Break-even Analysis In A Nutshell


A break-even analysis is commonly used to determine the point at which a new product or service will become profitable. The analysis is a financial calculation that tells the business how many products it must sell to cover its production costs. A break-even analysis is a small business accounting process that tells the business what it needs to do to break even or recoup its initial investment.
Understanding a break-even analysisFor example, a break-even analysis may tell a business how many hours of service it needs to sell to cover its office space costs. Another business may use the analysis to determine how many cars it needs to sell to cover the cost of import tariffs.
Regardless of the context, the break-even analysis enables businesses to determine the point at which their endeavor becomes profitable. The results of the analysis may encourage the business to borrow money until the break-even point is reached. Alternatively, it may abandon the endeavor entirely.
Calculating the break-even pointThe break-even analysis involves a relatively simple calculation, with the equation as follows:
Break-even quantity = fixed costs / (sales price per unit – variable costs per unit)
Also note that:
Fixed costs are those that do not change with varying output, such as depreciation, rent, and management salaries.The sales price per unit is the price the product is sold at, andThe variable cost per unit includes the variable costs incurred during product creation. Variable costs are affected by increases or decreases in production output.Let’s break down the above equation by considering the example of a television manufacturer.
The company has fixed costs of $750,000, which include machinery depreciation and the lease on the factory.
The company also has variable costs of $100 which are derived from the purchasing of components, sales commissions, and production taxes. Each finished television sells for $1500.
Thus, the break-even point for the manufacturer is 750,000 / (1500-100) = 535.71. In other words, the company would need to sell at least 536 televisions to break even.
When should a break-even analysis be performed?The break-even analysis is useful in four common scenarios, including:
Starting a new businessThe break-even analysis is particularly important in determining whether a new business venture is economically viable. The analysis forces entrepreneurs to define realistic costs and pricing strategies.
Adding a new sales channelWhen a new sales channel is added, costs will change even if the prices do not. For example, an eCommerce shoe retailer looking to establish a new physical store will need to ensure the store breaks even. Otherwise, it may put the more profitable online store at risk. Costs may also increase if the retailer decides to sell shoes on Instagram and expenses associated with advertising and marketing must also be considered.
Creating a new productA break-even analysis should always be performed before committing to product development. Even if fixed costs remain the same, it is important to quantify the important variable costs that could make or break the initiative.
Changing business modelIf, for example, the shoe retailer wants to transition from holding physical inventory to drop shipping, a break-even analysis will determine whether prices need to change to reflect the new business model.
Key takeaways:A break-even analysis is a small business accounting process that tells the business what it needs to do to break even or recoup its initial investment. The break-even point tells the business how many products it must sell to cover its production costs. Calculating the break-even point involves accurately determining fixed costs, variable costs, and the sales price per unit. A break-even analysis is commonly used in four scenarios, including starting a new business, adding a new sales channel, creating a new product, and changing the company’s business model.Connected Frameworks To The Break-Even AnalysisFailure Mode And Effects Analysis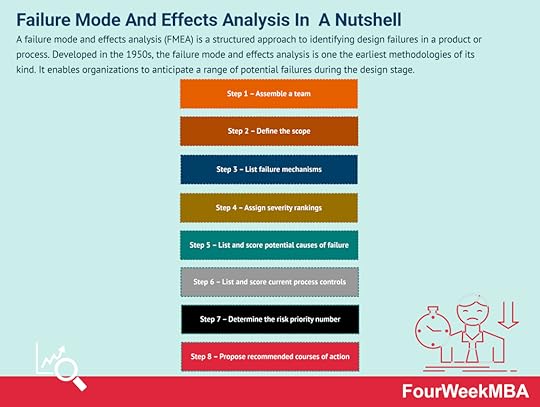 A failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to identifying design failures in a product or process. Developed in the 1950s, the failure mode and effects analysis is one the earliest methodologies of its kind. It enables organizations to anticipate a range of potential failures during the design stage.Agile Business Analysis
A failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to identifying design failures in a product or process. Developed in the 1950s, the failure mode and effects analysis is one the earliest methodologies of its kind. It enables organizations to anticipate a range of potential failures during the design stage.Agile Business Analysis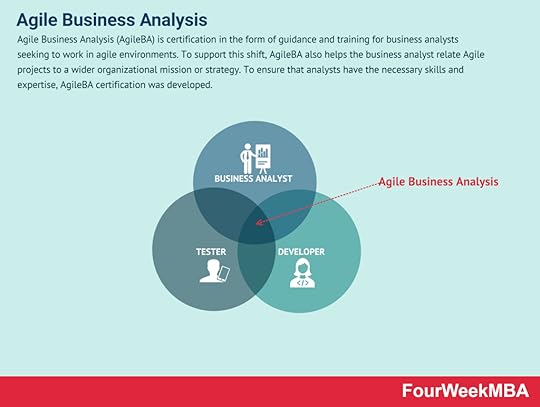 Agile Business Analysis (AgileBA) is certification in the form of guidance and training for business analysts seeking to work in agile environments. To support this shift, AgileBA also helps the business analyst relate Agile projects to a wider organizational mission or strategy. To ensure that analysts have the necessary skills and expertise, AgileBA certification was developed.Business Valuation
