Paul Gilster's Blog, page 33
June 7, 2022
Solar Sailing: The Beauties of Diffraction

Knowing of Grover Swartzlander’s pioneering work on diffractive solar sails, I was not surprised to learn that Amber Dubill, who now takes the idea into a Phase III study for NIAC, worked under Swartzlander at the Rochester Institute of Technology. The Diffractive Solar Sailing project involves an infusion of $3 million over the next two years, with Dubill (JHU/APL) heading up a team that includes experts in traditional solar sailing as well as optics and metamaterials. A potential mission to place sails into a polar orbit around the Sun is one possible outcome.
But let’s fall back to that phrase ‘traditional solar sailing,’ which made me wince even as I wrote it. Solar sailing relies on the fact that while solar photons have no mass, they do impart momentum, enough to nudge a sail with a force that over time results in useful acceleration. Among those of us who follow interstellar concepts, such sails are well established in the catalog of propulsion possibilities, but to the general public, the idea retains its novelty. Sails fire the imagination: I’ve found that audiences love the idea of space missions with analogies to the magnificent clipper ships of old.
We know the method works, as missions like Japan’s IKAROS and NASA’s NanoSail-D2 as well as the Planetary Society’s LightSail 2 have all demonstrated. Various sail missions – NEA Scout and Solar Cruiser stand out here – are in planning to push the technology forward. These designs are all reflective and depend upon the direction of sunlight, with sail designs that are large and as thin as possible. What the new NIAC work will examine is not reflection but diffraction, which involves how light bends or spreads as it encounters obstacles. Thus a sail can be built with small gratings embedded within the thin film of its structure, and the case Swartzlander has been making for some time now is that such sails would be more efficient.
A diffractive sail can work with incoming light at a variety of angles using new metamaterials, in this case ‘metafilms,’ that are man-made structures with properties unlike those of naturally occurring materials. Sails made of them can be essentially transparent, meaning they will not absorb large amounts of heat from the Sun, which could compromise sail substrates.
Moreover, these optical films allow for lower-mass sails that are steered by electro-optic methods as opposed to bulky mechanical systems. They can maintain more efficient positions while facing the Sun, which also makes them ideal for the use of embedded photovoltaic cells and the collection of solar power. Reflective sails need to be tilted to achieve best performance, but the inability to fly face-on in relation to the Sun reduces the solar flux upon the sail.
The Phase III work for NIAC will take Dubill and team all the way from further analyzing the properties of diffractive sails into development of an actual mission concept involving multiple spacecraft that can collectively monitor solar activity, while also demonstrating and fine-tuning the sail strategy. The description of this work on the NIAC site explains the idea:
The innovative use of diffracted rather than reflected sunlight affords a higher efficiency sun-facing sail with multiplier effects: smaller sail, less complex guidance, navigation, and attitude control schemes, reduced power, and non-spinning bus. Further, propulsion enhancements are possible by the reduction of sailcraft mass via the combined use of passive and active (e.g., switchable) diffractive elements. We propose circumnavigating the sun with a constellation of diffractive solar sails to provide full 4π (e.g., high inclination) measurements of the solar corona and surface magnetic fields. Mission data will significantly advance heliophysics science, and moreover, lengthen space weather forecast times, safeguarding world and space economies from solar anomalies.
Delightfully, a sail like this would not present the shiny silver surface of the popular imagination but would instead create a holographic effect that Dubill’s team likens to the rainbow appearance of a CD held up to the Sun. And they need not be limited to solar power. Metamaterials are under active study by Breakthrough Starshot because they can be adapted for laser-based propulsion, which Starshot wants to use to reach nearby stars through a fleet of small sails and tiny payloads. The choice of sail materials that can survive the intense beam of a ground-based laser installation and the huge acceleration involved is crucial.
The diffractive sail concept has already been through several iterations at NIAC, with the testing of different types of sail materials. Grover Swartzlander received a Phase I grant in 2018, followed by a Phase II in 2019 to pursue the work, a needed infusion of funding given that before 2017, few papers on diffractive space sails existed in the literature. In a 2021 paper, Dubill and Swartzlander went into detail on the idea of a constellation of sails monitoring solar activity. From the paper:
We have proposed launching a constellation of satellites throughout the year to build up a full-coverage solar observatory system. For example a constellation of 12 satellites could be positioned at 0.32 AU and at various inclinations about the sun within 6 years: Eight at various orbits inclined by 60 and four distributed about the solar ecliptic. We know of no conventionally powered spacecraft that can readily achieve this type of orbit in such a short time frame. Based on our analysis, we find that diffractive solar sails provide a rapid and cost-effective multi-view option for investigating heliophysics.
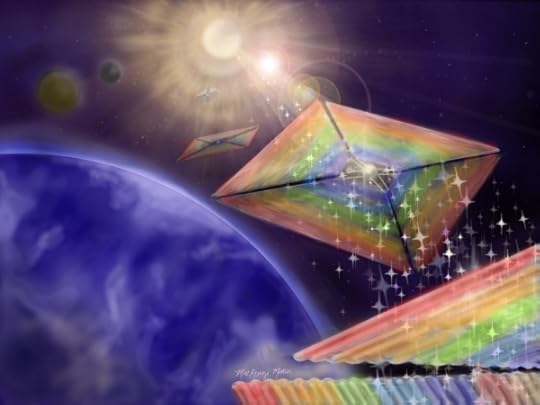

Image: The new Diffractive Solar Sailing concept uses light diffraction to more efficiently take advantage of sunlight for propulsion without sacrificing maneuverability. Incidentally, this approach also produces an iridescent visual effect. Credit: NASA/MacKenzi Martin.
Dubill thinks an early mission involving diffractive sails can quickly prove their value:
“While this technology can improve a multitude of mission architectures, it is poised to significantly impact the heliophysics community’s need for unique solar observation capabilities. Through expanding the diffractive sail design and developing the overall sailcraft concept, the goal is to lay the groundwork for a future demonstration mission using diffractive lightsail technology.”
A useful backgrounder on diffractive sails and their potential use in missions to the Sun is Amber Dubill’s thesis at RIT, “Attitude Control for Circumnavigating the Sun with Diffractive Solar Sails” (2020), available through RIT Scholar Works. See also Dubill & Swartzlander, “Circumnavigating the sun with diffractive solar sails,” Acta Astronautica
Volume 187 (October 2021), pp. 190-195 (full text). Grover Swartzlander’s presentation “Diffractive Light Sails and Beam Riders,” is available on YouTube.

June 3, 2022
Venus Life Finder: Scooping Big Science

I’ve maintained for years that the first discovery of life beyond Earth, assuming we make one, will be in an extrasolar planetary system, through close and eventually unambiguous analysis of an exoplanet’s atmosphere. But Alex Tolley has other thoughts. In the essay below, he looks at a privately funded plan to send multiple probes into the clouds of Venus in search of organisms that can survive the dire conditions there. And while missions this close to home don’t usually occupy us because of Centauri Dreams’ deep space focus, Venus is emerging as a prominent exception, given recent findings about anomalous chemistry in its atmosphere. Are the clouds of Venus concealing an ecosystem this close to home?
IntroductionThe discovery of phosphine (PH3), an almost unambiguous biosignature on Earth, in the clouds of Venus in 2021 increased interest in reinvestigating the planet’s clouds for life, a scientific goal that had been on hiatus since the last atmospheric entry and lander vehicle mission, Vega-2 in 1984. While the recent primary target for life discovery has been Mars, whether extinct, or extant in the subsurface, it has taken nearly half a century since the Viking landers to once again look directly for Martian life with the Perseverance rover.
However, if the PH3 discovery is real (and it is supported by a reanalysis of the Pioneer Venus probe data), then maybe we have been looking at the wrong planet. The temperate zone in the Venusian clouds is the nearest habitable zone to Earth. If life does exist there [see Figure 1] despite the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4), then it is likely to be in this temperate zone layer, having evolved to live in such conditions.
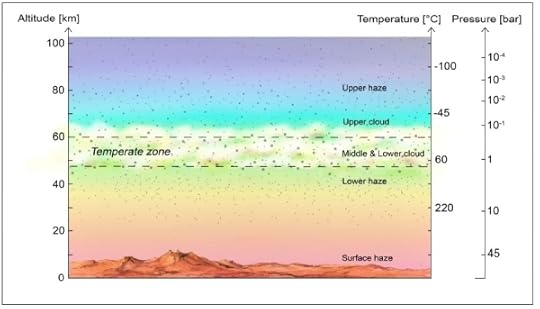
Figure 1. Schematic of Venus’ atmosphere. The cloud cover on Venus is permanent and continuous, with the middle and lower cloud layers at temperatures that are suitable for life. The clouds extend from altitudes of approximately 48 km to 70 km. Credit: J Petkowska.
But why launch a private mission, rather than leave it to a well-funded, national one?
National space agencies haven’t been totally idle. There are four planned missions, two by NASA (DAVINCI+, VERITAS), one by ESA (EnVision) to investigate Venus, all due to be launched around 2030, as well a Russian one (Venera-D) to be launched at the same time:
VERITAS and DAVINCI+ are both Discovery-class missions. They are budgeted up to $500 million each. EnVision is ESA’s mission launching in the same timeframe. All three missions have target launch dates ranging from 2028 (DAVINCI+, VERITAS) to 2031 (EnVision). As with any large budget mission, these missions have taken a long time to develop. DAVINCI was proposed in 2015, the revised DAVINCI+ proposed again in 2019, and selected in 2021 for a 2028 launch. VERITAS was proposed in 2015, and selected only in 2021. Then there is the seven years of development, testing, and finally launch in 2028. EnVision was selected in 2021, and faces a decade before launch.[5,6,7].
DAVINCI+’s goals include:
1. Understanding the evolution of the atmosphere
2. Investigating the possibility of an early ocean
3. Returning high resolution images of the geology to determine if plate tectonics ever existed.
[PG note: NASA GSFC just posted a helpful overview of this mission.]
VERITAS’s rather similar goals involve answering these questions:
1. How has the geology of Venus evolved over time?
2. What geologic processes are currently operating on it?
3. Has water been present on or near its surface?
EnVision’s goals include:
1. Determining the level and nature of current activity
2. Determining the sequence of geological events that generated its range of surface features
3. Assessing whether Venus once had oceans or was hospitable for life
4. Understanding the organizing geodynamic framework that controls the release of internal heat over the history of the planet
In addition, Russia has the Venera-D mission planned for a 2029 launch that has a lander. One of its goals is to analyze the chemical composition of the cloud aerosols. [8]
There is considerable overlap in the science goals of the four missions, and notably none have the search for life as a science goal, although the 3rd EnVision science goal could be the preparatory “follow the water” approach before a follow-up mission to search for life if there is evidence that Venus did once have oceans.
As with the Mars missions post Viking up to Perseverance, none of these missions is intended to look directly for life itself. Given the 2021 selection date for all three missions and the end of decade launch dates, it will be somewhat frustrating for scientists interested in searching for life on Venus.
Cutting through the slow progress of the national missions, the privately funded Venus Life Finder mission aims to start the search directly. The mission to look for life is focused on small instruments and a low-cost launcher. Not just one but a series of missions is planned, each increasing in capability. The first is intended to launch in 2023, and if the three anticipated missions are successful, Venus Life Finder would scoop the big science missions in being the first to detect life in Venus should it exist.
Some history of our views about VenusBefore the space age, both Venus and Mars were thought to have life. Mars stood out because of the seasonal dark areas and Schiaparelli’s observation of channels, followed by Lowell’s interpretation of these channels as canals, which carried the implication of intelligence. Von Braun’s “Mars Projekt” (1952) inferred that the atmosphere was thin, but the astronauts would just need O2 masks, and his technical tale had the astronauts discover an advanced Martian civilization. The popular science book “The Exploration of Mars” (1956) written by Willy Ley and Wernher Von Braun and illustrated by Chesley Bonestell, supported the idea of Martian vegetation, speculating that it was likely to be something along the lines of hardy terrestrial lichens.
Unlike Mars, the surface of Venus was not observable, just the dense permanent cloud cover. It was believed that Venus was younger than Earth and that the clouds covered a primeval swamp full of animals like those in our planet’s past. With the many probes starting in 1962 with the successful flyby of Mariner 2, it was determined that the surface of Venus was a hellish 438-482 C (820-900 degrees F), by far the hottest place in the Solar System. Worse, the clouds were not water as on Earth, but H2SO4, in a concentration that would rapidly destroy terrestrial life. Seemingly Venus was lifeless.
Some scientists thought Venus was much more Earth Like in the past, and that a runaway greenhouse state accounted for its current condition. If Venus was more Earth Like, there could have been oceans, and with them, life. On Earth, bacteria are carried up from the surface by air currents and have been found living in clouds and are part of the cloud formation process. Bacteria have been found in Earth’s stratosphere too. Bacteria living in the Venusian oceans would likely have been carried up into the atmosphere and occupy a similar habitat. If so, it has been hypothesized that bacterial life may have evolved to live in the increasingly acidic Venusian clouds just as terrestrial extreme acidophiles have evolved, and that this life is the source of the detected PH3.
The First Science InstrumentIs there any other evidence for life on Venus? Using two instruments, a particle size spectrometer and a nephelometer, the Pioneer Venus probe (1978) suggested that some tiny droplets in the clouds were not spherical, as physics would predict, and therefore might be living [unicellular] organisms.
But these probes could not resolve some anomalies of the Venusian atmosphere that might as a whole, indicate life.
1. Anomalous UV Absorber – spatial and temporal variability reminiscent of algal blooms.
2. Non-spherical large droplets – possible cells
3. Non-volatile elements such as phosphorus that could reduce the H2SO4 concentration and a required element of terrestrial life
4. Gases in disequilibrium, including PH3, NH3
Enter the Venus Life Finder (VLF) team, led by Principal Investigator Sara Seager, whose team includes the noted Venus expert David Grinspoon. The project isfunded by Breakthrough Initiatives. The initial idea was to do some laboratory experiments to determine if the assumptions about possible life in the clouds were valid.
As the VLF document states up front:
The concept of life in the Venus clouds is not new, having been around for over half a century. What is new is the opportunity to search for life or signs of life directly in the Venus atmosphere with scientific instrumentation that is both significantly more technologically advanced and greatly miniaturized since the last direct in situ probes to Venus’ atmosphere in the 1980s.
The big objection to life in the Venusian clouds is their composition: extremely concentrated sulfuric acid. Any terrestrial organism subjected to the acid is dissolved. [There is a reason serial killers use this method to remove evidence of their victims!]
To check on the constraints of cloud conditions on potential life and the ability to detect organic molecules, the VLF team conducted some experiments that showed that:
1. Organic molecules will autofluoresce in up to 70% H2SO4. Therefore organic molecules are detectable in the Venusian cloud droplets.
2. Lipids will form micelles in up to 70% H2SO4 and are detectable. Cell membranes are therefore possible containers for biological processes.
3. Terrestrial macromolecules – proteins, sugars, and nucleic acids – all rapidly become denatured in H2SO4, ruling out false positives from terrestrial contamination
4. The Miller-Urey experiment will form organic molecules in H2SO4. Therefore abiogenesis of precursor molecules is also possible on Venus.
With these results, the team focused on building a single instrument to investigate both the shapes of particles and the presence of organic compounds. Non-spherical droplet shapes containing organic compounds would be a possible indication of life. This instrument, an Autofluorescing Nephelometer, is being developed from an existing instrument, as shown in figure 2.

