Monroe’s Motivated Sequence In A Nutshell

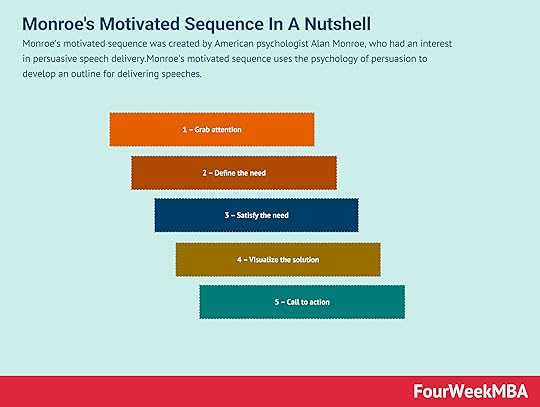
Monroe’s motivated sequence was created by American psychologist Alan Monroe, who had an interest in persuasive speech delivery. Monroe’s motivated sequence uses the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for delivering speeches.
Understanding Monroe’s motivated sequencePersuasive public speaking skills are important in business. Persuasion can create cohesion within a group around a specific goal or vision. Persuasion can also be used to motivate and encourage team members to hit important deadlines.
Some of these greatest persuasive speakers include Steve Jobs, Martin Luther King, Winston Churchill, and Barack Obama. Many believe that these individuals were simply born with the tools required to become effective public speakers.
However, this is not entirely true. Monroe discovered that these skills can be learned by following a simple methodology.
The five steps of Monroe’s motivated sequenceTo assist in crafting a compelling and persuasive speech, Monroe advocated following these five steps:
1 – Grab attentionFirst and foremost, grab the attention of the audience by telling a joke or asking a rhetorical question. This step is crucial. Depending on the quality of the introduction, people will decide whether your speech is worth their attention.
Primarily, this is achieved through trust and authority. Show the audience why the topic is relevant to them and give the speech credibility with supporting data, videos, charts, or images.
2 – Define the needUse this second step to help the audience understand that there is a problem or challenge that needs addressing. Explain the consequences of the problem not being solved in a way that is relevant to them.
Relevancy can be emphasized by using practical, real-world examples. Again, each should be supported by appropriate facts or data.
3 – Satisfy the needNow it is appropriate to let the audience know that you can satisfy their needs. It’s important to elaborate on the solution in terms that are easily understood. To ensure that the audience is on the same page, it can be useful to repeat the main concepts periodically.
4 – Visualize the solutionHow will the speech prepare the audience for taking action to satisfy their need? Without coming across the wrong way, the speaker should clarify what the future will entail if the solution is not enacted.
Conversely, the benefits of enacting the solution should also be highlighted to contrast both choices.
5 – Call to actionIn the final step, the speaker must tell the audience what they want them to do. In some cases, the plan of action may simply be to do nothing or refrain from certain actions.
The audience must feel they are a part of the solution. Provide several courses of action and allow them to choose. This increases a sense of empowerment as each individual feels in control of their destiny.
Lastly, the speaker should conclude with a powerful closing remark that ties the speech together. Some will also opt to take questions from the audience at this point.
Key takeawaysMonroe’s motivated sequence is an outline for delivering effective speeches using the power of persuasion.Monroe’s motivated sequence can be used in business to motivate employees to work toward a shared vision or meet important deadlines.Monroe’s motivated sequence provides five steps for delivering a persuasive speech. Importantly, the skill of persuasive public speaking can be learned.Connected Frameworks To The Monroe’s Motivated SequenceSix Thinking Hats The Six Thinking Hats model was created by psychologist Edward de Bono in 1986, who noted that personality type was a key driver of how people approached problem-solving. For example, optimists view situations differently from pessimists. Analytical individuals may generate ideas that a more emotional person would not, and vice versa.Value Stream Mapping
The Six Thinking Hats model was created by psychologist Edward de Bono in 1986, who noted that personality type was a key driver of how people approached problem-solving. For example, optimists view situations differently from pessimists. Analytical individuals may generate ideas that a more emotional person would not, and vice versa.Value Stream Mapping Value stream mapping uses flowcharts to analyze and then improve on the delivery of products and services. Value stream mapping (VSM) is based on the concept of value streams – which are a series of sequential steps that explain how a product or service is delivered to consumers.Affinity Grouping
