R.E. Kearney's Blog, page 6
August 31, 2023
Leprosy: The Return
When you mention the medical condition Leprosy your mind will naturally think back in time to a period in history when living conditions were poor and life expectancy was limited. Leprosy is a bacterial infection than damages nerves, lungs, skin and eyes, and is well known by the dramatic loss of fingers, arms or legs through uncontrolled infection and wounds. Leprosy still occurs globally, with India accounting for more than half of the diagnosed cases. In some areas of India, China, Thailand, and parts of Africa, Leper colonies are still used to restrict movement and contain Leprosy. Fortunately most people are cured of Leprosy today through drug therapy, and interestingly there are also groups of people who are genetically less likely to contract the infection even if exposed to it.
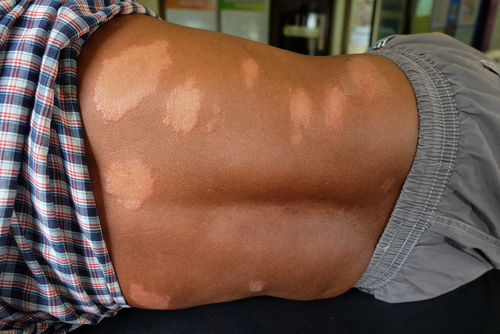
The social spread and mortality was greatest during the Middle Ages, resulting in segregation and leper asylums. Even as recent as 1983 the Indian government introduced the National Leprosy Elimination Programme to tackle the problem. Until 2019, an Indian could even petition for divorce based on a spouse’s diagnosis.
The last place you might expect to hear of Leprosy cases surging is in Florida. Leprosy has now been classed as Endemic in the state, meaning it’s consistently present but limited to that specific area, just like Malaria is. Florida now accounts for 81% of all Leprosy cases in the US.
“Several cases in central Florida demonstrate no clear evidence of zoonotic exposure or traditionally known risk factors,” the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) wrote in their report, adding that data suggests that “leprosy has become an endemic disease process in Florida.”
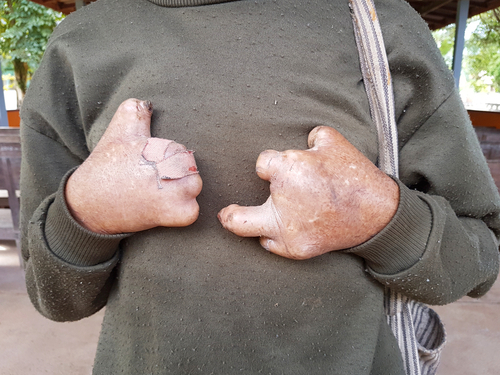
The south east region of America has seen the number of cases double over the last decade, and according to the CDC it appears that people are not catching the bacterial infection through the normal routes of exposure to disease carrying animals or travelers. Conclusions from the CDC seem to suggest that the cases they’ve looked into tend to be occurring in patients who are spending long periods of time outdoors and think there may be a link to “environmental reservoirs” as a potential source of the bacteria, which can be found in soil, water and vegetation.
But why now? Could the increasing global temperatures or the reintroduction of bacteria once frozen in the thawing Siberian permafrost, be contributing factors?
August 10, 2023
Shrinking Populations
With the world’s population hitting the 8 billion point recently, it’s easy to think that the human race is continuing to grow and expand at an uncontrolled rate, absorbing land, exploiting the Earth’s resources, polluting the sea and air, and taking us to an inevitable point of mutual destruction. But, that’s not necessarily true – at least not for every part of the planet.

Surprisingly Japan’s population has been dropping year on year, and it’s getting so bad it’s created an internal crisis that could have devastating effects on the country. During 2022, the total number of Japanese residents fell by more than 800,000 in just one year. This follows thirteen years of continual population contraction. Other figures released by the Ministry of Internal Affairs also highlighted the increasing death rate of over 1.56 million on top of only 771,000 births – the lowest since records began.
Life expectancy is high in Japan, but coupled with low fertility rates, which is also seen in many other east Asian countries too, Japan is seeing a rapidly aging population. In order to balance a stable population Japan needs approximately two births per woman, but the fertility rate is currently only 1.3 births.
As the population gets older, so does the workforce, which also slowly starts to decline, resulting in disastrous implications for almost all areas of the economy. Prime Minister Fumio Kishida has even been stated saying that “Japan is standing on the verge of whether it can continue to function as a society.” The number of schools closing in rural areas has increased rapidly while the number of small businesses are stuck with aged owners and no one to take them over.
There are ways to counter a declining population. The simplest is to relax immigration rules, allowing workers from other countries to settle and work, which Japan has done, however that has still not had the desired effect. The number of foreign residents hit a record high recently, but that was still not sufficient to balance the declining population.

