Bruce Clay's Blog, page 50
March 13, 2014
#SMX Liveblog: Power Boosting Sales with PLAs #32B
#SMX Liveblog: Power Boosting Sales with PLAs #32B was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Hey, online retailers! You’ve got to be doing product listing ads with Google and now Bing!
Bing Product Ads
Speaker: Brittney Thomas from Bing Ads
Brittney is the retail vertical lead for Bing Ads in Microsoft. She’s bringing the Microsoft vision for retail and Bing Product Ads to this audience. She shows us a video about how Bing interviewed consumers in their research to bring marketers and consumers closer together — the “Consumer First Advertising Approach.”
The foundation of this approach is the retailers most powerful asset: the product. Product ads starts addressing that for consumers on the front end. This month there will be product feeds across the Yahoo-Bing Network.
Product Ads give consumers rich info in an engaging format. It will show custom images from an advertiser’s own product catalog plus promo text and pricing.
Product Ads set up in 3 steps:

A campaign import tool will let you transfer your Google PLAs into Bing. And shopping ads are in the Bing roadmap as of a couple weeks ago. She notes that campaigns should be optimized for the Yahoo-Bing Network since the audience is different than Google.
Campaign Management: If your campaigns aren’t properly organized, you’re less likely to succeed.
There are a set of required feed attributes that you should figure out how to scale. Then, adding info in the recommended attributes makes the experience richer.
An optimized data feed can be considered in terms of data validation, product discoverability and conversion.
Setting up your campaigns: the more specific your product targets are, the more control you have over which product serves. Create at least one Product Target that targets all products. Group similar product IDs. Then create additional Product Targets that include specific brands or product types. Product Target attributes are critical for success. As a rule of thumb, think of reporting. You’re looking at what can be manipulated to increase ROI. (Brand, Condition, Product Type, BingAds label, BingAds group, etc.)
Advertisers sometimes spend a lot of time getting granular in setting up campaigns but fail to create a product target “all” bucket. This lets ads and opportunities slip through the cracks. Don’t use a blanket strategy for your Google PLAs and Bing PLAs since audience is different and performance is different.
Google Shopping Ads
Speaker: Santiago Andrigo, Product Manager for Bidding Strategies within Google Shopping
Google Shopping in 2013:
1+ billion products promoted
200% growth (PLA clicks YOY in September)
23 countries
Retailers are enjoying the experience of showing their products online as though on a digital shelf. Feedback is a desire for operational improvements and better insights for optimization. The biggest insight they found overall is that retailers would like to manage their online inventory in the same way they manage it offline (brands, models, manufacturers, etc.). Google is changing the Google Shopping campaigns for advertisers in 3 ways.
1. Retail-centric campaign management
Streamline how you manage and bid on your products.
Browse your data feed directly in AdWords.
Select the products you want to bid on more granularly with product groups.
Ensure all products are covered within your campaign.
2. Advanced reporting
View your performance by product attributes or individual products.
Analyze and expert performance metrics.
Able to track item-level performance regardless of product group structure.
Identify new opportunities to optimized your campaign.
3. Competitive landscape data
Optimize with competitive metrics reported in a new bid landscape report.
Track against your competitors with benchmark max CPC and CTR.
Get insights into your competitive landscape with impression share.
Estimate your opportunity with a bid simulator.
3 steps to getting started:
Create a Shopping campaign in AdWords, customize your Shopping campaign, switch to your new Shopping campaign.
In one beta tester they saw a 13% increase in conversion rate and 20% decrease in CPA.
Optimize PLA Campaigns
Speaker: Patrick Bennett, co-founder of Showroom Logic
Some of his hacks got trumped by Santiago because the new Google Shopping Ads fix the problems. These things are sure to make a positive impact on your sales.
1. Get in alignment. Think how consumers think, not how manufacturers think. Shoppers aren’t looking for a specific product, they’re looking for a category of products.
In his experience, out of 360 sales in 3 months, only 40 had the product title n the ad. 89% of all sales from PLAs were not from keywords that contained the product title.
2 Play with your feed. Let search queries drive your product titles. Put that high volume search term at the beginning of your product titles.
3. Be descriptive in your “product_type” column. Messing with this column has given him more results than any other column. He calls this PLA keyword expansion. He’ll see more data coming in from Google, then he can scale back with negative keywords and removing words from the product type. Think of your Product_Type as a breadcrumb.
Additional columns worth testing:
Price: test moving the price up/down look at CTR/conv impact
Images: if your product has option, test using the best seller and variations like little logos around the product, or showing all the options
Campaign structure (this advice is obsolete under Google’s updates): Have a separate AdGroup for each product to allow you insight into keywords and have control over bidding.
Search queries = $ — he uses 3 filters weekly:
1. Costly conversion – draw a line in the sand
2. Keyword heroes – may want to break this into its own ad group or create a search campaign on it
3. Keyword hopefuls
4. Create search campaigns off your search query reports. Let your PLA campaigns dictate other search network campaigns. CPCs are very low in PLAs so it’s a good testing ground. Build a search campaign off search query data to see high volume and low CPAs.
