How to Enter 2023 ESPP Sales in H&R Block: Adjust Cost Basis
[Updated on January 28, 2024 with screenshots from H&R Block tax software for 2023 tax filing.]
If your employer offers an Employee Stock Purchase Program (ESPP), you should max it out. You come out ahead even if you sell the shares as soon as you can. See Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP) Is A Fantastic Deal.
After you sell the shares from the ESPP, part of the income will be included on your W-2. However, the tax form you receive from the broker still reflects your discounted purchase price. This post shows you how to make the necessary adjustment on your tax return using H&R Block tax software.
Don’t pay tax twice!
If you use other software, please read:
How to Report ESPP Sale in TurboTaxHow to Report ESPP Sale in FreeTaxUSATable of ContentsWhen to Report1099-B From BrokerUse H&R Block DownloadEnter 1099-B FormVerify on Form 8949When to ReportBefore you begin, be sure to understand when you need to report. You report when you sell the shares you bought under your ESPP. If you only bought shares but you didn’t sell during the tax year, there’s nothing to report yet.
Wait until you sell, but write down the full per-share price (before the discount) when you bought. If you purchased multiple times, write down for each purchase:
The purchase dateThe closing price on the grant dateThe closing price on the purchase dateThe number of shares you boughtThis information is very important when you sell.
Let’s use this example:
You bought 1,000 shares under your ESPP on 9/30/20xx. The closing price on the purchase date was $12 per share. The closing price on the grant date six months ago was $10 per share. You bought at $8.50 per share with the discount.
You would write down:
Grant Date4/1/20xxMarket Price on the Grant Date$10 per sharePurchase Date9/30/20xxMarket Price on the Purchase Date$12 per shareShares Purchased1,000Discounted Price$8.50 per shareKeep this information until you sell.
1099-B From BrokerWhen you sell, you will receive a 1099-B form from the broker in the following year. You will report your gain or loss using this 1099-B form and the information you accumulated for each purchase.
Let’s continue our example:
You sold 1,000 shares from your purchase above on 10/5/20xx at $11.95 per share. After commission and fees, you netted $11,925. You received a 1099-B form from your broker showing a sales proceed of $11,925 in the following year. The 1099-B form shows the cost basis as $8,500, which reflects your discounted purchase price.
Because you didn’t hold the shares for two years after the grant date and one year after the purchase date, your sale was a “disqualifying disposition.” The discount is added as income to your W-2. This raises your cost basis. If you just accept the 1099-B as-is, you will be double-taxed!
Now let’s account for it in the H&R Block software.
Use H&R Block DownloadThe screenshots below are from H&R Block Deluxe downloaded software. The downloaded software is both less expensive and more powerful than online software. If you haven’t paid for your H&R Block online filing yet, you can buy H&R Block download from Amazon, Walmart, and many other places. If you’re already too far along, make this year your last year of using the online service.
Enter 1099-B Form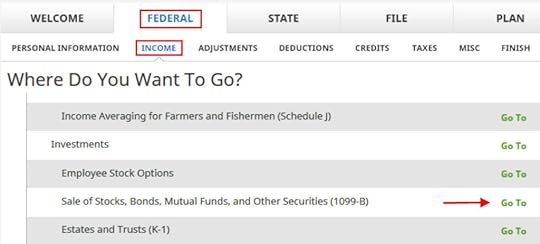
Click on Federal -> Income. Scroll down to find the Investments section. Click on the “Go To” link next to “Sale of Stocks, Bonds, Mutual Funds, and Other Securities (1099-B).”
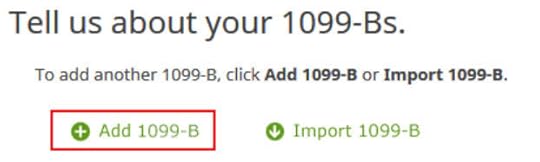
Import your 1099-B if you’d like. I’m adding it manually.
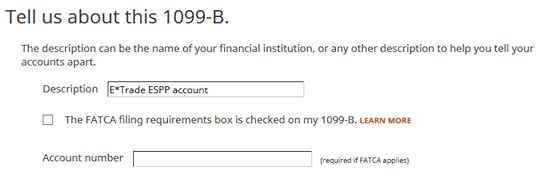
Give your account a description. Suppose this is from the ESPP account at E*Trade.
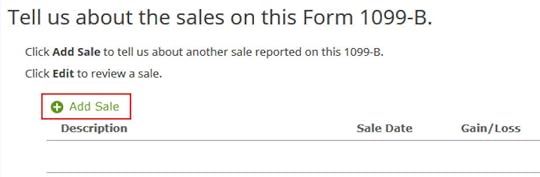
Now we add a sale.