Figure 2. Evolution of the Autofluorescing Nephelometer (AFN) from the Backscatter Cloud Probe (BCP) (left of arrow) to the Backscatter Cloud Probe with Polarization Detection (BCPD) (right of arrow). The BCPD is further evolved to the AFN by replacement of the BCPD laser with a UV source and addition of fluorescence-detection compatible optics.
All this in a package of just 1 kg to be carried in the atmosphere entry vehicle.
Reaching VenusThe VLF team has partnered with the New Space company Rocket Lab which is developing its Venus mission. The company has small launchers that are marketed to orbit tiny satellites for organizations that don’t want to use piggy-backed rides with other satellites as part of a large payload. Its Electron rocket launcher has so far racked up successes. The Electron can place up to 300kg in LEO.
For the Venus mission, the payload includes the Photon rocket to make the interplanetary flight and deliver a 20 kg Venus atmosphere entry probe that includes the 1 kg AFN science package. To reach Venus, the Photon rocket using bi-propellant generates the needed 4 km/s delta V. It employs multiple Oberth maneuvers in LEO to most efficiently raise the orbit’s apogee until it is on an escape trajectory to Venus. Travel time is several months.
The Electron rocket, the Photon rocket, and the entry probe are shown in the next three figures.
The photon rocket powers the cruise phase from LEO to Venus intercept. This rocket uses an unspecified hypergolic fuel and will carry the entry probe across the 60 million km trajectory of its 3-month Venus mission.

Figure 3a. Electron small launch vehicle. The Electron ELV has successfully launched 146 satellite missions to date for a low per launch cost. A recent test of a helicopter retrieval of the 1st stage indicates that reusability is possible using this in-flight capture approach, therefore potentially saving costs. The kick stage in the image is replaced by the Photon rocket for interplanetary flight.
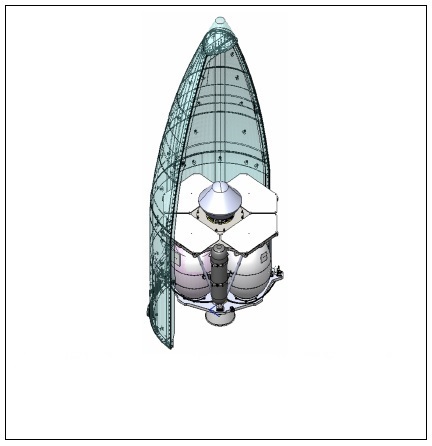
Figure 3b. High-energy Photon rocket and Venus entry probe.
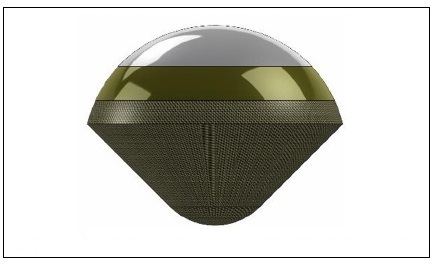
Figure 3c. The small Venus probe is a 45-degree half-angle cone approximately 0.2m in diameter. Credit: NASA ARC.
Fast and CheapThe cost of the mission to Venus is not publicized, but we know the cost of a launch of the Electron rocket to LEO is $7.5m [12]. Add the photon cruise stage, the entry probe, the science instruments, the operations and science teams. All in, a fraction of the Discovery mission costs, but with a faster payback and more focussed science. Rocket Lab has not launched an interplanetary mission before, so there is risk of failure. The company does have other interplanetary plans, including a Mars mission using two Photon cruise stage rockets for a Mars orbiter mission in 2024.
Is the Past the Future?The small probe and dedicated instrument package, while contrasting with the big science missions of the national programs, harkens back to the early scientific exploration of space at the beginning of the space age. The smaller experimental rockets had limited launch capacity and the scientific payloads had to be small. Some examples include the Pioneer 4 lunar probe [11] and the Explorer series [10].
These relatively simple early experiments resulted in some very important discoveries. The lunar flyby Pioneer 4, launched in 1958, massed just 6.67 kg, with a diameter of just 0.23 m, a size comparable to the VLF’s first mission [11]. These early missions could be launched with some frequency, each probe or satellite containing specific instruments for the scientific goal. Today with miniaturization, instruments can be made smaller and controlled with computers, allowing more sophisticated measurements and onboard data analysis. Miniaturization continues, especially in electronics.
Breakthrough StarShot’s interstellar concept aims at have a 1 gm sail with onboard computer, sensors, and communications, increasing capabilities, reducing costs, and multiplying the numbers of such probes. With private funding now equaling that of the early space age experiments, and the lower costs of access to space, there has been a flowering of the technology and range of such private space experiments. The VLF mission is an exemplar of the possibilities of dedicated scientific interplanetary missions bypassing the need to be part of “big science” missions.
Just possibly, this VLF series of missions will return results from Venus’ atmosphere that show the first evidence of extraterrestrial life in our system. Such a success would be a scoop with significant ramifications.
References1. Seager S, et al “Venus Life Finder Study” (2021) Web accessed 02/18/2022
https://venuscloudlife.com/venus-life-finder-mission-study/
2. Clarke A The Exploration of Space (1951), Temple Press Ltd
3. Ley, W, Von Braun W, Bonestell C The Exploration of Mars (1956), Sidgwick & Jackson
4. RocketLab “Electron Rocket: web accessed 02/18/2022 https://www.rocketlabusa.com/launch/electron/
5. Wikipedia “List of missions to Venus” en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_missions_to_Venus
6. Wikipedia “DAVINCI” en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_missions_to_Venus
7. Wikipedia “VERITAS” en.wikipedia.org/wiki/VERITAS_(spacecraft)
8. Wikipedia “EnVision” en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EnVision
9. Wikipedia “Venera-D” en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Venera-D
10. LePage, A, “Vintage Micro: The Second-Generation Explorer Satellites” (2015) www.drewexmachina.com/2015/09/03/vintage-micro-the-second-generation-explorer-satellites/
11. LePage, A, “Vintage Micro: The Pioneer 4 Lunar Probe” (2014)
www.drewexmachina.com/2014/08/02/vintage-micro-the-pioneer-4-lunar-probe/
12. Wikipedia “Rocket Lab Electron”, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rocket_Lab_Electron

May 31, 2022
A Radium Age Take on the ‘Wait Equation’

If you’ll check Project Gutenberg, you’ll find Bernhard Kellermann’s novel The Tunnel. Published in 1913 by the German house S. Fischer Verlag and available on Gutenberg only in its native tongue (finding it in English is a bit more problematic, although I’ve seen it on offer from online booksellers occasionally), the novel comes from an era when the ‘scientific romance’ was yielding to an engineering-fueled uneasiness with what technology was doing to social norms.