In-House Campaign Management
Speaker: Onrpaka Vudhikosit
PLA Profit Maximization Goal
ROAS = Online Revenue / Advertising Spend
The question they had to ask is, while they may be making sales, are they getting revenue. There are a number of multipliers that you have to calculate
How to apply to concept of product/category profit maximization?
1. Obtain historical data of avg CPC, spend, clicks, and online sales
2. Determine offline impact from your online sales
3. Understand related adjustments and expenses
4. Test target ROAS/CPC at different level of bidding spend
March 12, 2014
#SMX Liveblog: Evening Forum with Danny Sullivan on Google and SEO
#SMX Liveblog: Evening Forum with Danny Sullivan on Google and SEO was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
We’re here at the evening forum. Danny doesn’t have a presentation or agenda; he walks around and talks. Everyone here may be called upon to participate. We’re going to hear the assorted issues that the assembled community is experiencing.
 Question: If you have $500 to spend on marketing, where would you spend it? Context is small non-local brand.
Question: If you have $500 to spend on marketing, where would you spend it? Context is small non-local brand.
Danny: First he’d make sure there’s a website. A lot of small businesses don’t even have that. Spend some of that money on your own domain name (instead of somesite.tumblr.com). He’s spend some time educating himself on SEO. He’d read Google’s own SEO tips guide. You never go wrong starting off with the things Google’s recommending. He’d spend time opening social media accounts on Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and possibly LinkedIn. If it was a location-based business he’d make sure he had a Google+ Biz page. As part of the SEO process he’d spend time understanding the key terms for his site. AdWords might be good to dip into to get a sense of the kind of traffic coming from those terms, but he’d probably spend more time learning about organic.
This conversation between Danny and the questioner evolves into a debate about black hat SEO as the questioner suggests black hat is one of the only ways to get fast traction in the organic space. I don’t have to tell you I disagree. Danny’s argument is that if your business is offering something uniquely valuable you’ll grow naturally.
The audience makes suggestions:
Your own manual labor of learning and growing fueled by coffee
Highly targeted Facebook ads can perform well on small budgets, and Twitter ads too
Question: What are the negative and positive directions that Google has been moving in, as far as our community is concerned?
Danny: Amit Singhal taking the time to come out is a sign that there’s some encouraging moves by Google toward the SEO community. Until that point there’ve been a lot of discouraging moves, like the shopping search engine that requires payment for inclusion as well as the switch to not-provided. There’s a big conflict between Google as a search engine and Google as a product provider and publisher. As an example, when Google purchased a travel content service there was then conflict for any travel sites that would then have to compete with a Google property. Danny has also been concerned by a convoluted system of links; it seems like it’s easier to just recommend “don’t get links” because it’s way too complicated. He wishes Google would just say we’ll count links we think are good and not count links we think are no good. That said, Google deserves credit for providing the majority (or big portion) of free traffic to websites.
Question: Given what we heard from Amit Singhal last night, what’s your gut feeling about what we’ll hear about not provided next?
Danny: He wrote up an article of 5 possible things that could happen in “Google Reviewing “Not Provided,” Withholding Keywords From Organic But Not Paid Search Clicks.” Most likely it’s one of two things:
1. Google will recommend making your site secure because in that case secure search and secure sites keep the chain and the web will be more secure as an added bonus.
2. Or the paid search terms will be turned off. Several times Amit mentioned talking to the ad team and you wouldn’t need to get them involved unless the change involved them.
Question: From a coding and value add perspective should you use structured data markup?
Danny: Oh yeah. Any opportunity, especially when Google says you’d do well to do this, you should do. This is data that Google will need to add to their understanding of “things not strings.”
Question: I have a niche question and theory. When the great Authorship Apocalypse happened, authorship pics started disappearing. If you go into the Rich Snippets tool and you don’t have authorship set up you’ll see the publisher logo show up.
Danny: He thinks “publishership” is definitely coming, and may be just that Google is waiting to get more accurate with Authorship first.
Question: Do you see Google Trusted Stores effecting ad rankings and PLAs?
Danny: Yes, any trust signals Google will use. Throw yourself into the Google system. If I told you the way to rank #1 on Google is add this code, you’d do it. The number one way really is Google+ — it trumps any other signal, given you have anyone following you. If you’re following someone and you’re in the Google+ system, that’s automatically going to show up.
Question Rant: Penguin was a disaster and Google penalized many sites doing things Google has been saying don’t do for years but a ton of innocent sites got pulled into the mess. Why isn’t the disavow list we SEOs are providing to Google not the direction that Google is going in as far as fighting spam?
Danny: Penguin was a disaster for innocent sites, you say? He won’t make that concession. Yes, innocent sites get caught up but most who claim that aren’t so clear cut. But the disavow tool is also a questionable move — a tool we wouldn’t need if Google didn’t just not count bad links they detect. When they don’t do that they open themselves up to the spectrum of negative SEO. He thinks there’s a misunderstanding that Penguin both penalized sites and took away the votes from bad links that previously counted for them.
