Have we been miscalculating planetary hours?
Recently a fellow astrologer asked me how we define sunrise and sunset in the determination of planetary hours, a method of measuring time which dates back to ancient Babylonia. Looking up Babylonian time measurement online, I found the following at https://www.babylonianhours.com/:
“There are two different types of units of time in the Babylonian system, the first is set by homogeneous phenomena (i.e. always the same length), either astronomical (appearance of a star or movement of a celestial body) or physical (water clock), the second is a seasonal system whereby the length of an hour changes depending on the length of daylight. The Babylonians used multiple methods for measuring the passage of time throughout the day, a common system was dividing the 24-day up into 12 “double”-hours (bēru), these units of time were equivalent to 30° of the sun’s movement around the earth (360° divided by 12 is 30°) …”
My understanding is that the Babylonians used direct observation of the first appearance of the Sun or of a fixed star on the eastern horizon, and during the day they used a sundial to track to movement of the sun across the sky for time-keeping purposes.
The Sun measures about 32′ to 33′ of arc as viewed from the Earth, depending on the time of year and how close the Earth is to the Sun in its annual orbit.
 The angular diameter of the Sun varies between about 32′ and 33′ of arc, as viewed from Earth.
The angular diameter of the Sun varies between about 32′ and 33′ of arc, as viewed from Earth.Today we are aware of the refraction of light, which causes the Sun to appear to have risen above the eastern horizon while the body of the Sun is still below the horizon. I could find no references to indicate that the Babylonians were aware of the refraction of sunlight at sunrise, but they may have been because Claudius Ptolemy mentions refraction in his writings. The earliest reference I could find to the modern scientific law of refraction was to a text by the Persian astronomer Ibn Sahl in Baghdad in the year 984 CE. I don’t know whether Sahl and the medieval Persian and Arabic astrologers accounted for the refraction of sunlight to calculate planetary hours.
 Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snell%27s_law
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Snell%27s_law Now let’s consider the modern calculation of sunrise and sunset. According to the site https://stardate.org/astro-guide/sunrise-and-sunset:
“The official timekeeper for the United States, the U.S. Naval Observatory, defines sunrise and sunset as the moments when the center of the Sun is physically 50 minutes of arc below the horizon, which is a bit less than one degree. That accounts for the size of the Sun itself, and the “bending” properties of the atmosphere.”
This definition takes into account the fact that, due to refraction of its light, the sun appears to rise a few minutes before the body of the sun actually reaches the eastern horizon. Let me give an example. Suppose someone lives in New York City. What time would the sun rise on 8 November 2023?
According to the site https://sunrise-sunset.org/us/new-york-ny, the sun rose in NYC on 8 Nov 2023 at 6:33:05 AM EST. Let’s look at the astrological chart for that time in NYC, calculated using Solar Fire software.
 Scientifically calculated sunrise in NYC on 8 Nov 2023, taking account of refraction of light. Note that the entire body of the sun lies below the eastern horizon at the moment the upper rim of the sun appears to be just coming up over the eastern horizon. Based on the definition used by the official timekeeper for the United States, the U.S. Naval Observatory. The program PlanetDance gives the time of sunrise in NYC on this date as 6:34:03 AM EST..
Scientifically calculated sunrise in NYC on 8 Nov 2023, taking account of refraction of light. Note that the entire body of the sun lies below the eastern horizon at the moment the upper rim of the sun appears to be just coming up over the eastern horizon. Based on the definition used by the official timekeeper for the United States, the U.S. Naval Observatory. The program PlanetDance gives the time of sunrise in NYC on this date as 6:34:03 AM EST..Now let’s look at the table of planetary hours produced by Solar Fire for this chart:
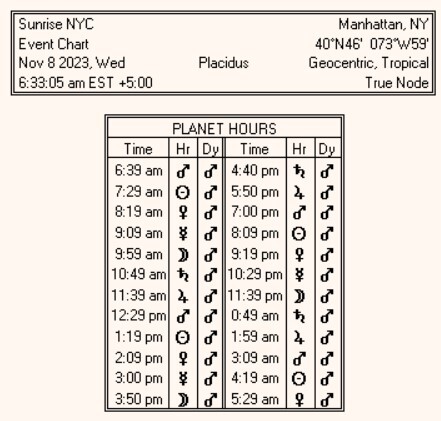 Sunrise, based on direct observation and taking into account the refraction of light, occurred at 6:33:05 AM EST, but this table lists sunrise as being at 6:39 AM EST (a rounded figure), some 6 minutes after the sun appears to have risen.
