Eric C. Sheninger's Blog, page 13
October 30, 2022
Strategies to Empower Reluctant Staff
As a leader, have you ever been so excited about a new initiative or innovative idea only to learn that some of your staff weren’t as equally thrilled? Early in my career, this was more the norm than the exception. I vividly remember getting excited about improving parent communication with, at the time, a state-of-the-art app. Since I saw the inherent value that it would have in the hands of my teachers to get information out readily while building relationships in the process, I couldn’t wait to usher in this change.
I began with a detailed email with attachments and planned a more formal presentation at an upcoming faculty meeting. The time finally came, and I facilitated a demonstration of the tool and then had my staff discuss the merits and possible issues with incorporating the tool across the entire school. To my dismay, at the time, my staff was primarily lukewarm to the idea or totally against everyone using a digital tool for communications. I felt both blindsided and confused. After meeting with some of my most trusted teachers, I decided not to move forward with the app. However, this was an invaluable learning experience for me, which helped when I tried to lead other change initiatives.
There were times, like the example above, when I did not find success with change. It’s not that they were bad ideas or a waste of time and resources. Instead, it was human nature in terms of a resistance to change that was the cause of reluctance in some of my staff. Fear of the unknown and being comfortable where one is at can stymie even the noblest efforts. As a leader, it was my responsibility to help my staff overcome both of these potential impediments and you can as well.

Know your stuff
It is critical to deeply understand what you are trying to achieve, why this journey is essential to embark on, and how it will lead to better outcomes. Begin embracing a scholarly mindset so you can connect research and evidence when it is time to lay out a path forward. Be sure to be transparent along the way, so your staff knows the advantages of the change and potential disadvantages. Most importantly, look for opportunities to model new ideas.
I shared the following in Digital Leadership.
Leadership is about action. Don’t expect others to do what you have not done or are not willing to do yourself.
Listen and learn to understand needs
Knowing your stuff also means you are willing to listen to staff concerns to gain greater insight that can be leveraged to overcome reluctance. Consider this a vital learning experience that can be used to influence both the decision process and future implementation. Incorporating feedback and addressing concerns openly can shift the tide. The opposite also holds true. When big decisions are made unilaterally, stiff resistance typically follows.
Instill value
There is no more significant catalyst for accepting change than when people clearly know the why behind the endeavor. It works to help people embrace what is being asked of them and, in the process, increases the likelihood of success. Value can also be secured by supplying clear evidence that the change is warranted and providing ongoing professional learning support.
Human nature can be a fickle thing. Reluctance to change might never be fully overcome. As leaders, it is prudent to be proactive when pursuing anything that bucks the status quo to empower staff to want to be part of the solution.
What strategies have you found to work when it comes to reluctant staff?
October 23, 2022
Better Feedback for Deeper Learning
In order to learn and grow, some type of feedback is needed along the way. While an experience can be a foundation for learning, it is the feedback that often serves as a catalyst for reflection. At this point, learners gain valuable insight into the strategies being used so that adjustments can be made to make better progress. There is also a robust research base to validate its importance. Goodwin & Miller (2012) provided this summary:
In Marzano, Pickering, and Pollock's 2001 meta-analysis, McREL researchers found an effect size for feedback of 0.76, which translates roughly into a 28-percentile point difference in average achievement (Beesley & Apthorp, 2010; Dean, Pitler, Hubbell, & Stone, 2012). John Hattie (2009) found a similar effect size of 0.73 for feedback in his synthesis of 800 meta-analyses of education research studies. It was found that feedback ranked among the highest of hundreds of education practices he studied.
All feedback isn’t created equal. For it to have an impact, it must be timely, practical, specific, facilitated in a positive manner, and consistent. Hattie and Timperley (2017) shared the following.
Hattie and Timperley (2007) say that effective feedback must answer three major questions: Where am I going? (What are the goals?) How am I going? (What progress is being made toward the goal?) Where to next? (What activities need to be undertaken to make better progress?)

Besides the elements listed above, the medium used matters, especially in the classroom, since time is at a premium for teachers. While the desire is there to engage learners in a feedback dialogue, the reality is that it can be a challenge with large class sizes in addition to other demands. Hence, the reason I shared the feedback log concept in Disruptive Thinking in Our Classrooms.
