Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 169
February 13, 2021
What is A Business Model Wheel? Business Model Wheel In A Nutshell
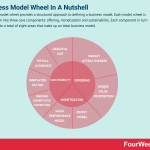
A business model wheel provides a structured approach to defining a business model. Each model wheel is broken down into three core components: offering, monetization and sustainability. Each component in turn contributes to a total of eight areas that make up an ideal business model.
Understanding a business model wheelBusiness models can be created in myriad ways, from the stereotypical back-of-a-napkin approach to a much more structured and formal methodology. The business model wheel lies somewhere in the middle of these two approaches.
At this point, it is important to make the distinction between a business model and a business plan. A business model explains the mechanisms for profit generation and explains how the business organizes supplier, client, or partner relationships to generate profits.
Conversely, a business plan translates the important business relationships into an actionable strategy and quantifies their financial impact through projected milestones.
The business model wheel is represented as a segmented circle. In the next section, we will take a closer look at its structure.
The core components of a business model wheelEach model wheel is broken down into three core components. Each component in turn contributes to a total of eight areas that make up an ideal business model.
Component 1 – OfferingThe offering includes two areas:
Market attractiveness – or the niche, industry, market, or customer segment that will be sold to.Unique value proposition – in terms of value, how does the offering differentiate itself in the marketplace?Component 2 – MonetizationMonetization also encompasses two areas:
Profit model – describing potential income streams and their associated profit margins.Sales performance model – this is the process of converting prospective leads into paying customers through marketing.Component 3 – SustainabilityThe last component, sustainability, details four areas:
Ongoing competitive advantage – this must be created and then maintained through meaningful product differentiation.Innovation factor – or the ability to balance innovation with remaining competitive.Pitfall avoidance – how can the business model avoid the pitfalls of litigation, short-lived consumer trends, or regulation?Graceful exit – how can the business model be structured in such a way that the business itself can be sold for a profit?Scoring a business model wheelBusinesses can score model wheels to highlight the strengths or weaknesses of their particular model and distribute resources accordingly.
Weighted scores are given according to how well the business can satisfy each area, giving a total score out of 100 for each of the three components.
Following is a breakdown of the scoring that should be used:
Offering (maximum of 34 points) – or 17 points each for market attractiveness and unique value proposition.Monetization (33 points) – or 17 points for the profit model and 16 points for the sales performance model.Sustainability (33 points) – or 11 points for ongoing competitive advantage, 9 points for innovation factor, 7 points for pitfall avoidance, and 6 points for a graceful exit.Key takeaways:A business model wheel provides a structured, evaluative approach to creating a business model.A business model wheel is divided into three segments that represent core components: offering, monetization, and sustainability. Each component has several focus areas.A business model wheel can be used to score the potential or actual effectiveness of an organization. Weighted scores are assigned to each area for a total score out of 100.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is A Business Model Wheel? Business Model Wheel In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is Scientific Management Theory? Scientific Management Theory In A Nutshell
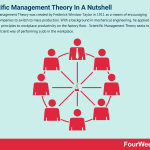
Scientific Management Theory was created by Frederick Winslow Taylor in 1911 as a means of encouraging industrial companies to switch to mass production. With a background in mechanical engineering, he applied engineering principles to workplace productivity on the factory floor. Scientific Management Theory seeks to find the most efficient way of performing a job in the workplace.
Understanding Scientific Management TheoryIn the early 20th century, there was also a general belief that workers were lazy and inefficient. Taylor argued that the remedy for inefficiency was to be found in systematic management – there was no use trying to recruit men who had extraordinary work ethics.
Taylor was one of the first to look at productivity from a scientific standpoint, believing in universal laws that governed labor productivity and efficiency. For this reason, “Taylorism” is often referred to as one of the first forms of scientific management.
Taylor’s classic assumptions about workersTaylor’s belief that workers were only motivated by money provides the basis for several classic assumptions:
Workers find their work unenjoyable and have a natural tendency to slack off in a process he called natural soldiering. To counter this tendency, they must be closely monitored and controlled.To increase worker investment in their job, it should be broken down into bite-sized actions.Training should be provided to all employees to create a standardized way of working.Workers should be paid based on how much they produce (piece rate). Taylor argued that this would create a win-win scenario where the employee would earn more money and the business would maximize its profits.The four core principles of Scientific Management TheoryTaylor was perhaps a product of his time, viewing employee labor as an extension of machine labor. He was also a strong proponent of autocratic leadership, which an increasing number of modern companies are shying away from.
However, his principles of scientific management are still relevant today.
Here is a look at each principle:
Select methods backed by science. Businesses should avoid giving workers the freedom to perform their jobs in any way they see fit. The scientific method must be used to identify the single, most efficient way of doing the job.Assign workers to jobs that match their aptitude. Instead of assigning workers to jobs at random, assign them to roles where their unique capabilities will allow them to work at peak efficiency.Monitor worker performance. Monitor efficiency and ensure that necessary instruction is given on how to maintain productivity.Divide the workload between management and staff. Here, roles and responsibilities should clearly be defined. Management should train workers and workers should implement lessons learned.Examples of modern companies employing Scientific Management TheoryAlthough slightly outdated, scientific management theory is useful in highly competitive industries where labor costs need to be kept as low as possible.
