Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 171
February 10, 2021
Ad-Ops In A Nutshell And Why It Matters In Business

Ad Ops – also known as Digital Ad Operations – refers to systems and processes that support digital advertisements’ delivery and management. The concept describes any process that helps a marketing team manage, run, or optimize ad campaigns, making them an integrating part of the business operations.
Understanding Ad OpsAd Ops is a somewhat generic term describing any process that helps a marketing team manage, run, or optimize ad campaigns. Traditionally, this process was very simple. But many consumers now interact with brands in a multi-screen digital world with attention split between desktops, smartphones, and tablets.
Each of these devices provides a different user experience, displaying advertisements through banners, video, text, search, and mobile to name a few. Marketing teams must be able to interact with various platforms including ad networks, ad servers, ad exchanges, supply-side platforms (SSPs), and data management platforms (DMPs). Ultimately, each campaign must respect the device it is being displayed on while maximizing ad revenue for the company.
As demands increase, Ads Ops teams are utilizing new trends such as programmatic advertising, where automated software purchases digital ad space on their behalf. However, these teams must manage a range of unautomated tasks while understanding both sides of the advertising ecosystem. In other words, they must be sensitive to the needs of the sell-side (publishers) and buy-side (advertisers).
Some major responsibilities of Ad Ops teamsIndividuals within an Ad Ops team enjoy a dynamic and varied role, with no two days being the same.
Nevertheless, there are some core responsibilities unique to most campaigns:
Scheduling. In other words, when should the ad be scheduled for maximum ROI? Scheduling may revolve around a certain time of day, or it may focus on holidays, weekends, or special events.Trafficking. This requires a specialist role to oversee the monitoring and delivery of ads across various exchanges or servers. Tasks may include the tracking of third-party vendor ad tags or the implementation of ad campaigns using dedicated services such as Google Ad Manager.Optimization. Every ad must be optimized for the number of clicks it receives. Optimization can be achieved through correct ad placement, word choice, and proper SEO. In some instances, ads must reflect an awareness of changing trends or standards.Yield management. Each task that an Ad Ops team performs should have some relation to driving revenue. Yield managers search for opportunities to increase revenue generation through advertising. This may involve the restructuring of content based on user behavior analytics or the reallocation of inventory pricing to increase profits.Ad Ops best practicesAll Ad Ops teams should incorporate these best practices as the basis of a sound campaign:
Define objectives – what is the goal of the campaign? It is not enough to broadly state a goal of increasing profits or brand recognition. Use the SMART goals system to help define thoughtful, effective objectives.Define the correct medium – how should the message of the campaign be delivered? Mediums such as email, social media, video, and content will be most suited to a specific target audience or device.Craft the message – make sure that the ad campaign centers on one key idea or message. Importantly, it must be relatable to the target audience and company objectives.Evaluate and adjust as necessary – continually evaluate campaigns for effectiveness and reconfigure if important targets or metrics are not being met. Key takeawaysAd Ops refers to a suite of systems and processes that support digital advertisement delivery across multiple devices.Ad Ops is a broad and dynamic industry requiring responsive and multi-skilled teams. These teams must be well versed in the scheduling, optimization, and trafficking of ads.Some aspects of Ad Ops have been automated to reflect the increasing complexity of online advertising. Nevertheless, Ad Ops requires that practitioners be competent using a range of ad networks, servers, exchanges, and platforms.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Ad-Ops In A Nutshell And Why It Matters In Business appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Remote Working In A Nutshell

Remote working is a means of working beyond the confines of a traditional, centralized workplace using digital technology.
Understanding remote workingWhile many associate remote work with the advent of the internet or even the coronavirus pandemic, it has existed since the 1970s.
Remote working exists in many forms, including:
Education – the explosion in popularity of digital learning platforms means that many teachers can work remotely in a variety of individual or group formats. Teachers can also work remotely when teaching students who live in areas without access to schools.Writing – the archetypal remote worker is usually a writer who is well placed to take advantage of high-speed internet and a penchant for the low cost of living in many third-world countries.Healthcare – the internet is enabling healthcare professionals to interact with their patients online. Prescriptions, consultations, and post-op care are but some of the services that these professionals offer remotely.The difference between remote working and working from homeIn understanding remote working, it’s important to make the distinction between remote work and working from home. The latter is a temporary arrangement that occurs sporadically. For example, an office worker may work from home on the odd day where a meeting has not been scheduled or they need to work uninterrupted.
By contrast, remote working requires a different set of skills, abilities, and character traits. It requires a degree of self-discipline, good time-management, and good communication skills. Instead of escaping a traditional work environment by working from home, remote workers create their own work environment in any way or location they see fit.