Kellermann was a poet and novelist whose improbable literary hit in 1913, one of several in his career, was a science fiction tale about a tunnel so long and deep that it linked the United States with Europe. It was written at a time when his name was well established among readers throughout central Europe. His 1908 novel Ingeborg saw 131 printings in its first thirty years, so this was a man often discussed in the coffee houses of Berlin and Vienna.
Image: Author Bernhard Kellermann, author of The Tunnel and other popular novels as well as poetry and journalistic essays. Credit: Deutsche Fotothek of the Saxon State Library / State and University Library Dresden (SLUB).
The Tunnel sold 10,000 copies in its first four weeks, and by six months later had hit 100,000, becoming the biggest bestseller in Germany in 1913. It would eventually appear in 25 languages and sell over a million copies. By way of comparison – and a note about the vagaries of fame and fortune – Thoman Mann’s Death in Venice, also published that year, sold 18,000 copies for the whole year, and needed until the 1930s to reach the 100,000 mark. Short-term advantage: Kellermann.
I mention this now obscure novel for a couple of reasons. For one thing, it’s science fiction in an era before popular magazines filled with the stuff had begun to emerge to fuel the public imagination. This is the so-called ‘radium age,’ recently designated as such by Joshua Glenn, whose series for MIT press reprints works from the period.
We might define an earlier era of science fiction, one beginning with the work of, say, Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley and on through H. G. Wells, and a later one maybe dating from Hugo Gernsback’s creation of Amazing Stories in 1926 (Glenn prefers to start the later period at 1934, which is a few years before the beginning of the Campbell era at Astounding, where Heinlein, Asimov and others would find a home), but in between is the radium age. Here’s Glenn, from a 2012 article in Nature:
[Radium age novels] depict a human condition subverted or perverted by science and technology, not improved or redeemed. Aldous Huxley’s 1932 Brave New World, with its devastating satire on corporate tyranny, behavioral conditioning and the advancement of biotechnology, is far from unique. Radium-age sci-fi tends towards the prophetic and uncanny, reflecting an era that saw the rise of nuclear physics and the revelation that the familiar — matter itself — is strange, even alien. The 1896 discovery of radioactivity, which led to the early twentieth-century insight that the atom is, at least in part, a state of energy, constantly in movement, is the perfect metaphor for an era in which life itself seemed out of control.
All of which is interesting to those of us of a historical bent, but The Tunnel struck me forcibly because of the year in which it was published. Radiotelegraphy, as it was then called, had just been deployed across the Atlantic on the run from New York to Germany, a distance (reported in Telefunken Zeitschrift in April of that year) of about 6,500 kilometers. Communicating across oceans was beginning to happen, and it is in this milieu that The Tunnel emerged to give us a century-old take on what we in the interstellar flight field often call the ‘wait equation.’
How long do we wait to launch a mission given that new technology may become available in the future? Kellermann’s plot involved the construction of the tunnel, a tale peppered with social criticism and what German author Florian Illies calls ‘wearily apocalyptic fantasy.’ Illies is, in fact, where I encountered Kellermann, for his 2013 title 1913: The Year Before the Storm, now available in a deft new translation, delves among many other things into the literary and artistic scene of that fraught year before the guns of August. This is a time of Marcel Duchamp, of Picasso, of Robert Musil. The Illies book is a spritely read that I can’t recommend too highly if you like this sort of thing (I do).
In The Tunnel, it takes Kellermann’s crews 24 years of agonizing labor, but eventually the twin teams boring through the seafloor manage to link up under the Atlantic, and two years later the first train makes the journey. It’s a 24 hour trip instead of the week-long crossing of the average ocean liner, a miracle of technology. But it soon becomes apparent that nobody wants to take it. For even as work on the tunnel has proceeded, aircraft have accelerated their development and people now fly between New York and Berlin in less than a day.
The ‘wait equation’ is hardly new, and Kellermann uses it to bring all his skepticism about technological change to the fore. Here’s how Florian Illies describes the novel:
…Kellermann succeeds in creating a great novel – he understands the passion for progress that characterizes the era he lives in, the faith in the technically feasible, and at the same time, with delicate irony and a sense for what is really possible, he has it all come to nothing. An immense utopian project that is actually realized – but then becomes nothing but a source of ridicule for the public, who end up ordering their tomato juice from the stewardess many thousand meters not under but over the Atlantic. According to Kellermann’s wise message, we would be wise not to put our utopian dreams to the test.
Here I’ll take issue with Illies, and I suppose Kellermann himself. Is the real message that utopian dreams come to nothing? If so, then a great many worthwhile projects from our past and our future are abandoned in service of a judgment call based on human attitudes toward time and generational change. I wonder how we go about making that ‘wait equation’ decision. Not long ago, Jeff Greason told Bruce Dorminey that it would be easier to produce a mission to the nearest star that took 20 years than to figure out how to fund, much less to build, a mission that would take 200 years.
He’s got a point. Those of us who advocate long-term approaches to deep space also have an obligation to reckon with the hard practicalities of mission support over time, which is not only a technical but a sociological issue that makes us ask who will see the mission home. But I think we can also see philosophical purpose in a different class of missions that our species may one day choose to deploy. Missions like these:
1) Advanced AI will at some point negate the question of how long to wait if we assume spacecraft that can seamlessly acquire knowledge and return it to a network of growing information, a nascent Encyclopedia Galactica of our own devising that is not reliant on Earth. Ever moving outward, it would produce a wavefront of knowledge that theoretically would be useful not just to ourselves but whatever species come after us.
2) Human missions intended as generational, with no prospect of return to the home world, also operate without lingering connections to controllers left behind. Their purpose may be colonization of exoplanets, or perhaps simple exploration, with no intention of returning to planetary surfaces at all. Indeed, some may choose to exploit resources, as in the Oort Cloud, far from inner systems, separating from Earth in the service of particular research themes or ideologies.
3) Missions designed to spread life have no necessary connection with Earth once launched. If life is rare in the galaxy, it may be within our power to spread simple organisms or even revive/assemble complex beings, a melding of human and robotics. An AI crewed ship that raises human embryos on a distant world would be an example, or a far simpler fleet of craft carrying a cargo of microorganisms. Such journeys might take millennia to reach their varied targets and still achieve their purpose. I make no statement here about the wisdom of doing this, only noting it as a possibility.
In such cases, creating a ‘wait equation’ to figure out when to launch loses force, for the times involved do not matter. We are not waiting for data in our lifetimes but are acting through an imperative that operates on geological timeframes. That is to say, we are creating conditions that will outlast us and perhaps our civilizations, that will operate over stellar eras to realize an ambition that transcends humankind. I’m just brainstorming here, and readers may want to wrangle over other mission types that fit this description.
But we can’t yet launch missions like these, and until we can, I would want any mission to have the strongest possible support, financial and political, here on the home world if we are talking about many decades for data return. It’s hard to forget the scene in Robert Forward’s Rocheworld where at least one political faction actively debates turning off the laser array that the crew of a starship approaching Barnard’s Star will use to brake into the planetary system there. Political or social change on the home world has to be reckoned into the equation when we are discussing projects that demand human participation from future generations.
These things can’t be guaranteed, but they can be projected to the best of our ability, and concepts chosen that will maintain scientific and public interest for the duration needed. You can see why mission design is also partly a selling job to the relevant entities as well as to the public, something the team working on a probe beyond the heliopause at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Lab knows all too well.
Back to Bernhard Kellermann, who would soon begin to run afoul of the Nazis (his novel The Ninth November was publicly burned in Germany). He would later be locked out of the West German book trade because of his close ties with the East German government and his pro-Soviet views. He died in Potsdam in 1951.

Image: A movie poster showing Richard Dix and C. Aubrey Smith discussing plans for the gigantic project in Transatlantic Tunnel (1935). Credit: IMDB.
The Tunnel became a curiosity, and spawned an even more curious British movie by the same name (although sometimes found with the title Transatlantic Tunnel) starring Richard Dix and Leslie Banks. In the 1935 film, which is readily available on YouTube or various streaming platforms, the emphasis is on a turgid romance, pulp-style dangers overcome and international cooperation, with little reflection, if any, on the value of technology and how it can be superseded.
The interstellar ‘wait equation’ could use a movie of its own. I for one would like to see a director do something with van Vogt’s “Far Centaurus,” the epitome of the idea.
The Glenn paper is “Science Fiction: The Radium Age,” Nature 489 (2012), 204-205 (full text).

