Model, How Does Trivago Make Money, How Does Airbnb Make Money, How Does RedFin Make Money.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post How Does OpenTable Make Money? The OpenTable Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does SpaceX Make Money?
SpaceX, formally known as Space Exploration Technologies Corp., is an aerospace manufacturer and space transportation service founded by Elon Musk in 2002.
SpaceX was created to reinvigorate public interest in space exploration which Musk hoped would channel more funds to NASA.
In the early years, he made a failed trip to Russia after attempting to buy cheap rockets. During the flight home, Musk decided he could start a company and build the rockets himself. But this would only be achievable by using cheaper, off-the-shelf componentry incorporating the modular nature of software engineering.
Rocket engineer Tom Mueller joined SpaceX soon after the company was founded. By 2005, it had already amassed 150 employees. SpaceX now has an impressive list of achievements, becoming the first privately-owned company to launch, orbit, and then recover a spacecraft. It was also the first such company to send a spacecraft to the International Space Station (ISS) and re-use an orbital rocket.
SpaceX is now valued at $74 billion and continues to attract strong attention from investors for its visionary products.
SpaceX revenue generationSpaceX is essentially a delivery service. If an organization wants to send goods to the ISS or launch a satellite into orbit, the company uses its fleet of vehicles including the Dragon, Falcon Heavy, and Falcon 9.
As successful as SpaceX has been, it should be noted that it competes with several other companies for space delivery services. These include Boeing, Lockheed-Martin, and Northrop-Grumman.
With all of that said, let’s take a look at some specific SpaceX revenue streams.
Governmental supply contractsSpaceX has won several NASA contracts to resupply the International Space Station. The most recent contract involves $2.9 billion in funding to build a spacecraft to send astronauts to the moon.
The company has also worked with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), launching a satellite in 2012 to monitor global sea levels and oceanic circulation. The cost of this launch was approximately $82 million.
Similar contracts for the Air Force saw the launch of a GPS satellite in 2015 and in 2020, SpaceX won a contract to provide 40% of all U.S. military launch requirements.
In more recent years, SpaceX has made more money from commercial service deliveries. Each delivery using the Falcon 9 rocket is advertised at $62 million.
StarlinkStarlink is a network of satellites designed to give high-speed internet access to every citizen on Earth.
Although the project is in its infancy, SpaceX has already secured government contracts to bring high-speed internet to rural U.S customers. Finance services firm Morgan Stanley estimate that the service will be offered for $50/month, giving SpaceX $24 billion in annual free cash flow by 2040.
Read Also: Tesla Business Model, Elon Musk Companies, Who Owns Tesla, Transitional Business Models, Tesla Competitors.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does SpaceX Make Money? appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Elon Musk Make Money? Elon Musk Net Worth In A Nutshell
Elon Musk has made most of his money by investing in ideas and companies he is passionate about. After eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion in 2002, Musk used his personal wealth to fund his new ventures: Tesla and SpaceX. Most of Elon Musk’s wealth comes from Tesla, as he’s the major shareholder for the company. Making Elon Musk’s net worth well past the hundred billion-dollar mark.
Elon Musk StoryPerhaps counterintuitively, billionaire entrepreneur Elon Musk owes much of his financial success to not focusing on making money.
Musk has largely invested in ideas he is passionate about, with the viability of an idea being a more secondary concern to pursuing it. As a child, he had a passion for code, selling the source code for his first video game for $500 at age 12.
In 1999 he founded X.com, one of the first FDIC-insured online banks in the world. After seeing promise in its easy payment service, Musk merged his company with Confinity the following year. In 2001, the company became PayPal and Musk became an 11.7% shareholder.
When eBay acquired PayPal for $1.5 billion in 2002, Musk received $180 million which he would later reinvest into some of his most famous passion projects.
 PayPal makes money primarily by processing customer transactions on the Payments Platform and from other value-added services. Thus, the revenues streams are divided into transaction revenues based on the volume of activity or total payments volume. And value-added services, such as interest and fees earned on loans and interest receivable. As of 2017 PayPal generated over $13 billion in net revenues and almost $1.8 billion in net income.