Japan is not the only country in the world where the decrease in population is becoming significant. The number of people living in Europe has been declining since 2020 for much the same reason – longer life expectancy and decreasing birth rates. This immediate decline could also be as a result of the COVID pandemic disproportionately increasing the number deaths. China’s population also fell for the first time in 2022 since the 1960’s.
Scientists and researchers now believe that instead of persistent exponential global population growth, the numbers might stabilize around 2100 before consistently falling. That could be a good thing, but could also create one of the biggest social problems for humanity.
July 27, 2023
Fungal Structures
As mankind develops and expands, the need for buildings and other structures grew with it. Most of those building involved concrete, sometimes on a huge scale, which is damaging to the environment on so many levels. Other materials like wood and plastic are also not sustainable or suitable either. However, a group of scientists believe that we could theoretically create buildings from fungus – and not just the structure, but the internal plumbing and electrics too, making a sustainable, self growing and repairing building.
“We propose to develop a structural substrate by using live fungal mycelium,” explained the European academics in their paper. “Fungal buildings will self-grow, build, and repair themselves.”

In a world which has already begun to see the physic changes caused by climate changes, the need for biological building materials would be a huge step forward in reducing fossil fuels and environmentally-destructive mining processes.
“Fungal materials can have a wide variety of mechanical properties ranging from foam-like to wood-like to polymer-like to elastomer-like,” explained co author microbiologist Han Wösten from The Netherlands’ Utrecht University. “The fact that we can make wood-like materials implies that we can use it for the building industry. The selling point of our materials is that it is biodegradable, thereby helping to create a circular economy. At the same time, it should not degrade when actually used as a building material. We can work around this apparent paradox by coating the material. In fact, we also coat wood with paint of oils to protect it against degradation.”

You might be surprised to know that NASA is also testing whether or not fungus could potentially grow in Martian soil, with an aim to using it to build low cost, sustainable structures on Mars. So far, all experiments have involved killing off the fungus once a structure has been built so that it solidifies and hardens sufficiently to carry the loads needed in structural walls. The aim is to find a way to keep the fungus alive so that it remains a living structure, allowing for further growth, repairs and alterations.
And it doesn’t stop with the main structure. Computer scientist, Andrew Adamatzky, another author of the paper, explained that they are looking to build fungal neuromorphic circuits to replace the electronics inside the building. “The living circuits will be self-growing, self-assembling and self-repairing, which no traditional circuitry can do.”
Overall, a circular economy for construction is the goal, minimizing the use of the Earth’s limited resources and reducing energy consumption.
July 13, 2023
Amazon Deforestation
Brazil’s former far-right President Jair Bolsonaro was responsible for one the worst periods of destruction of the Amazon rainforest over the last fifteen years, following his removal of environmental protection legislation. However, following the election of a new President, things are beginning to look a little hopeful for the future of the rainforest, as well as the rest of the planet.

The Amazon rainforest is huge, covering an area the size of Australia. It absorbs carbon, soaking up damaging greenhouses gases and releasing essential Oxygen into the atmosphere – it’s no coincidence that it’s called the “lungs of the planet”. Higher carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere increases the temperature of the planet, melting the icecaps, affecting crop success, increasing droughts, flooding, fires and extinction events.
During the first six months of Brazil’s new President, Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva, destruction of the rainforest has reduced to the lowest levels since 2019, and shows a 33% reduction in deforestation compared to the same period last year. But, don’t get too excited. That still represents 1000 square miles of forest that has been cleared. President Lula has vowed to eliminated deforestation completely by 2030, so a positive start, but is his goal achievable, especially when there is so much economical pressure on him.
During Bolsonaro’s term in office Brazil’s environmental agency was stripped of the majority of it’s enforcement agents, something that President Lula will need to rapidly change if the control and eventual elimination of the destruction of the world’s largest forest is to be enforced effectively.

