Matthew S. Williams's Blog, page 36
September 9, 2014
The Future is Here: DARPA’s Nervous System Implants
 Hard on the heels of their proposed BRAIN initiative – a collaborative research initiative to map the activity of every neuron in the human brain – DARPA has announced a bold new program to develop tiny electronic implants that will be able to interface directly with the human nervous system to control and regulate many different diseases and chronic conditions, such as arthritis, PTSD, Crohn’s disease, and depression.
Hard on the heels of their proposed BRAIN initiative – a collaborative research initiative to map the activity of every neuron in the human brain – DARPA has announced a bold new program to develop tiny electronic implants that will be able to interface directly with the human nervous system to control and regulate many different diseases and chronic conditions, such as arthritis, PTSD, Crohn’s disease, and depression.
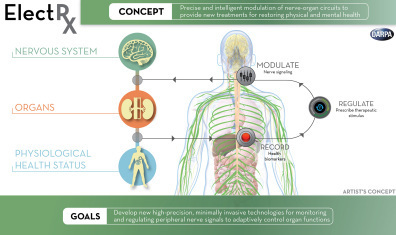
The program, called ElectRx (pronounced ‘electrics’), ultimately aims to replace medication with “closed-loop” neural implants which monitor the state of your health and then provide the necessary nerve stimulation to keep your organs and biological systems functioning properly. The work is primarily being carried out with US soldiers and veterans in mind, but the technology will certainly percolate down to civilians as well.
 The ElectRx program will focus the relatively new area of medical therapies called neuromodulation, which seeks to modulate the nervous system to improve neurological problem. Notable examples of this are cochlear implants which restore hearing by modulating your brain’s auditory nerve system, and deep brain stimulation (DBS) which is apparently capable of curing/regulating conditions like depression and Parkinson’s by overriding erroneous neural spikes.
The ElectRx program will focus the relatively new area of medical therapies called neuromodulation, which seeks to modulate the nervous system to improve neurological problem. Notable examples of this are cochlear implants which restore hearing by modulating your brain’s auditory nerve system, and deep brain stimulation (DBS) which is apparently capable of curing/regulating conditions like depression and Parkinson’s by overriding erroneous neural spikes.
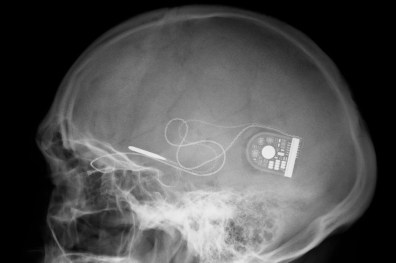
So far, these implants have been fairly large, which makes implantation fairly invasive and risky. Most state-of-the-art implants also lack precision, with most placing the stimulating electrodes in roughly the right area, but which are unable to target a specific bundles of nerves. With ElectRx, DARPA wants to miniaturize these neuromodulation implants so that they’re the same size as a nerve fiber.
 This way they can be implanted with a minimally invasive procedure (through a needle) and attached to specific nerve fibers, for very precise stimulation. While these implants can’t regulate every condition or replace every medication (yet), they could be very effective at mitigating a large number of conditions. A large number of conditions are caused by the nervous system misfiring, like inflammatory diseases, brain and mental health disorders.
This way they can be implanted with a minimally invasive procedure (through a needle) and attached to specific nerve fibers, for very precise stimulation. While these implants can’t regulate every condition or replace every medication (yet), they could be very effective at mitigating a large number of conditions. A large number of conditions are caused by the nervous system misfiring, like inflammatory diseases, brain and mental health disorders.
Currently, a variety of drugs are used to try and cajole these awry neurons and nerves back in-line by manipulating various neurotransmitters. However, the science behind these drugs is not yet exact, relying heavily on a trial-and-error approach and often involving serious side-effects. Comparatively, an electronic implant that could “catch” the misfire, cleans up the signal, and then retransmits it would be much more effective.
 As DARPA’s Doug Weber explained:
As DARPA’s Doug Weber explained:
The technology DARPA plans to develop through the ElectRx program could fundamentally change the manner in which doctors diagnose, monitor and treat injury and illness. Instead of relying only on medication — we envision a closed-loop system that would work in concept like a tiny, intelligent pacemaker. It would continually assess conditions and provide stimulus patterns tailored to help maintain healthy organ function, helping patients get healthy and stay healthy using their body’s own systems.
Despite requiring a lot of novel technological breakthroughs, DARPA is planning to perform human trials of ElectRx in about five years. The initial goal will be improving the quality of life for US soldiers and veterans. And while they have yet to announce which conditions they will be focusing on, it is expected that something basic like arthritis will be the candidate – though there are expectations that PTSD will become a source sooner other than later.
 And this is just the latest neurological technology being developed by DARPA. Earlier in the year, the agency announced a similar program to develop a brain implant that can restore lost memories and experiences. A joint fact sheet released by the Department of Defense and the Veteran’s Association revealed that DARPA also secured 78 million dollars to build the chips as part of the government’s Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) program.
And this is just the latest neurological technology being developed by DARPA. Earlier in the year, the agency announced a similar program to develop a brain implant that can restore lost memories and experiences. A joint fact sheet released by the Department of Defense and the Veteran’s Association revealed that DARPA also secured 78 million dollars to build the chips as part of the government’s Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) program.
While DARPA’s ElectRx announcement is purely focused on the medical applications of miniature neural implants, there are of course a variety of other uses that might arise from elective implantation – for soldiers as well as civilians. With a few well-placed implants in a person’s spine, they could flip a switch and ignore any pain reported by your limbs, allowing them to withstand greater physical stress or ignore injuries.
 Implants placed in muscle fibers could also provide added electrostimulation to provide extra boosts of raw muscle power. And With precision-placed implants around the right nerve fibers, people could gain manual control of their organs, allowing them to speed up or slow down their hearts, turbo-charge their livers, or tweak just about any other function of their bodies.
Implants placed in muscle fibers could also provide added electrostimulation to provide extra boosts of raw muscle power. And With precision-placed implants around the right nerve fibers, people could gain manual control of their organs, allowing them to speed up or slow down their hearts, turbo-charge their livers, or tweak just about any other function of their bodies.
The age of the Transhuman looms, people!
Source: extremetech.com, motherboard.vice.com, darpa.mil


September 8, 2014
Is the Universe One Big Hologram?
 “You know how I can tell we’re not in the Matrix? If we were, the food would be better.” Thus spoke Sheldon Cooper, the socially-challenged nerd from The Big Bang Theory. And yet, there is actually a scientific theory that posits that the universe itself could be a 2D hologram that is painted on some kind of cosmological horizon and only pops into 3D whenever we observe it (aka. always).
