R.E. Kearney's Blog, page 38
May 26, 2016
Seasteading – Cities Riding the Waves
A combination of the sea and homesteading, which is a self-sufficient lifestyle; seasteading is the idea of creating permanent accommodation at sea. The idea originated with modifying cruise ships in order to create a home on the water. The first one that was adapted to facilitate living in this way cost in excess of USD$10 million to transform. One of the things that is the most appealing about these cities is the fact that they would be outside of any government’s control, and the residents would choose to be under the rules of the country that the ship displays its flag.
The Seasteading Institute
Founded on April 15, 2008 by Wayne Gramlich and Patri Friedman, after a USD$500,000 contribution by Paypal founder, Peter Thiel, the institute has undertaken the task of facilitating the creation of affordable living conditions at sea.
In 2013, the floating city project was launched with the idea of setting up the cities within shallow waters controlled by a nation. The calm waters and the close proximity of the shore would make it easy to get necessary deliveries. The goal of the institute is to have the first floating city established by 2020.
The founders have approached three (currently unknown) nations to offer to develop the construction near their shores and, therefore, under their jurisdiction. The value that this would have to these nations is undeniable, in terms of setting up a separate economy where new political structures and laws can be tried out.
Each city would be made up of 10-15 platforms each housing 20 people. This would mean a total of 200-300 people per city. The cost to set up these structures has been estimated at USD$15 million per platform and $150-165 million per city. Fortunately, the project will be privately funded and there are already many people interested in the prospect.
The concept has been supported by several architects and different designs have been entertained. One example of a unique concept was developed by Belgian architect, Vincent Callebaut, who designed a floating aquatic home, made of algae and garbage. One can only imagine the advantages of building cities out of the waste of the rest of the world. This is not the only concept that has been presented, however, and most of us will have to wait until closer to the year 2020 to see which one will prevail.
Humanity is always searching for new horizons and ways to expand our territory. Seasteading, and the idea of living outside of the jurisdiction of a specific country will continue to have its appeal, and more than likely there will soon be other projects similar to The Seasteading Institute’s that will follow the same intention.
 In my science based fiction, Endless Fire Future Furies, I employ the seasteading concept with the Society Preserving Endangered Agriculture or SPEA establishing itself as an independent state through seasteading. SPEA constructs its city-state on a forty acre platform above the Pacific island of Kiritimati, or as we pronounce it – Christmas Island. As a totally independent state SPEA engages the most advanced technologies to ensure that is completely self-sufficient as regards to energy and food. I see it as a very possible and probable future.
In my science based fiction, Endless Fire Future Furies, I employ the seasteading concept with the Society Preserving Endangered Agriculture or SPEA establishing itself as an independent state through seasteading. SPEA constructs its city-state on a forty acre platform above the Pacific island of Kiritimati, or as we pronounce it – Christmas Island. As a totally independent state SPEA engages the most advanced technologies to ensure that is completely self-sufficient as regards to energy and food. I see it as a very possible and probable future.
For more information about seasteading: http://www.seasteading.org


May 19, 2016
Protecting the Seas through Science – The US Navy fulfils a Mission
 The core mission of the United States Navy is to meet America’s global security commitments at sea. In order to do this they are continuously carrying out tests and training, in the major water bodies surrounding the country. These include using sonar technology and carefully monitored underwater explosions. The effects of these tests on marine life are still not completely understood. In order to ensure that the animals are being protected as well as possible the US Navy monitors and reports conditions that might affect them, following guidelines which are outlined under the Endangered Species and the Marine Mammal Protection Acts.
The core mission of the United States Navy is to meet America’s global security commitments at sea. In order to do this they are continuously carrying out tests and training, in the major water bodies surrounding the country. These include using sonar technology and carefully monitored underwater explosions. The effects of these tests on marine life are still not completely understood. In order to ensure that the animals are being protected as well as possible the US Navy monitors and reports conditions that might affect them, following guidelines which are outlined under the Endangered Species and the Marine Mammal Protection Acts.
The Navy forms partnerships with other agencies, universities and private companies in order to get the best results. Together they conduct research which shows them the most efficient way to monitor and protect marine life. Many of the scientists are civilian employees, even though the projects that they work on are funded by the Navy. All the findings are reviewed by leaders in the field to determine how accurate they are, before the results are published.
