Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 160
April 20, 2021
How Does Bumble Make Money?

Bumble is an American social media company with a core focus on online dating. Bumble drives revenue through the purchase of in-app services using its currency Bumble Coins and via subscriptions. Bumble generates revenues in a few key ways: Spotlight is Bumble’s answer to Tinder’s Boost capability. The Bumble Boost function allows users to swipe without daily limits or extend matches for up to 48 hours.
Origin StoryBumble is an American social media company with a core focus on online dating. The company was founded by Whitney Wolfe Herd, a former Tinder user who sued the platform for sexual discrimination and harassment in 2014.
As a result of media attention surrounding the case, the founder of the Russian dating app Badoo Andrey Andreev reached out to Heard. He proposed a new dating app using Badoo infrastructure and investment funds. Together, Heard and Andreev recruited fellow Tinder departees Sarah Mick and Chris Gulczynski to design the Bumble interface ready for launch in December 2014.
Bumble has since expanded to become more than just a dating app. Bumble BFF allows users to search for platonic friends, while Bumble Bizz focuses on business communication. In 2020, the platform reached 100 million users and is the second most popular platform in the U.S. after Tinder.
Understanding Bumble value propositionIn its financial prospectus Bumble highlighted:
Bumble was founded because we noticed two different, yet related issues in our society: antiquated gender norms, and a lack of kindness and accountability on the internet. We observed that women were often treated unequally in society, especially in romantic relationships. At the same time, social networks created possibilities for connections, but they were focused on connections with people you already know and lacked guardrails to encourage better behavior online.
Thus, as the company hihghlihgted the brand was built with the “women at the center.”
The Bumble tech platform emphasizes a design “to be safe and empowering for women, and, in turn, provides a better environment for everyone.”
Therefore, as the company highlights, the value proposition moves along few key values:
Meaningful Connections and Healthy Relationships.Trust and Safety.Innovative Features.A Large, Growing, Engaged Community.Understanding Bumble tech platform and productThe company operates two main products:
Bumble: launched in 2014, is one of the first dating apps built with women at the center. And Badoo: launched in 2006, one of the pioneers of web and mobile free-to-use dating products. The Bumble Timeline (Image Source: Bumble Financial Prospectus)
The Bumble Timeline (Image Source: Bumble Financial Prospectus)The users’ experience consist of three main paths/journeys:
Setting Up a Profile The platform has been designed to enable a straightforward set up and interaction
The platform has been designed to enable a straightforward set up and interaction (Image Source: Bumble Financial Prospectus).Matching
 The matching experience is a distinctive element of the platform and it’s engineered to empower women in the choice of a potential match
The matching experience is a distinctive element of the platform and it’s engineered to empower women in the choice of a potential match(Image Source: Bumble Financial Prospectus).Chatting
 Bumble’s users must initiate a chat within 24 hours or the connection disappears
Bumble’s users must initiate a chat within 24 hours or the connection disappears(Image Source: Bumble Financial Prospectus).Premium Features
Bunble subscription offerings (Bumble Boost and Bumble Premium) enable a set of premium features like:
Beeline: a feature that shows you who likes you.Rematch: enabling subscribers to rematch with any of the prior matches that have already expired after a 24-hour period.Extend: access to an unlimited number of 24-hour extensions on conversations.Other features can be enabled as in-app purchases:
SuperSwipe: to inform potential matches that they are confidently interested in them.Spotlight: to advance their profile to the top of the list of potential matches.Travel Mode: change location to anywhere in the world (thus opening up to new matches).Backtrack: enabling users to undo a “no” vote to revisit potential matches.Bumble revenue generation
 Bumble KPIs (Image Source: Financial Prospectus)
Bumble KPIs (Image Source: Financial Prospectus)It’s important to point out that the core features of Bumble are free to use. Users can swipe and match with interested parties without having to pay for the privilege.
Instead, Bumble drives revenue through the purchase of in-app services using its currency Bumble Coins.
SpotlightSpotlight is Bumble’s answer to Tinder’s Boost capability.
Users can pay to have their profiles placed at the front of a match queue using Bumble coins.
The coins themselves are available for purchase within the app, with pricing depending on the country of the user and the number of coins purchased. In general, Bumble offers discounts for bulk purchases. In the United States, for example, 1 Bumble Coin costs $1.99 while 20 Bumble Coins can be had for $24.99.
BoostThe Bumble Boost function allows users to swipe without daily limits or extend matches for up to 48 hours. They can also instantly access those who have liked their profile and re-match with old connections.
Boost features are also purchased with Bumble Coins but on a more recurring basis. Using a subscription-based model, users can sign up to Boost for a week, month, three months, or a lifetime.
Again, prices depend on the region and the renewal frequency chosen. But Bumble can charge up to $25/month for this premium membership.
Badoo ownershipIn 2020, Bumble replaced MagicLab as the parent company of both Bumble and Badoo.
