Sustainable Competitive Advantage In A Nutshell
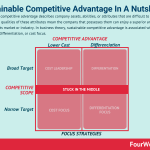
Sustainable competitive advantage describes company assets, abilities, or attributes that are difficult to duplicate or exceed. The qualities of these attributes mean the company that possesses them can enjoy a superior and long-term position in its market or industry. In business theory, sustainable competitive advantage is associated with cost leadership, differentiation, or cost focus.
Understanding sustainable competitive advantageThe business environment of today is extremely competitive, with technology and innovation allowing companies to be established with relative ease and attract consumers from all over the world.
One such example is the explosion in online retail businesses. While these are undoubtedly popular and the industry evergreen, the challenge for a new organization is to avoid becoming a copycat business with little to differentiate itself.
Harvard Business School Professor Michael Porter wrote the definitive sustainable competitive advantage textbook in 1985. Porter argued that for competitive advantage to be sustained, businesses must establish clear strategies, operations, and goals. The values of the company and corporate culture created must also be in alignment with said goals.
While he was writing the textbook, Porter researched hundreds of companies to identify what gave them a long-term competitive advantage.
In the following section, we’ll discuss the results of his research.
Three means of sustainable competitive advantage According to Michael Porter, a competitive advantage, in a given industry could be pursued in two key ways: low cost (cost leadership), or differentiation. A third generic strategy is focus. According to Porter a failure to do so would end up stuck in the middle scenario, where the company will not retain a long-term competitive advantage.Cost leadership
According to Michael Porter, a competitive advantage, in a given industry could be pursued in two key ways: low cost (cost leadership), or differentiation. A third generic strategy is focus. According to Porter a failure to do so would end up stuck in the middle scenario, where the company will not retain a long-term competitive advantage.Cost leadership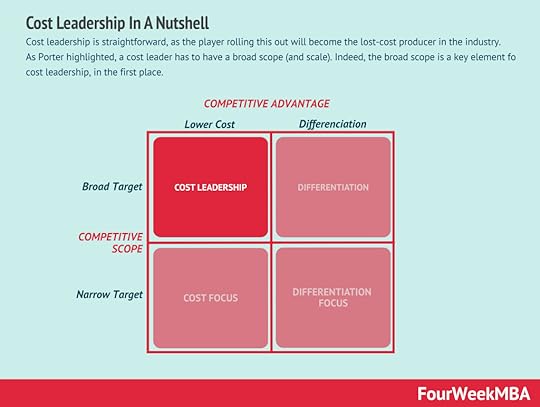 According to Porter there are three core strategies for competitive positioning: cost leadership, differentiation and focus. Cost leadership is straightforward, as the player rolling this out will become the lost-cost producer in the industry.
According to Porter there are three core strategies for competitive positioning: cost leadership, differentiation and focus. Cost leadership is straightforward, as the player rolling this out will become the lost-cost producer in the industry. Cost leadership means organizations consistently provide value at a lower price.
This means improving operational efficiency and, more often than not, paying workers less. Some companies will offset low wages with less tangible benefits such as stock options, loyalty programs, or promotional offers. Others simply take advantage of a surplus of unskilled labor and set their own wages.
Walmart and Costco are two examples of sustainable competitive advantage derived from cost leadership. These two businesses in particular use economies of scale to drive prices down to a point where other companies cannot compete.
Differentiation Product differentiation is a marketing strategy used by a business to differentiate its products or services from the competition, thus enabling your business to gain a long-term advantage (an economic moat), thus building a viable business model.
Product differentiation is a marketing strategy used by a business to differentiate its products or services from the competition, thus enabling your business to gain a long-term advantage (an economic moat), thus building a viable business model. In this case, the company differentiates itself by delivering better benefits than its competitors.
Differentiation can be facilitated by product quality or innovation, exemplary customer service, or rapid delivery time, among other things.