The program that the US Navy has put in place to minimise the harm of at sea training and testing, is the Marine Mammal Research Program. In order to fulfil this objective, the program is divided into 4 main areas of study which work together to determine the possible effects on marine mammals.
 Marine Mammal Ecology and Population Dynamics.
Marine Mammal Ecology and Population Dynamics.This team’s main objectives are to determine the number of species that are located in areas that the navy conducts training. In addition, it aims to understand their seasonal distribution and unique behaviours.
Criteria and Thresholds to Measure the Effects of Navy Generated Sounds.
This area is responsible for concluding what the effects of sound are on the animals’ behaviour, including both manmade and natural noises. The main concern is that the mid-frequency sonar does not reach levels that might affect any of the mammals.
Improving Monitoring Techniques
Properly monitoring a species is the best way to determine how to provide the safest possible environment for them. This department spends most of its time trying to decide what the best way to observe, detect and classify marine life is, in order to help them as much as possible.
Sound Field Characterization
Directly concerned with the results of their sonar experiments, this branch is tasked with developing protocols and models to predict how the sounds will spread in water.
The US Navy has already committed to continuing its research and monitoring of the animals throughout the next decade. This will allow the Navy to meet its national security requirements, by protecting the US as well as our beautiful marine mammals.


May 12, 2016
Viruses and their Threat to Mankind
Even though we are exposed to viruses in various forms from as early as we can remember, they still remain beyond our control. Many of them such as chicken pox and the common cold have symptoms that are very uncomfortable, while others pose a much more serious threat to humanity. The significant difference between the size of the organism and the amount of damage that it can do to the human population, almost seems to be a mockery of our systems.
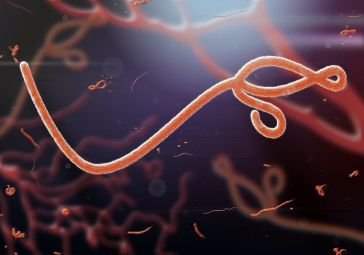 Ebola is one of the viruses that is currently associated with many human deaths. It is believed to have originated in bats in West Africa, and is transferred in humans quickly and easily through contact with those that are affected. It is associated with an extremely high fatality rate, as approximately 50% of those that are infected end up dying from the virus. The symptoms are very flu-like in appearance but quickly escalate to include nausea and diarrhoea. In order to find a cure or vaccine to help decrease the amount of people that die from the virus, scientists are continuously studying the survivors.
Ebola is one of the viruses that is currently associated with many human deaths. It is believed to have originated in bats in West Africa, and is transferred in humans quickly and easily through contact with those that are affected. It is associated with an extremely high fatality rate, as approximately 50% of those that are infected end up dying from the virus. The symptoms are very flu-like in appearance but quickly escalate to include nausea and diarrhoea. In order to find a cure or vaccine to help decrease the amount of people that die from the virus, scientists are continuously studying the survivors.
HIV is another virus that has affected the world population significantly. It is caught mainly from sexual or blood contact, and breaks down the immune system by attacking CD4 white blood cells directly. Different medications, over the years, have made it possible for people to live for very long periods without the virus advancing any further.
 Even though the regular influenza virus is responsible for a large number of deaths each year, it becomes even more dangerous when a new strain develops. One example of an influenza epidemic was the outbreak of the Spanish Flu in 1918, where in excess of 40% of the world’s population got sick and more than 25 million people died. Another strain of influenza that has proved fatal in more modern times was the swine flu (H1N1 virus) attack in 2009.
Even though the regular influenza virus is responsible for a large number of deaths each year, it becomes even more dangerous when a new strain develops. One example of an influenza epidemic was the outbreak of the Spanish Flu in 1918, where in excess of 40% of the world’s population got sick and more than 25 million people died. Another strain of influenza that has proved fatal in more modern times was the swine flu (H1N1 virus) attack in 2009.
