Gennaro Cuofano's Blog, page 170
February 12, 2021
Seven Decision-Making Models You Need To Know
 The STAR method is an interview technique that is used to answer behavioral interview questions. The STAR method is a technique that an interviewee can use to help prepare for behavioral or situational interview questions that assess important skills. STAR is an acronym comprised of four factors that make the question answering framework: situation, task, action, and result. Vroom-Yetton Decision Model
The STAR method is an interview technique that is used to answer behavioral interview questions. The STAR method is a technique that an interviewee can use to help prepare for behavioral or situational interview questions that assess important skills. STAR is an acronym comprised of four factors that make the question answering framework: situation, task, action, and result. Vroom-Yetton Decision Model The Vroom-Yetton decision model is a decision-making process based on situational leadership. According to this model, there are five decision-making styles guides group-based decision-making according to the situation at hand and the level of involvement of subordinates: Autocratic Type 1 (AI), Autocratic Type 2 (AII), Consultative Type 1 (CI), Consultative Type 2 (CII), Group-based Type 2 (GII).TDODAR Decision Model
The Vroom-Yetton decision model is a decision-making process based on situational leadership. According to this model, there are five decision-making styles guides group-based decision-making according to the situation at hand and the level of involvement of subordinates: Autocratic Type 1 (AI), Autocratic Type 2 (AII), Consultative Type 1 (CI), Consultative Type 2 (CII), Group-based Type 2 (GII).TDODAR Decision Model The TDODAR decision model helps an individual make good decisions in emergencies or any scenario with a high degree of uncertainty. TDODAR is an acronym of the six sequential steps that every practitioner must follow, comprising: time, diagnosis, options, decide, act/assign, review.Blindspot Analysis
The TDODAR decision model helps an individual make good decisions in emergencies or any scenario with a high degree of uncertainty. TDODAR is an acronym of the six sequential steps that every practitioner must follow, comprising: time, diagnosis, options, decide, act/assign, review.Blindspot Analysis A Blindspot Analysis is a means of unearthing incorrect or outdated assumptions that can harm decision making in an organization. The term “blindspot analysis” was first coined by American economist Michael Porter. Porter argued that in business, outdated ideas or strategies had the potential to stifle modern ideas and prevent them from succeeding. Furthermore, decisions a business thought were made with care caused projects to fail because major factors had not been duly considered.Foursquare Protocol
A Blindspot Analysis is a means of unearthing incorrect or outdated assumptions that can harm decision making in an organization. The term “blindspot analysis” was first coined by American economist Michael Porter. Porter argued that in business, outdated ideas or strategies had the potential to stifle modern ideas and prevent them from succeeding. Furthermore, decisions a business thought were made with care caused projects to fail because major factors had not been duly considered.Foursquare Protocol The Foursquare Protocol is an ethical decision-making model. The Foursquare Protocol helps businesses respond to challenging situations by making decisions according to a code of ethics. It can also be used to help individuals make decisions in the context of their own moral principles. It consists of four steps: gather the facts, understand previous decisions, assess the degree of similarity to past events, and assess yourself. Working Backwards
The Foursquare Protocol is an ethical decision-making model. The Foursquare Protocol helps businesses respond to challenging situations by making decisions according to a code of ethics. It can also be used to help individuals make decisions in the context of their own moral principles. It consists of four steps: gather the facts, understand previous decisions, assess the degree of similarity to past events, and assess yourself. Working Backwards The Amazon Working Backwards Method is a product development methodology that advocates building a product based on customer needs. The Amazon Working Backwards Method gained traction after notable Amazon employee Ian McAllister shared the company’s product development approach on Quora. McAllister noted that the method seeks “to work backwards from the customer, rather than starting with an idea for a product and trying to bolt customers onto it.”SCAMPER Method
The Amazon Working Backwards Method is a product development methodology that advocates building a product based on customer needs. The Amazon Working Backwards Method gained traction after notable Amazon employee Ian McAllister shared the company’s product development approach on Quora. McAllister noted that the method seeks “to work backwards from the customer, rather than starting with an idea for a product and trying to bolt customers onto it.”SCAMPER Method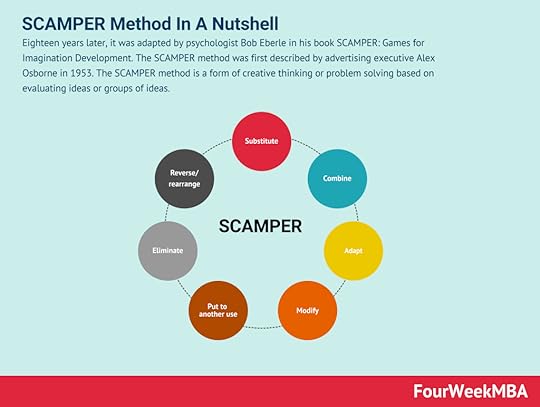 Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.
Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Seven Decision-Making Models You Need To Know appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Six Brainstorming Techniques You Need To Know
 Starbursting is a structured brainstorming technique with a focus on question generation. Starbursting is a structured form of brainstorming allowing product teams to cover all bases during the ideation process. It utilizes a series of questions to systematically work through various aspects of product development, forcing teams to evaluate ideas based on viability.Appreciative Inquiry
Starbursting is a structured brainstorming technique with a focus on question generation. Starbursting is a structured form of brainstorming allowing product teams to cover all bases during the ideation process. It utilizes a series of questions to systematically work through various aspects of product development, forcing teams to evaluate ideas based on viability.Appreciative Inquiry Appreciate Inquiry (AI) is an organizational change methodology that focuses on strengths and not on weaknesses. Appreciate Inquiry was created by management professors David Cooperrider and Suresh Srivastva in the 1980s. The Appreciate Inquiry is also known as the 5-D Cycle, an iterative cycle describing five distinct phases, made of define, discover, dream, design, and destiny.Round-robin Brainstorming
Appreciate Inquiry (AI) is an organizational change methodology that focuses on strengths and not on weaknesses. Appreciate Inquiry was created by management professors David Cooperrider and Suresh Srivastva in the 1980s. The Appreciate Inquiry is also known as the 5-D Cycle, an iterative cycle describing five distinct phases, made of define, discover, dream, design, and destiny.Round-robin Brainstorming Round-robin brainstorming is a collective and iterative approach to brainstorming. Brainstorming is an effective way of generating fresh ideas for an organization. Round-robin brainstorming is a balanced approach, employing an iterative, circular process that builds on the previous contribution of each participant. Constructive Controversy
Round-robin brainstorming is a collective and iterative approach to brainstorming. Brainstorming is an effective way of generating fresh ideas for an organization. Round-robin brainstorming is a balanced approach, employing an iterative, circular process that builds on the previous contribution of each participant. Constructive Controversy Constructive controversy is a theory arguing that controversial discussions create a good starting point for understanding complex problems. A constructive controversy discussion is performed by following six steps: organize information and derive conclusions; presenting and advocating decisions; being challenged by opposing views; conceptual conflict and uncertainty; epistemic curiosity and perspective-taking; and reconceptualization, synthesis, and integration.Affinity Grouping
Constructive controversy is a theory arguing that controversial discussions create a good starting point for understanding complex problems. A constructive controversy discussion is performed by following six steps: organize information and derive conclusions; presenting and advocating decisions; being challenged by opposing views; conceptual conflict and uncertainty; epistemic curiosity and perspective-taking; and reconceptualization, synthesis, and integration.Affinity Grouping Affinity grouping is a collaborative prioritization process where group participants brainstorm ideas and opportunities according to their similarities. Affinity grouping is a broad and versatile process based on simple but highly effective ideas. It helps teams generate and then organize teams according to their similarity or likeness.The Fishbone Diagram
Affinity grouping is a collaborative prioritization process where group participants brainstorm ideas and opportunities according to their similarities. Affinity grouping is a broad and versatile process based on simple but highly effective ideas. It helps teams generate and then organize teams according to their similarity or likeness.The Fishbone Diagram The Fishbone Diagram is a diagram-based technique used in brainstorming to identify potential causes for a problem, thus it is a visual representation of cause and effect. The problem or effect serves as the head of the fish. Possible causes of the problem are listed on the individual “bones” of the fish. This encourages problem-solving teams to consider a wide range of alternatives.
