Guest Contribution: âArgentina: A Big Change with Problematic Initial Conditionsâ
Today, we are pleased to present a guest contribution written by Maria Muniagurria, faculty member in Economics at the University of Wisconsin – Madison.
A little over two months ago, Mauricio Macri began his tenure as president after his coalition of center-right parties prevailed over the ruling partyâs candidate by a small margin.
This is the first significant political change in many years, since the left leaning branch of âperonistâ party held the executive office since 2003 (both husband and wife Nestor and Cristina Kichner held the presidency). The following statement by former Finance Minister Kicillof summarizes the previous administrationâs approach to economic policy: âsince 2003, Argentina has been implementing … an economic model of growth with social inclusion, where inclusion and redistribution of income are seen as a precondition for growth and not vice-versa, as stated by the mainstream economic preceptsâ (October 2015 statement to the IMF).
Very favorable primary commodity prices and high export taxes financed large government expenditures (social programs, variety of subsidies) for many years but when the conditions started to reverse the country slipped into a path characterized by government deficits, inflation and foreign exchange controls. The 2001 default and the subsequent one in 2014 resulted in an almost complete exclusion of the country from international financial markets and since 2007 the government engaged in the manipulation of statistical data.
Since it took office last December 10th, the new administration has taken a number of important steps towards the elimination of major distortions, restoration of data transparency and return to international financial markets in the midst of a complicated political and social environment.
The economic team inherited a very difficult situation with an inflation rate reaching about 25-30 % a year, a government deficit of 7.1% of GDP and almost depleted foreign exchange reserves.
The main economic policy measures have been: 1) elimination of the foreign currency controls (âcepoâ or âclampâ) and unification of the foreign exchange market; 2) declaration of an âstatistical emergencyâ; 3) partial elimination of utility subsidies; 4) decrease of export taxes on soy (from 35% to 30%) and elimination of those for beef, wheat and corn, 5) negotiations towards the return of the country international financial markets (negotiations with debt âholdoutsâ ).
Data Transparency Issues and Inflation
Until 2007, Argentina had a high quality and internationally recognized national statistical office: the Instituto Nacional de Estadisticas y Censos (INDEC). At that time, political considerations motivated an âinterventionâ designed first to manipulate the inflation index. Unqualified political appointees replaced skilled statisticians and irregularities were commonplace both in data collection and reporting. Several indicators were no longer reported (poverty data among them), ânew indexesâ replaced long running ones and the unreliability of the economic data reported was documented by many (see for example Cavallo 2012)
In 2012, the IMF issued a warning to Argentine (Reuters) for not taking the necessary steps to improve the quality of its reported data (after earlier complains were not addressed) and proceeded to a motion of censure/official reprimand in 2013 (Bloomberg). The displaced statisticians received support from the American Statistical Association and in 2012 The Economist removed official price data from its tables.
The new government identified as a top priority the âreconstructionâ of INDEC and the return to accurate data reporting. A âstatistical emergencyâ was declared in December with two goals: facilitate the removal of unqualified staff /political appointees and temporarily suspend the report of inaccurate data while revisions are taking place. The task has proven to be quite challenging since there is political urgency to come up with an official inflation indicator (used by the powerful trade unions for salary negotiations and for many indexed contracts) and statisticians differ in their assessment of the time needed to produce quality data (see Buenos Aires Herald 2-16-16 for an account of a recent departure from the team).
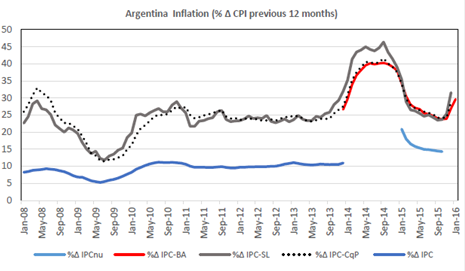
After 2007, alternative price indexes gained relevance and new ones were calculated and widely used by economic actors and politicians. Figure 1 shows the large discrepancy between INDEC data (blue lines, two versions of the CPI) and alternative ones. The gray line shows data from the statistical office of the province of San Luis, the red one is from the statistical office of the city of Buenos Aires and the dotted line is from a private group.
Figure 1: Sources: INDEC, Cosas que Pasan, DPEyC-San Luis, DGEyC-Ciudad de Buenos Aires
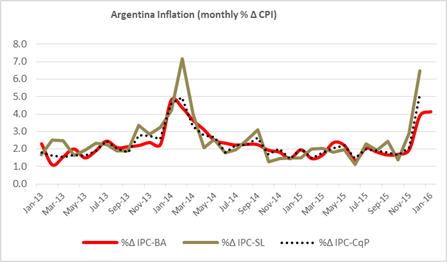
Inflation surged in November and December (even before the official change of government) fueled by expectations regarding the future value of the dollar.
Figure 2: Sources: Cosas que Pasan, DPEyC-San Luis, DGEyC-Ciudad de Buenos Aires
Foreign Exchange / Trade and Finance
In November 2011 the government began to impose strict controls on the foreign exchange markets (trying to stop the decrease of the Central Bankâs foreign reserves) what made almost impossible for ordinary citizens to purchase dollars and severely restricted imports. The âcepoâ (or clamp) resulted in the emergence of a black market for foreign currency, and the âofficialâ value of the dollar was kept artificially low. Exports suffered (producers were hoarding grain), import restrictions severely affected the availability of industrial inputs, and tourists expenses overseas (at an undervalued exchange rate) ballooned.
