Suman Sourabh's Blog, page 3
May 25, 2024
2024 Guide to Infinite Scrolling in React/Next.js
Ever saw how posts keep on displaying on the feed section of X (Twitter) or Instagram if you keep scrolling down?
That “thing” is called infinite scrolling and we are going to implement it in React.
What is Infinite Scrolling?Infinite scrolling is a technique or approach in web development where more resources are fetched and displayed on the page as the user scrolls down.
 X’s feed
X’s feedFor example, in social media platforms such as X (Twitter), if you scroll down in the feed, more posts will display to you.
This approach is helpful when you have a lot of resources to show on the page and you do not want to fetch them all at once and slow down the application.
How to use Infinite Scrolling in React/Next.js?Of course, you can build your own infinite scrolling component from scratch but in many cases, it is better to use a library.
On Libertas, I have used a popular library called react-infinite-scroll-component.
This library has an inbuilt component which does the behaviour of infinite scrolling for us. We just have to dump our code of fetching multiple items inside this code.
Understanding the ScenarioFeedback is appreciated about this approach.
I have a feed page on Libertas where I show all the posts that the users have created. It is just like how different items are displayed on the feed page on Reddit, X, Medium, Nike and other such platforms.
Our aim is to fetch some posts/items when the page loads fully. When the user scrolls to the bottom of the page or the last item that was fetched when the page loaded, we trigger a GET request to fetch more posts.
This process repeats until all the items are fetched, which may not be possible if the items are huge in numbers (>500 items). Hence, the name “Infinite scroll”! Users will get exhausted, won’t they?
Steps to Implement react-infinite-scroll-componentBelow are the steps where I mention how I added this component into Libertas.
1. Install the packageFor npm:
npm i react-infinite-scroll-componentFor yarn:
yarn add react-infinite-scroll-component2. Copy and paste the below code for infinite scroll in Libertas dataLength={items.length} //This is important field to render the next datanext={fetchData}
hasMore={true}
loader={Loading...}
endMessage={
Yay! You have seen it all
}
>
{items}
3. Understanding the props
According to react-infinite-scroll-component GitHub page:
4. Further Steps:Fetch some posts when the page loadsDisplay the list of posts on the pageMake a slight change on the API GET request (Backend) to fetch the next list of postsFetch the next list of posts on the frontendFinal code: const [posts, setPosts] = useState([]);dataLength: set the length of the data. This will unlock the subsequent calls to next.
next: a function which must be called after reaching the bottom. It must trigger some sort of action which fetches the next data. The data is passed as children to the InfiniteScroll component and the data should contain previous items too. e.g. Initial data = [1, 2, 3] and then next load of data should be [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6].
hasMore: it tells the InfiniteScroll component on whether to call next function on reaching the bottom and shows an endMessage to the user
loader: you can send a loader component to show while the component waits for the next load of data. e.g.
Loading… or any fancy loader elementendMessage: this message is shown to the user when he has seen all the records which means he’s at the bottom and hasMore is false
items: The list of items to be fetched and displayed on the page. In case of Libertas, the {items} are the list of posts created by users.
const [count, setCount] = useState(4);
const [currentCount, setCurrentCount] = useState(null);
const [total, setTotal] = useState(null);
const fetchPosts = async () => {
const data = await fetchAllPosts(count);
console.log(data?.data?.data);
setPosts(data?.data?.data);
setCurrentCount(data?.data?.currentLength);
setTotal(data?.data?.total);
setCount(count + 2);
};
useEffect(() => {
fetchPosts();
}, []);
return (
dataLength={posts?.length} //This is important field to render the next data
next={fetchPosts}
hasMore={currentCount !== total}
loader={Loading...}
endMessage={
Yay! You have seen it all
}
>
{posts.map((post) => (
key={post._id}
post={post}
id={post._id}
handleUpvote={() => handleVote(upvoteAPost, post._id)}
handleDownvote={() => handleVote(downvoteAPost, post._id)}
individualView={false}
/>
))}
);Breakdown of the codeI created a GET request named fetchAllPosts which fetches 4 posts when the page loads. I used map function to list all the posts inside the InfiniteScroll component.In order to fetch the next set of posts, I had to make a slight change in the API of the request (written in Node.js) where I fetch the posts. That change was adding a count or a number that will tell me how many posts to fetch. When the user scrolls down the web page, those number of posts will be fetched from the database and displayed.// @desc Get all the posts
// @route GET /api/user/posts
// @access Public
const getAllPosts = asyncHandler(async (req, res, next) => {
const { count } = req.query;
const posts = await PostModel.find();
const postsToDisplay = posts.reverse().slice(0, count);
res.status(200).json({
success: true,
total: posts.length,
currentLength: postsToDisplay.length,
data: postsToDisplay,
});
});
I added a count variable which comes from the query in the URL just like this: api/v1/posts?count=4. This fetches only 4 posts.
