Nate Silver's Blog, page 32
November 9, 2020
Politics Podcast: Where The Rest Of The 2020 Races Stand
More: Apple Podcasts |
ESPN App |
RSS
Joe Biden is the president-elect, but our colleagues at ABC News have yet to project four states in the presidential contest, not to mention outstanding races in the House and Senate. In this installment of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew reviews who is leading in the outstanding races and how the two parties are reacting to the results. They also discuss what positive vaccine news could mean for Biden’s first term.
You can listen to the episode by clicking the “play” button in the audio player above or by downloading it in iTunes , the ESPN App or your favorite podcast platform. If you are new to podcasts, learn how to listen .
The FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast is recorded Mondays and Thursdays. Help new listeners discover the show by leaving us a rating and review on iTunes . Have a comment, question or suggestion for “good polling vs. bad polling”? Get in touch by email, on Twitter or in the comments.
November 7, 2020
This Was A Pretty Good Map For Biden
In this episode of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew reacts to the news that Joe Biden and Kamala Harris are set to become the next president and vice president, respectively, of the United States.
Politics Podcast: Biden Is Set To Be President. What Comes Next?
More: Apple Podcasts |
ESPN App |
RSS
On Saturday, the major networks declared that Joe Biden is set to be the next president of the United States. In this installment of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew reacts to the news, breaks down trends within the electorate and discusses what comes next.
Biden Won — Pretty Convincingly In The End
Even if you knew in advance about the “blue shift” that would occur in states like Pennsylvania — and we did know in advance about it! — it’s been hard to make enough of a mental adjustment for it this week. Numbers flashing across a TV ticker have a certain magnetic power and certitude to them. It was easy to forget that Joe Biden would gain ground once mail votes were added to the tallies because such votes were overwhelmingly Democratic this year in Pennsylvania and most other states.
But just because of that blue shift — and the red shift that occurred in states where mail votes were counted first — that doesn’t mean the presidential race was all that close in the end. Joe Biden’s win was on the tighter side of the likely range of outcomes suggested by polls, but it was a thoroughly convincing one judged on its own merits.
So put aside your anxieties of the past few days and the premature media narratives that have been circulating since Tuesday night. Suppose, instead, that you’d been on one of those weekslong rafting trips in the Grand Canyon (sounds pleasant, doesn’t it?) and woke up to this map:
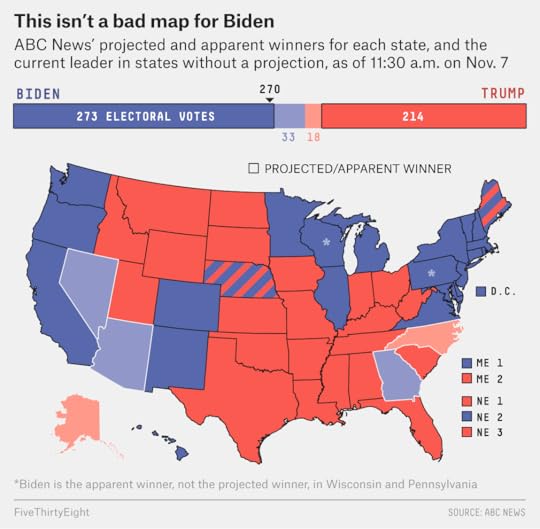 [image error]
[image error]It’s not a landslide, by any means, but this is a map that almost any Democrat would have been thrilled about if you’d shown it to them a year ago. Biden looks to have reclaimed the three “blue wall” states — Pennsylvania, Michigan and Wisconsin (ABC News has announced that Biden is the “apparent winner” in Pennsylvania and Wisconsin1) — that were central to Hillary Clinton’s loss. He may also win Arizona (he would become the first Democrat to do so since 1996) and, in the opposite corner of the country, Georgia (the first Democratic winner there since 1992). Additionally, Biden easily won Nebraska’s 2nd Congressional District, which could be a thorn in the side of Republicans going forward. He also ran far ahead of Clinton in rural northern states such as Maine, Minnesota and New Hampshire.