Therefore it is not unreasonable to suggest that Bumble makes a significant amount of money from Badoo – which is also a popular dating platform with a similar business model.
Badoo is the world’s most widely used dating network, operating in 190 countries with over 400 million registered users.
Key takeaways:Bumble is a social media dating company co-founded by former Tinder user Whitney Wolfe Herd and Badoo founder Andrey Andreev.The Bumble app works on a freemium model. However, users can unlock additional features using Bumble Coins, either through one-off purchases or a subscription model.In 2020, Bumble also became the parent company of Badoo – the world’s most popular online dating service with a similar business model.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Bumble Make Money? appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Scrum Anti-Patterns And How To Avoid Them
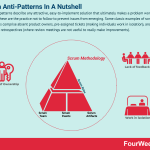
Scrum anti-patterns describe any attractive, easy-to-implement solution that ultimately makes a problem worse. Therefore, these are the practice not to follow to prevent issues from emerging. Some classic examples of scrum anti-patterns comprise absent product owners, pre-assigned tickets (making individuals work in isolation), and discounting retrospectives (where review meetings are not useful to really make improvements).
Understanding scrum anti-patternsScrum concepts are relatively easy to understand, but their successful execution is contingent upon overcoming ingrained habits. As successful as agile methodologies have been, they are not a panacea for inefficient or outdated practices.
Indeed, certain behaviors or ways of operating are going to be detrimental to agile principles and processes. These frequently exhibited behaviors – which can masquerade as solutions – are known as scrum anti-patterns.
No one in an agile team is immune from scrum anti-patterns. This includes the Scrum Master and Product Owner.
In the next section, let’s take a look at some of the more common patterns and how to solve them.
Three common scrum anti-patternsAbsent Product OwnersProduct Owners are responsible for creating product value for the customer via the development team. They must be present throughout the sprint to give impetus to decision-making and clarify queries.
Absent Product Owners inhibit the collective personal development of the team and cause product reworks because of misunderstandings. Absences are sometimes exacerbated by a Product Owner having to manage multiple Scrum teams. Active engagement between the PO and the team they are leading is vital.
Pre-assigning ticketsThe assigning of tickets by the Product Owner or Scrum Muster to competent individuals is crucial. However, this compartmentalized means of assigning duties causes individuals to work in isolation and not as part of a team. Worse still, it hinders personal and professional growth.
Team members should be given the freedom to add tasks to their in-progress work. Ideally, less experienced individuals in a given task should partner with those who are more experienced.
Discounting retrospectivesScrum teams must review every sprint at its conclusion. These review sessions are used to discuss what went well and also identify areas for improvement.
Many teams become bored of repetitive retrospectives, causing them to drop these important meetings from their scheduling altogether. Many other teams will hold the meetings but make no effort to actively plan to improve.
To facilitate buy-in for these important meetings, mediators should discard the standardized talking points around strengths and weaknesses.
The 4 Ls ApproachA fresher approach involves something called the 4 Ls:
Liked – what did individuals like?Learned – what did they learn?Lacked – are there actions the team is performed that could be improved on?Longed for – what does the team desire or wish to have?Key takeaways:Scrum anti-patterns describe actions that follow the path of least resistance. Although they initially seem attractive, these actions are detrimental to agile principles and company growth.No member of an agile team is immune from exhibiting scrum anti-pattern behavior. As leaders setting an example, positions such as Product Owner and Scrum Master have a particular responsibility to set high standards.Some common anti-scrum patterns include Product Owners who fail to lead their teams during product development. Pre-assigning tickets to the most qualified personnel and the avoidance of retrospectives are also detrimental to a business.Read Next: Scrum, Kanban, Scrumban, Agile, Poka-Yoke.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Scrum Anti-Patterns And How To Avoid Them appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is AIOps And Why It Matters In Business
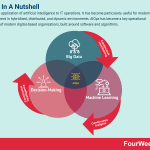
AIOps is the application of artificial intelligence to IT operations. It has become particularly useful for modern IT management in hybridized, distributed, and dynamic environments. AIOps has become a key operational component of modern digital-based organizations, built around software and algorithms.
Understanding AIOpsThe term AIOps was first coined by global research and advisory company Gartner in 2016.
AIOps uses big data and machine learning capabilities to enhance IT operations. It enables businesses to:
Identify significant events and patterns related to system performance and availability.Diagnose and report root causes swiftly for either human or machine intervention and resolution.Aggregate large volumes of IT operations data relating to applications, analytics tools, and infrastructure components.In each of the above examples, AIOps replaces multiple and sometimes convoluted manual IT operations with a single, intelligent AI platform. As a result, teams can respond to issues quickly and proactively. In some cases, human teams may not need to respond at all.
AIOps also seeks to bridge the gap between an increasingly dynamic IT environment and user expectations around application performance and availability. In the next section, we will take a closer look at how this gap is being bridged in more detail.
How does AIOps bridge the gap?It should be noted that AIOps is not a panacea to increased efficiency and performance. Businesses will realize the most value from AIOps by using it as an independent platform incorporating data from all IT monitoring sources.
