Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 168
February 14, 2021
Frameworks For Decision-Making
 The Cynefin Framework gives context to decision making and problem-solving by providing context and guiding an appropriate response. The five domains of the Cynefin Framework comprise obvious, complicated, complex, chaotic domains and disorder if a domain has not been determined at all. SWOT Analysis
The Cynefin Framework gives context to decision making and problem-solving by providing context and guiding an appropriate response. The five domains of the Cynefin Framework comprise obvious, complicated, complex, chaotic domains and disorder if a domain has not been determined at all. SWOT Analysis A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.Pareto Analysis
A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.Pareto Analysis The Pareto Analysis is a statistical analysis used in business decision making that identifies a certain number of input factors that have the greatest impact on income. It is based on the similarly named Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of the effect of something can be attributed to just 20% of the drivers.Failure Mode And Effects Analysis
The Pareto Analysis is a statistical analysis used in business decision making that identifies a certain number of input factors that have the greatest impact on income. It is based on the similarly named Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of the effect of something can be attributed to just 20% of the drivers.Failure Mode And Effects Analysis A failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to identifying design failures in a product or process. Developed in the 1950s, the failure mode and effects analysis is one the earliest methodologies of its kind. It enables organizations to anticipate a range of potential failures during the design stage. Blindspot Analysis
A failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to identifying design failures in a product or process. Developed in the 1950s, the failure mode and effects analysis is one the earliest methodologies of its kind. It enables organizations to anticipate a range of potential failures during the design stage. Blindspot Analysis A Blindspot Analysis is a means of unearthing incorrect or outdated assumptions that can harm decision making in an organization. The term “blindspot analysis” was first coined by American economist Michael Porter. Porter argued that in business, outdated ideas or strategies had the potential to stifle modern ideas and prevent them from succeeding. Furthermore, decisions a business thought were made with care caused projects to fail because major factors had not been duly considered.
A Blindspot Analysis is a means of unearthing incorrect or outdated assumptions that can harm decision making in an organization. The term “blindspot analysis” was first coined by American economist Michael Porter. Porter argued that in business, outdated ideas or strategies had the potential to stifle modern ideas and prevent them from succeeding. Furthermore, decisions a business thought were made with care caused projects to fail because major factors had not been duly considered.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Frameworks For Decision-Making appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
4 McKinsey Frameworks You Must Know
 The McKinsey 7-S Model was developed in the late 1970s by Robert Waterman and Thomas Peters, who were consultants at McKinsey & Company. Waterman and Peters created seven key internal elements that inform a business of how well positioned it is to achieve its goals, based on three hard elements and four soft elements. GE McKinsey Matrix
The McKinsey 7-S Model was developed in the late 1970s by Robert Waterman and Thomas Peters, who were consultants at McKinsey & Company. Waterman and Peters created seven key internal elements that inform a business of how well positioned it is to achieve its goals, based on three hard elements and four soft elements. GE McKinsey Matrix The GE McKinsey Matrix was developed in the 1970s after General Electric asked its consultant McKinsey to develop a portfolio management model. This matrix is a strategy tool that provides guidance on how a corporation should prioritize its investments among its business units, leading to three possible scenarios: invest, protect, harvest, and divest.McKinsey Horizon Model
The GE McKinsey Matrix was developed in the 1970s after General Electric asked its consultant McKinsey to develop a portfolio management model. This matrix is a strategy tool that provides guidance on how a corporation should prioritize its investments among its business units, leading to three possible scenarios: invest, protect, harvest, and divest.McKinsey Horizon Model The McKinsey Horizon Model helps a business focus on innovation and growth. The model is a strategy framework divided into three broad categories, otherwise known as horizons. Thus, the framework is sometimes referred to as McKinsey’s Three Horizons of Growth.McKinsey’s Seven Degrees Framework
The McKinsey Horizon Model helps a business focus on innovation and growth. The model is a strategy framework divided into three broad categories, otherwise known as horizons. Thus, the framework is sometimes referred to as McKinsey’s Three Horizons of Growth.McKinsey’s Seven Degrees Framework McKinsey’s Seven Degrees of Freedom for Growth is a strategy tool. Developed by partners at McKinsey and Company, the tool helps businesses understand which opportunities will contribute to expansion, and therefore it helps to prioritize those initiatives.