Value stream mapping uses flowcharts to analyze and then improve on the delivery of products and services. Value stream mapping (VSM) is based on the concept of value streams – which are a series of sequential steps that explain how a product or service is delivered to consumers.Affinity Grouping Affinity grouping is a collaborative prioritization process where group participants brainstorm ideas and opportunities according to their similarities. Affinity grouping is a broad and versatile process based on simple but highly effective ideas. It helps teams generate and then organize teams according to their similarity or likeness.Fishbone Diagram
Affinity grouping is a collaborative prioritization process where group participants brainstorm ideas and opportunities according to their similarities. Affinity grouping is a broad and versatile process based on simple but highly effective ideas. It helps teams generate and then organize teams according to their similarity or likeness.Fishbone Diagram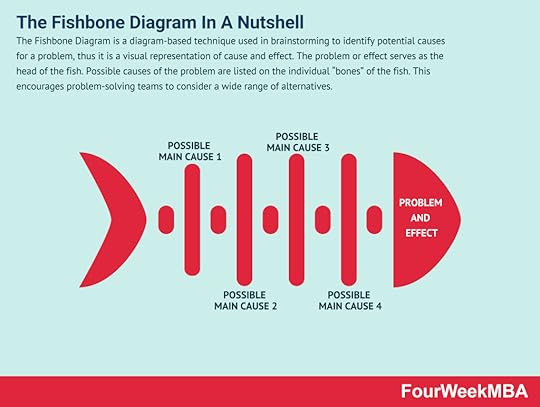 The Fishbone Diagram is a diagram-based technique used in brainstorming to identify potential causes for a problem, thus it is a visual representation of cause and effect. The problem or effect serves as the head of the fish. Possible causes of the problem are listed on the individual “bones” of the fish. This encourages problem-solving teams to consider a wide range of alternatives.SCAMPER Method
The Fishbone Diagram is a diagram-based technique used in brainstorming to identify potential causes for a problem, thus it is a visual representation of cause and effect. The problem or effect serves as the head of the fish. Possible causes of the problem are listed on the individual “bones” of the fish. This encourages problem-solving teams to consider a wide range of alternatives.SCAMPER Method Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.MECE Framework
Eighteen years later, it was adapted by psychologist Bob Eberle in his book SCAMPER: Games for Imagination Development. The SCAMPER method was first described by advertising executive Alex Osborne in 1953. The SCAMPER method is a form of creative thinking or problem solving based on evaluating ideas or groups of ideas.MECE Framework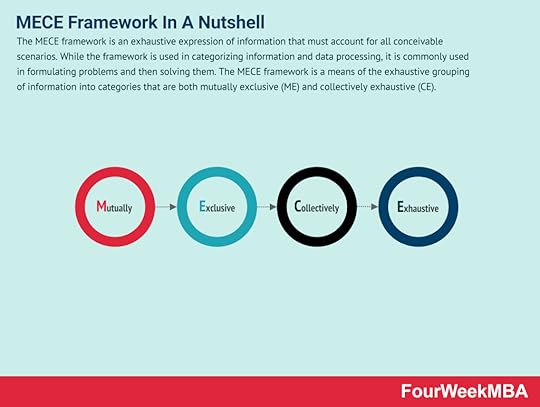 The MECE framework is an exhaustive expression of information that must account for all conceivable scenarios. While the framework is used in categorizing information and data processing, it is commonly used in formulating problems and then solving them. The MECE framework is a means of the exhaustive grouping of information into categories that are both mutually exclusive (ME) and collectively exhaustive (CE).Nadler-Tushman Congruence
The MECE framework is an exhaustive expression of information that must account for all conceivable scenarios. While the framework is used in categorizing information and data processing, it is commonly used in formulating problems and then solving them. The MECE framework is a means of the exhaustive grouping of information into categories that are both mutually exclusive (ME) and collectively exhaustive (CE).Nadler-Tushman Congruence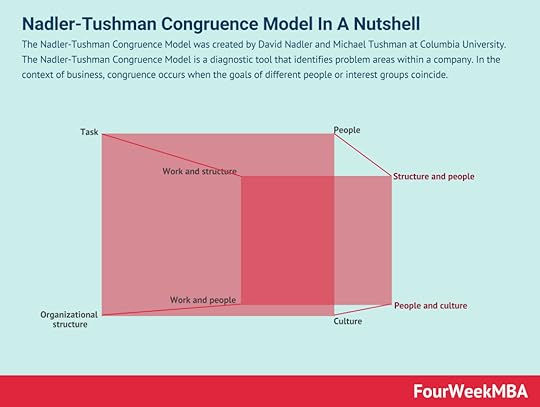 The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model was created by David Nadler and Michael Tushman at Columbia University. The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model is a diagnostic tool that identifies problem areas within a company. In the context of business, congruence occurs when the goals of different people or interest groups coincide.Lewin’s Change Management
The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model was created by David Nadler and Michael Tushman at Columbia University. The Nadler-Tushman Congruence Model is a diagnostic tool that identifies problem areas within a company. In the context of business, congruence occurs when the goals of different people or interest groups coincide.Lewin’s Change Management Lewin’s change management model helps businesses manage the uncertainty and resistance associated with change. Kurt Lewin, one of the first academics to focus his research on group dynamics, developed a three-stage model. He proposed that the behavior of individuals happened as a function of group behavior.
Lewin’s change management model helps businesses manage the uncertainty and resistance associated with change. Kurt Lewin, one of the first academics to focus his research on group dynamics, developed a three-stage model. He proposed that the behavior of individuals happened as a function of group behavior.Main Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsNetwork EffectsMain Case Studies:
Amazon Business ModelApple Mission StatementNike Mission Statement Amazon Mission StatementApple DistributionThe post Monroe’s Motivated Sequence In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



