Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 96
September 8, 2022
What Is The Service-Profit Chain? Service-Profit Chain In A Nutshell
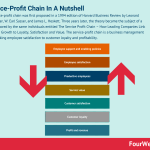

The service-profit chain was first proposed in a 1994 edition of Harvard Business Review by Leonard Schlesinger, W. Earl Sasser, and James L. Heskett. Three years later, the theory became the subject of a book authored by the same individuals entitled The Service Profit Chain – How Leading Companies Link Profit and Growth to Loyalty, Satisfaction and Value. The service-profit chain is a business management theory linking employee satisfaction to customer loyalty and profitability.
Understanding the service-profit chainMany consider management, staff, customers, and other stakeholders to be the most important components of a marketing mix – and for good reason. The way a company communicates with its employees and provides a suitable workplace for them impacts those outside the organization and the relationships built. This notion was echoed by entrepreneur Richard Branson, who once suggested training people so well they could find employment elsewhere while treating them so well that they didn’t want to leave.
While the service-profit chain is a relatively simple concept, many businesses do not understand the impact of their internal functions and processes on customer interaction. To better synthesize this relationship, the chain itself is based on cause and effect and comprises various components.
In the next section, we will take a look at these components in more detail.
The seven links of the service-profit chainThe service-profit chain consists of seven links that describe how internal processes impact customer loyalty:
Employee support and enabling policies – at the start of the chain are employee rewards, incentives, programs, and policies that motivate performance and create a stronger culture.Employee satisfaction – with employees properly supported and motivated, satisfaction increases.Productive employees – satisfied employees are more likely to be productive employees. What’s more, productive employees tend to go above and beyond for the company and its customers.Service value – occupying the next link in the chain is service value, which argues productive and satisfied employees bring more value to the customer. This value may take the form of friendlier customer service or higher quality products, among many other things.Customer satisfaction – naturally, a customer who receives better service or a high-quality product is more satisfied in their dealings with the company.Customer loyalty – while satisfied customers are more likely to buy from a company multiple times, it’s important to note that the relationship between satisfaction and loyalty is not linear. Satisfaction exists on a scale, with low to moderate amounts unlikely to see the customer recommend a product to a friend or leave a positive review. At the other end of the scale, however, satisfaction becomes enthusiasm. It is this enthusiasm for a product or company that ultimately drives loyalty.Profit and revenue – at the end of the service-profit chain is profit and revenue, which increases as the number of loyal customers increases.Key takeaways:The service-profit chain is a business management theory linking employee satisfaction to customer loyalty and profitability. It was first proposed in 1994 by Leonard Schlesinger, W. Earl Sasser, and James L. Heskett.The service-profit chain is a straightforward concept, but many businesses fail to recognize the relationship between their internal processes and interactions with customers.The service-profit chain is based on seven links, with each link interacting with the rest of the chain through cause and effect. The seven links are employee support and enabling policies, employee satisfaction, productive employees, service value, customer satisfaction, customer loyalty, and profit and revenue.Organizational Structure Case StudiesAirbnb Organizational Structure
 Airbnb follows a holacracy model, or a sort of flat organizational structure, where teams are organized for projects, to move quickly and iterate fast, thus keeping a lean and flexible approach. Airbnb also moved to a hybrid model where employees can work from anywhere and meet on a quarterly basis to plan ahead, and connect to each other.
Airbnb follows a holacracy model, or a sort of flat organizational structure, where teams are organized for projects, to move quickly and iterate fast, thus keeping a lean and flexible approach. Airbnb also moved to a hybrid model where employees can work from anywhere and meet on a quarterly basis to plan ahead, and connect to each other.  eBay was until recently a multi-divisional (M-form) organization with semi-autonomous units grouped according to the services they provided. Today, eBay has a single division called Marketplace, which includes eBay and its international iterations.
eBay was until recently a multi-divisional (M-form) organization with semi-autonomous units grouped according to the services they provided. Today, eBay has a single division called Marketplace, which includes eBay and its international iterations. IBM has an organizational structure characterized by product-based divisions, enabling its strategy to develop innovative and competitive products in multiple markets. IBM is also characterized by function-based segments that support product development and innovation for each product-based division, which include Global Markets, Integrated Supply Chain, Research, Development, and Intellectual Property.
IBM has an organizational structure characterized by product-based divisions, enabling its strategy to develop innovative and competitive products in multiple markets. IBM is also characterized by function-based segments that support product development and innovation for each product-based division, which include Global Markets, Integrated Supply Chain, Research, Development, and Intellectual Property. Sony has a matrix organizational structure primarily based on function-based groups and product/business divisions. The structure also incorporates geographical divisions. In 2021, Sony announced the overhauling of its organizational structure, changing its name from Sony Corporation to Sony Group Corporation to better identify itself as the headquarters of the Sony group of companies skewing the company toward product divisions.
Sony has a matrix organizational structure primarily based on function-based groups and product/business divisions. The structure also incorporates geographical divisions. In 2021, Sony announced the overhauling of its organizational structure, changing its name from Sony Corporation to Sony Group Corporation to better identify itself as the headquarters of the Sony group of companies skewing the company toward product divisions.Facebook Organizational Structure
 Facebook is characterized by a multi-faceted matrix organizational structure. The company utilizes a flat organizational structure in combination with corporate function-based teams and product-based or geographic divisions. The flat organization structure is organized around the leadership of Mark Zuckerberg, and the key executives around him. On the other hand, the function-based teams based on the main corporate functions (like HR, product management, investor relations, and so on).
Facebook is characterized by a multi-faceted matrix organizational structure. The company utilizes a flat organizational structure in combination with corporate function-based teams and product-based or geographic divisions. The flat organization structure is organized around the leadership of Mark Zuckerberg, and the key executives around him. On the other hand, the function-based teams based on the main corporate functions (like HR, product management, investor relations, and so on).Google Organizational Structure
 Google (Alphabet) has a cross-functional (team-based) organizational structure known as a matrix structure with some degree of flatness. Over the years, as the company scaled and it became a tech giant, its organizational structure is morphing more into a centralized organization.
Google (Alphabet) has a cross-functional (team-based) organizational structure known as a matrix structure with some degree of flatness. Over the years, as the company scaled and it became a tech giant, its organizational structure is morphing more into a centralized organization. Tesla Organizational Structure
 Tesla is characterized by a functional organizational structure with aspects of a hierarchical structure. Tesla does employ functional centers that cover all business activities, including finance, sales, marketing, technology, engineering, design, and the offices of the CEO and chairperson. Tesla’s headquarters in Austin, Texas, decide the strategic direction of the company, with international operations given little autonomy.
Tesla is characterized by a functional organizational structure with aspects of a hierarchical structure. Tesla does employ functional centers that cover all business activities, including finance, sales, marketing, technology, engineering, design, and the offices of the CEO and chairperson. Tesla’s headquarters in Austin, Texas, decide the strategic direction of the company, with international operations given little autonomy. McDonald’s Organizational Structure
 McDonald’s has a divisional organizational structure where each division – based on geographical location – is assigned operational responsibilities and strategic objectives. The main geographical divisions are the US, internationally operated markets, and international developmental licensed markets. And on the other hand, the hierarchical leadership structure is organized around regional and functional divisions.
McDonald’s has a divisional organizational structure where each division – based on geographical location – is assigned operational responsibilities and strategic objectives. The main geographical divisions are the US, internationally operated markets, and international developmental licensed markets. And on the other hand, the hierarchical leadership structure is organized around regional and functional divisions. Walmart Organizational Structure
 Walmart has a hybrid hierarchical-functional organizational structure, otherwise referred to as a matrix structure that combines multiple approaches. On the one hand, Walmart follows a hierarchical structure, where the current CEO Doug McMillon is the only employee without a direct superior, and directives are sent from top-level management. On the other hand, the function-based structure of Walmart is used to categorize employees according to their particular skills and experience.
Walmart has a hybrid hierarchical-functional organizational structure, otherwise referred to as a matrix structure that combines multiple approaches. On the one hand, Walmart follows a hierarchical structure, where the current CEO Doug McMillon is the only employee without a direct superior, and directives are sent from top-level management. On the other hand, the function-based structure of Walmart is used to categorize employees according to their particular skills and experience.Microsoft Organizational Structure
 Microsoft has a product-type divisional organizational structure based on functions and engineering groups. As the company scaled over time it also became more hierarchical, however still keeping its hybrid approach between functions, engineering groups, and management.