The destruction of the forest is not only man made. In June, the number of fires hit a record high of over 3000, thought to be the result of the deforestation caused last year, weakening the forest and making it more susceptible to fires in the face of droughts.
To support the preservation aim, President Lula has launched a grant program for the indigenous population in the region to sustain their livelihood and serve as wards of the rainforest, whilst at the same time increasing the amount of recognized indigenous land.
It’s long been documented that there is a direct link between the health of the rainforest and climate change, and this is perhaps mankind’s greatest chance to prevent that change from escalating and taking the planet over the tipping point.
June 29, 2023
Virgin Births
Recently we heard stories about a captive crocodile that had given birth to a baby despite never coming into contact with a male crocodile to create a viable fertilized embryo. Although the baby was stillborn, it shared virtually all DNA with the mother, confirming its single parent origin. Could this be part of a new phase of evolution in the animal kingdom – in order to survive, even in captivity, could they adapt to still produce the next generation without the normal reproductive processes? I suppose, only time will tell if we eventually hear of a successful virgin birth.
Never to be outdone – humans are at it too!!! While the process of fertilization of a viable human egg with a donor’s sperm outside of the human body has been used for several years, it still requires a mother and a father, as well as implantation of the fertilized egg inside the mother to enable it to grow and survive. However, things are beginning to change.

A group of scientists have used stem cells to create a completely synthetic human embryo without an egg, and without sperm. These fabricated embryos are in the very early stages of development so it’s unknown how far they could continue to viably grow or whether they would even reach a “birth” stage. At present they have not been allowed to develop sufficiently to form a brain or heart. Scientists have agreed not to allow the embryos to grow beyond 14 days, but it’s clearly a step towards something new and different for the human race.
The purpose of this research and experimentation is to help study genetic disorders as well as the causes of miscarriages.
“Our human model is the first three-lineage human embryo model that specifies amnion and germ cells, precursor cells of egg and sperm,” explained team leader Magdalena Zernicka-Goetz, biological engineering professor at the University of Cambridge. “It’s beautiful and created entirely from embryonic stem cells.”
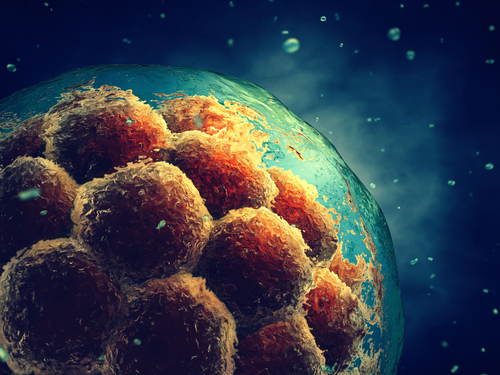
The cells are developed to form a yolk sac, placenta, and embryo. With this type of research being such a sensitive area, Professor Zernicka-Goetz gave some clarity on the synthetic embryo. “I just wish to stress that they are not human embryos. They are embryo models, but they are very exciting because they are very looking similar to human embryos and a very important path towards discovering why so many pregnancies fail, as the majority of the pregnancies fail around the time of the development at which we build these embryo-like structures.”
Previously, Zernicka-Goetz and her team have taken mice stem cells and developed them into early embryos that possess the early growth of a brain and a heart.
There is some confusion on whether or not these synthetic embryos should be governed by the same laws that apply to actual human embryos. Clearly, the creation of synthetic human beings as well as the birth of AI, are huge challenges for the future of mankind.
June 15, 2023
Blood-Sucking Parents
Some people will go to extraordinary lengths to try and prolong their life span. There never goes a month by without there being some food or drink fad that improves your health and allegedly adds a few years to your life expectancy. Tablets and extracts from various sources claim to be wonder panaceas that delay the inevitable. But it seems a tech millionaire has taken a step further and received a blood transfusion from his teenage son! Not only that – the millionaire is also giving some of his son’s blood to his father too.
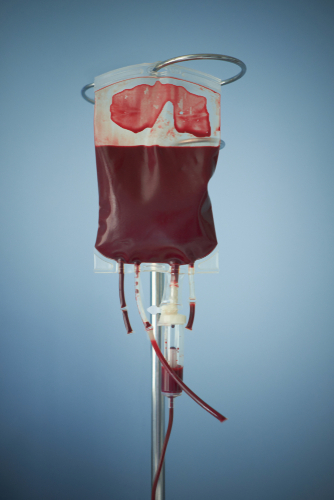
Bryan Johnson, who is 45 years old, took his 17 year old son and 70 year old father to a clinic in Dallas for an intergenerational blood swap. And this wasn’t the first time. Bryan Johnson had received young people’s blood on previous visits to the clinic from anonymous donors. The profile of the donor was carefully filtered according to blood type, diet, body mass index as well as general health. Has it helped make him younger or prolonged his life span – no one can truly know yet.
This is not the first time Mr Johnson has been on a quest for eternal youth. He has spent $2million each year employing a team of doctors to advise him how to turn back the clock to a time when his body was in peak physical condition. Johnson’s specific aim is to return his “brain, heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, tendons, teeth, skin, hair, bladder, penis and rectum” to the state they were in when he was 18 years old.
“We start from evidence first,” Johnson explained. “We do nothing based on feeling.”
Other millionaires have followed the same path and transfused young people’s blood into their bodies in the hope of defying age and degeneration. Some researchers are suggesting there might be science to back up this unusual trend. When two mice were joined together in a laboratory so that they shared one circulation system, the older of the two mice showed some improvements in their body, but could this also apply to humans?
The Food and Drug Administration issued a warning as far back as 2019 against the use of blood transfusions from young people into the bodies of older people because it was untested and unknown what the possible outcomes could be for either party. They stated that “There is no proven clinical benefit of infusion of plasma from young donors to cure, mitigate, treat, or prevent these conditions, and there are risks associated with the use of any plasma product.”
Charles Brenner, a biochemist in Los Angeles, has these thoughts on the matter. “To me, it’s gross, evidence-free and relatively dangerous. The people going into these clinics who want anti-aging infusions basically have an anxiety problem. They have an anxiety problem about their mortality.” With that in mind, maybe the millionaires should be paying for counseling for their anxiety issues, rather than draining the blood of the young.
May 25, 2023
Protective Mutations
The human race is constantly evolving, however most changes are subtle and unnoticeable unless looking back across large chunks of time and making comparisons. Some might consider that we are longer changing and that we have reached an ‘optimum’ point in our evolution and the next logical step is a symbiosis between man and machine, but nature, and humans, might still have some surprises to reveal.
You might be surprised that a man with an unusual mutation has been discovered who exhibits potential resistance to Alzheimer’s disease. A Colombian man who possessed a genetic marker which virtually guaranteed he would develop early onset Alzheimer’s had a brain scan which showed atrophy of the brain as well as amyloid plaques and tae proteins, which together indicated with certainty that he would develop Alzheimer’s in his early 40s.
However, despite the genetic and biological indications, the man did not develop the condition. Only when he reached the age of 67 did he begin to experience the effects.
“The male remained cognitively intact until 67 years of age despite carrying the PSENI-E280A mutation,” explained one of the scientists in the study.
PSEN1-E280A is a genetic mutation seen in the population of the Colombian state of Antioquia. Other studies have shown that every carrier of the mutation shows impairment in verbal fluency by 45 and dementia by 50 and death at an average age of 59.
So why was this man, a carrier of the PSEN1-E280A genetic mutation different?