Sunrise, based on direct observation and taking into account the refraction of light, occurred at 6:33:05 AM EST, but this table lists sunrise as being at 6:39 AM EST (a rounded figure), some 6 minutes after the sun appears to have risen.It seem likely that the Babylonians, who gave us planetary hours, based their definition on direct observation, which would be in accord with the modern definition of sunrise by the U.S. Naval Observatory. If so, our modern astrological software may be off by several minutes in calculating the onset of planetary hours during the day. My view is that we should take account of refraction because the light of the morning sun reaches the Earth when the center of the sun arrives at 50′ of arc below the horizon and carries the influences of the sun to the sublunar world at that moment. It does not matter when the light of the sun has traveled a perfectly straight path or has been bent a bit on its journey from the sun to the Earth. What matters is that at a certain moment the light from the Sun first reaches the surface of the Earth at a given location.
In other words, I believe we should be calculating planetary hours based on the definitions that sunrise and sunset are the moments when the center of the Sun is physically 50 minutes of arc below the horizon. These definitions appear to be consistent with the ancient Babylonian use of direct observation of the sun rising over the eastern horizon as the start of the day to determine the first planetary hour of the day. This site is useful for calculating exactly when you can first see the morning sunbeams at your location: https://sunrise-sunset.org/
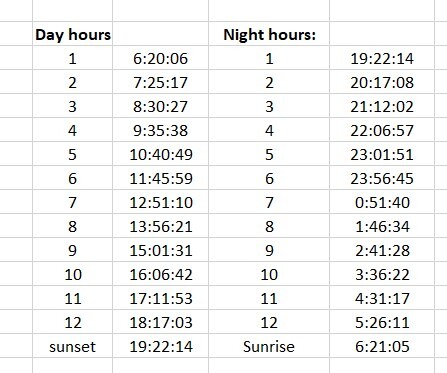
Experimenting with my own chart, I created an Excel spreadsheet to calculate planetary hours based on the U.S. Naval Observatory definition, which takes into account the refraction of sunlight. Here is the result:
A table of planetary hours from the Janus 6 program (which is very similar to the list generated by Solar Fire) for the same birth chart looks like this:

The Janus list of hours is off by about 4 minutes, as is the one from Solar fire.
The program PlanetDance does a much better job and is quite close to the list generated by the Excel spreadsheet differing by less than half a minute. The difference may be due to the fact that Planet Dance only allows coordinates to the nearest minute of arc, whereas I calculated the birth chart in Solar Fire with more exact coordinates of the birth place to the nearest second of arc. It may also be that PlanetDance uses a slightly different formula that that of the U.S. Naval Observatory:
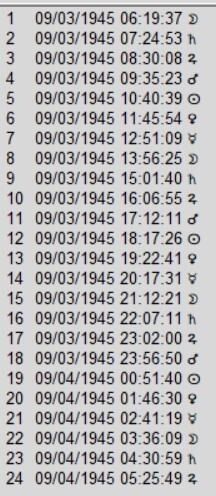 From Planet Dance
From Planet DanceMy recommendation, based on my current understanding of the history of planetary hours, would be to calculate them using the program Planet Dance (https://www.jcremers.com/) because the commercial programs do not appear to take into account the refraction of sunlight. Planet Dance differs slightly from the U.S. Naval Observatory formula, and it is possible that the program uses a slightly different formula to calculate sunrise and sunset, and it may even be more precise than the use of 50′ of arc from the center of the sun to the horizon. (For example, one site commented that the UTC time of sunrise (or sunset) in minutes is sunrise = 720 – 4*(longitude + ha) – eqtime where longitude and hour angle are in degrees and the equation of time is in minutes. See https://gml.noaa.gov/grad/solcalc/solareqns.PDF for details on using the longitude and latitude of the location and the Equation of Time to measure the time of sunrise and sunset in a given location. The values in PlanetDance are consistent with those found at this site: https://gml.noaa.gov/grad/solcalc/sunrise.html and its updated version at https://gml.noaa.gov/grad/solcalc/, which appears to be highly accurate. Unfortunately, this site only give the result to the nearest minute on the clock.
To use Planet Dance, go to the “TIME” menu and select “PLANETARY HOUR.” Put in the date and location and press “GO.” The program will then generate a list of planetary hours.
—————————-
Addendum: In a comment a reader mentioned that the online program Astro-seek.com produces a list of planetary hours very similar to the one produced by PlanetDance. Experimenting with Astro-seek, I got the following planetary hours list for my own chart, which is almost identical to the list calculated in excel using the U.S. Navy Observatory definitions.
 Planetary hours for my own chart calculated by Astro-seek, which is essentially identical to the one produced in my excel spreadsheet based on the U.S. Naval Observatory definitions of sunrise and sunset.
Planetary hours for my own chart calculated by Astro-seek, which is essentially identical to the one produced in my excel spreadsheet based on the U.S. Naval Observatory definitions of sunrise and sunset.
Anthony Louis's Blog
- Anthony Louis's profile
- 29 followers