The Fishbone Diagram is a diagram-based technique used in brainstorming to identify potential causes for a problem, thus it is a visual representation of cause and effect. The problem or effect serves as the head of the fish. Possible causes of the problem are listed on the individual “bones” of the fish. This encourages problem-solving teams to consider a wide range of alternatives.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Six Brainstorming Techniques You Need To Know appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is Starbursting? Starbursting In A Nutshell
Starbursting is a structured brainstorming technique with a focus on question generation. Starbursting is a structured form of brainstorming allowing product teams to cover all bases during the ideation process. It utilizes a series of questions to systematically work through various aspects of product development, forcing teams to evaluate ideas based on viability.
Understanding starburstingDuring product development, many teams use traditional brainstorming techniques to generate a list of potential features. However, this is often done before the team defines a target audience or clarifies the vision for the product. With no definitive guidelines established, these teams create products that consumers have no interest in buying. What’s more, product development invariably runs over time or over budget.
Starbursting is a structured form of brainstorming allowing product teams to cover all bases during the ideation process. It utilizes a series of questions to systematically work through various aspects of product development, forcing teams to evaluate ideas based on viability.
Starbursting is named after a six-point star, with each point representing one of six fundamental questions.
Applying the starbursting methodApplying the starbursting method is a matter of following three steps. A good facilitator should be employed to mediate the discussion and ensure that every group member has an opportunity to give input.
Step 1 – Create a six-point starTeams can opt to draw a star on a large sheet of paper or download a template online. The name of the project should be written in the center of the star.
Then, label each of the six points using the following titles: who, what, how, where, when, and why.
Step 2 – Brainstorm potential questionsIn the second step, generate a list of potential questions without answering them.
Some examples of questions for each point are listed below (aim for at least three per point):
Who – who will use the application or work on product development itself? Who are the primary competitors? Who will market or produce the product?What – what are the product dimensions? What will the packaging be made from? What is the most suitable price point?When – when might production start? When will marketing commence? When do we envisage that product updates will be required?Where – where will the product be sold? Where will the funding come from? Why – why should the product be created in the first place? Why will it be competitive in the market? Why will consumers use it?How – how will the product be promoted, marketed, or advertised? How will it complement existing products or services?Step 3 – Formulate answersIn the final step, the team should concisely answer each of the questions generated above. It should be noted that starbursting is an idea generation process and not a means of creating an action plan.
Nevertheless, the answers gleaned in step three will yield important insights that the team should incorporate before proceeding with product development.
Key takeaways:Starbursting is a structured brainstorming technique with a focus on generating questions to assist in robust product development.Starbursting helps product development teams create products that consumers want. With less emphasis on product features, the team is free to consider a new product from the point of view of the consumer.Implementing starbursting is a relatively simple process. However, a good facilitator will ensure that the individual perspective of each team member is heard and considered.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What Is Starbursting? Starbursting In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Appreciative Inquiry In A Nutshell
Appreciate Inquiry (AI) is an organizational change methodology that focuses on strengths and not on weaknesses. Appreciate Inquiry was created by management professors David Cooperrider and Suresh Srivastva in the 1980s. The Appreciate Inquiry is also known as the 5-D Cycle, an iterative cycle describing five distinct phases, made of define, discover, dream, design, and destiny.
Understanding Appreciate InquiryAppreciate Inquiry was created by management professors David Cooperrider and Suresh Srivastva in the 1980s.
In understanding Appreciate Inquiry, it was David Cooperrider who said it best.
He explains his methodology as “the coevolutionary search for the best in people, their organizations, and the relevant world around them. In its broadest focus, it involves systematic discovery of what gives “life” to a living system when it is most alive, most effective, and most constructively capable in economic, ecological, and human terms. AI involves, in a central way, the art and practice of asking questions that strengthen a system’s capacity to apprehend, anticipate, and heighten positive potential.”