Think about all the conversations that educators have with learners on a daily basis. The valuable information, in many cases, aligns with what the research has said constitutes good feedback. The problem, though, is the reasonable possibility that learners forget what they have been told regarding progress or improvement and don’t have the ability to later reflect on the feedback given. Having students create a feedback log solves this issue by helping them remember, retain, reflect upon, and chart their progress of improvement. Best of all, it requires no extra time on the part of the teacher.
While I presented the concept in my book, it wasn’t until recently that I saw an exemplary feedback log during a coaching cycle with Quest Academy Junior High School in Utah. I am still in awe of the vision and culture that principal Nicki Slaugh has worked with her staff to create. So many sound strategies were seen consistently, such as exit tickets, learning targets, self-pacing, and learner autonomy for personalization. When visiting Courtney Hutchins’ ELA class, I saw students following their own path in a self-paced format. As they worked, she used data to call up individuals and engage in a feedback dialogue. During the conversation, students were asked to write down the feedback in a log. You can see an example of this below.

Try This
Develop your own feedback log template or adapt the example pictured above. The most important aspect is to unpack the standard(s) into learning targets and ensure that the feedback that is verbalized helps students advance to these goals.Have students keep this log in a binder or online document and have them reflect on what they have done to incorporate the feedback.Let families know you are using this strategy so they can review and support their kids at home.Implementing feedback logs saves precious time, can be seamlessly aligned with research-based strategies, will help students monitor their understanding of concepts, and can be used to provide more targeted support to those who really need it to succeed. Best of all, they can serve as an empowerment tool to help kids exert more ownership over their learning.
Goodwin, B. & Miller, K. (2012). Research says good feedback is targeted, specific, timely. Educational Leadership, 70(1), 82–83
Hattie & Timperley (2007) The Power of Feedback. Review of Educational Research (Vol 77, No1).
October 16, 2022
Your Ticket to More Effective Lessons
During my training to become a teacher, I was immersed in the work of Madeline Hunter when it came to lesson plan design. Her Instructional Theory into Practice (ITIP) model helped me identify the strategies I would use on a daily basis to help my students learn. These included the anticipatory set (hook), reviewing prior learning, checking for understanding, forms of practice, and closure. Every lesson had these elements and I often received positive feedback from administrators on these when they observed me. Closure is something I was incredibly proud of and I always ended lessons with some form of paper exit ticket. I shared the following in Disruptive Thinking:
While the opening moments with students are crucial, so are the final minutes. Think about this for a second. What’s the point of an objective or learning target, whether stated, on the board, or students having the opportunity to discover for themselves, if there is no opportunity at the end of the lesson to determine if it was achieved? Learning increases when lessons are concluded in a manner that helps students organize and remember the point of the lesson.
At the time, this model was both a practical and effective means for planning direct instruction and was readily embraced as this was the primary strategy used in classrooms. It streamlined practices in an efficient way that could be replicated day in and day out. Herein lies the main disadvantage of ITIP. It was a one-size-fits-all approach centered on the teacher making all the decisions from an instructional standpoint at the expense of developing competent learners who can think.
Like many things in education, elements of ITIP still have value depending on how they are used. Closure is still critical, in my opinion, as a means to determine lesson effectiveness and serve as a catalyst for reflective growth. Exit tickets, when constructed well, represent a sound strategy to be implemented at the conclusion of a lesson. In simple terms, these are ungraded formative assessments that assess what students learned during the course of the lesson. The data from then can be used to identify the following:
Level of masteryAreas of difficultyOpportunities to reteachGaps in learner understanding
The information gleaned from them provides the teacher with additional insight as to how the lesson went and what can be done to improve it in the future. A recent visit to Quest Academy Junior High School, where I began longitudinal work on personalized competency-based learning (PCBL), got me thinking more deeply about this strategy. The principal, Nicki Slaugh, is a trailblazer in this area and I am fortunate enough to be providing coaching support to her staff to take them to the next level. While visiting classrooms with Nicki, we saw a slew of outstanding practices in action. However, I was incredibly impressed with the exit ticket created by science teacher Melanie Hueftle, which you can see below.