Our battles with these miniscule killers are long and continuous, but there is sometimes a great victory on our side. Smallpox was one of the most deadly viruses to plague us for centuries, leaving at least 1/3 of its victims dead and many survivors permanently scarred or blind. In 1980, it was announced that the world was now free of the threat of smallpox. Virologists, and doctors, took advantage of the distinct symptoms and began treating those exposed to the virus by giving them the ‘ring vaccine’ as soon as possible after exposure, resulting eventually in its complete eradication.
After being affected by certain viruses, our immune system produces natural anti-bodies so they cannot infect us more than once. Getting the full blown virus can be deadly so vaccines are made by introducing weakened forms of the viruses into the body, to allow it to develop its own immunity. This has been very successful in limiting the amount of people certain viruses affect. Virologists and other scientists continue to work diligently at finding ways to make vaccines for the ones that still continue to prove fatal.


May 5, 2016
Genetic Engineering – The Human Quest for Perfection
The human genetic composition is what determines our health, personal traits and even our behaviour. Genes are passed on to us from our parents, and can also be the source of many imperfections as well as hereditary diseases. As humans we are always trying to make everything better, including ourselves. This has resulted in the desire to modify the genes in embryos, and foetuses, in order to improve our genetic make-up. The biggest controversy associated with genetic engineering is whether or not it is an ethical practice and should be continued, or even advanced.
 ‘Gene therapy’ is currently as far as human genetic engineering has extended, meaning that the process is applied to non-reproductive cells. Doing this has facilitated the ability to find cures for certain diseases. As a result, it has become a revered application in the medical field.
‘Gene therapy’ is currently as far as human genetic engineering has extended, meaning that the process is applied to non-reproductive cells. Doing this has facilitated the ability to find cures for certain diseases. As a result, it has become a revered application in the medical field.
These advancements have made also it possible for us to clone entire species, and in 1996 the first ever fully cloned mammal, Dolly the sheep, was ‘born.’ She lived for six years and, even after her death, is still the cause of much speculation about whether this is a procedure that should ever have been undertaken because with the ability to clone another mammal comes the ability to ‘make’ a human. This is a possibility that comes too close to playing God for the majority of society to handle.
Europe, for ethical reasons, has a ban on the cloning of human embryos. There is no limit on what many other countries can experiment with, however, and China has recently genetically engineered embryos with the intention of modifying the gene responsible for thalassaemia (a fatal blood disorder). The embryos used in their experiments were non-viable and obtained from IVF banks where they had been fertilised by two sperm, and had no possibility of a live birth. There has still been public demand that action be taken to stop this from continuing, due to the fact that nobody can be certain whether or not the embryos used will remain non-viable.
 China isn’t the only country experimenting with human genetic engineering, and in the western world there is a lot of development in the field as well. In the United States, James Grifo has found a way to transfer cell nuclei from eggs of older women to younger ones with the aim of overcoming infertility. The infants that will be born, from these eggs, will genetically have three parents.
China isn’t the only country experimenting with human genetic engineering, and in the western world there is a lot of development in the field as well. In the United States, James Grifo has found a way to transfer cell nuclei from eggs of older women to younger ones with the aim of overcoming infertility. The infants that will be born, from these eggs, will genetically have three parents.
The search for perfection has always been a fascination for humans, and James Watson conducts seminars promoting of the use of genetic engineering for enhancing ourselves. He is adamant that as soon as the technology is available people should be able to add genes to themselves, to improve who they are. There has also been the suggestion made by French Anderson, a US gene therapy pioneer, that we do gene therapy on foetuses to treat genetic conditions. These modified genes will then continue to be passed on to all future generations, stopping the undesirable genes from returning altogether.
Human genetic engineering does bring with it the possibility of becoming ‘perfect.’ The question that arises from this, however, is whether this should really be our aim? It is quite possible that our imperfections are what actually make us human in the first place.


April 28, 2016
Nanotechnology Today – Remarkable Feats Achieved by Miniscule Technology
Nanotechnology, being conducted at such a small scale, was once thought of as beyond our capabilities. The microscope that allows us to see Nano particles has only been available in the last 30 years, so all of the relevant advances have taken place since then. With the constant developments in the field, nanotechnology has been integrated into our lives without us even being completely aware of when it happened. The way in which nanotechnology works is by controlling individual atoms and molecules, and as technology increases its uses are guaranteed to expand.