Advantages and disadvantages of remote workingAdvantagesFlexibility. Remote workers enjoy the flexibility of working in a location or setting of their choosing. For employees considering maternity leave or having a partner working in another city, remote working allows them to respond to life changes without sacrificing their careers.Less distraction. Multiple studies have shown that distraction costs employees in a centralized workforce up to 6 hours per day. Remote workers can design environments where they can work uninterrupted in a flow state. This results in deep, focused, and productive work.Improved health. A flexible workplace without a morning and evening commute has also been shown to reduce stress and burnout. Remote workers are also less likely to catch seasonal illnesses such as a cold or flu.DisadvantagesIsolation. Extroverted individuals who need a high level of human interaction may find remote work isolating – even if they possess desirable traits such as self-discipline and autonomy.Incompatibility. Remote workers in different time zones who are part of the same team may have difficulty in communicating effectively. To some extent, proper planning can help overcome issues associated with location.Work/life balance. Some remote workers have trouble “switching off” at the end of a workday. Constant access to the internet and work communications is one reason for poor work/life balance. An improperly defined work area is another. Wherever possible, remote work employees should avoid working in areas traditionally reserved for leisure, such as the bed or kitchen table.Key takeaways:Remote working is means of working beyond the confines of a traditional, centralized workplace.Remote working is commonly associated with the digital age, but it has existed since the 1970s. It is prevalent in the health, education, and freelance writing industry.Remote working provides individuals with the right set of traits a flexible, healthy, and focused way to work. However, it can be isolating for some individuals. Inefficiencies can also impact global companies with remote employees working in different time zones.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Remote Working In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Retail Investing In A Nutshell

Retail investing is the act of non-professional investors buying and selling securities for their own purposes. Retail investing has become popular with the rise of zero commissions digital platforms enabling anyone with small portfolio to trade.
Understanding retail investingWhen compared to institutional investors, retail investors tend to trade less frequently and in much smaller quantities. With high brokerage fees and no requirement to generate a return over a short period, retail investors tend to invest for the long-term in companies of their choosing.
As a result, they exert less influence over corporate decisions and the share market. Retail investors seldom have access to corporate boardroom discussions and generally have little opportunity to liaise with company executives.
Nevertheless, retail investors provide capital to growing businesses when other sources of financing are unavailable. Given that they tend to invest for a longer period, they are a preferred source of stable capital.
Retail investors are also important drivers of market sentiment, defined as the overall attitude of investors toward a particular security or market.
Different types of retail investingWithin retail investing exist several different types of investors:
Those who invest through a retail brokerage service with full control over their investments. This includes those who participate in crowdfunded private equity investment.Those who have account managers to oversee their portfolio and make decisions on their behalf. Groups of retail investors who pool money and knowledge to make decisions that benefit every group member. These are otherwise known as investment clubs.Advantages of retail investingAlthough retail investors do not have the financial influence of institutions, they enjoy several advantages:
Long-term focus. As noted in the introduction, retail investors differ from institutional investors in that they are under no pressure to generate returns in a short period. The patient “buy-and-hold” strategy of retail investing is less sensitive to short-term market corrections.Freedom of choice. While many institutional investors are limited in the types of companies they can consider, retail investors have the freedom to invest at their leisure. Many choose to take advantage of the small firm effect, which describes the ability of a company with a small market capitalization to outperform a larger company.Personal interest and attention. Given that retail investors are investing their own hard-earned capital, there is a higher likelihood that their investments are backed by robust due diligence. Combined with a tendency for patience, retail investors have the conviction to hold and realize profits when it suits them. Key takeaways:Retail investing describes investors who make investment decisions for their own accounts.Retail investing is associated with smaller, less frequent trades and a lack of access to corporate discussions or company executives. However, it is a stable source of capital for emerging businesses and has significant impacts on market sentiment.Retail investing has several advantages over institutional investing. Retail investors are unconstrained by the need to generate a return in a predetermined timeframe. This gives them the ability to maintain a long-term focus backed by robust due diligence, conviction, and personal interest.Read Next: Robinhood Business Model.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Retail Investing In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
State Capitalism In A Nutshell

State capitalism is an economic system where business and commercial activity is controlled by the state through state-owned enterprises. In a state capitalist environment, the government is the principal actor. It takes an active role in the formation, regulation, and subsidization of businesses to divert capital to state-appointed bureaucrats. In effect, the government uses capital to further its political ambitions or strengthen its leverage on the international stage.
Understanding state capitalismIn a capitalist country operating under a free market economy, the government provides and upholds a legal framework under which businesses operate. In general, there is little to no governmental intervention in business matters. Multinational corporations are the principal actors.
In a state capitalist environment, the government is the principal actor, and it takes an active role. In his book entitled State Capitalism, author Joshua Kurlantzick argues that state capitalism in its modern form is “more protectionist, more dangerous to global security and prosperity, and more threatening to political freedom” than free-market economics.