Example organizations include:
Amazon – where warehouse staff are paid on a piece-rate basis according to their level of productivity. The company has also recently introduced patented wristbands that track employee performance in real-time.McDonald’s – the homogenization of McDonald’s restaurants worldwide has meant that processes have had to become extremely refined. The procedure for everything from making a burger to mopping the floor is the same – regardless of geographic location. These processes are ultra-efficient and are broken down into actionable steps, which is a core component of Taylorism.Key takeaways:Scientific Management Theory is a theory of management that seeks to analyze and synthesize workflow to improve labor productivity.Scientific Management Theory was originally based on the assumption that workers were only motivated by money and is heavily geared toward autocratic leadership styles. Nevertheless, it is still relevant to modern organizations.Scientific Management Theory is particularly effective in industries with a high prevalence of menial or repetitive tasks where costs need to be minimized. Examples include Amazon and McDonald’s.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is Scientific Management Theory? Scientific Management Theory In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is Resource Dependence Theory? Resource Dependence Theory In A Nutshell

Resource dependence theory was first introduced in the 1970s in a publication entitled The External Control of Organizations: A Resource Dependence Perspective. Resource dependence theory (RDT) is the study of the impact of resource acquisition on the behavior of an organization. In the publication, authors Jeffrey Pfeffer and Gerald R. Salancik argue that resources are key to organizational success. However, an organization does not always have control over the resources it needs and must devise strategies that sustain access.
Understanding resource dependence theoryResource dependence theory notes that those who control critical resources have power, and power influences behavior. Similarly, the behavior of an organization with a dependence on these critical resources is also influenced.
Resource dependencies can relate to raw materials, labor, and capital to name a few.
Foundational assumptions of resource dependence theoryRDT is based on three core assumptions:
Organizations contain internal and external actors that influence and control resources and by extension, behavior. For example, how abundant are the resources? How much competition is there? How easy are the resources to acquire? Is there a more cost-effective acquisition method?The environment contains valued resources essential to the continued operation of the organization. Uncertainty develops around resource acquisition for those who do not control access.Organizations work toward two core objectives. They must seek to minimize dependence on critical resources from other organizations. They must also increase the dependence that other organizations have on them for resources. Achieving either of these two objectives has benefits for the power level of the organization. Factors that determine organizational dependencePfeffer and Salancik also identified three factors that determine the degree of dependence of one organization on another:
The importance of the resource – defined as the extent to which the organization relies on a resource for its continued viability. Such resources are valuable in that their removal from business operations would cause rapid and serious harm.The extent of discretion over the use or allocation of the resource by the controlling company.The availability of alternative resources or the concentration of resource control. How many companies control the majority of the resources?Based on these factors, the business can minimize resource uncertainty by tweaking processes, relationships, and structures. Identifying substitute resources or establishing a supply from multiple sources are effective ways to reduce dependency.
If a business has the necessary capital, resource dependency can also be addressed by mergers or acquisitions. In this instance, each entity develops resource interdependence – which is a more favorable scenario when compared to complete dependence on either side.
Key takeaways:Resource dependence theory describes the impact of resource acquisition on the behavior of a company.Resource dependence theory argues that organizations with the most access to critical resources exert power and influence over those with less access.Resource dependence occurs when an organization has little control over a resource it deems crucial to daily operations. Dependence can be reduced by identifying multiple resource suppliers and adjusting internal processes and structures.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is Resource Dependence Theory? Resource Dependence Theory In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is the Johari Window Model? Johari Window Model In A Nutshell
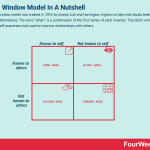
The Johari window model was created in 1955 by Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham to help individuals better understand themselves. The word “Johari” is a combination of the first names of each inventor. The Johari window model is a self-awareness tool used to improve relationships with others.
Understanding the Johari window modelA core premise of the model is that our interactions with others are ultimately shaped by:
How we see ourselves, andHow we are perceived by others.If both views are aligned, then the interaction is more likely to be effective and engaging.
The four panes of the Johari windowAlignment can be assessed by populating a matrix with four cells, commonly referred to as the four panes of a Johari window.
Each pane helps the individual evaluate the degree of alignment (or disparity) in their interactions with others.