McKinsey’s Seven Degrees of Freedom for Growth is a strategy tool. Developed by partners at McKinsey and Company, the tool helps businesses understand which opportunities will contribute to expansion, and therefore it helps to prioritize those initiatives.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post 4 McKinsey Frameworks You Must Know appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
8 Business Model Frameworks You Must Know
 A business model is a framework for finding a systematic way to unlock long-term value for an organization while delivering value to customers and capturing value through monetization strategies. A business model is a holistic framework to understand, design, and test your business assumptions in the marketplace.VTDF Tech Business Model Framework
A business model is a framework for finding a systematic way to unlock long-term value for an organization while delivering value to customers and capturing value through monetization strategies. A business model is a holistic framework to understand, design, and test your business assumptions in the marketplace.VTDF Tech Business Model Framework A tech business model is made of four main components: value model (value propositions, mission, vision), technological model (R&D management), distribution model (sales and marketing organizational structure), and financial model (revenue modeling, cost structure, profitability and cash generation/management). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build a solid tech business model.Business Model Canvas
A tech business model is made of four main components: value model (value propositions, mission, vision), technological model (R&D management), distribution model (sales and marketing organizational structure), and financial model (revenue modeling, cost structure, profitability and cash generation/management). Those elements coming together can serve as the basis to build a solid tech business model.Business Model Canvas The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in Busines Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising: key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.Lean Startup Canvas
The business model canvas is a framework proposed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur in Busines Model Generation enabling the design of business models through nine building blocks comprising: key partners, key activities, value propositions, customer relationships, customer segments, critical resources, channels, cost structure, and revenue streams.Lean Startup Canvas The lean startup canvas is an adaptation by Ash Maurya of the business model canvas by Alexander Osterwalder, which adds a layer that focuses on problems, solutions, key metrics, unfair advantage based, and a unique value proposition. Thus, starting from mastering the problem rather than the solution.Blitzscaling Canvas
The lean startup canvas is an adaptation by Ash Maurya of the business model canvas by Alexander Osterwalder, which adds a layer that focuses on problems, solutions, key metrics, unfair advantage based, and a unique value proposition. Thus, starting from mastering the problem rather than the solution.Blitzscaling Canvas The Blitzscaling business model canvas is a model based on the concept of Blitzscaling, which is a particular process of massive growth under uncertainty, and that prioritizes speed over efficiency and focuses on market domination to create a first-scaler advantage in a scenario of uncertainty.Business Model Wheel
The Blitzscaling business model canvas is a model based on the concept of Blitzscaling, which is a particular process of massive growth under uncertainty, and that prioritizes speed over efficiency and focuses on market domination to create a first-scaler advantage in a scenario of uncertainty.Business Model Wheel A business model wheel provides a structured approach to defining a business model. Each model wheel is broken down into three core components: offering, monetization, and sustainability. Each component in turn contributes to a total of eight areas that make up an ideal business model.Business Model Innovation Framework
A business model wheel provides a structured approach to defining a business model. Each model wheel is broken down into three core components: offering, monetization, and sustainability. Each component in turn contributes to a total of eight areas that make up an ideal business model.Business Model Innovation Framework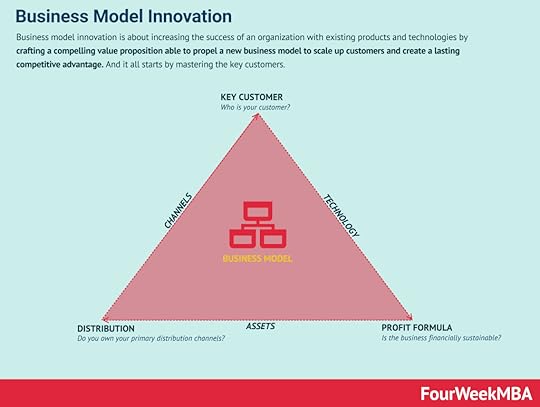 Business model innovation is about increasing the success of an organization with existing products and technologies by crafting a compelling value proposition able to propel a new business model to scale up customers and create a lasting competitive advantage. And it all starts by mastering the key customers.3C Business Model Analysis
Business model innovation is about increasing the success of an organization with existing products and technologies by crafting a compelling value proposition able to propel a new business model to scale up customers and create a lasting competitive advantage. And it all starts by mastering the key customers.3C Business Model Analysis The 3C Analysis Business Model was developed by Japanese business strategist Kenichi Ohmae. A 3C Model is a marketing tool that focuses on customers, competitors, and the company. At the intersection of these three variables lies an effective marketing strategy to gain a potential competitive advantage and build a lasting company.