PayPal makes money primarily by processing customer transactions on the Payments Platform and from other value-added services. Thus, the revenues streams are divided into transaction revenues based on the volume of activity or total payments volume. And value-added services, such as interest and fees earned on loans and interest receivable. As of 2017 PayPal generated over $13 billion in net revenues and almost $1.8 billion in net income. Read Also: How Does PayPal Make Money?
He is also a proponent of the spend-money-to-make-money philosophy. Indeed, Musk is a notorious workaholic who prefers to reinvest capital into his businesses over lavish vacations.
 Elon Musk is one of the richest people in the world, with his main ownership in Tesla, making him worth more than a hundred billion dollars. The companies founded by Elon Musk range from electric vehicles and renewable energies, with Tesla, rockets, with SpaceX, infrastructure, with The Boring Company, and neurotechnology with Neuralink. SpaceX
Elon Musk is one of the richest people in the world, with his main ownership in Tesla, making him worth more than a hundred billion dollars. The companies founded by Elon Musk range from electric vehicles and renewable energies, with Tesla, rockets, with SpaceX, infrastructure, with The Boring Company, and neurotechnology with Neuralink. SpaceXMusk has always had a passion for space exploration. Even before the eBay acquisition of PayPal, he conceived of greenhouses to grow food crops on Mars. Such was his passion that he traveled to Moscow to purchase intercontinental ballistic missiles that could send payloads into space.
In Moscow however, Musk was seen as an amateur and rejected. Undeterred, he returned to the U.S. and founded SpaceX in 2002 using $100 million of his own capital. In 2008, SpaceX received a $1.6 billion NASA grant for rockets to resupply the International Space Station. The company then became the first to berth a private vehicle with the ISS. Reusable rockets with large payloads were also launched into space and successfully returned to Earth using SpaceX autonomous drone ships.
By March of 2018, SpaceX had over 100 launches on its manifest worth approximately $12 billion in revenue. SpaceX’s most recent contract is the $2.89 billion NASA program to carry American astronauts to the moon.
Tesla Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates Tesla’s plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores.
Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates Tesla’s plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores. Tesla is perhaps the biggest accelerator of Elon Musk’s net worth. When the company debuted on the stock market in 2010, Musk instantly amassed a personal fortune of $2 billion.
In 2018, he bought more than $35 million worth of Tesla shares to take his total to approximately 241 million shares. Given that Tesla shares are valued at just over $700, it is not difficult to appreciate how wealthy Tesla has made Musk.
 Elon Musk, an early investor and CEO of Tesla, is the major shareholder with 21.7% of stocks. Other major shareholders comprise investment firms like Baillie Gifford & Co. (7.7%), FMR LLC (5.3%), Capital Ventures International (5.2%), T. Rowe Price Associates (5.2%), and Capital World Investors (5%). Another major individual shareholder is Larry Ellison (co-founder and CEO of Oracle), with a 1.7% stake.
Elon Musk, an early investor and CEO of Tesla, is the major shareholder with 21.7% of stocks. Other major shareholders comprise investment firms like Baillie Gifford & Co. (7.7%), FMR LLC (5.3%), Capital Ventures International (5.2%), T. Rowe Price Associates (5.2%), and Capital World Investors (5%). Another major individual shareholder is Larry Ellison (co-founder and CEO of Oracle), with a 1.7% stake. Indirectly, the Tesla share price appreciation is the result of a new wave of younger investors and strong demand for electric vehicles – particularly from China. A Biden election win has also helped Tesla benefit from legislation designed to bring electric vehicles to the mainstream.
Today Tesla is an electric empire, which potential goes way beyond the automotive sector!
 As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with self-driving software. Key takeawaysElon Musk has made most of his money by investing in ideas and companies he is passionate about. After PayPal was acquired by eBay, he used his significant stake in the company to fund the creation of SpaceX.After initial teething problems, SpaceX grew to become a company with 100 launches on its manifest worth $12 billion. The company has also made Musk money through several, multi-billion dollar contracts with NASA.Tesla and its rapidly appreciating share price are responsible for a large proportion of Musk’s net worth. A sizeable shareholding combined with an influx of young investors and favorable legislation has seen Musk become one of the richest men on the planet.
