Febin John James's Blog, page 7
February 26, 2018
Hayato Ise You can translate all my articles into japanese :) If you are profiting from ads or…
Hayato Ise You can translate all my articles into japanese :) If you are profiting from ads or something. I would request you to share some profits by donating me Ethereum 0xc0c3aD24bdc8351e4bE29034Ff0a4E27B5066690 . It’s not mandatory. Only if you are benefiting :) .

February 25, 2018
Decentralised Platforms Need Breakthrough Thinking, Here Is What You Need to Know

I recently visited Venture Catalysts (an incubator) in Mumbai. Having conversations with the top thinkers(Vishal, Anuj, Ram, Vaibhav) about Blockchain and ICOs stretched my thinking. I didn’t have answers to all the questions they asked. Later, deeply thinking about the questions led to few insights.
How does decentalised platforms make profits?Imagine you are starting a decentralised crypto exchange. The typical way of making revenue on a platform which facilitates services by connecting people is by charging a commission. In a crypto exchange, you gain commissions for every trade, withdrawal, etc.
In a centralized exchange, there is a reason for you to charge such fees. Because you have to maintain the infrastructure. In a decentralised exchange, there are no infrastructure costs. In the long run, decentralised exchanges are likely to win because they are cheap for customers since the platform is self-maintained.
Decentralised platforms would generate no profit from services customer avails on the platform. This is because you are thinking like a middleman. The purpose of a blockchain is to eliminate the middleman. It doesn’t make sense to be the problem which the system is destined to eliminate.
In a Blockchain future, the producers will generate more revenue. Currently if I have to sell a book on Amazon, they take 50% of the sale as commission. If a decentralised platform replaces Amazon, I would get 90–95% of the profits. Blockchain systems are designed to benefit the producer and the consumer.
Does that mean decentralise platforms won’t be profitable?No, you can be profitable. Let me explain!
The typical steps in building a platform are as follows.
Step 1: Raise Investment from Investors
Step 2: Build the platform , market it and gain massive adoption.
Step 3: If profitable investors get return on their investment
Step 4: If not profitable got back to Step 1, otherwise shut down and move on.
I have simplified the steps, the reality is a lot more complicated. Decentralised platforms need to break the typical flow and design a good system to be profitable.
Here are the steps I think a decentralised platform should take.
Step 1: Sell tokens to consumers and promise them to return a service in the future.
Step 2: Build the first version of your product.
Step 3: Build a community around your platform.
Step 4: Deliver the promised service to your customers.
Step 5: Slowly your community will take ownership of your platform and you make an exit.
Huh? What is in it for people who built the platform in the first place?
In Step 1, based on your market you would be able to generate substantial investment from issuing coins or launching an ICO. The amount you raise would be drastically high compared to your expenses to build and sustain the platform.
This is because you only need to make the first or second version of the product. The subsequent versions will be built by the community. Bitcoin now has less than 2% of the code written by its original creator Satoshi Namokato. He even abandoned Bitcoin. He is now worth $19.6 billion. That would make him 44th richest person in the world.
If you plan your decentralised platform in a typical way, you are likely to be in trouble. You don’t need 100’s of programmers, managers, and an expensive marketing budget. You need to carefully design the platform to incentivise the community who will build and evangalise your platform for massive adoption.
People will buy your tokens for two reasons. The primary reason being they hope to trade the token for a service your platform offers in the future. The second reason being they expect your platform to do good and increase its net-worth. This would increase the value of their tokens. They can exchange them for more tokens from another decentralised platform or service with lesser net-worth.
Claps Please
February 21, 2018
Houmn Kargaran I have updated the video :)
Houmn Kargaran I have updated the video :)

What Happens When You Combine Blockchain and Education?
 Blockchain In Education
Blockchain In EducationMy college life was hard because it was easy. In my sports startup, I built mobile apps, wrote backend code and deployed them on AWS. In my college, I was forced to listen to programming lectures like “Adding two numbers”, “Generating Fibonacci series”, etc. It was frustrating!
In order to earn a degree, I had to go through this mental torture. Even if I reach the final year, I would be learning about cloud only in words. Nothing practical! I should be allowed to learn what I wanted and not what someone thinks I should. In India, only a few institutions offer quality education. On my day one in the engineering college my lecturer made the following statement.
“I came to this profession because I couldn’t find another job.”
Since the teaching profession has a huge demand, the job is almost guaranteed. In some institution, students don’t even get lecturers. They bribe the government to get a sanction for running the college.
https://medium.com/media/4e25efc1d9082d4b75a9be6a009c66ac/hrefThe above video demonstrates a scene in a typical Indian Institution. A Java class! The lecturer is literally reading from the book. I wish I had an English version.