The 3C Analysis Business Model was developed by Japanese business strategist Kenichi Ohmae. A 3C Model is a marketing tool that focuses on customers, competitors, and the company. At the intersection of these three variables lies an effective marketing strategy to gain a potential competitive advantage and build a lasting company.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post 8 Business Model Frameworks You Must Know appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
10 Consulting Frameworks You Need To Know
 In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.Porter’s Five Forces
In the 1970s, Bruce D. Henderson, founder of the Boston Consulting Group, came up with The Product Portfolio (aka BCG Matrix, or Growth-share Matrix), which would look at a successful business product portfolio based on potential growth and market shares. It divided products into four main categories: cash cows, pets (dogs), question marks, and stars.Porter’s Five Forces Porter’s Five Forces is a model that helps organizations to gain a better understanding of their industries and competition. Published for the first time by Professor Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Strategy” in the 1980s. The model breaks down industries and markets by analyzing them through five forcesSix Forces Model
Porter’s Five Forces is a model that helps organizations to gain a better understanding of their industries and competition. Published for the first time by Professor Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Strategy” in the 1980s. The model breaks down industries and markets by analyzing them through five forcesSix Forces Model The Six Forces Model is a variation of Porter’s Five Forces. The sixth force, according to this model, is the complementary products. In short, the six forces model is an adaptation especially used in the tech business world to assess the change of the context, based on new market entrants and whether those can play out initially as complementary products and in the long-term substitutes. Porter’s Value Chain
The Six Forces Model is a variation of Porter’s Five Forces. The sixth force, according to this model, is the complementary products. In short, the six forces model is an adaptation especially used in the tech business world to assess the change of the context, based on new market entrants and whether those can play out initially as complementary products and in the long-term substitutes. Porter’s Value Chain In his 1985 book Competitive Advantage, Porter explains that a value chain is a collection of processes that a company performs to create value for its consumers. As a result, he asserts that value chain analysis is directly linked to competitive advantage. Porter’s Value Chain Model is a strategic management tool developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter. The tool analyses a company’s value chain – defined as the combination of processes that the company uses to make money.Porter’s Generic Strategies
In his 1985 book Competitive Advantage, Porter explains that a value chain is a collection of processes that a company performs to create value for its consumers. As a result, he asserts that value chain analysis is directly linked to competitive advantage. Porter’s Value Chain Model is a strategic management tool developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter. The tool analyses a company’s value chain – defined as the combination of processes that the company uses to make money.Porter’s Generic Strategies According to Michael Porter, a competitive advantage, in a given industry could be pursued in two key ways: low cost (cost leadership), or differentiation. A third generic strategy is focus. According to Porter a failure to do so would end up stuck in the middle scenario, where the company will not retain a long-term competitive advantage.McKinsey 7s Model
According to Michael Porter, a competitive advantage, in a given industry could be pursued in two key ways: low cost (cost leadership), or differentiation. A third generic strategy is focus. According to Porter a failure to do so would end up stuck in the middle scenario, where the company will not retain a long-term competitive advantage.McKinsey 7s Model The McKinsey 7-S Model was developed in the late 1970s by Robert Waterman and Thomas Peters, who were consultants at McKinsey & Company. Waterman and Peters created seven key internal elements that inform a business of how well positioned it is to achieve its goals, based on three hard elements and four soft elements. GE McKinsey Matrix
The McKinsey 7-S Model was developed in the late 1970s by Robert Waterman and Thomas Peters, who were consultants at McKinsey & Company. Waterman and Peters created seven key internal elements that inform a business of how well positioned it is to achieve its goals, based on three hard elements and four soft elements. GE McKinsey Matrix The GE McKinsey Matrix was developed in the 1970s after General Electric asked its consultant McKinsey to develop a portfolio management model. This matrix is a strategy tool that provides guidance on how a corporation should prioritize its investments among its business units, leading to three possible scenarios: invest, protect, harvest, and divest.McKinsey Horizon Model
The GE McKinsey Matrix was developed in the 1970s after General Electric asked its consultant McKinsey to develop a portfolio management model. This matrix is a strategy tool that provides guidance on how a corporation should prioritize its investments among its business units, leading to three possible scenarios: invest, protect, harvest, and divest.McKinsey Horizon Model The McKinsey Horizon Model helps a business focus on innovation and growth. The model is a strategy framework divided into three broad categories, otherwise known as horizons. Thus, the framework is sometimes referred to as McKinsey’s Three Horizons of Growth.McKinsey’s Seven Degrees Framework
The McKinsey Horizon Model helps a business focus on innovation and growth. The model is a strategy framework divided into three broad categories, otherwise known as horizons. Thus, the framework is sometimes referred to as McKinsey’s Three Horizons of Growth.McKinsey’s Seven Degrees Framework McKinsey’s Seven Degrees of Freedom for Growth is a strategy tool. Developed by partners at McKinsey and Company, the tool helps businesses understand which opportunities will contribute to expansion, and therefore it helps to prioritize those initiatives.MECE Framework
McKinsey’s Seven Degrees of Freedom for Growth is a strategy tool. Developed by partners at McKinsey and Company, the tool helps businesses understand which opportunities will contribute to expansion, and therefore it helps to prioritize those initiatives.MECE Framework The MECE framework is an exhaustive expression of information that must account for all conceivable scenarios. While the framework is used in categorizing information and data processing, it is commonly used in formulating problems and then solving them. The MECE framework is a means of the exhaustive grouping of information into categories that are both mutually exclusive (ME) and collectively exhaustive (CE).