Data is digested via algorithms that streamline and automate IT operations monitoring. There are five types:
Data selection – here, algorithms are used to filter through vast amounts of superfluous data to find elements indicating a problem. In most businesses, AIOps uses entropy algorithms to filter data from networks, infrastructure, applications, cloud, and storage components.Pattern discovery – are there relationships or correlations between selected data elements? What are the causes and the subsequent events? How can they be grouped for further analysis using text, time, and topology?Inference – or identifying the root causes of problems or other recurring issues to immediately rectify them. Collaboration – how can an algorithm apply the insights gleaned from problem resolution for future incidents? That is, can the problem-solving process be accelerated or better still, can problems be identified before they occur? Results are shared in a virtual collaborative environment which is particularly important for problems that transcend boundaries associated with technology, department, or skill level.Automation – wherever possible, response and remediation should be automated to make solutions more precise, timely, and cost-effective. Improved workflows can be triggered with or without human intervention.Key takeaways:AIOps uses big data and machine learning capabilities in the application of artificial intelligence to IT operations. The term was first coined by research company Gartner in 2016.AIOps replaces multiple and somewhat convoluted manual processes with a single, intelligent solution. More generally speaking, it helps businesses meet user expectations in the face of increasingly dynamic IT operations.AIOps uses algorithms to streamline and automate operations monitoring by way of data selection, pattern discovery, inference, collaboration, and automation.Other examples merging development with internal operational departmentsDevOps Engineering DevOps refers to a series of practices performed to perform automated software development processes. It is a conjugation of the term “development” and “operations” to emphasize how functions integrate across IT teams. DevOps strategies promote seamless building, testing, and deployment of products. It aims to bridge a gap between development and operations teams to streamline the development altogether.DevSecOps
DevOps refers to a series of practices performed to perform automated software development processes. It is a conjugation of the term “development” and “operations” to emphasize how functions integrate across IT teams. DevOps strategies promote seamless building, testing, and deployment of products. It aims to bridge a gap between development and operations teams to streamline the development altogether.DevSecOps DevSecOps is a set of disciplines combining development, security, and operations. It is a philosophy that helps software development businesses deliver innovative products quickly without sacrificing security. This allows potential security issues to be identified during the development process – and not after the product has been released in line with the emergence of continuous software development practices. FullStack Development
DevSecOps is a set of disciplines combining development, security, and operations. It is a philosophy that helps software development businesses deliver innovative products quickly without sacrificing security. This allows potential security issues to be identified during the development process – and not after the product has been released in line with the emergence of continuous software development practices. FullStack Development There are three segments of web development and design. One is dealing with the user interface or what the customer sees. Front End development is responsible for the crucial elements that make up the presentation of the page. The next is Back End, which handles the processes involved in the web page. It deals with information validation, database management, as well as transactions. As businesses continue to grow, the third segment emerged to accommodate their increasing needs and lucrative goals. Building applications from end-to-end is what makes a full stack developer. It is a more versatile role that is considered the Jack of All Trades.MLOps
There are three segments of web development and design. One is dealing with the user interface or what the customer sees. Front End development is responsible for the crucial elements that make up the presentation of the page. The next is Back End, which handles the processes involved in the web page. It deals with information validation, database management, as well as transactions. As businesses continue to grow, the third segment emerged to accommodate their increasing needs and lucrative goals. Building applications from end-to-end is what makes a full stack developer. It is a more versatile role that is considered the Jack of All Trades.MLOps Machine Learning Ops (MLOps) describes a suite of best practices that successfully help a business run artificial intelligence. It consists of the skills, workflows, and processes to create, run, and maintain machine learning models to help various operational processes within organizations. RevOps
Machine Learning Ops (MLOps) describes a suite of best practices that successfully help a business run artificial intelligence. It consists of the skills, workflows, and processes to create, run, and maintain machine learning models to help various operational processes within organizations. RevOps RevOps – short for Revenue Operations – is a framework that aims to maximize the revenue potential of an organization. RevOps seeks to align these departments by giving them access to the same data and tools. With shared information, each then understands their role in the sales funnel and can work collaboratively to increase revenue.AdOps
RevOps – short for Revenue Operations – is a framework that aims to maximize the revenue potential of an organization. RevOps seeks to align these departments by giving them access to the same data and tools. With shared information, each then understands their role in the sales funnel and can work collaboratively to increase revenue.AdOps Ad Ops – also known as Digital Ad Operations – refers to systems and processes that support digital advertisements’ delivery and management. The concept describes any process that helps a marketing team manage, run, or optimize ad campaigns, making them an integrating part of the business operations.