Extrapolating out from current vote totals, I project Biden winning the popular vote by 4.3 percentage points and getting 81.8 million votes to President Trump’s 74.9 million, with a turnout of around 160 million. This is significant because no candidate has ever received 70 million votes in an election — former President Barack Obama came the closest in 2008, with 69.5 million votes — let alone 80 million. That may also be a slightly conservative projection, given the blue shift we’ve seen so far and the fact that late-counted votes such as provisional ballots often lean Democratic. I’d probably bet on Biden’s popular vote margin winding up at closer to 5 points than to 4, and 6 points isn’t entirely out of the question either.
The margin is also a bit more impressive in the context of our highly polarized political era, which has tended to produce close elections. If I’m right about the popular vote margin, Biden’s win would come via the second-largest popular vote margin since 2000, exceeding Obama’s 3.9-point margin against Mitt Romney in 2012 but lagging behind Obama’s 7.3-point win over John McCain in 2008.
Biden also defeated an elected incumbent, which is relatively rare. Since World War II, five elected incumbents who sought reelection have won it — Dwight Eisenhower, Richard Nixon, George W. Bush, Bill Clinton and Obama. Trump is now the third sitting president to lose his reelection bid in that time, along with Jimmy Carter and George H.W. Bush.
What about the polls? Didn’t they show a wider margin for Biden? Yes, they did — Biden led in the final national polls by around 8 points. So we’re probably going to wind up with a polling error of around 3 to 4 points, both nationally and at the state level. (Although that will reflect a combination of states like Georgia, where the polls were spot-on, and others like Wisconsin, where there were big misses.) This is, of course, a subject on which we’ll have more to say in the coming days. For now, it’s safe to say that pollsters will have some questions to answer, especially about how they missed in the same direction (underestimating Trump) in some of the same states two elections in a row.
At the same time, this election’s polling error may wind up being fairly normal by historical standards. Indeed, the final polls miss by around 3 points, on average, in presidential elections. The error this year may be somewhat wider than that, but we should wait for all the votes to be counted because margins may shift substantially in some states before results are certified.
In any case, Biden’s ability to survive a polling error of the size that sank Clinton was precisely the reason he was a fairly heavy favorite in our forecast. Biden won (or is likely to win) several states — Georgia, Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, Arizona2 — by margins that will probably be between 0 and 2 percentage points, in contrast to Clinton, who lost Wisconsin, Michigan, Pennsylvania and Florida by margins of 1 percentage point or less. Biden’s 89 percent chance of winning the Electoral College included the possibility of nail-biter wins in critical states — although, again, it’s hard to know if this race would be regarded as that much of a nail-biter if not for the timing of ballot counting and the blue shift.
The bigger problems — both for Democrats and for the polls — were in races for Congress.
There weren’t necessarily any huge upsets in the Senate; it’s just that Democrats lost most of the toss-up races. Among races where winners have been projected so far, Democrat Sara Gideon is the only Senate candidate favored in our forecast to have lost, and she had only a 59 percent chance of beating Sen. Susan Collins, according to our final forecast. Gideon, however, is likely to eventually be joined by Cal Cunningham in North Carolina, who had a 68 percent chance, although the polling in that Senate race had tightened in the closing days of the campaign following a Cunningham sexting scandal. Republican Joni Ernst held off challenger Theresa Greenfield in Iowa, although Ernst was a narrow favorite in our forecast.
Democrats do retain a chance at a Senate majority, or more likely a 50-50 split in which Vice President-elect Kamala Harris would be the deciding vote. Democrats currently hold 48 seats,3 but there are two runoffs in Georgia on Jan. 5 that are sure to attract hundreds of millions of dollars worth of advertising. I’m a little too exhausted to prognosticate about the Georgia runoffs all that much, but Democrats are at least mathematically alive here in a state that Biden appears likely to win. They also retain some outside chances at winning a Senate seat in Alaska, where mail votes have not yet been counted.
But Democrats underperformed in the U.S. House, where they’ve lost almost every toss-up race that has been projected so far and Republicans have made a net gain of five seats and counting. It also appears as though Democrats will underperform in the House popular vote relative to the presidential vote and the generic ballot, where Democrats led by about 7 percentage points. That looks like a significant polling miss (although the House popular vote can take a long time to finalize). In that sense, the election could be described as more of a repudiation of Trump specifically than of Republicans writ large.