One of the areas where nanotechnology is currently making the biggest impact is in the medical field, helping to revolutionise the way we detect and treat disease. It is currently used in wound dressings to cease excessive bleeding, to help in early recognition of plaque build-up in arteries, and gold nanoparticles can detect Alzheimer’s in its early stages. Other big achievements in the field include:
Artificial Muscles – Made from billions of microscopic, straw-like carbon nanotubes which have been twisted together, these muscles move in a similar way to an elephant’s trunk and squid’s tentacles. They are able to change their shape in response to stimuli, and with this there is great potential in terms of propelling medication throughout the body.
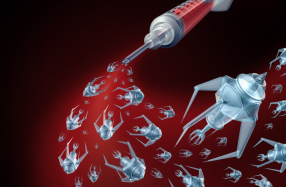 Targeted Drug Delivery Capsules – Developed with the aim of getting medication straight to the targeted cells, it is hoped that these capsules transform the way in which we treat cancer patients. The drugs are transported in nanoscale capsules and move through the body towards the sick cells. When they are within the correct range they will release the medication, which attacks and kills the cancer cells but doesn’t harm the rest of your body.
Targeted Drug Delivery Capsules – Developed with the aim of getting medication straight to the targeted cells, it is hoped that these capsules transform the way in which we treat cancer patients. The drugs are transported in nanoscale capsules and move through the body towards the sick cells. When they are within the correct range they will release the medication, which attacks and kills the cancer cells but doesn’t harm the rest of your body.
Nanotechnology is also being used in other areas, and some of the ways that it is creating a difference are with:
Self-healing Plastic – Made to respond to damage in the same way as human skin, by bleeding and then healing (much like the terminator does), this material will be able to fix itself in the case of any damage. It won’t be very long before this technology is being used on vehicle fenders and the outside of aeroplanes.
 Electricity Generating Viruses – Scientists have discovered that when pressure is applied to certain viruses, they are able to convert it into electricity. This concept means that in the near future we will be able to start powering our kitchen appliances by stepping on a mat made of viruses on the floor, or similar methods.
Electricity Generating Viruses – Scientists have discovered that when pressure is applied to certain viruses, they are able to convert it into electricity. This concept means that in the near future we will be able to start powering our kitchen appliances by stepping on a mat made of viruses on the floor, or similar methods.
Like all other technological advancements, there is more that is surfacing about nanotechnology every day, and within a short period of time other methods that include it will be employed to make our daily lives easier. The feats that have already been accomplished using this technology are proof that objects don’t need to be big in order to make a gigantic difference in our world.


April 21, 2016
Part Human, Part Machine – Cyborg Technology already among us
The idea of making ourselves superhuman via technological advancements used to be a hypothetical concept. Becoming a cyborg has always been supported by a part of the population but considered taboo by others. Regardless of personal beliefs and opinions it is a concept that has started becoming a reality, much quicker than anybody really expected. Even though it is normally portrayed as ideas that will make our species more advanced, in reality they are also allowing people with disabilities to enjoy doing the things that the rest of us consider normal.
As this technology increases our cyborg prospects will expand rapidly, and eventually there may be full body enhancements that will be accepted as the norm. Until then, let’s look at some of the ones that have already begun to change our lives.
Prosthetic Limbs – One of the first set of experiments with cyborg technology included attempting to make artificial limbs that work as well as our human ones do. This gives amputees the opportunity to move in the best way possible.
The BeBionic limb is taking this goal to new heights. It is a prosthetic hand that’s connected to the wearer’s skin and muscles in their upper arm. It is operated via muscular movements, and each individual finger joint can be moved separately. This means that it enables amputees to do some of the things that other prosthetic hands don’t allow, such as being able to tie their own shoelaces.
Eyeborg – Designed by Neil Harbisson, an artist who was born completely colour blind, the eyeborg is a one of a kind invention. Harbisson wears a colour sensor that is mounted on an antenna on his head and then connected to a microchip in his skull. The sensor turns colours into sounds which he hears via bone conduction. This means instead of seeing colours he is actually hearing them. It took him a while to differentiate the different sounds each colour makes on the spectrum, but he is now able to recognise many more than the average person  can see. After a battle between Harbisson and the British government, the eyeborg is now acknowledged as a part of his body.
can see. After a battle between Harbisson and the British government, the eyeborg is now acknowledged as a part of his body.