As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with self-driving software. Key takeawaysElon Musk has made most of his money by investing in ideas and companies he is passionate about. After PayPal was acquired by eBay, he used his significant stake in the company to fund the creation of SpaceX.After initial teething problems, SpaceX grew to become a company with 100 launches on its manifest worth $12 billion. The company has also made Musk money through several, multi-billion dollar contracts with NASA.Tesla and its rapidly appreciating share price are responsible for a large proportion of Musk’s net worth. A sizeable shareholding combined with an influx of young investors and favorable legislation has seen Musk become one of the richest men on the planet.Read Also: Tesla Business Model, Elon Musk Companies, Who Owns Tesla, Transitional Business Models, Tesla Competitors.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Elon Musk Make Money? Elon Musk Net Worth In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
April 24, 2021
BAT Token: The Basic Attention Token Business Model In A Nutshell
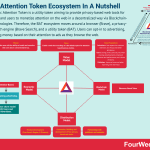
BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web.
VBDE Blockchain Business Model Template[image error]A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model.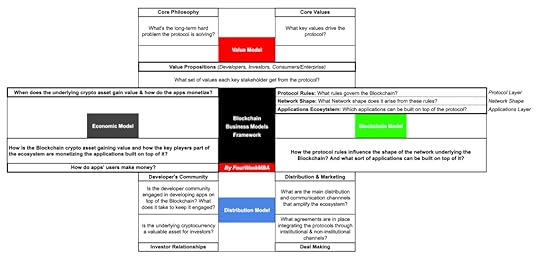 What is BAT?
What is BAT?Basic Attention Token (BAT) is among the renowned cryptocurrency tokens that many people already know. Compared with other blockchain tokens, BAT differs in the motivation behind its creation. Developed by the people behind the open-source internet browser Brave, BAT’s introduction promoted privacy protection and anonymous browsing. It is also the same reason why most people prefer BAT over any cryptocurrency token readily available.
The co-creator behind the popular browser, Mozilla Firefox, is responsible for developing the Basic Attention Token (BAT). Brendan Eich’s initial idea behind creating this blockchain technology is to further security, fairness, and digital advertising efficiency. The primary goal of BAT is to resolve the arising issues in web browsing and web-based advertising using an innovative digital currency and blockchain technology. Currently, BAT is developed on top of Ethereum and integrated into Brave web browser as its native token.
BAT Value Model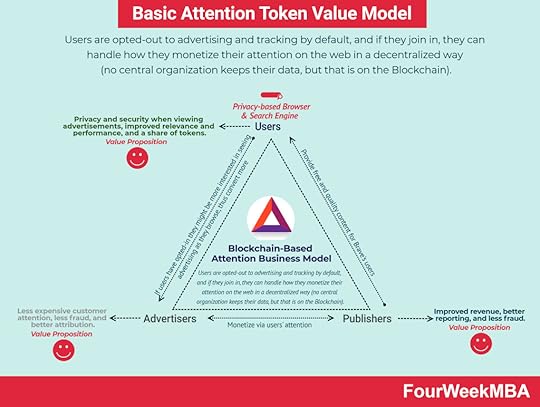 Users are opted-out to advertising and tracking by default, and if they join in, they can handle how they monetize their attention on the web in a decentralized way
Users are opted-out to advertising and tracking by default, and if they join in, they can handle how they monetize their attention on the web in a decentralized way(no central organization keeps their data, but that is on the Blockchain). Core Philosophy & Solution
As emphasized in the BAT White Paper:
Digital advertising is broken. The marketplace for online advertising, once dominated by advertisers, publishers and users, has become overrun by “middleman” ad exchanges, audience segmentation, complicated behavioral and cross-device user tracking, and opaque cross-party sharing through data management platforms.
And it continues:
Publishers face falling revenue, users feel increasingly violated, and advertisers’ ability to assess effectiveness is diminished.
The solution:
A decentralized, transparent digital ad exchange based on Blockchain.