Scientists found that the man also had a second gene mutation that prevented the disease from affecting him for much longer. This second mutation, called COLBOS by the researchers, blocked the disease from entering the part of the brain responsible for memory and produced a protective protein which prevented the Alzheimer’s own tau proteins from forming into large strands, thereby slowing down the damage to the brain.
What researchers hope to do is to replicate this protective protein to create an effective treatment for Alzheimer’s.
“This really holds the secret to the next generation of therapeutics,” explained cell biologist and study coauthor Joseph Arboleda-Velasquez, who has already founded a biotech company with the purpose of using this research to create pharmaceuticals.
May 11, 2023
Innerspace
It seems that science fiction movies have yet again been able to accurately predict the future. Back in 1987 Dennis Quaid starred in a film called Innerspace, where a man and his machine were shrunk down so much that they could then be injected into the blood stream of Martin Short. From there he could interact with the cells, nerves etc.
Whilst the movie may be just been a work of fiction at the time, just 35 years later a team of scientists in Israel have created a micro robot that is so small it can inspect individual cells to assess their health, as well as move cells to a different location by electro magnetic means. The scope for these micro robots is huge and this progress could be a game changer in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
“Developing the micro-robot’s ability to move autonomously was inspired by biological micro-swimmers like bacteria and sperm cells,” said Gilad Yossifon, biomedical engineering professor at Tel Aviv University. “This is an innovative area of research that is developing rapidly, with a wide variety of uses in fields such as medicine and the environment and as a research tool.”
“Our new development significantly advances the technology in two main aspects — hybrid propulsion and navigation by electric and magnetic mechanisms that are very different. In addition, the micro-robot has an improved ability to identify and capture a single cell for local testing or retrieval and transport to an external instrument.”
As well as being able to identify healthy and dying cells, the team is now looking to develop the micro robot so that it can also be used as an effective drug carrier that can precisely target specific areas of the body.
The merging of robot and animals has been experimented with in many ways over the years. Early in 2023 scientists managed to make a robot move using muscle cells taken from a mouse, laying the path for potential complex cyborg technology in the future.
Like a scene from Frankenstein, the experimental cyborg was created from a 3D printed skeleton, wireless LED control chip and lab grown mouse muscle cells, and maneuvered through a maze. The power to move the cells came from the use of light and heat on the LED controllers. “You can basically beam energy into the chip,” explained Mattia Gazzola, mechanical engineer at the University of Illinois, “so that means that you don’t need power onboard.”
Combine this with the recent explosion in AI development and biohybrid robots with their own intelligent neural network and internal self healing micro robots could possibly overtake the human race as the dominant species on planet Earth.
April 27, 2023
Chinese Space Construction
While a lot of space agencies are looking towards Mars as a possible future solution for the survival of the human race, China is looking a lot closer to home – somewhere you can see every night from your window. The Moon.
A Chinese state run news outlet has recently reported that China intends to begin building a Moon base within the next five years. But they’re not shipping tons of concrete to the lunar surface, they intend to make the bricks for the building from the Moon soil itself, making it the first country to build a permanent structure outside of the Earth that is anchored to another celestial body. It’s proposed that the Moon base will be manned and is also likely to involve robots too.

