Febin John James's Blog, page 4
June 22, 2018
The Pioneers of Programmable Money, Introducing 0x

If you give someone $50 and instruct them to only use it to buy healthy food. They can choose to ignore the instruction and lie to you. You won’t even know about it.
In our day to day transactions, we expect people to satisfy our instructions. When they break those instructions, you are likely to face a loss.
What if we can strictly enforce instructions in our transactions?
Ethereum is a cryptocurrency that provides you with a system to facilitate transactions only when a given set of instructions are satisfied. The system is transparent because it keeps a log of the decision making process.
If you are funding a non-profit, you can provide an instruction to release funds only if the organization reach the target of sheltering a thousand people.
The beauty is you can have more instructions, you can also instruct to release half the funds if 500 people are sheltered.
Hence, we have the ability to program money that can move at the speed of computers. Currently, money moves according to the speed of people involved.
Let’s take startup fundraising as an example. After you convince an angel investor or a venture capitalist, it would take three to four months for the process to complete and then money is transferred.
On Ethereum you can raise investments in few hours.
You can instruct the Ethereum computer through a smart contract to issue the investor a token when he transfers money. The investor will be able to redeem the token for a product or service your company provides in the future.
Presently there are more than 18,000 tokens on the Ethereum platform which are worth several billion dollars.
People will buy your tokens for two reasons.
They want to redeem your service on a future date.They believe in your idea and expect its price to increase in the future and they can exchange it for profit.Your customers are likely to hold tokens of other companies. If they are frequent traders they are likely to keep them in exchanges.
Keeping tokens in centeralised exchanges is a bad idea. The following is a list of attacks on centeralised exchanges. If your tokens are stolen, your company can be at risk.

If you have instructed your Ethereum contract to follow instructions of your majority stakeholders, hackers will dictate your company’s terms.
Centeralised exchanges are closed systems. An open system like Ethereum is easily extendable since anyone is allowed to interface with it to build applications.
In a closed exchange, the company can choose to extend only certain functionalities to a certain set of people. Hence, it’s hard to build autonomous applications on closed systems. Now, how do we solve the problem of security and closed system?
Decentralised ExchangesIn a decentralized exchange, trading happens directly between people’s wallets. The decenteralised exchange doesn’t hold their user’s assets.
Traders create an order at the price in which they want to buy or sell and pre-authorises a transaction. The order is broadcasted through out the network, traders who are willing to counter the order fills it.
If Sara wants to exchange BAT for ETH, she specifies the price at which wants to sell it and create an order in a decentralized exchange. The decentralised exchange pings her wallet to take her approval in order to pre-authorise the transaction.
After her approval, the order is visible to other traders who can choose to fill the trade. Mark chooses to fill the trade, he authorizes the transaction through his wallet.
The trade happens, Sara’s BAT token get transferred to Mark’s wallet and his ETH is sent to her wallet. The trade didn’t require a middleman to hold tokens.
Key Features of Decentralised ExchangesThe security risk is minimised because no assets are held.Trading happens faster because the time taken to transfer assets to exchanges is eliminated.Governments cannot regulate or ban it since the Ethereum system approves only decisions given by the majority stakeholders.The cost involved in maintaining a decentralized exchange is drastically less when compared to managing centralized ones.The trading fee is comparatively less because the infrastructure costs are optimised and the withdrawal fee is eliminated. Decentralised exchanges are also extendible since it supports application integration. It is an open platform and anyone can build relayers/services on top of it. Introducing 0xOpen frameworks played an important role on the internet we see today. If you want to build a web app from scratch you have to do a lot of things yourself (listening to requests from port 80, writing a wrapper to interact with your database, etc).
But, people hardly code from scratch. Instead, they use MVP frameworks like Laravel, CodeIgniter, Django, Flask, etc. You can reuse their code which was refined over time by the community. This process can save you time and help you take your ideas to market faster.
Now back to programmable money!
Building autonomous systems that can facilitate transactions on Ethereum from scratch is hard and time-consuming. Your code needs to be optimised because you have to pay for the computational power utilised.
0x is a protocol that takes care of the core architecture. Hence you can focus on the core business logic and worry less about the architecture. 0x smart contracts are rent free and open source. It is backed by a strong community who continuously refine and optimise its code.

You can use their APIs to easily program money or even build a decentralised exchange/relayer. We already have a lot of projects built on top of 0x. Radar Relay, ERC Dex, DDEX, Paradex (Acquired by Coinbase) are the popular relayers built on 0x.
They are called relayers because they use 0x’s infrastructure to enable trading. These relayers can charge its users a fee for its services. This is a win-win situation for both 0x and relayers because they will individually market and compete to build quality services on top of 0x.
When relayers attract more users, 0x will start growing as an open platform. This would also enhance 0x architecture since its open source and contributed by the community. Relayers thus don’t have to worry about maintenance and system upgrades, they can focus on the core business model.
 How Does Trading Happen on 0x?
How Does Trading Happen on 0x?In order for the trading to happen, we need a system to create, match and fill orders. As discussed in the earlier example, Sara creates the order and Mark sees the order and chooses to fill it.
These created orders need not be filled. Frequently writing data on Ethereum is inefficient and costly. 0x uses a brilliant approach and take the order creating, matching and filling process off-chain.
0x matches orders by broadcasting signed messages across the network, only when an order is filled, trade is executed on the blockchain. This approach reduces the load on the blockchain and enables efficient trading.
The Four Key Components of 0x Protocol0x protocol is made up of four key components. Makers, takers, relayers and smart contracts. Let’s see how these components worth together to enable decentralized trading.
Relayers offers interfaces(web or mobile apps) to users. There is a fee for using the 0x platform which needs to be paid using ZRX. Relayers offer competitive pricing to its users.
The makers are users who want to sell or buy tokens. In one of the earlier examples we discussed, Sara is a maker who wants to trader her BAT tokens. Makers use the relayer’s interface(eg. Radar Relay) to create orders by authorizing the transaction using their private keys.
The order will contain parameters like the tokens they like to trade, the price at which they want to buy or sell, the relayer fee and time in which the order will expire if it’s not filled.
Relayers validates the maker’s order and appends it to their order book. These orders are also visible to other traders using the relayer. When a trader chooses to fill the order created by the maker he becomes a taker. Some relayers automatically matchmakers who make opposite orders.
Once the order is matched, the Ethereum smart contract executes the order on-chain. Tokens get exchanged directly between the wallets of maker and taker. The relayer receives the agreed amount of fee.
Relayers are only one of the use cases of 0x, the potential applications of 0x are infinite, let’s have a look at some of the application.
Applications of 0xThe process of creating a decenteralised organization on Ethereum, issuing tokens, developing code to manage the governance by voting, etc requires technical resources. It’s also time-consuming and costly.
Aragon is a decentralised application that uses 0x protocol to help users easily built decentralised organisations on Ethereum.

