Tesla Business Model – Updated 2022
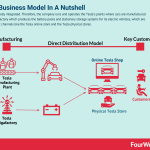

Tesla is vertically integrated. The company runs and operates the Tesla’s plants. Cars are manufactured at the Gigafactory which also produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles. These are sold via direct channels (Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores). In 2021, Tesla generated $53.8 billion in revenues. Automotive sales generated $47.2 billion (almost 88% of the total revenues); services/other genearted $3.8 billion; and energy generation and storage generated about $2.8 billion in revenues.
Revenues breakdown2021%Automotive sales$44.12B81.98%Automotive regulatory credits$1.46B2.72%Automotive leasing$1.64B3.05%Services and other$3.8B7.06%Energy generation and storage segment revenue$2.79B5.18%Total Revenues$53.8B Key Facts FoundersElon Musk, Martin Eberhard, JB Straubel, Marc Tarpenning, Ian WrightYear FoundedJuly 1, 2003, San Carlos, CAYear of IPOJune 29, 2010IPO Price$17.00Total Revenues at IPO$93.35 millions, as of Nine Months EndedSeptember 30 2009, prior to the IPOElon Musk becomes CEO2008Total Revenues in 2021$53.8 BillionEmployees99,290 full-time subsidiaries’ employees worldwideRevenues per Employee$542,079.00Who owns Tesla?Elon Musk is the primary individual shareholder, with 23.1% of the company’s sharesTesla business model quick breakdown
We describe the Tesla business model via the VTDF framework developed by FourWeekMBA.
Tesla Business ModelDescriptionValue Model: Transition to renewable energy.Tesla’s mission is “to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.” The company does that through mobility products (cars for now) powered by electric engines. And by building the infrastructure to produce energy from renewable sources (solar primarily).Technological Model: Multi-sided network effects. Mass manufacturingAs of now, Tesla is a car company, but it’s also and primarily a software company. When Tesla releases new software updates, these consistently improve its cars (from suspensions to self-driving and more). When it comes to certain features, like self-driving, Tesla enjoys network effects, where the more the software is used to record mileage, the better it gets. And the more Teslas are on the road, the more it creates the infrastructure where these cars understand each other. And the more energy stations are available, the more EVs become convenient vs. gas-powered vehicles. Also, Tesla is one of the few companies that managed to build a sold car business at scale, in the last century.Distribution Model: Direct Distribution. Leasing arm.Tesla leverages its online and physical stores. Since the start, the company opted for a direct approach, bypassing car dealers. In addition, Tesla built, over the years, stores that mimicked Apple successfully. Another important element for distribution over the years will be the company’s leasing arm. Suppose Tesla can make leasing convenient to its customers. In that case, it might be able to exponentially grow its revenues (just like the iPhone was subsidized by mobile carriers, a Tesla should be subsidized through convenient leasing agreements to make it scale at mass level in the US).Financial Model: automotive regulatory credits, leasing, generating margins at mass production for both cars and energy storage.Tesla’s regulatory credits will exponentially grow as the company scales its operations. In fact, those credits are given to Tesla because it produces 100% electric vehicles. Thus, as the production scales, Tesla will get more credits at no additional cost or effort. In addition, as Tesla scales, it might be able to build its leasing arm, which might work as the real cash cow, on the one hand, and also the driver of the company car sales in the future (a Tesla might be too expensive for many, without a lease). In addition, Tesla isn’t just a car company; it’s transitioning to become a major energy producer with its superchargers and electric infrastructure. From energy production to distribution, Tesla might become the Exxon of the future!Tesla founding storyThe electric carmaker company is owned by entrepreneur/visionary Elon Musk. Tesla was founded by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning in July 2003. Elon Musk entered Tesla in 2006, first as investor and chairman, then he took the role of CEO which he still holds today.
After many delays to the first production of the Tesla Roadster prototype (the first version of the Tesla, which was both a way to validate the market and to generate revenues to be invested in the production of new Tesla models), Martin Eberhard would eventually be ousted, and Musk would, later on, by 2008, become CEO of the compamy.