“You know how I can tell we’re not in the Matrix? If we were, the food would be better.” Thus spoke Sheldon Cooper, the socially-challenged nerd from The Big Bang Theory. And yet, there is actually a scientific theory that posits that the universe itself could be a 2D hologram that is painted on some kind of cosmological horizon and only pops into 3D whenever we observe it (aka. always).
And in what may be the most mind-boggling experiment ever, the US Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab) seeks to test this theory for the first time. Their tool for this is the Holometer, a device which has been under construction for a couple of years. It is now operating at full power and will gather data for the next year or so, at which time it will seek to uncover if the universe is a hologram, and what it’s composed of.
 The current prevailing theories about how the universe came to be are the Big Bang, the Standard Model of particle physics, quantum mechanics, and classical physics. These hypotheses and models don’t fully answer every question about how the universe came to be or continues to persist – which is why scientists are always investigating other ideas, such as supersymmetry or string theory.
The current prevailing theories about how the universe came to be are the Big Bang, the Standard Model of particle physics, quantum mechanics, and classical physics. These hypotheses and models don’t fully answer every question about how the universe came to be or continues to persist – which is why scientists are always investigating other ideas, such as supersymmetry or string theory.
The holographic universe principle is part of string theory – or at least not inconsistent with it – and goes something like this: From our zoomed out vantage point, the universe seems to be a perfectly formed enclave of 4D spacetime. But what happens if you keep zooming in, past the atomic and subatomic, until you get down to the smallest possible unit that can exist in the universe?
 In explaining their theory, the scientists involved make much of the analogy of moving closer to an old-style TV until you can see the individual pixels. The holographic principle suggests that, if you zoom in far enough, we will eventually see the pixels of the universe. It’s theorized that these universal pixels are about 10 trillion trillion times smaller than an atom (where things are measured in Planck units).
In explaining their theory, the scientists involved make much of the analogy of moving closer to an old-style TV until you can see the individual pixels. The holographic principle suggests that, if you zoom in far enough, we will eventually see the pixels of the universe. It’s theorized that these universal pixels are about 10 trillion trillion times smaller than an atom (where things are measured in Planck units).
The Holometer at Fermilab, which on the hunt for these pixels of the universe, is essentially an incredibly accurate clock. It consists of a twin-laser interferometer, which – as the name suggests – extracts information from the universe by measuring interference to the laser beams. Each interferometer directs a one-kilowatt laser beam at a beam splitter and then down two 40-m (130-ft) arms located at right-angles to one another.
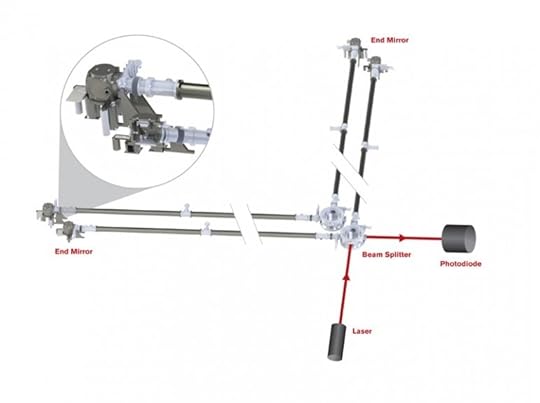 These beams are then reflected back towards the source, where they are combined and analyzed for any traces of interference. As Craig Hogan, the developer of the holographic noise theory and a director at Fermilab, explained:
These beams are then reflected back towards the source, where they are combined and analyzed for any traces of interference. As Craig Hogan, the developer of the holographic noise theory and a director at Fermilab, explained:
We want to find out whether space-time is a quantum system just like matter is. If we see something, it will completely change ideas about space we’ve used for thousands of years.
After any outside influences are removed, any remaining fluctuations – measured by slightly different frequencies or arrival times – could be caused by the ever-so-slight quantum jitter of these universal pixels. If these universal pixels exist, then everything we see, feel, and experience in the universe is actually encoded in these 2D pixels. One major difficulty in such a test will be noise – aka. “Holographic noise” – which they expect to be present at all frequencies.
 To mitigate this, the Holometer is testing at frequencies of many megahertz so that motions contained in normal matter are claimed not to be a problem. The dominant background noise of radio wave interference will be the most difficult to filter out, according to the team. As Holometer lead scientist Aaron Chou explained:
To mitigate this, the Holometer is testing at frequencies of many megahertz so that motions contained in normal matter are claimed not to be a problem. The dominant background noise of radio wave interference will be the most difficult to filter out, according to the team. As Holometer lead scientist Aaron Chou explained:
If we find a noise we can’t get rid of, we might be detecting something fundamental about nature – a noise that is intrinsic to space-time.
This would have some serious repercussions. For a start, it would mean that spacetime itself is a quantum system, just like matter. The theory that the universe consists of matter and energy would be annulled, replaced with the concept that the universe is made of information encoded into these universal pixels, which in turn create the classical concepts of matter and energy.
 And of course, if the universe is just a 3D projection from a 2D cosmological horizon, where exactly is that cosmological horizon? And does this mean that everything we know and love is just a collection of quantum information carrying 2D bits? And perhaps most importantly (from our point of view at least) what does that make us? Is all life just a collection of pixels designed to entertain some capricious audience?
And of course, if the universe is just a 3D projection from a 2D cosmological horizon, where exactly is that cosmological horizon? And does this mean that everything we know and love is just a collection of quantum information carrying 2D bits? And perhaps most importantly (from our point of view at least) what does that make us? Is all life just a collection of pixels designed to entertain some capricious audience?
All good and, if you think about it, incredibly time-honored questions. For has it not been suggested by many renowned philosophies that life is a deception, and death an escape? And do not the Hindu, Buddhist and Abrahamic religions tells us that our material existence is basically a facade that conceals our true reality? And were the ancient religions not all based on the idea that man was turned loose in a hostile world for the entertainment of the gods?
Well, could be that illusion is being broadcast in ultra-high definition! And getting back to The Big Bang Theory, here’s Leonard explaining the hologram principle to Penny, complete with holograms:
Sources: extremetech.com, gizmag.com


The Future is Here: Sweat-Powered Smart Tatoo
 Smart tattoos are the hot ticket item of modern medicine, combining ultra-thin electronics with flexible materials. When they become commonplace, they will be a great way to monitor vital signs and health. The only thing that seems to be holding them back, is finding a way to power them. Tiny batteries are one possibility, but lack practicality, and microwaves are several years away from being feasible.