Microsoft has a product-type divisional organizational structure based on functions and engineering groups. As the company scaled over time it also became more hierarchical, however still keeping its hybrid approach between functions, engineering groups, and management. Read Next: Organizational Structure
Read Also: Business Model
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What Is The Service-Profit Chain? Service-Profit Chain In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
24 Fintech Companies And Their Business Models
 Acorns
Acorns Acorns is a fintech platform providing services related to Robo-investing and micro-investing. The company makes money primarily through three subscription tiers: Lite – ($1/month), which gives users access to Acorns Invest, Personal ($3/month) that includes Invest plus the Later (retirement) and Spend (personal checking account) suite of products, Family ($5/month) with features from both the Lite and Personal plans with the addition of Early. Affirm
Acorns is a fintech platform providing services related to Robo-investing and micro-investing. The company makes money primarily through three subscription tiers: Lite – ($1/month), which gives users access to Acorns Invest, Personal ($3/month) that includes Invest plus the Later (retirement) and Spend (personal checking account) suite of products, Family ($5/month) with features from both the Lite and Personal plans with the addition of Early. Affirm Started as a pay-later solution integrated to merchants’ checkouts, Affirm makes money from merchants’ fees as consumers pick up the pay-later solution. Affirm also makes money through interests earned from the consumer loans, when those are repurchased from the originating bank. In 2020 Affirm made 50% of its revenues from merchants’ fees, about 37% from interests, and the remaining from virtual cards and servicing fees.Alipay
Started as a pay-later solution integrated to merchants’ checkouts, Affirm makes money from merchants’ fees as consumers pick up the pay-later solution. Affirm also makes money through interests earned from the consumer loans, when those are repurchased from the originating bank. In 2020 Affirm made 50% of its revenues from merchants’ fees, about 37% from interests, and the remaining from virtual cards and servicing fees.Alipay Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.Betterment
Alipay is a Chinese mobile and online payment platform created in 2004 by entrepreneur Jack Ma as the payment arm of Taobao, a major Chinese eCommerce site. Alipay, therefore, is the B2C component of Alibaba Group. Alipay makes money via escrows transaction fees, a range of value-added ancillary services, and through its Credit Pay Instalment fees.Betterment Betterment is an American financial advisory company founded in 2008 by MBA graduate Jon Stein and lawyer Eli Broverman. Betterment makes money via investment plans, financial advice packages, betterment for advisors, betterment for business, cash reserve, and checking accounts. Braintree
Betterment is an American financial advisory company founded in 2008 by MBA graduate Jon Stein and lawyer Eli Broverman. Betterment makes money via investment plans, financial advice packages, betterment for advisors, betterment for business, cash reserve, and checking accounts. Braintree Venmo is a peer-to-peer payments app enabling users to share and make payments with friends for a variety of services. The service is free, but a 3% fee applies to credit cards. Venmo also launched a debit card in partnership with Mastercard. Venmo got acquired in 2012 by Braintree, and Braintree got acquired in 2013 by PayPal.Chime
Venmo is a peer-to-peer payments app enabling users to share and make payments with friends for a variety of services. The service is free, but a 3% fee applies to credit cards. Venmo also launched a debit card in partnership with Mastercard. Venmo got acquired in 2012 by Braintree, and Braintree got acquired in 2013 by PayPal.Chime Chime is an American neobank (internet-only bank) company, providing fee-free financial services through its mobile banking app, thus providing personal finance services free of charge while making the majority of its money via interchange fees (paid by merchants when consumers use their debit cards) and ATM fees. Binance
Chime is an American neobank (internet-only bank) company, providing fee-free financial services through its mobile banking app, thus providing personal finance services free of charge while making the majority of its money via interchange fees (paid by merchants when consumers use their debit cards) and ATM fees. Binance Binance is a cryptocurrency exchange domiciled in the Cayman Islands. It was founded in 2017 by Changpeng “CZ” Zhao and Yi He. During a game of poker in 2013, Zhao first learned of the potential of bitcoin. Soon after, he decided to go all-in on the cryptocurrency, selling his apartment to buy as much as he could. Binance revenue generation comes from six key areas: trading, withdrawal, and deposit fees; margin-borrow interest, futures’ trading fees, and cross collateral interest rates. Coinbase
Binance is a cryptocurrency exchange domiciled in the Cayman Islands. It was founded in 2017 by Changpeng “CZ” Zhao and Yi He. During a game of poker in 2013, Zhao first learned of the potential of bitcoin. Soon after, he decided to go all-in on the cryptocurrency, selling his apartment to buy as much as he could. Binance revenue generation comes from six key areas: trading, withdrawal, and deposit fees; margin-borrow interest, futures’ trading fees, and cross collateral interest rates. Coinbase Coinbase is among the most popular platforms for trading and storing crypto-assets, whose mission is “to create an open financial system for the world” by enabling customers to trade cryptocurrencies. Its platform serves both as a search and discovery engine for crypto assets. The company makes money primarily through fees earned for the transactions processed through the platform, custodial services offered, interest, and subscriptions.Compass
Coinbase is among the most popular platforms for trading and storing crypto-assets, whose mission is “to create an open financial system for the world” by enabling customers to trade cryptocurrencies. Its platform serves both as a search and discovery engine for crypto assets. The company makes money primarily through fees earned for the transactions processed through the platform, custodial services offered, interest, and subscriptions.Compass Compass is a licensed American real-estate broker incorporating online real estate technology as a marketing medium. The company makes money via sales commissions (collected whenever a sale is facilitated or tenants are found for a rental property) and bridge loans (a service allowing the seller to purchase a home before the revenue from the sale of their previous home is available).Dosh
Compass is a licensed American real-estate broker incorporating online real estate technology as a marketing medium. The company makes money via sales commissions (collected whenever a sale is facilitated or tenants are found for a rental property) and bridge loans (a service allowing the seller to purchase a home before the revenue from the sale of their previous home is available).Dosh Dosh is a Fintech platform that enables automatic cash backs for consumers. Its business model connects major card providers with online and offline local businesses to develop automatic cash back programs. The company makes money by earning an affiliate commission on each eligible sale from consumers. E-Trade
Dosh is a Fintech platform that enables automatic cash backs for consumers. Its business model connects major card providers with online and offline local businesses to develop automatic cash back programs. The company makes money by earning an affiliate commission on each eligible sale from consumers. E-Trade E-Trade is a trading platform, allowing investors to trade common and preferred stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), options, bonds, mutual funds, and futures contracts, acquired by Morgan Stanley in 2020 for $13 billion. E-Trade makes money through interest income, order flow, margin interests, options, future and bonds trading, and through other fees and service charges. Klarna
E-Trade is a trading platform, allowing investors to trade common and preferred stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), options, bonds, mutual funds, and futures contracts, acquired by Morgan Stanley in 2020 for $13 billion. E-Trade makes money through interest income, order flow, margin interests, options, future and bonds trading, and through other fees and service charges. Klarna Klarna is a financial technology company allowing consumers to shop with a temporary Visa card. Thus it then performs a soft credit check and pays the merchant. Klarna makes money by charging merchants. Klarna also earns a percentage of interchange fees as a commission and for interests earned on customers’ accounts.Lemonade
Klarna is a financial technology company allowing consumers to shop with a temporary Visa card. Thus it then performs a soft credit check and pays the merchant. Klarna makes money by charging merchants. Klarna also earns a percentage of interchange fees as a commission and for interests earned on customers’ accounts.Lemonade Lemonade is an insurance tech company using behavioral economics and artificial intelligence to process claims efficiently. The company leverages technology to streamline onboarding customers while also applying a financial model to reduce conflicts of interest with customers (perhaps by donating the variable premiums to charity). The company makes money by selling its core insurance products, and via its tech platform, it tries to enhance its sales. Monzo
Lemonade is an insurance tech company using behavioral economics and artificial intelligence to process claims efficiently. The company leverages technology to streamline onboarding customers while also applying a financial model to reduce conflicts of interest with customers (perhaps by donating the variable premiums to charity). The company makes money by selling its core insurance products, and via its tech platform, it tries to enhance its sales. Monzo Monzo is an English neobank offering a mobile app and a prepaid debit card for consumers and businesses. It was one of the first app-based banks to enter the UK market, founded by Gary Dolman, Jason Bates, Jonas Huckestein, Paul Rippon, and Tom Blomfield in 2015. All were employees of Starling Bank, a similar neobank challenging the dominance of established financial institutions in England. The company enjoys many revenue streams: business and consumer subscriptions, interchange and overdraft fees, personal loans, and more. NerdWallet
Monzo is an English neobank offering a mobile app and a prepaid debit card for consumers and businesses. It was one of the first app-based banks to enter the UK market, founded by Gary Dolman, Jason Bates, Jonas Huckestein, Paul Rippon, and Tom Blomfield in 2015. All were employees of Starling Bank, a similar neobank challenging the dominance of established financial institutions in England. The company enjoys many revenue streams: business and consumer subscriptions, interchange and overdraft fees, personal loans, and more. NerdWallet NerdWallet is an online platform providing tools and tips on all matters related to personal finance. The company gained traction as a simple web application comparing credit cards. NerdWallet makes money via affiliate commissions determined according to the affiliate agreements. Quadpay
NerdWallet is an online platform providing tools and tips on all matters related to personal finance. The company gained traction as a simple web application comparing credit cards. NerdWallet makes money via affiliate commissions determined according to the affiliate agreements. Quadpay Quadpay was an American fintech company founded by Adam Ezra and Brad Lindenberg in 2017. Ezra and Lindenberg witnessed the rising popularity of buy-now-pay-later service Afterpay in Australia and similar service Klarna in Europe. Quadpay collects a range of fees from both the merchant and the consumer via merchandise fees, convenience fees, late payment, and interchange fees. Revolut
Quadpay was an American fintech company founded by Adam Ezra and Brad Lindenberg in 2017. Ezra and Lindenberg witnessed the rising popularity of buy-now-pay-later service Afterpay in Australia and similar service Klarna in Europe. Quadpay collects a range of fees from both the merchant and the consumer via merchandise fees, convenience fees, late payment, and interchange fees. Revolut Revolut an English fintech company offering banking and investment services to consumers. Founded in 2015 by Nikolay Storonsky and Vlad Yatsenko, the company initially produced a low-rate travel card. Storonsky in particular was an avid traveler who became tired of spending hundreds of pounds on currency exchange and foreign transaction fees. The Revolut app and core banking account are free to use. Instead, money is made through a combination of subscription fees, transaction fees, perks, and ancillary services.Robinhood
Revolut an English fintech company offering banking and investment services to consumers. Founded in 2015 by Nikolay Storonsky and Vlad Yatsenko, the company initially produced a low-rate travel card. Storonsky in particular was an avid traveler who became tired of spending hundreds of pounds on currency exchange and foreign transaction fees. The Revolut app and core banking account are free to use. Instead, money is made through a combination of subscription fees, transaction fees, perks, and ancillary services.Robinhood Robinhood is an app that helps to invest in stocks, ETFs, options, and cryptocurrencies, all commission-free. Robinhood earns money by offering: Robinhood Gold, a margin trading service, which starts at $6 a month, earn interests from customer cash and stocks, and rebates from market makers and trading venues.
Robinhood is an app that helps to invest in stocks, ETFs, options, and cryptocurrencies, all commission-free. Robinhood earns money by offering: Robinhood Gold, a margin trading service, which starts at $6 a month, earn interests from customer cash and stocks, and rebates from market makers and trading venues.SoFi
 SoFi is an online lending platform that provides affordable education loans to students, and it expanded into financial services, including loans, credit cards, investment services, and insurance. It makes money primarily via payment processing fees and loan securitization.
SoFi is an online lending platform that provides affordable education loans to students, and it expanded into financial services, including loans, credit cards, investment services, and insurance. It makes money primarily via payment processing fees and loan securitization. Squarespace
 Squarespace is a North American hosting and website building company. Founded in 2004 by college student Anthony Casalena as a blog hosting service, it grew to become among the most successful website building companies. The company mostly makes money via its subscription plans. It also makes money via customizations on top of its subscription plans. And in part also as transaction fees for the website where it processes the sales.Stash
Squarespace is a North American hosting and website building company. Founded in 2004 by college student Anthony Casalena as a blog hosting service, it grew to become among the most successful website building companies. The company mostly makes money via its subscription plans. It also makes money via customizations on top of its subscription plans. And in part also as transaction fees for the website where it processes the sales.Stash Stash is a FinTech platform offering a suite of financial tools for young investors, coupled with personalized investment advice and life insurance. The company primarily makes money via subscriptions, cashback, payment for order flows, and interest for cash sitting on members’ accounts. Venmo
Stash is a FinTech platform offering a suite of financial tools for young investors, coupled with personalized investment advice and life insurance. The company primarily makes money via subscriptions, cashback, payment for order flows, and interest for cash sitting on members’ accounts. Venmo Venmo is a peer-to-peer payments app enabling users to share and make payments with friends for a variety of services. The service is free, but a 3% fee applies to credit cards. Venmo also launched a debit card in partnership with Mastercard. Venmo got acquired in 2012 by Braintree, and Braintree got acquired in 2013 by PayPal.