Given its multi-faceted nature, practitioners of Appreciate Inquiry describe it as not simply a way of doing, but a way of being. Indeed, it offers a perspective that helps the individual understand how an appreciation of the world can shape their destiny. In business, this means that organizational change is a mystery that must be embraced – and not a problem to be solved.
Ultimately, Appreciate Inquiry encourages the organization to consider the role of unconditional, positive questioning in shaping perspective.
In turn, these questions strengthen system capacity and enhance positive potential. Some of the core AI principles around questions include:
Questions create the world we live in.Questions determine the results we achieve.Positive questions are more effective at creating positive outcomes.Questions create movement, momentum, and change.The Appreciate Inquiry processThe Appreciate Inquiry is also known as the 5-D Cycle, an iterative cycle describing five distinct phases. In the middle of the cycle resides the “positive core” of the organization, a combination of each phase representing a way of being and doing.
To better understand this cycle, let’s look at each phase in more detail:
Define – this initial phase requires that stakeholders come together and define the topic that will undergo an Appreciate Inquiry experience. What change to the system is the topic seeking to make?Discover – stakeholders then identify the strengths and best practices of the organization. How does it excel? What are the sources of high performance, excellence, innovation, or vitality? They may relate to leadership, technology, values, planning methods, and so on.Dream – with the strength of an organization identified, it must then envision its future. Planning methodologies must be based on examples of where the company has excelled in the past. This motivates both the individual carrying out the plan and by extension, the company itself.Design – what are the high-impact strategies that move the organization in the right direction? The planning and execution of these strategies should be prioritized.Destiny – in the final phase, individuals execute on strategy. The movement of a company toward its destiny must be sustained by a collective sense of purpose. This means creating an environment of continuous learning, revision, and in some cases, improvisation.Key takeaways:Appreciative Inquiry is a change methodology that focuses on the strengths and positive aspects of an organization.Appreciative Inquiry is a multi-faceted approach that becomes a way of being and a way of doing. Asking the correct questions is essential to driving high performance and maintaining a focus on organizational strengths.Appreciative Inquiry is also known as the 5-D Cycle. The cycle is an iterative process that helps organizations embody certain traits that help their systems become less resistant to change.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Appreciative Inquiry In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Is Round-robin Brainstorming? Round-robin Brainstorming In A Nutshell
Round-robin brainstorming is a collective and iterative approach to brainstorming. Brainstorming is an effective way of generating fresh ideas for an organization. Round-robin brainstorming is a balanced approach, employing an iterative, circular process that builds on the previous contribution of each participant.
Understanding round-robin brainstormingiI a group situation, brainstorming can be dominated by one or two personalities who discourage others from sharing their opinions.
Round-robin brainstorming is a more balanced approach, employing an iterative, circular process that builds on the previous contribution of each participant.
The technique makes it more difficult for large personalities to dominate by adding structure and organization to the brainstorming process. This makes it suitable for any situation where a range of personality types need to be considered. Which is to say, most situations.
Implementing a round-robin brainstorming sessionTeams should know that implementing a round-robin brainstorming session is rather easy.