Let’s look at each pane:
Open area (known to self, known to others) – this area contains well-known information that most individuals are happy to talk about. It encompasses skills, values, experience, personality, values, and feelings.Blind area (not known to self, known to others) – or things that people know about us that we are unaware of. Information is often withheld for fear of hurting feelings or starting an argument. In a business context, this area includes blind spots that are crucial for professional development. They can be both positive and negative traits.Hidden area (known to self, not known to others) – commonly referring to information that the individual chooses not to disclose. These may include fears or ambitions that are withheld for fear of reprisal or judgment. Unknown area (not known to self, not known to others) – as the name suggests, this is information unknown to either party. It may relate to talents or abilities that, through a lack of opportunity or confidence, have not yet been discovered.Creating a Johari window for individualsCreating a Johari window involves self-reflection and as such, the insights gleaned may be uncomfortable for some.
But it need not be a daunting process. Here is how you can use a Johari window to accelerate self-improvement:
Choose a group of trusted peers. This may be a group of people who know you intimately. In business, it may simply be members of your team.Select your Johari words, otherwise known as Johari adjectives. Many teams choose to use a preselected list of 56 terms that include such descriptors as brave, confident, energetic, intelligent, shy, wise, warm, trustworthy, mature, quiet, proud, or idealistic. Teams can choose to use their own adjectives so long as there is a large and varied group to choose from. Then, select 5-10 words you believe best describe your personality.Ask each member of the group of peers to then select 5-10 adjectives.Place words selected by both you and others in the “open” pane. Place words only selected by yourself in the “hidden” pane.Place words that were selected by peers but not selected by you in the “blind” pane. All remaining words should be placed in the “unknown” pane.Evaluate the results. How much overlap is there between how you see yourself and how others perceive you? Whatever the results, the goal must be to increase the size of the “open” pane relative to the others.Key takeaways:The Johari window model is a self-awareness tool that seeks to bridge the gap between how the individual perceives themselves and how others perceive them.The Johari window model is named after a matrix, or window, with four panes. Each pane is called an area, representing varying degrees of alignment or disparity in perception.The Johari window model can be a daunting process for those not accustomed to detailed self-awareness. But by focusing efforts in the right areas, the model can be a very effective tool for self-improvement.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is the Johari Window Model? Johari Window Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is The Teece model? Teece Model In A Nutshell
The Teece model is a framework that enables competitive advantage to be gained through innovation. The Teece model was named after economist David Teece who created a framework for building profit through innovation in 1986. Teece noted that being first to market with a new product was no guarantee of success. He also argued that in the history of innovation, some companies were winners and some were losers. Ultimately, whether a company wins or loses is a result of how easily its innovation is replicated.
Understanding the Teece ModelRoyal Crown Cola is an example of a loser. After being the first to introduce diet cola in 1962, the company quickly lost market share to Coca-Cola and Pepsi with their superior branding and distribution channels. Conversely, glass manufacturer Pilkington was able to revolutionize the flat glass industry through first-to-market innovations that were difficult to replicate.
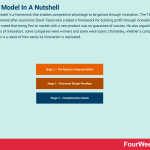
The three stages of the Teece modelFundamentally, the Teece model aims to help businesses maintain a competitive advantage by preventing rival companies from replicating (and then benefitting from) their innovation.
Three stages guide making money from innovation.
Stage 1 – The Regime of AppropriabilityInitially, the innovator must secure the innovation from its competitors. Patents are a good place to start, but Teece notes that they cannot always be relied upon.
Securing the innovation may also involve intellectual property rights, tacit knowledge, or complex internal systems that make replication difficult.
Stage 2 – Dominant Design ParadigmThe next step is to gain benefits of scale as quickly as possible. Innovative products are commonly popular products, so the organization must be able to meet demand by scaling production.
Scaling can be performed internally, but not without a significant investment of capital. Alternatively, a third-party can be utilized to outsource some or all the process.
Stage 3 – Complimentary AssetsTeece notes that simply possessing an innovative product is not a one-way ticket to profitability. Good marketing combined with a suitable market to channel is a complementary asset crucial to increasing awareness and driving sales.
Suppliers, licensing agreements, customer relationships, and distribution channels also play an important role in creating and then maintaining market dominance.
The Teece model matrixIn a different interpretation of the Teece model, businesses can use a matrix to compare two factors:
Imitability (low or high) – or how easily a competitor can replicate the innovation, andComplementary assets (freely available or tightly held) – noted above as any factor that supports or maintains profitability in an innovation.Comparing each factor against the other allows the business to make four predictions about innovation profitability.
These predictions are listed below:
High imitability/freely available complementary assets – innovation will find it difficult to make a profit.Low imitability/freely available complementary assets – the innovator has a higher likelihood of making a profit.High imitability/tightly held complementary assets – the company that owns the assets will most likely profit.Low imitability/tightly held complementary assets – the company with the highest bargaining power in a negotiation will be the one that profits the most.Key takeaways:The Teece Model is a framework that analyzes and predicts competitive advantage gained through innovation.The Teece Model argues that successfully profiting from innovation involves a combination of reducing replicability and scaling production as quickly as possible. Complimentary assets that support the core innovation are also crucial.The Teece Model can also be represented by a matrix that compares imitability and complementary assets to gauge profitability.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is The Teece model? Teece Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is An After-Action Review? After Action Review In A Nutshell

An after-action review (AAR) is a structured process of reflecting on the work of a group by identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. After action reviews were first utilized by the United States Army on combat missions. Since then, modern companies such as British Petroleum, Motorola, and General Electric have all become proponents. AARs are also used to identify gaps in public health emergency preparedness systems. After Hurricane Katrina in 2005, a searching review of the emergency response led to new methods of communicating during natural disasters.