Kurlantzick asserts that the two biggest state-capitalist countries in China and Russia are using their powers globally to:
Employ state-owned companies as weapons during conflict.Control access to natural resources such as water and precious metals.Steal sensitive information or technology.Undermine entrenched environmental or labor laws in countries where their state companies operate. Other examples of state capitalismChina and Russia are the most high-profile examples of state capitalism, but several other examples deserve mention.
To that end, Kurlantzick argues that state capitalism exists on a continuum of efficiency. The continuum is in turn determined by the degree of innovation, global trade, and modern management techniques, among other things. Efficient countries include Norway and Singapore, while Brazil is less efficient.
NorwayState capitalism in Norway is a result of post-World War II democratic reform and public ownership of vast oil reserves in the country.
The Norwegian government has significant stakes in many of the largest publicly listed companies, owning 37% of the Oslo stock market. It also has full ownership of the two largest private companies in Norway that operate in the petroleum and hydropower industries.
SingaporeFrom a collection of small villages just a few decades ago, Singapore is now a world city home to many of the most powerful global corporations. It has achieved this remarkable feat through business-friendly legislation and close collaboration between the state and corporations.
The government is a majority shareholder in many major companies and, like Norway, favors investment in sovereign wealth funds.
BrazilBrazil has a long history of state capitalism. As early as 1930, the Brazilian government provided subsidies to support specific industries in the role of de-facto owner.
Private companies in the banking, utility, shipping, and railway industries were guaranteed survival – even if they went bankrupt.
In more recent times, the government has invested billions of dollars in Brazilian meat processing company JBS. This company has been actively involved in acquiring international food companies and, unsurprisingly, is one of the Brazilian government’s biggest donors.
Key takeaways:State capitalism is an economic system where the government controls business and commercial activity.State capitalism is prevalent in Russia and China where state-owned enterprise is used during conflict or to control access to important resources. State capitalism is also used to steal sensitive information or subvert laws and regulations.State capitalism exists in many countries to varying degrees. Some argue that an efficiency continuum can best describe the way certain countries have used state capitalism to their advantage while others have faltered.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post State Capitalism In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Metaverse And Why It Matters In Business

The metaverse describes an alternate digital reality where people work, play, and socialize. The word metaverse is a portmanteau of the prefix “meta” (meaning beyond) and “universe”. It was first coined by sci-fi author Neal Stephenson in his book Snow Crash, which tells the story of humans interacting with each other using avatars in a 3D world.
Understanding the metaverseThe metaverse describes a general and somewhat poorly defined future iteration of the internet. This iteration is predicted to comprise of persistent and shared three-dimensional spaces linked together to form a virtual world. This will enable users to do anything they want, from hanging out with friends to creating art, shopping, and virtual travel.
It will be different from the current incarnation of the internet where the user must make a conscious choice to access it. Instead, the metaverse will encompass the convergence of the physical realm with the virtual realm to create a shared virtual space. This space will be created via interaction between the internet, augmented reality, and virtual reality.
The seven core attributes of the metaverseThe metaverse is still in its infancy, but there seems to be consensus on seven core attributes that will comprise it:
Persistence – which is to say, it never ends, pauses, or resets. Instead, it continues indefinitely.Synchronicity – the metaverse is a living experience that exists for everyone and in real-time.Accessibility – involvement in a specific event, place, or activity is open to everyone with no restriction on concurrent participation.Economic function – much like the current iteration of the internet, individuals and businesses alike will have the ability to create, own, invest in, or sell goods and services that are valued by others. Scope – the metaverse will be an experience that spans private and public networks in the digital and physical world. It will also feature open and closed platforms.Interoperability – data, content, items, and assets can be traded or utilized across different platforms. For example, a decorated Fortnite gun could serve as a gift to a friend on Facebook.Contribution – the metaverse is populated by content and experiences created by a wide range of contributors. These contributors range from individuals to informally organized groups to large, commercial organizations.Why is the metaverse important?There is no single owner of the internet, but many of the most valuable organizations in the world are tech companies who exert great influence online.
As a natural successor to the internet, the metaverse will level the playing field and become the next great labor platform. Aspiring laborers will be able to access the metaverse irrespective of their geographic location or socioeconomic background, thereby tapping into a high-value economy of virtual labor. With greater functionality, opportunity, and reach, the metaverse is likely to become a highly lucrative and decentralized content platform.
New creators will also have a chance to build a large following on a virgin platform. Furthermore, new companies will need to be created to manage similarly new technology. This includes payment processing, ID verification, security, and ad delivery technology, among others.