Venmo is a peer-to-peer payments app enabling users to share and make payments with friends for a variety of services. The service is free, but a 3% fee applies to credit cards. Venmo also launched a debit card in partnership with Mastercard. Venmo got acquired in 2012 by Braintree, and Braintree got acquired in 2013 by PayPal.Wealthfront
 Wealthfront is an automated Fintech investment platform providing investment, retirement, and cash management products to retail investors, mostly making money on the annual 0.25% advisory fee the company charges for assets under management. It also makes money via a line of credits and interests on the cash accounts.
Wealthfront is an automated Fintech investment platform providing investment, retirement, and cash management products to retail investors, mostly making money on the annual 0.25% advisory fee the company charges for assets under management. It also makes money via a line of credits and interests on the cash accounts.Zelle
 Zelle is a peer-to-peer payment network that indirectly benefits the banks’ consortium that backs it. Zelle also enables users to pay businesses for goods and services, free for users. Merchants pay a 1% fee to Visa or Mastercard, who share it with the bank that issued the card.
Zelle is a peer-to-peer payment network that indirectly benefits the banks’ consortium that backs it. Zelle also enables users to pay businesses for goods and services, free for users. Merchants pay a 1% fee to Visa or Mastercard, who share it with the bank that issued the card.Read Next: How Does Venmo Make Money
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsThe post 24 Fintech Companies And Their Business Models appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
September 7, 2022
14 Decision-Making Models You Need To Know
 The STAR method is an interview technique that is used to answer behavioral interview questions. The STAR method is a technique that an interviewee can use to help prepare for behavioral or situational interview questions that assess important skills. STAR is an acronym comprised of four factors that make the question answering framework: situation, task, action, and result. Vroom-Yetton Decision Model
The STAR method is an interview technique that is used to answer behavioral interview questions. The STAR method is a technique that an interviewee can use to help prepare for behavioral or situational interview questions that assess important skills. STAR is an acronym comprised of four factors that make the question answering framework: situation, task, action, and result. Vroom-Yetton Decision Model The Vroom-Yetton decision model is a decision-making process based on situational leadership. According to this model, there are five decision-making styles guides group-based decision-making according to the situation at hand and the level of involvement of subordinates: Autocratic Type 1 (AI), Autocratic Type 2 (AII), Consultative Type 1 (CI), Consultative Type 2 (CII), Group-based Type 2 (GII).TDODAR Decision Model
The Vroom-Yetton decision model is a decision-making process based on situational leadership. According to this model, there are five decision-making styles guides group-based decision-making according to the situation at hand and the level of involvement of subordinates: Autocratic Type 1 (AI), Autocratic Type 2 (AII), Consultative Type 1 (CI), Consultative Type 2 (CII), Group-based Type 2 (GII).TDODAR Decision Model The TDODAR decision model helps an individual make good decisions in emergencies or any scenario with a high degree of uncertainty. TDODAR is an acronym of the six sequential steps that every practitioner must follow, comprising: time, diagnosis, options, decide, act/assign, review.Blindspot Analysis
The TDODAR decision model helps an individual make good decisions in emergencies or any scenario with a high degree of uncertainty. TDODAR is an acronym of the six sequential steps that every practitioner must follow, comprising: time, diagnosis, options, decide, act/assign, review.Blindspot Analysis A Blindspot Analysis is a means of unearthing incorrect or outdated assumptions that can harm decision making in an organization. The term “blindspot analysis” was first coined by American economist Michael Porter. Porter argued that in business, outdated ideas or strategies had the potential to stifle modern ideas and prevent them from succeeding. Furthermore, decisions a business thought were made with care caused projects to fail because major factors had not been duly considered.Foursquare Protocol
A Blindspot Analysis is a means of unearthing incorrect or outdated assumptions that can harm decision making in an organization. The term “blindspot analysis” was first coined by American economist Michael Porter. Porter argued that in business, outdated ideas or strategies had the potential to stifle modern ideas and prevent them from succeeding. Furthermore, decisions a business thought were made with care caused projects to fail because major factors had not been duly considered.Foursquare Protocol The Foursquare Protocol is an ethical decision-making model. The Foursquare Protocol helps businesses respond to challenging situations by making decisions according to a code of ethics. It can also be used to help individuals make decisions in the context of their own moral principles. It consists of four steps: gather the facts, understand previous decisions, assess the degree of similarity to past events, and assess yourself. Working Backwards
The Foursquare Protocol is an ethical decision-making model. The Foursquare Protocol helps businesses respond to challenging situations by making decisions according to a code of ethics. It can also be used to help individuals make decisions in the context of their own moral principles. It consists of four steps: gather the facts, understand previous decisions, assess the degree of similarity to past events, and assess yourself. Working Backwards The Amazon Working Backwards Method is a product development methodology that advocates building a product based on customer needs. The Amazon Working Backwards Method gained traction after notable Amazon employee Ian McAllister shared the company’s product development approach on Quora. McAllister noted that the method seeks “to work backwards from the customer, rather than starting with an idea for a product and trying to bolt customers onto it.”SCAMPER Method
The Amazon Working Backwards Method is a product development methodology that advocates building a product based on customer needs. The Amazon Working Backwards Method gained traction after notable Amazon employee Ian McAllister shared the company’s product development approach on Quora. McAllister noted that the method seeks “to work backwards from the customer, rather than starting with an idea for a product and trying to bolt customers onto it.”SCAMPER Method Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.Decision Matrix
Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.Decision Matrix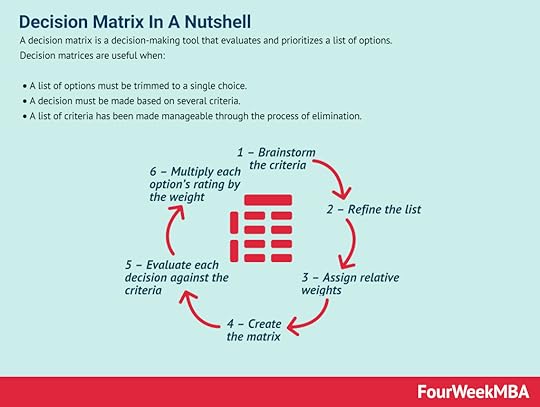 A decision matrix is a decision-making tool that evaluates and prioritizes a list of options. Decision matrices are useful when: A list of options must be trimmed to a single choice. A decision must be made based on several criteria. A list of criteria has been made manageable through the process of elimination.Cost-Benefit Analysis
A decision matrix is a decision-making tool that evaluates and prioritizes a list of options. Decision matrices are useful when: A list of options must be trimmed to a single choice. A decision must be made based on several criteria. A list of criteria has been made manageable through the process of elimination.Cost-Benefit Analysis A cost-benefit analysis is a process a business can use to analyze decisions according to the costs associated with making that decision. For a cost analysis to be effective it’s important to articulate the project in the simplest terms possible, identify the costs, determine the benefits of project implementation, assess the alternatives.Go/No-Go Decision
A cost-benefit analysis is a process a business can use to analyze decisions according to the costs associated with making that decision. For a cost analysis to be effective it’s important to articulate the project in the simplest terms possible, identify the costs, determine the benefits of project implementation, assess the alternatives.Go/No-Go Decision In general, terms, go/no-go decision making is a process of passing or failing a proposition. Each proposition is assessed according to criteria that determine whether a project advances to the next stage. The outcome of the go/no-go decision making is to assess whether to go or not to go with a project, or perhaps proceed with caveats. Speed-Reversibility
In general, terms, go/no-go decision making is a process of passing or failing a proposition. Each proposition is assessed according to criteria that determine whether a project advances to the next stage. The outcome of the go/no-go decision making is to assess whether to go or not to go with a project, or perhaps proceed with caveats. Speed-Reversibility  Asymmetric Betting
Asymmetric Betting
 Growth Matrix
Growth Matrix In the FourWeekMBA growth matrix, you can apply growth for existing customers by tackling the same problems (gain mode). Or by tackling existing problems, for new customers (expand mode). Or by tackling new problems for existing customers (extend mode). Or perhaps by tackling whole new problems for new customers (reinvent mode).Revenue Streams Matrix
In the FourWeekMBA growth matrix, you can apply growth for existing customers by tackling the same problems (gain mode). Or by tackling existing problems, for new customers (expand mode). Or by tackling new problems for existing customers (extend mode). Or perhaps by tackling whole new problems for new customers (reinvent mode).Revenue Streams Matrix In the FourWeekMBA Revenue Streams Matrix, revenue streams are classified according to the kind of interactions the business has with its key customers. The first dimension is the “Frequency” of interaction with the key customer. As the second dimension, there is the “Ownership” of the interaction with the key customer.