Understanding an after-action reviewThe process of running through an after action review centers on four questions:
What did we expect to happen?What actually happened?What went well, and why?What can we improve on, and how?These questions provide knowledge to the business, and knowledge is power. Put differently, improvement cannot be realized without an understanding of what went wrong.
The five steps of an after action reviewConducting a successful after action review is a matter of following five steps.
Step 1 – Make it a priorityToo many organizations let the review process fall by the wayside. Ideally, a review should be a non-negotiable component of every project.
Prioritizing the completion of an AAR means the project is still fresh in the mind of the project team. No more than 2 weeks should elapse after project completion before an AAR is undertaken.
Step 2 – Involve everyoneThe facilitator should gather the project team together and involve them in the entire review process. This ensures that each individual perspective is heard and that no weakness or struggle goes undetected.
Importantly, the facilitator should create an atmosphere of shared improvement. They should stress that the AAR is not a personal performance review.
Step 3 – Conducting the reviewThe facilitator should then guide the group through the four questions mentioned earlier.
What was expected to happen? Define the purpose, objectives, and initial timeline. Who was the audience? What were the intended outcomes? What barriers were expected to occur?What actually happened? The focus should be a non-judgmental account of what transpired. Involve each member of the project team and resolve inconsistencies in the story if required.What went well, and why? The goal here is to identify best practices that can be built into systems for future use. If time is limited, the facilitator can ask every team member what they believed had the greatest direct impact on success.What can be improved, and how? How could the team have performed better given the tools at their disposal? How can stumbling blocks or pitfalls be avoided in the future? How might processes change with new insights? What advice would the project team give to a future team?In answering these questions, some basic ground rules must also be established:
Participants should share honest observations without resorting to blame or praise.Every individual has something important to contribute. No one person possesses all the answers.Every idea has equal value. There are no right or wrong ideas.Consensus is preferable, but clarification is important in cases where consensus is not possible.No record of the AAR will be distributed without the express permission of all participants. The same applies to direct quote usage.Step 4 – Crafting the reportThe final report does not need to be a masterpiece, but it should summarize the points made in the meeting in a shareable format. Include basic information such as the name of the project and the names of those in attendance.
It’s also important to document the best practices that should be repeated and the weaknesses that should be remedied. The document can then be shared with the project sponsor or other relevant leaders.
Step 5 – Implement the changesChange implementation will vary depending on the industry. But in any case, it should be implemented as quickly as possible.
Key takeaways:An after action review is a structured project review that assesses strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.An after action review is centered around four key questions that give a business important insights into what worked and what could be improved in future.An after action review can be completed in five steps. A facilitator is important in maintaining a constructive, collaborative, and open discussion that enhances strengths and remedies weaknesses.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is An After-Action Review? After Action Review In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Commercial Applications of GPT-3

GPT-3 is Open AI’s latest natural language prediction model. With the emergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the business landscape, this is one of the tools that will quickly increase in popularity. The Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3 offers limitless access to computing on top of its cloud infrastructure, promoting scalability. Nevertheless, GPT-3 should be the next big thing in tech. Following the rise of deep learning, advanced technology will transform how business gets conducted globally.
What is GPT-3?The Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3, also known as GPT-3, is developed by OpenAI, a San Francisco startup founded by Elon Musk. The GPT-3 is an extensive neural network formed from the deep learning segment of machine learning technology. Machine learning is the extension of artificial intelligence (AI), which uses computer algorithms to automate specific actions. The latest version of GPT offers advanced features that produce lines of text that come off as something created by humans. Imitating human-like actions, this provides a personalized approach to transactions and crucial business decisions.
As a result, a growing number of commercial industries found the potential of leveraging GPT-3 to automate mundane tasks. GPT-3 prompts a generated response to any text that the person enters into the computer. It creates a reaction following the information presented.
For instance, typing a string of statements into the search box can respond within the given statement’s context. GPT-3 has the potential to amplify human effort in a variety of situations. It can be applied in different business processes such as customer service, documentation, and producing various content.
Interesting Ways GPT-3 Is Used in Commercial ApplicationsGPT-3 can help businesses accomplish mundane, repetitive tasks. For instance, developers can build a tool that generates various layouts for the design required in different situations. It can also simplify programming by translating natural language into SQL queries. Formulating complex spreadsheets, building complex CSS, or even deploying Amazon Web Services (AWS) instances, GPT-3 can get applied in almost any business process.
The novel applications mentioned above can automate simple tasks helping employees focus on value-adding projects.
However, the commercial applications that businesses can take advantage of using GPT-3 are even greater.