Key takeaways:The metaverse is a shared virtual space created by the convergence of augmented reality, virtual reality, and the internet.The metaverse concept is relatively new, but there is agreeance that the future iteration of the internet portrays seven core attributes: persistence, synchronicity, accessibility, economic function, scope, interoperability, and contribution.The metaverse has the potential to become the next great labor platform, giving individuals diversity of opportunity through access to a high-value virtual economy.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Metaverse And Why It Matters In Business appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) In A Nutshell For Business People
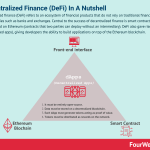
Decentralized finance (DeFi) refers to an ecosystem of financial products that do not rely on traditional financial intermediaries such as banks and exchanges. Central to the success of decentralized finance is smart contracts, which are deployed on Ethereum (contracts that two parties can deploy without an intermediary). DeFi also gave rise to dApps (decentralized apps), giving developers the ability to build applications on top of the Ethereum blockchain.
Understanding decentralized financeDecentralized finance is as much a philosophy as it is a way of doing business. Indeed, DeFi advocates a transparent financial ecosystem that is open-source, available to everyone, and operates without a central authority.
Central to the success of decentralized finance is the use of smart contracts, which are deployed on Ethereum. Smart contracts avoid the need to involve traditional intermediaries, who often charge exorbitant fees to facilitate financial transactions. Decentralized finance provides these same services in a faster and cheaper way that is also more secure.
Smart contracts also give developers increased functionality. Instead of simply building programs that send or receive cryptocurrency, smart contracts can be used to build programs on the blockchain that execute when certain conditions are met.
These programs are now commonly referred to as decentralized apps, or dApps. Collectively, dApps comprise a DeFi ecosystem.
The core components and criteria of dAppsTo understand DeFi it is important to first understand dApps.
Structurally, a dApp consists of:
A front-end interface – such as an app or website.A smart contract – or a program that facilitates online transactions autonomously according to programmed rules. Smart contract code can be audited to verify that it is bug-free and non-malicious.The Ethereum blockchain – which ensures that the smart contract cannot be hacked or otherwise tampered with. It’s also important to note that a fee (calculated in ETH) is charged to the user every time a smart contract is utilized.The dApp architecture is also characterized by four criteria:
It must be entirely open-source. No entity must own the majority of tokens and protocol changes must be decided via network user consensus.Data must be stored on a decentralized blockchain.Each dApp must generate tokens acting as proof of value.Tokens must be distributed as rewards on the network.Potential applications of decentralized financeIn theory, the applications of decentralized finance are limitless.
Having said that, here are a few of the most salient:
Monetary banking servicesMonetary banking is an obvious use, but one that is maturing through the creation of stablecoins. These coins are a type of crypto-asset, usually pegged to a real-world asset such as fiat money or exchange-traded commodities.
Decentralized stablecoins help mitigate the volatility seen in cryptocurrencies, allowing them to be used as a form of cash without the need for a central authority. Stablecoins might also be beneficial in processes that require many intermediaries, such as mortgage or insurance applications.
Borrowing and lendingDeFi has several advantages over the traditional credit system of borrowing and lending. These include the ability to collateralize digital assets and provide instantaneous settlement. DeFi also negates the need for credit checks and through standardization, can make the process more efficient.
For the lender, blockchain reduces the risk of default. Lenders can also offer cheap and fast services to a broader audience of borrowers.
Decentralized marketplacesSome argue that decentralized marketplaces offer the most room for DeFi innovation.
This is most applicable to decentralized exchanges (DEXes), which allow users to trade digital assets without requiring the exchange to hold their funds.
Platforms that issue security tokens, for example, may give users the tools and resources necessary to launch tokenized securities on the blockchain. The same might also be possible for derivative, futures, and synthetic asset markets.
Key takeaways:Decentralized finance is a suite of financial products and services that operate without a traditional intermediary such as a bank or exchange.Decentralized finance is based on decentralized apps, or dApps. Each dApp has a user interface and smart contract based on the Ethereum blockchain.Decentralized finance has the potential to revolutionize monetary banking services, borrowing and lending, and traditional, centralized marketplaces.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Decentralized Finance (DeFi) In A Nutshell For Business People appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Non-fungible Tokens In A Nutshell For Business People
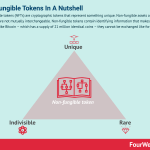
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are cryptographic tokens that represent something unique. Non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like.
Understanding non-fungible tokensUnderstanding non-fungible tokens mean first defining the concept of fungibility.
Fungibility sounds complicated, but it is a rather simple concept relating to the things people own and use every day. Physical cash is one example of a fungible asset because it can easily be replaced by something identical. For example, a $20 bill with one serial number can be replaced by another $20 bill with a different serial number. Both bills also hold equal value.
Conversely, non-fungible assets are those that are not mutually interchangeable. A rare baseball card is not interchangeable with a more common card. A first-class plane ticket is not interchangeable with an economy class ticket.
Non-fungible tokens contain identifying information that makes them unique. Unlike Bitcoin – which has a supply of 21 million identical coins – they cannot be exchanged like for like.
Non-fungible tokens also address the problem of a lack of unity in traditional digital assets. For example, an in-game collectible is likely to be very different from an event ticketing system. Using Blockchain, NFT unifies these assets and provides a simple way to transfer ownership and manage access.