In the FourWeekMBA Revenue Streams Matrix, revenue streams are classified according to the kind of interactions the business has with its key customers. The first dimension is the “Frequency” of interaction with the key customer. As the second dimension, there is the “Ownership” of the interaction with the key customer.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post 14 Decision-Making Models You Need To Know appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
11 Business Process Frameworks
 Change is an important and necessary fact of life for all organizations. But change is often unsuccessful because the people within organizations are resistant to change. Change management is a systematic approach to managing the transformation of organizational goals, values, technologies, or processes.Operating Model
Change is an important and necessary fact of life for all organizations. But change is often unsuccessful because the people within organizations are resistant to change. Change management is a systematic approach to managing the transformation of organizational goals, values, technologies, or processes.Operating Model The operating model is a visual representation and mapping of the processes and how the organization delivers value and, therefore, how it executes its business model. Therefore, the operating model is how the whole organization is structured around the value chain to build a viable business model. Ladder of Inference
The operating model is a visual representation and mapping of the processes and how the organization delivers value and, therefore, how it executes its business model. Therefore, the operating model is how the whole organization is structured around the value chain to build a viable business model. Ladder of Inference The ladder of inference is a conscious or subconscious thinking process where an individual moves from a fact to a decision or action. The ladder of inference was created by academic Chris Argyris to illustrate how people form and then use mental models to make decisions.Four-Step Innovation Process
The ladder of inference is a conscious or subconscious thinking process where an individual moves from a fact to a decision or action. The ladder of inference was created by academic Chris Argyris to illustrate how people form and then use mental models to make decisions.Four-Step Innovation Process The four-step innovation process is a simple tool that businesses can use to drive consistent innovation. The four-step innovation process was created by David Weiss and Claude Legrand as a means of encouraging sustainable innovation within an organization. The process helps businesses solve complex problems with creative ideas instead of relying on low-impact, quick-fix solutions.TQM Framework
The four-step innovation process is a simple tool that businesses can use to drive consistent innovation. The four-step innovation process was created by David Weiss and Claude Legrand as a means of encouraging sustainable innovation within an organization. The process helps businesses solve complex problems with creative ideas instead of relying on low-impact, quick-fix solutions.TQM Framework The Total Quality Management (TQM) framework is a technique based on the premise that employees continuously work on their ability to provide value to customers. Importantly, the word “total” means that all employees are involved in the process – regardless of whether they work in development, production, or fulfillment.Balanced Scorecard
The Total Quality Management (TQM) framework is a technique based on the premise that employees continuously work on their ability to provide value to customers. Importantly, the word “total” means that all employees are involved in the process – regardless of whether they work in development, production, or fulfillment.Balanced Scorecard First proposed by accounting academic Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system that allows an organization to focus on big-picture strategic goals. The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard include financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. From there, according to the balanced scorecard, it’s possible to have a holistic view of the business.Sales Cycle
First proposed by accounting academic Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system that allows an organization to focus on big-picture strategic goals. The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard include financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. From there, according to the balanced scorecard, it’s possible to have a holistic view of the business.Sales Cycle A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products. In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.CHAMP Methodology
A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products. In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.CHAMP Methodology The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process
The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process
The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. STP Marketing
The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. STP Marketing STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.
STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsNetwork EffectsThe post 11 Business Process Frameworks appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
16 Sales Methodologies To Gain Traction For Your Business
 Business Development
Business Development Business development comprises a set of strategies and actions to grow a business via a mixture of sales, marketing, and distribution. While marketing usually relies on automation to reach a wider audience, and sales typically leverage a one-to-one approach. The business development’s role is that of generating distribution.Sales vs. Marketing
Business development comprises a set of strategies and actions to grow a business via a mixture of sales, marketing, and distribution. While marketing usually relies on automation to reach a wider audience, and sales typically leverage a one-to-one approach. The business development’s role is that of generating distribution.Sales vs. Marketing The more you move from consumers to enterprise clients, the more you’ll need a sales force able to manage complex sales. As a rule of thumb, a more expensive product, in B2B or Enterprise, will require an organizational structure around sales. An inexpensive product to be offered to consumers will leverage on marketing.Sales Cycle
The more you move from consumers to enterprise clients, the more you’ll need a sales force able to manage complex sales. As a rule of thumb, a more expensive product, in B2B or Enterprise, will require an organizational structure around sales. An inexpensive product to be offered to consumers will leverage on marketing.Sales Cycle A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products. In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.RevOps
A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products. In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.RevOps RevOps – short for Revenue Operations – is a framework that aims to maximize the revenue potential of an organization. RevOps seeks to align these departments by giving them access to the same data and tools. With shared information, each then understands their role in the sales funnel and can work collaboratively to increase revenue.Revenue Modeling
RevOps – short for Revenue Operations – is a framework that aims to maximize the revenue potential of an organization. RevOps seeks to align these departments by giving them access to the same data and tools. With shared information, each then understands their role in the sales funnel and can work collaboratively to increase revenue.Revenue Modeling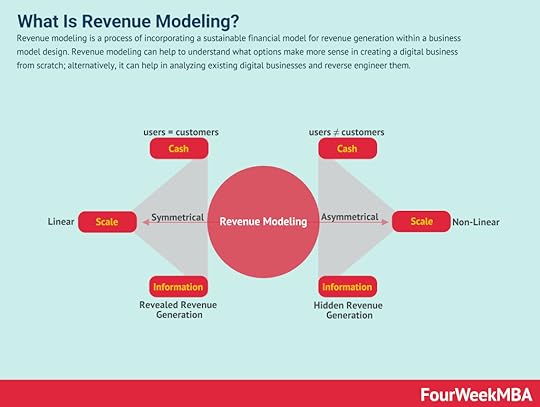 Revenue modeling is a process of incorporating a sustainable financial model for revenue generation within a business model design. Revenue modeling can help to understand what options make more sense in creating a digital business from scratch; alternatively, it can help in analyzing existing digital businesses and reverse engineer them. Customer Experience Map
Revenue modeling is a process of incorporating a sustainable financial model for revenue generation within a business model design. Revenue modeling can help to understand what options make more sense in creating a digital business from scratch; alternatively, it can help in analyzing existing digital businesses and reverse engineer them. Customer Experience Map Customer experience maps are visual representations of every encounter a customer has with a brand. On a customer experience map, interactions called touchpoints visually denote each interaction that a business has with its consumers. Typically, these include every interaction from the first contact to marketing, branding, sales, and customer support.AIDA Model
Customer experience maps are visual representations of every encounter a customer has with a brand. On a customer experience map, interactions called touchpoints visually denote each interaction that a business has with its consumers. Typically, these include every interaction from the first contact to marketing, branding, sales, and customer support.AIDA Model AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys. Social Selling
AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys. Social Selling Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.CHAMP Methodology
Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.CHAMP Methodology The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process
The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process
The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. STP Marketing
The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. STP Marketing STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels
STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.Pirate Metrics
The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.Pirate Metrics Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand. Bootstrapping
Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand. Bootstrapping The general concept of Bootstrapping connects to “a self-starting process that is supposed to proceed without external input.” In business, Bootstrapping means financing the growth of the company from the available cash flows produced by a viable business model. Bootstrapping requires the mastery of the key customers driving growth.Virtuous Cycles
The general concept of Bootstrapping connects to “a self-starting process that is supposed to proceed without external input.” In business, Bootstrapping means financing the growth of the company from the available cash flows produced by a viable business model. Bootstrapping requires the mastery of the key customers driving growth.Virtuous Cycles The virtuous cycle is a positive loop or a set of positive loops that trigger a non-linear growth. Indeed, in the context of digital platforms, virtuous cycles – also defined as flywheel models – help companies capture more market shares by accelerating growth. The classic example is Amazon’s lower prices driving more consumers, driving more sellers, thus improving variety and convenience, thus accelerating growth.
The virtuous cycle is a positive loop or a set of positive loops that trigger a non-linear growth. Indeed, in the context of digital platforms, virtuous cycles – also defined as flywheel models – help companies capture more market shares by accelerating growth. The classic example is Amazon’s lower prices driving more consumers, driving more sellers, thus improving variety and convenience, thus accelerating growth.The post 16 Sales Methodologies To Gain Traction For Your Business appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Leadership Tools To Take Your Company To The Next Level
 Core Leadership Styles
Core Leadership Styles Leadership styles encompass the behavioral qualities of a leader. These qualities are commonly used to direct, motivate, or manage groups of people. Some of the most recognized leadership styles include Autocratic, Democratic, or Laissez-Faire leadership styles. Transformational Leadership
Leadership styles encompass the behavioral qualities of a leader. These qualities are commonly used to direct, motivate, or manage groups of people. Some of the most recognized leadership styles include Autocratic, Democratic, or Laissez-Faire leadership styles. Transformational Leadership Transformational leadership is a style of leadership that motivates, encourages, and inspires employees to contribute to company growth. Leadership expert James McGregor Burns first described the concept of transformational leadership in a 1978 book entitled Leadership. Although Burns’ research was focused on political leaders, the term is also applicable for businesses and organizational psychology.Lightning Decision Jam
Transformational leadership is a style of leadership that motivates, encourages, and inspires employees to contribute to company growth. Leadership expert James McGregor Burns first described the concept of transformational leadership in a 1978 book entitled Leadership. Although Burns’ research was focused on political leaders, the term is also applicable for businesses and organizational psychology.Lightning Decision Jam The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model Harvard Business School professor Dr. John Kotter has been a thought-leader on organizational change, and he developed Kotter’s 8-step change model, which helps business managers deal with organizational change. Kotter created the 8-step model to drive organizational transformation. Value Disciplines
Harvard Business School professor Dr. John Kotter has been a thought-leader on organizational change, and he developed Kotter’s 8-step change model, which helps business managers deal with organizational change. Kotter created the 8-step model to drive organizational transformation. Value Disciplines The Value Disciplines Model was developed by authors Michael Treacy and Fred Wiersema. In their model, the authors use the term value discipline to represent any method a business may use to differentiate itself. The Value Disciplines Model argues that for a business to be viable, it must be successful in three key areas: customer intimacy, product leadership, and operational excellence.OKR
The Value Disciplines Model was developed by authors Michael Treacy and Fred Wiersema. In their model, the authors use the term value discipline to represent any method a business may use to differentiate itself. The Value Disciplines Model argues that for a business to be viable, it must be successful in three key areas: customer intimacy, product leadership, and operational excellence.OKR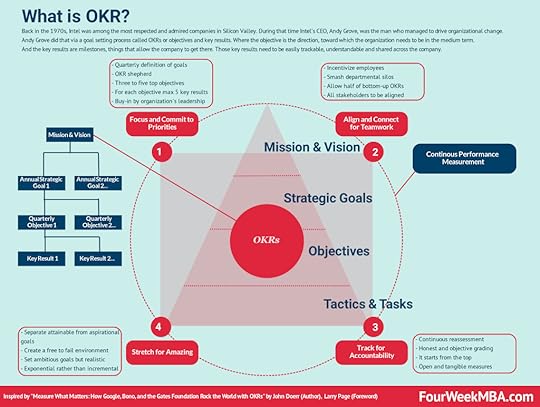 Andy Grove, helped Intel become among the most valuable companies by 1997. In his years at Intel, he conceived a management and goal-setting system, called OKR, standing for “objectives and key results.” Venture capitalist and early investor in Google, John Doerr, systematized in the book “Measure What Matters.”Tipping Point Leadership
Andy Grove, helped Intel become among the most valuable companies by 1997. In his years at Intel, he conceived a management and goal-setting system, called OKR, standing for “objectives and key results.” Venture capitalist and early investor in Google, John Doerr, systematized in the book “Measure What Matters.”Tipping Point Leadership Tipping Point Leadership is a low-cost means of achieving a strategic shift in an organization by focusing on extremes. Here, the extremes may refer to small groups of people, acts, and activities that exert a disproportionate influence over business performance.Self-Evolved Leader
Tipping Point Leadership is a low-cost means of achieving a strategic shift in an organization by focusing on extremes. Here, the extremes may refer to small groups of people, acts, and activities that exert a disproportionate influence over business performance.Self-Evolved Leader The Self-Evolved Leader by Dave McKeown is a practical guide for those leading teams who wish to adopt new ways of thinking which will take their leadership skills to the next level.Amazon Leadership Principles
The Self-Evolved Leader by Dave McKeown is a practical guide for those leading teams who wish to adopt new ways of thinking which will take their leadership skills to the next level.Amazon Leadership Principles Amazon fundamental principles that drove and drive the company are: Customer Obsession Ownership Invent and Simplify Are Right, A Lot Learn and Be Curious Hire and Develop the Best Insist on the Highest Standards Think Big Bias for Action Frugality Earn Trust Dive Deep Have Backbone; Disagree and Commit Deliver Results.Porter’s Generic Strategies
Amazon fundamental principles that drove and drive the company are: Customer Obsession Ownership Invent and Simplify Are Right, A Lot Learn and Be Curious Hire and Develop the Best Insist on the Highest Standards Think Big Bias for Action Frugality Earn Trust Dive Deep Have Backbone; Disagree and Commit Deliver Results.Porter’s Generic Strategies In his book, “Competitive Advantage,” in 1985, Porter conceptualized the concept of competitive advantage, by looking at two key aspects. Industry attractiveness, and the company’s strategic positioning. The latter, according to Porter, can be achieved either via cost leadership, differentiation, or focus. Organizational Structure Case Studies
In his book, “Competitive Advantage,” in 1985, Porter conceptualized the concept of competitive advantage, by looking at two key aspects. Industry attractiveness, and the company’s strategic positioning. The latter, according to Porter, can be achieved either via cost leadership, differentiation, or focus. Organizational Structure Case StudiesAirbnb Organizational Structure
 Airbnb follows a holacracy model, or a sort of flat organizational structure, where teams are organized for projects, to move quickly and iterate fast, thus keeping a lean and flexible approach. Airbnb also moved to a hybrid model where employees can work from anywhere and meet on a quarterly basis to plan ahead, and connect to each other.