Smart tattoos are the hot ticket item of modern medicine, combining ultra-thin electronics with flexible materials. When they become commonplace, they will be a great way to monitor vital signs and health. The only thing that seems to be holding them back, is finding a way to power them. Tiny batteries are one possibility, but lack practicality, and microwaves are several years away from being feasible.
Luckily, Joseph Wang – a researchers from UCSD – has come up with a way to generate power for these devices without using any external equipment. The secret, is to harness electrons from lactate acid secreted in sweat. These acids are produced when our muscles work to exhaustion, a waste product that causes muscles to “burn”, but which the brain thrives upon. Hence why it is the endpoint in lactate’s metabolization cycle.
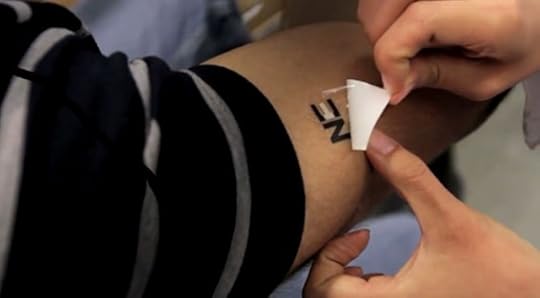 When lactate was discovered to be released in sweat, exercise physiologists began developing sensor technology to measure its levels in the sweat and blood. Wang has taken the next logical step of adding provisions to accumulate charge when lactate is enzymatically sensed. By embedding enzymes that process lactate into the tattoo, he was able to extract 70 microwatts per cm² of skin.
When lactate was discovered to be released in sweat, exercise physiologists began developing sensor technology to measure its levels in the sweat and blood. Wang has taken the next logical step of adding provisions to accumulate charge when lactate is enzymatically sensed. By embedding enzymes that process lactate into the tattoo, he was able to extract 70 microwatts per cm² of skin.
The only catch with this tattoo is that you need to be hot – as in pedaling your heart out on a bike for 30 minutes – to get the lactate out. That, however, may not be a barrier to this technology, since it is possible to selectively activate the sympathetic nerves that control the sweat glands in a discrete patch of skin. That way, you override the normal control and can sweat without the heat or exertion.
 The other part of the puzzle would be to actually generate the lactic acid. Preferably, this would be done locally as well, rather than having to have high levels circulating in the blood. But in the end, such steps would not even be necessary considering that a vitals and health monitoring that occurs into a workout – after an initial warm-up and good sweat have taken place – could be just what the doctor ordered (no pun intended!).
The other part of the puzzle would be to actually generate the lactic acid. Preferably, this would be done locally as well, rather than having to have high levels circulating in the blood. But in the end, such steps would not even be necessary considering that a vitals and health monitoring that occurs into a workout – after an initial warm-up and good sweat have taken place – could be just what the doctor ordered (no pun intended!).
Other researchers have already imagined e-tattoos to read your thoughts and desires, either by reading unvocalized words or EEG readings. And compared to past generations of sensor devices, these tattoos represent a sophisticated electronic package with on-board signal processing and communications. With a discrete way to power such devices, a formidable tool for self discovery might be had.
Source: extremetech.com, acs.org


September 6, 2014
News from Space: Space Launch Systems Good to Go!
 NASA’s Space Launch System, the US’s first exploration-class spacecraft since the Space Shuttle, is a central component in the agency’s plan to restore its ability to independently launch missions into space. An after a thorough review of cost and engineering issues, NASA managers formally approved the mammoth rocket past the whiteboard formulation stage and moved it into full-scale development.
NASA’s Space Launch System, the US’s first exploration-class spacecraft since the Space Shuttle, is a central component in the agency’s plan to restore its ability to independently launch missions into space. An after a thorough review of cost and engineering issues, NASA managers formally approved the mammoth rocket past the whiteboard formulation stage and moved it into full-scale development.
As the world’s most powerful rocket ever built and is intended to take astronauts farther beyond Earth into deep space than ever before possible. This includes the first-ever manned mission to Mars, the Asteroid Belt, and perhaps other planets and moons throughout the Solar System as well. The first SLS mission should lift off no later than 2018, sending the Orion capsule around the Moon, with asteroid and Mars-bound missions following after 2030 or 2032.
 NASA began the SLS’s design process back in 2011. Back then, the stated goal was to try and re-use as many Space Shuttle components and get back into deep space as quickly and as cost effectively as possible. But now that the formulation stage has been completed, and focus has shifted to actually developing and fabricating the launch system’s millions of constituent components, what kind of missions the SLS will be capable of has become much clearer.
NASA began the SLS’s design process back in 2011. Back then, the stated goal was to try and re-use as many Space Shuttle components and get back into deep space as quickly and as cost effectively as possible. But now that the formulation stage has been completed, and focus has shifted to actually developing and fabricating the launch system’s millions of constituent components, what kind of missions the SLS will be capable of has become much clearer.
At a press briefing that took place at their Operations Mission Directorate in Washington, Aug. 27th, NASA officials shared details about the maiden test launch. Known as EM-1, the launch is targeted for November 2018 and will involve the SLS carrying an uncrewed Orion spacecraft on a journey lasting roughly three weeks that will take it beyond the Moon to a distant retrograde orbit.
 Previously NASA had been targeting Dec. 2017 for the inaugural launch from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. But the new Nov. 2018 target date has resulted from the rigorous assessment of the technical, cost and scheduling issues. The decision to move forward with the SLS comes after a wide ranging review of the technical risks, costs, schedules and timing known as Key Decision Point C (KDP-C).
Previously NASA had been targeting Dec. 2017 for the inaugural launch from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. But the new Nov. 2018 target date has resulted from the rigorous assessment of the technical, cost and scheduling issues. The decision to move forward with the SLS comes after a wide ranging review of the technical risks, costs, schedules and timing known as Key Decision Point C (KDP-C).
As Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot, who oversaw the review process, said at the briefing:
After rigorous review, we’re committing today to a funding level and readiness date that will keep us on track to sending humans to Mars in the 2030s – and we’re going to stand behind that commitment. Our nation is embarked on an ambitious space exploration program. We are making excellent progress on SLS designed for missions beyond low Earth orbit. We owe it to the American taxpayers to get it right.
 The SLS involved in the test flight will be configured to its 70-metric-ton (77-ton) version. By comparison, the Saturn V — which took NASA astronauts to the Moon — had a max Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) payload capacity of 118 metric tons, but it has long since been retired. SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy, which is a much smaller and cheaper rocket than the SLS, will be able to put 55 metric tons into LEO.