We don’t want to add sales as a group because we need to make an adjustment.
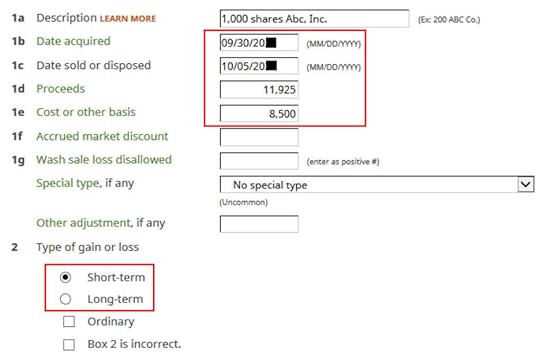
Enter a description. Enter the dates and numbers from the 1099-B form as they appear. Make sure to match the type of gain or loss reported on your 1099-B form. It was short-term on my form.
The cost basis on your 1099-B was reported to the IRS but it was too low. Don’t change it here directly.

Scroll down and check the box for “The basis was reported to the IRS.” Enter your purchase cost plus the amount added to your W-2 as your correct basis amount.
When you did a “disqualifying disposition” your cost basis was the full value of the shares on the date of the purchase. The market price was $12 per share when you purchased those 1,000 shares at $8.50 per share. Your employer added the $3,500 discount as income to your W-2. Therefore your true basis is $8,500 + $3,500 = $12,000.
If you didn’t sell all the shares purchased in that batch, multiply the number of shares you sold by the discount price on the date of purchase and add the discount included on your W-2. For example, if you sold only 500 shares and your employer added $1,750 to your W-2, your corrected cost basis is:
$8.50 * 500 + $1,750 = $6,000
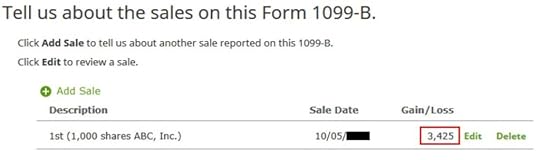
You are done with this entry. The summary gives the impression that you are paying tax again on a large gain, but don’t panic. We’ll verify it’s done correctly in the next section.
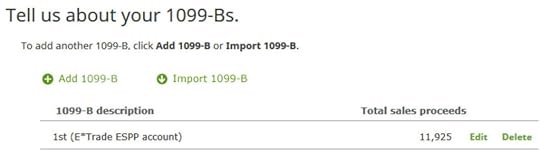
This shows a summary of the 1099-B form.
Verify on Form 8949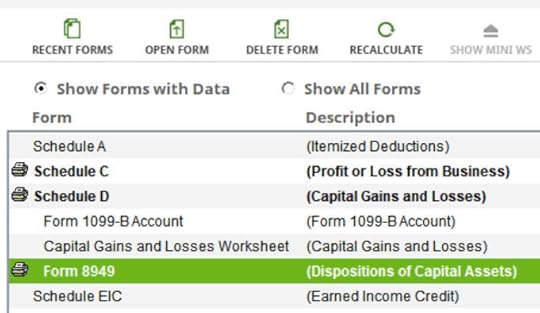
Click on the “Forms” button in the toolbar. Find Form 8949 and double-click on it.
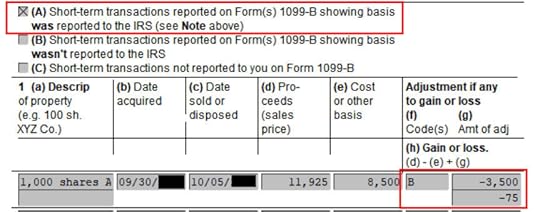
Find your sale in either Part I or Part II depending on whether it was short-term or long-term on your 1099-B form.
You see the negative adjustment in column (g). If you didn’t make the adjustment and you just accepted the 1099-B as-is, you will pay capital gains tax again on the $3,500 discount you are already paying taxes through your W-2. Remember to make the adjustment!
Learn the Nuts and Bolts I put everything I use to manage my money in a book. My Financial Toolbox guides you to a clear course of action.Read Reviews
I put everything I use to manage my money in a book. My Financial Toolbox guides you to a clear course of action.Read ReviewsThe post How to Enter 2023 ESPP Sales in H&R Block: Adjust Cost Basis appeared first on The Finance Buff.
Harry Sit's Blog
- Harry Sit's profile
- 1 follower