Let’s take a look at some of them below:
Automate Translation of Various DocumentsThe automated translation of large volumes of documents from various languages can bring many opportunities to businesses. Apart from streamlining the delivery of services, they can increase their capacity outside the country. GPT-3 can learn over 499 billion words of different languages to produce translations at a given time seamlessly.
As we all know, some statements can get lost in translation even when every word gets translated correctly. Each language has sayings and context that controls the conversation. With GPT-3, that context is taken into consideration to understand further what the statement means.
Priming AI to Deal with DataOne of the applications of GPT-3 that businesses find exceptionally fascinating is priming AI to respond to English inputs with structured data output like JSON or XML. Through this feature, developers can take advantage of its machine learning capabilities to comprehend the theorems and their underlying structure. While it can produce answers to mathematical questions with the highest accuracy, it also considers those values’ context. This consideration provides better results and can help the advancement of the research promptly.
Programming Without the Use of CodeWithout the need for manual intervention, GPT-3 generates structured data for developing specialized programs and software. Eliminating the need for writing algorithms using traditional programming languages allows some developers to embrace natural languages. Adopting natural languages becomes vital to prime the AI. Although it does not require expert skills in coding, this opens up new opportunities needing unique skills to expand software development jobs.
Generate Automated RegexComposed of a sequence of characters that define the search pattern, Regex is vital in creating string-searching algorithms. Through GPT-3, developers can acquire Regex for various use-cases. All you need to do is type the Regular expression that you wish to generate in plain English. You have to enter an example string to help GPT-3 develop relevant Regex in a matter of seconds.
Create a Clone of a WebsiteGPT-3 works with the UI and UX designer application called Figma to create clones of a website. Cloning websites is necessary to test the updates and the compatibility of certain features safely. This breakthrough in designing websites and generating robust tools can boost their functionalities. All you need to do is to input the URL of the website to produce its clone.
Produce Quizzes and TestsNow that most of the classes became online, most teachers and students find it challenging to manage their time in the middle of the pandemic. A quiz generator powered by GPT-3 can ease their burden and also improve learning. It produces test questions of different topics and subject matter for students to answer. It also contains a thorough explanation of the answers to help students understand how they find the result.
Formulate Unique AnimationsAmong many other things you can create from GPT-3, production companies leverage this tool to automate animations. GPT-3 combined with a Figma plugin can produce frame-by-frame animations and a text prompt. It can also formulate 3D scenes with the help of the three.js Javascript API. All you need to do is enter the details of the location that you desire to create and take care of the rest.
Automate DocumentationEven though you don’t have prior accounting knowledge, it is possible to generate financial statements using GPT-3. This tool transforms natural language into Python code to automate balance sheets.
The Future of GPT-3Everything that involves a particular language structure can get automated through GPT-3. From answering queries, producing content, summarizing a long string of texts, translating languages, to programming code, there are multiple ways for businesses to leverage this tool.
Overall, GPT-3 helps businesses get a few steps ahead into providing a future that makes business data and communication much more manageable. After all, communicating effectively is one of the best business tools, and GPT-3 makes that communication more accessible.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Commercial Applications of GPT-3 appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
The Evolution of DeepMind And Why It’s So Hard To Monetize Machine Learning (So Far)
As one of the largest artificial intelligence research facilities, DeepMind aims to advance the technologies of AI. DeepMind was acquired by large tech corporation Google for $600 million in 2014. Since the organization’s founding, it raked plenty of achievements shaping the world we live in today.
A Brief History of DeepMindDeepMind is a British artificial intelligence research unit subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., founded in 2010. Founded by tech-experts Demis Hassabis, Mustafa Suleyman, and Shane Legg, they made it their mission to leverage AI in facilitating deep learning. Following its success, Google acquired the organization for $600 million. Although Google became the parent company of DeepMind, Alphabet Inc. remained its subsidiary. There are multiple research centers all over the United States, Canada, and France under DeepMind Technologies.
DeepMind earned its reputation after introducing AlphaGo in 2016. This computer program utilizes AI to play the board game Go. Subsequent versions of this program became so powerful that it beat a professional player and world champion in Go, Lee Sedol. The success of AlphaGo inspired the creation of another program called AlphaZero, which expanded on other board games, including chess, shogi, and Go Best.
After gaining a lot of traction, DeepMind received a lot of financial support from prominent venture capital firms such as Horizon Ventures and Founders Fund and influential entrepreneurs like Elon Musk and Scott Banister. After Google has taken over DeepMind, it often gets referred to as Google DeepMind.
DeepMind’s Exploration to Machine LearningThe primary goal of DeepMind is to leverage the advanced disciplines of machine learning and neuroscience to build general-purpose learning algorithms. The organization has a belief that these algorithms are not only the key to improve AI but to understand the human mind better. Since the organization started, it has been releasing publications surrounding the topic of artificial intelligence. A year after Google’s acquisition of DeepMind, it released an open-source testing tool called GridWorld. This program evaluates the behavior of specific algorithms under particular circumstances. This testbed has a kill switch when undesired behavior gets detected from the algorithms to promote AI safety while exploring the discipline’s capacity.