Fintech products that help people invest their money efficiently aren’t something new. However, these products lack transparency.
Auctus is retirement planning platform that makes use of the 0x protocol. You get human and robotic advisory to help you manage your assets efficiently. Advisors are incentivised based on their advice.

A lot of experts who make predictions, most of these predictions fail. What if we can make them accountable for their predictions?
Augur is a prediction market platform that uses 0x protocol. An expert can make predictions on the platform by holding their money. If their prediction comes true they are incentivised else they lose their money.

The kind of applications that can be built on 0x is vast. We are yet to see its true potential. You can have a look at the story “18 Ideas for 0x Relayers in 2018” written by Tom Schmidt from the 0x team.
This story is part of our “Deep Dive Into ERC20 Ecosystem” Series. The second part of the story will be published soon. In the next story, we will be reviewing relayers built on top of 0x.
Claps Please
June 19, 2018
Stages of Blockchain Implementation
The blockchain is a tool to minimize discrepancies, it enables trustless transactions between counterparties. Since it replicates its data on all the computers in the network it promotes transparency and accountability. But, how does a company go about implementing blockchain? This article walks you through the process.
 Assess whether blockchain is the right solution
Assess whether blockchain is the right solutionThough blockchain is a powerful tool, it might be the wrong solution to some problems because it can be expensive and inefficient. A couple of researchers from Switzerland have written a paper to help an organization to check if a blockchain based solution is required.
When is blockchain not required?Since blockchain is a database, we can assume there is a need to store information. Information that is likely to be records of events (actions of different entities). If there is no need to store such information, blockchain is not required.
Blockchain creates trust between counterparties. If you are the only person who is writing and reading information, blockchain is not necessary. If you have an inexpensive third party who is trusted by the counterparties, then blockchain is not needed.
When is blockchain required?The blockchain is required in situations when people cannot trust each other. Situations where the information one authorizes needs to be publically verified. If there is a need to record events, that can be verified on a future date. Transactions involving multiple entities, where data must be instantly tallied. A situation which involves business where people don’t trust each other and an inexpensive trusted third party is not available. We will go through some examples to gain clarity on the above points.
UniversitiesUniversities issue a physical certificate to students which stand as a proof that a student has accomplished a program/course. However, these certificates can be falsified. Some universities support online verifications, but these are recorded in databases that can be easily modified.
On a blockchain, data once entered cannot be altered. It will exist there for eternity. A university can digitally certify a student’s academic information into a public blockchain. Since the data in a public blockchain is accessible, anyone can verify the records. The university has to bear only a one-time writing cost, reading data on a public blockchain is free.
Identity VerificationThis is very similar to the above examples, except instead of university it can be any reputable organization that certifies the identity of a person. Since the records are queriable, any entity can verify the record on a blockchain.
Logging EventsIn the tuna fishing industry, fish gets exchanged across various hands. How can we ensure that fish was caught from an authorized location? If the fish was processed by a trusted entity?
A private blockchain can be deployed across the organizations involved in the tuna supply chain. When the fish is caught, the fisherman’s IoT device will log the information into blockchain. As fish passes through various parties for processing, distribution, etc. the data gets logged on to the blockchain. Any person can verify the fish’s life cycle from the point it was caught.
Transferring OwnershipOne of the prominent use cases of blockchain is smart contracts. A smart contract is a digital contract that enforces itself. Two or more entities can enter into a smart contract agreement with each other. A smart contract usually contains condition based triggers (e.g. if A sends $500, then transfer the ownership of the car from B to A).
 How to get higher management’s agreement on its implementation?
How to get higher management’s agreement on its implementation?If you can prove that implementation can save a justifiable amount of time or money, higher leadership is likely to approve your request.
Has someone misused your organization’s name in the past?In this case, you can digitally sign information on a public blockchain that can be publically verified. This only has a one-time writing cost. If the information you want to certify is not large, your expenses are likely to be less.
Does your business have a substantial amount of discrepancies with other parties that cost a lot of money?In this case, you need to deploy a private blockchain with the entities involved in the business. It makes sense as long as you are involved in continuous transactions and your losses are higher than the cost of implementing and maintaining a private blockchain network.
How often do you have legal issues when involved in business with different entities?This is a tricky question because in the digital world we have only two answers, yes or no. However, in the real world, we encounter situations where the answer is both yes and no. As long as your contract can be coded into a smart contract and your legal costs are higher when compared to the implementation of a private blockchain, this approach makes sense.
Things to consider when implementing blockchainBlockchain is a tool which ensures integrity as long as it is programmed correctly. If there are any flaws/loopholes in the implementation, undesired outcomes are likely to happen.
Organizations on a blockchain network are issued a public key and a private key. A public key is visible to anyone (e.g. username), whilst the private key must be kept as a secret (e.g. password). If the private keys are compromised then the integrity of the blockchain is threatened. The blockchain network must be able to handle such situations. An admin can be assigned to the blockchain network who can make the compromised private keys obsolete and new keys can be issued.
The data entered on a blockchain cannot be altered.
Hence it can go through multiple authorizations before it is permanently recorded on the blockchain. People might try to beat the system and try to act selfishly. Transactions on a blockchain should undergo continuous assessments and the system must be upgraded if any loophole is found.
Since blockchain-based solutions can cause irreversible damage, it would be a good idea to take a module of the system, instead of taking the entire system into the blockchain immediately. Once the module is thoroughly tested and proven successful, other modules can be moved into the blockchain.
In certain situations, it is not possible to check on paper if blockchain is viable. In those cases, one can test traditional systems and blockchain-based solutions on similar modules. Later, the time and cost can be compared to check if blockchain is the right solution. If the blockchain based solution comes out costly and time-consuming, then a traditional solution can be used.
Blockchain is a tool that enables integrity in a system by increasing its transparency and accountability. Though blockchain is a powerful tool, it is not the right solution to certain problems. One must assess if blockchain is required and if it is cheaper when compared with traditional solutions before its implementation.
In cases when such assessment is not possible, blockchain can be run on a trial basis and the results can be compared with traditional solutions. Blockchain is a software that will act as instructed. If there are loopholes in the instructions people can take advantage to act for their own benefit. Continuous assessments are required to prevent such outcomes.