Ad Ops – also known as Digital Ad Operations – refers to systems and processes that support digital advertisements’ delivery and management. The concept describes any process that helps a marketing team manage, run, or optimize ad campaigns, making them an integrating part of the business operations. Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is AIOps And Why It Matters In Business appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is A Fintech Business Model? Fintech Business Model Examples

Fintech business models leverage tech and digital to enhance the financial service industry. Fintech business models, therefore, apply tech to various financial service use cases. Fintech business model examples comprise Affirm, Chime, Coinbase, Klarna, Paypal, Stripe, Robinhood, and many others whose mission is to digitize the financial services industry.
Some use cases comprise:
Digital bankingAlternative credit scoringUnbundlingDemographic-focused productsDifferent fee structuresInsurtechBackgroundFintech companies incorporate technology into financial services and in so doing, have changed the way financial assets are managed, created, and exchanged.
Compared to traditional financial organizations, fintech operations are more streamlined and manage risk in a different yet more efficient way.
Many fintech organizations also adopt a more inclusive approach to personal finance, giving a broad swathe of consumers access to financial products and services. Furthermore, these products and services are typically available on mobile devices and do not have convoluted sign-up processes.
So how is the fintech approach different, exactly? This article will briefly explore some common fintech business models.
Digital bankingFintech organizations offer individual and business bank accounts based on a complete digital infrastructure.
While this model is more or less the same as a traditional banking institution, fintech companies save money on having to maintain physical branches. A portion of this saving is passed to the customer.
Importantly, companies like Aspiration, Chime, and Varo are bringing simple digital banking to the North American market with elegant design and better customer experiences.
Alternative credit scoringSelf-employed individuals typically have difficulties securing finance from a traditional lender. To some extent, this trend has been exacerbated by the gig economy and the rising popularity of entrepreneurship.
Instead of assessing strict credit scores, fintech companies are using social signal data in conjunction with AI algorithms to assess the creditworthiness of an applicant more accurately.
UnbundlingMost traditional financial organizations offer a suite of bundled products and services including investment banking, insurance, car loans, home loans, and credit cards.
Fintech companies are challenging the status quo by becoming specialists in just a few select services. This is particularly true of start-up fintechs who, because of their limited product offering, can focus value delivery more effectively.
Demographic-focused productsSome fintech companies are creating products based on the specific demographic of their target audience.
For example, True Link Financial offers fraud protection for elderly customers. Camino Financial offers lending designed for Latino-owned small and medium-sized businesses. Brex is a service designed for start-ups, eCommerce companies, and other smaller business segments.
Different fee structuresRobinhood is an investment application offering free stock trading. Instead, the company makes money selling retail order flow.
Wise (formerly TransferWise) offers consumers who want to send money abroad the mid-market exchange rate. Using economies of scale, its fee structure is based on transparent transaction charges.
Built on low-cost digital infrastructure, many neobanks have been able to turn a profit on debit exchanges and deposit brokering. These are options that would not be cost-effective for a traditional banking institution.
InsurtechMany insurance companies are changing to the “insurtech” fintech business model – a portmanteau of insurance and technology.
This model utilizes AI, data analytics, and blockchain to help companies sell insurance using virtual branches and process claims more efficiently. It also has important applications in sales, distribution, underwriting, and lead management.
Key takeaways:Using technology, fintech company business models are changing the way consumers access financial products and services. Consumers can now create accounts on handheld devices regardless of their physical location.Specialized fintech companies that offer just a few select services are an example of unbundling. Specialization together with more elegant user interfaces increases customer value.Fintech companies are also targeting a broader swathe of user demographics. Some companies offer fraud protection to elderly customers while others offer loans to Latino small and medium-sized business owners.Read Next: Affirm Business Model , Chime Business Model, Coinbase Business Model, Klarna Business Model, Paypal Business Model, Stripe Business Model, Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is A Fintech Business Model? Fintech Business Model Examples appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Developer Marketing And Why It Matters To Grow Your Digital Business
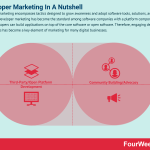
Developer marketing encompasses tactics designed to grow awareness and adopt software tools, solutions, and SaaS platforms. Developer marketing has become the standard among software companies with a platform component, where developers can build applications on top of the core software or open software. Therefore, engaging developer communities has become a key element of marketing for many digital businesses.
Understanding developer marketingIn most businesses, the sales and marketing teams communicate with other businesses (B2B) and consumers (B2C) to drive revenue.
With the increasing prevalence of tech start-ups, however, there is a growing demand for business-to-developer (B2D) engagement. Developers are consumers in the theoretical sense of the word, but they are very different from the typical consumer.
Consumers who are also developers are more discerning and tend to default to skepticism and analysis as a general rule. They become quickly disenfranchised with traditional sales and marketing methods.
Developer marketing means thinking like a developer. Most developers are well-read and are aware of the latest methods and technologies. These are only adopted once the developer has seen them in action and experimented with their use in a low-risk environment.
Furthermore, developers are not the only end-users of software tools and solutions. Marketing messages for a developer would be inappropriate for a product leader, and vice versa.