In 2018, the company started developing systems that can compete in a variety of games. The system began playing the 1999 multiplayer-focused first-person game called Quake III Arena. It allows them to test the capabilities of the systems as several games modify their behaviors. Leveraging machine learning in strategic games, including chess, hones the critical thinking capabilities of computer systems. They can retain what they have learned upon being immersed in complex games. Simply put, gamification’s objective is to let the system learn to acquire human-like intelligence and behavior.
Transitioning Towards Reinforcement LearningAs the research advances towards machine learning, DeepMind began exploring more of its aspects. Taking deep learning to a whole different level, researchers studied deep reinforcement learning. Unlike other artificial intelligence systems that most of us are familiar with, it makes decisions and executes actions independently. In other words, reinforcement learning systems are not pre-programmed. The system solely relies on experience to learn and develop, just like human beings.
DeepMind tests the capability of systems by letting them play the game without programming them with its instructions. They need to work their way towards the top after going through multiple matches against a human opponent. After a couple of attempts, systems often become more knowledgeable of the gameplay and become much better than their opponents. The goal of leveraging reinforcement learning is to eliminate human error from affecting the gameplay’s efficiency level. Since its introduction, many researchers have tested its potential for programs other than games.
DeepMind’s Contribution to the Healthcare IndustryOne of the most notable contributions of the organization is its collaboration with WaveNet. DeepMind established WaveNet to advance healthcare services and promote patient care. The software generates speech that emphasizes human-like features. WaveNet offers text-to-speech systems that are less robotic and natural-sounding to assist people who have a speech impairment.
The organization coordinated with individuals who have suffered from the same condition as the program’s target market. They worked with former NFL player Tim Shaw, who has Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). DeepMind created a system that produces the natural voice as if it was them uttering the words. Other programs may have required the patients to spend a long time recording audios and reading scripts. Unfortunately, speech-impaired patients do not have the luxury to record audios to have the system recreate their voice. WaveNet only needs a few audio recordings, and the algorithm will take care of the rest. It took them six months to perfectly recreate the voice of Tim Shaw. The text-to-speech program presents Shaw’s voice before his disease.
Developments of DeepMind Under GoogleFollowing the acquisition of Google to the notable AI research organization, it brought several changes to the platform’s operations. DeepMind influenced the AI department of the popular search engine website in a few ways:
One of the most current use-cases of DeepMind is the advancement of application recommendations within the Google platforms. Algorithms get leveraged to make the feed more personalized for the user. All they had to do is to gather data based on the user preferences, app behavior, and actions. This use allows the users to quickly find the applications that they will most likely find useful.Secondly, another major project involving DeepMind is algorithms’ production to cool down the servers across Google platforms. These features allow better usage and more efficient navigation around the application. Offering adaptive brightness and optimized battery, browsing through Google platforms can be a breeze. You can leverage machine learning to conserve the energy of mobile devices, laptops, and computers. From the app itself, users can modify lighting under certain conditions.Overall, continuing the evolution of DeepMind allows Google to improve the user experience. When they create a platform that everyone finds easy to use, more people can trust and rely on it. With the advancements of DeepMind, it seems Google has the opportunity to make nearly anything user-friendly.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post The Evolution of DeepMind And Why It’s So Hard To Monetize Machine Learning (So Far) appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
The Evolution of OpenAI And The Business Of Machine Learning
Founded less than six years ago, OpenAI maintains a philosophy that giant corporations should not control progressive technology development. The non-profit organization aims to research artificial intelligence (AI) to discover its potential and benefits to society. The goal is to produce open-source software and applications that allow various researchers to develop AI systems. Since the beginning of the organization, it has racked up several impressive achievements, which is the primary focus of this article.
What is OpenAI?The non-profit organization OpenAI established a research laboratory that aims to promote AI tech that benefits society. It was initially founded in late 2015 by several entrepreneurs, including Elon Musk, Sam Altman, and many others. They all pledged $1 billion to support the development of AI systems that are developer-friendly. Although Musk resigned from the organization after three years, he remained a donor and an advocate for OpenAI.
The organization seemingly drifted away from its initial objectives of avoiding developing software to generate financial returns. In 2019, OpenAI accepted a $1 billion investment from Microsoft, one of the world’s most prominent tech companies.
OpenAI Products Throughout the YearsThe organization was structured to be non-profit to focus on its main goal — researching AI technology. The primary purpose of OpenAI is to leverage artificial intelligence that brings a positive, long-term impact. There are always risks in advancing a powerful technology such as AI. Exploring such complex technology tends to become abused. With such great power, they make it their mission to guarantee a positive and prosperous future. Overall, the organization develops technologies to empower people to utilize AI for the betterment of the world.