Author
Febin John James is one of the top writers in Innovation and Technology on Medium. He writes for publications like Hackernoon, FreeCodeCamp, etc.

Blockchain Business Review from Apla provides high-quality educational material from the world of blockchain to inform the business community of the competitive advantage that can be gained by integrating distributed ledger data storage within organizations. Our mission is to promote knowledge about blockchain and its uses in both the private and public sector and demonstrate the value of blockchain integration.

Stages of Blockchain Implementation was originally published in Apla on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
You can never run a marathon with baby steps alone
 Interview with Prathiba Sastry
Interview with Prathiba SastryI was first introduced to Prathibha at the orientation day of Microsoft Ventures, Batch 4. Observing the audience switch to focused/silent mode as she spoke, I realised they already knew her.
She was the Head of Operations at Microsoft Ventures for 3 years. Later, she created and led #InnovationYatra. It lasted over 18 days and took them through some of the most beautiful routes and roads of the country while on their 3500+ kilo-meter road trip in search of all the hidden jewels of innovation that she and her team were determined to uncover along the way.
 A prosthetic bionick hand cost from 1000$ to 5000$ and due to such a large price these prosthetic hands are not affordable in developing countries like India . So, Prashant Gade looked for a solution to develop an electronic prosthetic hand which can be made under 100$ and eliminated all the electronics part which normally increases the price of a prosthetic hand. (Credits : Innofest)
A prosthetic bionick hand cost from 1000$ to 5000$ and due to such a large price these prosthetic hands are not affordable in developing countries like India . So, Prashant Gade looked for a solution to develop an electronic prosthetic hand which can be made under 100$ and eliminated all the electronics part which normally increases the price of a prosthetic hand. (Credits : Innofest) Amogh Desai an engineering student has invented this metal cutter. Inexpensive and lightweigth to carry around, made by the using the waste body of a cycle and other scaps that are easy to find. Based on the principle of the converstion of the rotation motion to the oscilary motion. Cost to buy $50. (Credits : Innofest)
Amogh Desai an engineering student has invented this metal cutter. Inexpensive and lightweigth to carry around, made by the using the waste body of a cycle and other scaps that are easy to find. Based on the principle of the converstion of the rotation motion to the oscilary motion. Cost to buy $50. (Credits : Innofest)[Live Blog] Innovation Yatra: The Search For India's True Innovations - Inc42 Media
She now runs The PS Show, which brings together Entrepreneurial, Adventurous and Innovative men and women in a quest to enable women to dwell deeper on the events that shape their life.
https://medium.com/media/01fa08afbee6ec8020161a407206fbb7/hrefI had the chance to interview her, she was more than happy to share her learnings.
What Inspired You to Start the P.S Show?Sometimes, all you need is a little push. To me, that little nudge came from Oprah Winfrey. When you are trapped in an abusive relationship in a foreign land, you are not just trapped physically. Before I knew it, I was trapped mentally in a nebulous existence, counting and re-counting the tiles in the floor over a dozen times.At that time, watching Oprah Winfrey Show and witnessing ordinary men and women do extraordinary things was strangely comforting. May be, because I knew deep down that I was meant to do greater things and this was not the life I wanted. And one day, when I heard Oprah repeatedly say ‘You need to get out of that abusive relationship’, it stripped my veil of nebulous existence and made me feel alive again.
Few years ago, when I reflected on my life, I was not only surprised but was also funnily inspired by how far I have come. As I traveled across India, I met many enterprising women, who I knew, could be impacted to help better their lives in various aspects including Health, Wealth and Career. Who knew, what we see as a little nudge might make a huge difference in someone’s life. And that’s what motivated me to start The Prathibha Sastry Show.
What Are Your Top learnings from Interviewing People Across Disciplines?That I should push myself more to achieve better. Inspiration is contagious. When I listen to people talk excitedly about their goals and passion, I invariably push myself to take baby steps towards realizing my dream. When I listen to them talk about how they overcome a situation, I identify my strengths and weaknesses. When I see the audacity with which they believe in the unbelievable, I challenge myself to dream bigger.
Have You Noticed Anything Common Among the Adventurers/Entrepreneurs/Innovators You Met?There are few attributes that stand out regardless of which discipline they are from, whether their idea is big or small or what their background is. The biggest game changer is Passion, the excitement with which they talk about what they are doing. And the will to tirelessly pursue their goals in spite of everything. Also, I feel the key to their success is finding their own tribe and collaborating with them.
I Have Observed Your Quality of Being Decisive in the Middle of Chaos, How Can One Cultivate Such Abilities?By letting oneself face the chaos. When you can clearly define and see your destination, finding your way through the chaos is a cake walk. There is a popular saying, Hold the stone closer to your eye and all you see is the stone. Hold it a little farther, you can see the world.
Any Principles You Adopted over the Course of Your Life and Work Experiences?One of the Mantras that I have adopted over the years is to question “How can I make this Happen” and I go and make it happen.
What Are the Three Necessary Skills Every Dreamer Must Cultivate?A dreamer has already acquired the first skill, to dream. The next is to connect with his/her own tribe and take action. The third is to grow, by putting yourself and your doubts in the backseat and letting your dream drive you.
What’s the First Step You Think a Dreamer Should Take?The obvious one is to take action. A Dreamer should connect with his/her own tribe. Take at least one baby step everyday towards realizing your dream. But remember, baby steps are only a start to running a marathon. You can never run a marathon with baby steps alone.
body[data-twttr-rendered="true"] {background-color: transparent;}.twitter-tweet {margin: auto !important;}In this season of @The_PS_Show are tackling an important life subject #financialindependence and why it should not be ignored! The earlier you begin, the better it serves your life's goals and ambitions! @ShonaliAdvani @write2kavita @fisdomApp https://t.co/g1dWGSD11w
You can follow The P.S Show on Facebook. You can reach her on twitter @PrathibhaSastry. You can also follow her on Medium(Prathibha Sastry).