Biden did have some shortcomings, however. One major one was his apparent underperformance among key groups of Hispanic voters, especially Cuban Americans in South Florida and Mexican Americans in South Texas. As you can see in this chart from The New York Times, there were huge shifts toward Trump in these areas:
Indeed, even with the addition of Georgia and Arizona in their column, Democrats’ Electoral College coalition is somewhat fragile if it doesn’t contain Florida or Texas. It’s not clear yet what the tipping-point state will be in this election — but mostly likely it will be Arizona or Wisconsin, where it appears as though Biden will win by around 1 percentage point. That could mean there’s around a 4-point gap between the roughly 5-point popular vote victory that we eventually expect from Biden and his margin in the tipping-point state, a bigger Electoral College disadvantage than Clinton had in 2016 (3 points).
Still, this brings up one last point: This is the seventh election out of the past eight in which Democrats have won the popular vote for president. If American elections were contested on the basis of the popular vote, this race could probably have been called fairly early on Tuesday night, and we could all have gotten a lot more sleep the past few days. But don’t let bleary eyes obscure Biden’s accomplishment.
Biden Wins — Pretty Convincingly In The End
Even if you knew in advance about the “blue shift” that would occur in states like Pennsylvania — and we did know in advance about it! — it’s been hard to make enough of a mental adjustment for it this week. Numbers flashing across a TV ticker have a certain magnetic power and certitude to them. It was easy to forget that Joe Biden would gain ground once mail votes were added to the tallies because such votes were overwhelmingly Democratic this year in Pennsylvania and most other states.
But just because of that blue shift — and the red shift that occurred in states where mail votes were counted first — that doesn’t mean the presidential race was all that close in the end. Joe Biden’s win was on the tighter side of the likely range of outcomes suggested by polls, but it was a thoroughly convincing one judged on its own merits.
So put aside your anxieties of the past few days and the premature media narratives that have been circulating since Tuesday night. Suppose, instead, that you’d been on one of those weekslong rafting trips in the Grand Canyon (sounds pleasant, doesn’t it?) and woke up to this map:
 [image error]
[image error]It’s not a landslide, by any means, but this is a map that almost any Democrat would have been thrilled about if you’d shown it to them a year ago. Biden looks to have reclaimed the three “blue wall” states — Pennsylvania, Michigan and Wisconsin (ABC News has announced that Biden is the “apparent winner” in Pennsylvania and Wisconsin1) — that were central to Hillary Clinton’s loss. He may also win Arizona (he would become the first Democrat to do so since 1996) and, in the opposite corner of the country, Georgia (the first Democratic winner there since 1992). Additionally, Biden easily won Nebraska’s 2nd Congressional District, which could be a thorn in the side of Republicans going forward. He also ran far ahead of Clinton in rural northern states such as Maine, Minnesota and New Hampshire.
Extrapolating out from current vote totals, I project Biden winning the popular vote by 4.3 percentage points and getting 81.8 million votes to President Trump’s 74.9 million, with a turnout of around 160 million. This is significant because no candidate has ever received 70 million votes in an election — former President Barack Obama came the closest in 2008, with 69.5 million votes — let alone 80 million. That may also be a slightly conservative projection, given the blue shift we’ve seen so far and the fact that late-counted votes such as provisional ballots often lean Democratic. I’d probably bet on Biden’s popular vote margin winding up at closer to 5 points than to 4, and 6 points isn’t entirely out of the question either.
The margin is also a bit more impressive in the context of our highly polarized political era, which has tended to produce close elections. If I’m right about the popular vote margin, Biden’s win would come via the second-largest popular vote margin since 2000, exceeding Obama’s 3.9-point margin against Mitt Romney in 2012 but lagging behind Obama’s 7.3-point win over John McCain in 2008.
Biden also defeated an elected incumbent, which is relatively rare. Since World War II, five elected incumbents who sought reelection have won it — Dwight Eisenhower, Richard Nixon, George W. Bush, Bill Clinton and Obama. Trump is now the third sitting president to lose his reelection bid in that time, along with Jimmy Carter and George H.W. Bush.