3. Now, things were easier. Time to add the frontend code to fetch the next set of posts.
const [posts, setPosts] = useState([]);const [count, setCount] = useState(4);
const [currentCount, setCurrentCount] = useState(null);
const [total, setTotal] = useState(null);
const fetchPosts = async () => {
const data = await fetchAllPosts(count);
setPosts(data?.data?.data);
setCurrentCount(data?.data?.currentLength);
setTotal(data?.data?.total);
setCount(count + 2);
};The above code first fetches 4 posts (coming from the initial value of the count state variable).It also sets the current count or the current length of the posts which will be 4 on the first fetch.The value of total no. of posts is also set as it is being returned in the API response.Lastly, the value of count updates to 6, which will be used for the next fetch function call.
The above values are used in the InfiniteScroll component below:
dataLength={posts?.length} //This is important field to render the next datanext={fetchPosts}
hasMore={currentCount !== total}
loader={Loading...}
endMessage={
Yay! You have seen it all
}
>
{posts.map((post) => (
key={post._id}
post={post}
id={post._id}
handleUpvote={() => handleVote(upvoteAPost, post._id)}
handleDownvote={() => handleVote(downvoteAPost, post._id)}
individualView={false}
/>
))}
Working of InfiniteScroll component
In the above code, the list of posts are displayed. After this:
The value of dataLength gets assigned to the number of posts fetched for the first time.When the user scrolls down, the hasMore prop comes into action.hasMore tells us that if it is true, initiate the function available in the next prop. In our code, when the current count or current length of the posts is not equal to the total no. of posts, call the fetchPosts function.Then fetchPosts is called with the updated count value of 6, then 6 posts are fetched and the value of posts array is updated. The value of dataLength is also updated.If all the posts are not fetched, the content inside the loader prop is displayed after the latest post. Ideally, this can be a skeleton component or a loading text/animation.If hasMore is false or in other words, all the posts are fetched from the database, the element inside the endMessage prop is displayed after the last post.ConclusionInfinite scroll is a good approach to make a website perform a bit better but like everything in tech, this approach is not for every website. It mostly depends on the type of platform and the type of users (target audience).
I added this to Libertas, the online discussion platform built with Next.js, because the users will create multiple posts and it will be a headache/nightmare to render everything at once on a single web page. Wouldn’t it?
Hope, with this guide you will be able to add infinite scrolling in your React/Next.js project.
Wondering what Libertas is?Libertas is an online discussion website for users where they can just discuss. Discuss freely. No rules, no moderators.
You can just look at the posts that the users have created or if you feel hooked, you can sign up and start creating! You can upvote/downvote posts and comment on them. If you forget your password, there is an option reset it too!
You can let me know on LinkedIn or Twitter if you want any feature or would like to have a suggestion.
Any feedback is deeply appreciated!
The post 2024 Guide to Infinite Scrolling in React/Next.js appeared first on Suman Sourabh | Tech Blog.
May 23, 2024
How to Actually Upgrade Expo and React Native Versions to Latest?
I saw some extremely frustrating Reddit threads discussing about why it is so difficult to upgrade to the latest React Native version. I was at this sorry state because I was upgrading it incorrectly!
Recently, I was given a task to upgrade an Expo managed React Native mobile application to the latest version, i.e., Expo version 50.0.0.
Table of Contents1. Always upgrade one version at a time2. If you use a development build, create a new development build after each version upgradeUpgrade to Latest Expo Version1. Open the documentation on Upgrade Expo SDK and read it first!2. Upgrade Expo version3. Upgrade all dependencies to match the installed SDK version.4. Create a new development build (new apk file)5. Run development server6. Build the application7. Submit the application to Play StoreImportant NoteIf you also use an Expo managed project, here are the two most important things that you need to keep in mind:
1. Always upgrade one version at a timeUpgrading one version at a time is extremely important as even Expo has recommended the developers to do so in their upgrade documentation.
