How Does Steam Make Money? The Steam Business Model In A Nutshell
Steam is a digital, video game distribution service created by American video game developer and publisher Valve Corporation in 2003.
Steam started as a way for Valve to control the patching process for games like Counter-Strike. The platform was also used to prevent cheating and provide easier access to content produced by the game developer. However, Steam required a constant internet connection at a time when only 20% of American households had access to broadband internet. What’s more, the interface was clunky and players were often locked out of the games they purchased as the platform’s authentication servers struggled to cope with demand.
Nevertheless, the 2004 release of Half-Life 2 – which could only be played with a Steam account – increased the popularity of the platform with three prominent packages emblazoned across the Steam storefront. The following year, Valve made a decision that would essentially make the platform what is today. They decided that Steam would move away from being a humble patch distributor and allow third-party developers to host and sell their own games.
Steam continued to grow in the following years, adding a competitive eSport scene and features more common to social media sites such as friend community groups and integration with review service Metacritic. The Steam Workshop was released in 2011 after a major user interface overhaul, enabling gamers to create and upload content directly to the platform. Many such contributions were used in Counter-Strike Global Offensive and Team Fortress 2, with Valve’s introduction of skins to CSGO saving the game from ruin.
The Steam Marketplace was released in 2012, allowing in-game items to be bought and sold using funds from digital wallets. Two years later, Steam transitioned from a gaming platform to one providing game services. Users could transform their laptops and tablets into wireless monitors to stream games or broadcast their sessions live to family and friends.
Steam now features almost 30,000 games from major publisher releases to independent titles and everything in between. There are an estimated 120 million monthly active users who logged a combined total of 31.3 billion hours of playtime in 2020.
Steam revenue generationSteam utilizes the online marketplace model where it connects buyers with sellers. The company collects various fees and commissions for providing services, facilitating transactions, and giving game developers exposure to a vast audience.
With that in mind, here is a more detailed look at how the company makes money.
CommissionsMost company revenue comes from the commissions Steam charges on the sale of a game.
The exact commission depends on the game’s net sales volume:
Net sales volume of under $10 million – 30% commission.Net sales volume between $10-50 million – 25% commission.Net sales volume over $50 million – 20% commission.Steam Direct feeSteam Direct is a submission path designed to provide a streamlined, transparent, and affordable route for new game developers to submit games to the Steam platform.
For each new submission, the developer is required to pay an app deposit fee of $100. The deposit fee is recoupable from the payment made if the app reaches $1,000 in gross adjusted revenue.
Transaction feesSteam collects a transaction fee of 5% to protect against fraudulent incidents and also to cover the cost of future Steam economy features.
The minimum transaction fee is $0.01 and is charged to the buyer based on the total item cost.
Connected Business Models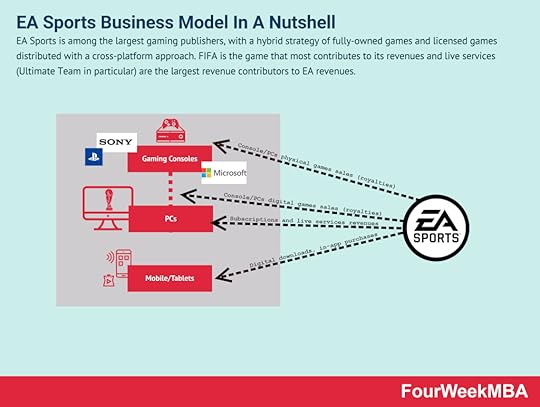 EA Sports is among the largest gaming publishers, with a hybrid strategy of fully-owned games and licensed games distributed with a cross-platform approach. FIFA is the game that most contributes to its revenues and live services (Ultimate Team in particular) are the largest revenue contributors to EA revenues.