Who owns Tesla? By 2021, most of Tesla’s shares are still owned by Elon Musk, among the company’s co-founders and currently the CEO. Elon Musk is the top individual investor, with a 23.1% stake in the company, equivalent to over 244 million shares. Musk is followed by Lawrence Ellison (founder of Oracle), with a 1.5% company’s stake. Ellison also sits on Tesla’s board. And Antonio Gracias, among the company’s first investors, has over 1.6 million shares of the company. Other institutional investors and mutual funds like The Vanguard Group, Blackrock, and Capital Ventures International also have a good chunk of the company’s stocks.
By 2021, most of Tesla’s shares are still owned by Elon Musk, among the company’s co-founders and currently the CEO. Elon Musk is the top individual investor, with a 23.1% stake in the company, equivalent to over 244 million shares. Musk is followed by Lawrence Ellison (founder of Oracle), with a 1.5% company’s stake. Ellison also sits on Tesla’s board. And Antonio Gracias, among the company’s first investors, has over 1.6 million shares of the company. Other institutional investors and mutual funds like The Vanguard Group, Blackrock, and Capital Ventures International also have a good chunk of the company’s stocks.As of March 2022, Elon Musk is worth more than $240 billion, and this counting Tesla stocks only.
Understanding Tesla long-term strategyWhile we all know Tesla today, its strategy was shaped already a few years back. Usually effective strategies get rolled out in years, and only after they become successful those become obvious.
Yet, when they are getting rolled out they are not obvious at all. So much so, that those rolling out the unconventional strategy, are getting criticized, ostracized, and only at the end idolized.
This is the case of Tesla’s long-term strategy, which is worth analyzing to understand what entry-strategy Tesla employs, and what its long-term strategy looks like.
Targeting a subsegment of the automotive marketBased on the market context, companies, especially startups have to find ways to enter markets, often dominated by other players, and roll out a temporary business model, which is only viable in the short-term, as it helps the company to transition to a more mature business model, to achieve scale.

When Tesla entered the market, it did it via the launch of the Roadster, a sports electric car, so it could start validating the market gradually, by a sub-segment of the automotive industry.
This enabled Tesla to enter with a product priced competitively (Tesla wasn’t able at the time to offer an electric vehicle at a competitive price). As sports cars are higher-priced, that segment of the market was in fit with Tesla’s temporary business model.
At the same time, the sports car segment also had customers open to more innovative products, as long as they would be highly differentiated.
Yet before transitioning to a new business model, the company will need to validate smaller segments of the market by attracting the psychographic which is ready to take on the new technology.

Yet often new technologies require the development of a whole ecosystem. For instance, in the case, of Tesla, it’s not about convincing people that electric cars are “cool” (not only that).
But also, initially, about providing the infrastructure to make the electric vehicle competitive in terms of everything else (availability of charging stations, charging vs. refilling, cost of batteries, time to recharge, and so on).
Only a few years after, in 2012, Tesla would finally start to roll out a business model based on potential mass adoption of its electric cars:

Only in 2012, Tesla would finally launch its Model S, the electrical sedan, intended to be adopted at mass-level. This strategy is still getting rolled out, and it might still take years to get to the level of mass-production.
Successful strategies take years to become viable, as in some cases, they require the fit between the technology and the ecosystem it encompasses and the market.
When this happens the company rolling out the business model will reach its full potential in terms of scale.
Back in 2012, Elon Musk explained that well:
“In 2006 our plan was to build an electric sports car followed by an affordable electric sedan, and reduce our dependence on oil…delivering Model S is a key part of that plan and represents Tesla’s transition to a mass-production automaker and the most compelling car company of the 21st century.”
Is Tesla profitable yet?Tesla turned a profit for the first time in the third quarter of 2019. Indeed the company posted $143 million in net profits. However, annualized the company net losses were $862 million.
What’s Tesla’s value proposition?As highlighted in its financial statements, Tesla offers three core values to its customers:
Long Range and Recharging FlexibilityHigh-Performance Without Compromised Design or FunctionalityEnergy Efficiency and Cost of OwnershipTesla Core TechnologySource: Tesla Financials
Tesla’s core technology moves around three core parts:
Autopilot & Full Self Driving (FSD).Vehicle Software.Battery & Power train.Breaking down Tesla business modelFor the first time in its history, in January 2020, Tesla passed the $100 billion market capitalization.