The focus of OpenAI research goes beyond artificial intelligence itself. They dived into the paradigm of machine learning called reinforcement learning. It involves the training of learning models that become the basis for future actions. With that in mind, here are the products and applications that OpenAI developed throughout the years.
GymOne of the first software that the non-profit organization created is called Gym. It is an open-source library where researchers can discover reinforcement learning algorithms. This software provides a plethora of opportunities for developers to explore various AI environments. The toolkit also involves AI research publications for easier discovery of their latest developments.
In late 2017, developers failed to maintain the documentation site and transferred information regarding their recent work on Open AI’s GitHub page.
RoboSumoRoboSumo involves humanoid “meta-learning” robots that compete against one another. The main goal is to let simulated AI technologies learn physical skills, including ducking, pushing, and moving around. While in the arena, the competitive environment creates an intelligence that allows AI to overcome adversity and adapt to changing conditions. The result of this research concluded that agents face a whole new environment with high winds. Through adversarial learning, it applied its newfound intelligence in a generalized way.
Debate GameThe Debate Game is another application developed by Open AI in 2018. Machines debate various toy problems in the presence of a human judge. In hopes of developing explainable AI, this research explores the influence of AI in making crucial decisions.
DactylOpen AI developed Dactyl to manipulate objects with the use of a Shadow Dexterous Hand. Accompanied by reinforcement learning algorithm code utilized in Open AI Five, Dactyl explores AI’s role in robotics.
Generative Models of Open AIOne of the most important subjects that Open AI explored is generative models. To determine the capabilities of artificial intelligence, researchers leveraged these models. It involves training the models through the large volumes of data generated from a domain. For instance, generative models read a book to reinforce their learning and create data that resembles it.
For this to be more successful, the neural networks integrate into multiple parameters significantly smaller than their training networks. In this way, the models need to explore the data’s extent independently and generate a copy.
GPTThe first-ever publication on the language model of generative pre-training (GPT) unveiled in June 2018. Researchers developed in-depth data about how the generative model of language acquires knowledge from the Open AI website.
GPT-2As the successor to GPT, GPT-2 utilizes generative models to predict the following words within a 40-gigabyte internet text. This transformer-based language model can reach 1.5 billion parameters on a data set of 8 million pages. Reinforcement learning gets leveraged to train models on a simple objective, which predicts the next word. It is after being provided with strings of text that talk about a particular topic. Although the models get exposed to diverse domains, it is fascinating that they can predict text within the sample text context.
GPT-2 can perform tasks involving question answering, reading comprehension, summarization, and translation. The models begin to predict text accurately after learning from a couple of language tasks that showcase raw text. As a result, tasks can get achieved while unsupervised.
Following the concerns about the potential abuse of such advanced technology, Open AI did not release the training model for GPT-2. However, those who are interested can still experiment on a smaller model to try out its capabilities.
GPT-3GPT-3 was initially introduced by Open AI in May 2020. Access to the private beta version of this technology is only available to a few people that sent requests before the release. Open AI is encouraging those with access to explore the capabilities of GPT-3. GPT-3 should be integrated with business operations as a commercial product shortly. The ultimate goal is to set up subscription-based payment options for those who want to take advantage of the model via the cloud. However, GPT-3 was acquired to be licensed exclusively to Microsoft in September 2020.
As a predecessor to GPT-2, it improves the predictive capacities when exposed to streams of texts with a range of different styles. Increasing its parameters to 175 billion, GPT-3 strides as the leading language model that surpasses certain limitations that cannot be overcome by GPT-2.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post The Evolution of OpenAI And The Business Of Machine Learning appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Overview of the Self-Driving Industry

The idea behind autonomous vehicles traces much further back than when Google introduced self-driving cars. In fact, the idea dramatically predates Google.
During the 1939 World’s Fair held in New York, a renowned company called General Motors introduced driverless cars. Described as the automotive industry’s future, the company was hopeful that self-driving vehicles would be the primary source of cars in the coming years. General Motors envisioned high-tech vehicles along with an automated highway system that would guide self-driving cars.
Decades later, the self-driving industry is still at its early stages. We are still far from fully autonomous vehicles, but significant automotive companies strive towards this goal. After all, they share a common objective of transforming cars into a catalyst of safe transportation and convenience.
There is no doubt that fully autonomous vehicles are coming sooner than we think, seeing the self-driving industry’s stride throughout the years.
A Brief History of Self-Driving Car TechnologyThe idea behind the self-driving car technology began during General Motors’ exhibit at the 1939 New York World’s Fair. Norman Bel Geddes, an American industrial designer, conceptualized the first-ever autonomous vehicle controlled by electromagnetic fields generated from the radio. In 1958, General Motors developed the concept, further making the initial design a reality.
The first self-driving car had several sensors in its front end. These sensors aimed to capture the signals from the magnetized spikes embedded in the roadway. It allows vehicles to detect their environment and steer the wheel left or right accordingly.