Some important developer marketing strategiesThere are several ways developers can be marketed to. These include:
Developer content – in the form of an authentic and consistent blog that speaks the language of a developer. This means writing about development stacks, engineering teams, and common use cases.Advertising – traditional forms of advertising can work provided the message is crafted in such a way that it resonates with developers.Source code – whether that be sample applications to open source, code is usually effective at attracting developer attention.Documentation – a form of content rare in traditional marketing strategies that developers prioritize. However, documentation content must be high quality to be successful.Social media – this means determining where developers spend time and marketing to them. CodeProject, CodePlex, HTML.net, Hacker News, and StackOverflow are good places to start. Reaching developer communities in this way adds value to community conversations and increases peer validation. It also allows marketing teams to identify and then solve real-world developer problems.Advocate creation – the most successful businesses will use developers who are akin to influencers. These individuals will champion software products across their personal and professional networks.Measuring the effectiveness of developer marketingTraditional marketing uses KPIs around breadth and reach to gauge success.
On the other hand, developer marketing should focus on the depth of engagement as a determinant of success. Specifically, early adopters of the software product must be empowered to mobilize their contacts – whether that be through tools, knowledge, or other resources.
Businesses can also ask themselves three questions, with each being a key indicator of success:
Are early adopters talking about the product organically? In other words, without provocation or incentivization?Does the target developer audience see the brand or company behind the product as a solution provider or a solution partner?Are target developers actually using the product beyond initial adoption? Are they integrating the solution into their workflow without being prompted to do so?Key takeaways:Developer marketing involves the marketing of software services, tools, and SaaS products to developers to grow awareness and adoption.While developers are end-users, they tend to be more skeptical and analytical than the typical retail consumer. They are also highly resistant to traditional marketing strategies.Developer marketing uses many of the same mediums as traditional marketing. However, the message is much different. Developers respond well to content marketing provided the content speaks their language and is well documented.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Developer Marketing And Why It Matters To Grow Your Digital Business appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
April 19, 2021
Elon Musk Companies: Inside The Musk’s Empire
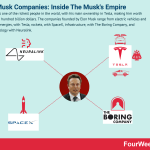
Elon Musk is one of the richest people in the world, with his main ownership in Tesla, making him worth more than a hundred billion dollars. The companies founded by Elon Musk range from electric vehicles and renewable energies, with Tesla, rockets, with SpaceX, infrastructure, with The Boring Company, and neurotechnology with Neuralink.
Musk’s Origin StoryAfter a circuitous route from his home country of South Africa to the United States, Musk secured two internships in Silicon Valley in 1994. One was with an energy-storage start-up, while the other was a game developer company.
The following year, he got accepted into a Stanford University doctorate program but dropped out soon after. He instead chose to capitalize on the booming popularity of the internet and launched his own start-ups including Zip2 and X.com – a precursor to PayPal.
Musk has since gone on to found companies in the exploration, artificial intelligence, aerospace, green energy, and transportation industries. Let’s take a look at some of them below.
SpaceXSpaceX is a space exploration company with a core focus on reusable rockets, space tourism, and satellites that can provide better internet connectivity. Musk created SpaceX out of a need to reduce transportation costs in space and ultimately, facilitate the colonization of Mars.
SpaceX has notoriously lofty ambitions and is never far from the headlines, but the company is making significant progress on its projects. The company recently won a $2.9 billion NASA contract to develop a system for landing astronauts on the moon.
Tesla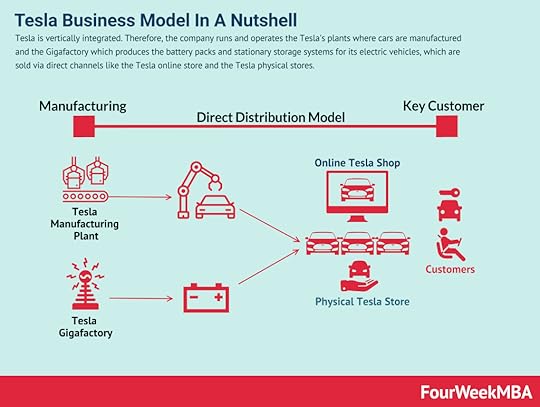 Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates Tesla’s plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores.
Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates Tesla’s plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores. Tesla is perhaps the company for which Elon Musk is best known. Through the popularization of electric vehicles, Musk is seeking to make green vehicles more affordable to consumers.
After rolling out the prototype Tesla Roadster in 2005, the company now offers an SUV, sedan, and sports car variant. Tesla’s pick-up truck, dubbed the Cybertruck, is due for production commencement in late 2021.
Tesla has also expanded into non-automatic products, acquiring solar power business SolarCity in 2016. To complement solar systems, Tesla also sells batteries to store generated energy.