By 2022, Tesla passed a trillion dollar market cap, a 10x growth. For some context, in the same period, a company like Ford had a 60-70 billion dollars market cap.
Tesla sells three main products:
Model 3: for mass adoptionA four-door mid-size sedan with a base price for mass-market appeal produced both in the Fremont Factory and. at the Gigafactory in Shanghai.
Model Y: the SUVThat is a compact sport utility vehicle (“SUV”) built on the Model 3 platform with the capability for seating for up to seven adults.
Model S and Model X: the full-size sedanThat is a four-door full-size sedan that features large touchscreens driver interface, Autopilot hardware, over-the-air software updates, and fast charging through our Supercharger network.
Related: What Is a Business Model? Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know
Elon Musk’s long-term vision for TeslaBack in 2018, Elon Musk highlighted the long-term vision for Tesla:
Our goal is to become the best manufacturer in the automotive industry, and having cutting edge robotic expertise in-house is at the core of that goal. Our recent acquisitions of advanced automation companies have added to our talent base and are helping us increase Model 3 production rates more effectively. We don’t want to simply replicate what we have built previously while designing additional capacity. We want to continuously push the boundaries of mass manufacturing.
Tesla’s mission can be summarized as:
to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
As the company highlights:
Tesla builds not only all-electric vehicles but also infinitely scalable clean energy generation and storage products. Tesla believes the faster the world stops relying on fossil fuels and moves towards a zero-emission future, the better.
Elon Musk is getting ready to share a further Master Plan, for Tesla’s coming decade.
Tesla revenue streams explainedMain Tesla subjects will be scaling to extreme size, which is needed to shift humanity away from fossil fuels, and AI.
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 21, 2022
But I will also Include sections about SpaceX, Tesla and The Boring Company.
 In 2021, Tesla generated over $53.8 billion in revenues, compared to the $31.5 billion in 2020. The largest segment in the automotive sales (comprising regulatory credits revenues), followed by leasing (as part of the automotive), generated $1.6 billion in 2021. Outside the automotive sales, services (non-warranty after-sales vehicle services, sales of used vehicles, retail merchandise, and more) accounted for $3.8 billion. And energy generation and storage accounted for $2.8 billion. US and China are the primary markets, with almost $24 billion and nearly $14 billion respectively, in 2021. In 2021, Tesla generated $5.6 billion in Net Income, a net margin of over 10%.
In 2021, Tesla generated over $53.8 billion in revenues, compared to the $31.5 billion in 2020. The largest segment in the automotive sales (comprising regulatory credits revenues), followed by leasing (as part of the automotive), generated $1.6 billion in 2021. Outside the automotive sales, services (non-warranty after-sales vehicle services, sales of used vehicles, retail merchandise, and more) accounted for $3.8 billion. And energy generation and storage accounted for $2.8 billion. US and China are the primary markets, with almost $24 billion and nearly $14 billion respectively, in 2021. In 2021, Tesla generated $5.6 billion in Net Income, a net margin of over 10%.Tesla has four main sources of income:
AutomotiveAutomotive leasingServices and otherEnergy generation and storageBased on Tesla’s financial statements, in 2021 the company almost doubled its revenues while improving substantially its bottom line.
The most important revenue stream is the Automotive sales revenue (which includes revenues related to the sale of new Model S, Model X and Model 3 vehicles, including access to Supercharger network, internet connectivity, Autopilot, full self-driving, and over-the-air software updates, as well as sales of regulatory credits to other automotive manufacturers) with over $45 billion, followed by automotive leasing with over $1.6 billion and services and other with over £3.8 billion.
How can we explain such a growth? In 2021, Tesla experienced a 58% growth YoY in automotive revenues. Primarily driven by the ramped up production and deliveries of Model 3 (and Model Y).