The three characteristics of non-fungible tokensHere are three characteristics that differentiate NFTs from traditional cryptocurrencies:
Unique – each NFT is defined by metadata that describes how it is different from the rest. Metadata is rich in the sense that owners can describe many of the attributes that make the NFT special and identifiable. This record is permanent and unalterable and as a result, can be used to validate authenticity.Rare – non-fungible tokens are attractive in part because of scarcity. In theory, developers have the freedom to generate an endless supply of certain assets. But they can also limit the number of certain assets, increasing rareness and desirability.Indivisible – in much the same way that 40% of a rare baseball card is worthless, NFTs cannot be split into smaller denominations. They can only be held, bought, and sold as whole entities. Applications of non-fungible tokensAlthough non-fungible digital assets have existed for many years, the tokenization of these assets has the potential to deliver significant benefits.
These include:
Providing ownership. While an Instagram page can be deleted in a matter of seconds, a non-fungible token paired with Blockchain technology helps solidify ownership rights. Transferable. NFT ownership rights can be easily traded on specialist markets. In a gaming scenario, non-fungible tokens help avoid the problem of “walled gardens”. Here, desirable assets in one game can be used or exchanged for assets in another game – even between titles with different publishers.Authentic – fraud is synonymous with high-value non-fungible assets in art, gaming, collectibles, and other virtual or real-world assets. Blockchain helps negate counterfeiting and deceptive behavior, reassuring buyers that their purchase is authentic and original.Key takeaways:Non-fungible tokens are digital tokens that represent something unique. They use Blockchain technology to simplify the managing of access and ownership of traditional digital assets.Non-fungible tokens are rare, unique, and indivisible. These three characteristics help distinguish them from cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.Non-fungible tokens solidify ownership of digital assets that have existed for many years. Importantly, they make such ownership transferable and help reduce the chances of fraudulent transactions.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Non-fungible Tokens In A Nutshell For Business People appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
February 9, 2021
Nine Tech Industries To Look At In This Decade
 Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AlaaS) helps organizations incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) functionality without the associated expertise. Usually, AIaaS services are built upon cloud-based providers like Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IMB Cloud, used as IaaS. The AI service, framework, and workflows built upon these infrastructures are offered to final customers for various use cases (e.g., inventory management services, manufacturing optimizations, text generation).Augmented and Virtual Reality
Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AlaaS) helps organizations incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) functionality without the associated expertise. Usually, AIaaS services are built upon cloud-based providers like Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IMB Cloud, used as IaaS. The AI service, framework, and workflows built upon these infrastructures are offered to final customers for various use cases (e.g., inventory management services, manufacturing optimizations, text generation).Augmented and Virtual Reality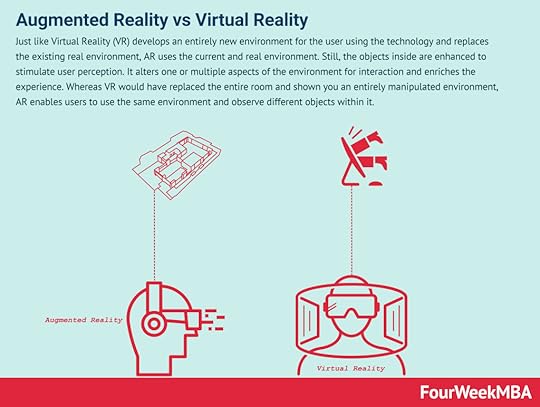 Just like Virtual Reality (VR) develops an entirely new environment for the user using the technology and replaces the existing real environment, AR uses the current and real environment. Still, the objects inside are enhanced to stimulate user perception. It alters one or multiple aspects of the environment for interaction and enriches the experience. Whereas VR would have replaced the entire room and shown you an entirely manipulated environment, AR enables users to use the same environment and observe different objects within it.Quantum Computing
Just like Virtual Reality (VR) develops an entirely new environment for the user using the technology and replaces the existing real environment, AR uses the current and real environment. Still, the objects inside are enhanced to stimulate user perception. It alters one or multiple aspects of the environment for interaction and enriches the experience. Whereas VR would have replaced the entire room and shown you an entirely manipulated environment, AR enables users to use the same environment and observe different objects within it.Quantum Computing Quantum Computing involves the use of several quantum phenomena to perform computations. One of these is entanglement. These phenomena help speed up exponentially the computational power, thus bringing computing to the next level as quantum computers operate at much higher speeds than classical computers. It also allows them to use less energy in performing the same operations as a classical one. 5G Technology