Simply follow these steps:
Arrange the team in a circle and give each member an index card so that they can record their ideas.Then, the facilitator clearly articulates the problem to be solved and details company objectives. At this point, the facilitator can take questions but should actively discourage discussion among group members. In the third step, each individual should brainstorm ideas in complete silence.After brainstorming, each person should pass their idea to the person seated adjacent. Team members should then use the idea of their neighbor as the inspiration for a new idea. In some interpretations of round-robin brainstorming, the individual identifies possible risks or obstacles to their idea. The neighbor card initially swapped in the previous step should be handed to the facilitator. Then, everyone passes their new idea to the next person to begin step four again.The circular swapping process should continue for as long as the facilitator deems it necessary. Ideas should be collated, discussed, and voted on by the group.Advantages and disadvantages of round-robin brainstormingAdvantagesThe silent, collaborative, and iterative approach allow all ideas to be given equal consideration and the chance to be improved upon.The ideation process can gain momentum as it moves around the circle, resulting in ideas that may have been overlooked in a traditional brainstorming method. Momentum can also lead to empowered teams that feel confident to act on larger or more creative ideas.DisadvantagesSome argue that a lack of idea anonymity might cause some team members to withhold their ideas. Although there is no requirement to label each idea card with a name, the process does not make it difficult to connect match an idea with a specific individual.Round-robin brainstorming effectiveness can be limited since each team member can only improve on the idea of the person seated next to them. There is no capacity to gather input from every member of the group on a single idea.Key takeaways:Round-robin brainstorming is a collective and iterative approach to generating creative ideas.Round-robin brainstorming is implemented in six easy steps. Each step should be completed without discussion to give creative ideas equal weight. Discussion should only be encouraged at the sixth and final step when ideas are evaluated.Round-robin brainstorming helps teams build momentum and confidence, leading to creative insights that may not have been apparent in other brainstorming techniques. However, some argue that a relative lack of anonymity might still allow larger personalities to dominate the ideation process.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What Is Round-robin Brainstorming? Round-robin Brainstorming In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
STAR Method In A Nutshell
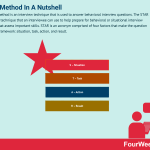
The STAR method is an interview technique that is used to answer behavioral interview questions. The STAR method is a technique that an interviewee can use to help prepare for behavioral or situational interview questions that assess important skills. STAR is an acronym comprised of four factors that make the question answering framework: situation, task, action, and result.
Understanding the STAR methodThe method has important implications for behavioral interviewing. This is a form of interviewing where questions are asked about past behavior and how it contributed to overcoming challenging work situations.
The STAR method is ideal for anyone who has difficulty answering these questions using real-world examples. It can be used to demonstrate competency in a range of skills relating to problem-solving, creativity, public speaking, teamwork, and perseverance.
Using the STAR methodSTAR is an acronym comprised of four factors that make the question answering framework.
Here is a look at each.
S – SituationStart by sharing the context in which you faced and then overcame a challenge. Context should preferably relate to relevant work experience. But for those with less job experience, referencing academic achievements or volunteer work is also useful.
Brevity is very important in setting the context. Only share what is required to adequately set the context for the interviewer.
T – TaskIn other words, what role or responsibility did you hold in your chosen situation? What task did you have to complete?
Tasks most often relate to hitting sales targets and resolving conflict. Again, it is vital to be succinct and avoid superfluous detail.
A – ActionWhat specific actions did your task entail? How did you overcome the challenge or handle the situation? This answer should be in-depth because it largely determines how suitable you are for similar roles.
Define the steps you took to achieve success, even if working as part of a team. While it may be tempting to describe the collective actions of the team, you must maintain a focus on the role that you played as part of the team.
R – ResultLastly, explain the outcome(s) generated by the action taken. Outcomes may take the form of accomplishments, but it never hurts to mention what you learned as a result of the challenge itself.
Preparing for a job interview using the STAR methodWith an understanding of how to structure questions, it is time to get more specific on the potential questions that may be asked.
To prepare, follow these steps:
Review the job description. What sorts of challenges may arise during a typical workday? Evaluating the required or relevant skills may yield important clues.Review general, evergreen interview questions. Most interviewers will ask at least one question about time management, stress, or working under pressure.Write out past experiences. Using the STAR method as a guide, articulate past instances where a challenge was met and overcome.Read each experience out loud. Does it sound coherent? Is it concise? Does it address a required or relevant skill? Refine until you can speak about each experience confidently without referring to your notes.Key takeaways:The STAR method is a means of preparing for behavioral questions that will be asked in a job interview.The STAR method is an acronym of four components vital to a thoughtful answer: situation, task, action, and result.Preparing for an interview using the STAR method involves reviewing job requirements and common behavioral interview questions. Interview answers that are relevant to the position can then be formulated and refined.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post STAR Method In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
February 11, 2021
Deplatforming In A Nutshell
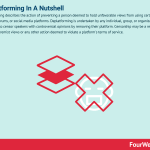
Deplatforming describes the action of preventing a person deemed to hold unfavorable views from using certain websites, forums, or social media platforms. Deplatforming is undertaken by any individual, group, or organization that wants to censor speakers with controversial opinions by removing their platform. Censorship may be a result of racist or extremist views or any other action deemed to violate a platform’s terms of service.