You can never run a marathon with baby steps alone was originally published in ART + marketing on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
June 4, 2018
Please connect with me on linkedin.
Please connect with me on linkedin.

May 30, 2018
There is a limit on how much bitcoins can be mined altogether.
There is a limit on how much bitcoins can be mined altogether. We haven’t reached the limit yet, we might hit it in 2021. After which no more bitcoins can be mined.

A Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain Programming

I had a lot of questions on my quest to understand how Blockchain works. The important one was “How do I build applications on it?”. It took a few weeks of digging up, reading and experimenting to finally get it. I couldn’t find a short but comprehensive guide. Now, that I have some decent understanding, I thought of writing one that could help others. This is a light speed guide, I have kept only the important parts in order to reduce the learning curve.
 ChaptersThe Purpose of BlockchainHow was the Blockchain invented?Introduction to Ethereum & Smart ContractsProgramming Smart Contracts on EthereumThe Way AheadThe Purpose of Blockchain
ChaptersThe Purpose of BlockchainHow was the Blockchain invented?Introduction to Ethereum & Smart ContractsProgramming Smart Contracts on EthereumThe Way AheadThe Purpose of Blockchain
Roopa lives in one of the remote areas of Delhi. The government of India has allocated her few resources of food every month. Since she belongs to the BPL(Below Poverty Line) category. The government uses a middleman to distribute these food resources. Only one-third of the allocated food resources reach people like Roopa, the rest is sold by the middleman for profit.
Sara writes fiction books, she publishes them on Amazon. She’s upset because Amazon takes 50% of the sale as commission. That’s unfair because she alone has put in the efforts of writing and marketing.

The problem is middleman is hungry for power and money. Their motto has become “profit at any cost”, to support producers and to empower the poor, we need middlemen to act ethically. That’s almost impossible to achieve, but what if we can replace middleman with an autonomous system?

Since computers don’t have biases they neither need money or power. This could have been Satoshi Namakato’s thought when he invented bitcoin using the blockchain technology in 2008.
How was the Blockchain Invented?
Money has evolved over time, each evolution reduced its cost of production and made their transactions more convenient. Gold coins were costly to produce. The invention of paper currency solved this problem. But, after the invention of computers and internet, people found a better way to make transactions convenient and faster.
To safe keep our lifetime’s earnings and to facilitate digital transactions we need a middleman(bank). This made banks powerful, they can impose a heavy fee on our withdrawals /transactions, sell our private information, etc