May 27, 2022
Microlensing: Expect Thousands of Exoplanet Detections

We just looked at how gravitational microlensing can be used to analyze the mass of a star, giving us a method beyond the mass-luminosity relationship to make the call. And we’re going to be hearing a lot more about microlensing, especially in exoplanet research, as we move into the era of the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (formerly WFIRST), which is scheduled to launch in 2027. A major goal for the instrument is the expected discovery of exoplanets by the thousands using microlensing. That’s quite a jump – I believe the current number is less than 100.
For while radial velocity and transit methods have served us well in establishing a catalog of exoplanets that now tops 5000, gravitational microlensing has advantages over both. When a stellar system occludes a background star, the lensing of the latter’s light can tell us much about the planets that orbit the foreground object. Whereas radial velocity and transits work best when a planet is in an orbit close to its star, microlensing can detect planets in orbits equivalent to the gas giants in our system.
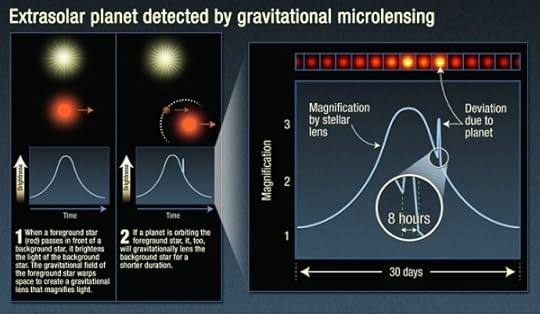
Image: This infographic explains the light curve astronomers detect when viewing a microlensing event, and the signature of an exoplanet: an additional uptick in brightness when the exoplanet lenses the background star. Credit: NASA / ESA / K. Sahu / STScI).
Moreover, we can use the technique to detect lower-mass planets in such orbits, planets far enough, for example, from a G-class star to be in its habitable zone, and small enough that the radial velocity signature would be tricky to tease out of the data. Not to mention the fact that microlensing opens up vast new areas for searching. Consider: TESS deliberately works with targets nearby, in the range of 100 light years. Kepler’s stars averaged about 1000 light years. Microlensing as planned for the Roman instrument will track stars, 200 million of them, at distances around 10,000 light years away as it looks toward the center of the Milky Way.
So this is a method that lets us see planets at a wide range of orbital distances and in a wide range of sizes. The trick is to work out the mass of both star and planet when doing a microlensing observation, which brings machine learning into the mix. Artificial intelligence algorithms can parse these data to speed the analysis, a major plus when we consider how many events the Roman instrument is likely to detect in its work.
The key is to find the right algorithms, for the analysis is by no means straightforward. Microlensing signals involve the brightening of the light from the background star over time. We can call this a ‘light curve,’ which it is, making sure to distinguish what’s going on here from the transit light curve dips that help identify exoplanets with that method. With microlensing, we are seeing light bent by the gravity of the foreground star, so that we observe brightening, but also splitting of the light, perhaps into various point sources, or even distorting its shape into what is called an Einstein ring, named of course after the work the great physicist did in 1936 in identifying the phenomenon. More broadly, microlensing is implied by all his work on the curvature of spacetime.
However the light presents itself, untangling what is actually present at the foreground object is complicated because more than one planetary orbit can explain the result. Astronomers refer to such solutions as degeneracies, a term I most often see used in quantum mechanics, where it refers to the fact that multiple quantum states can emerge with the same energy, as happens, for example, when an electron orbits one or the other way around a nucleus. How to untangle what is happening?
A new paper in Nature Astronomy moves the ball forward. It describes an AI algorithm developed by graduate student Keming Zhang at UC-Berkeley, one that presents what the researchers involved consider a broader theory that incorporates how such degeneracies emerge. Here is the university’s Joshua Bloom, in a blog post from last December, when the paper was first posted to the arXiv site:
“A machine learning inference algorithm we previously developed led us to discover something new and fundamental about the equations that govern the general relativistic effect of light- bending by two massive bodies… Furthermore, we found that the new degeneracy better explains some of the subtle yet pervasive inconsistencies seen [in] real events from the past. This discovery was hiding in plain sight. We suggest that our method can be used to study other degeneracies in systems where inverse-problem inference is intractable computationally.”
What an intriguing result. The AI work grows out of a two-year effort to analyze microlensing data more swiftly, allowing the fast determination of the mass of planet and star in a microlensing event, as well as the separation between the two. We’re dealing with not one but two brightness peaks in the brightness of the background star, and trying to deduce from this an orbital configuration that produced the signal. Thus far, the different solutions produced by such degeneracies have been ambiguous.
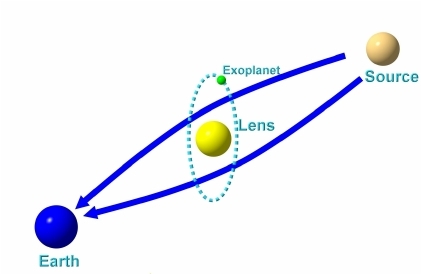
Image: Seen from Earth (left), a planetary system moving in front of a background star (source, right) distorts the light from that star, making it brighten as much as 10 or 100 times. Because both the star and exoplanet in the system bend the light from the background star, the masses and orbital parameters of the system can be ambiguous. An AI algorithm developed by UC Berkeley astronomers got around that problem, but it also pointed out errors in how astronomers have been interpreting the mathematics of gravitational microlensing. Credit: Research Gate.
Zhang and his fellow researchers applied microlensing data from a wide variety of orbital configurations to run the new AI algorithm through its paces. Let’s hear from Zhang himself:
“The two previous theories of degeneracy deal with cases where the background star appears to pass close to the foreground star or the foreground planet. The AI algorithm showed us hundreds of examples from not only these two cases, but also situations where the star doesn’t pass close to either the star or planet and cannot be explained by either previous theory. That was key to us proposing the new unifying theory.”
Thus to existing known degeneracies labeled ‘close-wide’ and ‘inner-outer,’ Zhang’s work adds the discovery of what the team calls an ‘offset’ degeneracy. An underlying order emerges, as the paper notes, from the offset degeneracy. In the passage from the paper below, a ‘caustic’ defines the boundary of the curved light signal. Italics mine:
…the offset degeneracy concerns a magnification-matching behaviour on the lens-axis and is formulated independent of caustics. This offset degeneracy unifies the close–wide and inner–outer degeneracies, generalises to resonant topologies, and upon re- analysis, not only appears ubiquitous in previously published planetary events with 2-fold degenerate solutions, but also resolves prior inconsistencies. Our analysis demonstrates that degenerate caustics do not strictly result in degenerate magnifications and that the commonly invoked close–wide degeneracy essentially never arises in actual events. Moreover, it is shown that parameters in offset degenerate configurations are related by a simple expression. This suggests the existence of a deeper symmetry in the equations governing 2-body lenses than previously recognised.
The math in this paper is well beyond my pay grade, but what’s important to note about the passage above is the emergence of a broad pattern that will be used to speed the analysis of microlensing lightcurves for future space-and ground-based observations. The algorithm provides a fit to the data from previous papers better than prior methods of untangling the degeneracies, but it took the power of machine learning to work this out.
It’s also noteworthy that this work delves deeply into the mathematics of general relativity to explore microlensing situations where stellar systems include more than one exoplanet, which could involve many of them. And it turns out that observations from both Earth and the Roman telescope – two vantage points – will make the determination of orbits and masses a good deal more accurate. We can expect great things from Roman.
The paper is Zhang et al., “A ubiquitous unifying degeneracy in two-body microlensing systems,” Nature Astronomy 23 May 2022 (abstract / preprint).

May 24, 2022
Proxima Centauri: Microlensing Yields New Data

It’s not easy teasing out information about a tiny red dwarf star, even when it’s the closest star to the Sun. Robert Thorburn Ayton Innes (1861-1933), a Scottish astronomer, found Proxima using a blink comparator in 1915, noting a proper motion similar to Alpha Centauri (4.87” per year), with Proxima about two degrees away from the binary. Finding out whether the new star was actually closer than Centauri A and B involved a competition with a man with a similarly august name, Joan George Erardus Gijsbertus Voûte, a Dutch astronomer working in South Africa. Voûte’s parallax figures were more accurate, but Innes didn’t wait for debate, and proclaimed the star’s proximity, naming it Proxima Centaurus.

The back and forth over parallax and the subsequent careers of both Innes and Voûte make for interesting reading. I wrote both astronomers up back in 2013 in Finding Proxima Centauri, but I’ll send you to my source for that article, Ian Glass (South African Astronomical Observatory), who published the details in the magazine African Skies (Vol. 11 (2007), p. 39). You can find the abstract here.
Image: Shining brightly in this Hubble image is our closest stellar neighbour: Proxima Centauri. Although it looks bright through the eye of Hubble, as you might expect from the nearest star to the Solar System, the star is not visible to the naked eye. Its average luminosity is very low, and it is quite small compared to other stars, at only about an eighth of the mass of the Sun. However, on occasion, its brightness increases. Proxima is what is known as a “flare star”, meaning that convection processes within the star’s body make it prone to random and dramatic changes in brightness. The convection processes not only trigger brilliant bursts of starlight but, combined with other factors, mean that Proxima Centauri is in for a very long life. Astronomers predict that this star will remain on the main sequence for another four trillion years, some 300 times the age of the current Universe. These observations were taken using Hubble’s Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2). Credit: NASA/ESA.
It’s a long way from blink comparators to radial velocity measurements, the latter of which enabled our first exoplanet discoveries back in the 1990s, measuring how the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet could pull its parent star away from us, then towards us on the other side of the orbit, with all the uncertainties that implies. We’re still drilling into the details of Proxima Centauri, and radial velocity occupies us again today. The method depends on the mass of the star, for if we know that, we can then make inferences about the mass of the planets we find around it.
Thus the discovery of Proxima Centauri’s habitable zone planet, Proxima b, a planet we’d like to know much more about given its enticing minimum mass of about 1.3 Earths and an orbital period of just over 11 days. Radial velocity methods at exquisite levels of precision rooted out Proxima b and continue to yield new discoveries.
We’re learning a lot about Alpha Centauri itself – the triple system of Proxima and the central binary Centauri A and B. Just a few years ago, Pierre Kervella and team were able to demonstrate what had previously been only a conjecture, that Proxima Centauri was indeed gravitationally bound to Centauri A and B. The work was done using high-precision radial velocity measurements from the HARPS spectrograph. But we still had uncertainty about the precise value of Proxima’s mass, which had in the past been extrapolated from its luminosity.
This mass-luminosity relation is useful when we have nowhere else to turn, but as a new paper from Alice Zurlo (Universidad Diego Portales, Chile) explains, there are significant uncertainties in these values, which point to higher error bars the smaller the star in question. As we learn more about not just other planets but warm dust belts around Proxima Centauri, we need a better read on the star’s mass, and this leads to the intriguing use to which Zurlo and team have put gravitational microlensing.
Here we’re in new terrain. The gravitational deflection of starlight is well demonstrated, but to use it, we need to have a background object move close enough to Proxima Centauri so that the latter can deflect its light. A measurement of this kind was recently made on the star Stein 3051 B, a white dwarf, using data from the Hubble instrument, the first use of gravitational lensing to measure the mass of a star beyond our Solar System. Zurlo and team have taken advantage of microlensing events at Proxima involving two background stars, one in 2014 (source 1), the other two years later (source 2), but the primary focus of their work is with the second event.
Using the Spectro-Polarimetric High-contrast Exoplanet REsearch instrument (SPHERE) at the Very Large Telescope at Cerro Paranal in Chile, the researchers observed Proxima Centauri and the background stars from March of 2015 to June of 2017. You can see Proxima in the image below, with the two background stars. In the caption, IRDIS refers to the near-infrared imager and spectrograph which is a part of the SPHERE/VLT installation.
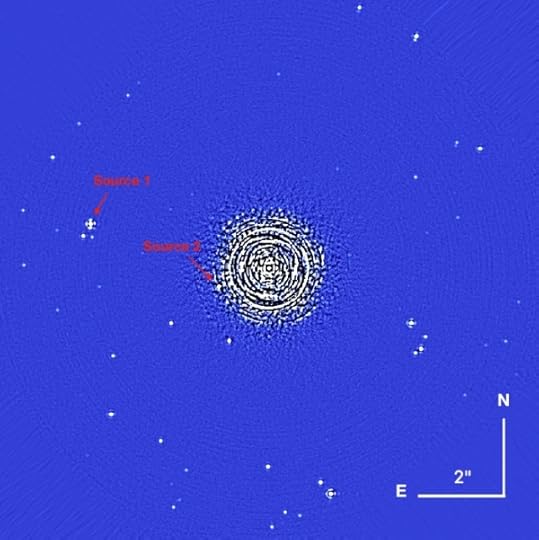
Image: This is Figure 1 from the paper. Caption: IRDIS FoV for the April 2016 epoch. The image is derotated, median combined, and cleaned with a spatial filter. At the center of the image, inside the inner working angle (IWA), the speckle pattern dominates, in the outer part of the image our reduction method prevents the elongation of the stars’ point spread functions (PSFs). The bars in the lower right provide the spatial scale. North is up and East is to the left. Credit: Zurlo et al.
The extraordinary precision of measurement needed here is obvious, and the mechanics of making it happen are described in painstaking detail in the paper. The authors note that the SPHERE observations will not be further refined because the background star they call Source 2 is no longer visible on the instrument’s detector. Nonetheless:
The precision of the astrometric position of this source is the highest ever reached with SPHERE, thanks to the exquisite quality of the data, and the calibration of the detector parameters with the large population of background stars in the FoV. Over the next few years, Proxima Cen will be followed up to provide a better estimation of its movement on the sky. These data will be coupled with observations from HST and Gaia to take advantage of future microlensing events.
The results of the two-year monitoring program show deflection of the background sources’ light consistent with our tightest yet constraints on the mass of Proxima Centauri. The value is 0.150 solar masses, with possible error in the range of +0.062 to -0.051, or roughly 40%. This is, the authors note, “the first and the only currently possible measurement of the gravitational mass of Proxima Centauri.”
The previous value drawn from mass-luminosity figures was 0.12 ± 0.02 M⊙. What next? While Source 2 may be out of the picture using the SPHERE installation, the authors add that Gaia measurements of the proper motion and parallax of that star may further refine the analysis. Future microlensing will have to wait, for no star as bright as Source 2 will pass within appropriate range of Proxima for another 20 years.
The paper is Zurlo et al., “The gravitational mass of Proxima Centauri measured with SPHERE from a microlensing event,” Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Vol. 480, Issue 1 (October, 2018), 236-244 (full text). The paper on Proxima Centauri’s orbit in the Alpha Centauri system is Kervella et al., “Proxima’s orbit around α Centauri,” Astronomy & Astrophysics Volume 598 (February 2017) L7 (abstract).