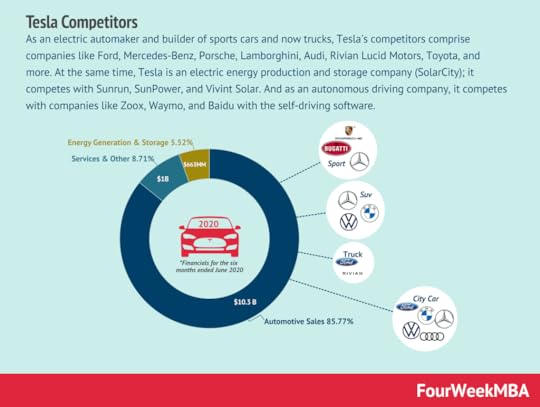 As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with the self-driving software. OpenAI
As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with the self-driving software. OpenAIOpenAI is an artificial intelligence research lab with a stated goal of creating artificial intelligence that benefits humanity.
Musk has openly stated that he created the company because of the fear of a so-called “intelligence explosion” – or a hypothetical point where artificial intelligence growth becomes unmanageable and poses a threat to humanity.
In 2019, OpenAI transitioned from a non-profit to a for-profit organization. Soon after, it partnered with Microsoft after securing $1 billion in investment funding.
The Boring CompanyMusk founded The Boring Company on a whim after being stuck in Los Angeles traffic and lamenting the limitations of two-dimensional transport.
As a result, the company aims to construct underground tunnels that allow easier access from A to B. This includes traffic and freight movement, but it also encompasses better access for pedestrians and utility networks.
The Boring Company was infamous for randomly selling 20,000 flamethrowers to consumers. Critics suggest that the move was a non-dilutive capital raising or publicity stunt, or perhaps both.
NeuralinkNeuralink is a relative newcomer to Elon Musk’s suite of companies. Founded in 2016, the company employs neuroscientists to develop implantable brain-machine interfaces (BMIs).
This important work is intended to give those suffering from paralysis more independence – whether that be through increased mobility, communication, or self-expression.
In 2020 the company released a proof of concept in the form of a pig called Gertrude which had a small computer chip embedded in its brain. However, Musk accepts that it will be some time before the product is safe to use in people.
Read Next: Tesla Business Model, Tesla Competitors, Tesla Mission.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post Elon Musk Companies: Inside The Musk’s Empire appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is Decentralized Autonomous Organization? DAO In A Nutshell

A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) operates autonomously on blockchain protocol under rules governed by smart contracts. DAO is among the most important innovations that Blockchain has brought to the business world, which can create “super entities” or large entities that do not have a central authority but are instead managed in a decentralized manner.
Understanding a decentralized autonomous organizationThe blockchain-centric model of a decentralized autonomous organization seeks to address a problem present in almost every business – regardless of industry or size.
This is sometimes referred to as the principal-agent dilemma and occurs when an individual or entity (the “agent”) can make decisions on behalf of another individual or entity (the “principal”). Under this system, the needs and priorities of the agent often differ from those of the principal. This causes the agent to make self-interested decisions, even if they had been originally tasked with looking after the principal.
DAOs are one way to bypass or at least reduce the need for centralized, hierarchical decision-making in organizations. Using blockchain, a DAO ensures that information flow and incentive structures are properly aligned in a codified format. Indeed, organizations of the future will have their systems, management, charters, and performance bonuses written into smart contracts.
One of the primary goals of the DAO is the automation of all essential and non-essential processes, which has obvious benefits to the organization in terms of efficiency and cost. Blockchain also mitigates the potential for fraud and as noted earlier, directors acting according to their own self-interest.
How does a decentralized autonomous organization work?While each organization will have specific needs, establishing a DAO using blockchain requires some important groundwork:
Smart contract set up – initially, the underlying rules of each smart contract must be defined and encoded. The organization must reach a consensus on governance, operations, and incentivization before proceeding with smart contracts. This enables the DAO to become truly autonomous and sustainable and avoids potentially destabilizing changes from having to be made in the future.Funding – in other words, what will power the DAO? Smart contracts must create and distribute some form of internal property that allows the organization to establish a voting mechanism and incentivize activities. Native tokens are one such form of property, giving interested individuals the right to vote among other things.Deployment – a decentralized autonomous organization reaches critical mass when it has secured enough funding for deployment. Moving forward, strategic decisions are made by token holders who automatically become stakeholders in the organization. Provided that the token distribution policy and consensus mechanisms are robust, these stakeholders will make decisions that result in beneficial outcomes for the business.DAO builders and infrastructure platformsSeveral service providers exist to provide the tools and platforms necessary to create a decentralized organization.
Following is a look at some of the best-known platforms:
DAOstack – providing a large coordination platform for DAOs with a focus on solving the problems associated with large-scale decentralized decision making. Decision-makers can use the native token GEN to promote proposals they deem important.Aragon – a dApp on the Ethereum blockchain allowing the creation and management of a range of organization types. These include companies, NGOs, hedge funds, and open source projects. Members who hold ANT native tokens have the right to be involved in decision-making proposals regarding smart contract upgrades and fiscal and token policy.Colony – ideal for the community-led organization that wants to utilize “plug-in style” payment and collaboration tools. Colony is web-based and as a consequence is more open than organization-based platforms like Aragon.Key takeaways:A decentralized autonomous organization is any organization run autonomously using smart contracts on a blockchain network. Instead of the centralized, hierarchical decision-making model, power resides with those who own native tokens.
