Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 136
December 12, 2021
What Is Disruptive Innovation? Disruptive Innovation In A Nutshell
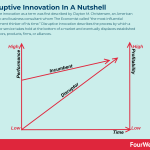

Disruptive innovation as a term was first described by Clayton M. Christensen, an American academic and business consultant whom The Economist called “the most influential management thinker of his time.” Disruptive innovation describes the process by which a product or service takes hold at the bottom of a market and eventually displaces established competitors, products, firms, or alliances.
Understanding disruptive innovationChristensen first introduced the theory behind disruptive innovation in his 1997 book The Innovator’s Dilemma and a follow-up entitled The Innovator’s Solution. In the books, he posited that there were two types of technologies businesses dealt with. Sustainable technologies enabled a business to improve its performance over a predictable timeframe and remain competitive. Disruptive technologies, on the other hand, were less predictable and potentially more devastating to industry competitiveness.
Disruptive innovation typically occurs when a product or service establishes itself at the bottom of a market. This process is facilitated by the product being less expensive and thus more accessible than competitor products, which tend to be expensive, sophisticated, and accessible to relatively few consumers.
It’s important to note that disruptive innovations are not breakthrough technologies that turn good products into great products. Instead, they are simply innovations that make products or services more accessible and affordable to a larger percentage of the population.
Why does disruptive innovation occur?Disruptive innovation occurs because most companies tend to innovate faster than their customers’ needs evolve. This causes a situation where the end product or service is too sophisticated, complex, or expensive for the majority of consumers in a target audience.
So why do companies pursue innovation? Historically, innovation has been associated with success as it helps the business corner the higher end of the market with the most profitable products. But this strategy leaves room at the bottom end of the market for a disruptive innovator to enter and potentially become a threat.
Disruptive innovators tend to operate in markets characterized by lower gross margins, smaller target markets, and simpler products and services. These traits make the bottom end of the market unprofitable and undesirable for firms that have already developed sustaining innovations.
What are the ingredients for disruptive innovation?In the previous section, we talked about the conditions necessary for a new company to enter the bottom end of the market.
Let’s now explain how this new company can become disruptive by looking at the required ingredients:
Enabling technology – or technology that can significantly change or improve the way consumers do things. The speed with which disruptive innovation can occur is a function of how quickly enabling technology is developed and improved upon for mass uptake. Having said that, it should be noted that the speed of disruption is not the sole determinant of success.Coherent value network – for disruptive innovation to occur, the network of suppliers, distributors, and partners must also benefit from the enabling technology. It is not enough for consumers alone to benefit.Innovative business model – this is simply a business model that targets consumers at the bottom end of the market with innovative products. Since the model is characterized by low-profit margins and simpler product design, the solutions should be easy to use and economical to produce. Examples of disruptive innovationThere are countless examples of disruptive innovation in business. In this section, we’ll take a look at some of the more interesting case studies.
AcademiaEncyclopedia Britannica was a market leader in encyclopedias and had been printed for 244 years until the last copy was released in 2012.
The publisher, Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc., had the high end of the market cornered, with each edition selling for over $1000.
However, print encyclopedias were quickly usurped by free, digital versions such as Wikipedia. Wikipedia offered an encyclopedia of unlimited size that was portable and updated constantly. Encyclopedia Britannica, with its vast bulk and update cycles lasting more than a year, was ultimately displaced by a disruptive innovator.
Media entertainmentAt its peak, video and game rental company Blockbuster operated more than 9,000 stores and employed approximately 84,300 people.
Though video and game rentals were relatively cheap, increasing data speeds and bandwidth instituted a general shift toward video streaming.
Blockbuster was displaced by smaller players such as Netflix, who offered a cheaper and more convenient alternative. Today, the company owns the rights to more than 13,000 titles, with prices starting a mere $8.99/month.
PhotographyFilm companies such as Kodak enjoyed market dominance in the photography industry for decades. The company’s photographic film products were synonymous with quality and professionalism, but Kodak was eventually displaced by digital camera manufacturers such as Canon, Sony, Pentax, and Nikon.
Digital photography disrupted film photography because it was more convenient and required less expertise to develop photographs. Though digital cameras were relatively expensive when they first appeared, the number of digital photographs a consumer could take was not limited by the cost or restrictiveness of film.
TransportationTo date, Concorde is the only supersonic jet that has entered into commercial production. High operating costs and limited seat capacity meant Concorde tickets were mostly purchased by the wealthy or super-wealthy.
Concorde services ended in 2003 due to high operating costs and a high-profile accident. However, the rising affordability of small, private jets was also a contributing factor. Though these jets did not travel at supersonic speed, their quieter operation meant they could fly routes off-limits to the extremely loud Concorde.
Many private jet owners also enjoyed the ability to fly between airports without having to move through the airport terminal with hundreds of commercial passengers.
Key takeaways:Disruptive innovation describes the process by which a product or service takes hold at the bottom of a market and eventually displaces established competitors, products, firms, or alliances. The term was popularised by American academic and business consultant Clayton M. Christensen.Disruptive innovation occurs since most companies tend to innovate faster than their customers’ needs evolve. Innovation typically favors products or services that are too sophisticated, complex, or expensive for the target audience.For a market entrant to become a disruptive innovator, there are three crucial ingredients. Technology with the capacity to significantly improve the way consumers do things must first exist. This technology must also benefit suppliers and contractors. Lastly, there must also be a business model that targets consumers at the bottom end of the market with innovative products.Connected Strategy Frameworks Ansoff Matrix You can use the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic framework to understand what growth strategy is more suited based on the market context. Developed by mathematician and business manager Igor Ansoff, it assumes a growth strategy can be derived by whether the market is new or existing, and the product is new or existing.
You can use the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic framework to understand what growth strategy is more suited based on the market context. Developed by mathematician and business manager Igor Ansoff, it assumes a growth strategy can be derived by whether the market is new or existing, and the product is new or existing.Read: Ansoff Matrix In A Nutshell
BCG Matrix In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.
In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.Read: BCG Matrix
Balanced Scorecard First proposed by accounting academic Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system that allows an organization to focus on big-picture strategic goals. The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard include financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. From there, according to the balanced scorecard, it’s possible to have a holistic view of the business.
First proposed by accounting academic Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system that allows an organization to focus on big-picture strategic goals. The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard include financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. From there, according to the balanced scorecard, it’s possible to have a holistic view of the business.Read: Balanced Scorecard
Blue Ocean Strategy A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created. At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken. Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.
A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created. At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken. Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.Read: Blue Ocean Strategy
PEST Analysis The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization. This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses that can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.
The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization. This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses that can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.Read: Pestel Analysis
Scenario Planning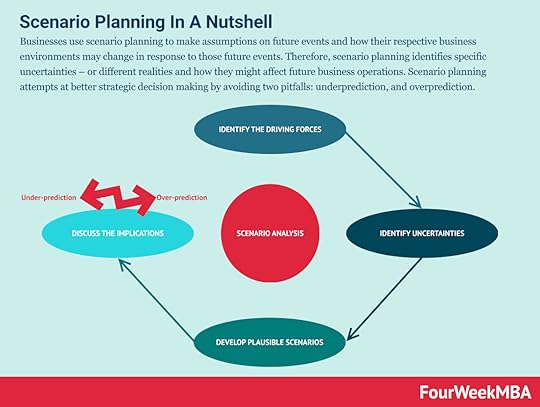 Businesses use scenario planning to make assumptions on future events and how their respective business environments may change in response to those future events. Therefore, scenario planning identifies specific uncertainties – or different realities and how they might affect future business operations. Scenario planning attempts at better strategic decision making by avoiding two pitfalls: underprediction, and overprediction.
Businesses use scenario planning to make assumptions on future events and how their respective business environments may change in response to those future events. Therefore, scenario planning identifies specific uncertainties – or different realities and how they might affect future business operations. Scenario planning attempts at better strategic decision making by avoiding two pitfalls: underprediction, and overprediction.Read: Scenario Planning
SWOT Analysis A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.
A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.Read: SWOT Analysis In A Nutshell
Growth Matrix In the FourWeekMBA growth matrix, you can apply growth for existing customers by tackling the same problems (gain mode). Or by tackling existing problems, for new customers (expand mode). Or by tackling new problems for existing customers (extend mode). Or perhaps by tackling whole new problems for new customers (reinvent mode).
In the FourWeekMBA growth matrix, you can apply growth for existing customers by tackling the same problems (gain mode). Or by tackling existing problems, for new customers (expand mode). Or by tackling new problems for existing customers (extend mode). Or perhaps by tackling whole new problems for new customers (reinvent mode).Read: Growth Matrix In A Nutshell
Comparable Analysis Framework A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company. To find comparables you can look at two key profiles: the business and financial profile. From the comparable company analysis it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.
A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company. To find comparables you can look at two key profiles: the business and financial profile. From the comparable company analysis it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.Read: Comparable Analysis Framework In A Nutshell
Business Model Canvas The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in Busines Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising: key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.
The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in Busines Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising: key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.Read: Business Model Canvas In A Nutshell
Business Experimentation Business experiments help entrepreneurs test their hypotheses. Rather than define the problem by making too many hypotheses, a digital entrepreneur can formulate a few assumptions, design experiments, and check them against the actions of potential customers. Once measured, the impact, the entrepreneur, will be closer to define the problem.
Business experiments help entrepreneurs test their hypotheses. Rather than define the problem by making too many hypotheses, a digital entrepreneur can formulate a few assumptions, design experiments, and check them against the actions of potential customers. Once measured, the impact, the entrepreneur, will be closer to define the problem.Read: Business Experimentation
Speed Reversibility
The speed-reversibility Matrix, by FourWeekMBA will help you understand how to allocate the resources based on the worst-case-scenario-test.
Read: Speed-Reversibility Matrix
Blue Ocean A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created. At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken. Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.
A blue ocean is a strategy where the boundaries of existing markets are redefined, and new uncontested markets are created. At its core, there is value innovation, for which uncontested markets are created, where competition is made irrelevant. And the cost-value trade-off is broken. Thus, companies following a blue ocean strategy offer much more value at a lower cost for the end customers.Read: Blue Ocean Strategy
BCG Matrix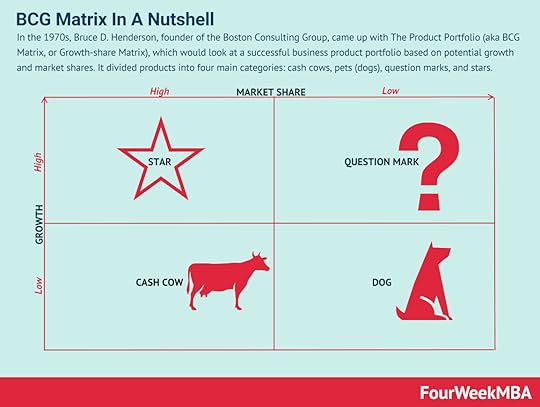 In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.
In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.Read more: BCG Matrix
AIDA Model AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys.
AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys.Read more: AIDA Model
Pirate Funnel Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.
Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.Read more: Pirate Funnel
The post What Is Disruptive Innovation? Disruptive Innovation In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
December 9, 2021
How Does FTX Work And Make Money?
 FTX is a cryptocurrency exchange platform headquartered in the Bahamas but incorporated in Antigua and Barbuda. The platform was founded by Sam Bankman-Fried who became inspired to make money for the greater social good while studying at MIT.On a mobile-based trading app, retail and institutional traders can buy and sell futures, options, leveraged tokens, fiat currency, cryptocurrency, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Users can receive discounts on trading fees by using the native token FTT.FTX makes money through various trading fees, including maker fees, taker fees, NFT fees, and margin borrower interest. The company also charges interest on its institutional loan service and collects a fee from merchants that want to accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment.FTX Origing Story
FTX is a cryptocurrency exchange platform headquartered in the Bahamas but incorporated in Antigua and Barbuda. The platform was founded by Sam Bankman-Fried who became inspired to make money for the greater social good while studying at MIT.On a mobile-based trading app, retail and institutional traders can buy and sell futures, options, leveraged tokens, fiat currency, cryptocurrency, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Users can receive discounts on trading fees by using the native token FTT.FTX makes money through various trading fees, including maker fees, taker fees, NFT fees, and margin borrower interest. The company also charges interest on its institutional loan service and collects a fee from merchants that want to accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment.FTX Origing StoryFTX is a cryptocurrency exchange platform headquartered in the Bahamas but incorporated in Antigua and Barbuda. The platform was founded by Sam Bankman-Fried in 2019.