The SLS involved in the test flight will be configured to its 70-metric-ton (77-ton) version. By comparison, the Saturn V — which took NASA astronauts to the Moon — had a max Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) payload capacity of 118 metric tons, but it has long since been retired. SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy, which is a much smaller and cheaper rocket than the SLS, will be able to put 55 metric tons into LEO.
With the retirement of the Space Shuttle, there aren’t really any heavy lift launchers in operation. Ariane 5, produced by commercial spacecraft manufacturer Arianespace, can only do 21 metric tons to LEO, while the Delta IV (United Launch Alliance) can do 29 metric tons to LEO. In short, NASA’s Space Launch System should be by far the most powerful operational rocket when it arrives in 2017-2018.
 SpaceX could decide to scale-up the Falcon Heavy, but the rocket’s main purpose is to compete with United Launch Alliance and Arianespace, which currently own the incredibly lucrative heavy lift market. A payload capacity of 55 tons is more than enough for that purpose. A capacity of 150 tons is only for rockets that are intended to aim at targets that are much farther than geostationary orbit — such as the Moon, Mars or Europa.
SpaceX could decide to scale-up the Falcon Heavy, but the rocket’s main purpose is to compete with United Launch Alliance and Arianespace, which currently own the incredibly lucrative heavy lift market. A payload capacity of 55 tons is more than enough for that purpose. A capacity of 150 tons is only for rockets that are intended to aim at targets that are much farther than geostationary orbit — such as the Moon, Mars or Europa.
The SLS’s primary payload will be the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV), though it will undoubtedly be used to send other large spacecraft into deep space. The Orion capsule is what NASA will use to land astronauts on the Moon, captured asteroids, Mars, and any other manned missions throughout the Solar System. The first manned Orion launch, to a captured asteroid in lunar orbit, is scheduled to occur in 2021.
 Combined with SpaceX’s crewed Dragon spacecraft, Boeing’s CST-100, and a slew of crowd-funded projects to place boots on Mars and Europa in the next few decades, things are looking up for human space exploration!
Combined with SpaceX’s crewed Dragon spacecraft, Boeing’s CST-100, and a slew of crowd-funded projects to place boots on Mars and Europa in the next few decades, things are looking up for human space exploration!
Source: universetoday.com, extremetech.com


News from Mars: Beam Me to Mars
 In the latest ambitious plan to make space exploration accessible to the general public, Uwingu has unveiled a new campaign where people can send messages and pictures to the Red Planet. It’s called “Beam Me to Mars”, and the company is inviting people to contribute, for a fee, to a “digital shout-out” that will send messages from Earth to Mars on Nov. 28 — the 50th anniversary of Mars exploration.
In the latest ambitious plan to make space exploration accessible to the general public, Uwingu has unveiled a new campaign where people can send messages and pictures to the Red Planet. It’s called “Beam Me to Mars”, and the company is inviting people to contribute, for a fee, to a “digital shout-out” that will send messages from Earth to Mars on Nov. 28 — the 50th anniversary of Mars exploration.
The first successful Mars mission, NASA’s Mariner 4 – launched on Nov. 28, 1964 – performed the first flyby of the Red Planet and returned the first pictures of the Martian surface. This was the first time that images were captured of another planet and returned from deep space. and their depiction of a cratered, seemingly dead world largely changed the view of the scientific community on life on Mars.
 According to representative from Uwingu, “Beam Me to Mars” celebrates that landmark effort in a new and original way by inspiring people to get on board with Martian exploration. Other goals include raising lots of money to fund space science, exploration and education (Uwingu’s stated chief purpose) and letting policymakers know how important space exploration is to their constituents.
According to representative from Uwingu, “Beam Me to Mars” celebrates that landmark effort in a new and original way by inspiring people to get on board with Martian exploration. Other goals include raising lots of money to fund space science, exploration and education (Uwingu’s stated chief purpose) and letting policymakers know how important space exploration is to their constituents.
As CEO Alan Sterm, a planetary scientist and former NASA science chief, said in an interview with Space.com:
We want it to inspire people. There has never been an opportunity before for people of Earth to shout out across the solar system their hopes and wishes for space exploration, for the future of mankind — for any of that… We want to make an impression on leaders. The more messages, the bigger impression it makes. If this thing goes viral, and it becomes the thing to do, then it’ll make a huge impression.
 For $4.95, people can beam their name (or someone else’s) to Mars, whereas $9.95 gets people a chance to beam a name and a 100-character message. $19.95 gets a 1,000-character note instead of the shorter one, and for those willing to spend $99 will be able to send their name, a long message and an image of their choosing. All messages submitted for “Beam Me to Mars” will also be hand-delivered to Congress, NASA and the United Nations.
For $4.95, people can beam their name (or someone else’s) to Mars, whereas $9.95 gets people a chance to beam a name and a 100-character message. $19.95 gets a 1,000-character note instead of the shorter one, and for those willing to spend $99 will be able to send their name, a long message and an image of their choosing. All messages submitted for “Beam Me to Mars” will also be hand-delivered to Congress, NASA and the United Nations.
Submissions must be made via uwingu.com by Nov. 5. And the company – whose name means “sky” in Swahili – and its transmission partner, communications provider Universal Space Network, will use radio telescopes to beam the messages at Mars on Nov. 28 at the rate of 1 million bits per second. The transmission, traveling at the speed of light, will reach the Red Planet on that day in just 15 minutes.
 For comparison, it took Mariner 4 more than seven months to get to Mars a half-century ago. The probe didn’t touch down, but its historic flyby in July 1965 provided the first up-close look at the surface of another planet from deep space. Mariner 4’s observations revealed that Mars is a dry and mostly desolate world, dashing the hopes of those who had viewed it as a world crisscrossed by canals and populated by little green men.
For comparison, it took Mariner 4 more than seven months to get to Mars a half-century ago. The probe didn’t touch down, but its historic flyby in July 1965 provided the first up-close look at the surface of another planet from deep space. Mariner 4’s observations revealed that Mars is a dry and mostly desolate world, dashing the hopes of those who had viewed it as a world crisscrossed by canals and populated by little green men.
Already, several celebrities have signed on to the campaign, including actors Seth Green and wife Clare Grant, George (“Sulu”) Takei of Star Trek fame and his husband Brad, Bill Nye “The Science Guy”, astronaut and former ISS commander Chris Hadfield, commercial astronaut Richard Garriott, former NASA senior executive Lori Garver, Pulitzer winning author and playwright Dava Sobel, and Author and screenwriter Homer Hickam.