How does the Basic Attention Token ecosystem address that? Via three core pieces:
Brave: as highlighted in the White Paper that is “a fast, open source, privacy-focused browser that blocks third party ads and trackers, and builds in a ledger system that measures user attention to reward publishers accordingly.”BAT: a token that, as highlighted in the White Paper “for a decentralized ad exchange. It compensates the browser user for attention while protecting privacy. BAT connects advertisers, publishers, and users and is denominated by relevant user attention, while removing social and economic costs associated with existing ad networks, e.g., fraud, privacy violations, and malvertising.”Brave Search: a search engine that doesn’t track users. Indeed, back in March 2021, the Brave foundation acquired Tailcat, a search engine focused on privacy, which becomes the foundation of Brave Search. Core ValuesSome of the core values highlighted in the launch of the BAT ecosystem are:
Fairness: users will opt in to receive advertising.Anonymity: if users do opt in, “their attention will be privately monitored on-device in the Brave browser, without tracking.”Impact using proven blockchain technology: as users opt in to the advertising served by BAT, all is encrypted via a Blockchain infrastructure. Anonymous machine learning for relevance; Open source for transparency Value Propositions of BATBAT’s extensive value proposition is the main reason it gets a lot of attention from different users. With that in mind, here are some of the specified groups who can take advantage of BAT:
Marketers/AdvertisersLess expensive customer attention, less fraud, and better attribution .
BAT provides attractive incentives especially valuable for those working in the marketing and advertising industries. Integrating BAT into their advertisements enables them to acquire a plethora of data and various analytics. Using tools such as attention measurement systems and machine learning-based algorithms allow marketers to extract as much data as they need to produce effective strategies better. In other words, BAT provides them an opportunity to utilize objective data to deliver personalized, user-friendly advertisements that reap high ROI.
Publishing CompaniesImproved revenue, better reporting, and less fraud .
Publishing companies can benefit from BAT for being compensated by both marketers and other users. With that in mind, they can benefit from expanding their reach with different advertisers. The feedback that publishers receive from the users themselves also allows them to improve their display and advertising elements.
Web UsersStrong privacy and security when viewing advertisements, improved relevance and performance, and a share of tokens.
Integrating BAT as the native token for Brave web browser leads to several benefits. For example, users can receive BAT for just looking at a handful of advertisements. Many users choose to utilize their BAT to acquire different products and services. Additionally, some also prefer to donate the BAT back to the publishing companies to extend their support.
Get The Full Analysis Of The BAT Ecosystem In Blockchain Business Models

Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post BAT Token: The Basic Attention Token Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
April 22, 2021
Business Logic Layer And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models
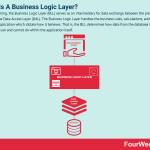
In programming, the Business Logic Layer (BLL) serves as an intermediary for data exchange between the presentation layer and the Data Access Layer (DAL). The Business Logic Layer handles the business rules, calculations, and logic within an application which dictate how it behaves. That is, the BLL determines how data from the database is used and what it can and cannot do within the application itself.
Understanding a Business Logic LayerIn this way, the Business Logic Layer manages communication between the database and the presentation layer – sometimes referred to as the end-user interface. It forms part of the multi-tier architecture of software engineering where various functions are physically separated.
Separation typically involves functions assigned to one of three layers:
User Interface Layer (UI) – where all presentation and user interaction occurs. Data is displayed to the user. The user sends and also receives data.Business Logic Layer (BLL) – as we have noted, the BLL deals with application processing and coordinates the flow of data between the UI and DAL.Data Access Layer (DAL) – or the layer where data management takes place. In most cases, this is via a web service or database.Defining a Business Logic LayerBoth the UI and DAL are relatively easy to define and understand. However, there is less clarity on what constitutes a BLL. As a result, many businesses (including Apple and Microsoft) exclude the BLL from their applications entirely and have UI code communicate directly with the DAL.
In coding, this leads to what is colloquially called the “Fat Controller”. This describes a controller with domain logic servicing too many requests. In turn, controller logic becomes overly complex and too dependent on domain concepts. Ultimately, this complexity makes code maintenance difficult.
A better option is to design the application to support multiple different user interfaces. Code that is common to each user interface then becomes the Business Logic Layer.
Generally speaking, this code is any which deals with the following:
Persisting data (to the DAL).Displaying data (to the UI layer).Accessing data (from the DAL).Making logical decisions.Performing calculations.Maintaining application state.Coordinating workflow.Processing commands (from the UI layer).Used properly, the BLL centralizes as much common logic as possible and is not tied to a particular UI. This enables the application to support any number of user interfaces and minimizes instances of code duplication.
It’s also important to note that the code in the UI layer must necessarily shrink as it grows in the BLL. This concept is central to the “Thin Controller” theory.