Not only does this meet the criteria for a well-designed exit ticket, but it also goes much more profound and serves as a more powerful reflective tool for both the teacher and the student. As reported by John Hattie, self-reported grades/student expectations are one of the most effective strategies out there (effect size = 1.44). The exit ticket puts the “personal” in personalized as each learner determines where they are in relation to the learning target. I also love the fact that they can advocate for support from not one but two different teachers. Knowing Nicki and her incredible staff, what you see above is most likely the norm in many Quest Academy classrooms.
Try This
First, if you’re already using exit tickets or some other means of lesson closure, that’s great, but take a minute to reflect on whether they’re providing the type of substantive info I’ve outlined here, or if they’re simply making your lessons slightly longer. Consider if your use of closure elements might be tweaked to provide greater value to you and to your students. As you approach future lessons, zero in on what these tasks are telling you about student learning—on an individual basis and as a whole group. Are you seeing any patterns? How might you adjust your instruction to provide more focus where each student needs it?If exit tickets are new to you, that’s great, too—what an opportunity! First, consider what feedback would be most helpful to you and your students. The example I provided here is just one, but Google “exit tickets” and you’ll see a number of examples. Don’t reinvent the wheel. Find one that fits your needs and modify it to make it yours. What lesson this week is a natural fit for an exit ticket? Choose one, develop your ticket, and just try it with your class. Then reflect on the information it provides—how does this align with your expectations around what you want your students to understand? What steps will you take to adjust your instruction? Remember, data is great, but it’s what we do with it that matters.My hope is that these simple tips help you improve what you are already doing or provide the means to develop powerful exit tickets that not only serve as closure, but set the stage for your next lesson.
October 9, 2022
Core Elements of Personalization
Many concepts are looked upon negatively as they are associated with buzzwords, fads, or a lack of substance. You won’t get much of an argument from me as to the validity of this view because it is true in many cases. Educators want proven strategies that can be implemented readily that will address diverse learner needs while leading to an improvement in outcomes. Personalization is far from a fad or buzzword as it represents an equitable approach to learning. I shared the following definition in Disruptive Thinking in Our Classrooms:
Personalization constitutes pedagogical approaches that ensure all learners get what they need when and where they need it to succeed.
Personalization represents a shift in focus from the “what” (content, curriculum, tests, programs, technology) to the “who” to create a more personal learning experience for all kids. At the forefront is developing and sustaining a culture that imparts purpose, meaning, relevance, ownership, and various paths that cater to all students' strengths and weaknesses. Tools such as the Rigor Relevance Framework and technology can certainly assist, but what is more important is an emphasis on three core elements. While these are not new by any stretch, it is valuable to see how they seamlessly connect to create a personalized experience.

Learner agency
The underlying premise is to move learners from a state of engagement to empowerment so that they exert more ownership over their learning. To achieve this goal, they need to be granted more autonomy in the classroom and beyond. It is driven by high-agency strategies such as voice, choice, path, pace, and place. These aid in developing critical competencies needed for success in a disruptive world.
Differentiation
While not a new concept by any means, the challenge has always been with effective and consistent implementation. The overall premise is that instruction is tailored to better meet students' needs in the areas of content, process, and product. Whereas agency focuses more on what the learner is doing, differentiation is typically driven by the teacher. Ongoing assessment is vital as this provides the teacher with the necessary information to develop lessons and tasks that are more personalized. A simple Google search will unveil all the many strategies and techniques that are available to educators to make this a reality.
RTI
Response to Intervention (RTI) represents a multi-tiered process to identify the behavior and learning needs of struggling students early on and then provide specific support in the form of interventions. Components include:
Tier 1 – Teacher provides research-based instruction to the entire class using extensive checks for understanding as a means of formative assessment. This data, and that collected through routine benchmarking, is utilized to determine what supports are needed in Tier 2. Behavior screenings are implemented as well.Tier 2 – Targeted supports using the data collected from the Tier 1 interventions are used to provide small-group instruction that focuses on specific learning and behavioral needs. Tier 3 – At this level, the most at-risk students are provided individualized support, typically in a one-on-one setting.Data is a huge component as it influences the types of supports used in each tier above. For specific strategies that can be used in each tier, click HERE.