While studying at MIT, Bankman-Fried stumbled upon the philosophy of effective altruism. The movement, which was founded by two Oxford University professors, encourages individuals to use evidence and reason to determine how to benefit others as much as possible. Inspired by a meeting with one of these professors, he decided to devote his life to earning money for the express purpose of giving it away to those in need.
In the summer of his junior year, he decided to intern at Wall Street firm Jane Street Capital. There, he discovered a passion for trading ETFs and Bitcoin, with the latter making him thousands of dollars in arbitrage profit between American and Japanese exchanges. This income was then used to found Alameda Research, a quantitative trading firm moving as much as $25 million in Bitcoin daily.
Over time, however, Bankman-Fried and his associates grew tired of the one-dimensionality of mainstream exchanges. Since they were mostly designed for inexperienced retail traders, most only allowed the buying and selling of cryptocurrencies. This provided the impetus for the launching of FTX in June 2019, a platform now known for offering more sophisticated derivative products including futures, options, and tokenized stocks that track the value of real shares in companies such as Tesla and BioNTech.
In July 2021, it was reported that FTX was averaging $10 billion in daily trading volume across more than 1 million users. Recent figures suggest the company is worth around $18 billion.
How does FTX work?On the FTX platform, retail and institutional traders can buy and sell futures, options, leveraged tokens, fiat currency, cryptocurrency, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Trading is performed in a mobile-based app, which lets traders build a customized interface layout using drag and drop boxes.
The company has also developed an exchange token for use in the FTX ecosystem called FTT. Users receive lower trading fees for holding FTT and the token can also be used as futures collateral and for staking.
FTX customers can also receive a branded debit card which lets them spend crypto assets on offline purchases.
How does FTX make money?In line with its diverse product offering, FTX has a varied revenue generation strategy. In this section, we’ll take a look at some of the main sources of income.
Trading feesMost revenue is derived from trading fees, with the company utilizing a tiered structure as follows:
Tier 1 – 0.020% maker fee and 0.070% taker fee.Tier 2 (30-day volume over $2 million USD) – 0.015% maker fee and 0.060% taker fee.Tier 3 (30-day volume over $5 million) – 0.010% maker fee and 0.055% taker fee.Tier 4 (30-day volume over $10 million) – 0.005% maker fee and 0.050% taker fee.Tier 5 (30-day volume over $25 million) – 0.000% maker fee and 0.045% taker fee.Tier 6 (30-day volume over $50 million) – 0.000% maker fee and 0.040% taker fee.As noted earlier, these fees can be reduced if the user stakes FTT. Taker fees can be reduced to as little as 0.015% depending on the amount staked.
What’s more, the company charges borrowers a daily interest rate when margin trading. Leveraged tokens, which allow users to take a leveraged position in a cryptocurrency of their choice, also come with a 0.10% redemption fee and 0.03% daily management fee.
LoansFor its most sophisticated traders that meet certain criteria, FTX will extend a line of credit.
The company collects interest on these loans, with the interest rate likely to be dependent upon the prior trading performance of the entity and how much collateral they can access.
NFT feesFTX NFTs is an NFT marketplace launched in September 2021 and built on the Solana blockchain.
Here, the company makes money by charging a 5% fee to both the buyer and the seller on each trade or sale.
InvestmentsSince its inception, FTX has made several investments in other related start-ups.
These include $150 million to acquire the cryptocurrency tracking app Blockfolio and a $100 million investment with two other partners in Web3 gaming development.
In many cases, FTX sells the investment at a later date for a profit. In the interim, it collects valuable user data that guides its expansion or product development strategies.
Interchange and payment feesLike many neobanks and related organizations, FTX makes money on interchange fees.
These fees are paid by the merchant to FTX whenever a customer uses its branded debit card to make a purchase. Note that FTX has to share this fee with the card issuer Visa.
For businesses that want to accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment, they can sign up for FTX Pay. For the privilege, FTX charges a 1% fee of the total purchase amount.
Connected Business Concepts According to Joel Monegro, a former analyst at USV (a venture capital firm) the blockchain implies value creation in its protocols. Where the web has allowed the value to be captured at the applications layer (take Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others). In a Blockchain Economy, this value might be captured by the protocols at the base of the blockchain (for instance Bitcoin and Ethereum). However, according to blockchain investor Paivinen due to ease of forking, incentives to compete and improved interoperability and interchangeability also in a blockchain-based economy, protocols might get thinner. Although the marginal value of scale might be lower compared to a web-based economy, where massive scale created an economic advantage. The success of the Blockchain will depend on its commercial viability!
According to Joel Monegro, a former analyst at USV (a venture capital firm) the blockchain implies value creation in its protocols. Where the web has allowed the value to be captured at the applications layer (take Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others). In a Blockchain Economy, this value might be captured by the protocols at the base of the blockchain (for instance Bitcoin and Ethereum). However, according to blockchain investor Paivinen due to ease of forking, incentives to compete and improved interoperability and interchangeability also in a blockchain-based economy, protocols might get thinner. Although the marginal value of scale might be lower compared to a web-based economy, where massive scale created an economic advantage. The success of the Blockchain will depend on its commercial viability! A Proof of Stake (PoS) is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. As such it is, together with Proof of Work, among the key consensus algorithms for Blockchain protocols (like the Ethereum’s Casper protocol). Proof of Stake has the advantage of security, reduced risk of centralization, and energy efficiency.
A Proof of Stake (PoS) is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. As such it is, together with Proof of Work, among the key consensus algorithms for Blockchain protocols (like the Ethereum’s Casper protocol). Proof of Stake has the advantage of security, reduced risk of centralization, and energy efficiency. A Proof of Work is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. In a Proof of Work, miners compete to complete transactions on the network, by commuting hard mathematical problems (i.e. hashes functions) and as a result they get rewarded in coins.
A Proof of Work is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. In a Proof of Work, miners compete to complete transactions on the network, by commuting hard mathematical problems (i.e. hashes functions) and as a result they get rewarded in coins. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like. A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model.
A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model. Ethereum was launched in 2015 with its cryptocurrency, Ether, as an open-source, blockchain-based, decentralized platform software. Smart contracts are enabled, and Distributed Applications (dApps) get built without downtime or third-party disturbance. It also helps developers build and publish applications as it is also a programming language running on a blockchain.
Ethereum was launched in 2015 with its cryptocurrency, Ether, as an open-source, blockchain-based, decentralized platform software. Smart contracts are enabled, and Distributed Applications (dApps) get built without downtime or third-party disturbance. It also helps developers build and publish applications as it is also a programming language running on a blockchain. The Graph is an ERC20 Utility Token (built on top of Ethereum) to enable consumers to freely query the blockchain through a fully decentralized database kept by indexers, incentivized by the payment of tokens (called GRT). The network is also ministered by curators and delegators that help maintain a high-quality index.
The Graph is an ERC20 Utility Token (built on top of Ethereum) to enable consumers to freely query the blockchain through a fully decentralized database kept by indexers, incentivized by the payment of tokens (called GRT). The network is also ministered by curators and delegators that help maintain a high-quality index. BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web.
BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web. In 2012, co-founders Christian Larsen and Jed McCaleb created Ripple, a technology acting as both a pre-mined cryptocurrency called XRP and a digital payment platform enabling monetary transactions. Where Ripple is the tech company, XRP is the decentralized ledger.
In 2012, co-founders Christian Larsen and Jed McCaleb created Ripple, a technology acting as both a pre-mined cryptocurrency called XRP and a digital payment platform enabling monetary transactions. Where Ripple is the tech company, XRP is the decentralized ledger. In 2014, Jed McCaleb – which also played a key role in the development of Ripple – created a cryptocurrency to provide fast, reliable, and affordable money transactions. The same cryptocurrency has considerably grown seven years later. It is now one of the most stellar cryptocurrencies to provide a real-time platform that links banks, payment systems, and people. Meet, Stellar!
In 2014, Jed McCaleb – which also played a key role in the development of Ripple – created a cryptocurrency to provide fast, reliable, and affordable money transactions. The same cryptocurrency has considerably grown seven years later. It is now one of the most stellar cryptocurrencies to provide a real-time platform that links banks, payment systems, and people. Meet, Stellar! In early 2019, a joint project between TRON and BitTorrent Foundation called BitTorrent Token came to fruition. BitTorrent Token launched to tokenize in-demand file-sharing protocol and enhance content delivery and bandwidth accessibility with blockchain technology.
In early 2019, a joint project between TRON and BitTorrent Foundation called BitTorrent Token came to fruition. BitTorrent Token launched to tokenize in-demand file-sharing protocol and enhance content delivery and bandwidth accessibility with blockchain technology. Chainlink is considered the most established decentralized oracle network. As an ecosystem housing several decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. As a decentralized oracle service built on Ethereum, Chainlink has the power to support the development of blockchain solutions for both traditional businesses and enterprises.
Chainlink is considered the most established decentralized oracle network. As an ecosystem housing several decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. As a decentralized oracle service built on Ethereum, Chainlink has the power to support the development of blockchain solutions for both traditional businesses and enterprises. Uniswap is a renowned decentralized crypto exchange created in 2018 and based on the Ethereum blockchain, to provide liquidity to the system. As a cryptocurrency exchange technology that operates on a decentralized basis. The Uniswap protocol inherited its namesake from the business that created it — Uniswap. Through smart contracts, the Uniswap protocol automates transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
Uniswap is a renowned decentralized crypto exchange created in 2018 and based on the Ethereum blockchain, to provide liquidity to the system. As a cryptocurrency exchange technology that operates on a decentralized basis. The Uniswap protocol inherited its namesake from the business that created it — Uniswap. Through smart contracts, the Uniswap protocol automates transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. In essence, Polkadot is a cryptocurrency project created as an effort to transform and power a decentralized internet, Web 3.0, in the future. Polkadot is a decentralized platform, which makes it interoperable with other blockchains.
In essence, Polkadot is a cryptocurrency project created as an effort to transform and power a decentralized internet, Web 3.0, in the future. Polkadot is a decentralized platform, which makes it interoperable with other blockchains. Designed and created as an alternative to Ethereum, Cardano claims to be the first decentralized blockchain protocol to use a scientific approach and undergo a peer evaluation.
Designed and created as an alternative to Ethereum, Cardano claims to be the first decentralized blockchain protocol to use a scientific approach and undergo a peer evaluation. Solana is a blockchain network with a focus on high performance and rapid transactions. To boost speed, it employs a one-of-a-kind approach to transaction sequencing. Users can use SOL, the network’s native cryptocurrency, to cover transaction costs and engage with smart contracts.
Solana is a blockchain network with a focus on high performance and rapid transactions. To boost speed, it employs a one-of-a-kind approach to transaction sequencing. Users can use SOL, the network’s native cryptocurrency, to cover transaction costs and engage with smart contracts.Get The 450 Pages Blockchain Business Models Book

Read Next: Coinbase Business Model, Metamask, Rainbow.