During the admission process, submitting your High School and Pre-University certificates is mandatory. In case you change your mind to switch the college after the second trimester, you have to pay the fee for all eight trimesters. Only then they would return your certificates.
The next thing I couldn’t digest in India is caste based scholarships. I had a classmate who is filthy rich. He gets a huge discount on his college fee. At the same time, my other classmate who can’t afford his fee is thrown out.
I like Coursera. The quality of the materials is great. However, I find some topics difficult. Discussion forums are helpful only to some extent. I wish I could interact with the professor directly. Coursera certificates are slowly seeing adoption here. However, it needs improvement. The problem being Coursera profiles are not queryable.
If I were to hire a mobile app developer. I would go to Github and search for projects that are aligned with the product milestones. Then I query individual developer profiles behind those projects. I can even see the code they have written. If I am satisfied with their profile, I shoot an email to them. In most cases they will have an Upwork profile, I can send a proposal immediately. Though there are skilled people in Coursera, they go unnoticed.
Blockchain won’t magically solve these problems. But it is an indispensable tool. Let us explore how this tool will help in solving challenging problems of the educational sector.
No More Broken PromisesGoing to a court when educational institutions break their promises is impossible. Students can’t even afford their tuition fee! How can they afford to pay a lawyer?
Blocks of digital information connected with a chain is what makes a Blockchain. These blocks of digital information are distributed around the computers worldwide. This information once deployed cannot be altered. One of the key features of blockchain is smart contracts.
Smart contracts solve the problem of broken promises. Smart contracts are normal contracts with life in it. In a normal contract, two or more people agree on certain conditions they are obliged to keep.
John is a freelancer working with Tony. One of the conditions they agree on is the payment.
Normal Contract
* Once the project is delivered, we will pay you $4000* ....
* ....
Here Tony has an option to pay. John can drag him to court. You can imagine rest of the story.
Smart Contract
If the project is deliveredTransfer of $4000 from John's account is irreversibly authorised
Here Tony doesn’t have an option. If the work is complete, the money will go from his account. Now imagine how smart contracts can help students.
If 15 lectures on subject X is deliveredCharge the student a fee of $100
If the majority of the students agree that lectures were not delivered, no students will be charged. Students now hold a leverage for the university to act truthfully.
The above smart contract can be deployed on multiple computers around the world (Ethereum Blockchain). The smart contract once deployed cannot be altered. No single entity can control the entire deployment. Hence blockchain enables to build a system that is truly democratic.
ODEM is a decentralised education marketplace. They use smart contracts to mediate financial relationships between its members (eg. students, tutors). I recommend you to read the interview between David Smooke and the founder of ODEM.
Remember, blockchain can be used to build a democratic system. This depends on how it is programmed and designed. Hence, all blockchain solutions need not be democratic. So don’t believe all organisation who advertise they are on blockchain to act truthfully.
ScholarshipsThe problem of caste-based reservation is not a problem Blockchain can solve. However, instead of depending on government funds we can open investment to anyone. Blockchain brings transparency to the system. Hence goodwill donators can be assured that their money was put to good use. They would be able to see where exactly the money was spent
Queryable RecordsPeople make fake profiles, copy projects from other resumes and lot of institutions issue fake certificates. We can’t trust them.
Building a queryable infrastructure is costly for a platform like Coursera. On the Blockchain, we have the infrastructure built already. Reading data from Ethereum Blockchain is free of cost. Imagine if we can have a place like Github where we can see the courses and the projects students worked on.
On a blockchain, an authority can sign a certificate mentioning this person has learned digital marketing or this person worked on a Facebook campaign that brought 25% conversion. Anyone can easily verify this certificate on the Blockchain. If an institution issues fake certificates, their rating on the blockchain will be irreversibly affected.
One-One SupportAs I mentioned earlier, though MOOC has great content it fails to provide one-one support. We need a substantial number of tutors on the platform to support the massive number of students. Blockchain enables us to build a platform that removes geographic restriction and eliminates cost by cutting out the middleman. ODEM is focusing on solving this problem.
Can an Education Token Unlock Higher Learning?
In the coming days we can expect more such innovations of Blockchain In Education.
Claps Please
February 16, 2018
How To Protect Yourself From Cryptocurrency Scams
 Simple Filters That Can Protect You
Simple Filters That Can Protect YouWhen I was eleven or twelve years old (I don’t remember). I was jumping with excitement when I got an email that said “You have won $500”. My euphoria didn’t last long because of a mean friend who yelled “It’s a scam, you idiot”.