As the BLL grows and starts to become bloated, the layer can be separated further by moving from a three-tier to an n-tier architecture.
Key takeaways:A Business Logic Layer serves as an intermediary for data exchange between the Data Access Layer (DAL) and the User Interface Layer (UI).
Finding it too difficult to define, many businesses omit the Business Logic Layer completely. With the DAL communicating directly with the UI, code becomes overly complex and maintenance problematic.
A Business Logic Layer allows developers to design applications that support multiple user interfaces. This minimizes the chances of needless code duplication.
Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Business Logic Layer And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Hard-Fork: What Happens When Blockchain Protocols Split?
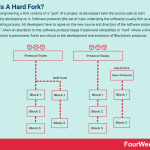
In software engineering, a fork consists of a “split” of a project, as developers take the source code to start independently developing on it. Software protocols (the set of rules underlying the software) usually fork as a group decision-making process. All developers have to agree on the new course and direction of the software protocol. A fork can be “soft” when an alteration to the software protocol keeps it backward compatible or “hard” where a divergence of the new chain is permanent. Forks are critical to the development and evolution of Blockchain protocols.
What are soft forks and hard forks?In a Blockchain, a soft fork occurs when an alteration to the software protocol keeps it backward compatible. In other words, the new forked chain follows new rules while also honoring the old rules.
In a hard fork, a divergence of the new chain is permanent. Nodes running older versions will no longer be accepted by (or be able to communicate with) the new version.
Understanding soft forks and hard forksWhen a consumer updates a digital banking app on their smartphone, the process is painless and seamless. Updates only take a few minutes and some apps do so automatically. What’s more, there are rarely any usability issues with the new version.
Open-source cryptocurrencies are very different. There is no central authority releasing updates or making changes as it sees fit. There is also no requirement for Bitcoin users to understand the code that underpins it. Nevertheless, freely accessible code is an important facet of a decentralized, open-source platform.
Soft and hard forks are the cryptocurrency versions of updates for computer programs, allowing networks to be upgraded in the absence of a central authority. Forking as a term describes any scenario where a cryptocurrency project needs to make technical updates to its code.
Forking necessitates that a Blockchain splits into two branches. The nature of the split can be categorized as either hard or soft.
In the next section, we’ll take a look at each in more detail.
Soft forksAs noted earlier, a soft fork is backward compatible with the original chain continuing to follow old rules. Upgraded nodes can still communicate with non-upgraded nodes, which is another way of stating that new rules do not clash with old rules.
This kind of fork requires that a majority of miners upgrade before the new rules are enforced. A recent example of a soft fork is the Segregated Witness (SegWit) fork which occurred after the Bitcoin/Bitcoin Cash split. This update changed the format of transactions and blocks, but old nodes could still validate them without breaking the rules.
Hard forksHard forks are backwards-incompatible updates. Since nodes add rules that conflict with older nodes, new nodes can only communicate with those operating on the latest version.
Here, the blockchain must split into two, parallel chains that continue to propagate blocks and transactions separately. One operates under the old rules while the other under the new rules.
It’s important to note that until the point of divergence, each separate chain has a shared history. If a user held Bitcoins before the split, they end up holding coins on each of the two subsequent chains.
An example of a hard fork is the 2017 split that saw Bitcoin separate into two chains: Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash. This occurred before the aforementioned SegWit soft fork and was the result of disagreement over increasing the block size.
Since an increase in block size required a rule change, nodes only accepted blocks smaller than 1MB. This meant that an otherwise valid 2MB block would be rejected and thus be incompatible with the previous version.
Key takeaways:Forking helps cryptocurrency Blockchain make important updates to its code in the absence of a central authority. Hard and soft forks describe the nature of these updates as Blockchain networks split in two.A soft fork is backward-compatible with the original chain. Older nodes can communicate (and are compatible with) new nodes without breaking rules.A hard fork is backward-incompatible with the original chain. This split is a permanent divergence from a previous version of the Blockchain. As a result, nodes running previous versions are no longer compatible with the newest version.Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Hard-Fork: What Happens When Blockchain Protocols Split? appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is Sharding And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models
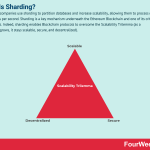
Blockchain companies use sharding to partition databases and increase scalability, allowing them to process more transactions per second. Sharding is a key mechanism underneath the Ethereum Blockchain and one of its critical components. Indeed, sharding enables Blockchain protocols to overcome the Scalability Trilemma (as a Blockchain grows, it stays scalable, secure, and decentralized).