May 20, 2022
"If Loud Aliens Explain Human Earliness, Quiet Aliens Are Also Rare”: A review

What can we say about the possible appearance and spread of civilizations in the Milky Way? There are many ways of approaching the question, but in today’s essay, Dave Moore focuses on a recent paper from Robin Hanson and colleagues, one that has broad implications for SETI. A regular contributor to Centauri Dreams, Dave was born and raised in New Zealand, spent time in Australia, and now runs a small business in Klamath Falls, Oregon. He adds: “As a child, I was fascinated by the exploration of space and science fiction. Arthur C. Clarke, who embodied both, was one of my childhood heroes. But growing up in New Zealand in the ‘60s, such things had little relevance to life, although they did lead me to get a degree in biology and chemistry.” Discovering like-minded people in California, he expanded his interest in SETI and began attending conferences on the subject. In 2011, he published a paper in JBIS, which you can read about in Lost in Time and Lost in Space.
by Dave Moore
I consider the paper “If Loud Aliens Explain Human Earliness, Quiet Aliens Are Also Rare,” by Robin Hanson, Daniel Martin, Calvin McCarter, and Jonathan Paulson, a significant advance in addressing the Fermi Paradox. To explain exactly why, I need to go into its background.
Introduction and HistoryIn our discussions and theories about SETI, the Fermi paradox hangs over them all like a sword of Damocles, ready to fall and cut our assumptions to pieces with the simple question, where are the aliens? There is no reason not to suppose that Earth-like planets could not have formed billions of years before Earth did and that exosolar technological civilizations (ETCs) could not have arisen billions of years ago and spread throughout the galaxy. So why then don’t we see them? And why haven’t they visited us, given the vast expanse of time that has gone by?
Numerous papers and suggestions have tried to address this conundrum, usually ascribing it to some form of alien behavior, or that the principle of mediocrity doesn’t apply, and intelligent life is a very rare fluke.
The weakness of the behavioral arguments is they assume universal alien behaviors, but given the immense differences we expect from aliens—they will be at least as diverse as life on Earth—why would they all have the same motivation? It only takes one ETC with the urge to expand, and diffusion scenarios show that it’s quite plausible for an expansive ETC to spread across the galaxy in a fraction (tens of millions of years) of the time in which planets could have given rise to ETCs (billions of years).
And there is not much evidence that the principle of mediocrity doesn’t apply. Our knowledge of exosolar planets shows that while Earth as a type of planet may be uncommon, it doesn’t look vanishingly rare, and we cannot exclude from the evidence we have that other types of planets cannot give rise to intelligent life.
Also, modest growth rates can produce Kardeshev III levels of energy consumption in the order of tens of thousands of years, which in cosmological terms is a blink of the eye.
In 2010, I wrote a paper for JBIS modeling the temporal dispersion of ETCs. By combining this with other information, in particular diffusion models looking at the spread of civilizations across the galaxy, it was apparent that it was just not possible for spreading ETCs to occur with any frequency at all if they lasted longer than about 20,000 years. Longer than that and at some time in Earth’s history, they would have visited/colonized us by now. So, it looks like we are the first technological civilization in our galaxy. This may be disappointing for SETI, but there are other galaxies out there—at least as many as there are stars in our galaxy.
My paper was a very basic attempt to deduce the distribution of ETCs from the fact we haven’t observed any yet. Robin Hanson et al’s paper, however, is a major advance in this area as it builds a universe-wide quantitative framework to frame this lack of observational evidence and produces some significant conclusions.
It starts with the work done by S. Jay Olsen. In 2015, Olson began to bring out a series of papers assuming the expansion of ETCs and modeling their distributions. He reduced all the parameters of ETC distribution down to two: (α), the rate at which civilizations appeared over time, and (v) their expansion rate, which was assumed to be similar for all civilizations as ultimately all rocketry is governed by the same laws of physics. Olsen varied these two parameters and calculated the results for the following: the ETC-saturated fraction of the universe, the expected number and angular size of their visible domains, the probability that at least one domain is visible, and finally the total expected fraction of the sky eclipsed by expanding ETCs.
In 2018, Hanson et al took Olsen’s approach but incorporated the idea of bringing in the Hard Steps Power Law into modeling the appearance rate of ETCs, which they felt was more accurate and predictive than the rate-over-time models Olsen used.
The Hard Steps Power LawThe Hard Steps power law was first introduced in 1953 to model the appearance of cancer cells. To become cancerous an individual cell must undergo a number of specific mutations (hard steps i.e. improbable steps) in a certain order. The average time for each mutation is longer than a human lifetime, but we have a lot of cells in our body, so 40% of us develop cancer, the result of a series of improbabilities in a given cell.
If you think of all the planets in a galaxy that life can evolve on as cells and the ones that an ETC arises on being cancerous, you get the idea. The Hard Steps model is a power law, so the chances of an outcome happening in a given period of time is the inverse of the chance of a step happening (its hardness) to the power of the number of steps. Therefor the chance of anything happening in a given time goes down very rapidly with the number of hard steps required.
In Earth’s case, the given period of time is about 5.5 billion years, the time from Earth’s origin until the time that a runaway greenhouse sets in about a billion years from now.
The Number of Hard Steps in our EvolutionIn 1983 Brandon Carter was looking into how likely it was for intelligent life to arise on Earth, and he thought that due to the limitations on the time available this could be modeled as a hard step problem. To quote:
This means that some of the essential steps (such as the development of eukaryotes) in the evolution process leading to the ultimate emergence of intelligent life would have been hard, in the sense of being against the odds in the available time, so that they are unlikely to have been achieved in most of the earth-like planets that may one day be discovered in nearby extra-solar systems.
Carter estimated that the number of hard steps it took to reach our technological civilization was six: biogenesis, the evolution of bacteria, eukaryotes, combogenisis [sex], metazoans, and intelligence. This, he concluded, seemed the best fit for the amount of time that had taken for us to evolve. There has been much discussion and examination of the number of hard steps in the literature, but the idea has held up fairly well so Hanson et al varied the number of hard steps around six as one of their model variables.
The PaperThe Hanson paper starts out by dividing ETCs into two categories: loud aliens and quiet aliens. To quote:
Loud (or “expansive”) aliens expand fast, last long, and make visible changes to their volumes. Quiet aliens fail to meet at least one of these criteria. As quiet aliens are harder to see, we are forced to accept uncertain estimates of their density, via methods like the Drake equation. Loud aliens, by contrast, are far more noticeable if they exist at any substantial density.
The paper then puts aside the quiet aliens as they are, with our current technology, difficult to find and focuses on the loud ones and, in a manner similar to Olsen, runs models but with the following three variables:
i) The number of hard steps required for an ETC to arise.
ii) The conversion rate of a quiet ETC into a loud, i.e. visible, one.
iii) The expansion speed of a civilization.
In their models, (like the one illustrated below) a civilization arises. At some point, it converts into an expansive civilization and spreads out until it abuts a neighbor at which point it stops. Further civilizations in the volume that is controlled are prevented from happening. Results showing alien civilizations that are visible from our point of view are discarded, narrowing the range of these variables. (Note: time runs forward going down the page.)
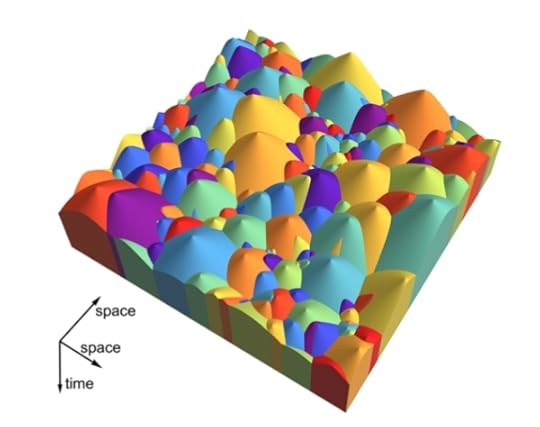 Results
ResultsIn a typical run with parameters resulting in them not being visible to us, expansive civilizations now control 40-50% of the universe, and they will finish up controlling something like a million galaxies when we meet one of them in 200 million year’s time. (Note, this paradoxical result is due to the speed of light. They control 40-50% of the universe now, but the electromagnetic radiation from their distant galaxies has yet to reach us.)
From these models, three main outcomes become apparent:
Our Early AppearanceThe Hard Step model itself contains two main parameters, number of steps and the time in which they must be concluded in. By varying these parameters, Hanson et al showed that, unless one assumes fewer than two hard steps (life and technological civilizations evolve easily) and a very restrictive limit on planet habitability lifetimes, then the only way to account for a lack of visible civilizations is to assume we have appeared very early in the history of civilizations arising in the universe. (In keeping with the metaphor, we’re a childhood cancer.)
All scenarios that show a higher number of hard steps than this greatly favor a later arrival time of ETCs, so an intelligent life form producing a technological civilization is at this stage of the universe is a low probability event.
Chances of other civilizations in our galaxyAnother result coming from their models is that the higher the chance of an expansive civilization evolving from a quiet civilization, the less the chance there is of there being any ETCs aside from us in our galaxy. To summarize their findings: assuming a generous million year average duration for a quiet civilization to become expansive, very low transition chances (p) are needed to estimate that even one other civilization was ever active anywhere along our past light cone (p < 10−3), or existed in our galaxy (p < 10−4), or is now active in our galaxy (p < 10−7).
For SETI to be successful, there needs to be a loud ETC close by, and for one to be close by, the conversion rate of quiet civilizations to expansive, loud ones must be in the order of one per billion. This is not a good result pointing to SETI searches being productive.
Speed of expansionThe other variable used in the models is the speed of expansion. Under most assumptions, expansive civilizations cover significant portions of the sky. However, when taking into account the speed of light, the further distant these civilizations are, the earlier they must form for us to see them. One of the results of this relativistic model is that the slower civilizations expand on average, the more likely we are to see them.
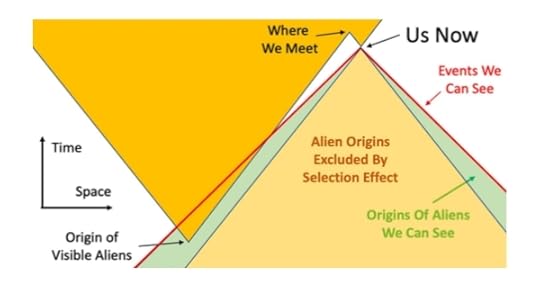
This can be demonstrated with the above diagram. The orange portion of the diagram shows the origin and expansion of an ETC at a significant proportion of the speed of light. We—by looking out into space are also looking back in time—can only see what is in our light cone (that which is below the red line), so we see the origin of our aliens (say one billion years ago) and their initial spread up to about half that age. After which, the emissions from their spreading civilization have not yet had time to reach us.
The tan triangle represents the area in space from which an ETC spreading at the same rate as the orange aliens would already have arrived at our planet (in which case we would either not exist or we would know about it), so we can assume that there were no expansive aliens having originated in this portion of time and space.
If we make the spread rate a smaller proportion of the speed of light, then this has the effect of making both the orange and tan triangles narrower along the space axis. The size of the tan exclusion area becomes smaller, and the green area, which is the area that can contain observable alien civilizations that haven’t reached us yet, becomes bigger.
You’ll also notice that the narrower orange triangle of the expansive ETC crosses out of out of our light cone at an earlier age, so we’d only see evidence of their civilization from an earlier time.
The authors note that the models rely on us being able to detect the boundaries between expansive civilizations and unoccupied space. If the civilizations are out there, but are invisible to our current instruments, then a much broader variety of distributions is possible.
ConclusionsWe have always examined the evolution of life of Earth for clues as to the distribution alien life. What is important about this paper is that it connects the two in a quantitative way.
There are a lot of assumptions build into this paper (some of which I find questionable); however, it does give us a framework to examine them and test them, so it’s a good basis for further work.
To quote Hanson et al:
New scenarios can be invented and the observable consequences calculated immediately. We also introduce correlations between these quantities that are obtained by eliminating dependence on α [appearance rate], e.g. we can express the probability of seeing at least one domain as a function of v [expansion velocity] and the currently life-saturated fraction of the universe based on the fact we haven’t see or have encountered any.
I would point out a conclusion the authors didn’t note. If we have arisen at an improbably early time, then there should be lots of places (planets, moons) with life at some step in their evolution, so while SETI searches don’t look promising from the conclusions of this paper, the search for signs of exosolar life may be productive.
This paper has given us a new framework for SETI. Its parameters are somewhat tangential to the Drake Equation’s, and its approach is to basically work the equation backwards: if N=0 (number of civilizations we can communicate with in the Drake equation, number of civilizations we can observe in this paper), then what is the range in values for fi (fraction of planets where life develops intelligence), fc (fraction of civilizations that can communicate/are potentially observable) and (L) length of time they survive. The big difference is that this paper factors in the temporal distribution of civilizations arising, which is not something the Drake Equation addressed. The Drake equation, for something that was jotted down before a meeting 61 years ago, has had a remarkably good run, but we may be seeing a time where it gets supplanted.
ReferencesRobin Hanson, Daniel Martin, Calvin McCarter, Jonathan Paulson, “If Loud Aliens Explain Human Earliness, Quiet Aliens Are Also Rare,” The Astrophysical Journal, 922, (2) (2021)
Thomas W. Hair, “Temporal dispersion of the emergence of intelligence: an inter-arrival time analysis,” International Journal of Astrobiology 10 (2): 131–135 (2011)
David Moore, “Lost in Time and Lost in Space: The Consequences of Temporal Dispersion for Exosolar Technological Civilizations,” Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, 63 (8): 294-302 (2010)
Brandon Carter, “Five- or Six-Step Scenario for Evolution?” International Journal of Astrobiology, 7 (2) (2008)
S.J. Olson, “Expanding cosmological civilizations on the back of an envelope,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.06329 (2018)