RFID – Meaning radio frequency identification, these are chips that are imbedded between the index finger and the thumb. They allow the wearer to connect to Android devices, open doors, turn on lights and other useful every day activities. The surprising thing about having an RFID implanted is that it can be done anywhere, by anybody. There are even DIY kits available online for those that are daring enough to undertake the process themselves.
Terminator Lens – We all know about the terminators’ ability to zoom in on any object. As implied by its name this contact lens will do the same for the person wearing it. Even though it is not yet available for public purchase, it has been proven to work well. The terminator lens allows an individual to magnify their vision up to 2.8 times instantly, by using a liquid crystal shutter that is located in the lens itself. It works well in 3D glasses, but the manufacturers are still trying to come up with a way to put the crystal shutter in the softer plastic that is used to make normal contact lenses.
The human race has finally become advanced enough to begin to transform themselves. Let’s hope that with greater knowledge comes the acceptance of the added responsibility of using it wisely.


April 14, 2016
Surena III – humanoid robot
If you think that smart robots are a thing of the future, you need to meet Surena III. At 6 feet 3 inches tall, and weighing 216 lbs, Surena III is the closest thing the scientific community has ever had to a perfect humanoid robot. Equipped with sensors, 3D vision, powered joints and a sleek casing with LED lights, this robot can climb a ladder, stand on one foot, and can now walk at a faster pace than its predecessors at 0.2 m/s.
Robots like Surena have been in development for years, and some similar models were used at Fukushima.
The humanoid robot, funded by the Industrial Development and Renovation Organization of Iran, can walk up and down stairs, take hold of objects, kick a ball and can even adapt to different terrain. Video footage has shown the robot standing upright on uneven ground. It is the third robot in its series and has significant upgrades over its predecessors. Iranian researchers upgraded the robot’s sensors and actuators over the previous version. The vision system now allows the robot to detect faces and objects and track a person’s motions. A speech system can recognize some predefined sentences in Persian. Encoders embedded on all joints, six-axis force/torque sensors on the ankles, and an IMU on the torso help the robot remain stable. To power Surena’s hips and legs, the researchers used a combination of Maxon brushless DC motors, harmonic drives, and timing belt-pulley systems.
 Image: CAST (Center of Advanced Systems & Technologies)
Image: CAST (Center of Advanced Systems & Technologies)It took over seventy students, engineers, and professors from Tehran University and five other Iranian institutions to design and build Surena III. Local companies developing robotics software and speech systems also contributed to the project, and experts expect that some of the technology developed for the humanoid could find applications in manufacturing, healthcare, and other industries.
Scientists are now working to make the robot more autonomous and are working to help it increase its ability to interact with humans. Recent studies have also claimed that the level of AI shown in science-fiction movies can never actually happen. If consciousness is based on the integration of lots of pieces of information, computers can’t be conscious and capable of experiencing emotions like humans.


April 10, 2016
FREE until Monday
 You can download a copy of Future Furies on your kindle for FREE today by visiting Amazon.
You can download a copy of Future Furies on your kindle for FREE today by visiting Amazon.
A great read for the weekend.


April 7, 2016
Technology That Changed The World
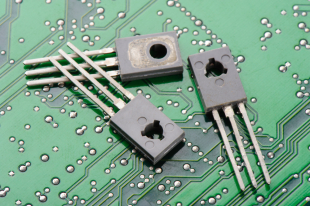 Without the transistor, pretty much all the technology we take for granted today wouldn’t exist – or if it did, our home computers would be the size of Belgium. The basic building block of everything electronic, the transistor is widely credited to Bell Labs’ William Shockley, who based his own research on findings by John Bardeen and Walter Brattain in 1947.
Without the transistor, pretty much all the technology we take for granted today wouldn’t exist – or if it did, our home computers would be the size of Belgium. The basic building block of everything electronic, the transistor is widely credited to Bell Labs’ William Shockley, who based his own research on findings by John Bardeen and Walter Brattain in 1947.
The IBM PC Gave Birth to the Home Computer.