EA Sports is among the largest gaming publishers, with a hybrid strategy of fully-owned games and licensed games distributed with a cross-platform approach. FIFA is the game that most contributes to its revenues and live services (Ultimate Team in particular) are the largest revenue contributors to EA revenues. The gaming industry, part of the entertainment industry, is comprised of three main types of players. From game engines, which help developers build their games. To publishing gaming houses. And gaming consoles. While the prevailing business model for decades has been that of selling the console at cost, and make money on games. Digital games changed the way games are distributed and sold, and it opened up the way to free-to-play models.
The gaming industry, part of the entertainment industry, is comprised of three main types of players. From game engines, which help developers build their games. To publishing gaming houses. And gaming consoles. While the prevailing business model for decades has been that of selling the console at cost, and make money on games. Digital games changed the way games are distributed and sold, and it opened up the way to free-to-play models. Roblox is an online gaming platform where users can create avatars and explore various gaming experiences. Each experience will be monetized based on how its developer has structured the game. For instance, free games allow users to spend the platform’s currency, called Robux, to get specific enhancements or purchase items like clothing accessories for the avatars, simulated gestures from the Roblox Avatar Marketplace. Therefore, Roblox makes money by earning a commission on each transaction and through its internal ad network.
Roblox is an online gaming platform where users can create avatars and explore various gaming experiences. Each experience will be monetized based on how its developer has structured the game. For instance, free games allow users to spend the platform’s currency, called Robux, to get specific enhancements or purchase items like clothing accessories for the avatars, simulated gestures from the Roblox Avatar Marketplace. Therefore, Roblox makes money by earning a commission on each transaction and through its internal ad network. Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in.
Tencent is a Chinese multinational conglomerate founded in 1998 by Ma Huateng, Zhang Zhidong, and Xu Chenye. Among its various global subsidiaries are companies in the online services, music, and artificial intelligence industries. But it is perhaps best known for its interest in the video game sector – both as a game developer for the Chinese market and the acquirer of several established gaming companies. Tencent is a vast company with a stake in more than 600 companies. Following is a look at some of the companies and subsidiaries it has a majority stake in. A free-to-play is a model that became particularly popular in gaming. Free-to-play is also commonly referred to as free-to-start. For instance, companies like Epic Games have launched popular games like Fortnite’s Battle Royale, which had ingrained a free-to-play model. This is a model that become extremely popular in the digital age of gaming.
A free-to-play is a model that became particularly popular in gaming. Free-to-play is also commonly referred to as free-to-start. For instance, companies like Epic Games have launched popular games like Fortnite’s Battle Royale, which had ingrained a free-to-play model. This is a model that become extremely popular in the digital age of gaming. The play-to-earn model is a business model allowing gamers to farm or collect cryptocurrency and NFTs that can be sold on the market. This model has become a standard already in the “crypto gaming industry,” where the blockchain-based games enable token economics to kick in as an incentives mechanism at scale for users to play and be engaged.
The play-to-earn model is a business model allowing gamers to farm or collect cryptocurrency and NFTs that can be sold on the market. This model has become a standard already in the “crypto gaming industry,” where the blockchain-based games enable token economics to kick in as an incentives mechanism at scale for users to play and be engaged. Candy Crush Saga is a match-three puzzle video game developed and published by King, a company specializing in social network-based games. Businessman Riccardo Zacconi co-founded King in 2003 after selling a subscription dating service he had also founded several years previous. The initial source of income for King was advertising revenue, but this strategy was abandoned in 2013. Today, Candy Crush Saga uses the freemium model (free to play) of revenue generation.
Candy Crush Saga is a match-three puzzle video game developed and published by King, a company specializing in social network-based games. Businessman Riccardo Zacconi co-founded King in 2003 after selling a subscription dating service he had also founded several years previous. The initial source of income for King was advertising revenue, but this strategy was abandoned in 2013. Today, Candy Crush Saga uses the freemium model (free to play) of revenue generation.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness CompetitionBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post How Does Steam Make Money? The Steam Business Model In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