Moving to decentralized and autonomous management requires important groundwork. Robust smart contracts and a native token system must be created before the management model can be deployed.
Depending on the needs of a business, there are several DAO service and platform providers. These include DAOstack, Aragon, and Colony.
Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is Decentralized Autonomous Organization? DAO In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is An Altcoin And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models

An altcoin is a general term describing any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. Indeed, as Bitcoin started to evolve since its inception, back in 2009, many other cryptocurrencies sprouted due to philosophical differences with the Bitcoin protocol but also to cover wider use cases that the Bitcoin protocol could enable.
Understanding altcoinAltcoins are cryptocurrency alternatives to Bitcoin using the same blockchain technology to enable secure peer-to-peer transactions.
In terms of investment potential, altcoins are considered high risk. With over 5,000 Bitcoin alternatives in circulation, most will never generate a substantial return. They are also highly volatile and so are more attractive to certain investors because of potentially higher ROI.
Dogecoin is one such example of a volatile altcoin. The cryptocurrency soared in value during early 2021 for no other reason than an increase in buyers. As the price began to rise, more investors purchased Dogecoin and continued to fuel its popularity. Of course, altcoin prices can drop just as dramatically as investor sentiment shifts.
Some of the more successful altcoin currencies
The most successful altcoins are those offering some perceived benefit over Bitcoin.
Following is a look at a few of them:Litecoin – compared to Bitcoins that are produced every 10 minutes, Litecoins are produced every 2.5 minutes. This makes payment processing more efficient. Litecoins can also be mined with common computer hardware – it does not require the costly hardware of Bitcoin mining.Stablecoins – designed specifically to combat typical cryptocurrency volatility by tying their value to an underlying security, index, or commodity. Facebook-owned Diem is one such example of a stablecoin. Ether – running on the Ethereum network, Ether is currently the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap behind Bitcoin. Unlike Bitcoin which serves primarily to be a store of value, Ether was developed to monetize Ethereum smart contracts and dApps.Cardano – a proof-of-stake (PoS) cryptocurrency where the creator of the next block in the chain is chosen according to their wealth or holdings. Aside from providing decentralized financial services, Cardano seeks to provide solutions for chain inoperability, voter fraud, and legal contract tracing among other things.Stellar Lumens – a cryptocurrency providing enterprise solutions on the open blockchain Stellar network. Stellar Lumens are utilized in large transactions between banks and investment firms that used to take several days and involve costly intermediaries. It also allows transactions across different currencies. Altcoin due diligenceIn addition to volatility, some altcoins have been subject to fraud, malware, and scams.
Here is a list of questions to consider before purchasing any alternative Bitcoin cryptocurrency:
Who is issuing the altcoin and how are they deriving value from transactions? What is the background in the industry?Can altcoin investment be bought and sold easily? Are there fees associated with selling?Do financial statements exist? Has the altcoin provider been audited?What legal protections exist in the event the network is compromised, hacked, and funds are stolen?What are the specific rights of the investor?Key takeaways:Altcoin is a term given to any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin. Most (but not all) use the same blockchain technology to provide secure peer-to-peer transactions.
Altcoins are generally developed to address shortfalls in Bitcoin. For example, Litecoin provides faster payment processing and stablecoins are tied to external assets to reduce volatility.
Many altcoin options have small market caps and are less regulated than some of the bigger players. This makes them vulnerable to fraud, malware, and scams.
Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is An Altcoin And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Application Binary Interface And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models
An Application Binary Interface (ABI) is the interface between two binary program modules that work together. An ABI is a contract between pieces of binary code defining the mechanisms by which functions are invoked and how parameters are passed between the caller and callee. ABIs have become critical in the development of applications leveraging smart contracts, on Blockchain protocols like Ethereum.
Understanding an Application Binary InterfaceIn understanding an Application Binary Interface, it can be helpful to first define the Application Programming Interface (API).
Think of an API as a contract between pieces of source code. This contract defines the return value and parameters of a function and dictates whether inheritance is allowed. An API is enforced by a compiler, or a program converting instructions into a format that can be read and executed by a computer. In other words, the API contains instructions on what the source code can and cannot do as part of a platform operating system.
An ABI, on the other hand, is a contract between pieces of binary code. An Application Binary Interface defines the mechanisms by which functions are invoked and how parameters are passed between the caller and callee. The ABI also governs how programs are loaded into memory and how libraries are implemented. Indeed, the ABI is enforced by the linker – defined as a program used with a compiler to provide links to libraries needed for an executable program.