May 17, 2022
A Habitable Exomoon Target List

Are there limits on how big a moon can be to orbit a given planet? All we have to work with, in the absence of confirmed exomoons, are the satellites of our Solar System’s planets, and here we see what appears to be a correlation between a planet’s mass and the mass of its moons. At least up to a point – we’ll get to that point in a moment.

But consider: As Vera Dobos (University of Groningen, Netherlands) and colleagues point out in a recent paper for Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, if we’re talking about moons forming in the circumplanetary disk around the young Sun, the total mass is on the order of 10-4Mp. Here Mp is the mass of the planet. A planet with 10 times Jupiter’s mass, given this figure, could have a moon as large as a third of Earth’s mass, and so far observational evidence supports the idea that moons can form regularly in such disks. There is no reason to believe we won’t find exomoons by the billions throughout the galaxy.
Image: The University of Groningen’s Dobos, whose current work targets planetary systems where habitable exomoons are possible. Credit: University of Groningen.
The mass calculation above, though, is what is operative when moons form in a circumplanetary disk. To understand our own Moon, we have to talk about an entirely different formation mechanism: Collisions. Here we’re in the fractious pin-ball environment of a system growing and settling, as large objects find their way into stable orbits. Collisions change the game: Moons are now possible at larger moon-to-planet ratios with this second mechanism – . our Moon has a mass of 10−2 Earth masses. Let’s also consider moons captured by gravitational interactions, of which the prime example in our system is probably Triton.
What we’d like to find, of course, is a large exomoon, conceivably of Earth size, orbiting a planet in the habitable zone, or perhaps even a binary situation where two planets of this size orbit a common barycenter (Pluto and Charon come closest in our system to this scenario). Bear in mind that exoplanet hunting, as it gets more refined, is now turning up planets with masses lower than Earth’s and in some cases lower than Mars. As we move forward, then, moons of this size range should be detectable.
But what a challenge exomoon hunters have set for themselves, particularly when it comes to finding habitable objects. The state of the art demands using radial velocity or transit methods to spot an exomoon, but both of these work most effectively when the host planet is closest to its star, a position which is likely not stable for a large Moon over time. Back off the planet’s distance from the star into the habitable zone and now you’re in a position that favors survival of the moon but also greatly complicates detection.
What Dobos and team have done is to examine exomoon habitability in terms of energy from the host star as well as tidal heating, leaving radiogenic heating (with all its implications for habitability under frozen ocean surfaces) out of the picture. Using planets whose existence is verified, as found in the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopedia, they run simulations on hypothetical exomoons that fit their criteria – these screen out planets larger than 13 Jupiter masses and likewise host stars below 0.08 solar masses.
Choosing only worlds with known orbital period or semimajor axis, they run 100,000 simulations for all 4140 planets to determine the likelihood of exomoon habitability. 234 planets make the cut, which for the purposes of the paper means exomoon habitability probabilities of ≥ 1 percent for these worlds. 17 planets of the 234 show a habitability probability of higher than 50 percent, so these are good habitable zone candidates if they can indeed produce a moon around them. It’s no surprise to learn that habitable exomoons are far more likely for planets already orbiting within their star’s habitable zone. But I was intrigued to see that this is not iron-clad. Consider:
Beyond the outer boundary of the HZ, where stellar radiation is weak and one would expect icy planets and moons, we still find a large number of planets with at least 10% habitability probability for moons. This is caused by the non-zero eccentricity of the orbit of the host planet (resulting in periodically experienced higher stellar fluxes) and also by the tidal heating arising in the moon. These two effects, if maintained on a long time-scale, can provide enough supplementary heat flux to prevent a global snowball phase of the moon (by pushing the flux above the maximum greenhouse limit).
More good settings for science fiction authors to mull over!
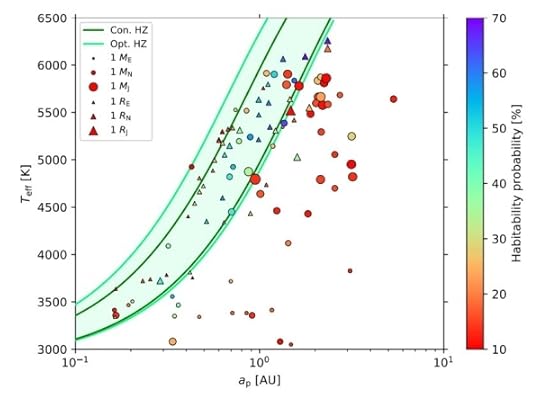
Image: This is Figure 2 from the paper. Caption: Habitability probability for exomoons around known exoplanets on the semi-major axis – stellar effective temperature plane. Planets with known masses (with or without radius data) are marked with circles, planets with known radii only are marked with triangles. Colours of the markers correspond to the fraction of habitable moons and the sizes of the markers represent the sizes of the planets as shown in the legend. Note that the legend only shows three
representative sizes (Earth, Neptune and Jupiter), while the size of the markers in the plot is scaled to the real size of the planets. Green curves represent the borders of the circumstellar habitable zone for a 1 Earth-mass planet: dark green for the consevative HZ (Con. HZ) and light green for the optimistic HZ (Opt. HZ). Credit: Dobos et al. 2022.
Given that the spectral type of over half of the stars in the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopedia is not listed, there is a good deal of play in these results, although the authors point to the mitigating effect of gas giant magnetospheres as shields against incoming stellar radiation for potentially habitable moons. Even so, stellar type is clearly an important factor, and it’s also noteworthy that while the paper mentions planet migration, its effects on exomoons are not under consideration. This is about as much as the authors have to say about migration:
It is likely that the giant planets in the circumstellar HZ were formed at larger distances from the star and then migrated inwards to their current orbit (see for example Morbidelli 2010). During the orbital migration they can lose some or all of their moons, especially if the moon orbit is close to the planet (Namouni 2010; Spalding et al. 2016). Depending on the physical and orbital parameters of the planet and the moon, as well as on the starting and final semi-major axes of the planet, some moons can survive this process, and new moons can also be captured during or after the migration of the planet.
Just how migration would affect the results of this study is thus an open question. What we do wind up with is what the authors consider a ‘target list’ for exomoon observations, although one replete with challenges. Most of these potential exomoons would orbit planets whose orbital period is in the hundreds of days, planets like Kepler-62f, with a 268 day period and a 53 percent habitability probability for an exomoon. This is an interesting case, as stable moon orbits are likely around this 1.38 Earth radius world. But what a tricky catch for both our exomoon detection techniques.
Because many of the planets in the target list are gas giants, we have to consider the probability that more than a single moon may orbit them, perhaps even several large moons where life might develop. That’s a scenario worth considering as well, independent emergence of life upon two moons orbiting the same exoplanet. But it’s one that will have to wait as we refine exomoon scenarios in future observations.
The paper is Dobos et al., “A target list for searching for habitable exomoons,” accepted at Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 05 May 2022 (abstract / preprint). Thanks to my friend Antonio Tavani for the heads-up on this work.

May 13, 2022
Dyson Spheres: The White Dwarf Factor

I often think of Dyson structures around stars as surprisingly benign places, probably motivated by encountering Larry Niven’s wonderful Ringworld when it was first published by Ballantine in 1970. I was reading it in an old house in Iowa on a windy night and thought to start with a chapter or two, but found myself so enthralled that it wasn’t until several hours later that I re-surfaced, wishing I didn’t have so much to do the next day that I had to put the book aside and sleep.