Airbnb follows a holacracy model, or a sort of flat organizational structure, where teams are organized for projects, to move quickly and iterate fast, thus keeping a lean and flexible approach. Airbnb also moved to a hybrid model where employees can work from anywhere and meet on a quarterly basis to plan ahead, and connect to each other.  eBay was until recently a multi-divisional (M-form) organization with semi-autonomous units grouped according to the services they provided. Today, eBay has a single division called Marketplace, which includes eBay and its international iterations.
eBay was until recently a multi-divisional (M-form) organization with semi-autonomous units grouped according to the services they provided. Today, eBay has a single division called Marketplace, which includes eBay and its international iterations. IBM has an organizational structure characterized by product-based divisions, enabling its strategy to develop innovative and competitive products in multiple markets. IBM is also characterized by function-based segments that support product development and innovation for each product-based division, which include Global Markets, Integrated Supply Chain, Research, Development, and Intellectual Property.
IBM has an organizational structure characterized by product-based divisions, enabling its strategy to develop innovative and competitive products in multiple markets. IBM is also characterized by function-based segments that support product development and innovation for each product-based division, which include Global Markets, Integrated Supply Chain, Research, Development, and Intellectual Property. Sony has a matrix organizational structure primarily based on function-based groups and product/business divisions. The structure also incorporates geographical divisions. In 2021, Sony announced the overhauling of its organizational structure, changing its name from Sony Corporation to Sony Group Corporation to better identify itself as the headquarters of the Sony group of companies skewing the company toward product divisions.
Sony has a matrix organizational structure primarily based on function-based groups and product/business divisions. The structure also incorporates geographical divisions. In 2021, Sony announced the overhauling of its organizational structure, changing its name from Sony Corporation to Sony Group Corporation to better identify itself as the headquarters of the Sony group of companies skewing the company toward product divisions.Facebook Organizational Structure
 Facebook is characterized by a multi-faceted matrix organizational structure. The company utilizes a flat organizational structure in combination with corporate function-based teams and product-based or geographic divisions. The flat organization structure is organized around the leadership of Mark Zuckerberg, and the key executives around him. On the other hand, the function-based teams based on the main corporate functions (like HR, product management, investor relations, and so on).
Facebook is characterized by a multi-faceted matrix organizational structure. The company utilizes a flat organizational structure in combination with corporate function-based teams and product-based or geographic divisions. The flat organization structure is organized around the leadership of Mark Zuckerberg, and the key executives around him. On the other hand, the function-based teams based on the main corporate functions (like HR, product management, investor relations, and so on).Google Organizational Structure
 Google (Alphabet) has a cross-functional (team-based) organizational structure known as a matrix structure with some degree of flatness. Over the years, as the company scaled and it became a tech giant, its organizational structure is morphing more into a centralized organization.
Google (Alphabet) has a cross-functional (team-based) organizational structure known as a matrix structure with some degree of flatness. Over the years, as the company scaled and it became a tech giant, its organizational structure is morphing more into a centralized organization. Tesla Organizational Structure
 Tesla is characterized by a functional organizational structure with aspects of a hierarchical structure. Tesla does employ functional centers that cover all business activities, including finance, sales, marketing, technology, engineering, design, and the offices of the CEO and chairperson. Tesla’s headquarters in Austin, Texas, decide the strategic direction of the company, with international operations given little autonomy.
Tesla is characterized by a functional organizational structure with aspects of a hierarchical structure. Tesla does employ functional centers that cover all business activities, including finance, sales, marketing, technology, engineering, design, and the offices of the CEO and chairperson. Tesla’s headquarters in Austin, Texas, decide the strategic direction of the company, with international operations given little autonomy. McDonald’s Organizational Structure
 McDonald’s has a divisional organizational structure where each division – based on geographical location – is assigned operational responsibilities and strategic objectives. The main geographical divisions are the US, internationally operated markets, and international developmental licensed markets. And on the other hand, the hierarchical leadership structure is organized around regional and functional divisions.
McDonald’s has a divisional organizational structure where each division – based on geographical location – is assigned operational responsibilities and strategic objectives. The main geographical divisions are the US, internationally operated markets, and international developmental licensed markets. And on the other hand, the hierarchical leadership structure is organized around regional and functional divisions. Walmart Organizational Structure
 Walmart has a hybrid hierarchical-functional organizational structure, otherwise referred to as a matrix structure that combines multiple approaches. On the one hand, Walmart follows a hierarchical structure, where the current CEO Doug McMillon is the only employee without a direct superior, and directives are sent from top-level management. On the other hand, the function-based structure of Walmart is used to categorize employees according to their particular skills and experience.
Walmart has a hybrid hierarchical-functional organizational structure, otherwise referred to as a matrix structure that combines multiple approaches. On the one hand, Walmart follows a hierarchical structure, where the current CEO Doug McMillon is the only employee without a direct superior, and directives are sent from top-level management. On the other hand, the function-based structure of Walmart is used to categorize employees according to their particular skills and experience.Microsoft Organizational Structure
 Microsoft has a product-type divisional organizational structure based on functions and engineering groups. As the company scaled over time it also became more hierarchical, however still keeping its hybrid approach between functions, engineering groups, and management.
Microsoft has a product-type divisional organizational structure based on functions and engineering groups. As the company scaled over time it also became more hierarchical, however still keeping its hybrid approach between functions, engineering groups, and management. Read Next: Organizational Structure
Read Also: Business Model
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Leadership Tools To Take Your Company To The Next Level appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
10 Conversion Rate Optimization Strategies To Make More Money In 2019


Conversion rate optimization, often abbreviated to ‘CRO’ is the most crucial performance metrics for all marketers and the most significant leverage point for any company.
However, driving conversions is apparently tricky and intimidating task. The increase in the competition has made it hard for marketers to understand their conversion dreams.
Every company has certain goals to achieve. For instance, for your website, your goal is to make visitors click on ‘subscribe’ or ‘buy now’ or ‘call now’ button. Every time a visitor clicks on these buttons, you earn a conversion.
Therefore, your conversion rate is the percentage of the people who have taken action v/s total number of visitors who have visited your website. In short, conversion rate optimization is the process of turning visitors that visits your website into customers.
The best practices for conversion rate optimization are not commercial. Instead, they depend on clever persuasion. Let’s have a look at some of the best conversion rate optimization tips that can help you in improving your objectives.
Whenever a person visits your website, headlines are the first thing that they probably notice. A great headline is the one that sums up the whole sales pitch in one bold sentence. It is meant to generate curiosity, solve a problem, answer the question, or be instructional.
Without an effective headline, there is a risk of losing a potential lead. Here are some types of headlines that have proven to be impactful in generating leads:
Question headlinesCommand headlinesHow-to & Instructional headlinesDirect headlinesProblem-solving headlinesStrategic CTA’s
Just like a name, the call-to-action button prompts visitors to take a specific action. It should be there on all your pages and should be visible to visitors. While creating CTA’s three things need to be kept in mind:
Color and shape: The color and shape of your CTA button should be such that it matches with other elements of the website. It should immediately catch the attention of visitors. Placement: Placing the CTA at the top of your fold is more helpful than one below the fold.Make it benefited oriented: Bland CTA’s like ‘Download’, ‘Continue’, etc. are not action-oriented. In place of that, make them benefited oriented like ‘Stay connected’, Get my ebook’, etc.Easy Navigation
A lot of website owners ignore the significance of navigation. They are unaware of the fact that even navigation plays an important role in visitors’ journey through your website. How? The answer is quite simple. The quicker a visitor gets what they want, the more chances that they will purchase it.
Therefore, it is vital to have simplistic navigation. Your visitor should reach any of your website pages with maximum two or three clicks. Since the usage of smartphones is at its highest than ever before, therefore, you should pay more attention to your website navigation on mobile devices.
The website loading speed plays an important role in engaging visitors and making them take the next step. The faster the page gets loaded, the lesser are the chances that the visitors will leave the website.