 This is not the first Mars effort for Uwingu, which was founded in 2012. In February, the company launched its “People’s Map of Mars,” asking the public to name Red Planet landmarks for a small fee. To date, people have named more than 12,000 Mars craters, and Uwingu has set aside more than $100,000 for grants. And when it comes to getting the general public involved with space science and travel, they are merely one amongst many. The age of public space exploration is near, people!
This is not the first Mars effort for Uwingu, which was founded in 2012. In February, the company launched its “People’s Map of Mars,” asking the public to name Red Planet landmarks for a small fee. To date, people have named more than 12,000 Mars craters, and Uwingu has set aside more than $100,000 for grants. And when it comes to getting the general public involved with space science and travel, they are merely one amongst many. The age of public space exploration is near, people!
Sources: space.com, uwingu.com, (2)


The Future is Here: First Brain-to-Brain Interface!
 In a first amongst firsts, a team of international researchers have reported that they have built the first human-to-human brain-to-brain interface; allowing two humans — separated by the internet — to consciously communicate with each other. One researcher, attached to a brain-computer interface (BCI) in India, successfully sent words into the brain of another researcher in France, who was wearing a computer-to-brain interface (CBI).
In a first amongst firsts, a team of international researchers have reported that they have built the first human-to-human brain-to-brain interface; allowing two humans — separated by the internet — to consciously communicate with each other. One researcher, attached to a brain-computer interface (BCI) in India, successfully sent words into the brain of another researcher in France, who was wearing a computer-to-brain interface (CBI).
In short, the researchers have created a device that allows people to communicate telepathically. And it’s no surprise, given the immense amount of progress being made in the field. Over the last few years, brain-computer interfaces that you can plug into your computer’s USB port have been commercially available. And in the last couple of years we’ve seen advanced BCIs that can be implanted directly into your brain.
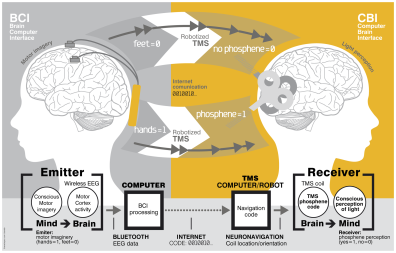 Creating a brain-to-brain connection is a bit more difficult though, as it requires that brain activity not only be read, but inputted into someone else’s brain. Now, however, a team of international researchers have cracked it. On the BCI side of things, the researchers used a fairly standard EEG (electroencephalogram) from Neuroelectrics. For the CBI, which requires a more involved setup, a transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) rig was used.
Creating a brain-to-brain connection is a bit more difficult though, as it requires that brain activity not only be read, but inputted into someone else’s brain. Now, however, a team of international researchers have cracked it. On the BCI side of things, the researchers used a fairly standard EEG (electroencephalogram) from Neuroelectrics. For the CBI, which requires a more involved setup, a transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) rig was used.
To break the process down, the BCI reads the sender’s thoughts, like to move their hands or feet, which are then broken down into binary 1s and 0s. These encoded thoughts are then transmitted via the internet (or some other network) to the recipient, who is wearing a TMS. The TMS is focused on the recipient’s visual cortex, and it receives a “1″ from the sender, it stimulates a region in the visual cortex that produces a phosphene.
 This is a phenomenon whereby a person sees flashes of light, without light actually hitting the retina. The recipient “sees” these phosphenes at the bottom of their visual field, and by decoding the flashes — phosphene flash = 1, no phosphene = 0 — the recipient can “read” the word being sent. While this is certainly a rather complex way of sending messages from one brain to another, for now, it is truly state of the art.
This is a phenomenon whereby a person sees flashes of light, without light actually hitting the retina. The recipient “sees” these phosphenes at the bottom of their visual field, and by decoding the flashes — phosphene flash = 1, no phosphene = 0 — the recipient can “read” the word being sent. While this is certainly a rather complex way of sending messages from one brain to another, for now, it is truly state of the art.
TMS is somewhat similar to TDCS (transcranial direct-current stimulation), in that it can stimulate regions of neurons in your brain. But instead of electrical current, it uses magnetism, and is a completely non-invasive way of stimulating certain sections of the brain and allowing a person to think and feel a certain way. In short, there doesn’t need to be any surgery or electrodes implanted into the user’s brain to make it happen.
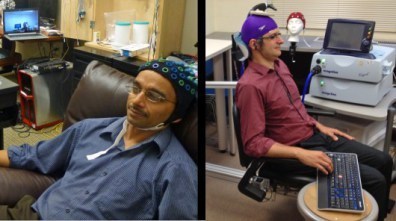 This method also neatly sidestep the fact that we really don’t know how the human brain encodes information. And so, for now, instead of importing a “native” message, we have to use our own encoding scheme (binary) and a quirk of the visual cortex. And even if it does seem a little bit like hard work, there’s no denying that this is a conscious, non-invasive brain-to-brain connection.
This method also neatly sidestep the fact that we really don’t know how the human brain encodes information. And so, for now, instead of importing a “native” message, we have to use our own encoding scheme (binary) and a quirk of the visual cortex. And even if it does seem a little bit like hard work, there’s no denying that this is a conscious, non-invasive brain-to-brain connection.
With some refinement, it’s not hard to imagine a small, lightweight EEG that allows the sender to constantly stream thoughts back to the receiver. In the future, rather than vocalizing speech, or vainly attempting to vocalize one’s own emotions, people could very well communicate their thoughts and feelings via a neural link that is accommodated by simple headbands with embedded sensors.
 And imagine a world where instant messaging and video conferencing have the added feature of direct thought sharing. Or an The Internet of Thoughts, where people can transfer terabytes worth of brain activity the same way they share video, messages and documents. Remember, the internet began as a small-scale connection between a few universities, labs and research projects.
And imagine a world where instant messaging and video conferencing have the added feature of direct thought sharing. Or an The Internet of Thoughts, where people can transfer terabytes worth of brain activity the same way they share video, messages and documents. Remember, the internet began as a small-scale connection between a few universities, labs and research projects.
I can foresee a similar network being built between research institutions where professors and students could do the same thing. And this could easily be followed by a militarized version where thoughts are communicated instantly between command centers and bunkers to ensure maximum clarity and speed of communication. My how the world is shaping up to be a science fiction novel!