Banks hunger for money caused the financial crisis in 2008. Banks failed to respect their customer’s privacy. Their weak security systems gave rise to digital fraud.
The next evolution of money had to solve the following problems.
It shouldn’t be stored with a central entity.It needs to be highly secure.It should ensure privacy.Since fiat currency is controlled by the government, Satoshi had no option but to invent a new currency (Bitcoin). He solved these problems with the help of peer-to-peer networks and cryptography.
Decentralisation Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcdTorrents use peer-to-peer technology to share files. The torrent app doesn’t download the file from a central server or a single computer, instead, it connects to the people in its network, finds out who has the file and download it from their computers.
You get the pieces of a file from different computers around the world. If one person in the network goes away, your download isn’t affected because there are other people who can share the file.
Satoshi adopted this technology since it stores money in a decentralized way. No single entity will have control over it.
Cryptography Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcdIn cryptography, one can digitally sign a message. In order to do this we need three things a public key, private key, and message.
The public key and private key are a set of long characters that are mathematically connected. A public key is public like your username, and the private key is a secret like your password.
A message is an information you want to authorise, ex: “I authorise you to pay John $100”.
If you input the algorithm with a public key, private key and message. The cryptographic algorithm will produce a signature. That is another set of characters unique to the contents of that message.
Public Key-----BEGIN EC PUBLIC KEY----- MFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYIKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAE50uE+YSxqDgMkFByhpcgTVqXCqHO h68Ljt1z0jklDff/WV7xo+U6o3REBtK/C0/LM+Ef3FB3wR9aXMGNMLb9EA== -----END EC PUBLIC KEY-----Private Key
-----BEGIN EC PRIVATE KEY----- MIGHAgEAMBMGByqGSM49AgEGCCqGSM49AwEHBG0wawIBAQQgwqIsXl9FqsgrzMdx axI6flBwWIev0Z7i+WF4j8BGnrKhRANCAATnS4T5hLGoOAyQUHKGlyBNWpcKoc6H rwuO3XPSOSUN9/9ZXvGj5TqjdEQG0r8LT8sz4R/cUHfBH1pcwY0wtv0Q -----END EC PRIVATE KEY-----Message
Hello WorldSignature
B0A9A4F641D3A2E3A65576B7311DCD62ABE78BBF4D3F5FE856598508E24FCB2E6F0277C2F8D57E9E2E108B7C493986E783F5316B8046597019951669B4EE6922
To verify the message, one has to input the public key, the message, and the signature. The cryptographic algorithm can verify if the message was signed by the owner of the public key.
It would take 1000’s of years to break the cryptographic algorithm. This cannot be done faster because of the computational limits we have. Quantum computers in the future might challenge this. But, the Bitcoin system can be upgraded to ensure security.
Satoshi incorporated cryptography in his system to help people authorise bitcoin transactions from their wallets.
Privacy Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcdYou register to bitcoin by generating a wallet (public key/private key). The systems collect no information such as email id, full name, etc. Hence you are anonymous unless you announce your public key.
Putting it TogetherSatoshi built a shared ledger using cryptography and peer-to-peer networks. When someone sends bitcoins to someone, a message is cryptographically signed and broadcasted to the entire people in the network. They update their ledger, hence everyone in the network knows who owns what.
Blockchain
Every ten minutes transactions are grouped together into a block and linked back to the previous blocks. This process makes a continuous blockchain. Mining is a process by which a block is confirmed, this involves computers in the network to solve a mathematical problem. The first computer/miner who solves the problem gets rewarded in bitcoins made out of thin air.
Once the block is confirmed and added to the network, it is replicated across the entire network. Blockchain was invented in the process of making the autonomous Bitcoin system which confirmed transactions without human intervention. If you are looking for a simplified explanation for blockchain, here’s a story.
A Beginner’s Guide to Blockchain
Introduction to Ethereum & Smart Contracts
Earlier we talked about replacing middleman with autonomous systems. This can be done through programming. Bitcoin’s system was difficult for people to code autonomous systems.
Hence Vitalik Buterin built a new cryptocurrency called Ethereum. It was not only a decentralised cryptocurrency but a network of computers which can host code in the form of smart contracts.
In smart contracts, we can program conditions. If you want to build a decentralised bookstore. You write instructions to help authors add new books, send the download link to an ebook once the customer makes a transaction etc.
Smart contracts not only store conditions but also data. A smart contract of a decentralised bookstore in itself stores the book listing, purchases, etc.

However, we should admit the limitations of the smart contract. Some systems need human support, computers can’t handle it. In the real world implementing smart contracts isn’t easy. Smart contracts once published cannot be altered, silly mistakes can be costly.
Programming Smart Contracts on Ethereum Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcdWe will build a simple smart contract that stores and retrieves grades of students. We will be coding the contract in solidity. Here’s the github repo.
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;contract Grades{}The first line tells the compiler which version of solidity we are using. Then we define the contract grades.

We need to store two things in our contract, names of students and their grades. Hence we will create an array to store student names and an associative array to store their grades.
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;contract Grades{mapping (bytes32 => string) public grades;bytes32[] public studentList;}
Now, we will create a way through which we can send the contract, a list of student names. We will do that in the constructor.
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;contract Grades{mapping (bytes32 => string) public grades;bytes32[] public studentList;function Grades(bytes32[] studentNames) public {
studentList = studentNames;
}}
In Solidity we would be calling the constructor only once. We will pass student names as an argument, which would be stored in the studentList array we declared earlier.
Now, we need to write a function to assign students their grade. We also need another function to check if the student is valid.
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;contract Grades{mapping (bytes32 => string) public grades;bytes32[] public studentList;function Grades(bytes32[] studentNames) public {
studentList = studentNames;
}function giveGradeToStudent(bytes32 student, string grade) public {
require(validStudent(student));
grades[student] = grade;
}function validStudent(bytes32 student) view public returns (bool) {
for(uint i = 0; i < studentList.length; i++) {
if (studentList[i] == student) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}}
The “giveGradeToStudent” function takes two arguments, student name, and grade. The require function checks if the “validStudent” function returns true or false. If it returns false, the execution is canceled.
Finally, we need to write a function to fetch the grade of a student. The “getGradeForStudent” function takes student name as an argument, return the respective grade from the associative array.
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;contract Grades{mapping (bytes32 => string) public grades;bytes32[] public studentList;function Grades(bytes32[] studentNames) public {
studentList = studentNames;
}function giveGradeToStudent(bytes32 student, string grade) public {
require(validStudent(student));
grades[student] = grade;
}function validStudent(bytes32 student) view public returns (bool) {
for(uint i = 0; i < studentList.length; i++) {
if (studentList[i] == student) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}function getGradeForStudent(bytes32 student) view public returns (string) {
require(validStudent(student));
return grades[student];
}}
For the sake of this tutorial, you can deploy this on a personal blockchain. You can create with Ganache. Here are the commands to install and run ganache.
npm install ganache-cli web3@0.20.3 solcnode_modules/.bin/ganache-cli
Keep ganache running, on a new terminal we will deploy our smart contract. Please save the smart contract as ‘Grades.sol’.
Let’s compile the code.
nodecode = fs.readFileSync('Grades.sol').toString()
solc = require('solc')
compiledCode = solc.compile(code)
Now let’s deploy the smart contract. Deploying contract on a blockchain will cost you gas, this is to reward people who rent their computational power to you. So we have to specify the amount of gas which you are willing to allocate. You can estimate that using a gas calculator. But, you don’t have to pay now because you are deploying on a personal blockchain and it’s your resources being used. You will have to pay when you deploy contracts on the public Ethereum blockchain.
Web3 = require('web3')web3 = new Web3(new Web3.providers.HttpProvider("http://localhost:8545"));abiDefi... = JSON.parse(compiledCode.contracts[':Grades'].interface)GradesContract = web3.eth.contract(abiDefinition)byteCode = compiledCode.contracts[':Grades'].bytecodedeployedContract = GradesContract.new(['John','James'],{data: byteCode, from: web3.eth.accounts[0], gas: 4700000})Now let’s call our functions to give grade ‘A+’ to our student John. Later, we will check if it has been updated using our ‘getGradeForStudent’ function.
deployedContract.giveGradeToStudent('John', 'A+', {from: web3.eth.accounts[0]})deployedContract.getGradeForStudent.call('John')'A+'
Congrats, you have deployed your smart contract. If you have questions/doubts please comment on this story, I will either comment back or update this story.
The Way AheadYou can get in-depth understanding about writing Ethereum smart contracts in the following websites.
CryptoZombiesYou don’t have to download anything, you can write code on their interactive compiler. You will learn the concepts of solidity programming by building a game. It’s free of cost.
CryptoZombies - Learn to code games on Ethereum. Powered by Loom Network
ZastrinZastrin has both free and paid courses. Mahesh Murthy covers all the important aspects. They even teach you to build a decentralised marketplace similar to eBay.
Zastrin | Learn Ethereum programming by doing real-world projects
Claps Please
May 27, 2018
Can Blockchain Technology Be Used to Improve Open Governance?