Read Also: BAT Token, Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Ethereum, Solana, Blockchain, BAT, Monero, Ripple, Litecoin, Stellar, Dogecoin, Bitcoin Cash, Filecoin.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does FTX Work And Make Money? appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
The Pinduoduo Business Model In A Nutshell
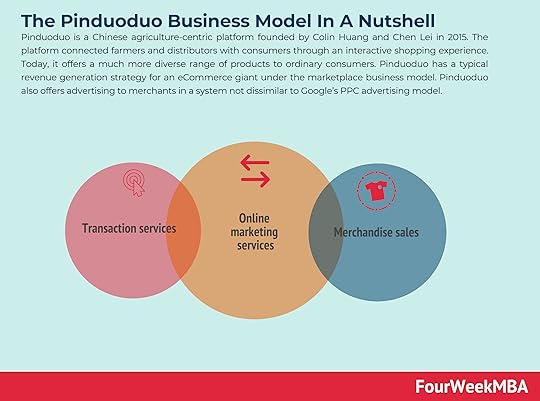 Pinduoduo is a Chinese agriculture-centric platform founded by Colin Huang and Chen Lei in 2015. The platform connected farmers and distributors with consumers through an interactive shopping experience. Today, it offers a much more diverse range of products to ordinary consumers.Pinduoduo has a typical revenue generation strategy for an eCommerce giant under the marketplace business model. Pinduoduo also offers advertising to merchants in a system not dissimilar to Google’s PPC advertising model.Pinduoduo Origin Story
Pinduoduo is a Chinese agriculture-centric platform founded by Colin Huang and Chen Lei in 2015. The platform connected farmers and distributors with consumers through an interactive shopping experience. Today, it offers a much more diverse range of products to ordinary consumers.Pinduoduo has a typical revenue generation strategy for an eCommerce giant under the marketplace business model. Pinduoduo also offers advertising to merchants in a system not dissimilar to Google’s PPC advertising model.Pinduoduo Origin StoryPinduoduo is a Chinese agriculture-centric platform founded by Colin Huang and Chen Lei in 2015. The platform originally connected farmers and distributors with consumers through an interactive shopping experience.
Pinduoduo is the fourth start-up for ex-Google employee Colin Huang, who had prior experience in developing eCommerce algorithms and chat-based gaming systems. Huang had the vision to combine the best elements of Chinese giants Alibaba and Tencent since the two companies did not understand how the other made money. Indeed, Alibaba struggled to create an online community despite achieving great success selling online goods. Tencent, on the other hand, was a social media conglomerate that had failed to leverage its massive user base in eCommerce.
Central to the future success of Pinduoduo was Huang’s belief that shopping was like a game. To that end, users on the platform could enjoy large discounts if they were able to convince family and friends to purchase in bulk. Translating this idea into a working platform required more work and an initial $8 million round of funding. Pinduoduo then went on an aggressive recruitment drive, seeking out new graduates hungry for success and single individuals unburdened by family commitments in particular.
Pinduoduo started by selling fruits and vegetables with more attractive fees than competitors such as Alibaba and JD.com. This attracted millions of working-class, price-conscious Chinese citizens who pushed monthly revenue to $152 million by 2016. Many of these citizens lived in remote or rural areas where it had been previously uneconomical to ship products.
To profit from the more affluent end of the market, Pinduoduo began onboarding international brands such as Nike and Apple. No longer confined to agricultural products, the platform now sells a range of items including liquor, cosmetics, clothing, electronics, and baby supplies.
In April 2021, Pinduoduo surpassed Alibaba to become China’s largest eCommerce site in terms of annual active users. Four months later, the company posted its first quarterly profit of $372 million.
Pinduoduo revenue generationPinduoduo has a typical revenue generation strategy for an eCommerce giant under the marketplace business model. The company makes money through transaction services, merchandise sales, and online marketing services.
Transaction servicesThe company charges merchants fees for transaction-related services provided, and it also rewards merchants who sell high-quality products
and provide superb services with preferential fee rates.
In this case, the company, as it highlights in the financials, “charges fees for transaction services to merchants for sales transactions completed on the Group’s platform, where the Group does not take control of the products provided by the merchants at any point in the time during the
transactions and does not have latitude over pricing of the merchandise.”
The fees are determined as a percentage of the purchase price of the merchandise sold by merchants.
Transaction services revenues represented about 10% of the company’s revenues in 2020, per its financials.
Merchandise salesMerchandise sales are generated as a small portion of revenues from online direct sales, where the company acquires products from suppliers and sells them directly to users.
How does the merchandise sales model work?
As the company shows in its financials, in certain cases it acquires merchandise from suppliers and sells directly to consumers. Thus acting as a principal for and taking control of the merchandise.
Merchandise sales revenues represented about 10% of the company’s revenues in 2020, per its financials.
Online marketing servicesAs reported in its financials, Pinduoduo provides online marketing services primarily to “allow merchants to bid for keywords that match product listings appearing in search results on its platform and advertising placements such as banners, links and logos. The placement and the price for such placement are determined through an online bidding system.”
In a similar vein to Google’s PPC advertising, Pinduoduo merchants can also bid for keywords to have their product listings show in search results.
The online bidding system determines the price paid by each merchant and where the ad will be placed on the platform, which uses recommendation algorithms to show highly targeted ads based on a user’s browsing behavior.
The advertising platform also covers video ads, through browsing rather than searching.
As the company highlights display marketing services are provided allowing merchants to place advertisements on the platform primarily at
fixed prices. As highlighted merchants will “prepay for display marketing which is accounted for as customer advances and deferred revenues and revenues are primarily recognized over the period during which the advertising services are provided.”
Over 80% of the company’s revenues came from online marketing services in 2020.
Connected Business Concepts Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.
Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees. Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees.
Taobao is a Chinese eCommerce website, and it is among the most visited websites in the world. Within it also comprises its payment arm, Alipay. Taobao is part of the Alibaba Group, founded by Chinese tech entrepreneur Jack Ma. The company makes money via its Tmalls (e-commerce platform), and through Alipay, mostly via its Escrow service fees. WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it.
WeChat is a “super app” or an app that can do many things, from messaging to mobile payments and social media. Developed by Tencent, WeChat is among the most popular Super Apps in China. WeChat makes money via value-added services (with services like Moments, Public Accounts, and Gaming), advertising, and payments on the transaction processed through it. Read Next: Alibaba Business Model, What Does Tencent Own, WeChat Business Model, Taobao Business Model, Alipay Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post The Pinduoduo Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does MetaMask Work And Make Money?

MetaMask is a software cryptocurrency wallet for the Ethereum blockchain. The platform is the brainchild of Ethereum blockchain advocate Joseph Lubin. The MetaMask wallet is available as a Chrome or Firefox browser extension. Alternatively, it can be accessed through an app. MetaMask makes money on swap fees when users compare or swap Ethereum-based tokens. The company also charges management fees to institutions that desire a more seamless DeFi investment experience.
MetaMask origin storyMetaMask is a software cryptocurrency wallet for the Ethereum blockchain. The platform was created by American blockchain software technology company ConsenSys in 2016.
ConsenSys in turn was founded by Joseph Lubin, a champion of Ethereum’s ecosystem construction responsible for more than 50 well-known growth projects. Lubin is also thought to be a multi-billionaire after being one of the biggest buyers of Ether during its initial crowdfunding.
Essentially, ConsenSys is a start-up studio that incorporates and launches Ethereum-based businesses and provides technology services to other companies. One such business was MetaMask, which was launched in July 2016 and developed by former Apple engineers Aaron Davis and Dan Finlay.
Though uptake was initially sluggish, MetaMask benefitted from the CryptoKitties NFT craze and the increased publicity around cryptocurrency in general. The wallet, which allowed users to exchange and store Ethereum-based tokens, surpassed 1 million downloads in early 2018. Beta versions of an app for Android and iPhone arrived just over a year later.
During the summer of 2020, MetaMask achieved the magical mark of 1 million active monthly users. This number was largely facilitated by the increased usage of DeFi protocols including Yearn Finance, Curve, and MakerDAO.
Today, MetaMask is known as the most useful Ethereum open-source wallet in the world, enabling users to manage their Ethereum assets easily. The platform now boasts more than 10 million monthly active users, with the surge in popularity coming from developing nations such as Vietnam and Nigeria.
How does MetaMask work?The MetaMask wallet is installed as a Chrome or Firefox browser extension. Alternatively, it can be accessed through an app.
The sign-up process requires the user to come up with a password, after which they will be shown twelve so-called “seed words” that they must remember. These words are used if a password is forgotten.
Users can then deposit or send currency and are protected by a private key which is stored locally on their computer. For near 100% security, the MetaMask wallet can be connected to hardware wallets such as Ledger and Trezor.
How does MetaMask make money?MetaMask revenue generation occurs via swap fees, management fees, and merchandise sales. Let’s take a look at these in more detail below.
Swap feesMost company revenue is derived from swap fees, which are charged when users compare and swap tokens within MetaMask itself.
A swap fee, or service fee, of 0.875% is automatically factored into each quote. This feature combines data from decentralized exchange aggregators and market makers to ensure network costs are minimized.
Management feesMetaMask also makes money from MetaMask Institutional, a wallet designed for trading firms and other financial organizations.
MetaMask Institutional offers the same functionality as the consumer wallet, but it also provides access to qualified custodial platforms that help the business make DeFi investments. This is done without comprising operational efficiency, compliance requirements, or institution-required security.
Management fees for this service are undisclosed.
Merchandise salesLastly, the company makes money by selling branded merchandise in its online store.
Items for sale include t-shirts, hats, mugs, activewear, and apparel for pets such as dogs.
Connected Business Concepts According to Joel Monegro, a former analyst at USV (a venture capital firm) the blockchain implies value creation in its protocols. Where the web has allowed the value to be captured at the applications layer (take Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others). In a Blockchain Economy, this value might be captured by the protocols at the base of the blockchain (for instance Bitcoin and Ethereum). However, according to blockchain investor Paivinen due to ease of forking, incentives to compete and improved interoperability and interchangeability also in a blockchain-based economy, protocols might get thinner. Although the marginal value of scale might be lower compared to a web-based economy, where massive scale created an economic advantage. The success of the Blockchain will depend on its commercial viability!
According to Joel Monegro, a former analyst at USV (a venture capital firm) the blockchain implies value creation in its protocols. Where the web has allowed the value to be captured at the applications layer (take Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others). In a Blockchain Economy, this value might be captured by the protocols at the base of the blockchain (for instance Bitcoin and Ethereum). However, according to blockchain investor Paivinen due to ease of forking, incentives to compete and improved interoperability and interchangeability also in a blockchain-based economy, protocols might get thinner. Although the marginal value of scale might be lower compared to a web-based economy, where massive scale created an economic advantage. The success of the Blockchain will depend on its commercial viability! A Proof of Stake (PoS) is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. As such it is, together with Proof of Work, among the key consensus algorithms for Blockchain protocols (like the Ethereum’s Casper protocol). Proof of Stake has the advantage of security, reduced risk of centralization, and energy efficiency.
A Proof of Stake (PoS) is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. As such it is, together with Proof of Work, among the key consensus algorithms for Blockchain protocols (like the Ethereum’s Casper protocol). Proof of Stake has the advantage of security, reduced risk of centralization, and energy efficiency. A Proof of Work is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. In a Proof of Work, miners compete to complete transactions on the network, by commuting hard mathematical problems (i.e. hashes functions) and as a result they get rewarded in coins.
A Proof of Work is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. In a Proof of Work, miners compete to complete transactions on the network, by commuting hard mathematical problems (i.e. hashes functions) and as a result they get rewarded in coins. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like. A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model.
A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model. Ethereum was launched in 2015 with its cryptocurrency, Ether, as an open-source, blockchain-based, decentralized platform software. Smart contracts are enabled, and Distributed Applications (dApps) get built without downtime or third-party disturbance. It also helps developers build and publish applications as it is also a programming language running on a blockchain.
Ethereum was launched in 2015 with its cryptocurrency, Ether, as an open-source, blockchain-based, decentralized platform software. Smart contracts are enabled, and Distributed Applications (dApps) get built without downtime or third-party disturbance. It also helps developers build and publish applications as it is also a programming language running on a blockchain. The Graph is an ERC20 Utility Token (built on top of Ethereum) to enable consumers to freely query the blockchain through a fully decentralized database kept by indexers, incentivized by the payment of tokens (called GRT). The network is also ministered by curators and delegators that help maintain a high-quality index.
The Graph is an ERC20 Utility Token (built on top of Ethereum) to enable consumers to freely query the blockchain through a fully decentralized database kept by indexers, incentivized by the payment of tokens (called GRT). The network is also ministered by curators and delegators that help maintain a high-quality index. BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web.
BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web. In 2012, co-founders Christian Larsen and Jed McCaleb created Ripple, a technology acting as both a pre-mined cryptocurrency called XRP and a digital payment platform enabling monetary transactions. Where Ripple is the tech company, XRP is the decentralized ledger.