The effectiveness of deplatformingThe platform itself may be a social media account or any public venue where a large or influential group of people has assembled.
Deplatforming assumes that people who are prohibited from speaking about a certain topic will not have their message heard. However, research has found that deplatforming has mixed results.
During a purge of alt-right accounts in 2016, tens of thousands of former Twitter users simply migrated to Gab. Consequently, Gab become a haven for extremists and gained notoriety after a mass shooter posted his manifesto there in 2018. Some argue that this is a classic case of the Streisand Effect, where attempts to suppress information have the opposite effect of making it more visible.
Conversely, a similar purge of discriminatory subreddits in 2015 was shown to be effective. While a small percentage of banned users migrated to Voat, Reddit itself saw a significant decrease in new accounts promoting hate speech after the purge was completed.
Research has also conclusively determined that mainstream social media is the primary driver of traffic to websites with extreme content. When this avenue is closed off, controversial figures lose their ability to whip social media users into a frenzy.
Unintended consequences of deplatformingIn limited cases, deplatforming can backfire on society. Consider these following instances:
GabAfter Gab users were eventually deplatformed, it managed to survive by using decentralized technologies. The platform has also shown some degree of innovation by creating its own browser, allowing it to circumvent moderation.
Forced to innovate, Gab became a stronger, more unified, and more radicalized community that was more resistant to moderation and censorship. Decentralization, so often lauded as a concept, also provided Gab users a free and unencumbered means of self-organization.
TelegramInstant messaging app Telegram became the platform of choice after several terrorist organizations were deplatformed from mainstream applications.
Although the audience had shrunk in relative terms, deplatforming caused terrorist activity to migrate to a less-visible and much less-regulated platform. Here, deplatforming shifted users to an app that was arguably more suited to hate speech. Telegram gives controversial individuals protection while giving them public and private messaging and broadcasting functionality.
This functionality solves what studies have called the “terrorist’s dilemma”, or the seeking of a medium with an ideal balance of operational security and public outreach.
Key takeaways:Deplatforming is the prevention of an individual, group, or organization holding defamatory views from disseminating those views to an audience.Deplatforming effectiveness is mixed, but it most beneficial for causes where large social media platforms drive traffic to third-party websites. Purges undertaken by Reddit and Twitter reduced the amount of hate speech on their platforms with an inconsequential number of users migrating to other platforms. Deplatforming can strengthen certain movements by forcing them to unite and innovate. It can also shift extremist groups to platforms that are better suited to their modus operandi.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Deplatforming In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Smart Contracts In A Nutshell
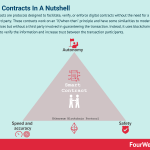
Smart contracts are protocols designed to facilitate, verify, or enforce digital contracts without the need for a credible third party. These contracts work on an “if/when-then” principle and have some similarities to modern escrow services but without a third party involved in guaranteeing the transaction. Instead, it uses blockchain technology to verify the information and increase trust between the transaction participants.
Understanding smart contractsSmart contracts are useful in any scenario where the presence of a third-party leads to inefficiencies. A classic example is an act of buying a house, requiring a large amount of paperwork, negotiation, communication, marketing, and risk management. Here, many simply opt to utilize the services of a third party – or in this case, a real estate agent.
The real estate agent is responsible for creating trust between the buyer and seller and overseeing the deal until it is done. As a result, they charge a high fee for their services.
Smart contracts have the potential to revolutionize the real estate industry by removing the third party from the process. Every facet of the role an estate agent would typically perform is written into the smart contract itself.
These contracts work on an “if/when-then” principle and have some similarities to modern escrow services. In other words, both the purchase money and ownership of the house are held in a system and then distributed to the relevant parties at the same time.