Quantum Computing involves the use of several quantum phenomena to perform computations. One of these is entanglement. These phenomena help speed up exponentially the computational power, thus bringing computing to the next level as quantum computers operate at much higher speeds than classical computers. It also allows them to use less energy in performing the same operations as a classical one. 5G Technology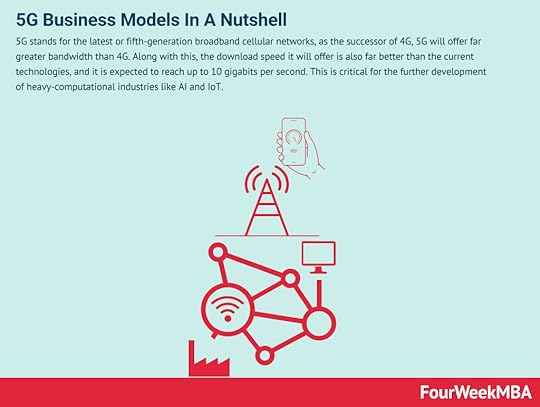 5G stands for the latest or fifth-generation broadband cellular networks, as the successor of 4G, 5G will offer far greater bandwidth than 4G. Along with this, the download speed it will offer is also far better than the current technologies, and it is expected to reach up to 10 gigabits per second. This is critical for the further development of heavy-computational industries like AI and IoT. Edge Computing
5G stands for the latest or fifth-generation broadband cellular networks, as the successor of 4G, 5G will offer far greater bandwidth than 4G. Along with this, the download speed it will offer is also far better than the current technologies, and it is expected to reach up to 10 gigabits per second. This is critical for the further development of heavy-computational industries like AI and IoT. Edge Computing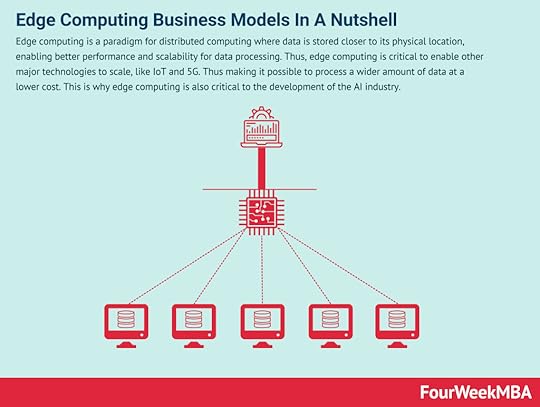 Edge computing is a paradigm for distributed computing where data is stored closer to its physical location, enabling better performance and scalability for data processing. Thus, edge computing is critical to enable other major technologies to scale, like IoT and 5G. Thus making it possible to process a wider amount of data at a lower cost. This is why edge computing is also critical to the development of the AI industry. 3D Printing
Edge computing is a paradigm for distributed computing where data is stored closer to its physical location, enabling better performance and scalability for data processing. Thus, edge computing is critical to enable other major technologies to scale, like IoT and 5G. Thus making it possible to process a wider amount of data at a lower cost. This is why edge computing is also critical to the development of the AI industry. 3D Printing 3D printing is the activity of transforming digital files into 3D objects. 3D printing has been used for various use cases, from small objects (like art pieces) to houses and more. This technology might democratize the production process by enabling cheaper manufacturing and, over the long run, people to manufacture objects from their homes, thus triggering decentralized mass manufacturing. Machine Learning
3D printing is the activity of transforming digital files into 3D objects. 3D printing has been used for various use cases, from small objects (like art pieces) to houses and more. This technology might democratize the production process by enabling cheaper manufacturing and, over the long run, people to manufacture objects from their homes, thus triggering decentralized mass manufacturing. Machine Learning Machine Learning Ops (MLOps) describes a suite of best practices that successfully help a business run artificial intelligence. It consists of the skills, workflows, and processes to create, run, and maintain machine learning models to help various operational processes within organizations. Blockchain and Cryptos
Machine Learning Ops (MLOps) describes a suite of best practices that successfully help a business run artificial intelligence. It consists of the skills, workflows, and processes to create, run, and maintain machine learning models to help various operational processes within organizations. Blockchain and Cryptos Establishing a robust infrastructure is the cornerstone of cloud computing. It often accounts for a third of the total amount spent on IT in a majority of businesses. Instead of taking computer workloads through the internal IT team, this traditional approach seemed to be long gone. Modern industries that embrace digital transformation with open arms gradually transfer systems into the cloud. Whether the information is on a private or public cloud, it offers increased security and safety against cyber threats. The result of increased cloud usage opens doors for cloud computing services provided by vendors and enterprises.
Establishing a robust infrastructure is the cornerstone of cloud computing. It often accounts for a third of the total amount spent on IT in a majority of businesses. Instead of taking computer workloads through the internal IT team, this traditional approach seemed to be long gone. Modern industries that embrace digital transformation with open arms gradually transfer systems into the cloud. Whether the information is on a private or public cloud, it offers increased security and safety against cyber threats. The result of increased cloud usage opens doors for cloud computing services provided by vendors and enterprises.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Nine Tech Industries To Look At In This Decade appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality

Just like Virtual Reality (VR) develops an entirely new environment for the user using the technology and replaces the existing real environment, AR uses the current and real environment. Still, the objects inside are enhanced to stimulate user perception. It alters one or multiple aspects of the environment for interaction and enriches the experience. Whereas VR would have replaced the entire room and shown you an entirely manipulated environment, AR enables users to use the same environment and observe different objects within it.