While digital tools, research on the brain, and an emphasis on high-agency strategies might be new, personalization is not. Developing an understanding of all the interconnected elements can assist you and others in creating experiences that meet the diverse needs of students while nurturing a positive school culture.
October 2, 2022
Humble Leadership
Suppose you were to research or Google the qualities of effective leaders. In that case, all you would come up with are the typical characteristics such as good communication, ability to make difficult decisions, having a vision, models, and listening intently, to name a few. What doesn’t show up in routine searches is humility. There is a strong link between this trait and effective leadership. Jeff Hyman shared the following in a Forbes article:
A number of research studies have concluded that humble leaders listen more effectively, inspire great teamwork and focus everyone (including themselves) on organizational goals better than leaders who don’t score high on humility. Case in point: A survey of 105 computer software and hardware firms published in the Journal of Management revealed that humility in CEOs led to higher-performing leadership teams, increased collaboration and cooperation and flexibility in developing strategies.
Humble leaders are able to get the most out of people through intrinsic means, which often leads to lasting change and a positive culture. Here is another bit from the Forbes piece referenced above:
Humble leaders understand that they are not the smartest person in every room. Nor do they need to be. They encourage people to speak up, respect differences of opinion and champion the best ideas, regardless of whether they originate from a top executive or a production-line employee. When a leader works to harness input from everyone, it carries through the organization. As other executives and line managers emulate the leader’s approach, a culture of getting the best from every team and every individual takes root.
So how does one become a humble leader? The first step is understanding who you are and how your actions might be perceived or impact others, something I dive into deeply in Digital Leadership. Humility is characterized by a low focus on the self and an honest assessment of one’s worth and accomplishments. It also requires an acknowledgment of one’s imperfections, limitations, mistakes, shortcomings, and other areas of growth. You basically need to understand who you are.
Humble leaders are highly effective because they:
Earn trustUse an equitable lensTreat everyone with respectEncourage teamworkAdmit mistakesFoster a culture of learning
Although this is a common misconception, being humble does not mean you are weak. While some might see humility as a weakness, it is possibly the most significant asset a leader can yield. You don’t need to have all the answers. Instead, you must know where to find them, or better yet, leverage your people as a means to build capacity. Humility means you trust the people who you work with, delegate when necessary, and provide feedback to spur growth. Sometimes you might need to evolve into a humble leader and daily reflection is critical using a window and mirror approach. In the words of C.S. Lewis, “Humility is not thinking less of yourself, it’s thinking of yourself less.”
September 25, 2022
Taking Learners Deeper with Reflection
“We do not learn from experience. We learn from reflecting on experience.” – John Dewey
The quote above from Dewey has always resonated with me, especially when I am outside doing yardwork in Texas. In the past, I used to often get stung by bees and wasps. There is a difference between the two species and how they sting. Some of them actually bite. While each encounter resulted in a painful experience, they also provided a valuable opportunity for me to reflect on why I was susceptible to stings and how to avoid them. I always learned to wear long-sleeved shirts and observe my surroundings to spot their nests. I also habitually tracked them when they were seen flying around the same areas, which allowed me to find their nests and take them out. The bottom line is that I have not been stung in a long time.
It goes without saying that experience plays a pivotal role in learning for students and adults. In Disruptive Thinking in Our Classrooms, I shared the need to provide more opportunities for this in lessons as well as specific strategies that can be used. When reflection is added, it helps to improve the connection between what has been experienced and the outcomes that were derived. The case can be made that it allows learners to go deeper into concepts while becoming more competent.
Reflection is not a simple process of introspection. Instead, it is an evidence-based, integrative, analytical, capacity-building approach that serves to generate, deepen, critique, and document learning. Developing reflective skills is central to students’ academic and professional development within a discipline. The ability to reflect on one’s practice when confronted by a novel, unusual, or complex situation distinguishes expert practitioners from novices (Schön, 1983).