The first IBM PC was powered by an Intel 8088 microprocessor, was the size of a portable typewriter and packed 16K of RAM. It cost nearly $2,000. It’s dated now, but if it weren’t for this first PC, we might not have computers at all. At the time, it would have been impossible to imagine that one day we would have computers small enough to fit inside our phones—but it all comes from the 8088 microprocessor.
The PC brought computing to the desktop, and its influence lives on. When IBM stopped fighting clone manufacturers and licensed technology to them instead, it led directly to today’s modular, upgradeable and customizable machines. When you’re upgrading your aging graphics card to play Crysis or swapping out your old DVD drive for a Blu-ray/HD DVD combo unit, you’ve got IBM to thank. Or curse.
TCP/IP Holds the Internet Together.
Developed by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency in the early 1970s, Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol is the glue that holds the Internet together. Without it, we’d just have a bunch of networks that couldn’t talk to one another.
The Apple iMac Made Technology Stylish.
The original iMac is one of the most influential designs of the last decade. In a world where computers were ugly, blocky and beige, Apple showed machine-makers a better way of doing things. And the iMac has influenced not just computers, but irons, vacuum cleaners and even baby bottle sterilizers. With the iMac, Apple rediscovered its groove, giving it the platform to design other icons of our time like iPods and iPhones. You may have heard of them, but without the Apple iMac we would never have had them.
The World Wide Web Makes It All Possible.
The World Wide Web isn’t the Internet. Created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 and released in 1992, the web took off in 1993 with the introduction of the Mosaic Web browser. Without the World Wide Web, modern Internet as you know it wouldn’t exist. Berners-Lee could probably have made enormous stacks of money from patenting and licensing his invention, but he gave it away instead.
 The Mouse.
The Mouse.Invented by Douglas Engelbart at the Stanford Research Institute in 1963, the mouse changed the way we interact with machines – but Engelbart didn’t receive a penny in royalties for his invention, because his patents ran out before the mouse turned up in PCs. The mouse ball came along in 1972, making tracking easier, and while the nuts and bolts have changed – today we have wireless mice and laser mice, not to mention mice with more buttons than a tailor’s shop – the mouse is still an essential part of our computing kit.
SMS Changes the World.
It may well have ruined the English language, but SMS (Short Message Service) has also transformed the way we communicate – and it was done so entirely by accident. While the idea was kicking around during the mid-1980s, nobody thought of it as a way for people to send messages to one another; instead, it was envisaged as a way to let people know they had new voicemails. The first mobile phone SMS was sent by a Nokia student engineer in 1993, and by 2000, the average user was sending 35 SMSes per month. We now know people who send that many messages every few minutes.


March 31, 2016
5 Futuristic Technologies That Already Exist
Did you ever think you’d fly in a car? Hover cars have always been considered too futuristic for reality. People have believed that it’s impossible to have cars that can fly, and we are happy with thinking of them as part of the movies. However, this is one of the 10 future technologies that already exist. Israeli scientists have been able to create unmanned battle vehicles for army evacuations. The next step will be to turn your sedan into a hovercraft!
Human Organ Printing.
Printing human organs can save precious human lives. This is a dream of not only the doctors, but of people around the world who see their loved ones die of deadly diseases. This is no longer a dream, however. Scientists have been able to print artificial arteries. The heart, lungs and other organs will soon follow.
 Thought-controlled Prosthetics.
Thought-controlled Prosthetics.It’s the Terminator! Thought-controlled prosthetics are one of the amazing inventions that nobody believes we have been able actually create yet. But that’s not the case. Scientists at DARPA labs at Pentagon have been able to create robotic arms that can controlled by thoughts with the help of a chip in the brain. The next step will be to create whole bodies that can think for themselves.
Retinal Implants.
We all think that science is still far behind the fulfilment of this promise of making the blind see again. However, scientists in Germany have already been able to create retinal implants that allow blind people to see.
Cloaking Devices.
This is another one of those way-out technologies that already exist. Cloaking devices are already a reality. Scientists in the United Kingdom have been able to make a paper clip invisible by use of meta materials. Once they perfect their work, they will be able to cloak everything under the sun.