In 2012, co-founders Christian Larsen and Jed McCaleb created Ripple, a technology acting as both a pre-mined cryptocurrency called XRP and a digital payment platform enabling monetary transactions. Where Ripple is the tech company, XRP is the decentralized ledger. In 2014, Jed McCaleb – which also played a key role in the development of Ripple – created a cryptocurrency to provide fast, reliable, and affordable money transactions. The same cryptocurrency has considerably grown seven years later. It is now one of the most stellar cryptocurrencies to provide a real-time platform that links banks, payment systems, and people. Meet, Stellar!
In 2014, Jed McCaleb – which also played a key role in the development of Ripple – created a cryptocurrency to provide fast, reliable, and affordable money transactions. The same cryptocurrency has considerably grown seven years later. It is now one of the most stellar cryptocurrencies to provide a real-time platform that links banks, payment systems, and people. Meet, Stellar! In early 2019, a joint project between TRON and BitTorrent Foundation called BitTorrent Token came to fruition. BitTorrent Token launched to tokenize in-demand file-sharing protocol and enhance content delivery and bandwidth accessibility with blockchain technology.
In early 2019, a joint project between TRON and BitTorrent Foundation called BitTorrent Token came to fruition. BitTorrent Token launched to tokenize in-demand file-sharing protocol and enhance content delivery and bandwidth accessibility with blockchain technology. Chainlink is considered the most established decentralized oracle network. As an ecosystem housing several decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. As a decentralized oracle service built on Ethereum, Chainlink has the power to support the development of blockchain solutions for both traditional businesses and enterprises.
Chainlink is considered the most established decentralized oracle network. As an ecosystem housing several decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. As a decentralized oracle service built on Ethereum, Chainlink has the power to support the development of blockchain solutions for both traditional businesses and enterprises. Uniswap is a renowned decentralized crypto exchange created in 2018 and based on the Ethereum blockchain, to provide liquidity to the system. As a cryptocurrency exchange technology that operates on a decentralized basis. The Uniswap protocol inherited its namesake from the business that created it — Uniswap. Through smart contracts, the Uniswap protocol automates transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
Uniswap is a renowned decentralized crypto exchange created in 2018 and based on the Ethereum blockchain, to provide liquidity to the system. As a cryptocurrency exchange technology that operates on a decentralized basis. The Uniswap protocol inherited its namesake from the business that created it — Uniswap. Through smart contracts, the Uniswap protocol automates transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. In essence, Polkadot is a cryptocurrency project created as an effort to transform and power a decentralized internet, Web 3.0, in the future. Polkadot is a decentralized platform, which makes it interoperable with other blockchains.
In essence, Polkadot is a cryptocurrency project created as an effort to transform and power a decentralized internet, Web 3.0, in the future. Polkadot is a decentralized platform, which makes it interoperable with other blockchains. Designed and created as an alternative to Ethereum, Cardano claims to be the first decentralized blockchain protocol to use a scientific approach and undergo a peer evaluation.
Designed and created as an alternative to Ethereum, Cardano claims to be the first decentralized blockchain protocol to use a scientific approach and undergo a peer evaluation. Solana is a blockchain network with a focus on high performance and rapid transactions. To boost speed, it employs a one-of-a-kind approach to transaction sequencing. Users can use SOL, the network’s native cryptocurrency, to cover transaction costs and engage with smart contracts.
Solana is a blockchain network with a focus on high performance and rapid transactions. To boost speed, it employs a one-of-a-kind approach to transaction sequencing. Users can use SOL, the network’s native cryptocurrency, to cover transaction costs and engage with smart contracts.Get The 450 Pages Blockchain Business Models Book

Read Also: BAT Token, Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Ethereum, Solana, Blockchain, BAT, Monero, Ripple, Litecoin, Stellar, Dogecoin, Bitcoin Cash, Filecoin.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does MetaMask Work And Make Money? appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
How Does Rainbow (Wallet) Work And Make Money?
 Rainbow is a fun, simple, and secure Ethereum wallet that helps users manage their assets. The platform was founded by Christian Baroni, Mike Demarais, and Jin Chung in 2019 to make Ethereum technologies more accessible to non-savvy consumers.Rainbow onboards casual users into Web3 in much the same way that Robinhood onboards casual investors into traditional equities. Users can pay for ETH using Apple Pay infrastructure and can connect to other wallets such as MetaMask. Unlike some cryptocurrency exchanges, Rainbow does not hold assets on the behalf of its users. Rainbow revenue generation is undisclosed, though it is likely the platform earns a commission from third-party cryptocurrency exchanges or other infrastructure providers. With a core focus on NFTs, the company may also take a percentage of NFT minting fees as a commission.Origin Story
Rainbow is a fun, simple, and secure Ethereum wallet that helps users manage their assets. The platform was founded by Christian Baroni, Mike Demarais, and Jin Chung in 2019 to make Ethereum technologies more accessible to non-savvy consumers.Rainbow onboards casual users into Web3 in much the same way that Robinhood onboards casual investors into traditional equities. Users can pay for ETH using Apple Pay infrastructure and can connect to other wallets such as MetaMask. Unlike some cryptocurrency exchanges, Rainbow does not hold assets on the behalf of its users. Rainbow revenue generation is undisclosed, though it is likely the platform earns a commission from third-party cryptocurrency exchanges or other infrastructure providers. With a core focus on NFTs, the company may also take a percentage of NFT minting fees as a commission.Origin StoryRainbow is a fun, simple, and secure Ethereum wallet that helps users manage their assets. The platform was founded by Christian Baroni, Mike Demarais, and Jin Chung in 2019.
The trio came together with a mission to make navigating Ethereum technologies simpler for the average consumer. Baroni used to contract design for Microsoft while he was at high school and then took a job at Stripe at the age of 17. Demarais immersed himself in computer design and website creation from a young age, dropping out of college to work as an engineer at several user-focused start-ups. Chung, on the other hand, was a relative newcomer to the industry. She majored in computer science engineering and would later write trading tools for equity derivatives and algorithms for eBay’s recommendation systems.
What resulted from this experience was Rainbow, which would become the world’s most well-known Ethereum mobile interfaces. The company founders leveraged their unique backgrounds to create narrowly-tailored UI/UX to both on-ramp non-crypto users and facilitate new Web3 behaviors.
Rainbow is also the wallet of choice for NFT collectors, with the company envisioning a future world where friends can follow each other across the Metaverse. More specifically, users will be able to showcase their on-chain history, on-chain collectibles, and on-chain access to others.
How does Rainbow work?Rainbow onboards casual users into Web3 in much the same way that Robinhood onboards casual investors into traditional equities.
Users can purchase ETH or other ERC-20 tokens using Apple Pay infrastructure, with the process of on-ramping casual users into the Ethereum ecosystem taking no more than thirty seconds.
Unlike crypto exchanges such as Coinbase, Rainbow does not hold assets on behalf of its users.
Rainbow also enables users to:
Send, receive, and trade assets from their wallet without going through a financial institution.Trade on the leading decentralized exchange Uniswap.Connect to dApps and websites such as Yearn, Aave, and Compound.Purchase and display crypto art from sites such as Foundation, Zora, and OpenSea. Showcase their favorite digital art on social media by sharing a Rainbow profile.Importantly, users can also use an existing Ethereum wallet such as MetaMask with Rainbow.
How does Rainbow make money?Like many cryptocurrency wallets, Rainbow charges transaction fees whenever a user performs actions like swapping currencies, sending assets, and minting NFTs.
Though exact revenue generation methods are undisclosed, many similar wallets earn commissions from a range of third-party services incorporated into the platform. These may include cryptocurrency exchanges such as Changelly and fiat infrastructure providers such as Simplex. The company may also charge a swap fee for users of Uniswap.
Rainbow also charges gas fees whenever a change is made to the Ethereum blockchain. However, it should be remembered that the company is simply passing these fees to the user and does not profit from them.
The company has plans to introduce additional features to reduce gas fees by making the Ethereum ecosystem more efficient.
Connected Business Concepts According to Joel Monegro, a former analyst at USV (a venture capital firm) the blockchain implies value creation in its protocols. Where the web has allowed the value to be captured at the applications layer (take Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others). In a Blockchain Economy, this value might be captured by the protocols at the base of the blockchain (for instance Bitcoin and Ethereum). However, according to blockchain investor Paivinen due to ease of forking, incentives to compete and improved interoperability and interchangeability also in a blockchain-based economy, protocols might get thinner. Although the marginal value of scale might be lower compared to a web-based economy, where massive scale created an economic advantage. The success of the Blockchain will depend on its commercial viability!
According to Joel Monegro, a former analyst at USV (a venture capital firm) the blockchain implies value creation in its protocols. Where the web has allowed the value to be captured at the applications layer (take Facebook, Twitter, Google, and many others). In a Blockchain Economy, this value might be captured by the protocols at the base of the blockchain (for instance Bitcoin and Ethereum). However, according to blockchain investor Paivinen due to ease of forking, incentives to compete and improved interoperability and interchangeability also in a blockchain-based economy, protocols might get thinner. Although the marginal value of scale might be lower compared to a web-based economy, where massive scale created an economic advantage. The success of the Blockchain will depend on its commercial viability! A Proof of Stake (PoS) is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. As such it is, together with Proof of Work, among the key consensus algorithms for Blockchain protocols (like the Ethereum’s Casper protocol). Proof of Stake has the advantage of security, reduced risk of centralization, and energy efficiency.
A Proof of Stake (PoS) is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. As such it is, together with Proof of Work, among the key consensus algorithms for Blockchain protocols (like the Ethereum’s Casper protocol). Proof of Stake has the advantage of security, reduced risk of centralization, and energy efficiency. A Proof of Work is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. In a Proof of Work, miners compete to complete transactions on the network, by commuting hard mathematical problems (i.e. hashes functions) and as a result they get rewarded in coins.
A Proof of Work is a form of consensus algorithm used to achieve agreement across a distributed network. In a Proof of Work, miners compete to complete transactions on the network, by commuting hard mathematical problems (i.e. hashes functions) and as a result they get rewarded in coins. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like. A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model.
A Blockchain Business Model according to the FourWeekMBA framework is made of four main components: Value Model (Core Philosophy, Core Values and Value Propositions for the key stakeholders), Blockchain Model (Protocol Rules, Network Shape and Applications Layer/Ecosystem), Distribution Model (the key channels amplifying the protocol and its communities), and the Economic Model (the dynamics/incentives through which protocol players make money). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build and analyze a solid Blockchain Business Model. Ethereum was launched in 2015 with its cryptocurrency, Ether, as an open-source, blockchain-based, decentralized platform software. Smart contracts are enabled, and Distributed Applications (dApps) get built without downtime or third-party disturbance. It also helps developers build and publish applications as it is also a programming language running on a blockchain.
Ethereum was launched in 2015 with its cryptocurrency, Ether, as an open-source, blockchain-based, decentralized platform software. Smart contracts are enabled, and Distributed Applications (dApps) get built without downtime or third-party disturbance. It also helps developers build and publish applications as it is also a programming language running on a blockchain. The Graph is an ERC20 Utility Token (built on top of Ethereum) to enable consumers to freely query the blockchain through a fully decentralized database kept by indexers, incentivized by the payment of tokens (called GRT). The network is also ministered by curators and delegators that help maintain a high-quality index.
The Graph is an ERC20 Utility Token (built on top of Ethereum) to enable consumers to freely query the blockchain through a fully decentralized database kept by indexers, incentivized by the payment of tokens (called GRT). The network is also ministered by curators and delegators that help maintain a high-quality index. BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web.
BAT or Basic Attention Token is a utility token aiming to provide privacy-based web tools for advertisers and users to monetize attention on the web in a decentralized way via Blockchain-based technologies. Therefore, the BAT ecosystem moves around a browser (Brave), a privacy-based search engine (Brave Search), and a utility token (BAT). Users can opt-in to advertising, thus making money based on their attention to ads as they browse the web. In 2012, co-founders Christian Larsen and Jed McCaleb created Ripple, a technology acting as both a pre-mined cryptocurrency called XRP and a digital payment platform enabling monetary transactions. Where Ripple is the tech company, XRP is the decentralized ledger.