Routine reflection can:
Foster cognitive flexibilityAid in the construction and understanding of new knowledgeEstablish links between academic, emotional, and social experiencesDevelop essential competencies for success in a disruptive world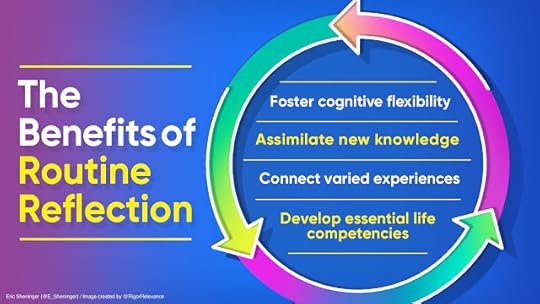
The outcomes listed above are supported by research:
Research has found that learning from direct experience can be more effective if coupled with reflection—that is, the intentional attempt to synthesize, abstract, and articulate the key lessons taught by experience. Additionally, the effect of reflection on learning is mediated by a greater perceived ability to achieve a goal resulting in self-efficacy.
Intentionality is key. The good news is that educators do not have to reinvent the wheel. When it comes to reflection in the classroom, the key is to make the time for it through alignment with routine pedagogy. Naturally, there is a tendency to include this at the end in the form of closure using the following prompts that can be answered using text, video, or audio:
What did you learn of value today?How might you apply what you learned outside of the classroom?Why was this learning important to you and your peers?However, educators can integrate opportunities to reflect throughout a lesson. I shared the following KWHLAQ chart in Disruptive Thinking, which educators can adapt as needed.

Reflection as a part of learning is something that must be cultivated in the classroom and beyond. We can’t assume that students are familiar with this process. Thus, they can benefit from guidance to help them derive meaning from experience. Without this support, reflections may be limited to descriptive accounts of an experience or “venting of feelings” (Ash & Clayton, 2009). Experience, when reflected upon, is the best teacher.
Ash, S. L., & Clayton, P. H. (2009). Generating, deepening, and documenting learning: The power of critical reflection in applied learning. Journal of Applied Learning in Higher Education, 1(1), 25-48.
Schön, D. (1983). The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in Action. London: Temple Smith.
September 18, 2022
3 Ways to Create a Culture of Belonging
Everyone wants to feel that they belong where they work. A culture of acceptance and respect can reap the rewards for all stakeholders. Hence, we have seen an increased emphasis on workplace diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives. Now, more than ever, getting people to feel valued is of utmost importance in the face of a myriad of challenges impacting morale. Susie Lee shared the following:
Studies have shown that a high sense of belonging at an organization was positively correlated with a 56% improvement in job performance and 75% fewer sick days. Employees have also told me that their sense of belonging is a key reason they want to work for the company.
Move beyond “one-size-fits-all.”
Just like the students you serve, your staff has unique gifts and needs. It is essential to look at how you cultivate and nurture these, respectively. Consider providing opportunities for staff to spread their wings by heading up committees, planning professional learning, and working side-by-side with you to develop new courses, electives, and schedules. Move away from drive-by professional development and blanket approaches to personalized, job-embedded models. Also, consider multi-faceted means of evaluation and feedback that genuinely support growth.

Strive for embracement
I have never been a fan of the term “buy-in” as it relies more on extrinsic as opposed to intrinsic means of motivation. As I shared in Digital Leadership, if you have to “sell” people on doing things differently or accepting a mandate, chances are your staff will never see the benefit of the change. The key is helping them see the inherent value of anything that is asked of them, especially large-scale change initiatives. There are many ways to empower your staff to embrace change, such as actively modeling what is expected, learning side-by-side with them, and using both data and research as a means for validation.
Model empathy
As a leader, people want you to understand what it is like to be in their shoes. Empathetic leaders work to provide time and support for staff so that they can do their job to the best of their ability. They are compassionate, flexible, show grace, and build people up by celebrating success.
As leaders, it is vital for us to imagine ourselves in the position of others as this gives us a better perspective on the challenges and feelings of those we are tasked to serve. Better, more informed decisions can result from “walking in the shoes” of those who will be most impacted by our decisions. The result is a better sense of belonging.