The MECE framework is an exhaustive expression of information that must account for all conceivable scenarios. While the framework is used in categorizing information and data processing, it is commonly used in formulating problems and then solving them. The MECE framework is a means of the exhaustive grouping of information into categories that are both mutually exclusive (ME) and collectively exhaustive (CE).Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post 10 Consulting Frameworks You Need To Know appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
AI Startups To Watch Out For in 2021

Several trends surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning emerged as large volumes of data and algorithms became widely accessible. The projected revenue in the AI market is to skyrocket by about $97.9 billion in 2023. For this reason, startups along with large tech corporations began to take an interest in this ever-growing field. The significant inventions involving AI are more focused on machine learning, leveraging smart decisions without human intervention.
Transitioning from research centers, organizations around the world began turning their studies into a reality. Applying theories into actual systems allows them to develop advanced technologies that simplify our day-to-day life.
So, here are 15 AI innovators that you should look out for in 2021:
BriskBrisk is a startup company based in the UK founded in late 2018. The organization began by creating AI systems that can provide thorough risk assessments for businesses. Businesses can determine their financial history, credit scores, and risk level using machine learning. The target market for this program are brokers, small and medium-sized enterprises, and accounting firms. The company’s ultimate goal is to help small businesses manage their finances, offering instant access to crucial information that can affect business decisions. The in-depth risk analysis allows the clients to anticipate individual decisions’ potential threats before even putting them to work. As one of the most successful startups in recent years, their funds reached over $300,000.
DataikuThe US-based Dataiku data science software platform established Dataiku DSS (Data Science Studio) to explore AI’s benefits in 2013. The organization can assist businesses with making data-driven decisions by taking advantage of machine learning. This software development is for data analysts and data scientists who want to automate specific tasks using machine learning. Since the release of Dataiku DSS, the organization has managed to raise about $100 million.
Dragonfly AIThe UK-based startup Dragonfly AI initially began its operations in 2018. This software is a predictive visual analytics platform that uses AI to measure the influence of design on the audience. It benefits retail companies by helping them understand the products that garner the most “customer attention.” Two AI systems within the platform can single out the products that the customers can likely notice first, improving the buyer journey. Another feature is the Dragonfly AI motion, which generates exclusive insight into the impact of customer attention and behavior on your business. Following the organization’s success, Dragonfly announced its partnership with outsourcing firm Capita’s IT in 2019.
Eightfold.AIEightfold AI is a startup based in Mountain View, California, founded in 2016. AI enthusiasts come together for a mission of establishing a platform that can manage the entire talent lifecycle. Staying true to their philosophy, which is to provide “the right career for everyone in the world,” they developed a program using AI. It can help businesses determine the top performers, upskill and reskill the workforce, recruit top talent efficiently, and reach diversity goals. Overall, the organization’s primary purpose is to empower businesses in producing top talent to gain a competitive edge. Forbes hailed Eightfold.AI as one of the Top 25 Machine Learning Startups to Watch in 2020 after it raised $125 million by the end of the year.
Frame AIA startup company based in New York established a collaborative messaging platform that improves customer services and business conversations. The platform brings the consumers’ voice to every channel necessary to streamline services and focus on them. Instead of wasting the workforce and spending a significant amount of time monitoring the customer’s voice, this tool helps businesses better understand their market. Offering data-driven CX priorities, natural language helps to understand how businesses communicate with customers. It can also become the company-wide channel for understanding the sentiments of customers for immediate action. The startup’s success is as clear as day, raising about $6.3 million in early 2020.
InstreamaticThe primary objective of the US-based startup is to revolutionize the advertising strategies of enterprises. Offering a marketing platform driven by voice command and AI, users navigate the platform hands-free. The program takes advantage of natural language to train voice AI and produce interactive, dialogue-based advertisements across mobile platforms. Using data-driven algorithms, marketers and media companies can gather insight on campaigns and customer engagement. Since it emerged in the business landscape in 2015, the organization raised over $2.2 million in funds.
PhotoneoPhotoneo became one of the pioneers of utilizing 3D robot vision to provide advanced automation solutions. Powered by AI algorithms, this startup involves the following pick-and-place systems:
Universal DepalletizerSingulation & Sorting SystemAnyPickAll three systems take advantage of machine learning to modify the behavior of large data sets of objects. Its actions depend on the new data presented, indicating that it can generalize and recognize specific environmental changes. Leveraging the convolutional neural network (CNN), the system can differentiate and detect various objects it encounters. Simply put, AI allows the program to recognize items of different shapes, sizes, textures, materials, and orientations. This platform aims to improve logistics, e-commerce, automotive, food and medical industries, and many others.