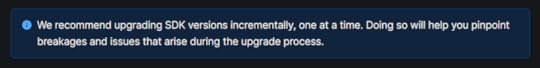
I was trying to upgrade from Expo v47 to v50 in one go!
That caused a lot of issues and much of my effort got wasted. It is easier to less errors by upgrading to v48 instead of resolving huge number of errors by upgrading to v50 directly.
2. If you use a development build, create a new development build after each version upgradeWhen I was first trying to upgrade, I didn’t follow this step. That resulted errors getting logged in on big red screens on my Android Studio virtual device.
Expo changelog documentation of v50 has mentioned this.

Now, here are the steps that you need to follow to upgrade to latest Expo/React Native versions.
Upgrade to Latest Expo Version1. Open the documentation on Upgrade Expo SDK and read it first!You will surely find some important information there.
2. Upgrade Expo versionHere, I am upgrading to v50
yarn add expo@50.0.03. Upgrade all dependencies to match the installed SDK version.This will help upgrade all the dependencies of the project and make them compatible with the current Expo SDK version.
npx expo install –fix4. Create a new development build (new apk file)I used a development build in my project, so I had to create new development build to test my application.
eas build --platform android --profile development5. Run development serverCheck and see if the app is running correctly and has no errors.
npx expo start --dev-client6. Build the applicationIf the application runs correctly, create a new production build.
eas build --platform android7. Submit the application to Play StoreIf the build is successful, initiate a new submission of your app to Google Play Store.
eas submit --platform androidThere you go! You have successfully upgraded the Expo and React Native versions of your project.
Important NoteEven if the steps are written here, it might not be a smooth sail to upgrade the Expo version of your application. You will encounter errors and warnings. The key is to research those on the internet by checking GitHub issues of those packages and checking going through discussions on StackOverflow.
Read more: How to Create Toggle Password Visibility with Material UI
The post How to Actually Upgrade Expo and React Native Versions to Latest? appeared first on Suman Sourabh | Web/Mobile Development Blog.
May 21, 2024
How to Create Toggle Password Visibility with Material UI
Have you ever entered your password in a password input field and forget what you just typed? And then you wanted to see it but wait! There was no option available to view your password.
To solve this problem, it is good to have a visibility icon in the password field which when once clicked, will allow the user to view their password and vice-versa.
Annoying, right?
This is how I created the same in Libertas, my Next.js full stack application with Material UI.
1. Create a component called PasswordInput
For reusing the same component in other pages, I created a separate component which will only have a TextField component of type “password”. You can name it whatever you want.
const PasswordInput = () => {
return (
);
};
export default PasswordInput;
This component has its own state which I used for the toggle visibility function.
Create a TextField of type “password”
I have used Material UI as the CSS library in Libertas, so I simply imported a TextField component (equivalent to input element of HTML) and pasted it into the PasswordInput component.
I installed Material UI with this command:
yarn add @mui/material @emotion/react @emotion/styled
If you have Material UI installed in your project, you can follow the same code given below.
import { TextField } from "@mui/material";
const PasswordInput = ({ password, handlePassword }) => {
return (
);
};
export default PasswordInput;
Notice how the value and onChange attribute values are coming through props.
2. Add toggle visibility functionality
I wanted to show the password when I click on the visibility icon (the eye icon) and when I click it again, password should get hidden.
To achieve this I added a state variable called showPassword which will take a Boolean value (true/false). I created it using useState hook.
const [showPassword, setShowPassword] = useState(false);
Initially, the value of showPassword should be false, meaning the password will remain hidden at the start.
When the user clicks on the eye icon, showPassword will change to true and password will be visible to the user.
So, I added a function responsible for clicking on the icon.
const handleClickShowPassword = () => {
setShowPassword(!showPassword);
};
The above function toggles the value of showPassword state variable.
But wait, something’s still missing right now.
Where’s the eye icon that I have been mentioning?
3. Add the toggle visibility icon on the TextField
To add the icons, I installed Material UI Icons package.
I used the following command to install it.
yarn add @mui/icons-material
I took a couple of icons from the Material icons page:
VisibilityOff
Visibility.
InputProps={{
endAdornment: (
aria-label="toggle password visibility"
onClick={handleClickShowPassword}
edge="end"
>
{showPassword ? : }
),
}}
If we want to add an icon inside the TextField component in Material UI, we have to use something called InputAdornment. It is one of the ways to add an icon to the TextField.