What about the polls? Didn’t they show a wider margin for Biden? Yes, they did — Biden led in the final national polls by around 8 points. So we’re probably going to wind up with a polling error of around 3 to 4 points, both nationally and at the state level. (Although that will reflect a combination of states like Georgia, where the polls were spot-on, and others like Wisconsin, where there were big misses.) This is, of course, a subject on which we’ll have more to say in the coming days. For now, it’s safe to say that pollsters will have some questions to answer, especially about how they missed in the same direction (underestimating Trump) in some of the same states two elections in a row.
At the same time, this election’s polling error may wind up being fairly normal by historical standards. Indeed, the final polls miss by around 3 points, on average, in presidential elections. The error this year may be somewhat wider than that, but we should wait for all the votes to be counted because margins may shift substantially in some states before results are certified.
In any case, Biden’s ability to survive a polling error of the size that sank Clinton was precisely the reason he was a fairly heavy favorite in our forecast. Biden won (or is likely to win) several states — Georgia, Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, Arizona2 — by margins that will probably be between 0 and 2 percentage points, in contrast to Clinton, who lost Wisconsin, Michigan, Pennsylvania and Florida by margins of 1 percentage point or less. Biden’s 89 percent chance of winning the Electoral College included the possibility of nail-biter wins in critical states — although, again, it’s hard to know if this race would be regarded as that much of a nail-biter if not for the timing of ballot counting and the blue shift.
The bigger problems — both for Democrats and for the polls — were in races for Congress.
There weren’t necessarily any huge upsets in the Senate; it’s just that Democrats lost most of the toss-up races. Among races where winners have been projected so far, Democrat Sara Gideon is the only Senate candidate favored in our forecast to have lost, and she had only a 59 percent chance of beating Sen. Susan Collins, according to our final forecast. Gideon, however, is likely to eventually be joined by Cal Cunningham in North Carolina, who had a 68 percent chance, although the polling in that Senate race had tightened in the closing days of the campaign following a Cunningham sexting scandal. Republican Joni Ernst held off challenger Theresa Greenfield in Iowa, although Ernst was a narrow favorite in our forecast.
Democrats do retain a chance at a Senate majority, or more likely a 50-50 split in which Vice President-elect Kamala Harris would be the deciding vote. Democrats currently hold 48 seats,3 but there are two runoffs in Georgia on Jan. 5 that are sure to attract hundreds of millions of dollars worth of advertising. I’m a little too exhausted to prognosticate about the Georgia runoffs all that much, but Democrats are at least mathematically alive here in a state that Biden appears likely to win. They also retain some outside chances at winning a Senate seat in Alaska, where mail votes have not yet been counted.
But Democrats underperformed in the U.S. House, where they’ve lost almost every toss-up race that has been projected so far and Republicans have made a net gain of five seats and counting. It also appears as though Democrats will underperform in the House popular vote relative to the presidential vote and the generic ballot, where Democrats led by about 7 percentage points. That looks like a significant polling miss (although the House popular vote can take a long time to finalize). In that sense, the election could be described as more of a repudiation of Trump specifically than of Republicans writ large.
Biden did have some shortcomings, however. One major one was his apparent underperformance among key groups of Hispanic voters, especially Cuban Americans in South Florida and Mexican Americans in South Texas. As you can see in this chart from The New York Times, there were huge shifts toward Trump in these areas:
Indeed, even with the addition of Georgia and Arizona in their column, Democrats’ Electoral College coalition is somewhat fragile if it doesn’t contain Florida or Texas. It’s not clear yet what the tipping-point state will be in this election — but mostly likely it will be Arizona or Wisconsin, where it appears as though Biden will win by around 1 percentage point. That could mean there’s around a 4-point gap between the roughly 5-point popular vote victory that we eventually expect from Biden and his margin in the tipping-point state, a bigger Electoral College disadvantage than Clinton had in 2016 (3 points).
Still, this brings up one last point: This is the seventh election out of the past eight in which Democrats have won the popular vote for president. If American elections were contested on the basis of the popular vote, this race could probably have been called fairly early on Tuesday night, and we could all have gotten a lot more sleep the past few days. But don’t let bleary eyes obscure Biden’s accomplishment.
November 5, 2020
Biden Appears On The Verge Of Overtaking Trump In Pennsylvania
In this installment of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew shares an update on where votes are still coming in and what to make of the overall results at this point.