In 2012, co-founders Christian Larsen and Jed McCaleb created Ripple, a technology acting as both a pre-mined cryptocurrency called XRP and a digital payment platform enabling monetary transactions. Where Ripple is the tech company, XRP is the decentralized ledger. In 2014, Jed McCaleb – which also played a key role in the development of Ripple – created a cryptocurrency to provide fast, reliable, and affordable money transactions. The same cryptocurrency has considerably grown seven years later. It is now one of the most stellar cryptocurrencies to provide a real-time platform that links banks, payment systems, and people. Meet, Stellar!
In 2014, Jed McCaleb – which also played a key role in the development of Ripple – created a cryptocurrency to provide fast, reliable, and affordable money transactions. The same cryptocurrency has considerably grown seven years later. It is now one of the most stellar cryptocurrencies to provide a real-time platform that links banks, payment systems, and people. Meet, Stellar! In early 2019, a joint project between TRON and BitTorrent Foundation called BitTorrent Token came to fruition. BitTorrent Token launched to tokenize in-demand file-sharing protocol and enhance content delivery and bandwidth accessibility with blockchain technology.
In early 2019, a joint project between TRON and BitTorrent Foundation called BitTorrent Token came to fruition. BitTorrent Token launched to tokenize in-demand file-sharing protocol and enhance content delivery and bandwidth accessibility with blockchain technology. Chainlink is considered the most established decentralized oracle network. As an ecosystem housing several decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. As a decentralized oracle service built on Ethereum, Chainlink has the power to support the development of blockchain solutions for both traditional businesses and enterprises.
Chainlink is considered the most established decentralized oracle network. As an ecosystem housing several decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. As a decentralized oracle service built on Ethereum, Chainlink has the power to support the development of blockchain solutions for both traditional businesses and enterprises. Uniswap is a renowned decentralized crypto exchange created in 2018 and based on the Ethereum blockchain, to provide liquidity to the system. As a cryptocurrency exchange technology that operates on a decentralized basis. The Uniswap protocol inherited its namesake from the business that created it — Uniswap. Through smart contracts, the Uniswap protocol automates transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
Uniswap is a renowned decentralized crypto exchange created in 2018 and based on the Ethereum blockchain, to provide liquidity to the system. As a cryptocurrency exchange technology that operates on a decentralized basis. The Uniswap protocol inherited its namesake from the business that created it — Uniswap. Through smart contracts, the Uniswap protocol automates transactions between cryptocurrency tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. In essence, Polkadot is a cryptocurrency project created as an effort to transform and power a decentralized internet, Web 3.0, in the future. Polkadot is a decentralized platform, which makes it interoperable with other blockchains.
In essence, Polkadot is a cryptocurrency project created as an effort to transform and power a decentralized internet, Web 3.0, in the future. Polkadot is a decentralized platform, which makes it interoperable with other blockchains. Designed and created as an alternative to Ethereum, Cardano claims to be the first decentralized blockchain protocol to use a scientific approach and undergo a peer evaluation.
Designed and created as an alternative to Ethereum, Cardano claims to be the first decentralized blockchain protocol to use a scientific approach and undergo a peer evaluation. Solana is a blockchain network with a focus on high performance and rapid transactions. To boost speed, it employs a one-of-a-kind approach to transaction sequencing. Users can use SOL, the network’s native cryptocurrency, to cover transaction costs and engage with smart contracts.
Solana is a blockchain network with a focus on high performance and rapid transactions. To boost speed, it employs a one-of-a-kind approach to transaction sequencing. Users can use SOL, the network’s native cryptocurrency, to cover transaction costs and engage with smart contracts.Get The 450 Pages Blockchain Business Models Book

Read Also: BAT Token, Proof-of-stake, Proof-of-work, Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Ethereum, Solana, Blockchain, BAT, Monero, Ripple, Litecoin, Stellar, Dogecoin, Bitcoin Cash, Filecoin.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Rainbow (Wallet) Work And Make Money? appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
December 7, 2021
What Is Product Orientation? Product Orientation In A Nutshell
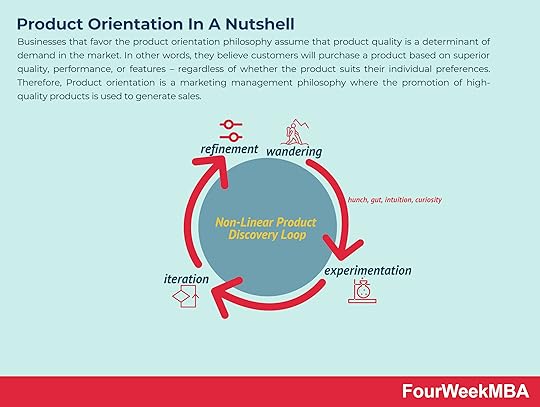
Businesses that favor the product orientation philosophy assume that product quality is a determinant of demand in the market. In other words, they believe customers will purchase a product based on superior quality, performance, or features – regardless of whether the product suits their individual preferences. Therefore, Product orientation is a marketing management philosophy where the promotion of high-quality products is used to generate sales.
Understanding product orientationProduct orientation is design-focused and commonly associated with research and development, so it is perhaps no surprise that many product-oriented companies are tech companies. They can innovate with new technologies to address customer needs and generate market demand. Sometimes, the customer needs are unknown or yet to be identified.
Product orientation is sometimes called the “no fear strategy” because there is the implication that the business is bold, proactive, and comfortable with risk. By prioritizing what it is good at, the business also assumes customers will adapt to whatever product it releases on the market.
Examples of product-oriented companiesSome examples of mostly product-oriented companies include:
Apple – a company famous for envisioning products before consumers knew they needed them. Apple relies on quality and innovation to enter new markets and create demand with products such as the iPod, iPhone, and iPad. Netflix – though technically a service, Netflix made companies such as Blockbuster obsolete by giving consumers easy access to movies and television shows. The company capitalized on faster data speeds and recommendation algorithms to provide something consumers would not have thought possible. Robinhood – the Robinhood investing app revolutionized trading for the average investor by making the market more accessible. The company developed an innovative product by removing the once prohibitive brokerage fees for retail investors and enabling them to trade in smaller increments.Advantages and disadvantages of the product orientation approachAdvantagesHigher product quality – businesses that use the product orientation approach devote less time and energy to marketing and sales and more to product development. Product teams with a quality-first mindset are also free to work without restrictive deadlines that cause development to be rushed. Continuous innovation – by its very nature, continuous innovation enables a business to become the first mover in a new industry and importantly, maintain that advantage. What’s more, businesses that demonstrate the ability to innovate regularly tend to enjoy a brand following that is hard to replicate.DisadvantagesCompetition – while Apple will always have the premium end of the consumer electronics market cornered, there do exist individuals who balk at the price tag of Apple products. This has allowed competitors like Samsung and Sony to leverage Apple’s innovation and introduce cheaper alternatives.Product failure – the product orientation approach can be successful, but it is by no means infallible. With less credence given to consumer feedback, there is a risk the new product fails when released to the market. Ultimately, trends do sell and some businesses make money by simply giving consumers what they asked for. Key takeaways:Product orientation is a marketing management philosophy where the promotion of high-quality products is used to generate sales. Product orientation is designed-focused and commonly associated with tech companies that innovate with new technologies to address customer needs and generate market demand.Product orientation is otherwise known as the “no fear strategy” because there is an implication that the business is bold, proactive, and comfortable with risk. Some of the businesses embodying these traits include Netflix, Apple, and Robinhood.Product orientation results in higher product quality and continuous innovation, which can build a loyal and devoted brand following. However, innovation can be leveraged by competitors and there is also a risk that the innovative product is not what consumers wanted. Connected Product Development Frameworks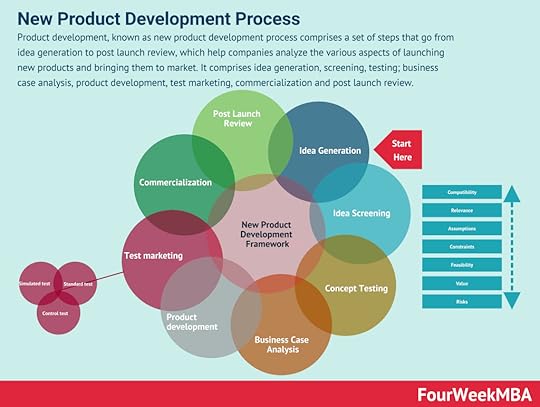 Product development, known as the new product development process comprises a set of steps that go from idea generation to post-launch review, which help companies analyze the various aspects of launching new products and bringing them to market. It comprises idea generation, screening, testing; business case analysis, product development, test marketing, commercialization, and post-launch review.
Product development, known as the new product development process comprises a set of steps that go from idea generation to post-launch review, which help companies analyze the various aspects of launching new products and bringing them to market. It comprises idea generation, screening, testing; business case analysis, product development, test marketing, commercialization, and post-launch review. In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.
In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars. You can use the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic framework to understand what growth strategy is more suited based on the market context. Developed by mathematician and business manager Igor Ansoff, it assumes a growth strategy can be derived by whether the market is new or existing, and the product is new or existing.
You can use the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic framework to understand what growth strategy is more suited based on the market context. Developed by mathematician and business manager Igor Ansoff, it assumes a growth strategy can be derived by whether the market is new or existing, and the product is new or existing.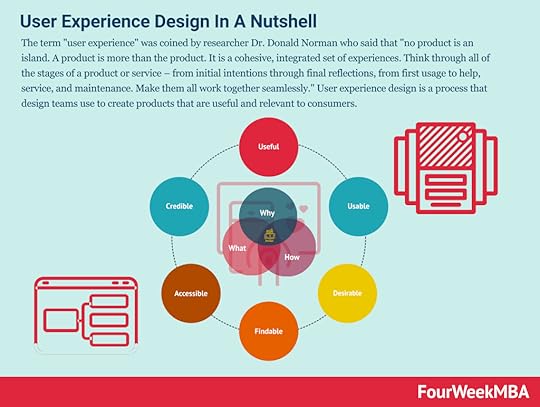 The term “user experience” was coined by researcher Dr. Donald Norman who said that “no product is an island. A product is more than the product. It is a cohesive, integrated set of experiences. Think through all of the stages of a product or service – from initial intentions through final reflections, from first usage to help, service, and maintenance. Make them all work together seamlessly.” User experience design is a process that design teams use to create products that are useful and relevant to consumers.
The term “user experience” was coined by researcher Dr. Donald Norman who said that “no product is an island. A product is more than the product. It is a cohesive, integrated set of experiences. Think through all of the stages of a product or service – from initial intentions through final reflections, from first usage to help, service, and maintenance. Make them all work together seamlessly.” User experience design is a process that design teams use to create products that are useful and relevant to consumers.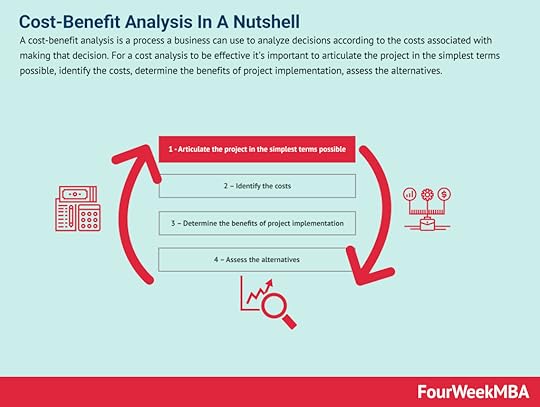 A cost-benefit analysis is a process a business can use to analyze decisions according to the costs associated with making that decision. For a cost analysis to be effective it’s important to articulate the project in the simplest terms possible, identify the costs, determine the benefits of project implementation, assess the alternatives.
A cost-benefit analysis is a process a business can use to analyze decisions according to the costs associated with making that decision. For a cost analysis to be effective it’s important to articulate the project in the simplest terms possible, identify the costs, determine the benefits of project implementation, assess the alternatives. Empathy mapping is a visual representation of knowledge regarding user behavior and attitudes. An empathy map can be built by defining the scope, purpose to gain user insights, and for each action, add a sticky note, summarize the findings. Expand the plan and revise.