Why does augmented reality (AR) matter in business?Visualization is important to humans. To better understand a certain phenomenon or to simply make them more interactive. A large variety of tools has been developed to aid humans in various activities. From introducing simulations to performing activities through virtual modules, the technology has taken leaps from when it was first introduced as a concept. One such marvel is Augmented Reality (AR).
Through digital manipulation, the users experience an alternate version of the environment. It is different from VR because AR simply uses the existing environment and adds 3D models or layers of virtual objects, and displays them to the user.
Difference between VR and ARAn extremely simple example could be an application that allows you to put 3D models of furniture into a room and see how well it suits your room or whether it goes with the aesthetics of the room or not. Whereas VR would have replaced the entire room and shown you an entirely manipulated environment, AR enables users to use the same environment and observe different objects within it.
How does AR work?The AR technology consists of three core components: the hardware, software and application.
The hardware can be smartphones, which have certain features that AR technology demands.
Within the hardware, the first important thing is the processor, which should successfully use this technology. Next comes the GPU or Graphic Processing Unit. Finally, it should be equipped with sensors as the AR technology uses these to incorporate objects within the environment. An example is Depth and Proximity sensor. The depth sensor is used by the technology to determine how deep an object is and how much distance it needs to be placed. The proximity sensor measures how far or how close an object is. These two, along with other sensors, are important for the successful integration of this technology. The next component is the software, which is at the core of the technology. The software is what makes AR possible. It enables devices to understand the environment that it is to be integrated into. The feature enables the device to properly comprehend the environment and how other objects are to be placed. Along with this, minute technicalities like the environment’s lighting are also considered by the software so that the objects to be inserted can adjust to the already existing lighting of the environment. It also takes care of the motion of objects and tracks them accordingly to adjust to the surroundings. The puzzle’s final piece is the application, which uses these technologies and put on the screen what the user expects. The hardware and software interact with the application to enhance user experience and make it worthwhile.AR commercial applicationsAR has far-reaching applications. One of the biggest sectors that it can help improve is the education sector. From primary schooling, all the way to college, using interactive AR technologies can enhance the thinking capabilities of the students and help them understand more creatively and effectively.
Successful integration will require training of the teaching staff, which should be the primary target to successfully augment this technology into the education system.
AR technologies have already made their way to Gaming platforms. A recent craze over the AR game Pokémon Go is the living proof of how creative design thinking and AR can be compiled to produce wonderful user experiences. However, the creativity and fun aspects are not the only potential uses of this technology.
From constructing rooms to decorating art galleries, AR has the potential to help and guide users in creating marvels. Urban planning has been recently integrated with the use of AR technologies to guide professionals by creating maps and structures, which gives an overview of the entire plan before being implemented.
In high technology industries where quick access might be required to manuals or control instructions, AR technologies can help by providing quick access to virtual manuals and completely disregard the need for physical manuals.
Another use of AR is found in the healthcare and fitness industry where smart glasses are developed for biking and running. These enable the users to be immersed in a fun and interactive environment while they workout. While VR in the same way changes entire surroundings, AR lets you stay within the environment and only adds to making your experience more creative and fun.
In the future, it is expected that AR technologies will be adopted by almost all sectors and industries to enhance both employee and user experience. Digital Marketing will be the norm which users will be able to see through their devices around the places that they live.
E-commerce stores can benefit from this technology by incorporating it into clothing stores. The idea is to give an augmented view of the user in a wide range of clothes instead of actually having to change them. It ensures ease and convenience for the user and makes service quick and effective.
The major obstacle for AR to scale upThere are some obstacles, which need to be addressed before the technology becomes available widespread. Objects recognition and how well they are incorporated into the environment needs to be flawless for the system to work properly. To add to the ease of convenience of the end-users, developments towards a “hands-free” interface should be pursued.
In large environments where far better integration is required, efforts need to be made to properly incorporate the surroundings through the technology. Improvements are being made and the technology is becoming widespread given its uniqueness and attractive features.
The possibilities that exist for AR are unlimited. From education to gaming and architecture to fitness, a comprehensive stream of technology applications is available and in demand. The only question is how quickly devices are developed and successfully integrated with this technology.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Augmented Reality vs Virtual Reality appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Quantum Computing Explained For Business People
Quantum Computing involves the use of several quantum phenomena to perform computations. One of these is entanglement. These phenomena help speed up exponentially the computational power, thus bringing computing to the next level as quantum computers operate at much higher speeds than classical computers. It also allows them to use less energy in performing the same operations as a classical one.