 For a bit of context, the Fremont factory churned out over 430 thousand vehicles in the last four quarters. And it’s ramping up production of the Model X:
For a bit of context, the Fremont factory churned out over 430 thousand vehicles in the last four quarters. And it’s ramping up production of the Model X:  Here all the key metrics trailing 12 months. With the spiked up sales of vehicles. Improved operating and free cash flows. Together with improved profitability. Therefore, Tesla today is a wholly different company than it was just three years before. As also highlighted by the financial metrics below:
Here all the key metrics trailing 12 months. With the spiked up sales of vehicles. Improved operating and free cash flows. Together with improved profitability. Therefore, Tesla today is a wholly different company than it was just three years before. As also highlighted by the financial metrics below: 
And to be sure, this was all but a linear process. As Elon Musk highlighted, Tesla’s success was far from taken for granted. The worst near to death experience was in 2018 when Tesla wasn’t able to hit its production target, in what Musk called a “production hell.”
In a November 2020 Tweet Elon Musk emphasized:That funding round completed 6pm on Christmas Eve in 2008. Last hour of last day possible, as investors were leaving town that night & we were 3 days away from bankruptcy. I put in all money I had, didn’t own a house & had to borrow money from friends to pay rent. Difficult time.Tesla distribution strategy
Tesla is vertically integrated, as its pipeline goes from manufacturing to direct sales of its vehicles.
As highlighted by Tesla “the benefits we receive from distribution ownership enable us to improve the overall customer experience, the speed of product development, and the capital efficiency of our business.”
Even though a vertically integrated network represented a substantial investment in terms of physical assets Tesla can keep control over the experience of its customers. While also being able to retain important feedbacks throughout the supply chain.
Indeed, in a model where the customer is reached via indirect distribution the company might lose control of the customer experience at the last mile, and the valuable feedback it can gather from the marketplace.
Tesla follows an unconventional distribution model compared to other car manufacturers where the final sale is made via car dealerships which not tied to the company.
Why did Tesla use a direct distribution approach?Back in October 2012, Elon Musk explained in a blog post, the whole philosophy around Tesla distribution strategy:
There are reasons why Tesla is pursuing a company owned store and service center model that we feel are really important. In many respects, it would be easier to pursue the traditional franchise dealership model, as we could save a lot of money on construction and gain widespread distribution overnight. Many smart people have argued over the years that we should do this, just like every other manufacturer in the United States, so why have I insisted that we take a unique path?
Some of the key elements that made Tesla go with this strategy, which was way more expensive, and hard in the short-term was:
Conflict of interest of franchise dealersFor traditional car dealers, gasoline cars constituted the vast majority of their business. Thus, the franchise dealer would have been in a conflict of interest in offering a Tesla product, as this would have required them to contrast their core business model.
Ability to educate and channel the customer toward choosing Tesla over established brandsAs Elon Musk highlighted back in 2012: “Tesla, as a new carmaker, would therefore rarely have the opportunity to educate potential customers about Model S if we were positioned in typical auto dealer locations.”
So Tesla built its own stores, located in central places (similar to Apple stores’ distribution or perhaps branding strategy) to educate and enable potential customers to place orders, but primarily as a long-term objective to educate consumers about the brand and the potential of electric vehicles.
Today, after almost a decade of this strategy, Tesla is among the most recognized brands, and its stores are places that people enjoy to visit, as the electric vehicles proposed by Tesla have become iconic.
Freedom to open direct stores anywhereWith a traditional distribution strategy, it would have been easy for Tesla to run in conflict with franchised stores, by opening direct stores in close proximity. By having only a direct distribution, Tesla doesn’t have such a problem.
Does Tesla spend nothing on marketing?Musk is famous for his unconventional stunts. For instance, the stunts of the flamethrowers or the Tesla roadsters sent on space managed to reach hundreds of millions of people worldwide without a dollar spent on ads.
However, this also fueled the myth that Tesla doesn’t spend a dollar on advertising campaigns or marketing.

Like any other company, Tesla has a marketing budget for advertising and marketing campaigns. As an example, in 2018 Tesla reported its “Marketing, Promotional and Advertising Costs:”
Marketing, promotional and advertising costs are expensed as incurred and are included as an element of selling, general and administrative expense in the consolidated statement of operations. We incurred marketing, promotional and advertising costs of $70.0 million, $66.5 million and $48.0 million in the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Thus, even though the former PayPal Mafia member Elon Musk is the master of unconventional PR, Tesla still needs advertising to push its sales.
