Joseph Lee And The Bread Making Machine
Bread is one of our oldest and most popular of foodstuffs, with British households buying the equivalent of twelve million loaves a day, of which just over nine million are white. There is a bewildering array of choice with over 200 different kinds of bread produced in the UK, ranging from butter-rich brioche and crisp baguettes to farmhouse loaves and focaccia, soft ciabatta and crumpets to chapattis and flaky croissants, all made possible courtesy of the vast range and quality of British flour.
The market may have been sliced up between the large bakeries (around 80% of UK bread production) and in-store bakeries (17%), but a very distinctive lockdown trend has been the increase in the number of people making their own bread at home. In the twelve weeks up to June 14, 2020 The Grocer was reporting a surge in sales of ingredients required by the home baker, flour up by 113.2%, other baking ingredients by 72.6%, baking fruits by 72.3%, and sugar by 49.7%. Such was the unanticipated demand for flour in 1.5kg bags that UK millers had to work around the clock to replenish supermarket shelves.
But, whose idea was the bread maker?
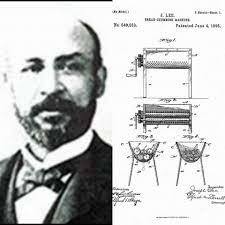
Joseph Lee was born in 1849, the son of slaves in South Carolina. After working as a servant in Beaufort, he served for eleven years in the US Coast Survey as a steward, where he developed his culinary skills. He was fascinated by the process of making bread and quickly recognised that evenly and thoroughly kneaded dough was the prerequisite for the perfect loaf.
Seeing that cooking offered him an opportunity to better himself, Lee took the bold step of opening a small local restaurant while still in his twenties. This did not satisfy his ambitions. In the 1880s he took over the Woodland Park Hotel in Newton, near Boston, a move which proved a great success, the Boston Daily Advertiser listing him as one of “Newton’s rich men” in 1886.
An extension to provide bowling alleys and billiard and pool rooms was opened to the public on May 7, 1890, completing an establishment that was “a picturesque structure with gables and towers, dormer windows, high chimneys and wide shady verandas… surrounded by seven acres of well-kept grounds”. It numbered the great and the good of Boston society amongst its clientele.
With America entering a depression in 1893, Lee had to keep a close eye on costs, focusing on a subject he knew well, bread making. Making bread by hand was laborious, delivered variable results and produced a lot of wastage. His solution was to automate the kneading process. On May 7, 1894 Lee secured a patent (No 524,042) for a kneading machine, “which will thoroughly mix and knead the dough and bring it to the desired condition without resorting to the tedious process of mixing and kneading the same by hand”.
Powered by a motor, pestles pounded the dough and screw conveyors moved it around the tray so that it was assaulted from all angles. Lee’s patent application stated that “the simplicity of construction and operation of the machine is such that it can be supplied at a minimum cost” saving time, labour and producing a superior product.
So effective was it that it did the work of six men, producing sixty pounds more bread from each barrel of flour than could be made by hand. As to quality, the Colored American magazine declared that “kneading done by it develops the gluten of the flour to an unprecedented degree, and the bread is made whiter, finer in texture, and improved in digestible qualities”.
Its efficiency meant that Lee had another problem on his hands – he was producing more bread than his guests could eat. His ingenuity knew no bounds and the following year he had devised and patented a device to mechanise the tearing, crumbling, and grinding of bread into crumbs. These were then used for everything from fried and battered fish to salad croutons and for one of America’s favourite breakfast meals before the advent of cereals, bread crumbs and milk.
Not content with the action of his kneading machine, he changed and patented the design in 1902 more closely to replicate the movement of the human hand. Eventually Lee assigned the rights to the kneading machine to The National Bread Co in return for shares and a slice of the royalties, while the bread-crumbing machine was sold to The Goodell Company of New Hampshire. He died in 1905.
By the mid-20th century automated ovens for bread making were widely used by commercial bakeries. A self-contained, all-in-one bread making machine for domestic use was a relatively recent concept, though, cooked up by the Matsushita Electric Industrial Company, now Panasonic, following research into the optimal method of kneading dough by Ikuko Tanaka. Launched in 1986, within a decade it was a must-have accessory in many an Occidental kitchen. Lee’s legacy is that all modern bread makers retain a miniaturised version of his original kneading design.
The best thing since sliced bread, you might say.