Open Governance is not about releasing information on ‘as they please’ basis. But, having a system that is truly transparent.
Before Blockchain we had centralized systems or computers owned by respective organizations. Data was stored on these computers and few were revealed to people.
An organization doesn’t own the computers on a blockchain. Here computers contributed by people around the world work together to execute programs. Data and code are replicated to every computer in the network. By design information on a blockchain is publicly visible and cannot be altered.
Can blockchain be used for governance because of its inbuilt features of transparency and immutability?
https://medium.com/media/689c215f23b84eb71b5e65200ef426a0/hrefMoving the entire government to blockchain immediately is not practical. But some of its parts can be moved.
Researchers from the University of London have made a proof of concept for a fair and transparent government tender process using Blockchain .
Tender is a process by which governments and financial institutions invite bids for large projects that must be submitted within a finite deadline.

Researchers have suggested these following conditions to ensure fair and transparent tendering process.
1.Once the government opens a tender with certain description they cannot change it. Each tender includes evaluation criteria to select the best possible bid. It’s not fair for the government to change the criteria to favour a particular commercial organization.
2.Bids must be kept confidential until the tender closes. Bids are not be tampered with. Organizations shouldn’t be able to find out if others have placed a bid or not.
3.The government can only publish the bids after the tender is closed. Bids can be made public so that losing organizations, citizens, and interested parties can evaluate the whole bidding process.
4.The government shouldn’t be able to reject proposals based on their biases. The process should ensure confidentiality, privacy, and integrity. The tender process should be auditable and the decisions should be supported by evidence.
 So how do you make it practically work?https://medium.com/media/bcfa87574f00f91bb8d90d28ffcbaca4/href
So how do you make it practically work?https://medium.com/media/bcfa87574f00f91bb8d90d28ffcbaca4/hrefResearchers have developed their proof of concept using one of they key features of blockchain, smart contracts.
A smart contract is computerised contract that enforces itself. In a normal contract we have conditions written in paper. On a smart contract conditions are written in computer code.
The key feature of a smart contract is we can tell it what to do when a condition fails or succeeds. Ex: If the tender is closed, then release the bids to public.
Let’s look how the tender process works using smart contracts.
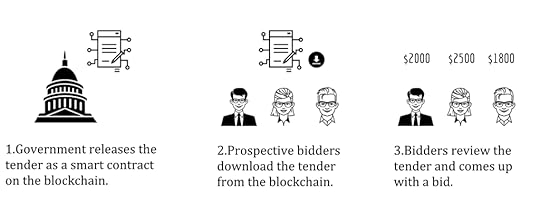
1.The smart contract will contain instruction in the form of computer code on how the evaluation is done. This released on the blockchain, once the code is deployed it cannot be altered.
2.Bidders can download the tender in the form of a smart contract from the blockchain.
3.Bidders can review the code and generate a bid response. Since the bids are encrypted bidders won’t be able to see each other’s bid.

4. When the bidders push their bid into the blockchain, they digitally sign it using their certified signature key. This measure prevents unauthorized bids.
5. The smart contract will reject bids that are sent after the deadline.
6. Government downloads the bids and runs evaluation to select the best possible bid. Here the evaluation is not manual, the computer runs the evaluation. But, only the government is authorized to start the evaluation process on a smart contract.

7. Evaluation results are now pushed to the blockchain along with bidder’s keys so that people can decrypt the bids and evaluate the code.
8.Citizens can access the smart contract anytime they want since data on a blockchain lies there for eternity.
9.Citizens can download the smart contract and run the evaluation for themselves and check if the evaluation process was fair.
Though we have a proof of concept, there would be some challenges when you deploy a real world tender on a blockchain. However, a fair and trasparent tender process on a blockchain is not impossible to achieve.
You can have a look at their research paper for more details, it contains algorithms for initiating a tender, placing a bid and evaluating bids.
Claps Please
May 26, 2018
A Practical Application of Blockchain In Open Governance

Open Governance is not about releasing information on ‘as they please’ basis. But, having a system that is truly transparent.
Before Blockchain we had centralized systems or computers owned by respective organizations. Data was stored on these computers and few were revealed to people.
An organization doesn’t own the computers on a blockchain. Here computers contributed by people around the world work together to execute programs. Data and code are replicated to every computer in the network. By design information on a blockchain is publicly visible and cannot be altered.
Can blockchain be used for governance because of its inbuilt features of transparency and immutability?
https://medium.com/media/689c215f23b84eb71b5e65200ef426a0/hrefMoving the entire government to blockchain immediately is not practical. But some of its parts can be moved.
Researchers from the University of London have made a proof of concept for a fair and transparent government tender process using Blockchain .
Tender is a process by which governments and financial institutions invite bids for large projects that must be submitted within a finite deadline.