Surveys have also shown that users expect a site to load in two or three seconds. It not only increase conversion but also helps in getting higher position in search engine results. Here are some of the best practices that can help in improving the page loading time:
Implement Content Delivery Network (CDN) — a server group that brings pages and other content near the physical place of the user. Just because the server is nearer to the customer, it loads more quickly.Compress the image sizeEvaluate and disable the plugins that are no longer in usePrevent ad scripts and pop-upsPayment Security
Since technology has developed so much and everything is online today, people are more concerned about keeping their information private. To win their trust and make them feel secure; it’s important to display security symbols on the checkout page.
The more trusted emblems you display, the more comfortable customers will feel, and this is a great way to increase online sales. Apart from displaying security symbols, you can also give users multiple payment options like debit card, debit card, mobile payments, etc. It will make visitors feel that your site is customer-friendly and trusted.
Time LimitThe more you give time to people think about making a purchase decision, the greater the chances are of them changing their mind or getting distracted by competitor’s offers. To improve your conversion rate, you should set a time limit.
Create a sense of urgency such as ‘Get 60% off on all purchases during the next 48 hours.’ In 2016, Amazon, the e-commerce king, took this approach, and its conversion rate increased by 74%.
Play on Scarcity EffectAnother great way to increase the conversion rate is to create a sense of scarcity. During your online shopping, you probably have experienced that you want something, and that item is out of stock.
And next day or probably two days later, when you visited the same website, you found the same product in stock with a small message below it ‘Limited stock.’ Well, that was a scarcity effect action.
That product probably never was out of stock. It was done by that particular website to drive sales because scarcity or short supply of the product makes people purchase the product quickly.
Optimize for MobileThe mobile industry is growing very fast. There has been a tremendous increase in smartphone users, and the numbers are expected to reach 4.78 billion by 2020. After knowing the fact, you cannot afford to ignore mobile users.
Check your mobile conversion rate and figure out the areas of improvement. Speed up your mobile site and have a responsive design for all your mobile pages.
Display TestimonialsTrust is the critical thing that encourages people to make their purchase decision. These days, because of cut-throat competition, customers have started giving importance to other customers’ reviews. No matter how persuasive your website is, the first time visitor will hesitate to make a purchase decision.
Showing the authentic testimonials of other customers may convince them to buy a particular product. If you have a well-known client and that client is very much happy with your services, then showing their logo along with their name will help you in building more trust among other clients or customers. You may also choose to display testimonials in the form of videos.
Shorten Checkout FunnelCheckout funnel is a series of a path that a user takes to get from a landing page to the ‘Thank you’ page. The shorter the checkout path, the more likely it is to convert a visitor. Imagine that you want to buy something, and after adding the item in a cart, you need to follow too many steps.
Don’t you feel irritated? Chances are you may leave the item in the cart and quit the website. Similarly, if your website also has the long checkout process, you may lose the potential client or customer. Therefore, it is advisable to keep the checkout funnel short. Users will feel comfortable during their checkout process, and they may become loyal customers of your website.
Key takeawayConversion rate optimization is a continuous process. You can always do better. We hope that the above tips will help you in growing your business. There is one piece of advice we would like to give at the end is to continuously experiment with new ideas and figure out which one performs better for your business.
Connected Business Frameworks Business development comprises a set of strategies and actions to grow a business via a mixture of sales, marketing, and distribution. While marketing usually relies on automation to reach a wider audience, and sales typically leverage a one-to-one approach. The business development’s role is that of generating distribution.
Business development comprises a set of strategies and actions to grow a business via a mixture of sales, marketing, and distribution. While marketing usually relies on automation to reach a wider audience, and sales typically leverage a one-to-one approach. The business development’s role is that of generating distribution. The more you move from consumers to enterprise clients, the more you’ll need a sales force able to manage complex sales. As a rule of thumb, a more expensive product, in B2B or Enterprise, will require an organizational structure around sales. An inexpensive product to be offered to consumers will leverage on marketing.
The more you move from consumers to enterprise clients, the more you’ll need a sales force able to manage complex sales. As a rule of thumb, a more expensive product, in B2B or Enterprise, will require an organizational structure around sales. An inexpensive product to be offered to consumers will leverage on marketing. A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products. In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale.
A sales cycle is the process that your company takes to sell your services and products. In simple words, it’s a series of steps that your sales reps need to go through with prospects that lead up to a closed sale. RevOps – short for Revenue Operations – is a framework that aims to maximize the revenue potential of an organization. RevOps seeks to align these departments by giving them access to the same data and tools. With shared information, each then understands their role in the sales funnel and can work collaboratively to increase revenue.
RevOps – short for Revenue Operations – is a framework that aims to maximize the revenue potential of an organization. RevOps seeks to align these departments by giving them access to the same data and tools. With shared information, each then understands their role in the sales funnel and can work collaboratively to increase revenue. Revenue modeling is a process of incorporating a sustainable financial model for revenue generation within a business model design. Revenue modeling can help to understand what options make more sense in creating a digital business from scratch; alternatively, it can help in analyzing existing digital businesses and reverse engineer them.
Revenue modeling is a process of incorporating a sustainable financial model for revenue generation within a business model design. Revenue modeling can help to understand what options make more sense in creating a digital business from scratch; alternatively, it can help in analyzing existing digital businesses and reverse engineer them.  Customer experience maps are visual representations of every encounter a customer has with a brand. On a customer experience map, interactions called touchpoints visually denote each interaction that a business has with its consumers. Typically, these include every interaction from the first contact to marketing, branding, sales, and customer support.
Customer experience maps are visual representations of every encounter a customer has with a brand. On a customer experience map, interactions called touchpoints visually denote each interaction that a business has with its consumers. Typically, these include every interaction from the first contact to marketing, branding, sales, and customer support. AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys.
AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys.  Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.
Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective. The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.
The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed. The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.
The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide. The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth.
The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth.  STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.
STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each. The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.
The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers. Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand.
Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand. Other business resources:
Successful Types of Business Models You Need to KnowThe Complete Guide To Business DevelopmentBusiness Strategy: Definition, Examples, And Case StudiesWhat Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas ExplainedBlitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A NutshellWhat Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas ExplainedWhat Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas ExplainedWhat Is Market Segmentation? the Ultimate Guide to Market SegmentationMarketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And ExamplesMarketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your BusinessHow To Write A Mission StatementWhat is Growth Hacking?Growth Hacking Canvas: A Glance At The Tools To Generate Growth IdeasThe post 10 Conversion Rate Optimization Strategies To Make More Money In 2019 appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
16 Frameworks For Solopreneurs
 Solopreneur
Solopreneur A solopreneur is usually (not always) a digital entrepreneur who leverages automation, work flexibility, and creativity to develop ultra-lean business models. Those can scale over the one-million-dollar revenue mark with a minimum business overhead, no venture capital funds, and mostly bootstrapped. Those solopreneurs start by mastering profitable microniches.Personal SWOT Analysis
A solopreneur is usually (not always) a digital entrepreneur who leverages automation, work flexibility, and creativity to develop ultra-lean business models. Those can scale over the one-million-dollar revenue mark with a minimum business overhead, no venture capital funds, and mostly bootstrapped. Those solopreneurs start by mastering profitable microniches.Personal SWOT Analysis The SWOT analysis is commonly used as a strategic planning tool in business. However, it is also well suited for personal use in addressing a specific goal or problem. A personal SWOT analysis helps individuals identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.SMART Goals
The SWOT analysis is commonly used as a strategic planning tool in business. However, it is also well suited for personal use in addressing a specific goal or problem. A personal SWOT analysis helps individuals identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.SMART Goals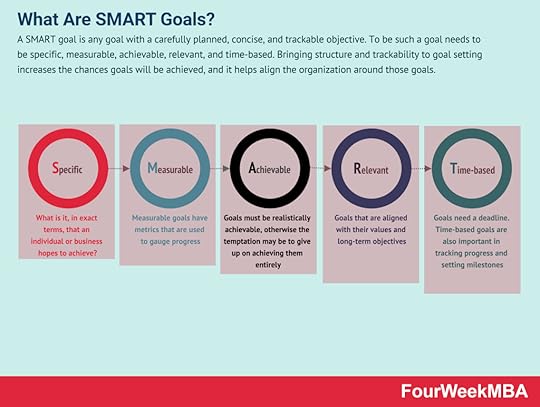 A SMART goal is any goal with a carefully planned, concise, and trackable objective. To be such a goal needs to be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based. Bringing structure and trackability to goal setting increases the chances goals will be achieved, and it helps align the organization around those goals.Personal Mission Statement
A SMART goal is any goal with a carefully planned, concise, and trackable objective. To be such a goal needs to be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based. Bringing structure and trackability to goal setting increases the chances goals will be achieved, and it helps align the organization around those goals.Personal Mission Statement A personal mission statement clarifies what is important in life to an individual. A personal mission statement is a written statement of purpose that allows individuals to define their calling in life. It helps clarify goals, values, beliefs, or passions, communicate them, and better execute a personal growth strategy. Elevator Pitch
A personal mission statement clarifies what is important in life to an individual. A personal mission statement is a written statement of purpose that allows individuals to define their calling in life. It helps clarify goals, values, beliefs, or passions, communicate them, and better execute a personal growth strategy. Elevator Pitch An elevator pitch is a short speech that introduces an individual, business, or product. Brevity is particularly important in sales, where a pitch must be able to sell itself quickly. Brevity also demonstrates that the person making a pitch has a personal and professional aptitude and can think on their feet during unexpected situations.Six Thinking Hats
An elevator pitch is a short speech that introduces an individual, business, or product. Brevity is particularly important in sales, where a pitch must be able to sell itself quickly. Brevity also demonstrates that the person making a pitch has a personal and professional aptitude and can think on their feet during unexpected situations.Six Thinking Hats The Six Thinking Hats model was created by psychologist Edward de Bono in 1986, who noted that personality type was a key driver of how people approached problem-solving. For example, optimists view situations differently from pessimists. Analytical individuals may generate ideas that a more emotional person would not, and vice versa.Brand Voice
The Six Thinking Hats model was created by psychologist Edward de Bono in 1986, who noted that personality type was a key driver of how people approached problem-solving. For example, optimists view situations differently from pessimists. Analytical individuals may generate ideas that a more emotional person would not, and vice versa.Brand Voice  The brand voice describes how a brand communicates with its target audience. The exact style of communication is based on the brand persona or the collection of personality traits and values that a brand embodies regularly, and it needs to communicate the brand’s essence to the desired target audience.Minimum Viable Audience