8topuzPromoting convenient ForEx trading powered by artificial intelligence, 8topuz is ideal for retail investors and individual traders. The platform automates machine learning, which several companies have implemented in the banking, investment, and fintech industries. The program’s leading role is to provide an automated trading solution while reducing the risks of participating in volatile trading activities.
Swim.AIA startup company based in the US allows businesses to analyze large data streams at any given time. They can also use this data and the contextual data powered by AI to make critical business decisions. A digital copy of the information gets stored within the physical system through shared objects or a digital twin. The clash between the virtual and physical environment allows in-depth analysis of data and detecting issues before they arise. As a result, businesses can eliminate as much downtime as possible, knowing potential problems in advance. Through machine learning, the platform can tell various critical events, find hidden patterns, predict future behaviors, and autonomously trigger fast actions at an individual or multiple coordinated edge devices.
OsaroOsaro is another notable startup based in the US. It combines the latest AI technology and industrial robotics to detect perception and control insights. The AI software embedded in robotics has sensors that recognize objects around it. It observes how the system behaves when pushed and grabbed. Like systems powered by AI, it can use its experience to determine the best course of action. While mimicking behavior around them, it can learn from surrounding machines and advance programming insights.
ArgoArgo is a startup that emerged to produce software, hardware, maps, and cloud-support infrastructure that businesses can integrate into its self-driving technology platform. The organization’s primary objective is to promote autonomous vehicles to make transportation more convenient, safer, and efficient. The software can never be distracted nor tired as it has 360-degree awareness features. It is also integrated with self-driving cars to set up the designated pick-up and drop-off points, reduce traffic congestion and manage assisted parking.
BigMLFounded in 2011, BigML aims to leverage machine learning to make life easier for everyone. The organization offers a plethora of machine learning resources all over the world. It is their role to provide automated machine learning as a service and fulfill complex data-driven tasks.
Various companies can access this platform to share and solve complex machine learning tasks. Multiple resources, including the following, can help anyone understand ML a little better:
BigML Dashboard: web-based interface offering a myriad of machine learning materials and modelsREST API: Access requests programmaticallyOverall, the goal of BigML is to promote the potential of machine learning through its educational materials. Since it was released, BigML raised $1.6 million in funds.
GoodVisionAlthough GoodVision started in early 2017, it gained significant attention in 2019 for its unique AI approach. The platform collects video recordings, live camera streams, or drone footage to obtain useful insights. The information gathered from the videos is extracted in real-time. Businesses can use the sensor to simulate and test specific scenarios. A growing number of retail stores and city infrastructures take advantage of this technology to increase security and experiment in various services. It also gets applied to traffic systems and other community infrastructures. In this way, people can retrieve security footage from the law enforcement and commercial establishments right away.
CureMetrixTransforming healthcare industries one software at a time, CureMetrix offers an AI-powered triage program for mammography. This software makes it easier for businesses to perform breast scanner screenings using high-precision technologies. With AI’s help, radiologists can obtain data-backed results for accurate, safe screening prognosis and treatment. More importantly, this technology is FDA approved for hospitals looking for improved healthcare services worldwide.
Pony.AIThe startup company based in three different locations, namely, Silicon Valley, Beijing, and Guangzhou, started in 2016. Pony.ai aims to provide a reliable platform for managing all things related to autonomous driving. The success of this company reflects in its funding that reached $267 million.
Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post AI Startups To Watch Out For in 2021 appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
5 HR Models You Should Know As An HR Professional
 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs was developed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow. His hierarchy, often depicted in the shape of a pyramid, helped explain his research on basic human needs and desires. In marketing, the hierarchy (and its basis in psychology) can be used to market to specific groups of people based on their similarly specific needs, desires, and resultant actions.Eisenhower Matrix