The benefits are clear because even leaders want to belong. Sally Boardman shared the following:
A sense of belonging is crucial to our life satisfaction, happiness, mental and physical health and even longevity. It gives us a sense of purpose and meaning.
As you look to implement, refine, or improve DEI initiatives, consider how they help to create a culture of belonging. With this in place, people will bend over backwards for students, each other, and you as a leader. Make the work a place where people want to be and perform their best.
September 11, 2022
Rethinking Normal
It always amazes me that we possess such vivid memories of some experiences yet tend to forget others. As the years' pass, I am always trying to retain as many as possible from my childhood. One that sticks out goes way back to my pre-school years. Now I can’t remember if my twin brother and I were actually in a year-long program or just a set number of days where high school students worked with us. What I do recollect was the teacher, Mrs. McDonald. Years later, she would be my senior class advisor and someone I admired and respected.
She was always a creative spirit in how she taught and motivated learners in culinary arts and early childhood development. Now I remember only two things from my pre-school years. The first was a big wooden train that all of us would fight over to play with, as it was the most popular toy at the time. Pretty normal, I would say, in the later 1970s. The other memory was of purple cow milk. Until now, “normal” milk was plain or flavored with chocolate or strawberry. Mrs. McDonald pushed us to move beyond our tastebud comfort zones and our perception that you could only put certain additives to flavor milk. We discovered that grape juice in milk looked cool and was quite tasty. She empowered us to rethink normal.

There is no better time than now to rethink education and the practices that are both favored and employed. Now I am not saying to throw out the baby with the bathwater. Instead, my call to action is to fight the urge to teach the way you were taught and lead the way you were led. Change can be a good thing as there is no such thing as perfection in education. This truth presents a constant opportunity to innovate and grow. However, there will always be challenges lurking in various forms. I shared the following in Disruptive Thinking in Our Classrooms:
The human brain is wired to keep us safe, and as a result, we often become averse to change. The status quo and our personal comfort zones create a perceived safety net that is difficult to relinquish. Our past experiences often dictate or influence our current professional practice. When this mindset is combined with silos erected to protect ourselves and organizations from external information and new ideas, it becomes clearer why transformational change is often just an idea that never gets put into motion.
In a previous post, I shared the image below, which is a great starting point when it comes to re-thinking normal.

It is ok to challenge conventional wisdom. The world is not sitting back and waiting for us to get on board with disruptive change. While “normal” might seem like the best or safest option, the question is, are we preparing kids for the present and future or the world where we grew up? There is no better time than now to change our practice for the betterment of those who we serve, whether that is students, colleagues, or other stakeholders. It begins with rethinking normal.
September 4, 2022
The Siri and Alexa Test
I absolutely love being at home. Having an intense travel schedule makes you cherish the little things that help alleviate stress and relax. One of my favorite pastimes is taking advantage of being outside any chance I get. Moving to Texas seven years ago meant the weather would stay warmer longer, making this more realistic. There is almost always music, whether in the pool, doing yard work, or hanging out with family and friends. My wife even got me a JBL boombox for my birthday last year, which is so much better than hardwired speakers, thanks to Bluetooth and super loud sound. We can’t even keep it on tables as the bass is so strong that the vibrations make it roll off.
Advances in technology make listening to music an incredible experience these days. Thanks to artificial intelligence in the form of Alexa, everyone is now their own DJ. With my outdoor setup, I connect the boombox to the Amazon Firestick and then use the remote to have Alexa play my favorite songs using voice recognition. Most of the time I choose the greatest hits from the 1980s, but my diversified tastes take me through numerous genres. No matter my listening mood Alexa never lets me down, although there are times that I need to repeat my request.
I share the personal story above as access to artificial intelligence in the form of Siri and Alexa has impacts on the education space. Whereas in the past, knowledge could be readily accessed from encyclopedias and books, this took time. The Internet drastically changed this process by ushering us all into the Information Age. Artificial intelligence is now a disruptive force that allows anyone to instantaneously access basic knowledge and facts. I see this as an opportunity in the classroom and beyond, but we must be honest about where some practices currently lie.