Researchers have suggested these following conditions to ensure fair and transparent tendering process.
1.Once the government opens a tender with certain description they cannot change it. Each tender includes evaluation criteria to select the best possible bid. It’s not fair for the government to change the criteria to favour a particular commercial organization.
2.Bids must be kept confidential until the tender closes. Bids are not be tampered with. Organizations shouldn’t be able to find out if others have placed a bid or not.
3.The government can only publish the bids after the tender is closed. Bids can be made public so that losing organizations, citizens, and interested parties can evaluate the whole bidding process.
4.The government shouldn’t be able to reject proposals based on their biases. The process should ensure confidentiality, privacy, and integrity. The tender process should be auditable and the decisions should be supported by evidence.
 So how do you make it practically work?https://medium.com/media/bcfa87574f00f91bb8d90d28ffcbaca4/href
So how do you make it practically work?https://medium.com/media/bcfa87574f00f91bb8d90d28ffcbaca4/hrefResearchers have developed their proof of concept using one of they key features of blockchain, smart contracts.
A smart contract is computerised contract that enforces itself. In a normal contract we have conditions written in paper. On a smart contract conditions are written in computer code.
The key feature of a smart contract is we can tell it what to do when a condition fails or succeeds. Ex: If the tender is closed, then release the bids to public.
Let’s look how the tender process works using smart contracts.

1.The smart contract will contain instruction in the form of computer code on how the evaluation is done. This released on the blockchain, once the code is deployed it cannot be altered.
2.Bidders can download the tender in the form of a smart contract from the blockchain.
3.Bidders can review the code and generate a bid response. Since the bids are encrypted bidders won’t be able to see each other’s bid.

4. When the bidders push their bid into the blockchain, they digitally sign it using their certified signature key. This measure prevents unauthorized bids.
5. The smart contract will reject bids that are sent after the deadline.
6. Government downloads the bids and runs evaluation to select the best possible bid. Here the evaluation is not manual, the computer runs the evaluation. But, only the government is authorized to start the evaluation process on a smart contract.