I hope I’m not stretching the definition of a Dyson construct too far when I assign the name to Niven’s ring. It is, after all, a structure built by technological means that runs completely around its star at an orbit allowing a temperate climate for all concerned, a vast extension of real estate in addition to whatever other purposes its creators may have intended. That a technological artifact around a star should be benign is a function of its temperature, which makes things possible for biological beings.
But a Dyson sphere conceived solely as a collection device to maximize the civilization’s intake of stellar energy would not be built to biological constraints. For one thing, as retired UCLA astrophysicist Ben Zuckerman points out in a new paper, it would probably be as close to its star as possible to minimize its size. That makes for interesting temperatures, probably in the range of 300 K at the low end and reaching perhaps 1000 K, which sets up emissions up to 10 µm in wavelength, and as Zuckerman points out, this would be in addition to any emission from the star itself.
Zuckerman refers to such structures as DSRs, standing for Dyson spheres/rings, so I guess working Niven in here fits as well. Notice that when talking about these things we also make an assumption that seems reasonable. If civilizations are abundant in the galaxy, they are likely long-lived, and that means that stellar evolution has to be something they cope with as yellow dwarf stars, for example, turn into red giants and, ultimately, white dwarfs. The DSR concept can accommodate the latter and offers a civilization the chance to continue to use the energy of its shrunken star. Whether this would be the route such a civilization chooses is another matter entirely.

Image: Artist depiction of a Dyson swarm. Credit: Kevin McGill/Wikimedia Commons.
One useful fact about white dwarfs is that they are small, around the size of the Earth, and thus give us plenty of transit depth should some kind of artificial construct pass between the star and our telescopes. Excess infrared emission might also be a way to find such an object, although here we have to be concerned about dust particles and other potential sources of the infrared excess. Zuckerman’s new paper analyzes the observational limits we can currently derive based on these two methods.
The paper, published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, uses data from Kepler, Spitzer and WISE (Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer) as a first cut into the question, revising Zuckerman’s own 1985 work on the number of technological civilizations that could have emerged around main sequence stars that evolved to white dwarfs within the age constraints of the Milky Way. Various papers exist on excess of infrared emissions from white dwarfs; we learn that Spitzer surveyed at least 100 white dwarfs with masses in the main sequence range of 0.95 to 1.25 solar masses. These correspond to spectral types G7 and F6, and none of them turned up evidence for excess infrared emission.
As to WISE, the author finds the instrument sensitive enough to yield significant limits for the existence of DSRs around main sequence stars, but concludes that for the much fainter white dwarfs, the excess infrared is “plagued by confusion…with other sources of IR emission.” He looks toward future studies of the WISE database to untangle some of the ambiguities, while going on to delve into transit possibilities for large objects orbiting white dwarfs. Kepler’s K2 extension mission, he finds, would have been able to detect a large structure (1000 km or more) if transiting, but found none.
It’s worth pointing out that no studies of TESS data on white dwarfs are yet available, but one ongoing project has already observed about 5000, with another 5000 planned for the near future. As with K2, a deep transit would be required to detect a Dyson object, again on the order of 1000 kilometers. If any such objects are detected, we may be able to distinguish natural from artificial objects by their transit shape. Luc Arnold has done interesting work on this; see SETI: The Artificial Transit Scenario for more.
Earlier Kepler data are likewise consulted. From the paper:
From Equation 4 we see that about a billion F6 through G7 stars that were on the main sequence are now white dwarfs. Studies of Kepler and other databases by Zink & Hansen (2019) and by Bryson et al. (2021) suggest that about 30% of G-type stars are orbited by a potentially habitable planet, or about 300 million such planets that orbit the white dwarfs of interest here. If as many as one in 30 of these planets spawns life that eventually evolves to a state where it constructs a DSR with luminosity at least 0.1% that of its host white dwarf, then in a sample of 100 white dwarfs we might have expected to see a DSR. Thus, fewer than 3% of the habitable planets that orbit sun-like stars host life that evolves to technology, survives to the white dwarf stage of stellar evolution, and builds a DSR with fractional IR luminosity of at least 0.1%.
Science fiction writers will want to go through Zuckerman’s section on the motivations of civilizations to build a Dyson sphere or ring, which travels deep into speculative territory about cultures that may or may not exist. It’s an imaginative foray, though, discussing the cooling of the white dwarf over time, the need of a civilization to migrate to space-based colonies and the kind of structures they would likely build there.
There are novels in the making here, but our science fiction writer should also be asking why a culture of this sophistication – able to put massive objects built from entire belts of asteroids and other debris into coherent structures for energy and living space purposes – would not simply migrate to another star. The author only says that if the only reason to travel between the stars is to avoid the inevitable stellar evolution of the home star, then no civilization would undertake such journeys, preferring to control that evolution through technology in the home system. This gives me pause, and Centauri Dreams readers may wish to supply their own reasons for interstellar travel that go beyond escaping stellar evolution.
Also speculative and sprouting fictional possibilities is the notion that main sequence stars may not be good places to look for a DSR. Thus Zuckerman:
…main sequence stars suffer at least two disadvantages as target stars when compared to white dwarfs; one disadvantage would be less motivation to build a substantial DSR because one’s home planet remains a good abode for life. In our own solar system, if a sunshield is constructed and employed at the inner Earth-Sun Lagrange point – to counter the increasing solar luminosity – then Earth could remain quite habitable for a few Gyr more into the future. Perhaps a more important consideration would be the greater luminosity, say about a factor of 1000, of the Sun compared to a typical white dwarf.
Moreover, detecting a DSR around a main sequence star becomes more problematic. In the passage below, the term τ stands for the luminosity of a DSR measured as a fraction of the luminosity of the central star:
For a DSR with the same τ and temperature around the Sun as one around a white dwarf, a DSR at the former would have to have 1000 times the area of one at the latter. While there is sufficient material in the asteroid belt to build such an extensive DSR, would the motivation to do so exist? For transits of main sequence stars by structures with temperatures in the range 300 to 1000 K, the orbital period would be much longer than around white dwarfs, thus relatively few transits per year. For a given structure, the probability of proper alignment of orbital plane and line of sight to Earth would be small and its required cross section would be larger than that of Ceres.
So we are left with that 3 percent figure, which sets an upper limit based on our current data for the fraction of potentially habitable planets that orbit stars like the Sun, produce living organisms that produce technology, and then construct a DSR as their system undergoes stellar evolution. No more than 3 percent of such planets do so.
There is a place for ‘drilling down’ strategies like this, for they take into account the limitations of our data by way of helping us see what is not there. We do the same in exoplanet research when we start with a star, say Proxima Centauri, and progressively whittle away at the data to demonstrate that no gas giant in a tight orbit can be there, then no Neptune-class world within certain orbital constraints, and finally we do find something that is there, that most interesting place we now call Proxima b.
As far as white dwarfs and Dyson spheres or rings go, new instrumentation will help us improve the limits discussed in this paper. Zuckerman points out that there are 5000 white dwarfs within 200 parsecs of Earth brighter than magnitude 17. A space telescope like WISE with the diameter of Spitzer could improve the limits on DSR frequency derived here, its data vetted by upcoming 30-m class ground-based telescopes (Zuckerman notes that JWST is not suited, for various reasons, for DSR hunting). The European Space Agency’s PLATO spacecraft should be several times more sensitive than TESS at detecting white dwarf transits, taking us well below the 1000 km limit.
The paper is Zuckerman, “Infrared and Optical Detectability of Dyson Spheres at White Dwarf Stars,” Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society stac1113 (28 April 2022). Abstract / Preprint.

May 10, 2022
Habitability: Look to Younger Worlds

A liquid water-defined habitable zone is a way of establishing parameters for life as we know it around other stars, and with this in mind, scientists study the amount of stellar radiation a planet receives as one factor in making the assessment. But of course, not everything in a habitable zone is necessarily habitable, as our decidedly uninhabitable Moon makes all too clear. Atmospheric factors and tectonic activity, for example, have to be weighed as we try to learn what the actual temperature at the surface would be. We’re learning as we go about other contributing factors.
A problem of lesser visibility in the literature, though perhaps just as crucial, is whether a given planet can stay habitable on timescales of billions of years. This is where an interesting new paper from Cayman Unterborn (Southwest Research Institute) and colleagues enters the mix. A key question in the view of these researchers is whether carbon dioxide, the greenhouse gas whose ebb and flow on our world is determined by the carbonate-silicate cycle, can come into play to stabilize climatic conditions.
The carbonate-silicate cycle involves delivering CO2 to the atmosphere through degassing in the planetary mantle or crust, with carbon returned as carbonates to the mantle. The effects on climate are substantial and changes to the cycle can be catastrophic in terms of habitability. If weathering sufficiently draws down the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere, for example, the planet can tilt in the direction of a ‘snowball’ state. So we need active degassing to keep the cycle intact, and the question becomes, how long can a planet’s mantle maintain this degassing?
Volcanic activity and tectonic processes, in turn, are powered by internal heat, and there we note the fact that a planetary heat budget decreases with time, affected by many things, one of which is the presence of radiative decay. Thorium, potassium and uranium have to be available in sufficient quantities, powering mantle convection, which gives us movement from a planetary core all the way to the crust. And radioactive elements, by their nature, decay with time. They are also not evenly distributed from one stellar system to another. If we’re looking for planets something like our own, in other words, let’s learn what we can about their radiogenic heat.
Not that this is the only factor involved in a planet’s heat budget, but it’s an effect that may account for, the authors say, from thirty to fifty percent of the Earth’s current surface heat flow (because of radioactive decay, the current flow represents only 20 percent of the Earth’s heat budget when it formed four and a half billion years ago).
The authors mention other planetary heat sources, as we’ll see below, but confine themselves in this paper to radiogenic heat. Their method: To estimate the distribution of these heat-producing elements by examining stellar composition as determined by spectroscopic data, using this as a proxy for the composition of planets. They combine this information with chemical evolution models for the galaxy at large. They then produce models of thermal evolution that maximize the cooling rate in a planetary mantle, resulting in what the authors call “a pessimistic estimate of lifetime a rocky, stagnant-lid exoplanet can support a global carbon cycle through Galactic history.”
Seventeen exoplanets are subjected to this framework in the paper, all with measured ages. Seven of these, the researchers predict, should be actively outgassing today. Says Unterborn:
[image error]“Using host stars to estimate the amount of these elements that would go into planets throughout the history of the Milky Way, we calculated how long we can expect planets to have enough volcanism to support a temperate climate before running out of power. Under the most pessimistic conditions we estimate that this critical age is only around 2 billion years old for an Earth-mass planet and reaching 5–6 billion years for higher-mass planets under more optimistic conditions. For the few planets we do have ages for, we found only a few were young enough for us to confidently say they can have surface degassing of carbon today, when we’d observe it with, say, the James Webb Space Telescope.”
Image: An SwRI-led study suggests that host-star age and radionuclide abundance will help determine both an exoplanet’s history and its current likelihood of being temperate today. For example, the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 is home to the largest group of roughly Earth-sized planets ever found in a single stellar system with seven rocky siblings including four in the habitable zone. But at around 8 billion years old, these worlds are roughly 2 billion years older than the most optimistic degassing lifetime predicted by this study and unlikely to support a temperate climate today. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech.
Remember that this is a deliberately pessimistic model. It’s also the case that abundances of heat-producing elements are only one factor that can change the degassing lifetime of a planet, and the authors are quick to point out that they do not include these in their model. Thus we could consider the current study a contribution toward a broader model for planetary heat budget analysis, one that should be expanded through examining such factors as cooling after planet formation, the energy released when core and mantle differentiate, and tidal heating induced by the host star or other planets in the system. As the authors describe their results:
The framework we present here that combines direct and indirect observational data with dynamical models not only provides us with a pessimistic baseline for understanding which parameter(s) most control a stagnant-lid exoplanet’s ability to support a temperate climate but also indicates where more lab-based and computational work is needed to quantify the reasonable range of these parameters (e.g., mantle reference viscosity). As we move to more in-depth characterization of individual targets in the James Webb Space Telescope era, these direct and indirect astronomic observables, coupled with laboratory data and models from the geoscience community, will allow us to better estimate whether a rocky exoplanet in both the canonical and temporal habitable zones has exhausted its internal heat and is simply too old to be Earth-like.
We are positioning ourselves, as highlighted by the ongoing commissioning of the James Webb Space Telescope, to begin the analysis of planetary atmospheres at scales smaller than gas giants, meaning that the kind of computational modeling at work in this paper will increasingly be refined by observation. The interactions between a planet’s surface and its interior then become better defined as markers for habitable worlds, with radionuclides a significant factor in producing climate stability.
The paper is Unterborn et al., “Mantle Degassing Lifetimes through Galactic Time and the Maximum Age Stagnant-lid Rocky Exoplanets Can Support Temperate Climates,” Astrophysical Journal Letters Vol. 930, No. 1, L6 (3 May 2022). Full text.