Empathy mapping is a visual representation of knowledge regarding user behavior and attitudes. An empathy map can be built by defining the scope, purpose to gain user insights, and for each action, add a sticky note, summarize the findings. Expand the plan and revise.Read the remaining product development frameworks here.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is Product Orientation? Product Orientation In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is Services Marketing? Services Marketing In A Nutshell


Services marketing originated as a separate field of study during the 1980s. Researchers realized that the unique characteristics of services required different marketing strategies to those used in the promotion of physical goods. Services marketing is a specialized branch of marketing that promotes the intangible benefits delivered by a company to create customer value.
Understanding services marketingServices marketing can be used in a broad and diverse range of contexts. The strategy can be used to promote medical care, spa treatments, rental vehicles, concerts, and dance lessons. However, it is perhaps most useful in the tourism industry since most tourism campaigns sell experiences and not products.
One of the most successful services marketing campaigns was the “What Happens Here, Stays Here” campaign created by the Las Vegas Convention and Visitors Authority. Launched in 2004, the campaign resulted in a record 37.3 million tourists visiting the city in the year following. The phrase itself associated the Vegas brand with adult freedom and the emotional connection between visitors and the city.
Whatever the application, services marketing calls upon marketing specialists to sell ideas, intangibles, and promises and communicate value to customers.
Services marketing characteristicsBroadly speaking, services marketing is exemplified by five characteristics:
Intangibility – that is, the service being promoted cannot be seen or touched – only experienced. This means value is derived from the consumption of experience and cannot be transferred from one consumer to another. What’s more, value is difficult to evaluate prior to the consumer having the experience.Tangible product use – with the above in mind, it is important to note that many services marketing campaigns make use of tangible products to deliver customer value. Airline companies sell physical tickets to consumers which they associate with the experience of flying or traveling. Perishability – intangible services cannot be managed in the same way physical product inventories are managed. As a result, inventory cannot serve as a buffer between supply and demand and there is a high opportunity cost of idle capacity. For example, a portrait photographer relies on their technical expertise and rapport-building skills to make money. Conversely, a merchant selling portraiture lenses must maintain a physical inventory of said items.Low price sensitivity – in the service industry, consumers are less sensitive to price and more sensitive to the quality of the experience. An experience considered to have zero defects has the highest earning potential.Value creation – service companies can differentiate themselves in the market in three ways. Value can be created by offering a superior delivery process or level of customer service. It can also be created by the company developing a superior physical environment in which the service will be delivered.The services marketing triangleThe services marketing triangle was developed in 2000 to depict the three essential elements of the service industry. Each point of the triangle emphasizes the division of tasks based on necessary skills, strategies, and priorities.
The three elements are:
Internal marketing – where employees are assisted and trained to deliver or provide services to customers. Service delivery values are aligned with organizational values, and the best performers are duly rewarded.External marketing – where the organization markets to consumers through channels including social media, television, email, and other platforms.Interactive marketing – or the delivery of the service itself according to internal and external marketing messages. Successful delivery is typically associated with customer satisfaction, customer retention, and brand equity. Service delivery is defined by many service interactions, where the business either keeps or breaks the promises made in other marketing messages.Key takeaways:Services marketing is a specialized branch of marketing that promotes the intangible benefits delivered by a company to create customer value.Services marketing is described by five characteristics: intangibility, tangible product use, perishability, low price sensitivity, and value creation.The services marketing triangle was developed in 2000 to depict the three essential elements of the service industry. Successful service delivery is defined by many service interactions, where the business keeps or breaks the promises made in its marketing campaigns.Other Types Of Marketing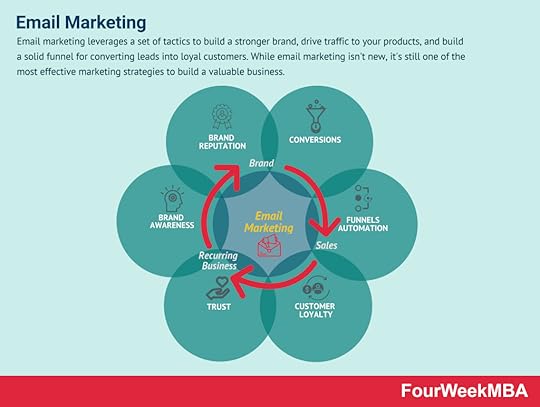 Email marketing leverages a set of tactics to build a stronger brand, drive traffic to your products, and build a solid funnel for converting leads into loyal customers. While email marketing isn’t new, it’s still one of the most effective marketing strategies to build a valuable business.
Email marketing leverages a set of tactics to build a stronger brand, drive traffic to your products, and build a solid funnel for converting leads into loyal customers. While email marketing isn’t new, it’s still one of the most effective marketing strategies to build a valuable business.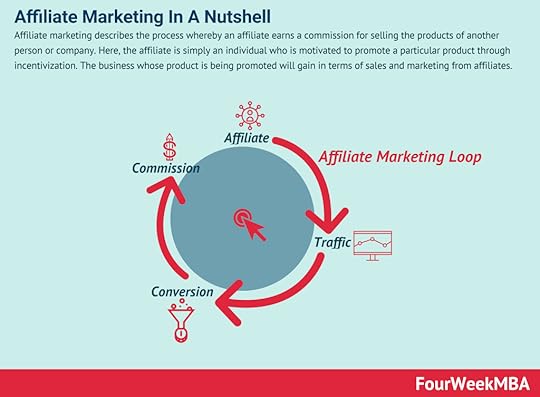 Affiliate marketing describes the process whereby an affiliate earns a commission for selling the products of another person or company. Here, the affiliate is simply an individual who is motivated to promote a particular product through incentivization. The business whose product is being promoted will gain in terms of sales and marketing from affiliates.
Affiliate marketing describes the process whereby an affiliate earns a commission for selling the products of another person or company. Here, the affiliate is simply an individual who is motivated to promote a particular product through incentivization. The business whose product is being promoted will gain in terms of sales and marketing from affiliates.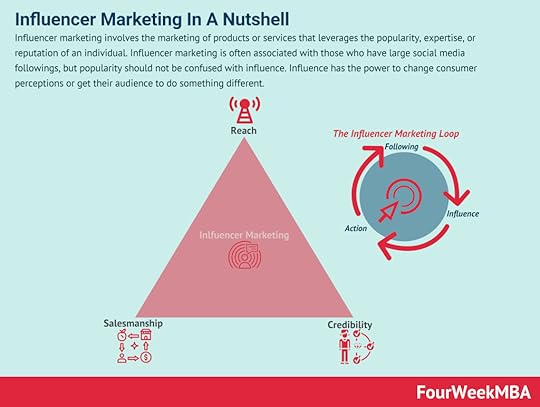 Influencer marketing involves the marketing of products or services that leverages the popularity, expertise, or reputation of an individual. Influencer marketing is often associated with those who have large social media followings, but popularity should not be confused with influence. Influence has the power to change consumer perceptions or get their audience to do something different.
Influencer marketing involves the marketing of products or services that leverages the popularity, expertise, or reputation of an individual. Influencer marketing is often associated with those who have large social media followings, but popularity should not be confused with influence. Influence has the power to change consumer perceptions or get their audience to do something different. Sustainable marketing describes how a business will invest in social and environmental initiatives as part of its marketing strategy. Also known as green marketing, it is often used to counteract public criticism around wastage, misleading advertising, and poor quality or unsafe products.
Sustainable marketing describes how a business will invest in social and environmental initiatives as part of its marketing strategy. Also known as green marketing, it is often used to counteract public criticism around wastage, misleading advertising, and poor quality or unsafe products.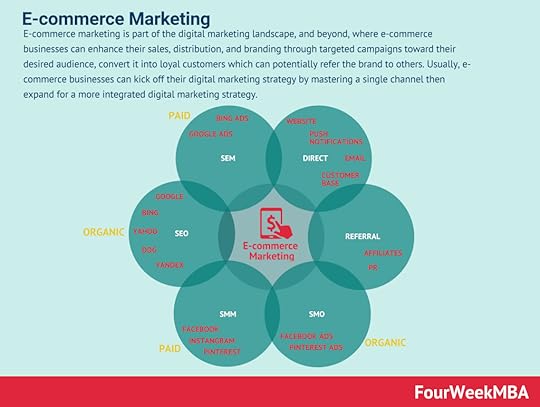 E-commerce marketing is part of the digital marketing landscape, and beyond, where e-commerce businesses can enhance their sales, distribution, and branding through targeted campaigns toward their desired audience, convert it into loyal customers which can potentially refer the brand to others. Usually, e-commerce businesses can kick off their digital marketing strategy by mastering a single channel then expand for a more integrated digital marketing strategy.
E-commerce marketing is part of the digital marketing landscape, and beyond, where e-commerce businesses can enhance their sales, distribution, and branding through targeted campaigns toward their desired audience, convert it into loyal customers which can potentially refer the brand to others. Usually, e-commerce businesses can kick off their digital marketing strategy by mastering a single channel then expand for a more integrated digital marketing strategy. Buzz marketing leverages the power of word-of-mouth advertising to create products or services with enough novelty that they go viral. In many cases, buzz marketing leverages on versatile content that can easily scale and be readapted to various contexts and fear of missing out (FOMO) to amplify the effect of word-of-mouth campaigns.
Buzz marketing leverages the power of word-of-mouth advertising to create products or services with enough novelty that they go viral. In many cases, buzz marketing leverages on versatile content that can easily scale and be readapted to various contexts and fear of missing out (FOMO) to amplify the effect of word-of-mouth campaigns. Shotgun marketing is a form of above-the-line (ATL) marketing, where popular mediums such as TV and radio are used to market to a mass audience. This technique of marketing targets as many consumers as possible. Also known as mass marketing, the technique attracts a large number of leads that, on average, might be of lower quality in nature.
Shotgun marketing is a form of above-the-line (ATL) marketing, where popular mediums such as TV and radio are used to market to a mass audience. This technique of marketing targets as many consumers as possible. Also known as mass marketing, the technique attracts a large number of leads that, on average, might be of lower quality in nature. Multichannel marketing executes a marketing strategy across multiple platforms to reach as many consumers as possible. Here, a platform may refer to product packaging, word-of-mouth advertising, mobile apps, email, websites, or promotional events, and all the other channels that can help amplify the brand to reach as many consumers as possible.
Multichannel marketing executes a marketing strategy across multiple platforms to reach as many consumers as possible. Here, a platform may refer to product packaging, word-of-mouth advertising, mobile apps, email, websites, or promotional events, and all the other channels that can help amplify the brand to reach as many consumers as possible.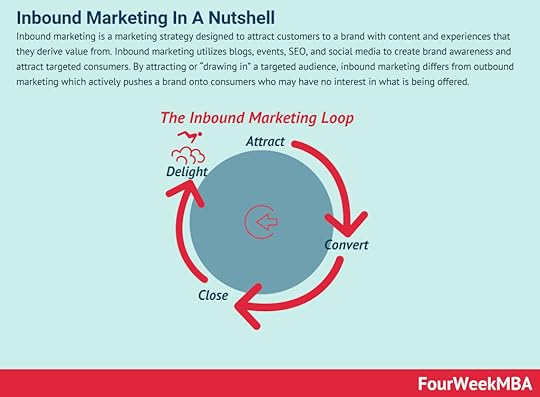 Inbound marketing is a marketing strategy designed to attract customers to a brand with content and experiences that they derive value from. Inbound marketing utilizes blogs, events, SEO, and social media to create brand awareness and attract targeted consumers. By attracting or “drawing in” a targeted audience, inbound marketing differs from outbound marketing which actively pushes a brand onto consumers who may have no interest in what is being offered.
Inbound marketing is a marketing strategy designed to attract customers to a brand with content and experiences that they derive value from. Inbound marketing utilizes blogs, events, SEO, and social media to create brand awareness and attract targeted consumers. By attracting or “drawing in” a targeted audience, inbound marketing differs from outbound marketing which actively pushes a brand onto consumers who may have no interest in what is being offered.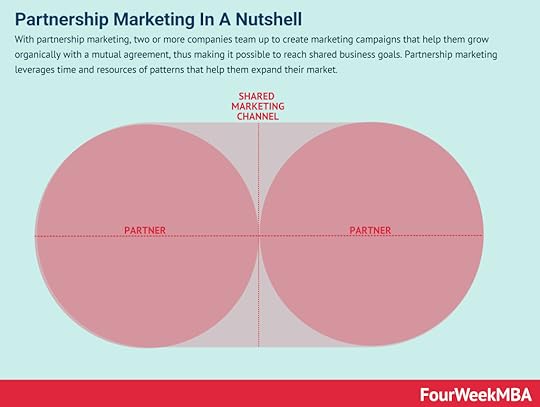 With partnership marketing, two or more companies team up to create marketing campaigns that help them grow organically with a mutual agreement, thus making it possible to reach shared business goals. Partnership marketing leverages time and resources of partners that help them expand their market.