After all these years nothing has changed. Things on the internet never die, they just come back in different forms. It’s never been so easy to scam people since we have an innovation that makes them difficult to trace.
Fake ICOsICOs allow you to invest in their company in exchange for tokens. I joined a couple of ICO groups on telegram through Earn’s emails. ICO pay to receive your attention. They issue free tokens if you join their telegram group. When I join the group if the first question they ask is “How much are you going to invest?” I blacklist them as a scam. This may not be true but they should talk about their vision and product before asking about my investment.
Before investing ask what problem they are trying to solve. If they confuse you with jargons, run. Query them on google and check if they have content about cryptocurrencies, blockchain, etc. I judge them based on the quality of their content. Scamsters are likely to pay cheap prices and get cheap content or have no content. Remember endorsements of reputable figures can be faked. Vitalik Buterin has been put in the team of an ICO which he has never heard about.
ImpersonationIt’s an old trick. Impersonating themselves as someone else. It takes hardly few minutes to open an account on social media. The Founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin is one among the popular Twitter accounts which got impersonated.
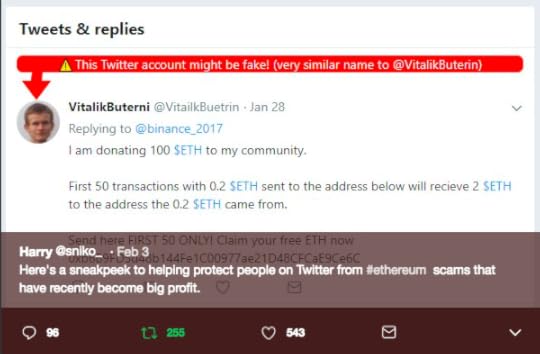 Original Tweet
Original Tweet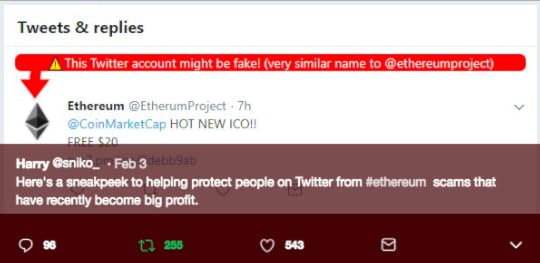 Fake Account of Ethereum Project (Original Tweet)body[data-twttr-rendered="true"] {background-color: transparent;}.twitter-tweet {margin: auto !important;}
Fake Account of Ethereum Project (Original Tweet)body[data-twttr-rendered="true"] {background-color: transparent;}.twitter-tweet {margin: auto !important;}And another... https://t.co/exgwGvRvrp
— @sniko_
Harry has developed a chrome extension to help you. EtherSecurityLookup highlights potential fake accounts.
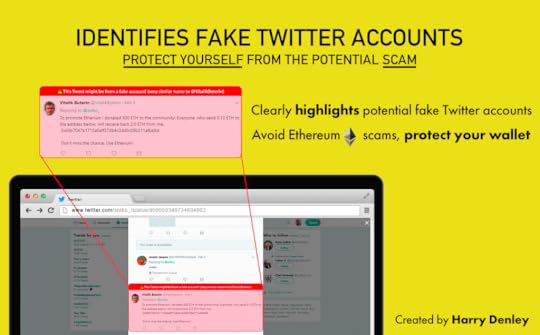 Source
SourceHe also helps maintain Etherscamdb. It has a collection of current Ethereum scams and phishing sites.
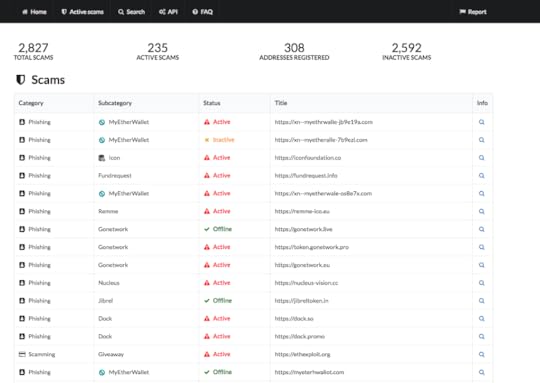 EtherscamdbFake Exchanges & Wallet Scams
EtherscamdbFake Exchanges & Wallet ScamsI haven’t used exchanges intensively. But here are some basic filters. Google them! If it’s a scam people would be talking about it. If the exchange doesn’t have a verification process it could be a scam. I tried to signup for a few reputable exchanges, they take verification process seriously.