May 6, 2022
Free-Floating Planets as Interstellar Arks

We haven’t found any technosignatures among the stars, but the field is young and our observational tools are improving steadily. It’s worth asking how likely an advanced civilization will be to produce the kind of technosignature we usually discuss. A Dyson swarm should produce evidence for its existence in the infrared, but not all advanced technologies involve megastructures. Even today we can see the movement of human attention into cyberspace. Would a civilization living primarily within virtual worlds produce a detectable signature, or would it more or less wink out of observability?
In 2020, Valentin Ivanov (ESO Paranal) and colleagues proposed a modification to the Kardashev scale based on how a civilization integrates with its environment (citation below). The authors offered a set of classes. Class 0 is a civilization that uses the environment without substantially changing it. Class 1 modifies its environment to fit its needs, while Class 2 modifies itself to fit its environment. A Class 3 civilization under this scheme would be maddeningly difficult to find because it is indistinguishable from its environment.
This gets speculative indeed, as the Ivanov paper illustrates:
‘Rogue’ Planets and Their UsesThe new classification scheme allows for the existence of quiet advanced civilizations that may co-exist with us, yet remain invisible to our radio, thermal or transit searches. The implicit underlying assumption of Hart (1975) is that the hypothetical ETC [Extraterrestrial Civilization] is interacting with matter on a similar level as us. We cannot even speculate if it is possible to detect a heat leak or a transiting structure build by an ETC capable of interacting with matter at sub-quark level, but the answer is more likely negative and not because that ETC would function according to some speculative physics laws, but because such an ETC would probably be vastly more efficient than us controlling its energy wastes and minimizing its construction projects. Would such an advanced ETC even need megastructures and vast astroengineering projects?
Apart from reconsideration of Kardashev assumptions about available energy as a metric of civilizational progress, it’s always useful to be reminded that we need to question our anthropocentric leanings. We need to consider the range of possibilities advanced civilizations may have before them, which is why a new paper from Irina Romanovskaya catches my eye. The author, a professor of physics and astronomy in the Houston Community College System, argues for planetary and interstellar migration as drivers for the kind of signature we might be able to spot. A star undergoing the transition to a red giant is a case in point: Here we would find a habitable zone being pushed out further from the star, and conceivably evidence of the migration of a culture to the more distant planets and moons of its home system.
Evidence for a civilization expanding to occupy the outer reaches of its system could come in the form of atmospheric technosignatures or infrared-excess, among other possibilities. But it’s in moving to other stars that Romanovskaya sees the likeliest possibility of a detectable signature, noting that stellar close passes could be times to expect movement on a large scale between stars. Other mechanisms also come to mind. We’ve discussed stellar engines in these pages before (Shkadov thrusters, for example), which can move entire stars. Romanovskaya introduces the idea that free-floating planets could be an easier and more efficient way to migrate.
Consider the advantages, as the author does in this passage:
Free-floating planets can provide constant surface gravity, large amounts of space and resources. Free-floating planets with surface and subsurface oceans can provide water as a consumable resource and for protection from space radiation. Technologies can be used to modify the motion of free-floating planets. If controlled nuclear fusion has the potential to become an important source of energy for humankind (Ongena and Ogawa, 2016; Prager, 2019), then it may also become a source of energy for interstellar travelers riding free-floating planets.
What a free-floating, or ‘rogue’ planet offers is plenty of real estate, meaning that a culture dealing with an existential threat may find it useful to send large numbers of biological or post-biological populations to nearby planetary systems. The number of free-floating planets is unknown, but recent studies have suggested there may be billions of these worlds, flung into the interstellar deep by gravitational interactions in their parent systems. We would expect some to move through the cometary clouds of planetary systems, just as stars like Scholz’s Star (W0720) did in our system 70,000 years ago, remaining within 100,000 AU of the Sun for a period of roughly 10,000 years.
A sufficiently advanced culture could also take advantage of events within its own system to ride an object likely to be ejected by a dying star. Here’s one science fictional scenario among many in this paper:
Extraterrestrial civilizations may ride Oort-cloud objects of their planetary systems, which become free-floating planets after being ejected by their host stars during the red giant branch (RGB) evolution and the asymptotic giant branch (AGB) evolution. For example, if a host star is a sun-like star and the critical semimajor axis acr ≈ 1000 AU, then extraterrestrials may use spacecraft to travel from their home planet to an object similar to 2015 TG387, when it is close to its periastron ~60–80 AU. They would ride that object, and they would leave the object when it would reach its apastron ~2100 AU. Then, they would use their spacecraft to transfer to another object of the Oort cloud that would be later ejected by its post-main-sequence star.
One recent study finds that simulations of terrestrial planet formation around stars like the Sun produce about 2.5 terrestrial-mass planets per star that are ejected during the planet formation process, many of these most likely near Mars in size. Louis Strigari (Stanford University) calculated in 2012 that for each main sequence star there may be up to 105 unbound objects, an enormous number that would argue for frequent passage of such worlds near other star systems. Let’s be more conservative and just say that free-floating planets likely outnumber stars in the galaxy. Some of these worlds may be ejected by later scattering interactions in multi-planet systems or by stellar evolution.
These planets are tricky observational targets, as the recent discovery of 70 of them in the Upper Scorpius OB association (420 light-years away from Earth) reminds us. They may exist in their countless billions, but we rely on chance and the momentary alignments with a background star to spot their passage via gravitational microlensing.

Image: This image shows the locations of 115 potential rogue planets, highlighted with red circles, recently discovered by a team of astronomers in a region of the sky occupied by Upper Scorpius and Ophiucus. Rogue planets have masses comparable to those of the planets in our Solar System, but do not orbit a star and instead roam freely on their own. The exact number of rogue planets found by the team is between 70 and 170, depending on the age assumed for the study region. This image was created assuming an intermediate age, resulting in a number of planet candidates in between the two extremes of the study. Credit: ESO/N. Risinger (skysurvey.org)
If we do find a free-floating planet in our data, does it become a SETI target? Romanovskaya thinks the idea has merit, suggesting several strategies for examining such worlds for technosignatures. One thing we might do is home in on post-main sequence stars with previously stable habitable zones, looking for signs of technology near them, under the assumption that a local civilization under duress might need a way out, whether via transfer to a passing free-floating planet or by other means.
Thus the stellar neighborhoods of red giants and white dwarfs that formed from G- and K-class stars merit study. A so-called ‘Dyson slingshot’ (a white dwarf binary gravitational assist) could accelerate a free-floating planet, and as David Kipping has shown, binaries with neutron stars and black holes are likewise candidates for such a maneuver. Thus we open up the technosignature space to white dwarf binaries and their neutron star counterparts being used by civilizations as planet accelerators.
To a Passing StarClose passes by other stars likewise merit study. A smattering of such attempts have already been made. In one recent study, Bradley Hansen (UCLA) looked at close stellar encounters near the Sun, using the Gaia database within 100 parsecs and identifying 132 pairs of stars passing within 10,000 AU of one another. No infrared excess of the sort that could flag migratory efforts appeared in the data around Sun-like stars.
Two years earlier, Hansen worked with UCLA colleague Ben Zuckerman on survival of technological civilizations given problematic stellar evolution, both papers appearing in the Astronomical Journal (I won’t cite all these papers below, as they’re cited in Romanovskaya’s paper, which is available in full-text online). In a system that has experienced interstellar migration, we would expect to see atmospheric technosignatures and possible evidence of terraforming on colonized planets. A clip from their 2020 paper:
…we associate the migration with a particular astrophysical event that is, in principle, observable, namely a close passage of two stars. One could reduce the vast parameter space of a search for evidence of technology with a focus on such a sample of stars in a search for communication signals or signs of activity such as infrared excesses or transient absorptions of stellar photospheres. However, our estimates suggest that the density of such systems is low compared to the confusing foreground of truly bound stars, and a substantial program of vetting false positives would be required.
Indeed, the list of technosignatures mentioned in the Romanovskaya paper, mostly culled from the literature, takes us far from the original SETI paradigm of listening for radio communications. It introduces the SETI potential of free-floating planets but then goes on to include infrared detection of self-reproducing probes, stellar engines (hypervelocity stars become SETI candidates), interstellar spacecraft communications or cyclotron radiation emitted by magnetic sails and other technologies, and the search for potential artifacts of other civilizations here in the Solar System, as examined by Robert Freitas and others and recently re-invigorated by Jim Benford’s work.
The whole sky seems to open up for search if we accept these premises; technosignatures rain down like confetti, especially given the free-floating planet hypothesis. Thus:
Unexplained emissions of electromagnetic radiation observed only once or a few times along the lines of observation of planetary systems, groups of stars, galaxies and seemingly empty regions of space may be technosignatures produced on free-floating planets located along the lines of observation; the search for free-floating planets is recommended in regions where unexplained emissions or astronomical phenomena occur.
How do we construct a coherent observational program from the enormous list of possibilities? The author makes no attempt to produce such, but brainstorming the possibilities has its own virtues that may prove useful as we try to make sense of future enigmatic data to ask whether what we see is of natural or technological origin.
The paper is Romanovskaya, “Migrating extraterrestrial civilizations and interstellar colonization: implications for SETI and SETA,” published online by Cambridge University Press (28 April 2022). Full text. The Ivanov et al. paper cited at the beginning is “A qualitative classification of extraterrestrial civilizations,” Astronomy & Astrophysics Vol. 639, A94 (14 July 2020). Abstract.

Paul Gilster's Blog
- Paul Gilster's profile
- 7 followers