Sources: extremetech.com, neurogadget.com, dailymail.co.uk


September 4, 2014
Climate Crisis: Solar-Powered Oasis to Feed Desert Cities
 Desertification is one of the biggest threats associated with Climate Change. In places like North Africa and the Middle East, where countries already import up to 90% of their food, the spread of the desert due to increasing temperatures and diminished rainfall is made worse by the fact that cities in the region continue to grow. It’s a situation that is getting more expensive and energy-intensive at a time when things need to be getting more cost-effective and sustainable.
Desertification is one of the biggest threats associated with Climate Change. In places like North Africa and the Middle East, where countries already import up to 90% of their food, the spread of the desert due to increasing temperatures and diminished rainfall is made worse by the fact that cities in the region continue to grow. It’s a situation that is getting more expensive and energy-intensive at a time when things need to be getting more cost-effective and sustainable.
Luckily, a team of architects hopes to create a new agricultural system that could grow and deliver food in the desert. It’s called OAXIS, a conceptual design for a modular set of prefab greenhouses, covered in solar panels, which would extend from a city into the desert. The design of the buildings aims to keep out intense summer heat while the solar panels would power the rest of the building’s infrastructure and send extra energy back into the city.
 Conceived by Forward Thinking Architecture, a Barcelona-based firm, the concept seeks to combine flexibility with a minimal carbon footprint. Towards this end, they chose to forgo usual transportation and create a unique conveyor system that would deliver produce without the use of any fossil fuels. The conveyor belt would be underground so it could keep running in a straight line even if buildings were in the way.
Conceived by Forward Thinking Architecture, a Barcelona-based firm, the concept seeks to combine flexibility with a minimal carbon footprint. Towards this end, they chose to forgo usual transportation and create a unique conveyor system that would deliver produce without the use of any fossil fuels. The conveyor belt would be underground so it could keep running in a straight line even if buildings were in the way.
Inside the prefab greenhouses, farmers would grow crops like tomatoes, lettuce, and strawberries using a hydroponic system that can reduce fertilizers and pesticides and save 80% of the water used in traditional agriculture, in part by recycling and reusing it. As for where the water comes from, the designers suggest that groundwater could supply the farm’s needs, but many Middle Eastern countries already rely on desalination.
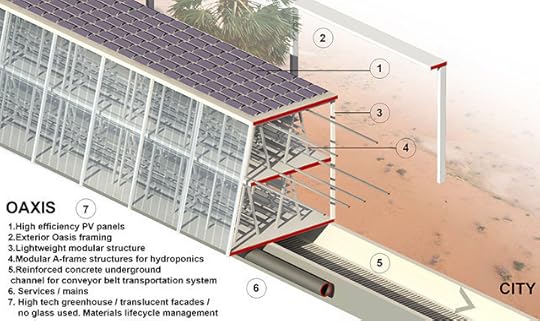 Ideally, desert populations would be small enough that the region’s sparse rainfall could support local crops. But that’s not the reality. In addition, a small part of the recycled water would also be used to create an outdoor garden for education. As architect Javier Ponce, principal and founder of Forward Thinking Architecture, explained:
Ideally, desert populations would be small enough that the region’s sparse rainfall could support local crops. But that’s not the reality. In addition, a small part of the recycled water would also be used to create an outdoor garden for education. As architect Javier Ponce, principal and founder of Forward Thinking Architecture, explained:
We thought it cannot only be a farming-only building, it must have a pedagogical approach and have to be attractive in order to become a biodiversity hub which can be visited by the local people and visitors… The cities should be smaller, denser, and compact, but this is not the current situation for some of the Arabian peninsula cities since they have exponentially grown and attract more people and workers. There has been a rapid urbanization in the area since the middle of the 20th century.
The project, he hopes, could help supply food as climate change makes the situation even more challenging. Already, countries in the worst-affected regions are desperately looking for solutions. For example, Qatar has already invested hundreds of millions in a plan to grow as much local food as possible by 2030. Other countries in the region, like Kuwait, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Jordan, and the desert-locked Saudi Arabia are expected to follow.
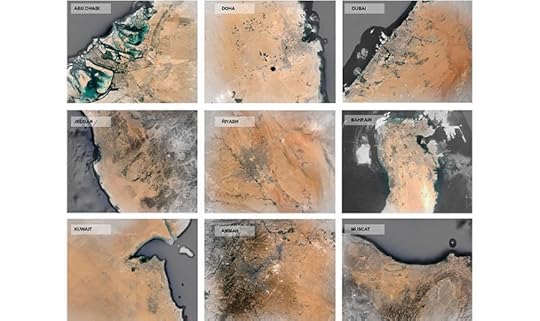 These regions in particular have felt the pressure brought on by the escalating price of importing food. This pressure is exacerbated due to the disappearance of peak oil, which accounted for the vast majority of this region’s wealth. However, the project has farther-reaching implications, as Climate Change threatens to turn much of the world’s arable land into dry, drought-ridden plains.
These regions in particular have felt the pressure brought on by the escalating price of importing food. This pressure is exacerbated due to the disappearance of peak oil, which accounted for the vast majority of this region’s wealth. However, the project has farther-reaching implications, as Climate Change threatens to turn much of the world’s arable land into dry, drought-ridden plains.
At the same time, it takes into account the need to reduce reliance on water and fossil-fuels. As our population continues to skyrocket, a smarter and more sustainable use of available resources are always needed. As Ponce explained:
The OAXIS project is an alternative or complementary way to respond to the food insecurity and water scarcity of the region in a self-sufficient way. It aims to help reduce the food imports to feed part of the people in a nearby future based on renewable energies.
And be sure to check out this OAXIS promotional video, courtesy of Forward Thinking Architecture:
Sources: fastcoexist.com, forwardthinkingarchitecture


September 3, 2014
Climate Crisis: London’s River Village and Pools
 One of the greatest challenges facing future urban planning is the very real prospect of running out of land. In addition to urban sprawl encroaching on neighboring farmlands, the concentration of people at the core eventually creates a situation where open spaces become incredibly scarce. Luckily, the city of London – one of the largest and most densely populated cities in the world – is coming up with some innovative solutions.
One of the greatest challenges facing future urban planning is the very real prospect of running out of land. In addition to urban sprawl encroaching on neighboring farmlands, the concentration of people at the core eventually creates a situation where open spaces become incredibly scarce. Luckily, the city of London – one of the largest and most densely populated cities in the world – is coming up with some innovative solutions.
For starters, the city is developing the area around some former dockyards in East London to accommodate a floating neighborhood. Borrowing from similar projects that were initiated in the Netherlands to prepare for rising sea levels, London’s new river-based housing program is designed to place housing in the one spot that hasn’t been converted to high-rise apartments or suburban dwellings.