With partnership marketing, two or more companies team up to create marketing campaigns that help them grow organically with a mutual agreement, thus making it possible to reach shared business goals. Partnership marketing leverages time and resources of partners that help them expand their market.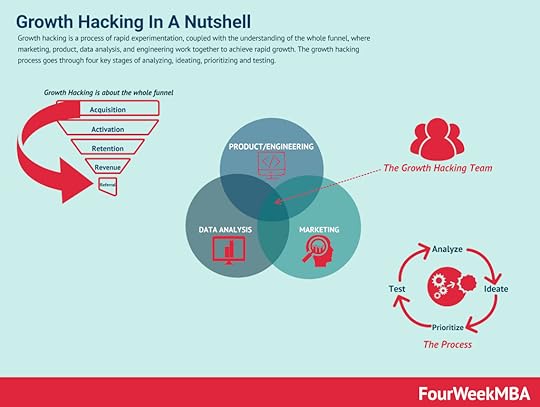 Growth marketing is a process of rapid experimentation, which in a way has to be “scientific” by keeping in mind that it is used by startups to grow, quickly. Thus, the “scientific” here is not meant in the academic sense. Growth marketing is expected to unlock growth, quickly and with an often limited budget.
Growth marketing is a process of rapid experimentation, which in a way has to be “scientific” by keeping in mind that it is used by startups to grow, quickly. Thus, the “scientific” here is not meant in the academic sense. Growth marketing is expected to unlock growth, quickly and with an often limited budget.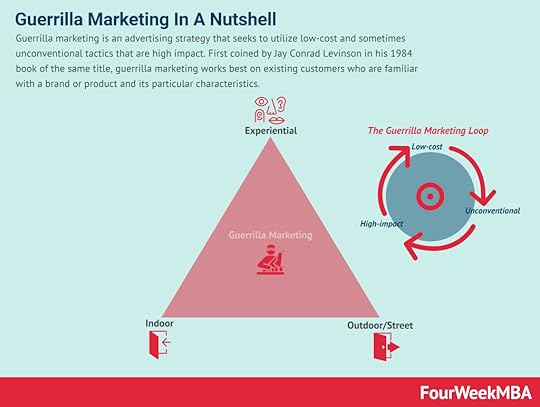 Guerrilla marketing is an advertising strategy that seeks to utilize low-cost and sometimes unconventional tactics that are high impact. First coined by Jay Conrad Levinson in his 1984 book of the same title, guerrilla marketing works best on existing customers who are familiar with a brand or product and its particular characteristics.
Guerrilla marketing is an advertising strategy that seeks to utilize low-cost and sometimes unconventional tactics that are high impact. First coined by Jay Conrad Levinson in his 1984 book of the same title, guerrilla marketing works best on existing customers who are familiar with a brand or product and its particular characteristics. As the name suggests, ambush marketing raises awareness for brands at events in a covert and unexpected fashion. Ambush marketing takes many forms, one common element, the brand advertising their products or services has not paid for the right to do so. Thus, the business doing the ambushing attempts to capitalize on the efforts made by the business sponsoring the event.
As the name suggests, ambush marketing raises awareness for brands at events in a covert and unexpected fashion. Ambush marketing takes many forms, one common element, the brand advertising their products or services has not paid for the right to do so. Thus, the business doing the ambushing attempts to capitalize on the efforts made by the business sponsoring the event.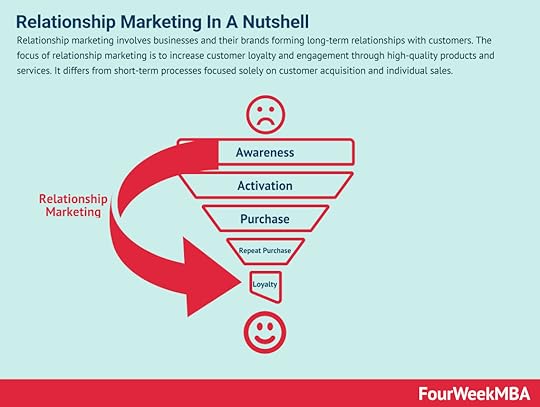 Relationship marketing involves businesses and their brands forming long-term relationships with customers. The focus of relationship marketing is to increase customer loyalty and engagement through high-quality products and services. It differs from short-term processes focused solely on customer acquisition and individual sales.
Relationship marketing involves businesses and their brands forming long-term relationships with customers. The focus of relationship marketing is to increase customer loyalty and engagement through high-quality products and services. It differs from short-term processes focused solely on customer acquisition and individual sales.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is Services Marketing? Services Marketing In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
December 5, 2021
What Is A Talent Management Strategy? Talent Management Strategy In A Nutshell
 A talent management strategy helps an organization manage its current and potential talent.A talent management strategy should incorporate the following principles: detailed job descriptions, employee-organization fit, mentoring, recognition, and continuous improvement.A robust talent management strategy helps attract and retain talent and improve organizational performance. The strategy achieves this by improving competitiveness, driving innovation, forming productive teams, and increasing the staff retention rate.Understanding talent management strategies
A talent management strategy helps an organization manage its current and potential talent.A talent management strategy should incorporate the following principles: detailed job descriptions, employee-organization fit, mentoring, recognition, and continuous improvement.A robust talent management strategy helps attract and retain talent and improve organizational performance. The strategy achieves this by improving competitiveness, driving innovation, forming productive teams, and increasing the staff retention rate.Understanding talent management strategiesTo better understand a talent management strategy, it may be helpful to first define talent management.
Talent management describes a suite of human resource processes that attract, recruit, develop, engage, and retain high-performing employees. Since business performance and profitability are associated with productive and engaged individuals, good talent management is a critical component of organizational longevity.
With all of that said, a talent management strategy is simply a broad plan of action to optimize the performance of employees. The plan may include action steps to:
Train those who lack skills in certain areas.Engage employees and measure engagement using questionnaires such as the Utrecht Work Engagement Scale (UWES) or GALLUP scale. Bring employees up to an adequate standard more quickly. This is known as optimizing the time to productivity.Recognize and reward high performers.Identify skill or resource gaps early in the strategy, andStandardize and schedule regular performance reviews to check in with employees and determine whether they need additional support.Each plan works under the basic assumption that well-resourced employees tend to perform better in their roles.
Talent management strategy principlesNumerous talent strategy frameworks have been developed over the years. Below are a few principles which should be common to each:
Detailed job descriptions – many businesses make the mistake of using very general job descriptions during the recruitment process. Without a detailed job description, the candidate and indeed the organization itself are confused about what is required. This leads to a raft of irrelevant applications which cost time and money to sort through. At the very least, a description should include job title, location, duties, required skills, tools and equipment used, and salary.Employee-organization fit – where possible, it is important to ascertain whether the candidate has the same values as the organization. Total overlap is uncommon, but an employee who cannot identify with company culture will likely be unhappy and unproductive – no matter how talented they are. Mentoring – effective talent management strategies must also contain a mentoring component. Constructive feedback helps employees realize their full potential and prepares them for inevitable setbacks. Recognition – to motivate, engage, and manage talent, they should be duly rewarded and recognized. This goes beyond financial rewards, with many organizations now rewarding employees in a way that is meaningful and relevant to them as individuals.Continuous improvement – this helps the employee ensure their skills are updated, upgraded, or upscaled as necessary. More broadly speaking, talent management strategies with continuous improvement help the organization remain agile and responsive to changing trends and market conditions.The benefits of a robust talent management strategyIn a three-year study conducted by McKinsey & Company, it was discovered that talent management was effective to very effective at attracting and retaining talent and improving performance.
Here is how this occurs within an organization:
Improved performance – three of the key practices for effective talent management also happen to support superior organizational performance. These include the rapid deployment of talent to strategic priorities, positive employee experience, and a human resource team that understands the strategy and broader organizational priorities.Improved competitiveness – organizations with the ability to identify, recruit, and develop talented individuals are more robust. What’s more, they are better able to navigate change and manage risk.Innovation – while opportunities for innovation always exist, only the most talented employees will be able to develop innovative products that are also commercially viable.Productive teams – talent management strategies also facilitate the development of productive teams. While every organisation must employee talented individuals, teams of talented individuals ultimately drive the company forward. Here, the whole is very much greater than the sum of the individual parts.Retention rate – when employees feel recognized and celebrated for their specific talents, they feel valued and tend not to seek opportunities elsewhere. This improves the company retention rate and since the hiring of new employees is expensive, it also improves the bottom line.Connected HR ModelsMaslow’s Hierarchy of Needs In A Nutshell Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs was developed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow. His hierarchy, often depicted in the shape of a pyramid, helped explain his research on basic human needs and desires. In marketing, the hierarchy (and its basis in psychology) can be used to market to specific groups of people based on their similarly specific needs, desires, and resultant actions.Eisenhower Matrix
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs was developed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow. His hierarchy, often depicted in the shape of a pyramid, helped explain his research on basic human needs and desires. In marketing, the hierarchy (and its basis in psychology) can be used to market to specific groups of people based on their similarly specific needs, desires, and resultant actions.Eisenhower Matrix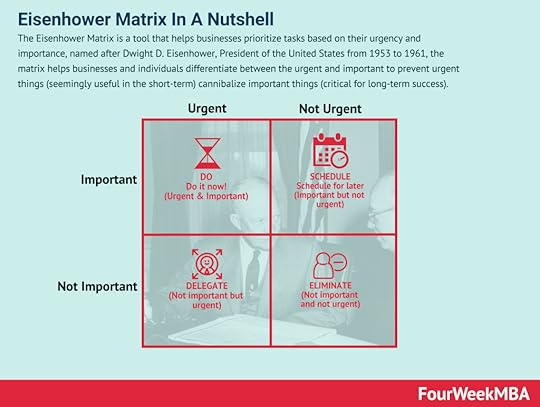 The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that helps businesses prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance, named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, President of the United States from 1953 to 1961, the matrix helps businesses and individuals differentiate between the urgent and important to prevent urgent things (seemingly useful in the short-term) cannibalize important things (critical for long-term success).Moonshot Thinking
The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that helps businesses prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance, named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, President of the United States from 1953 to 1961, the matrix helps businesses and individuals differentiate between the urgent and important to prevent urgent things (seemingly useful in the short-term) cannibalize important things (critical for long-term success).Moonshot Thinking Moonshot thinking is an approach to innovation, and it can be applied to business or any other discipline where you target at least 10X goals. That shifts the mindset, and it empowers a team of people to look for unconventional solutions, thus starting from first principles, by leveraging on fast-paced experimentation.Lightning Decision Jam
Moonshot thinking is an approach to innovation, and it can be applied to business or any other discipline where you target at least 10X goals. That shifts the mindset, and it empowers a team of people to look for unconventional solutions, thus starting from first principles, by leveraging on fast-paced experimentation.Lightning Decision Jam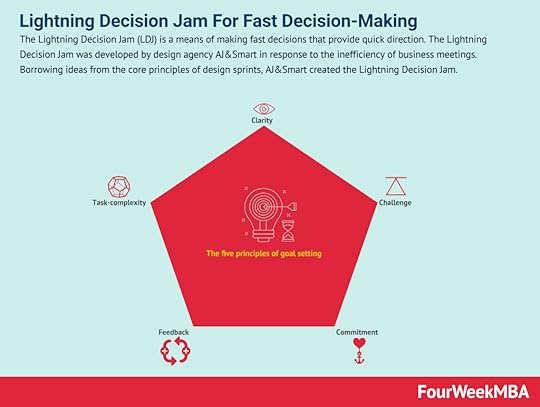 The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory Herzberg’s two-factor theory argues that certain workplace factors cause job satisfaction while others cause job dissatisfaction. The theory was developed by American psychologist and business management analyst Frederick Herzberg. Until his death in 2000, Herzberg was widely regarded as a pioneering thinker in motivational theory.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory argues that certain workplace factors cause job satisfaction while others cause job dissatisfaction. The theory was developed by American psychologist and business management analyst Frederick Herzberg. Until his death in 2000, Herzberg was widely regarded as a pioneering thinker in motivational theory.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is A Talent Management Strategy? Talent Management Strategy In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is A Burndown Chart? The Burndown Chart In A Nutshell
A burndown chart is a graphical representation of outstanding work versus time and is useful for predicting when all of the work will be completed. A burndown chart can be created by estimating the required effort to complete a project and tracking daily task progress. For the duration of the project, the team must also determine its actual effort against the estimated effort and plot the dataset to evaluate progress. A burndown chart is simple to understand and provides clarity on project scope and progress. However, the accuracy of a burndown chart relies on estimations invariably influenced by cognitive biases. In poorly defined projects, the quality of the resultant chart will be similarly poor.