Understanding sharding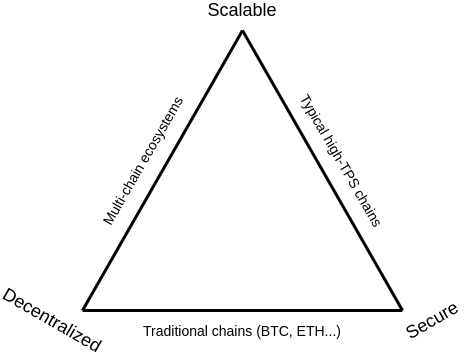
The Scalability Trilemma (Image Credit: vitalik.cal).
Blockchain is now used in everything from supply chain management to cross-border financial transactions.
While extremely versatile, one critical issue remains: scalability. This issue is already prevalent with cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether where more computers joining a peer-to-peer network cause the entire system to degrade.
For fintech companies that must compete with rapid payment networks, a lack of scalability is a particular concern. How can Blockchain be a viable solution in this industry? How can scalability and throughput be increased to address latency concerns?
Developers think sharding is the answer. To increase transactional throughput, sharding describes the partitioning of computational and storage workload across a P2P network. This avoids a situation where a single node is responsible for processing the entire transactional load of a network.
Sharding can help Blockchain provide all three (scalability, security and decentralization).
How is the workload partitioned?Sharding uses horizontal partitioning, a database architecture enabling businesses to scale their databases dynamically.
Each database table is separated into multiple tables by partitioning its rows. Data held in each partition is independent of other partitions and is unique, but the schema and columns of each partition remain the same.
Individual partitions are called logical shards, which are distributed across separate database nodes called physical shards. Each physical shard can hold multiple logical shards. Collectively, the shards comprise an entire logical dataset.
It’s important to note that database shards typify a shared-nothing architecture. Shards are autonomous in the sense that they do not share computing resources or the same data with other shards. However, shards can share information with other nodes if required. This maintains a decentralized ledger where all ledger entries can be viewed without every shard having to process and store all information.
Strengths and weaknesses of shardingStrengthsSharding allows horizontal scaling, or the act of adding machines to a stack to spread out the load and improve processing times. This method of scaling is preferable to vertical scaling, which involves adding more CPU or RAM to an existing server. In theory, horizontal scaling allows the network to be scaled up indefinitely. On the other hand, vertical scaling is inevitably constrained by the capabilities of the server.Sharding also decreases query response times. Non-sharded database queries have to search through every row in the table to find the result. This process can become extremely slow in large, monolithic applications. Through horizontal partitioning, queries search fewer rows and results are returned more quickly.WeaknessesImplementing a sharded database architecture is quite complex. Mistakes during implementation can lead to corrupted tables and loss of data. Even when implemented successfully, sharding can be disruptive to some teams. Instead of managing data from a single entry point, individuals must manage data across several locations.Sharded databases are almost impossible to return to an unsharded state. Backups of the database made before sharding won’t include any data written after partitioning. Returning to an unsharded architecture involves the combining of partitioned data with older backups or creating a single database from many partitioned databases. Both are expensive and time-consuming operations.Key takeaways:Sharding is the process of increasing the scalability of blockchain networks.Sharding separates database tables into horizontal partitions called logical shards. These shards are autonomous and do not share resources or data. Collectively, they comprise an entire data set and can share uncommon information when required.Sharding enables computing power to be increased by adding more machines to a stack. Partitioning also increases query response times as fewer rows need to be searched. However, implementing a sharded database is complex and is difficult to reverse.Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is Sharding And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
April 21, 2021
How Does Squarespace Make Money? The Squarespace Business Model In A Nutshell
Squarespace is a North American hosting and website building company. Founded in 2004 by college student Anthony Casalena as a blog hosting service, it grew to become among the most successful website building companies. The company mostly makes money via its subscription plans. It also makes money via customizations on top of its subscription plans. And in part also as transaction fees for the website where it processes the sales.