When department store Nordstrom became the first to allow item returns without question, it differentiated itself in the retail market. Jeweler Tiffany & Co. charges more for its products because its customers view its jewellery as higher quality than similar offerings.
Cost focusA business using cost focus as a sustainable competitive advantage understands and services its target market better than anyone else.
This can be achieved via cost leadership or differentiation. But more to the point, the business focuses on serving a very specific target audience and serving them well.
Community banks and credit unions use this strategy by targeting small businesses or affluent individuals. They can give a level of personal attention that would be unsustainable for a large banking institution with millions of customers on its books. Importantly, this personal touch is what the target audience craves.
Other factors that increase sustainable competitive advantageWhile Porter’s list of three traits is a good starting point, several other factors increase sustainable competitive advantage.
They include:
Branding – building a brand requires a large investment of time and money that is simply not replicable in most cases. Coca-Cola is one example of a company enjoying sustained dominance in the very competitive beverage industry.Strategic assets – companies with excellent research and development divisions tend to enjoy a sustainable competitive advantage. As a result of their efforts, they may hold patents, trademarks, and secure contracts that cannot be replicated.Geographic location – otherwise known as a national competitive advantage. Chinese firms are competitive globally because the standard of living is low in China, meaning companies can pay their workers less. The same can be said for Indian firms. In the United States, innovation is a national characteristic helping tech businesses dominate.Key takeaways:Sustainable competitive advantage describes company assets, abilities, or attributes that are difficult to duplicate or exceed. Sustainable competitive advantage was mentioned in a definitive 1985 paper by Harvard Business School Professor Michael Porter. After researching hundreds of companies, he identified three categories: cost leadership, differentiation, and cost focus.Sustainable competitive advantage can also occur because of high brand equity, strategic assets, and country-specific characteristics.Related Visual Concepts:
 Economic or market moats represent the long-term business defensibility. Or how long a business can retain its competitive advantage in the marketplace over the years. Warren Buffet who popularized the term “moat” referred to it as a share of mind, opposite to market share, as such it is the characteristic that all valuable brands have.
Economic or market moats represent the long-term business defensibility. Or how long a business can retain its competitive advantage in the marketplace over the years. Warren Buffet who popularized the term “moat” referred to it as a share of mind, opposite to market share, as such it is the characteristic that all valuable brands have.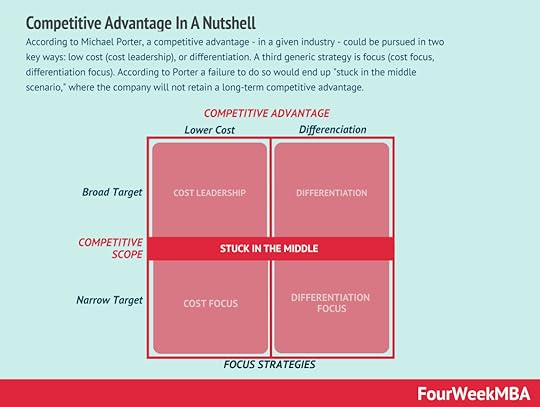 According to Michael Porter, a competitive advantage, in a given industry could be pursued in two key ways: low cost (cost leadership), or differentiation. A third generic strategy is focus. According to Porter a failure to do so would end up stuck in the middle scenario, where the company will not retain a long-term competitive advantage.
According to Michael Porter, a competitive advantage, in a given industry could be pursued in two key ways: low cost (cost leadership), or differentiation. A third generic strategy is focus. According to Porter a failure to do so would end up stuck in the middle scenario, where the company will not retain a long-term competitive advantage.Main Free Guides:
Business ModelsBusiness StrategyBusiness DevelopmentDigital Business ModelsDistribution ChannelsMarketing StrategyPlatform Business ModelsRevenue ModelsTech Business ModelsBlockchain Business Models FrameworkThe post Sustainable Competitive Advantage In A Nutshell appeared first on FourWeekMBA.