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs was developed by American psychologist Abraham Maslow. His hierarchy, often depicted in the shape of a pyramid, helped explain his research on basic human needs and desires. In marketing, the hierarchy (and its basis in psychology) can be used to market to specific groups of people based on their similarly specific needs, desires, and resultant actions.Eisenhower Matrix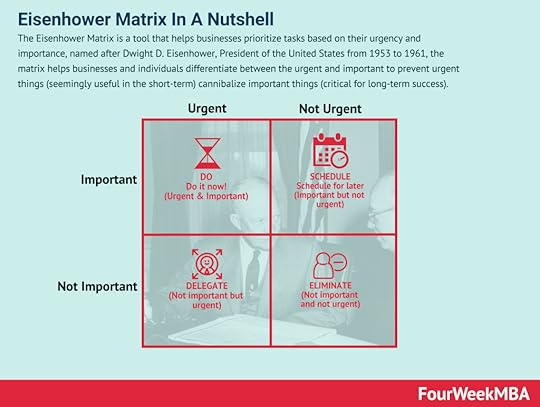 The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that helps businesses prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance, named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, President of the United States from 1953 to 1961, the matrix helps businesses and individuals differentiate between the urgent and important to prevent urgent things (seemingly useful in the short-term) cannibalize important things (critical for long-term success).Moonshot Thinking
The Eisenhower Matrix is a tool that helps businesses prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance, named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, President of the United States from 1953 to 1961, the matrix helps businesses and individuals differentiate between the urgent and important to prevent urgent things (seemingly useful in the short-term) cannibalize important things (critical for long-term success).Moonshot Thinking Moonshot thinking is an approach to innovation, and it can be applied to business or any other discipline where you target at least 10X goals. That shifts the mindset, and it empowers a team of people to look for unconventional solutions, thus starting from first principles, by leveraging on fast-paced experimentation.Lightning Decision Jam
Moonshot thinking is an approach to innovation, and it can be applied to business or any other discipline where you target at least 10X goals. That shifts the mindset, and it empowers a team of people to look for unconventional solutions, thus starting from first principles, by leveraging on fast-paced experimentation.Lightning Decision Jam The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
The theory was developed by psychologist Edwin Locke who also has a background in motivation and leadership research. Locke’s goal-setting theory of motivation provides a framework for setting effective and motivating goals. Locke was able to demonstrate that goal setting was linked to performance.Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory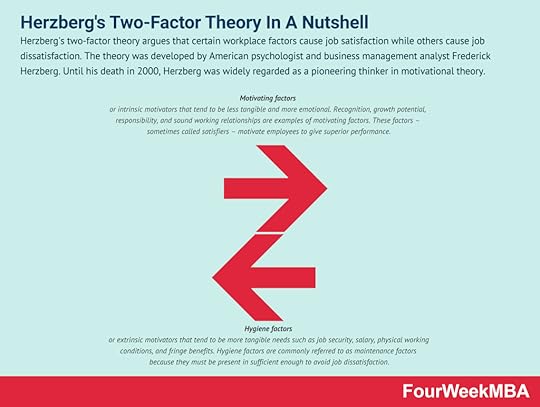 Herzberg’s two-factor theory argues that certain workplace factors cause job satisfaction while others cause job dissatisfaction. The theory was developed by American psychologist and business management analyst Frederick Herzberg. Until his death in 2000, Herzberg was widely regarded as a pioneering thinker in motivational theory.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory argues that certain workplace factors cause job satisfaction while others cause job dissatisfaction. The theory was developed by American psychologist and business management analyst Frederick Herzberg. Until his death in 2000, Herzberg was widely regarded as a pioneering thinker in motivational theory. Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post 5 HR Models You Should Know As An HR Professional appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
February 13, 2021
What is a Gemba Walk? Gemba Walk In A Nutshell

A Gemba Walk is a fundamental component of lean management. It describes the personal observation of work to learn more about it. Gemba is a Japanese word that loosely translates as “the real place”, or in business, “the place where value is created”. The Gemba Walk as a concept was created by Taiichi Ohno, the father of the Toyota Production System of lean manufacturing. Ohno wanted to encourage management executives to leave their offices and see where the real work happened. This, he hoped, would build relationships between employees with vastly different skillsets and build trust.
Understanding a Gemba WalkThe exact physical place will vary from industry to industry. For a jazz band, value is created in the recording studio. For a pilot training school, value is created in the classroom and the aircraft.
The three important elements of a Gemba WalkEach Gemba walk must respect three important elements:
Go and see. Management executives from every level of the hierarchy are encouraged to take regular tours of Gemba locations and be involved in finding wasteful activities.Ask why. A good leader must ask the right questions and also be a good listener. They must be able to liaise with workers to explore the value stream and locate problematic components.Respect people. It’s important to note that a Gemba Walk is not a “boss walk” – which often involves direct criticism of the way an employee works. Executives must focus on collaboratively identifying the weak spots of processes and not the weak spots of people. Seven steps for a successful Gemba WalkA Gemba Walk may seem like somewhat of an unstructured process, but a basic framework should be used depending on particular goals and objectives.