How do smart contracts work?Smart contracts use blockchain technology to verify information and increase trust between the participants in a transaction. Each smart contract features the terms of an agreement written as code that is committed to the blockchain and publicly available.
At some point, an event outlined in the smart contract is triggered. When selling a home, this event might be the house reaching a predetermined target price. Once triggered, the code executes and the transaction is completed.
It’s important to note that smart contract transactions do not occur in a vacuum. Regulators oversee contract activity on the blockchain to analyze the market while maintaining the privacy of each party.
Benefits of smart contractsThere are several important benefits to incorporating smart contracts into common transactions, including:
Autonomy – those affected by the transaction the most have full control over the agreement. There is no need to rely on a third party such as an agent, broker, or lawyer. Autonomy also means that a third party cannot enter a transaction and manipulate it for their own gain.Safety – smart contracts are extremely difficult to hack if written correctly. Since each record is connected to previous and subsequent records on a distributed ledger, altering one record would require altering the entire chain.Speed and accuracy – there is no need to waste time processing paperwork or reconciling data errors that often arise during large and complicated transactions. The code which underpins the smart contract is more exacting and rigorous than the legal-speak that underpins traditional contracts. Key takeaways:Smart contracts are digital, self-executing contracts where an agreement is written into lines of code. This negates the need for a third-party intermediary.Smart contracts work on an “if/when-then” principle. Code will only execute on an agreement once certain events have been satisfied.Smart contracts give autonomy to the actors in a transaction, avoiding the potential for manipulation by a self-interested third party. Based on blockchain technology, smart contracts are extremely difficult to compromise and provide a much more efficient way of creating robust agreements.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Smart Contracts In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
Natural Language Generation In A Nutshell
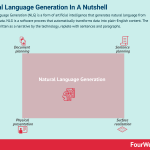
Natural Language Generation (NLG) is a form of artificial intelligence that generates natural language from structured data. NLG is a software process that automatically transforms data into plain-English content. The content is written as a narrative by the technology, replete with sentences and paragraphs.
Understanding Natural Language GenerationNatural Language Generation is a rapidly growing field that has seen great popularity among businesses. While NLG has an endless array of applications, it is useful for time or resource-intensive activities where is a need to generate content from data at scale.
Such applications include:
Written analysis for business intelligence dashboards.App or email-based customer communication.Client portfolio updates and summaries.Landing page content and eCommerce product descriptions.Internet of things (IoT) device maintenance and status reporting.Four processes of Natural Language Generation architectureNLG could never replicate the text generated by a real person, but it does use a range of methods to adapt its writing style according to the tone, structure, context, and purpose of the narrative.
To clarify these methods, researchers must define these processes:
Document planning – to determine what should be said, an abstract document is created based on the knowledge of the user. Information must also consider the goals of both the writer and reader.Sentence planning – what are the referring expressions or word choices? How will the sentences and paragraphs be structured? This step is sometimes called microplanning and involves techniques such as referring expressions, aggregation, grammaticalization, and lexicalization. Surface realization – or the generation of grammatically correct sentences using proper syntax and inflection.Physical presentation – depending on whether the information is written or spoken, the text must contain the right articulation, layout, or punctuation.Natural Language Generation and Natural Language ProcessingNatural Language Generation can write information, but it cannot read it.
This is where Natural Language Processing (NLP) comes in. NLP systems can “read” information in the sense that they can look at human language and determine what ideas are being communicated. Note that ideas are not communicated by words alone. Context, body language, and intonation are also vital in gauging the intent of the spoken word.
In this way, NLP systems incorporate ideas from computer science and computational linguistics to bridge the gap between nuanced human communication and computer understanding.