However, if we compare that to the revenue figures for 2018 (over $21 billion), the spending on marketing activities is around 0,3% which is an incredibly low figure, almost negligible, considering that large companies like Tesla spend billion of dollars in branding campaings!
Based on that, we can indeed affirm, that it’s like Tesla doesn’t have a marketing budget at all! And we’re talking about a company that pased a trillion-dollar in market cap!
Tesla manufacturing explainedThousands of purchased parts sourced from hundreds of suppliers across the world. For the key parts (battery cells, electronics, and complex vehicle assemblies) Tesla developed closed ties.
For most car manufacturers, components to build the cars, are often single-supplied. Other parts are instead available from multiple sources. For as much possible to diversify the suppliers’ components as car manufacturers also Tesla can experience high volatility in sourcing the components for its cars.
To prevent that, Tesla either looks for multiple sources or can stock up inventories of components.
Is Tesla worth more than GM?In January 2020, Tesla passed for the first time in its history the market cap of $100 billion, twice the market cap of GM (about $50 billion) in the same period even though in 2018 GM had 6-7 times the revenues of Tesla. Tesla though is valued as a tech company, which in the future can capture a wider and wider market, thus becoming way more valuable.
By October 2021, Tesla market cap would 10x, reaching over a trillion dollar! This in part, was due to the fact that the company managed to successfully pass the mass manufacturing stage.
Undoubtly, Tesla is getting valued as a tech company, an electric energy platform (not much different from its oil equivalent: Exxon or Chevron), and a company that might generate hundreds of billions in sales in the coming years. This is the bet markets are making.
Tesla as a business platformLooking at Tesla just as a company it’s a limited view. Tesla is much more than that. The company is a business platform, meaning it doesn’t just make and sell cars, but it is also an energy generation and storage platform. So it’s both a pipeline and a platform. To understand that let’s see the various components that make Tesla up as a company.
Breaking down Tesla competitors As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with the self-driving software.
As an electric automaker and builder of sports cars and now trucks, Tesla’s competitors comprise companies like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Lamborghini, Audi, Rivian Lucid Motors, Toyota, and more. At the same time, Tesla is an electric energy production and storage company (SolarCity); it competes with Sunrun, SunPower, and Vivint Solar. And as an autonomous driving company, it competes with companies like Zoox, Waymo, and Baidu with the self-driving software.Tesla isn’t just an automaker; it is an electric-only car automaker, an electric storage company, and an autonomous driving player. For that, we’ll have to analyze Tesla from these three perspectives.
AutomakingWithin the automaking segment, Tesla has over the years diversified its products‘ lines, to cover different segments of the market. When Tesla entered the market, as a go-to-market strategy it had to enter it (nonetheless Elon Musk’s long-term vision to make the electric car available to the masses) with the Roadster model.

While this model is still available, this is the highest-priced model and the product Tesla used to bootstrap its operations. Indeed, at the time, Tesla couldn’t produce a lower-cost electric car (Model 3 will finally achieve this goal), and that is how Tesla made its business model viable as it entered the new market for electric cars. This is what I call a transitional business model:

Note: A transitional business model is used by companies to enter a market (usually a niche) to gain initial traction and prove the idea is sound. The transitional business model helps the company secure the needed capital while having a reality check. It helps shape the long-term vision and scalability.
Over the years, as the market matures, Tesla grew, an electric ecosystem was born, and the technology to enhance battery performance improved, Tesla also expanded its products‘ lines to cover the various segments.
Sport & PerformanceThe primary models covering these segments are:
Roadster: here some of the competitors are Dodge Challenger, Porsche Chiron, and BugattiModel S: in this segment, Tesla competes with players like Mercedes S-Class, BMW 7 Series, Porsche Panamera, Audi A7 & A8, and more.SuvThe primary models covering these segments are:
Model X: here some of the competitors are BMW X5, Mercedes-Benz GLS-Class, Volvo XC90, Porsche Cayenne.Model Y (compact SUV): in this segment, Tesla competes with Renault Zoe, Nissan LEAF, Volksvagen e-Golf, Audi e-tron and more.TruckIn this segment, Tesla just launched the Cybertruck:

Cybertruck’s competitors comprise Rivian, Ford, Bollinger.