Educators love using game-based tools such as Kahoot, Quizizz, Blooket, and Gimkit as a means to review prior learning, check for understanding, and close lessons. I often see these in action a great deal when coaching in schools. The rub, however, comes in the form of the types of questions asked as the majority are simple recall or knowledge-based with stems such as who, what, where, and when. While this might be essential in the lower grades, it wanes in value as kids age. No longer do any of us have to “Google” an answer when we can just ask Siri or Alexa. I typically prove this point during workshops where I ask a low-level question using a “what” question stem and Siri responds with the correct answer every time.
With the tools above the key is to use question stems that get students to demonstrate understanding through comprehension. However, we shouldn’t stop there. In chapter 3 of Disruptive Thinking, I detailed how the Rigor Relevance Framework can be used to challenge all learners now and well into the future. Below are some simple strategies any educator can use to bump up the level of thinking in the classroom:
 Scaffold questions and tasks (specific strategies HERE)DifferentiateUse writing and work as a measure of thinkingCreate challenging problems to solve
Scaffold questions and tasks (specific strategies HERE)DifferentiateUse writing and work as a measure of thinkingCreate challenging problems to solveIf we are to prepare learners for success in a disruptive world, we must make efforts to ensure they are competent. This is how we can pass the Siri and Alexa test.
August 28, 2022
Leading Through Windows and Mirrors
There is no shortage of ways to reflect on how we lead in an effort to initiate and sustain change. Culture is everything. Establishing and maintaining relationships is paramount, which Is why I detailed research-based ways to improve morale in a previous post and in Digital Leadership. Another way to help ensure success in this area is to hold ourselves accountable through a self-efficacy lens. Windows and mirrors can be incredible metaphors when it comes to effective leadership. The essence of leaders who embrace this concept is crediting others for success and taking responsibility when things don’t go right. If mistakes occur, and they will, they are of the belief that it is their fault. Such leaders believe it is their fault if mishaps happen on their watch. We can refer to this as leading with a mirror in hand and looking out the window to see what matters most.
In Good to Great, Jim Collins shares the following:
Great leaders look out the window to apportion credit to factors outside themselves when things go well (and if they cannot find a specific person or event to give credit to, they credit good luck). At the same time, they look in the mirror to apportion responsibility, never blaming bad luck when things go poorly.
Windows and mirrors can be powerful leadership tools.

As you reflect on your practice, consider the following:
Do my actions inspire change?Do I lift others up?Am I open to feedback?Do I seek opportunities to grow?Do I seek the input of others when making certain decisions?Peer through a window and see who is most responsible for implementing and leading change that results in improved outcomes. The collective is bigger and more influential than one person. Be proactive when it comes to eliciting praise so that proper credit is given to those who are playing their part to ensure success for the system. It is essential to understand each other’s strengths and weaknesses and give credit accordingly where success is achieved (Brock et al., 2017). In the end, this will pay dividends not only for overall morale but also for your reputation as a leader.
When something doesn’t go right or as planned, take a look in the mirror to own the outcome. Trust erodes when others are blamed publicly. Research has found that people are reluctant to admit they have failed because of a general desire to avoid negative social evaluation and disapproval from others (Leary, 2007). The buck stops with the leader, plain and simple. Without trust, there is no relationship. Without relationships, no real, meaningful change will occur. If the leadership team or staff falters, look in the mirror and reflect on what you, as the leader, could have done differently. Then pick your people up and begin anew. If an individual(s) is the cause of a problem, speak with them directly behind closed doors to rectify the issue.
Leading through windows and mirrors can develop more humility and empathy, which will serve you well as you strive to support your staff. Both of these attributes are integral in developing relationships that underpin culture and are also necessary for leading change.
Brock, S.E., McAliney, P.J., Ma, C.H. and Sen, A. (2017), "Toward more practical measurement of teamwork skills", Journal of Workplace Learning, 29 (2): 124-133.
Leary, M.R. (2007). Motivational and emotional aspects of the self. Annual Review of Psychology. 58(1):317–344.