Politics Podcast: Biden Could Soon Win Pennsylvania … And The Presidency
More: Apple Podcasts |
ESPN App |
RSS
As votes continue to be counted in five key battleground states, and as Biden’s margins continue to improve, it looks very likely that the presidential race will eventually be called for Biden. In this installment of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew shares an update on where votes are still coming in and what to make of the overall results at this point.
You can listen to the episode by clicking the “play” button in the audio player above or by downloading it in iTunes , the ESPN App or your favorite podcast platform. If you are new to podcasts, learn how to listen .
The FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast is recorded Mondays and Thursdays. Help new listeners discover the show by leaving us a rating and review on iTunes . Have a comment, question or suggestion for “good polling vs. bad polling”? Get in touch by email, on Twitter or in the comments.
November 4, 2020
When Will We Finally Get Results In Unprojected States?
In this installment of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew discusses the election results so far, what results are left to come in, and some of the trends in the data.
Politics Podcast: Biden’s Path To Victory Is Looking Clearer
More: Apple Podcasts |
ESPN App |
RSS
After our colleagues at ABC News projected Joe Biden as the winner in Michigan, the former vice president’s path to victory is looking clearer. In this installment of the FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast, the crew discusses the results so far, what’s left to come in, and some of the trends in the data. They also begin to answer questions about polling errors in the 2020 election.
You can listen to the episode by clicking the “play” button in the audio player above or by downloading it in iTunes , the ESPN App or your favorite podcast platform. If you are new to podcasts, learn how to listen .
The FiveThirtyEight Politics podcast is recorded Mondays and Thursdays. Help new listeners discover the show by leaving us a rating and review on iTunes . Have a comment, question or suggestion for “good polling vs. bad polling”? Get in touch by email, on Twitter or in the comments.
November 2, 2020
Biden’s Favored In Our Final Presidential Forecast, But It’s A Fine Line Between A Landslide And A Nail-Biter
FiveThirtyEight has issued its final presidential forecast. There hasn’t been a lot of change over the past 24 or 48 hours, as most of the late polling either came in close to our previous polling averages, or came from — frankly — fairly random pollsters that don’t get a lot of weight in our forecast.
Of course, you can click over to the forecast right now if you’d like to see what it says — I’m sure most of you have already done that. But in these accompanying write-ups, I like to provide some context. When I wrote about our final presidential forecast in 2012, for example, I was trying to explain why a race that everyone assumed was close actually reflected a fairly decisive advantage for Barack Obama. When I wrote about our final forecast in 2016, conversely, it was pretty much the opposite. I was trying to explain that, although Hillary Clinton was favored, what most of the media was portraying as a sure thing was a highly competitive contest between her and Donald Trump.
This year … I’m not really sure what I’m trying to convince you of. If you think that polling is irrevocably broken because of 2016 — well, that’s not really correct. On the other hand, if it weren’t for 2016, people might look at Joe Biden’s large lead in national polls — the largest of any candidate on the eve of the election since Bill Clinton in 1996 — and conclude that Trump was certain to be a one-term president. If you do think that, please read my story from earlier this week about how Trump can win and why a 10 percent chance needs to be taken seriously.
Nonetheless, Biden’s standing is considerably stronger than Clinton’s at the end of the 2016 race. His lead is larger than Clinton’s in every battleground state, and more than double her lead nationally. Our model forecasts Biden to win the popular vote by 8 percentage points,1 more than twice Clinton’s projected margin at the end of 2016.
Indeed, some of the dynamics that allowed Trump to prevail in 2016 wouldn’t seem to exist this year. There are considerably fewer undecided voters in this race — just 4.8 percent of voters say they’re undecided or plan to vote for third-party candidates, as compared to 12.5 percent at the end of 2016. And the polls have been considerably more stable this year than they were four years ago. Finally, unlike the “Comey letter” in the closing days of the campaign four years ago — when then-FBI Director James Comey told Congress that new evidence had turned up pertinent to the investigation into the private email server that Clinton used as secretary of state — there’s been no major development in the final 10 days to further shake up the race.
Now, there are also some sources of error that weren’t as relevant four years ago. The big surge in early and mail voting — around 100 million people have already voted! — could present challenges to pollsters, for instance. Still, even making what we think are fairly conservative assumptions, our final forecast has Biden with an 89 percent chance of winning the Electoral College, as compared to a 10 percent chance for Trump. (The remaining 1 percent reflects rounding error, plus the chance of an Electoral College tie.)