The brand voice describes how a brand communicates with its target audience. The exact style of communication is based on the brand persona or the collection of personality traits and values that a brand embodies regularly, and it needs to communicate the brand’s essence to the desired target audience.Minimum Viable Audience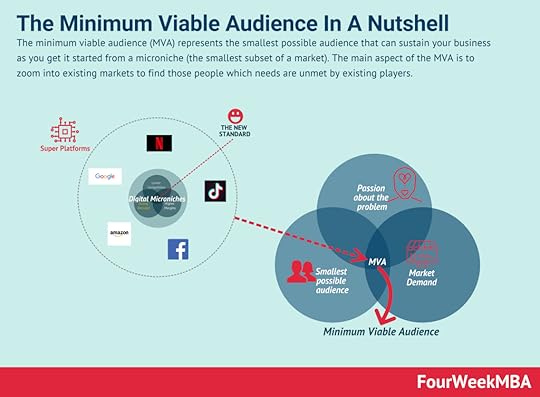 The minimum viable audience (MVA) represents the smallest possible audience that can sustain your business as you get it started from a microniche (the smallest subset of a market). The main aspect of the MVA is to zoom into existing markets to find those people which needs are unmet by existing players.Microniche
The minimum viable audience (MVA) represents the smallest possible audience that can sustain your business as you get it started from a microniche (the smallest subset of a market). The main aspect of the MVA is to zoom into existing markets to find those people which needs are unmet by existing players.Microniche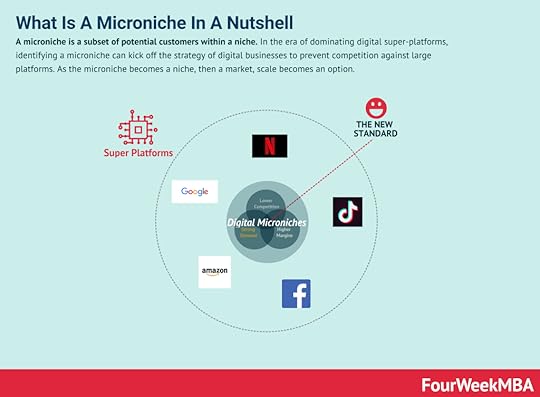 A microniche is a subset of potential customers within a niche. In the era of dominating digital super-platforms, identifying a microniche can kick off the strategy of digital businesses to prevent competition against large platforms. As the microniche becomes a niche, then a market, scale becomes an option.Customer Segmentation
A microniche is a subset of potential customers within a niche. In the era of dominating digital super-platforms, identifying a microniche can kick off the strategy of digital businesses to prevent competition against large platforms. As the microniche becomes a niche, then a market, scale becomes an option.Customer Segmentation Customer segmentation is a marketing method that divides the customers into sub-groups, that share similar characteristics. Thus, product, marketing, and engineering teams can center the strategy from go-to-market to product development and communication around each sub-group. Customer segments can be broken down in several ways, such as demographics, geography, psychographics, and more.Social Selling
Customer segmentation is a marketing method that divides the customers into sub-groups, that share similar characteristics. Thus, product, marketing, and engineering teams can center the strategy from go-to-market to product development and communication around each sub-group. Customer segments can be broken down in several ways, such as demographics, geography, psychographics, and more.Social Selling Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.AIDA Model
Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.AIDA Model AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys. Inverted Pyramid
AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys. Inverted Pyramid The inverted pyramid style is a process used in journalism which inverts the logic of the way a story is told. Rather than start from the story details, you start from a hook, which is critical to get the reader interested, thus giving it a quick pay off.CHAMP Methodology
The inverted pyramid style is a process used in journalism which inverts the logic of the way a story is told. Rather than start from the story details, you start from a hook, which is critical to get the reader interested, thus giving it a quick pay off.CHAMP Methodology The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process
The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process
The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth.
The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsNetwork EffectsThe post 16 Frameworks For Solopreneurs appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
21 Marketing Theories In A Nutshell
 Six Forces Models
Six Forces Models The Six Forces Model is a variation of Porter’s Five Forces. The sixth force, according to this model, is the complementary products. In short, the six forces model is an adaptation especially used in the tech business world to assess the change of the context, based on new market entrants and whether those can play out initially as complementary products and in the long-term substitutes. SWOT Analysis
The Six Forces Model is a variation of Porter’s Five Forces. The sixth force, according to this model, is the complementary products. In short, the six forces model is an adaptation especially used in the tech business world to assess the change of the context, based on new market entrants and whether those can play out initially as complementary products and in the long-term substitutes. SWOT Analysis A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.Balanced Scorecard
A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.Balanced Scorecard First proposed by accounting academic Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system that allows an organization to focus on big-picture strategic goals. The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard include financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. From there, according to the balanced scorecard, it’s possible to have a holistic view of the business.Marketing Mix
First proposed by accounting academic Robert Kaplan, the balanced scorecard is a management system that allows an organization to focus on big-picture strategic goals. The four perspectives of the balanced scorecard include financial, customer, business process, and organizational capacity. From there, according to the balanced scorecard, it’s possible to have a holistic view of the business.Marketing Mix The marketing mix is a term to describe the multi-faceted approach to a complete and effective marketing plan. Traditionally, this plan included the four Ps of marketing: price, product, promotion, and place. But the exact makeup of a marketing mix has undergone various changes in response to new technologies and ways of thinking. Additions to the four Ps include physical evidence, people, process, and even politics.PESTEL Analysis
The marketing mix is a term to describe the multi-faceted approach to a complete and effective marketing plan. Traditionally, this plan included the four Ps of marketing: price, product, promotion, and place. But the exact makeup of a marketing mix has undergone various changes in response to new technologies and ways of thinking. Additions to the four Ps include physical evidence, people, process, and even politics.PESTEL Analysis The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization. This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses that can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.BCG Matrix
The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization. This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses that can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.BCG Matrix In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs was developed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow. His hierarchy, often depicted in the shape of a pyramid, helped explain his research on basic human needs and desires. In marketing, the hierarchy (and its basis in psychology) can be used to market to specific groups of people based on their similarly specific needs, desires, and resultant actions.PESO Model
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs was developed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow. His hierarchy, often depicted in the shape of a pyramid, helped explain his research on basic human needs and desires. In marketing, the hierarchy (and its basis in psychology) can be used to market to specific groups of people based on their similarly specific needs, desires, and resultant actions.PESO Model To optimize its marketing communications, a business can categorize media as either paid, earned, shared, or owned media (PESO). Analyzing these four categories is particularly useful for content-driven, online marketing strategies to build brand awareness, customer loyalty, and gain market share.GE McKinsey Matrix
To optimize its marketing communications, a business can categorize media as either paid, earned, shared, or owned media (PESO). Analyzing these four categories is particularly useful for content-driven, online marketing strategies to build brand awareness, customer loyalty, and gain market share.GE McKinsey Matrix The GE McKinsey Matrix was developed in the 1970s after General Electric asked its consultant McKinsey to develop a portfolio management model. This matrix is a strategy tool that provides guidance on how a corporation should prioritize its investments among its business units, leading to three possible scenarios: invest, protect, harvest, and divest.Kotler’s Five Product Levels
The GE McKinsey Matrix was developed in the 1970s after General Electric asked its consultant McKinsey to develop a portfolio management model. This matrix is a strategy tool that provides guidance on how a corporation should prioritize its investments among its business units, leading to three possible scenarios: invest, protect, harvest, and divest.Kotler’s Five Product Levels Marketing consultant Philip Kotler developed the Five Product Levels model. He asserted that a product was not just a physical object but also something that satisfied a wide range of consumer needs. According to that Kotler identified five types of products: core product, generic product, expected product, augmented product, and potential product.New Product Development Process
Marketing consultant Philip Kotler developed the Five Product Levels model. He asserted that a product was not just a physical object but also something that satisfied a wide range of consumer needs. According to that Kotler identified five types of products: core product, generic product, expected product, augmented product, and potential product.New Product Development Process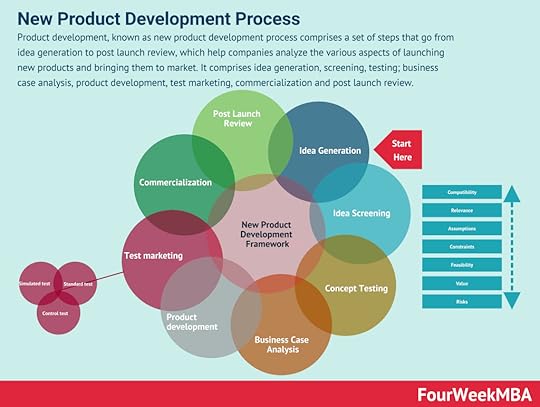 Product development, known as new product development process comprises a set of steps that go from idea generation to post launch review, which help companies analyze the various aspects of launching new products and bringing them to market. It comprises idea generation, screening, testing; business case analysis, product development, test marketing, commercialization and post launch review.Customer Experience Map
Product development, known as new product development process comprises a set of steps that go from idea generation to post launch review, which help companies analyze the various aspects of launching new products and bringing them to market. It comprises idea generation, screening, testing; business case analysis, product development, test marketing, commercialization and post launch review.Customer Experience Map Customer experience maps are visual representations of every encounter a customer has with a brand. On a customer experience map, interactions called touchpoints visually denote each interaction that a business has with its consumers. Typically, these include every interaction from the first contact to marketing, branding, sales, and customer support.AIDA Model
Customer experience maps are visual representations of every encounter a customer has with a brand. On a customer experience map, interactions called touchpoints visually denote each interaction that a business has with its consumers. Typically, these include every interaction from the first contact to marketing, branding, sales, and customer support.AIDA Model AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys. Social Selling
AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire, and action. That is a model that is used in marketing to describe the potential journey a customer might go through before purchasing a product or service. The AIDA model helps organizations focus their efforts when optimizing their marketing activities based on the customers’ journeys. Social Selling Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.CHAMP Methodology
Social selling is a process of developing trust, rapport, and a relationship with a prospect to enhance the sales cycle. It usually happens through tech platforms (like LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and more), which enable salespeople to engage with potential prospects before closing the sale, thus becoming more effective.CHAMP Methodology The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process
The CHAMP methodology is an iteration of the BANT sales process for modern B2B applications. While budget, authority, need, and timing are important aspects of qualifying sales leads, the CHAMP methodology was developed after sales reps questioned the order in which the BANT process is followed.BANT Sales Process The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process
The BANT process was conceived at IBM in the 1950s as a way to quickly identify prospects most likely to make a purchase. Despite its introduction around 70 years ago, the BANT process remains relevant today and was formally adopted into IBM’s Business Agility Solution Identification Guide.MEDDIC Sales Process The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. STP Marketing
The MEDDIC sales process was developed in 1996 by Dick Dunkel at software company Parametric Technology Corporation (PTC). The MEDDIC sales process is a framework used by B2B sales teams to foster predictable and efficient growth. STP Marketing STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels
STP marketing simplifies the market segmentation process and is one of the most commonly used approaches in modern marketing. The core focus of STP marketing is commercial effectiveness. Marketers use the approach to select the most valuable segments from a target audience and develop a product positioning strategy and marketing mix for each.Sales Funnels vs. Flywheels The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.Pirate Metrics
The sales funnel is a model used in marketing to represent an ideal, potential journey that potential customers go through before becoming actual customers. As a representation, it is also often an approximation, that helps marketing and sales teams structure their processes at scale, thus building repeatable sales and marketing tactics to convert customers.Pirate Metrics Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand. Bootstrapping
Venture capitalist, Dave McClure, coined the acronym AARRR which is a simplified model that enables to understand what metrics and channels to look at, at each stage for the users’ path toward becoming customers and referrers of a brand. Bootstrapping The general concept of Bootstrapping connects to “a self-starting process that is supposed to proceed without external input.” In business, Bootstrapping means financing the growth of the company from the available cash flows produced by a viable business model. Bootstrapping requires the mastery of the key customers driving growth.