Let’s now define each of the seven steps:
Pick a theme – where will the effort be focused? Common themes include safety, efficiency, and productivity. With a theme identified, executives should create a list of thematic questions.Prepare the team – the individuals who will be consulted must be made aware that a Gemba Walk will be occurring ahead of time. Importantly, they should be reassured that it is a continuous improvement opportunity and not an evaluation of their personal performance.Focus on the process – as noted, the main purpose of a Gemba Walk is to observe, understand, and improve processes. Follow the value stream – the biggest process improvements are often found during handoffs between processes, departments, or people. It is also beneficial to invite the employees to suggest other possible improvements.Record observations – either with pen or paper or digitally. Resist the temptation to make suggestions during the walk itself – no matter how obvious solutions may appear. Improvement should be analyzed later with a fact-based problem-solving tool such as the PDCA cycle.An extra pair of eyes – where possible, involve a colleague from another department to take part in the Gemba Walk. Those who are less familiar with the process may have a fresh perspective on any improvements to be made.Follow-up – Gemba Walk insights must be shared with participants, irrespective of the significance of process improvements. If improvements have been identified, give notice to the relevant employees and involve them in process changes. Good communication is vital. This helps avoid a scenario where employees believe that management is using Gemba Walks to interfere or criticize.Key takeaways:A Gemba Walk is a lean management practice that advocates the direct observation of work to identify process improvements.A Gemba Walk encourages upper management to build relationships with employees. This is facilitated by regularly liaising with process workers and listening to their concerns without interjecting.To some extent, a Gemba Walk should be allowed to flow in a natural direction. Nevertheless, some initial preparation before following a basic framework of steps is advisable.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is a Gemba Walk? Gemba Walk In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is Cognitive Restructuring? Cognitive Restructuring In A Nutshell

Cognitive restructuring describes the process of bringing awareness and change to negative thought patterns. Cognitive restructuring is integral to the principle of cognitive mediation. This principle states that the emotional reaction an individual has to a situation is not caused by the situation itself. Instead, it is largely governed by what the individual thinks about the situation. Using the power of cognitive mediation, cognitive restructuring helps the individual change their life by empowering them to change the way they think. This form of empowerment is a fundamental aspect of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
Understanding cognitive restructuringWhen an individual experiences trauma, certain thought patterns establish themselves and create a distorted view of reality. These negative thought patterns are called cognitive distortions, which over time lead to anxiety and depression.
Cognitive distortions are habitual ways of interacting with the world. They cause the individual to react negatively to certain people or stimuli – irrespective of whether the perceived threat is real or imagined.
Common cognitive distortions that need to be restructuredThere is of course no limit to the extent of scenarios that could elicit a negative response.
However, most people respond to such a situation by using common cognitive distortions including:
Black and white thinking – or a failure of judgement in thinking that fails to assess both the positive and negative aspects of self or others.Catastrophizing – where the individual tends to assume the worst will happen. It can also involve an exaggeration of the magnitude of a negative situation.Rumination – or a focus on repeatedly and obsessively thinking the same thoughts in a negative loop. There is a fixation on the causes and consequences of distress to the detriment of any solution.Personalization – a harmful distortion where someone believes that things that have nothing to do with them are their fault. Cognitive restructuring techniquesCognitive restructuring techniques provide a means of analyzing and then rebuilding negative thought patterns into something more beneficial.
Here is how this technique should play out.
Self-awareness practiceCognitive restructuring cannot occur without some degree of self-awareness. Indeed, negative thought patterns must first be observed before they can be remedied.
When these thoughts do arise, write them down in a journal. Where and when do they occur? Are there commonalities or trends? Record and observe self-analysis without judgment.
Question assumptionsMany negative thought patterns can be traced back to assumptions or generalizations.
When an individual catches themselves making an assumption, they should begin a process of self-inquiry:
Are my thoughts based on emotion or fact?Is there evidence that challenges my assumption?Is the situation black and white? Or are there shades of grey?In theory, this self-inquiry should unearth flaws in assumptive thinking.
Gather evidenceWhat is causing the negative thought pattern to be triggered? The individual should record any early memories they deem a potential culprit.
Create different thoughtsWith an understanding of the drivers of negative thought patterns, the individual can use evidence to guide future responses.
This starts by incorporating evidence-based thinking into their responses when triggered. Here, the focus is on small wins. Many will discover that replacing negative thought patterns is a slow and arduous process requiring patience.
Be self-compassionateThose who tend to be self-critical will suffer the most when their negative thought patterns make a comeback out of nowhere.
The individual must remember that no-one is perfect and have self-compassion for the difficult journey they have embarked on.
Key takeaways:Cognitive restructuring is an evidence-based approach to eliminating negative thought patterns.Cognitive restructuring is effective in treating cognitive distortions, or negative and habitual ways of interacting with the world. Self-awareness is key to successful cognitive restructuring. Without an ability to identify and observe negative thought patterns, the individual will be unable to incorporate more beneficial ways of thinking.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is Cognitive Restructuring? Cognitive Restructuring In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is a Project Execution Plan? Project Execution Plan In A Nutshell

A Project Execution Plan (PEP) details the strategy required for managing a project. It is sometimes referred to as a project management plan. Generally speaking, PEPs are drafted by the client’s project director or similarly skilled project manager. Each plan must have the appropriate systems in place and be supported by the right tools and resources. This increases project performance and helps mitigate risk in the process.
Understanding a Project Execution PlanSome may equate a Project Execution Plan with a simple Gantt chart showing timescales.