Agile Business Analysis (AgileBA) is certification in the form of guidance and training for business analysts seeking to work in agile environments. To support this shift, AgileBA also helps the business analyst relate Agile projects to a wider organizational mission or strategy. To ensure that analysts have the necessary skills and expertise, AgileBA certification was developed.Business Valuation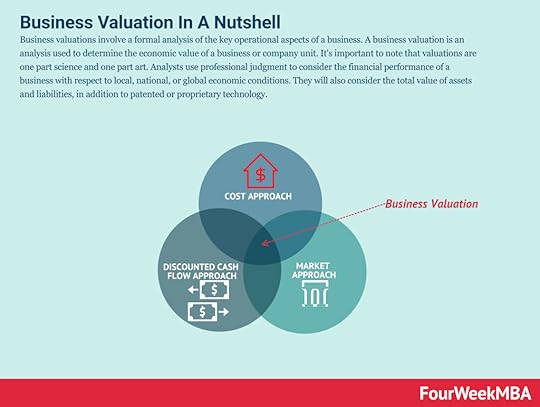 Business valuations involve a formal analysis of the key operational aspects of a business. A business valuation is an analysis used to determine the economic value of a business or company unit. It’s important to note that valuations are one part science and one part art. Analysts use professional judgment to consider the financial performance of a business with respect to local, national, or global economic conditions. They will also consider the total value of assets and liabilities, in addition to patented or proprietary technology.Paired Comparison Analysis
Business valuations involve a formal analysis of the key operational aspects of a business. A business valuation is an analysis used to determine the economic value of a business or company unit. It’s important to note that valuations are one part science and one part art. Analysts use professional judgment to consider the financial performance of a business with respect to local, national, or global economic conditions. They will also consider the total value of assets and liabilities, in addition to patented or proprietary technology.Paired Comparison Analysis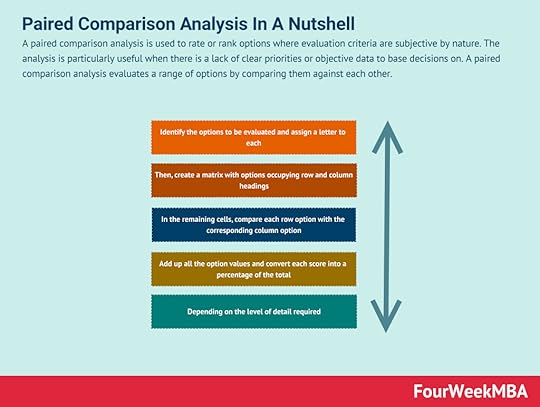 A paired comparison analysis is used to rate or rank options where evaluation criteria are subjective by nature. The analysis is particularly useful when there is a lack of clear priorities or objective data to base decisions on. A paired comparison analysis evaluates a range of options by comparing them against each other.Monte Carlo Analysis
A paired comparison analysis is used to rate or rank options where evaluation criteria are subjective by nature. The analysis is particularly useful when there is a lack of clear priorities or objective data to base decisions on. A paired comparison analysis evaluates a range of options by comparing them against each other.Monte Carlo Analysis The Monte Carlo analysis is a quantitative risk management technique. The Monte Carlo analysis was developed by nuclear scientist Stanislaw Ulam in 1940 as work progressed on the atom bomb. The analysis first considers the impact of certain risks on project management such as time or budgetary constraints. Then, a computerized mathematical output gives businesses a range of possible outcomes and their probability of occurrence.Cost-Benefit Analysis
The Monte Carlo analysis is a quantitative risk management technique. The Monte Carlo analysis was developed by nuclear scientist Stanislaw Ulam in 1940 as work progressed on the atom bomb. The analysis first considers the impact of certain risks on project management such as time or budgetary constraints. Then, a computerized mathematical output gives businesses a range of possible outcomes and their probability of occurrence.Cost-Benefit Analysis A cost-benefit analysis is a process a business can use to analyze decisions according to the costs associated with making that decision. For a cost analysis to be effective it’s important to articulate the project in the simplest terms possible, identify the costs, determine the benefits of project implementation, assess the alternatives.Financial Modeling
A cost-benefit analysis is a process a business can use to analyze decisions according to the costs associated with making that decision. For a cost analysis to be effective it’s important to articulate the project in the simplest terms possible, identify the costs, determine the benefits of project implementation, assess the alternatives.Financial Modeling Financial modeling involves the analysis of accounting, finance, and business data to predict future financial performance. Financial modeling is often used in valuation, which consists of estimating the value in dollar terms of a company based on several parameters. Some of the most common financial models comprise discounted cash flows, the M&A model, and the CCA model.CATWOE Analysis
Financial modeling involves the analysis of accounting, finance, and business data to predict future financial performance. Financial modeling is often used in valuation, which consists of estimating the value in dollar terms of a company based on several parameters. Some of the most common financial models comprise discounted cash flows, the M&A model, and the CCA model.CATWOE Analysis The CATWOE analysis is a problem-solving strategy that asks businesses to look at an issue from six different perspectives. The CATWOE analysis is an in-depth and holistic approach to problem-solving because it enables businesses to consider all perspectives. This often forces management out of habitual ways of thinking that would otherwise hinder growth and profitability. Most importantly, the CATWOE analysis allows businesses to combine multiple perspectives into a single, unifying solution.VTDF Framework