The general concept of Bootstrapping connects to “a self-starting process that is supposed to proceed without external input.” In business, Bootstrapping means financing the growth of the company from the available cash flows produced by a viable business model. Bootstrapping requires the mastery of the key customers driving growth.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsNetwork EffectsThe post 21 Marketing Theories In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
September 6, 2022
14 Management Tools for Business People
 Lean manufacturing seeks to maximize product value while minimizing waste without sacrificing productivity. According to the Lean Enterprise Research Centre (LERC), 60% of a typical manufacturing process is waste. While the removal of waste is perhaps synonymous with lean manufacturing, the goal of the methodology is the sustainable delivery of value to the customer.SCAMPER Method
Lean manufacturing seeks to maximize product value while minimizing waste without sacrificing productivity. According to the Lean Enterprise Research Centre (LERC), 60% of a typical manufacturing process is waste. While the removal of waste is perhaps synonymous with lean manufacturing, the goal of the methodology is the sustainable delivery of value to the customer.SCAMPER Method Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Monroe’s motivated sequence was created by American psychologist Alan Monroe, who had an interest in persuasive speech delivery. Monroe’s motivated sequence uses the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for delivering speeches.Paired Comparison Analysis
Monroe’s motivated sequence was created by American psychologist Alan Monroe, who had an interest in persuasive speech delivery. Monroe’s motivated sequence uses the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for delivering speeches.Paired Comparison Analysis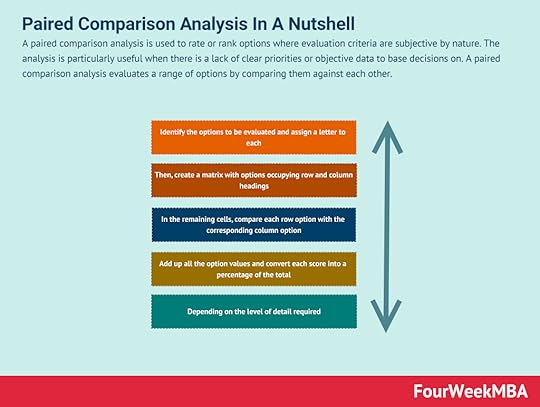 A paired comparison analysis is used to rate or rank options where evaluation criteria are subjective by nature. The analysis is particularly useful when there is a lack of clear priorities or objective data to base decisions on. A paired comparison analysis evaluates a range of options by comparing them against each other.Scaled Agile Framework
A paired comparison analysis is used to rate or rank options where evaluation criteria are subjective by nature. The analysis is particularly useful when there is a lack of clear priorities or objective data to base decisions on. A paired comparison analysis evaluates a range of options by comparing them against each other.Scaled Agile Framework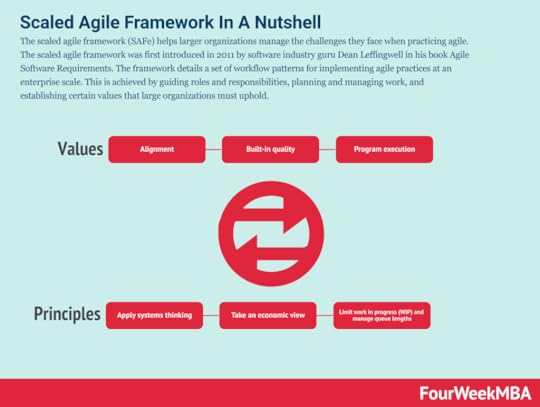 The scaled agile framework (SAFe) helps larger organizations manage the challenges they face when practicing agile. The scaled agile framework was first introduced in 2011 by software industry guru Dean Leffingwell in his book Agile Software Requirements. The framework details a set of workflow patterns for implementing agile practices at an enterprise scale. This is achieved by guiding roles and responsibilities, planning and managing work, and establishing certain values that large organizations must uphold.MVC Framework
The scaled agile framework (SAFe) helps larger organizations manage the challenges they face when practicing agile. The scaled agile framework was first introduced in 2011 by software industry guru Dean Leffingwell in his book Agile Software Requirements. The framework details a set of workflow patterns for implementing agile practices at an enterprise scale. This is achieved by guiding roles and responsibilities, planning and managing work, and establishing certain values that large organizations must uphold.MVC Framework The MVC framework is a predictable software design pattern separated into three main components and suitable for many programming languages. The goal of the MVC framework is to help structure the code-base and separate application concerns into three components: View, Model, and Controller. MoSCoW Method
The MVC framework is a predictable software design pattern separated into three main components and suitable for many programming languages. The goal of the MVC framework is to help structure the code-base and separate application concerns into three components: View, Model, and Controller. MoSCoW Method Prioritization plays a crucial role in every business. In an ideal world, businesses have enough time and resources to complete every task within a project satisfactorily. The MoSCoW method is a task prioritization framework. It is most effective in situations where many tasks must be prioritized into an actionable to-do list. The framework is based on four main categories that give it the name: Must have (M), Should have (S), Could have (C), and Won’t have (W).Operating Model
Prioritization plays a crucial role in every business. In an ideal world, businesses have enough time and resources to complete every task within a project satisfactorily. The MoSCoW method is a task prioritization framework. It is most effective in situations where many tasks must be prioritized into an actionable to-do list. The framework is based on four main categories that give it the name: Must have (M), Should have (S), Could have (C), and Won’t have (W).Operating Model The operating model is a visual representation and mapping of the processes and how the organization delivers value and, therefore, how it executes its business model. Therefore, the operating model is how the whole organization is structured around the value chain to build a viable business model. Lightning Decision Jam
The operating model is a visual representation and mapping of the processes and how the organization delivers value and, therefore, how it executes its business model. Therefore, the operating model is how the whole organization is structured around the value chain to build a viable business model. Lightning Decision Jam The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model
The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model was created by David Nadler and Michael Tushman at Columbia University. The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model is a diagnostic tool that identifies problem areas within a company. In the context of business, congruence occurs when the goals of different people or interest groups coincide.Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model was created by David Nadler and Michael Tushman at Columbia University. The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model is a diagnostic tool that identifies problem areas within a company. In the context of business, congruence occurs when the goals of different people or interest groups coincide.Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory Herzberg’s two-factor theory argues that certain workplace factors cause job satisfaction while others cause job dissatisfaction. The theory was developed by American psychologist and business management analyst Frederick Herzberg. Until his death in 2000, Herzberg was widely regarded as a pioneering thinker in motivational theory. Kepner-Tregoe Matrix
Herzberg’s two-factor theory argues that certain workplace factors cause job satisfaction while others cause job dissatisfaction. The theory was developed by American psychologist and business management analyst Frederick Herzberg. Until his death in 2000, Herzberg was widely regarded as a pioneering thinker in motivational theory. Kepner-Tregoe Matrix The Kepner-Tregoe matrix was created by management consultants Charles H. Kepner and Benjamin B. Tregoe in the 1960s, developed to help businesses navigate the decisions they make daily, the Kepner-Tregoe matrix is a root cause analysis used in organizational decision making.Eisenhower Matrix
The Kepner-Tregoe matrix was created by management consultants Charles H. Kepner and Benjamin B. Tregoe in the 1960s, developed to help businesses navigate the decisions they make daily, the Kepner-Tregoe matrix is a root cause analysis used in organizational decision making.Eisenhower Matrix The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that helps businesses prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance, named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, President of the United States from 1953 to 1961, the matrix helps businesses and individuals differentiate between the urgent and important to prevent urgent things (seemingly useful in the short-term) cannibalize important things (critical for long-term success).
The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that helps businesses prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance, named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, President of the United States from 1953 to 1961, the matrix helps businesses and individuals differentiate between the urgent and important to prevent urgent things (seemingly useful in the short-term) cannibalize important things (critical for long-term success). In the FourWeekMBA growth matrix, you can apply growth for existing customers by tackling the same problems (gain mode). Or by tackling existing problems, for new customers (expand mode). Or by tackling new problems for existing customers (extend mode). Or perhaps by tackling whole new problems for new customers (reinvent mode).Ansoff Matrix
In the FourWeekMBA growth matrix, you can apply growth for existing customers by tackling the same problems (gain mode). Or by tackling existing problems, for new customers (expand mode). Or by tackling new problems for existing customers (extend mode). Or perhaps by tackling whole new problems for new customers (reinvent mode).Ansoff Matrix You can use the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic framework to understand what growth strategy is more suited based on the market context. Developed by mathematician and business manager Igor Ansoff, it assumes a growth strategy can be derived by whether the market is new or existing, and the product is new or existing.
You can use the Ansoff Matrix as a strategic framework to understand what growth strategy is more suited based on the market context. Developed by mathematician and business manager Igor Ansoff, it assumes a growth strategy can be derived by whether the market is new or existing, and the product is new or existing.Main Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsNetwork EffectsThe post 14 Management Tools for Business People appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