Understanding a burndown chartSuccessful project managers realize the importance of statistics and graphical illustration tools in facilitating communication and collaboration amongst team members.
One of the more popular tools is the burndown chart, favored because of its simplicity and effectiveness. Broadly speaking, a burndown chart displays how much work remains to be completed on the y-axis with the number of days since work began on the x-axis. By comparing its actual progress with an ideal rate of progress, the project team can determine whether it is on or behind schedule.
In agile software development methodologies such as Scrum, these charts graphically illustrate the speed with which a team is working by plotting user stories against time. After the successful completion of a user story, the chart is updated. The chart can also record the pace of a team – otherwise known as velocity – and predict its performance.
Creating a burndown chartThough the burndown chart can be used in almost any context, it has seen renewed interest in agile software development.
With that in mind, we will now detail the steps required to complete a burndown chart:
Estimate effort – what is the ideal baseline for using the available hours throughout the sprint? In most cases, this is determined by dividing the available hours by the number of days the sprint will run across. For a sprint of 80 hours over 8 days, the effort required is 10 hours per day. Team leaders must then quantify the burndown as a daily running total with 80 hours remaining on Day 0, 70 hours remaining on Day 1, 60 hours remaining on Day 2, and so forth.Track daily progress – daily progress is then captured in the table against each daily task. Note that the hours assigned to each task are the estimated effort required for completion and not the actual effort.Determine the actual effort – at the conclusion of each day, the total remaining effort must be calculated by subtracting the actual effort from the running total. As the project progresses, the actual effort will fluctuate above and below the estimated effort. These disparities depend on how accurately the initial project work was estimated and whether individuals can work effectively as a team.Plot the final dataset – using the data from step three, the burndown chart itself can be created by using a simple application such as Microsoft Excel. Once plotted, the project team can compare planned and actual progress.Benefits and limitations of burndown chartsBenefitsThe most obvious benefit of a burndown chart is that it provides a clear and visible progress update to all members of the project team. The chart is easy to understand, which increases employee motivation and buy-in.
Burndown charts also help the project team deal with small issues before they become large problems. By tracking actual progress against ideal progress, the conversation is naturally steered toward the project and any obstacles to its timely completion.
LimitationsThe effectiveness of the burndown chart as a project management tool relies on the accuracy of time estimates. Unfortunately, these estimates are notoriously inaccurate because they are influenced by cognitive biases.
In a sprint, where story points deal with complexity and relative sizing, the problem isn’t as pronounced. But the cognitive biases associated with estimation remain. If a team overestimates project time requirements, progress will appear on track or ahead of schedule. Conversely, if a team underestimates time requirements, the chart will suggest they are behind schedule.
What’s more, the charts also show progress without providing clarity on whether the team is working on the right thing. In poorly defined projects, burndown charts do not reflect how close the team is to completing the work. This can lead to exaggerated or unrealistic expectations and team disunity.
Connected Visual Concepts Kanban is a lean manufacturing framework first developed by Toyota in the late 1940s. The Kanban framework is a means of visualizing work as it moves through identifying potential bottlenecks. It does that through a process called just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing to optimize engineering processes, speed up manufacturing products, and improve the go-to-market strategy.
Kanban is a lean manufacturing framework first developed by Toyota in the late 1940s. The Kanban framework is a means of visualizing work as it moves through identifying potential bottlenecks. It does that through a process called just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing to optimize engineering processes, speed up manufacturing products, and improve the go-to-market strategy.  Scrumban is a project management framework that is a hybrid of two popular agile methodologies: Scrum and Kanban. Scrumban is a popular approach to helping businesses focus on the right strategic tasks while simultaneously strengthening their processes.
Scrumban is a project management framework that is a hybrid of two popular agile methodologies: Scrum and Kanban. Scrumban is a popular approach to helping businesses focus on the right strategic tasks while simultaneously strengthening their processes. RACI matrices illustrate the functional role that each person plays on a project team. In creating these matrices, businesses can effectively balance project workloads and identify a clear project manager. A RACI matrix is a simple and effective means of documenting project roles and responsibilities.
RACI matrices illustrate the functional role that each person plays on a project team. In creating these matrices, businesses can effectively balance project workloads and identify a clear project manager. A RACI matrix is a simple and effective means of documenting project roles and responsibilities.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post What Is A Burndown Chart? The Burndown Chart In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Industry Types: The List Of Industry Types In A Nutshell
Every organization operates in at least one industry, with some operating in several. An industry can simply be defined as a group of companies with similar business activities, products, and services. There are now five main types of industry: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary. In this article, we’ll discuss the differences between each and list some specific examples.
Primary industriesPrimary industries are those that extract natural resources such as minerals, soil, plants, water, and those consumed to produce energy.
This includes industries such as:
Mining – where metals, minerals, oil, gas, coal, and other resources are extracted from the Earth’s surface. Agriculture – with a primary focus on cultivating plants, land, and animals to produce food, drink, and other essential items. Forestry – companies in the forestry industry manage and log native forest or timber plantations to produce wood for construction and furniture, among other uses.Fishing – the fishing industry encompasses any activity associated with the catching, culturing, processing, harvesting, or selling of fish. This includes recreational, commercial, and subsistence fishing.Hunting – or the practice of killing native or feral animals to harvest animal products, including meat, bone, fur, antlers, or tusks. The hunting industry also encompasses the act of removing predators dangerous to humans, taxidermy, and trophy hunting.Secondary industriesSecondary industries add value to the natural resources acquired by primary industries. They do this by converting raw materials into useful and profitable products for consumers and other businesses. For this reason, secondary industry is sometimes called the manufacturing industry.
Secondary industry examples include:
Manufacturing – where businesses convert raw components and materials into products. This is often done at scale in highly automated factories to produce low unit cost items.Construction – a broad industry dealing with the construction of residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. The construction industry also includes road, rail, tunnel, dam, and bridge infrastructure.Food and beverage – which involves the processing, preserving, and serving of food items. The food and beverage industry works closely with the agriculture industry to produce fresh and long-life food items for restaurants, supermarkets, and other food retailers.Fashion – or the design, production, and marketing of clothing, footwear, and other items that are worn by people. Technology – another broad industry category characterized by the innovation, design, and production of computers, software, apps, aerospace equipment, military equipment, and health care technology. Tertiary industriesIn a tertiary industry, the major economic activities include:
Exchange – or transportation, trade, and communication services that are used to bridge distance.Production – or the supply of a diverse range of services utilized by millions of people.Tertiary industries are mostly commerce and service-related businesses that produce non-tangible value. Examples of tertiary industries, which are a hallmark of wealthy and advanced nations, include:
Professional services – these are jobs requiring specialized knowledge or training, such as engineers, physicians, lawyers, architects, accountants, surgeons, dentists, and high-level administrators.Telecommunications – encompassing the transmission of signals, words, messages, sounds, images, or any other information via infrastructure such as cables, the internet, radio, and television. Franchise – where one company, the franchisor, gives the right for another company, the franchisee, to utilize its brand, systems, or other intellectual property. Many franchisors utilize this model to create commercial chains for the distribution of goods and services.Education – the education industry includes universities, schools, colleges, or training providers that help consumers acquire knowledge, skills, values, morals, or beliefs.Entertainment – an industry with many sub-industries devoted to the singular or mass entertainment of people, including comedy, film, music, theatre, and sport.Quaternary industriesThe definition of a quaternary industry is harder to define, but in general, it is any industry based on new technology and specialized knowledge. These industries are characterized by the individual relying on their education and intelligence to generate and operate advanced technologies.
Since it requires highly advanced technology, the quaternary industry is relatively young. Furthermore, it is only present in modern economies where the generation, analysis, and dissemination of knowledge is important enough to warrant it being separated from tertiary sectors.
Quaternary industries include:
Finance – including corporate finance, banking, personal finance, investing, and asset management. Consultancy – where specialists offer advice to businesses in a range of areas. Research and development – or innovative activities undertaken by governments and corporations to develop new products and services or improve existing ones.Quinary industriesQuinary industries focus on the creation, re-arrangement, and interpretation of new or existing ideas. They also deal with the use and evaluation of new technologies.
Many economists refer to those involved in quinary industries as “gold-collar professionals” because they hold extremely desirable skills and are involved in high-level decision-making.
Quinary industries may encompass specific sections of tertiary or quaternary industries, including government, science, education, health care, culture, media, and non-profit organizations.
To a lesser degree, some also suggest the domestic activities performed in a home by a family member or dependent are part of the quinary industry. These activities, which include housekeeping, child care, animal care, and maintenance, are typically unpaid and so are not measured by their monetary value. Nevertheless, they contribute to the economy by providing free services that would otherwise have to be paid for.
Key takeaways:While businesses may operate in one or more different industries, an industry can simply be defined as a group of companies with similar business activities, products, and services. Industries are categorized into five broad types: primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary.Primary industries extract raw materials from the Earth, including mining, agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting. Secondary industries, which turn those raw materials into useable products, include manufacturing, construction, food and beverage, fashion, and technology.Tertiary industries include any service that results in the creation of intangible value, such as those seen in professional services, telecommunications, franchising, education, and entertainment. In general, quaternary and quinary industries are associated with highly specialized knowledge and technology that tends to be found in modern, developed nations.Read Also: Gaming Industry, Fashion Industry, FinTech Industry, Food Delivery Industry, EdTech Industry.
Connected Business Concepts Fintech business models leverage tech and digital to enhance the financial service industry. Fintech business models, therefore, apply tech to various financial service use cases. Fintech business model examples comprise Affirm, Chime, Coinbase, Klarna, Paypal, Stripe, Robinhood, and many others whose mission is to digitize the financial services industry.
Fintech business models leverage tech and digital to enhance the financial service industry. Fintech business models, therefore, apply tech to various financial service use cases. Fintech business model examples comprise Affirm, Chime, Coinbase, Klarna, Paypal, Stripe, Robinhood, and many others whose mission is to digitize the financial services industry.  The gaming industry, part of the entertainment industry, is comprised of three main types of players. From game engines, which help developers build their games. To publishing gaming houses. And gaming consoles. While the prevailing business model for decades has been that of selling the console at cost, and make money on games. Digital games changed the way games are distributed and sold, and it opened up the way to free-to-play models.
The gaming industry, part of the entertainment industry, is comprised of three main types of players. From game engines, which help developers build their games. To publishing gaming houses. And gaming consoles. While the prevailing business model for decades has been that of selling the console at cost, and make money on games. Digital games changed the way games are distributed and sold, and it opened up the way to free-to-play models. Real-time retail involves the instantaneous collection, analysis, and distribution of data to give consumers an integrated and personalized shopping experience. This represents a strong new trend, as a further evolution of fast fashion first (who turned the design into manufacturing in a few weeks), ultra-fast fashion later (which further shortened the cycle of design-manufacturing). Real-time retail turns fashion trends into clothes collection in a few days cycle or a maximum of one week.
Real-time retail involves the instantaneous collection, analysis, and distribution of data to give consumers an integrated and personalized shopping experience. This represents a strong new trend, as a further evolution of fast fashion first (who turned the design into manufacturing in a few weeks), ultra-fast fashion later (which further shortened the cycle of design-manufacturing). Real-time retail turns fashion trends into clothes collection in a few days cycle or a maximum of one week.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Industry Types: The List Of Industry Types In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