City CarTesla has finally its mass-market product, the Model 3. This model competes with models such as BMW Series 2,3,4,5 Mercedes Class C, CLA, CLS, Audi A3, A4, A5, Lexus, ES, GS, and many others.
Energy StorageTesla acquired SolarCity back in 2016, for $2.6 billion, and with that, it competes in the electric production and storage industry with players like SunRun, SunPower, Vivint Sonar, Trinity Solar, and SolarWorld to mention a few.
Autonomous drivingTesla’s Autopilot is one of the key ingredients of its technology and one of the most interesting future developments for the company. In this segment, Tesla competes with other autonomous driving companies like Zoox (bought by Amazon), Waymo (an Alphabet bet), and Baidu.
Why the automotive regulatory credits matter for Tesla?Automotive Regulatory Credits generated over $1.4 billion in revenues to Tesla in 2021, compared to just 594 million in 2019.
How do they work? Since Tesla produces zero-emission vehicles (“ZEVs”), these credits are sold to other regulated entities “who can use the credits to comply with emission standards and other regulatory requirements.”
As Tesla rumps up its operations, those regulatory credits revenues will also grow together with the increased production of cars.
In fact, the credits are directly linked to Tesla’s new vehicle production.
This revenue stream is extremely imporant, because (even if small for now) it’s completely free. Meaning, there is no additional effort/cost for the company in having these credits, it only needs to produce more EVs.
And as the production scales, this number will grow exponentially, thus boosting the company’s profitability and cash flows (at least until this regulation will last)!
Key takeawaysBack in 2008, Tesla used a go-to-market strategy by targeting a small segment of the automotive industry (sports car) as it could offer at the time competitive options to customers in that segment.In 2012, Tesla started to roll out its long term mission to have electric cars, mass-produced with the launch of its Model S. This strategy is still getting rolled out, and as Tesla gains more market shares and build a more viable electric ecosystem it can also reduce its pricing, thus increasing the mass adoption for its cars.Tesla uses a direct distribution model where it sells directly through its e-commerce and physical stores across the world.Tesla also offers new vehicle sales with customers’ trade-in needs for its existing Tesla and non-Tesla vehicles. The Tesla and non-Tesla vehicles acquired through trade-ins are remarketed, either directly by Tesla or via third-parties.Tesla also owns several manufacturing facilities where it either single-source certain components or it diversifies components sources. Where possible Tesla stacks up components to reduce the risk and volatility of the supply chain.Tesla’s distribution strategy combined with its appeal as consumer brands with products like Model 3, priced with a base price for mass-market appeal, makes Tesla among the most valuable car manufacturers in the world.Read Also: Tesla SWOT Analysis, Transitional Business Models, Tesla Mission Statement.
Business resources:
The Ultimate Guide to Market SegmentationWhat Is a Business Model?The Complete Guide To Business DevelopmentBusiness Strategy ExamplesWhat Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas ExplainedBlitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A NutshellWhat Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas ExplainedWhat Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas ExplainedMarketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And ExamplesMarketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your BusinessHow To Write A Mission StatementWhat is Growth Hacking?Growth Hacking Canvas: A Glance At The Tools To Generate Growth IdeasCase studies:
Tesla Mission StatementWho Owns TeslaTesla SWOT AnalysisHow Does PayPal Make Money? The PayPal Mafia Business Model ExplainedHow Does Venmo Make Money? the Peer-To-Peer Payment App for MillennialsHow Does WhatsApp Make Money? WhatsApp Business Model ExplainedHow Does Google Make Money? It’s Not Just Advertising! How Does Facebook Make Money? Facebook Hidden Revenue Business Model ExplainedMarketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your BusinessThe Google of China: Baidu Business Model In A NutshellAccenture Business Model In A Nutshell Salesforce: The Multi-Billion Dollar Subscription-Based CRMHow Does Twitter Make Money? Twitter Business Model In A NutshellHow Does DuckDuckGo Make Money? DuckDuckGo Business Model ExplainedHow Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a NutshellHow Does Netflix Make Money? Netflix Business Model ExplainedThe post Tesla Business Model – Updated 2022 appeared first on FourWeekMBA.