However, a PEP is a much more complex document that defines:
The roles and responsibilities of each project team member.Policies, procedures, and priorities that will be adopted.Strategies that are outside the scope of the main contract. For example, supply contracts or other operational, equipment, relocation, or maintenance costs.Specific targets and the resources required to meet them. Targets usually revolve around project products, timescales, quality, benefits, and cost.Governance, monitoring, or control criteria.Creating a Project Execution PlanCreating a Project Execution Plan is an exhaustive process that is beyond the scope of this article.
However, it should at the very least contain the following elements:
Executive summary – containing a short description or summary of the contents of the plan.Project scope and deliverables – what are the boundaries of the project? What does the project hope to achieve in specific terms?Statement of goals – how will the project be segmented into smaller deliverables that are measurable? An actual goal statement should define the reasons for undertaking the project in addition to its purpose and expected benefits. There should also be mention of project-specific challenges and risks and how they might be overcome.Quality and technical specifications – what standards must be upheld to complete the project? Standards must be concise, measurable, attainable, and time-bound.Allocation of resources – how will resources be allocated to achieve stated goals and standards? Knowledge, experience, equipment, and time must all be considered.Project scheduling – or a general view of project tasks and their associated milestones. Gantt charts should be used to illustrate time-bound deliverables that must be agreed upon by all stakeholders. The Critical Path Method (CPM) is also effective for projects where the start of one deliverable depends on the completion of another. Lastly, scheduling should always incorporate risk tolerances for constraints such as standards, budgets, and deadlines.Organizational considerations – who are the key personnel responsible for managing the project? Who holds decision-making authority? How will progress be monitored, coordinated, or reported? Will there be a series of project teams or some other organizational structure?Key takeaways:A Project Execution Plan is a detailed document that defines the strategy for managing a project. For this reason, it is often referred to as a project management plan.A Project Execution Plan must be drafted by a highly skilled project director or manager. When projects are supported by the appropriate tools and resources, they tend to mitigate risk and be delivered on time and budget.A Project Execution Plan is a comprehensive document that must contain information on seven key elements: executive summary, project scope, statement of goals, quality and technical specifications, resource allocation, project scheduling, and organizational considerations.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is a Project Execution Plan? Project Execution Plan In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What is Business Process Improvement? Business Process Improvement In A Nutshell
Business process improvement (BPI) involves the evaluation and subsequent improvement of business processes. Business process improvement seeks to improve business processes, defined as any series of repeated tasks that create value for a customer, sponsor, or stakeholder. During BPI, each process is mapped out to identify inefficiencies. Then, the process undergoes a redesign so that it can meet new standards or performance benchmarks.
Understanding business process improvementIn the face of a rapidly shifting global marketplace, there has never been more need for business processes to adapt to advances in technology, labor, distribution, or consumer preferences.
Processes ripe for improvement usually fall into three categories:
Operational processes – or those associated with the value stream such as orders, distribution, and manufacturing.Management processes – including oversight, budgetary, and communicative procedures.Supporting processes – or those performed by support teams. In other words, technical support, recruitment, customer service, and accounting.Common goals of business process improvementSome of the more common process-oriented goals include:
Reducing process time – how can the process be faster or more efficient? This might be achieved through the adoption of new technology or the elimination of superfluous steps.Improving output quality – given the same input of resources, how can a better quality product be produced? Being able to identify factors that cause errors or defects is a good place to start.Eliminating waste – what are the most wasteful steps in a process? Removing waste is integral because it can help a business achieve all three process goals at once.Business process improvement methodologiesThere are many BPI methodologies available, with each helping the business to apply a tried and tested framework to their improvement initiative.
The most well-utilized methodologies include:
Six Sigma – first developed by Motorola engineers to measure process defects and produce a near-perfect final product. Indeed, a Six Sigma Process is one that produces less than 3.4 defects per one million outputs. The DMAIC framework is a popular process improvement tool that uses Six Sigma principles. Lean management – a process optimization tool that seeks to remove low value-adding steps with little impact on the final product. Lean was popularized by Toyota as a way to shorten the Order to Cash (O2C) cycle in vehicle manufacturing. The focus on lean management is maximizing consumer and business value while minimizing waste. Total Quality Management (TQM) – a process improvement approach with a focus on delivering long-term customer satisfaction. TQM is a more holistic methodology that is customer-focused, process-centric, and advocates continuous improvement. It also favors collaborative communication and fact-based decision-making. Agile – heavily used in the software development industry with a “fail fast” philosophy of iterative product development and delivery. Errors are detected and subsequently removed from agile development early on, leading to improvements in efficiency and customer value.Key takeaways:Business process improvement is a general term for the evaluation of business processes with the goal of improving them.Business process improvement is primarily focused on reducing process time, improving output quality, and eliminating waste.Business process improvement methodologies include the Six Sigma-based DMAIC framework. Lean management, Agile, and Total Quality Management are also popular.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What is Business Process Improvement? Business Process Improvement In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