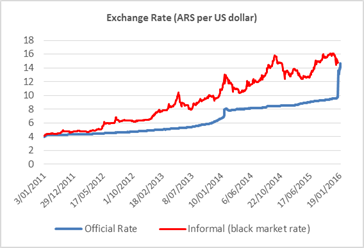
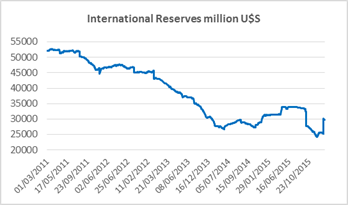
On December 16, after securing additional dollar reserves (due to a Yuan-dollar swap with China) and later a bridge loan from a group of international banks, the government fulfilled its campaign promise of lifting the âcepoâ. The exchange rate adjusted: there was an immediate devaluation of 35% and a gradual depreciation of the peso afterwards to arrive to a 55% devaluation since the lifting of the âcepoâ. The market has been operating without Central Bank intervention – except for one day last week – what should be considered as an important success. Figure 3 shows the paths of the official and black market rates and Figure 4 that of the international reserves.
Since the 2001 default, Argentina has been unable to borrow internationally and has been involved in a prolonged dispute with âholdoutâ bondholders (the 7% of that did not accept the 2005-7 restructuring). One of the judicial rulings (in New York courts) forced the default on the restructured debt in 2014. The current government has made significant progress in resolving the dispute and has stated its desire to return to the international financial markets (see The Economist 2-6-16).
Figure 3: Source: Diario La Nación
Figure 4: Source: BCRA (Argentine Central Bank) EstadÃsticas.
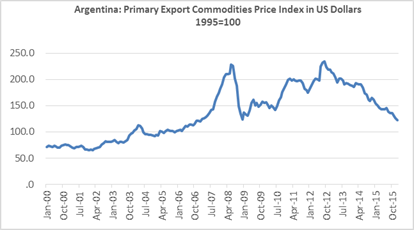
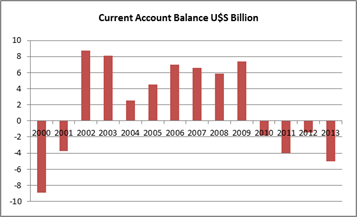
High primary commodity prices resulted in a favorable Current Account for many years but the decline in those prices and large energy imports moved the balance into negative territory (see Figures 5 and 6). The new economic team reduced export taxes on soy by 5% and eliminated those on wheat, corn and beef. These adjustments together with the devaluation are expected to increase exports and the local supply of dollars.
Figure 5: Source: BCRA (Argentine Central Bank) EstadÃsticas. (Weights are based on a commodityâs importance in Argentinaâs exports)
Figure 6: Source: IMF World Economic Outlook database, October 2015
The Fiscal Situation
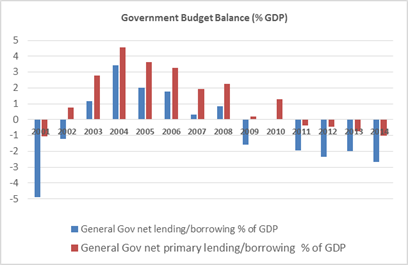
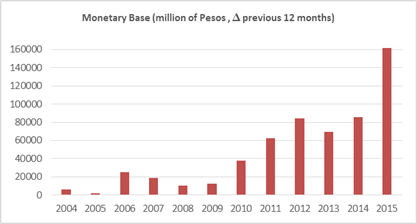
Argentina has a long history of lack of fiscal discipline but fiscal surpluses during the six years following the 2001 crisis provided a remarkable exception. The situation deteriorated after 2008, the deficits returned and the inability to finance them with debt left monetary emission as the only alternative to finance them (see Figures 7 and 8 and Maselli y Nicolini 2014).
Figure 7: Source: IMF World Economic Outlook database, October 2015
Figure 8: Source: IMF World Economic Outlook database, October 2015
Fiscal Plan and Inflation Targets, Central Bank Priorities
In early January, Finance Minister Alfonso Prat-Gay announced fiscal and inflationary targets stressing that government will stop financing deficits through transfers from the Central Bank to the treasury (monetary emission). The inherited primary fiscal deficit for 2015 was 5.8 % of GDP and increased to 7.1 % when interests and unpaid debts are included. The target is to reduce it by about 1.5 % GDP points per year to maintain governability. The inflation targets are 20-15% for the current year and 14%, 10% and 5% for the next ones.
According to Prat-Gay, President Macri directed him to keep social spending (welfare programs) untouched, increase investment if possible and find ways to reduce waste in every central government agency. The plan also includes removing subsidies to energy purchases in Buenos Aires, reducing the number of public employees that are not engaged in productive work (political appointees unqualified or not needed) while benefiting vulnerable citizens by cutting value added taxes on essential goods and increasing the threshold and brackets at which workers begin paying income taxes (Bloomberg 1-13-16, Enernews 1-13-16). The details of how the deficit will be financed during the first couple of years have not been announced.
Central Bank President Federico Sturzeneger also moved quickly to announce the bank’s policy objectives for 2016 and identified price stability as one of his main his priorities (also one of the missions of the bank according to its funding laws). He pointed out that in the past years, Treasury demands to finance fiscal shortfalls hindered the ability of the bank to fulfill this crucial part of its mission.
There is no doubt that lowering the inflation rate and reducing fiscal unbalances while maintaining governability will require not only sound economic policy but smart political decisions and a big dose of good luck. Macriâs team is very well qualified to take on this difficult task …so we hope for the best.
References
American Statistical Association, AMSTATNews
Banco Central de la Republica Argentina (BCRA)
Maselli, Luis y Nicolini , Juan Pablo. Monitor Fiscal , Marzo 2014, Foro Economico
Ministerio de EconomÃa: Plan Fiscal y Metas de Inflación 2016-19
This post written by Maria Muniagurria.
Menzie David Chinn's Blog