The CATWOE analysis is a problem-solving strategy that asks businesses to look at an issue from six different perspectives. The CATWOE analysis is an in-depth and holistic approach to problem-solving because it enables businesses to consider all perspectives. This often forces management out of habitual ways of thinking that would otherwise hinder growth and profitability. Most importantly, the CATWOE analysis allows businesses to combine multiple perspectives into a single, unifying solution.VTDF Framework It’s possible to identify the key players that overlap with a company’s business model with a competitor analysis. This overlapping can be analyzed in terms of key customers, technologies, distribution, and financial models. When all those elements are analyzed, it is possible to map all the facets of competition for a tech business model to understand better where a business stands in the marketplace and its possible future developments.Pareto Analysis
It’s possible to identify the key players that overlap with a company’s business model with a competitor analysis. This overlapping can be analyzed in terms of key customers, technologies, distribution, and financial models. When all those elements are analyzed, it is possible to map all the facets of competition for a tech business model to understand better where a business stands in the marketplace and its possible future developments.Pareto Analysis The Pareto Analysis is a statistical analysis used in business decision making that identifies a certain number of input factors that have the greatest impact on income. It is based on the similarly named Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of the effect of something can be attributed to just 20% of the drivers.Comparable Analysis
The Pareto Analysis is a statistical analysis used in business decision making that identifies a certain number of input factors that have the greatest impact on income. It is based on the similarly named Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of the effect of something can be attributed to just 20% of the drivers.Comparable Analysis A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company. To find comparables you can look at two key profiles: the business and financial profile. From the comparable company analysis it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.SWOT Analysis
A comparable company analysis is a process that enables the identification of similar organizations to be used as a comparison to understand the business and financial performance of the target company. To find comparables you can look at two key profiles: the business and financial profile. From the comparable company analysis it is possible to understand the competitive landscape of the target organization.SWOT Analysis A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.PESTEL Analysis
A SWOT Analysis is a framework used for evaluating the business’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It can aid in identifying the problematic areas of your business so that you can maximize your opportunities. It will also alert you to the challenges your organization might face in the future.PESTEL Analysis The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization. This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses that can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.Business Analysis
The PESTEL analysis is a framework that can help marketers assess whether macro-economic factors are affecting an organization. This is a critical step that helps organizations identify potential threats and weaknesses that can be used in other frameworks such as SWOT or to gain a broader and better understanding of the overall marketing environment.Business Analysis Business analysis is a research discipline that helps driving change within an organization by identifying the key elements and processes that drive value. Business analysis can also be used in Identifying new business opportunities or how to take advantage of existing business opportunities to grow your business in the marketplace.
Business analysis is a research discipline that helps driving change within an organization by identifying the key elements and processes that drive value. Business analysis can also be used in Identifying new business opportunities or how to take advantage of existing business opportunities to grow your business in the marketplace.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Break-even Analysis In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