I don’t register on any wallets unless it’s listed on ProductHunt. I judge them based on their upvotes. The other thing you can do is find about the team who developed their wallet. Search their Github repositories. If they don’t have good Git reputation they are not likely to keep your coins safe.
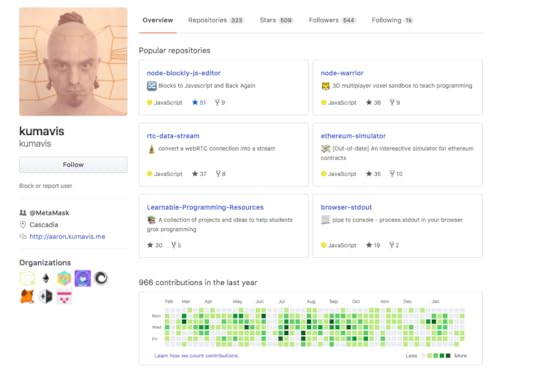 Example of a Reputed Github Profile (MetaMask Team)
Example of a Reputed Github Profile (MetaMask Team)Claps Please
February 15, 2018
Sure :) Go ahead , Knowledge should be free and open .
Sure :) Go ahead , Knowledge should be free and open .

February 13, 2018
3 Popular Types Of Blockchains You Need To Know
 3 Popular Types of Blockchains
3 Popular Types of BlockchainsIt took me a while to understand Blockchain. Now there are multiple types? Huh? For now, there are three types of Blockchain, since it is an emerging field I can’t assure you a number.
Permissionless BlockchainThis one, you already know. Bitcoin, Ethereum are examples of this kind of Blockchain. In this type of Blockchain, we don’t have an authority sanctioning a transaction. Let us consider Bitcoin. It is a shared ledger. If I send you 5 Bitcoins, I shout to the people in the network.
“Guys, look I am giving away 5 Bitcoins to this guy”.
Show off, isn’t it? The people in the Bitcoin network hears my message and starts the process of validating the transaction. The person who validates the transaction is not a chosen one. We can’t predict who gets a say. The point is no single person has the power to validate transactions. Permissionless Blockchain can be used when you want your system be truly democratic. Anyone can create smart contracts, transfer money or contribute data. Here users are likely to remain anonymous. Yes, you can protect sensitive information in a Permissionless Blockchain.
“Luke wants to build an app where anyone can voice their opinion about political parties. He wants to protect the privacy of the contributors.”
In Luke’s situation, we can use a Permissionless Blockchain. Anyone anywhere would be able to contribute their opinions on the app. No authority can remove their opinions, it will be permanently recorded.
 Credits : xkcdPublic Permissioned Blockchain
Credits : xkcdPublic Permissioned BlockchainHere we have chosen people who sanction a transaction. It could be an authority, senior employee, government, institution or anyone assigned. The data can be viewed by the public (Sensitive information can be protected).
“Elisha wants to bring transparency to Tuna fish supply chain. She wants people to know where the fish was caught, processed, packaged, etc”
Here when you buy the fish, you can scan the code and track its journey from the point it was caught. You are only allowed to view the data. You don’t have permission to write anything. The fisher man’s IOT device is allowed to write data when the fish is caught. The food processor who processes the fish is allowed to write data and so on. It doesn’t make sense for the public to write data into it. Here the data written like any Blockchain is permanently recorded.
 Credits : xkcdPrivate Permissioned Blockchain
Credits : xkcdPrivate Permissioned BlockchainThis is similar to Public Permissioned Blockchain expect for one thing. The data is not available for public view.
“Sara’s business involves two other small businesses and an accounting firm. They involve in regular transactions with each other.”
In Sara’s situation, her transaction with other businesses is private information. It shouldn’t be available for public view. The data, however, is permanently recorded. Here when they transact with each other, they don’t have to maintain a separate ledger. Every transaction will be tallied instantaneously.
I hope you got an idea of the types of Blockchain. Selecting the appropriate Blockchain is a must, you will save money and time. In some cases, you don’t even need a blockchain. I have prepared a questionnaire here to help you decide if you need a Blockchain. In the coming days we can expect more innovations in Blockchain.
Claps Please
February 12, 2018
How to Validate If Your Ideas Need a Blockchain
 The 6 Questions You Need to Answer
The 6 Questions You Need to Answer“I am a Blockchain engineer”.
This is a sentence I say when I meet people. I would tell them even if they don’t ask me what I do. I have an urge to occasionally add the word “Blockchain” in my conversations. It’s supposed to make me sound cool. I don’t know if it works but I keep trying. But, that’s not bad when compared to people who use Blockchain for all their problems. Yes, Blockchain does solve some hard problems. That doesn’t mean you can use it for everything. If you do then you will be creating more problems like your solution would be expensive and slow.
 Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcdThankfully Kurl Wust and Arthur Gervais, researchers from Switzerland have written a paper and explained when to use Blockchain. This story is a derived work. Here are a few questions you need to answer to figure out if your ideas need a Blockchain. The researchers have considered the current limitations of Blockchain (like cost and through output). In the future, Blockchain will be more efficient. These questions have a limited validity.
1. Is data storage required?
“John wants to build a speed reading app. Does he need a Blockchain?”
In John’s situation, he is developing a speed reading app, there is no data to be stored. Blockchain is a distributed database and purpose of a database is to store and access data. If you don’t have any data to be stored then no need of Blockchain. If you have data to be stored then let us continue our validation by asking the next question.
2. Are you the only one who is writing data?
“John wants to build an app to summarise news from different sources.”
“Mary’s business involves two other small businesses and an accounting firm. They involve in regular transactions with each other.”
According to the researchers, if you are the only person who is writing data, there is no need of Blockchain. In John’s situation, he doesn’t need a Blockchain. He can build an Android or an IOS app, use apple push or google messaging to push summaries. It would be cheaper. The purpose of a distributed database is to avoid inconsistencies. If you are the only person who wants to write data, there will be no inconsistency. Hence, no need for a blockchain. I would slightly disagree with them, if you are a university who wants to certify students, I think Blockchain would make sense here. Since you don’t have to build the tech infrastructure to certify students, instead you can use a Public Blockchain like Ethereum.
If multiple entities are regularly involved in financial transactions, each of you has to maintain a ledger. Here there are possibilities of inconsistencies since multiple people are involved and transactions need to be tallied. A Blockchain would make sense here. In Mary’s situation, the entities had to maintain a separate ledger before Blockchain. Here there are chances of inconsistencies, a Blockchain is required. If you have multiple writers, then let us move on to the next question.
3. Do you have trusted third party?
“During my childhood me and my brother involved in continuous trades (clothes, chocolates, etc). When there is a dispute our mom would interfere and settle it.”
In this situation, our mom is a trusted third party. We don’t need a Blockchain. If you can trust a third party who can be a mediator in your deal, then you don’t have to use a Blockchain. Of course, the fee should be nominal. If you don’t have a trusted third party, let us move on to the next question.
4. Are your writers anonymous?
“Mark wants to build an app where anyone can voice their opinion about political parties. He wants to protect the privacy of its contributors.”
We don’t want to reveal our identity when we purchase from a local store. Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc. solve the problem of revealing identity during a financial transaction. If you want to protect the privacy of your writers, use a Permissionless Blockchain like Ethereum. It would make sense in Mark’s situation because he can protect the identity of users (It again depends on the Blockchain, identities of several bitcoin users have been revealed). If people involved are not anonymous, let us ask the next question.
Persmissionless BlockchainIn a Permissionless Blockchain, there is no authority who is validating a transaction. It’s validated by the people involved in the network. For eg, when Bitcoin transactions are made.There is no authority who sanctions a transaction instead, the transactions are validated by miners in the network. If people involved are anonymous then you need a Permissionless Blockchain.
 Credits : xkcd5. Do the writers mutually trust each other?
Credits : xkcd5. Do the writers mutually trust each other?
“I can’t believe a few drivers on Uber have a rating of 4.5 stars. Am I being manipulated?”
Blockchain solves the problem of trust. For eg. In a centralised database, the authority can manipulate data to its viewers. In Uber’s situation, this could be a possibility. Maybe the riders are generous. In a Blockchain, all viewers will see the same data. If the data is contributed by people is within your circle of trust. Then you don’t need a Blockchain. If your writers don’t trust each other, let us ask the next question.
6. Do you need public verification?
“Sara wants to bring transparency to Tuna fish supply chain. She wants people to know where the fish was caught, processed, packaged, etc”
Do you want to make your data be transparent? In that case, you need to use Public Permissioned Blockchain. Here public will be allowed to read the data in your Blockchain. In Sara’s case, the person who buys tuna can be assured it doesn’t have any health risks. If you don’t want your data to be private and it should be only visible to the parties involved then you can use a Private Permissioned Blockchain (Hyperledger).
Answering these question will help you identify if your ideas need a Blockchain. Blockchain can be costly if you use it inappropriately. Since Blockchain would be slow in retrieving data when compared to a centralised server. But, if you use it for the appropriate problems it would be rewarding.
We need your claps
February 8, 2018
The terms would support both the buyer and the seller just like in the normal contracts.
The terms would support both the buyer and the seller just like in the normal contracts.