 Experts from the Netherlands are helping to plan the new “floating village,” which will include 50 floating homes around a neighborhood square that comes complete with floating restaurants, offices, and shops, and possibly a floating swimming pool (more on that below). A floating walkway will lead back to land, where the city plans a much larger development with tens of thousands of new homes.
Experts from the Netherlands are helping to plan the new “floating village,” which will include 50 floating homes around a neighborhood square that comes complete with floating restaurants, offices, and shops, and possibly a floating swimming pool (more on that below). A floating walkway will lead back to land, where the city plans a much larger development with tens of thousands of new homes.
Earlier in its history, the area, known as the Royal Docks, served hundreds of cargo and passenger ships each day. The three docks were the largest enclosed docks in the world – 250 acres of water and over 1000 acres of land – and got more use than any other port in London. But they haven’t been in use for the last several decades, and that’s why the city wants to transform the area.
 As Richard Blakeway, the city’s deputy mayor for housing, land and property
As Richard Blakeway, the city’s deputy mayor for housing, land and property
With demand for new homes in London soaring, we need to put every scrap of available land to the best possible use. Tens of thousands of new homes, workspace, leisure, and cultural facilities are being developed . . . The ‘Floating Village’ will be yet another draw, restoring London’s docklands to their former glory as a centre of enterprise and bringing jobs, growth, homes and visitors.
On the same front, the city of London is also contemplating turning its river waters into a massive public pools project. Known as the Thames Bath Project, this idea was inspired by similar ideas where swimming pools have been created out of waterways. For example, New York has a project called +Pool, which has raised more than $300,000 in crowd-funding, and looks set for a 2016 launch.
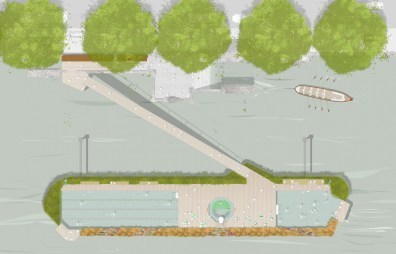
 The Thames Baths Project is similar, aiming to create a freshwater lagoon amid the meandering old waterway. The consortium responsible consists of Studio Octopi, Civic Engineers and Jonathan Cook Landscape Architects, all of whom won the competition last year to come up with new river uses. Initially, they hoped to create a pool using water from the Thames that would be filtered and treated.
The Thames Baths Project is similar, aiming to create a freshwater lagoon amid the meandering old waterway. The consortium responsible consists of Studio Octopi, Civic Engineers and Jonathan Cook Landscape Architects, all of whom won the competition last year to come up with new river uses. Initially, they hoped to create a pool using water from the Thames that would be filtered and treated.
However, that plan has since been updated and improved to something a little more sanitary. Now, they plan to pump in freshwater, rejected the New York City idea of filtering the water as it enters the pool space because of the concern of sewage. And though London has a major sewage system upgrade planned, the designers are worried it won’t be ready in time to ensure sufficient water quality.
 As Chris Romer-Lee, director of Octopi, explained:
As Chris Romer-Lee, director of Octopi, explained:
We’re using freshwater because of the sewage overflows from the aging [Sir Joseph William] Bazalgette sewers. They dump millions of tons of sewage into the river after even the shortest rain storm. A filtration system could work. We’ve been looking at natural swimming pools and the filtering systems they use. But the +Pool filtering system is as yet unproven.
The design calls for floating pontoons with space for three pools – one large, one medium, and one for paddling. A thick layer of vegetation will mark the edges and a ramp leading off the side will connect swimmers back to firm ground. The $8.5 million plans are still awaiting approval from the city, but, if all goes well, the baths could be completed sometime early in the next decade.
 The purpose, according to Romer-Lee, is about re-purposing something that would otherwise be forgotten:
The purpose, according to Romer-Lee, is about re-purposing something that would otherwise be forgotten:
We need these baths to reconnect Londoners with their largest public space. The river is used extensively for transporting building materials, passengers and the like but is increasingly becoming something that Londoners look over and don’t engage with.
Meanwhile, Berlin also has a proposal for an open river pool, as does Copenhagen, which actually already has swimming in its harbor. No doubt, it won’t be long before others follow. In fact, the idea of re-purposing public spaces that have fallen into disuse is becoming increasingly popular – not just as a response to sprawl, but as an innovative solution of what to do with infrastructure that has fallen into disuse.
Cities like Detroit, Philadelphia, Washington DC and Hamilton, Ontario and Montreal, Quebec – just to name a few – all might want to consider getting on board with this…
Sources: fastcoexist.com, (2)


Climate Crisis: London’s Floating Village and River Pools
 One of the greatest challenges facing future urban planning is the very real prospect of running out of land. In addition to urban sprawl encroaching on neighboring farmlands, the concentration of people at the core eventually creates a situation where open spaces become incredibly scarce. Luckily, the city of London – one of the largest and most densely populated cities in the world – is coming up with some innovative solutions.
One of the greatest challenges facing future urban planning is the very real prospect of running out of land. In addition to urban sprawl encroaching on neighboring farmlands, the concentration of people at the core eventually creates a situation where open spaces become incredibly scarce. Luckily, the city of London – one of the largest and most densely populated cities in the world – is coming up with some innovative solutions.
For starters, the city is developing the area around some former dockyards in East London to accommodate a floating neighborhood. Borrowing from similar projects that were initiated in the Netherlands to prepare for rising sea levels, London’s new river-based housing program is designed to place housing in the one spot that hasn’t been converted to high-rise apartments or suburban dwellings.
 Experts from the Netherlands are helping to plan the new “floating village,” which will include 50 floating homes around a neighborhood square that comes complete with floating restaurants, offices, and shops, and possibly a floating swimming pool (more on that below). A floating walkway will lead back to land, where the city plans a much larger development with tens of thousands of new homes.
Experts from the Netherlands are helping to plan the new “floating village,” which will include 50 floating homes around a neighborhood square that comes complete with floating restaurants, offices, and shops, and possibly a floating swimming pool (more on that below). A floating walkway will lead back to land, where the city plans a much larger development with tens of thousands of new homes.
Earlier in its history, the area, known as the Royal Docks, served hundreds of cargo and passenger ships each day. The three docks were the largest enclosed docks in the world – 250 acres of water and over 1000 acres of land – and got more use than any other port in London. But they haven’t been in use for the last several decades, and that’s why the city wants to transform the area.