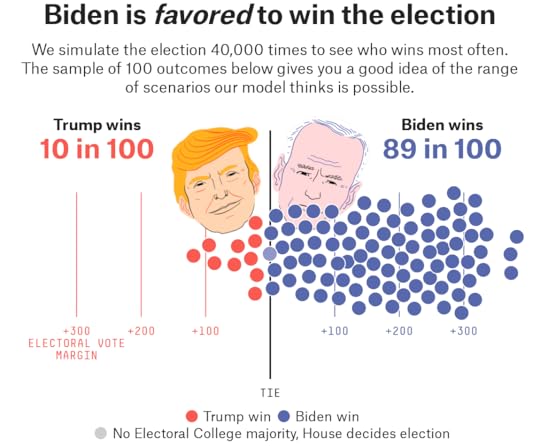 [image error]
[image error]
But what’s tricky about this race is that — because of Trump’s Electoral College advantage, which he largely carries over from 2016 — it wouldn’t take that big of a polling error in Trump’s favor to make the election interesting. Importantly, interesting isn’t the same thing as a likely Trump win; instead, the probable result of a 2016-style polling error would be a Biden victory but one that took some time to resolve and which could imperil Democrats’ chances of taking over the Senate. On the flip side, it wouldn’t take much of a polling error in Biden’s favor to turn 2020 into a historic landslide against Trump.
So as we did four years ago, let’s run through a few stress checks here. On average in past elections, the final polls have been off by around 3 percentage points. How would the map change if there were a 3-point error in Trump’s direction? And what about a 3-point error in Biden’s direction? Keeping in mind that some states move more than others in accordance with national trends, here’s what our final forecast shows:
How a 2016-sized polling error would change our forecast
Biden’s projected margin of victory or defeat in the most competitive states
with 3-point national error …
State
Final 538 Forecast
IN BIDEN’S FAVOR
IN TRUMP’S FAVOR
New Hampshire
+10.6
+14.5
+6.7
Minnesota
+9.1
+12.1
+6.0
Wisconsin
+8.3
+11.6
+5.1
Michigan
+8.0
+11.2
+4.9
Nevada
+6.1
+9.5
+2.8
Pennsylvania
+4.7
+7.7
+1.7
NE-2
+3.2
+6.4
-0.0
Arizona
+2.6
+5.8
-0.7
Florida
+2.5
+5.7
-0.7
North Carolina
+1.8
+4.7
-1.1
ME-2
+1.6
+4.8
-1.6
Georgia
+1.0
+3.6
-1.6
Ohio
-0.6
+2.5
-3.7
Iowa
-1.5
+2.0
-5.0
Texas
-1.5
+1.7
-4.7
Montana
-6.4
-3.3
-9.5
South Carolina
-7.5
-4.8
-10.2
Alaska
-8.5
-5.3
-11.7
Missouri
-9.4
-6.3
-12.5
First, before we get to the Biden-friendly or Trump-friendly scenarios: Suppose this is one of those happy years when there isn’t any systematic error in the polls — that is, Biden wins by about 8 points nationally. In that case, then Biden’s going to win the Electoral College, even if there might be polling misses in individual states. Biden’s easiest path to victory would be to win back three of the so-called “Blue Wall” states that Hillary Clinton lost: Michigan, Wisconsin and Pennsylvania. Coupled with the states that Clinton won in 2016, that would get Biden up to 278 electoral votes, more than the 270 required. Pennsylvania is the most tenuous of the “Blue Wall” group, but even if Biden lost it — unlikely if polls are about right overall — he’d have plenty of other options as he’s also narrowly ahead in our final forecast in Arizona, Florida, North Carolina and Georgia and only narrowly behind Trump in Ohio, Texas and Iowa.
What if there were a 3-point polling error in Biden’s favor? Then he’d be a favorite in all of the aforementioned states. Coupled with the 2nd Congressional Districts in Maine and Nebraska, where he’s also favored, that would result in his winning 413 electoral votes. Other states that are traditionally extremely red could even come into play for Biden too, with Montana being the most likely possibility, followed by South Carolina, Alaska and Missouri. This scenario would also make for an 11-point popular vote margin for Biden, the biggest by any candidate since Ronald Reagan in 1984, and the biggest winning margin against an incumbent since Franklin Delano Roosevelt against Herbert Hoover in 1932.