In a show of serious intent, 100 researchers from China’s scientific community came together at a conference to discuss everything from building the infrastructure to the use of robots.
“Eventually, building habitation beyond the earth is essential not only for all of humanity’s quest for space exploration, but also for China’s strategic needs as a space power,” Ding Lieyun, a scientist at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology, told state-run news outlet China Science Daily during the conference.
Ding Lieyun demonstrated how an egg-shaped prototype could be constructed from 3D printed bricks made from lunar soil by a robot, called ‘Chinese Super Mason’, which takes the bricks and builds the structure, eliminating the need to transport labor to the Moon.

This isn’t the only interest China has in the Moon. They’re already planning a mission to the far side of the Moon which is as yet a lot less studied. The mission is to bring samples back for examination and is scheduled to begin in 2025.
As well as interest in the Moon, China is also intending to launch a total of 13,000 satellites that will become it’s own broadband-beaming mega constellation in low Earth orbit later this year. This comes on top of the development of their Long March 5B rocket platform which has enabled modules to be delivered to the Tiangong space station.
The space race is still well and truly on and is becoming a very competitive commercial area.
April 13, 2023
Population Contraction
There’s no denying that the world’s population has grown at such a rapid rate over the last fifty years that it has literally put the future existence of our planet in danger. Overcrowding, animal displacement, global warming, plastic pollution – they can all be linked to the disproportionate volume of human beings living on a world that surpassed the level of a sustainable population back in the 1970’s. Some scientists predict the human population will continue to increase at an even fast rate leading to a sixth mass extinction event, but a new report suggests the opposite.

Researchers have found that population growth rates, which although they have continued to rise, have done so at a slower rate than was actually expected. Although the rate is still growing, it also looks possible that the global population will peak this century before starting to fall. Currently we have around eight billion people on the planet, a number that has quadrupled since just 1968. At that rate of growth the population could be estimated to increase to sixteen billion by 2100, but new research considers we might hit nine billion before it then starts to decrease.
“The global population could peak at a much lower level — around nine billion — by mid-century,” the Earth4All nonprofit collective research predicts. “And if the world invests more in economic development, education, and health, the global population could fall to levels at which everyone on Earth can have sustainable access to clean energy, shelter, food, and water.”

While the research may have retrospectively looked at population growth and found it hadn’t increased as rapidly as was initially predicted (even though it’s still at an alarming level) it seems to rely on life changes to make a difference for the future. And change, particularly when asking humans to alter their habits, is a very difficult thing to achieve.
“This research gives us evidence to believe the population bomb won’t go off, but we still face significant challenges from an environmental perspective. We need a lot of effort to address the current development paradigm of overconsumption and overproduction, which are bigger problems than population.”
If we don’t address social and environmental problems, and individually and collectively make a choice to change, it will be that which destroys the planet, not overpopulation.