 As Richard Blakeway, the city’s deputy mayor for housing, land and property
As Richard Blakeway, the city’s deputy mayor for housing, land and property
With demand for new homes in London soaring, we need to put every scrap of available land to the best possible use. Tens of thousands of new homes, workspace, leisure, and cultural facilities are being developed . . . The ‘Floating Village’ will be yet another draw, restoring London’s docklands to their former glory as a centre of enterprise and bringing jobs, growth, homes and visitors.
On the same front, the city of London is also contemplating turning its river waters into a massive public pools project. Known as the Thames Bath Project, this idea was inspired by similar ideas where swimming pools have been created out of waterways. For example, New York has a project called +Pool, which has raised more than $300,000 in crowd-funding, and looks set for a 2016 launch.
 The Thames Baths Project is similar, aiming to create a freshwater lagoon amid the meandering old waterway. The consortium responsible consists of Studio Octopi, Civic Engineers and Jonathan Cook Landscape Architects, all of whom won the competition last year to come up with new river uses. Initially, they hoped to create a pool using water from the Thames that would be filtered and treated.
The Thames Baths Project is similar, aiming to create a freshwater lagoon amid the meandering old waterway. The consortium responsible consists of Studio Octopi, Civic Engineers and Jonathan Cook Landscape Architects, all of whom won the competition last year to come up with new river uses. Initially, they hoped to create a pool using water from the Thames that would be filtered and treated.
However, that plan has since been updated and improved to something a little more sanitary. Now, they plan to pump in freshwater, rejected the New York City idea of filtering the water as it enters the pool space because of the concern of sewage. And though London has a major sewage system upgrade planned, the designers are worried it won’t be ready in time to ensure sufficient water quality.
 As Chris Romer-Lee, director of Octopi, explained:
As Chris Romer-Lee, director of Octopi, explained:
We’re using freshwater because of the sewage overflows from the aging [Sir Joseph William] Bazalgette sewers. They dump millions of tons of sewage into the river after even the shortest rain storm. A filtration system could work. We’ve been looking at natural swimming pools and the filtering systems they use. But the +Pool filtering system is as yet unproven.
The design calls for floating pontoons with space for three pools – one large, one medium, and one for paddling. A thick layer of vegetation will mark the edges and a ramp leading off the side will connect swimmers back to firm ground. The $8.5 million plans are still awaiting approval from the city, but, if all goes well, the baths could be completed sometime early in the next decade.
 The purpose, according to Romer-Lee, is about re-purposing something that would otherwise be forgotten:
The purpose, according to Romer-Lee, is about re-purposing something that would otherwise be forgotten:
We need these baths to reconnect Londoners with their largest public space. The river is used extensively for transporting building materials, passengers and the like but is increasingly becoming something that Londoners look over and don’t engage with.
Meanwhile, Berlin also has a proposal for an open river pool, as does Copenhagen, which actually already has swimming in its harbor. No doubt, it won’t be long before others follow. In fact, the idea of re-purposing public spaces that have fallen into disuse is becoming increasingly popular – not just as a response to sprawl, but as an innovative solution of what to do with infrastructure that has fallen into disuse.
Cities like Detroit, Philadelphia, Washington DC and Hamilton, Ontario and Montreal, Quebec – just to name a few – all might want to consider getting on board with this…
Sources: fastcoexist.com, (2)


September 2, 2014
Immortality Inc: Regrowing Body Parts
 Anyone who has ever observed a lizard must not have failed to notice that they are capable of detaching their tails, and then regenerating them from scratch. This propensity for “spontaneous regeneration” is something that few organisms possess, and mammals are sadly not one of them. But thanks to a team of Arizona State University scientists, the genetic recipe behind this ability has finally been unlocked.
Anyone who has ever observed a lizard must not have failed to notice that they are capable of detaching their tails, and then regenerating them from scratch. This propensity for “spontaneous regeneration” is something that few organisms possess, and mammals are sadly not one of them. But thanks to a team of Arizona State University scientists, the genetic recipe behind this ability has finally been unlocked.
This breakthrough is a small part of a growing field of biomedicine that seeks to improve human health by tampering with the basic components (i.e. our DNA). The research, which was funded by grants from the National Institutes of Health and Arizona Biomedical Research Commission, also involved scientists from the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Translational Genomic Research Institute, and Michigan State University.
 According to Prof. Kenro Kusumi, lead author of a paper on the genetic study, lizards are the most closely-related animals to humans that can regenerate entire appendages. They also share the same genetic language as us, so it’s theoretically possible that we could do what they do, if only we knew which genes to use and in what amounts. As Kusumi explains in the paper, which was published Aug. 20 in the journal PLOS ONE. :
According to Prof. Kenro Kusumi, lead author of a paper on the genetic study, lizards are the most closely-related animals to humans that can regenerate entire appendages. They also share the same genetic language as us, so it’s theoretically possible that we could do what they do, if only we knew which genes to use and in what amounts. As Kusumi explains in the paper, which was published Aug. 20 in the journal PLOS ONE. :
Lizards basically share the same toolbox of genes as humans. We discovered that they turn on at least 326 genes in specific regions of the regenerating tail, including genes involved in embryonic development, response to hormonal signals, and wound healing.
Other animals, such as salamanders, frog tadpoles, and fish, can also regenerate their tails. During tail regeneration, they all turn on genes in what is called the ‘Wnt pathway’ — a process that is required to control stem cells in many organs such as the brain, hair follicles and blood vessel. However, lizards have a unique pattern of tissue growth that is distributed throughout the tail.
 It takes lizards more than 60 days to regenerate a functional tail — forming a complex regenerating structure with cells growing into different tissues at a number of sites along the tail. According to Katsumi, harnessing this would be a boon for medicine for obvious reasons:
It takes lizards more than 60 days to regenerate a functional tail — forming a complex regenerating structure with cells growing into different tissues at a number of sites along the tail. According to Katsumi, harnessing this would be a boon for medicine for obvious reasons:
Using next-generation technologies to sequence all the genes expressed during regeneration, we have unlocked the mystery of what genes are needed to regrow the lizard tail. By following the genetic recipe for regeneration that is found in lizards, and then harnessing those same genes in human cells, it may be possible to regrow new cartilage, muscle or even spinal cord in the future.
The researchers also hope their findings will also help repairing birth defects and treating diseases such as arthritis. Given time, and enough positive results, I think it would be fair to expect that Google’s Clinical Immortality subsidiary – known as Calico – will buy up all the necessary rights. Then, it shouldn’t be more than a decade before a gene treatments is produced that will allow for spontaneous regeneration and the elimination of degenerative diseases.
The age of post-mortal is looming people. Be scared/enthused!
Sources: kurzweil.net, gizmag.com