But with a 3-point error in Trump’s direction — more or less what happened in 2016 — the race would become competitive. Biden would probably hold on, but he’d only be the outright favorite in states (and congressional districts) containing 279 electoral votes. In Pennsylvania, the tipping-point state, he’d be projected to win by 1.7 percentage points — not within the recount margin, but a close race.
Such a scenario would not be the end of the world for Biden. The extra cushion that he has relative to Clinton helps a lot; it means that with a 2016-style polling error, he’d narrowly win some states that she narrowly lost. Biden has polled well recently in Michigan and Wisconsin in particular and has big leads there. Still, this would not be the sort of outcome that Democrats were hoping for. For one thing, because Biden would probably be reliant on Pennsylvania in this scenario — a state that is expected to take some time to count its vote — the election might take longer to call. For another, it could yield a fairly bad map as far as Democrats’ Senate hopes go, as Biden would be a narrow underdog in several states with key Senate races, including Arizona, North Carolina, Georgia and Iowa. So while Biden isn’t a normal-sized polling error away from losing, he is a normal-sized polling error away from having a messy win that might not come with control of Congress.
Still, as much as we’ve tried to strike a note of caution, Democrats have a right to be pleased about where they wound up. Sure, Biden could be in a meaningly safer position with a larger polling lead in Pennsylvania or Arizona, where his numbers have slipped a bit down the stretch run. Nonetheless, if we’d told our Democratic readers six months ago that Biden would be heading into election morning ahead by 8 points nationally, also ahead by 8 points in Wisconsin and Michigan, by 5 points in Pennsylvania, by 2 or 3 points in Florida and Arizona, and even a little bit ahead in Georgia and with a pretty decent chance to win Texas, we think they’d be fairly pleased.
It’s also worth keeping in mind the background conditions in the country today. Trump only barely won the election four years ago, against a highly unpopular opponent in Clinton. In 2016, 18 percent of voters in the national exit poll disliked both Trump and Clinton, and those voters went for Trump by 17 points. If they’d merely split evenly, Clinton would have (narrowly) won the Electoral College. Many of those voters actually like Biden, though, who has much better favorability ratings than either Clinton or Trump.
Meanwhile, the election comes at a time where a 2:1 majority of voters are dissatisfied with the direction of the country amid a COVID-19 pandemic that his killed 233,000 Americans — and which has gotten worse in recent weeks — along with high (though improving) unemployment, a summer of racial protests, and continuous erosions of democratic norms by Trump and his administration. Trump’s approval rating has been in negative territory through virtually the entirety of his presidency. Trump’s electoral record is hardly unblemished: Democrats won the popular vote for the U.S. House by nearly 9 points in 2018, about the same margin that Trump now trails in national polls, in an election where polls and forecasts were highly accurate.
In other words, given everything going on in the country — and Biden’s popularity relative to Clinton — it simply shouldn’t be that hard to imagine a small number of voters switching from Trump to Biden. Indeed, that’s what polls show: There are more Trump-to-Biden voters than Clinton-to-Trump voters. The lion’s share of people who voted for Gary Johnson or another third party candidate four years ago also say they plan to vote for Biden.
Trump might be able to overcome this with a disproportionately high Republican turnout. But while Republican turnout might be very high, Democratic turnout almost certainly will be too, as evidenced by, among other things: Democrats’ equal or higher enthusiasm level in polls; their very high numbers in early and absentee voting, and their greater fundraising prowess throughout the cycle.
Again, this is not to deny that Trump will turn out his voters, too. Our model projects overall turnout in the race to be a record setting 158 million, with an 80th percentile range between 147 million and 168 million. But if persuadable voters and independents are mostly flipping to the other party, you need your turnout to be high and for the other party’s to be low to have much of a shot, and that latter condition doesn’t appear likely for Trump.
Still, 10 percent chances happen, there’s never been an election quite like this one and this isn’t a moment that anybody should be taking anything for granted. We hope you’ll follow our coverage for as long as it takes to determine who won.
Nate Silver's Blog
- Nate Silver's profile
- 729 followers