Why does quantum computing matter?The need for knowledge has always engulfed humans and is the major driver of technological evolutions. From what started as an abacus and turned into high-end calculators for everyday use, computers have seen a similar advancement. Within three decades, computing powers changed from a mere five thousand addition problems (ENIAC) to millions of complex problems in a matter of seconds.
This exponential advancement has not hindered the progress that humans still dream of achieving. Technological changes have always occurred whenever there has been a problem to solve. The work of decades upon decades in different technological areas has left little room for improvements. However, whenever existing technology was unable to solve the tasks at hand, humans have tried to resolve the issue with further advancement.
One similar case has been that of Quantum Computing. When complexities ensued and classical computers could not answer the underlying questions, quantum computers were invented. Hence, a new era of advancement followed.
How does quantum computing work?As the name suggests, Quantum Computing involves the use of several quantum phenomena to perform computations. One of these is entanglement. Quantum entanglement is basically a phenomenon that occurs when a group or a pair of particles interact or are in the same proximity but their quantum state cannot be determined independently of each other.
Similarly, another phenomenon that is part of Quantum Computing is superposition. Superposition states that any two quantum states can be added or “superposed”. The result will be another quantum state. In the same way, this also entails that every quantum state is a sum of other quantum states which can be two or more in number. Quantum Computing uses these phenomena to perform faster computations than classical computers such as integer factorization.
It is widely argued that whichever problems that quantum computers solve, can also be solved by classical computers. Alternatively, whichever problems can be solved by classical computers as well. The difference that exists between the two is the time that both take while solving the problems. This advantage of quantum computers over classical computers is known as “quantum supremacy”. Just like classical computers store information in the form of bits (0 or 1), quantum computers use what are known as “qubits”.
As mentioned before, using phenomena like superposition and entanglement quantum computers are able to allow subatomic participles in more than one state. This means that at the same time it could be a 1 or a 0. This makes quantum computers operate at much higher speeds than classical computers. It also allows them to use less energy in performing the same operations as a classical one.
Commercial applications for quantum computingQuantum Computing has a wide array of applications, which makes it one of the most exciting technologies to look forward to. Within the healthcare industry, it cannot only be used for research purposes but diagnostics and treatment as well. Since quantum computers have high processing power, it will enable researchers to use them in order to simulate interactions between different proteins of the human genome and drugs.
This will allow them to evaluate drugs based on their interactions and can lead to pharmacological advancements. In diagnostics, MRI machines can be made to operate at higher levels and provide greater detail which will help the doctors in identifying medical issues. Similarly, treatments like radiotherapy can be further enhanced due to the use of quantum computing as it will be able to withstand complex simulations and provide answers in a timely manner.
In the field of Finance, quantum computing can help in detecting fraud based on pattern recognition. Coupled with machine learning, neural networks can be trained timely and thereby improving the detection rate immensely. From a Marketing perspective, quantum computing can be used to process and analyze large amounts of data which can be used to put forward targeted advertisements at potential customers based on their behavior.
The same can be done through classical computers, but quantum computing certainly has an edge in providing better and timely service due to the data being in large amounts. Optimization problems, which are encountered by companies like delivery services or arranging flight schedules, can be solved using quantum computers. It has uses in almost all avenues, whether they are public projects or advancements in data handling. What would normally take unimaginable amounts of time can be solved through the use of quantum computers.
Major advantages of quantum computingThe major advantage that quantum computers hold is that they are equipped to find optimal solutions to problems that have infinitely many variables. Due to their high processing power, quantum computers are able to run millions of simulations to test whatever theories that users might have. This gives it an ultimate advantage over other systems.
Quantum computers at extremely cold temperatures. The temperatures required are near absolute zero. To achieve such a cold temperature, the chip is required to be cooled down. This is achieved through liquified helium, which makes the chip very cold. To achieve superconductivity, such low temperatures are essential for quantum computing.
Research is being conducted to make quantum computing possible at higher temperatures, but no such significant improvement is expected in the near future.
Scientists are developers are constantly in the run to make quantum computing possible given the large number of applications that it entails. Machine learning will benefit the most when stability is achieved in terms of quantum computations. Technology giants like Google and IBM are in the constant run to achieve quantum supremacy, with each taking steps to ensure the world witnesses a stable quantum computer in the next few years.
What’s the major drawback (for now) of quantum computing?One of the issues that quantum computers encounter is any disturbance in the computer’s surroundings. Since they are very fragile, vibrations in the surroundings can impact the atoms, and decoherence will be caused. Despite their high demands, quantum computers will actually reduce the power consumption to operate. This is achieved through a process known as “quantum tunneling.” The possibilities are endless, and researchers are in a rush to make it happen.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Quantum Computing Explained For Business People appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