Real-world applications of NLPMany of us encounter NLP during our lives without realizing it. Here are some of the more interesting applications:
Virtual assistants such as Siri, Amazon Echo, and Google Home.Email assistants that correct grammar or filters determine which emails are likely to be spam and which should be sent to the inbox.Chatbots that answer customer service inquiries on eCommerce sites in real-time.Aircraft maintenance, where NLP is being used to find meanings in the verbal and written descriptions of aircraft problems given by pilots.Predictive police work. Although in its infancy, NLP is being used to assist detectives in determining the motives for crimes based on the language of the offender.Key takeaways:Natural Language Generation is a type of artificial intelligence that generates natural language from structured data.Natural Language Generation uses four key processes to reconstruct the context, tone, structure, and purpose of a narrative or story. These processes are document planning, sentence planning, surface realization, and physical presentation.While Natural Language Generation can write information, Natural Language Processing can read it. Through detailed analysis of written and verbal information, NLP has several interesting and important applications.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post Natural Language Generation In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.
What Are Stablecoins And Why Does It Matter For Business People
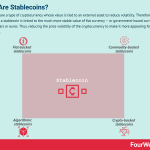
Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency whose value is tied to an external asset to reduce volatility. Therefore, the value of a stablecoin is linked to the much more stable value of fiat currency – or government-issued currency such as dollars or euros. Thus, reducing the price volatility of the cryptocurrency to make it more appealing for transactions.
Understanding stablecoinsTypical cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have revolutionized how people send and receive money. However, the main criticism of these currencies is their volatility and the subsequent uncertainty that this creates for everyday users. Consumers need to be relatively sure of the purchasing power of a currency, otherwise it may be devalued.
As the name suggests, the value of stablecoin is tied to the much more stable value of fiat currency – or government-issued currency such as dollars or euros. While fiat money is not without volatility, it is much more stable than traditional cryptocurrencies because it is backed by an underlying asset. Stability is also increased by a central authority actively managing supply and demand in response to market volatility.
The four categories of stablecoinsDepending on the nature of the collateral, stablecoins can be divided into four categories:
Fiat-backed stablecoins. When stablecoins use fiat money as collateral, an entity may choose to back one million units of stablecoin with $1 million held in a bank. The U.S. dollar is a popular form of collateral, but any currency subject to strict auditing and regulation is suitable.Commodity-backed stablecoins. Here, value is tied to commodities such as gold and silver. Oil is also being used to back stablecoins, with the Venezuelan government-issued “petro” a prime example. One unit of stablecoin is typically worth one unit of the predetermined commodity and may vary as a result. That is, gold value may be determined by ounces and oil by barrels.Crypto-backed stablecoins. The most volatile stablecoins. They often need to be “over-collateralized” to account for large swings in value. This means that a large number of cryptocurrency tokens serve as a reserve for a relatively low number of stablecoins. Smart contracts are used to handle the issuance of units and maintain integrity.Algorithmic stablecoins. These stablecoins track a fiat currency but are not backed by an underlying asset. Instead, their supply is managed by algorithms in much the same way central banks manage national currencies. In very general terms, the algorithm will reduce supply if the stablecoin price is below the fiat currency it tracks. If the price is higher than the fiat currency, new coins will be released to reduce stablecoin value.Some inherent risks of using stablecoinsWhile stablecoins are less volatile than traditional cryptocurrencies, it’s important to understand that some degree of risk remains. Ultimately, stablecoins are tied to the potential risks associated with the underlying asset. These risks include market fluctuations, theft, regulation, algorithm manipulation, or a change in consumer sentiment.
Fiat-collateralized stablecoins are also less decentralized than Bitcoin because a central entity must provide and hold the collateral. Users should research the entity to determine whether it has the necessary protocols in place to protect stablecoin value. Hypothetically, a central authority could print money without oversight and cause stablecoins to become backed by a hyperinflated currency.
Key takeaways:Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency backed by an external asset to reduce volatility and increase stability.Stablecoins can be divided into three categories based on the type of collateral used: fiat-backed, commodity-backed, and crypto-backed. The fourth category, algorithmic, maintains stablecoin value by manipulating supply and demand Stablecoins are less volatile than traditional cryptocurrencies, but they can be subject to the same risks encountered by the underlying asset.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsTech Business ModelThe post What Are Stablecoins And Why Does It Matter For Business People appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