I added both the icons using a conditional operator to toggle the visibility based on the showPassword state.
Now, the PasswordInput component looks like this:
import { Visibility, VisibilityOff } from "@mui/icons-material";
import { IconButton, InputAdornment, TextField } from "@mui/material";
import { useState } from "react";
const PasswordInput = ({ password, handlePassword }) => {
const [showPassword, setShowPassword] = useState(false);
const handleClickShowPassword = () => {
setShowPassword(!showPassword);
};
return (
size="small"
type="password"
label="Password"
value={password}
onChange={handlePassword}
required={true}
InputProps={{
endAdornment: (
aria-label="toggle password visibility"
onClick={handleClickShowPassword}
edge="end"
>
{showPassword ? : }
),
}}
fullWidth
/>
);
};
4. Display the PasswordInput component on the page
Now, we can use the component in any page by importing it and passing the props to it.
"use client";
import PasswordInput from "@/components/formComponents/PasswordInput";
const DisplayPasswordInput = () => {
const [password, setPassword] = useState("");
return (
style={{ display: "flex", justifyContent: "center", padding: "4rem 0" }}
>
password={password}
handlePassword={(e) => setPassword(e.target.value)}
/>
);
};
export default DisplayPasswordInput;
This is what we see on the page:

We are still not done though.
If you look carefully at the code, we wouldn’t we able to see what we have typed on the password field.
Why?
Because in the type attribute, we have specified the value as “password”. No matter how many times we click on the visibility icon, Material UI will only show the dots in the password field.
5. Add “text” to the type attribute based on condition
To actually see what we type, we have to set the type attribute’s value to “text” when showPassword is true.
type={showPassword ? "text" : "password"}
Final code for toggle password visibility
import { Visibility, VisibilityOff } from "@mui/icons-material";
import { IconButton, InputAdornment, TextField } from "@mui/material";
import { useState } from "react";
const PasswordInput = ({ password, handlePassword }) => {
const [showPassword, setShowPassword] = useState(false);
const handleClickShowPassword = () => {
setShowPassword(!showPassword);
};
return (
size="small"
type={showPassword ? "text" : "password"}
label="Password"
value={password}
onChange={handlePassword}
required={true}
InputProps={{
endAdornment: (
aria-label="toggle password visibility"
onClick={handleClickShowPassword}
edge="end"
>
{showPassword ? : }
),
}}
fullWidth
/>
);
};
export default PasswordInput;
This is how I created the toggle password visibility functionality in Libertas.
You can import that component in your login page, sign up page or any other page!
Hello world!
Welcome to Astra Starter Templates. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start blogging!
Hello world!
Welcome to WordPress. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start writing!
August 5, 2023
I wrote my 40,000 word novel in 4 months. You can do it too!
In just 4 months, I wrote a 40,000 fiction novel from scratch and published it on amazon through KDP. Here's how you can do it too!
The post I wrote my 40,000 word novel in 4 months. You can do it too! appeared first on Suman Sourabh.
July 19, 2023
Upper Moon 1, Kokushibo Explained – Demon Slayer
Why did Kokushibo become a demon? How did the Upper Moon 1 die? What was his relationship with Yoriichi? Learn everything about Kokushibo in this blog!
The post Upper Moon 1, Kokushibo Explained – Demon Slayer appeared first on Suman Sourabh.
July 16, 2023
Top 20 Anime And Manga YouTube Channels
There's so much anime content out there, so here's a list of top 20 anime and manga YouTube channels in the world that you will ever need.
The post Top 20 Anime And Manga YouTube Channels appeared first on Suman Sourabh.
July 12, 2023
Why Are Attack on Titan Characters so Impactful?
Do you know that why the Attack on Titan characters will keep on making a big impact on your mind and heart even when the show is long over? Well, read this 5 min blog to find out!
The post Why Are Attack on Titan Characters so Impactful? appeared first on Suman Sourabh.
July 8, 2023
Why Jujutsu Kaisen Season 2 can be A Major Hit
Mappa's Jujutsu Kaisen Season 2 anime is here and we are all thrilled!! But do you know what is special this time? Read this 3 minute blog!
The post Why Jujutsu Kaisen Season 2 can be A Major Hit appeared first on Suman Sourabh.