This means the ABI contains rules on how unrelated code must work together and how processes should coexist on the same system. While the API lists the functions that may be called, the ABI dictates how each function may be called. ABIs are commonly established between user programs and libraries but also in OS services and programming languages.
Application Binary Interface functionsABIs cover a variety of functions, including:
Processor instruction sets that denote details such as memory access types and register file structure.How an application makes system calls to the OS and whether direct systems calls or procedure calls are used to system call stubs.Basic data type layout, size, and alignment.Calling convention, which dictates how arguments of functions are passed and return values retrieved. Calling convention controls which parameters are passed on the stack and which are passed in registers. It also assigns registers to function parameters and determines whether the first function parameter passed on the stack is pushed first or last.
Complete and embedded ABIsComplete ABIsA complete ABI enables a program from the OS supporting it to run without modifications on any similar system. This is on the proviso that shared libraries exist and similar prerequisites are satisfied.
For example, the Intel Binary Compatibility Standard (iBCS) is the standardized ABI for Unix operating systems on Intel-compatible computers.
Embedded ABIsEmbedded ABIs (EABIs) specify conventions for register usage, data types, stack frame organization, and file formats for use in an embedded operating system.
Object code created by compilers to support the EABI is compatible with the code generated by other compilers. This enables developers to link the library generated with one compiler with the library generated by another using object code.
Ultimately, embedded ABIs are designed for performance optimization. Operating within the limits of an embedded system, the ABI removes the majority of abstractions made between kernel and user code in complex operating systems.
PowerPC – created in an alliance between Apple, IBM, and Motorola – is an example of a widely used EABI.
Key takeaways:An Application Binary Interface is the interface between two binary program module programs allowing them to work together.
While an Application Programming Interface (API) is a contract between two pieces of source code, an ABI is a contract between two sources of binary code. The ABI also dictates how functions may be called from the API.
Application Binary Interfaces are present in several scenarios. They influence processor instruction sets and determine how an application makes system calls to the OS. An ABI also dictates the layout, size, and alignment of basic data types.
Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Application Binary Interface And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
51% Attack And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models
A 51% Attack is an attack on the blockchain network by an entity or organization. The primary goal of such an attack is the exclusion or modification of blockchain transactions. A 51% attack is carried out by a miner or group of miners endeavoring to control more than half of a network’s mining power, hash rate, or computing power. For this reason, it is sometimes called a majority attack. This can corrupt a blockchain protocol that malicious attackers would take over.
Understanding a 51% attackIn controlling at least 51% of the blockchain network, miners can double-spend cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. This is achieved by reversing transactions that have already taken place. Consider the example of the purchase of a new car for 10 Bitcoins. Once the car has been delivered to the buyer, logic dictates that Bitcoins are transferred to the seller. In a 51% Attack, however, the buyer (attacker) cancels the transaction before it is confirmed. This means they take ownership of the car in addition to the 10 Bitcoins used to fund its “purchase”.
The attack relies on a few conditions being met. Miners intent on attacking the network need enough computational power to solve equations more quickly than other miners. This gives them the ability to act as somewhat of an auditor, reversing transactions that need to be confirmed while also preventing new transactions from being confirmed.
Invariably, attackers use their power to solve equations in secret and not broadcast solutions to the rest of the network. This results in the formation of a separate and secret blockchain operating in parallel to the original, legitimate chain. Corrupt miners then spend their surreptitiously mined Bitcoin rewards on this legitimate version.
Preventing a 51% attackGenerally speaking, the likelihood of a 51% attack occurring is almost nil. Some have gone as far as suggesting that such an attack is purely theoretical. As a blockchain grows large enough, it becomes near impossible for a single entity to obtain enough computing power to overwhelm all other users. Such a move would also require an exorbitant amount of capital to fund energy and hardware costs.
Nevertheless, the mining pool GHash.IO reached a level of approximately 55% of Bitcoin’s hash rate over 24 hours in June 2014. While this was not a deliberate attempt to gain control of the network, it does illustrate that an attack is possible. This is particularly salient for networks with a smaller hash rate such as Ethereum Classic, which has suffered from numerous 51% attacks in recent years.
Preventing attacks on smaller networks means following the example of Bitcoin. The first and most obvious strategy involves the decentralization of mining power to ensure that no one has more than 50% control.
The second (and arguably longer-term) strategy involves making smaller networks more robust. In the case of Bitcoin, the network is so robust that attackers can make more money mining legitimately than they can by orchestrating a 51% Attack. This fact alone reduces the vulnerability of the network significantly.
Key takeaways:A 51% attack is an attack on the blockchain network by an entity or organization for financial gain.A 51% attack allows the attacker to double-spend cryptocurrency by reversing or preventing transactions from being confirmed.A 51% attack on the Bitcoin network is near impossible because of the integrity and size of the blockchain network. Such an attack would also require immense financial resources. However, smaller networks such as Ethereum Classic are more vulnerable.Read Next: Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Ethereum, Blockchain.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post 51% Attack And Why It Matters To Understand Blockchain Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