Origin Story![[MISSING IMAGE: tm218193d1-pg_09square4c.jpg]](https://i.gr-assets.com/images/S/compressed.photo.goodreads.com/hostedimages/1619261776i/31229049._SY540_.jpg) The Squarespace Timeline (Image Source: Squarespace Financial Prospectus).
The Squarespace Timeline (Image Source: Squarespace Financial Prospectus).Squarespace is a North American hosting and website building company.
Squarespace was founded in 2004 by college student Anthony Casalena as a blog hosting service. Although Casalena developed the service for his personal use, he began to share it with friends and family while taking business programs at the University of Maryland.
After launching as a DIY website builder, Casalena worked as the company’s only employee for the next two years. When he graduated in 2007, Squarespace had attained $1 million in revenue and began to attract significant sums of venture capital.
The platform now offers a range of tools including eCommerce functionality, domain name services, and user analytics. By 2020, Squarespace surpassed 1,200 employees and $665 millions in bookings.
Squarespace revenue generation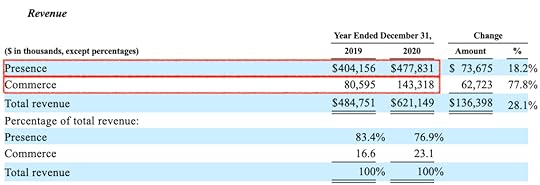 Squarespace revenue model moves around two main streams: presence and commerce, with the presence revenue stream representing more than 76% of the company’s revenues in 2020. Presence revenue increased $73.7 million (18.2%) by 2020 compared compared to 2019. The “presence” consists of the subscription plans offered by Squarespace. The “commerce” revenue increased $62.7 million (77.8%) by 2020 compared to 2019, based on the increased volume of transactions processed via the platform.
Squarespace revenue model moves around two main streams: presence and commerce, with the presence revenue stream representing more than 76% of the company’s revenues in 2020. Presence revenue increased $73.7 million (18.2%) by 2020 compared compared to 2019. The “presence” consists of the subscription plans offered by Squarespace. The “commerce” revenue increased $62.7 million (77.8%) by 2020 compared to 2019, based on the increased volume of transactions processed via the platform. The majority of Squarespace revenue generation comes from subscription plans that allow users to build their own websites using integrated tools.
These plans include:
Personal ($12/month) – the cheapest plan that will satisfy the majority of users. It offers a free custom domain, SSL security, unlimited bandwidth, site templates, and SEO features to increase site visibility. Business ($18/month) – containing features from the Personal plan plus business tools such as a professional Google email, advanced website analytics, promotional banners, and $100 in Google Ads credit. Squarespace also charges customers a 3% transaction fee on every sale made on the Business plan. Basic Commerce ($26/month) – a fully integrated commerce solution allowing businesses to sell unlimited products and accept donations with a dedicated point of sale system. The 3% transaction fee is waived for Basic Commerce customers. Advanced Commerce ($40/month) – including all Basic Commerce features plus functions such as abandoned cart recovery, advanced shipping and discounts, commerce APIs, and limited availability labels.For each plan, Squarespace offers a discount if the plan is purchased for a year in advance.
Custom domainsCustomers who sign up for an annual plan get their domain name free.
For monthly users, Squarespace charges $20 every year to maintain one domain. While cheaper deals on domain names can be had elsewhere, this price includes the connection of the domain name to Squarespace hosting and management of necessary annual renewals.
Squarespace SelectSquarespace Select allows users to access the most advanced Squarespace features with dedicated support.
This entails personalized account management and SEO advice, as well as guidance on how to match website design with brand vision. Experts also help site owners optimize site performance and maintain site integrity and security.
For this package, Squarespace charges $4,900 annually.
Key takeaways:Squarespace is a North American website builder platform founded by Anthony Casalena in 2004. Casalena developed the platform for his own purposes while studying at the University of Maryland.Squarespace derives the bulk of its revenue via the subscription model. Four plans with various levels of functionality are designed for individuals and businesses of all sizes.Squarespace also makes money from the somewhat boutique Squarespace Select service. This premium feature gives business owners personalized support and advice around best practices and site optimization.Read Also: WordPress Business Model, Shopify Business Model, Wix Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Squarespace Make Money? The Squarespace Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