7. Evaluation results are now pushed to the blockchain along with bidder’s keys so that people can decrypt the bids and evaluate the code.
8.Citizens can access the smart contract anytime they want since data on a blockchain lies there for eternity.
9.Citizens can download the smart contract and run the evaluation for themselves and check if the evaluation process was fair.
Though we have a proof of concept, there would be some challenges when you deploy a real world tender on a blockchain. However, a fair and trasparent tender process on a blockchain is not impossible to achieve.
You can have a look at their research paper for more details, it contains algorithms for initiating a tender, placing a bid and evaluating bids.
Claps Please
May 25, 2018
MIT’s Interesting Proposal for a More Stable Financial System
 MIT’s Digital Tradecoin
MIT’s Digital TradecoinOn the 16th of January 2018, three diamond firms approached Punjab National Bank requesting LOUs. (Letter of Understanding is a form of bank guarantee under which its customers can raise money from any other Indian bank’s foreign branch in the form of a short-term credit). Punjab National Bank demanded 100% cash margins (profitability) as a common requirement to issue LOUs. But, the firms responded back stating this requirement was not enforced for the previous LOUs they received since 2010.
That’s when the Punjab National Bank got suspicious. Few bank employees had been issuing fake LOUs through the SWIFT system(Messaging system between banks). The software which PNB used didn’t make a record of such transactions. Hence PNB was not aware of such activities. Later on 12th February 2018, PNB detected a scam worth around $1.8 billion.
Our current banking systems lack accountability and transparency. The Financial Depression of 2008 could have been discovered and prevented only if our banks were more transparent.
CryptocurrenciesIt’s no coincidence that Bitcoin was invented in 2009. Bitcoin is a digital currency which issues currencies and facilitates transactions directly between people with no help from intermediaries. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain (A shared digital ledger whose records cannot be altered).
Though the bitcoin system is innovative and brings transparency to the system. A lot of people have raised concerns about the following issues.
Bitcoin is not backed by assets, hence it has no intrinsic value.It has a limit on the number of transactions it can handle per second.The proof of work mechanism which the system uses to make itself secure and immutable demands insane amount of electricity (In one year Bitcoin will require as much energy required to power the entire United States).After Bitcoin, several other cryptocurrencies came into the picture like Ethereum, Ripple, etc. They innovated on bitcoin’s architecture. Though it solved several issues Bitcoin face, these currencies are still suspected to remain highly volatile. Since they have no intrinsic value.
The important innovation of these cryptocurrencies is its unchangeable distributed ledger. The central bank can abolish paper currency use the distributed ledger to introduce Central Bank Digital Currency. Though it’s distributed, central authorities have to create a controlled blockchain to add anti-money laundering functions. This gives them too much power over privacy and economy which can be misused.
Utility Settlement CoinUtility Settlement Coin was proposed by an association of banks. USC is a cryptocurrency backed by fiat currency(ex: USD) present as electronic cash balances in the participating banks. The problem is execution of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering functions.
Digital TradecoinHence MIT came up with Digital Trade Coin(DTC). DTC is similar to USC but instead of fiat currency, it is backed by assets to ensure stability. In DTC we have sponsors, administrator, a special bank, and users.
Sponsor bring in a pool of assets to the system. Assets like oil, gold, base metals etc. Administrator digitizes these assets and Digital Trade Coin is issued to the sponsors. Users who want to buy DTC approaches the bank with fiat currency (USD). The bank passes the money to the administrator who sends it to the sponsor. The administrator issues DTC tokens to the bank, who sends DTCs on a distributed ledger to the user.
In order to thrive, they need to solve the following issues.
A solution to the Know Your Customer problem.Anti-Money Laundering functions should be implemented.It should handle a high amount of transaction per second.The issuance of DTC must be transparent and economically meaningful.A mechanism to ensure the stability of DTC must be implemented.DTC proposes a semi-private distributed ledger to solve the know your customer and money laundering issues. This means sponsors in the system are publically visible and verified. However, users remain anonymous.
DTC uses a protocol similar to ripple to ensure high-speed transactions. It requires drastically less energy and time when compared to Bitcoin. Since it’s backed by assets that are logged on an immutable ledger, this approach is transparent and economically meaningful.
DTC has a mechanism for stabilization. If the market value starts to deviate upward compared to the intrinsic value of the assets, sponsors will contribute more assets to the pool and sell it on the open market. Hence pushing the price down. If the value goes down when compared to the asset pool, economic agents will sell DTC back to the administrator for cash. The administrator will sell part of the pool assets for cash and pass the obtained money to agents.
MIT’s proposal sounds good in theory. I hope they can pull it off. You can read more about DTC in the research paper Digital Trade Coin (DTC): Towards a more stable digital currency.
Claps Please
May 24, 2018
MIT’s Interesting Proposal for a More Stable Financial System
 MIT’s Digital Tradecoin
MIT’s Digital TradecoinOn the 16th of January 2018, three diamond firms approached Punjab National Bank requesting LOUs. (Letter of Understanding is a form of bank guarantee under which its customers can raise money from any other Indian bank’s foreign branch in the form of a short-term credit). Punjab National Bank demanded 100% cash margins (profitability) as a common requirement to issue LOUs. But, the firms responded back stating this requirement was not enforced for the previous LOUs they received since 2010.
That’s when the Punjab National Bank got suspicious. Few bank employees had been issuing fake LOUs through the SWIFT system(Messaging system between banks). The software which PNB used didn’t make a record of such transactions. Hence PNB was not aware of such activities. Later on 12th February 2018, PNB detected a scam worth around $1.8 billion.
Our current banking systems lack accountability and transparency. The Financial Depression of 2008 could have been discovered and prevented only if our banks were more transparent.
CryptocurrenciesIt’s no coincidence that Bitcoin was invented in 2009. Bitcoin is a digital currency which issues currencies and facilitates transactions directly between people with no help from intermediaries. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain (A shared digital ledger whose records cannot be altered).
Though the bitcoin system is innovative and brings transparency to the system. A lot of people have raised concerns about the following issues.
Bitcoin is not backed by assets, hence it has no intrinsic value.It has a limit on the number of transactions it can handle per second.The proof of work mechanism which the system uses to make itself secure and immutable demands insane amount of electricity (In one year Bitcoin will require as much energy required to power the entire United States).After Bitcoin, several other cryptocurrencies came into the picture like Ethereum, Ripple, etc. They innovated on bitcoin’s architecture. Though it solved several issues Bitcoin face, these currencies are still suspected to remain highly volatile. Since they have no intrinsic value.
The important innovation of these cryptocurrencies is its unchangeable distributed ledger. The central bank can abolish paper currency use the distributed ledger to introduce Central Bank Digital Currency. Though it’s distributed, central authorities have to create a controlled blockchain to add anti-money laundering functions. This gives them too much power over privacy and economy which can be misused.
Utility Settlement CoinUtility Settlement Coin was proposed by an association of banks. USC is a cryptocurrency backed by fiat currency(ex: USD) present as electronic cash balances in the participating banks. The problem is execution of Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering functions.
Digital TradecoinHence MIT came up with Digital Trade Coin(DTC). DTC is similar to USC but instead of fiat currency, it is backed by assets to ensure stability. In DTC we have sponsors, administrator, a special bank, and users.
Sponsor bring in a pool of assets to the system. Assets like oil, gold, base metals etc. Administrator digitizes these assets and Digital Trade Coin is issued to the sponsors. Users who want to buy DTC approaches the bank with fiat currency (USD). The bank passes the money to the administrator who sends it to the sponsor. The administrator issues DTC tokens to the bank, who sends DTCs on a distributed ledger to the user.
In order to thrive, they need to solve the following issues.
A solution to the Know Your Customer problem.Anti-Money Laundering functions should be implemented.It should handle a high amount of transaction per second.The issuance of DTC must be transparent and economically meaningful.A mechanism to ensure the stability of DTC must be implemented.DTC proposes a semi-private distributed ledger to solve the know your customer and money laundering issues. This means sponsors in the system are publically visible and verified. However, users remain anonymous.
DTC uses a protocol similar to ripple to ensure high-speed transactions. It requires drastically less energy and time when compared to Bitcoin. Since it’s backed by assets that are logged on an immutable ledger, this approach is transparent and economically meaningful.
DTC has a mechanism for stabilization. If the market value starts to deviate upward compared to the intrinsic value of the assets, sponsors will contribute more assets to the pool and sell it on the open market. Hence pushing the price down. If the value goes down when compared to the asset pool, economic agents will sell DTC back to the administrator for cash. The administrator will sell part of the pool assets for cash and pass the obtained money to agents.
MIT’s proposal sounds good in theory. I hope they can pull it off. You can read more about DTC in the research paper Digital Trade Coin (DTC): Towards a more stable digital currency.
Claps Please