By 1977, the Japanese automotive industry decided on adapting this concept to develop its own self-driving car technology. Bringing improvement to the idea, they utilized a camera system instead of metal sensors. The role of the camera is to relay the images of the road to the computer in real-time. The only issue with this development is its limitations. Autonomous vehicles are only allowed to travel at speeds below 20 mph.
A decade later, Germans introduced their very own self-driving car. VaMoRs is an automotive vehicle with built-in cameras that detect and react to its environment. Unlike the Japanese development, you can drive these vehicles at up to 56 mph.
Presently, several autonomous vehicles get introduced by large automotive corporations. Although most of these cars are considered semi-autonomous, they received a lot of traction from many consumers. Semi-autonomous vehicles have features such as assisted parking systems, braking, and steering functionalities. Instead of placing full reliance on camera systems, most autonomous vehicles of today utilize GPS to detect their environment. On top of that, there are state-of-the-art sensors that can tell if there are lane boundaries, unexpected boundaries and detect signs and signals.
As self-driving car technology becomes more widespread, we expect fully autonomous vehicles to become a reality shortly. Several US states already formulated legislation surrounding the use of autonomous cars in preparation for this breakthrough.
The Future of Autonomous VehiclesAmong many other benefits of self-driving automobiles, the most important one focuses on promoting road safety. The automotive industry continues to push this initiative to reduce the number of incidents that resulted from impaired driving. Driving under the influence has caused multiple casualties over the years, which is solvable by self-driving cars. Regardless of inevitable distractions, conditions of the driver, or their behavior, automated driving can transport passengers safe and sound.
Making roads safer for everyone, here are the efforts of the most popular automotive companies towards self-driving car technology:
General MotorsFollowing General Motors’ vision towards the automotive industry’s future, they continue to develop self-driving cars throughout the years. In 2016, GM invested $581 million to acquire Cruise Automation, a self-driving car startup company. A year later, the renowned company built research and development facilities to assist Cruise Automations. This initiative did not just bolster the development of autonomous vehicles but also opened thousands of new job opportunities.
Despite the continuous development of self-driving cars, GM did not notify the public about its timeline. They are seemingly taking their time to head in that direction, deploying many autonomous electric vehicles in the future. There are rumors that the notable carmaker is investing in a ride-sharing company called Lyft following its self-driving initiatives. Spending half a billion dollars on Lyft, GM purchased 9% of the ride-hailing platform’s stake. As a result, many experts predict that GM is leveraging self-driving cars into mobility-as-a-service. Establishing an integrated network for on-demand autonomous vehicles allows them to maximize to full potential without going beyond their capacity.
FordFord began its self-driving car initiatives investing about $1 billion in the robotics company Argo AI. Former leaders of Google and Uber initially founded Argo AI. This partnership combines the tech expertise of Argo AI and Ford’s industry experience to streamline Ford’s plans. Ultimately, the goal of the famous carmaker is to develop a fully autonomous vehicle in 2021. Similar to General Motors, these cars aim at ride-sharing platforms.
HondaIn late 2017, Honda revealed their plans with Waymo to develop self-driving cars. Waymo is an independent company of Alphabet, which is formerly the car project of Google. Honda released a statement that its primary objective is to promote autonomous vehicles by 2021. The automaker is planning to mass-produce self-driving cars from its newest Legend sedan. Featuring the Traffic Jam Pilot, it can detect the movement and elements in its surroundings. This advancement eliminates the need for drivers to pay attention to the traffic signages and signals.
VolvoVolvo aims to transform the ride-sharing industry along with the luxury market with autonomous vehicles. In 2016, Volvo spent $300 million for a partnership with ride-sharing platform Uber. To further the integrated network of on-demand self-driving cars, they supply the vehicles for Uber’s self-driving tests.
HyundaiThe efforts of Hyundai towards developing self-driving cars are focused on making them more affordable for the masses. They partnered with another renowned automaker called Kia, spending $4 billion for the joint venture. The company is planning on mass-producing autonomous vehicles in 2021 and introducing driverless cars in 2030.
BMWIn 2016, BMW collaborated with Intel and Mobileye to further the development of self-driving vehicles. They are aiming to introduce a series of fully automated cars in the future for commercial use. iNext EV is the newest semi-autonomous manufactured by BMW to be released in early 2021. Its automated driving system offers unparalleled performance providing access to highways at a maximum speed of 85 mph.
TeslaTesla continues to develop high-tech autonomous vehicles over the years. One of their latest production includes Tesla Autopilot, offering an advanced driver-assistance system. State-of-the-art features involve lane centering, traffic-aware cruise control, self-parking, automatic lane changes, semi-autonomous navigation on limited-access freeways, and automatic summoning car. Tesla is planning on introducing a full self-driving package paid via subscription. It is going to be available this year, priced at around $10,000. Although it seems like a breakthrough for the automotive industry, this package promotes semi-autonomous features. Sensors can help drivers automate parking, switch lanes, and detect stop signs and traffic lights.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Overview of the Self-Driving Industry appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