Question: Our company is an education company and we sell programs to students to help them graduate. We do a good job at publisher type ranking efforts. We have a challenge with the authorship part of it. I think the easiest answer is to get our instructors authoring content but they’re very unreliable. They also know that their students aren’t in the Google+ space.
Danny: Have this conversation: the best way to rank on Google is to have a company Google+ account. Your website needs to be linked into Google+ so people understand there’s a connection between your brand there. Authorship ideally will be set up for each instructor, and it doesn’t matter if they don’t use it — it’s still a digital business card.
#SMX Liveblog: Life After Not Provided (#24A)
#SMX Liveblog: Life After Not Provided (#24A) was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
So we lost our keyword data. Now what? What does life look like after not provided? This session is all about gleaning insights in a post-(not provided) search industry.
Benjamin Spiegel (Director of Search Operations, Catalyst) kicks it off.
What is Not Provided and What Does it Mean?
In 2011 Google started to encrypt search. HTTP changed to HTTPS and consumers probably didn’t notice much of a physical change, but marketers have since been noticing big changes in GA reporting data.
Pre-2011 if a searcher were to navigate from the search engine to a website, information was passed directly from the engine on to the end website giving web masters rich GA data about search queries and referral traffic.
Now… that is gone. Organic optimizers have basically lost the connection between the term and the activity on the site. (The connection between the term and the activity on the site (Keyword → landing page → activity). Paid marketers have limited access to this data, but organic optimizers cannot access this data in Google Analytics. That said, this doesn’t mean you can’t access actionable data that will allow you to glean insights from search traffic (as Benjamin and the other presenters will discuss throughout this presentation).
In a nutshell: Keyword data (and anything (not provided) is not coming back. Don’t hold your breath. You cant buy it, there is no substitution, and….. it just doesn’t really matter that much anymore. Google is about relevance, content, and context, NOT key phrases.
Coupon vs. Coupons vs. Couponing; it doesn’t really matter. It’s all about context anyway and keyword data never really lead to action anyway.
How to Glean Insights from Google Webmaster Tools (GWMT) at Scale
1) Collect the data
Google offers a couple data collection options:
- Webmaster Tools API
- Google Python Solution
- Scraping (Google does not like this option; we do not recommend it and either does Benjamin)
Catalyst (Benjamin’s parent company) is using option B, the Google Python solution. Bruce Clay, Inc. uses option A, the Webmaster Tools API option.
2) Connect the output to your Database
3) Enhance your data
(Add additional data using tools like Google Trends)
4) Segment your Data (key phrases) into themes
5) Connect your Data
6) Tell a Story with the Data
It all goes back to insights to action. (Remember: Data is worthless if it doesn’t convey information; if it doesn’t tell a story.)
Rather than asking “what keywords are driving traffic and rank” ask yourself questions like:
What day of the week are my consumers most interested in X head topic?
How does CTR change based on day of the week?
Does activity for X head topic differ for branded CTR versus unbranded CTR?
You can find all of this information in GWBT. (In GWMT make sure you’re looking at Pages rather than phrases).
______________
 Marty Weintraub is up next. He starts by asking the audience how many people were using keyword research to really granularly track keyword performance. (A good number of people raise their hands.) Then he asks how many people took a serious revenue hit because theyre not there anymore? (Basically no one raises his or her hand.) He says “Yeah… that’s what I thought.” (In a very Marty Weintraub way.)
Marty Weintraub is up next. He starts by asking the audience how many people were using keyword research to really granularly track keyword performance. (A good number of people raise their hands.) Then he asks how many people took a serious revenue hit because theyre not there anymore? (Basically no one raises his or her hand.) He says “Yeah… that’s what I thought.” (In a very Marty Weintraub way.)
Marty’s going talk SEO metrics, how to leverage Big Data, and what can you do with third-party big data to calculate/translate action.
What is Big Data?
“Big Data is whatever anyone says it is.”
“SEO measurement is actually better than before we lost keywords,” says Marty. He says he’s seen no loss from clients not being able to granularly analyze keywords.
SEO Metrics and Actionable Big Data
For your brand and competitors you don’t need to know keyword referral data, you need to know:
- Your unpersonalized rank (Authority Labs and Conductor = good tool options.)
- Your competitors trending unpersonalized rank
- How to calculate CTR potential based on rank
- Calculate SEO competitive traffic share
(Tool options = Ricon SpyFu or you can do this with BrightEdge)
Post not-provided a lot of organic keyword insight is coming from paid tool manufacturers like SpyFu (which, by the way, has been historically considered a PPC Competitive intelligence tool).
Remember: All data is just a bunch of junk if you don’t ask any good questions; if you don’t take your data and turn in into insights.
Ask yourself: How much organic conversion am I seeing and how am I doing at the asset level? What does my traffic share look like? How does overall traffic conversion weigh against conversion?
___________________________________________
Next are two speakers from Intel Laura Ann Mitchell and Ken Shults.
Laura Ann Mitchell starts
Prior to keyword (not provided) Intel had a huge variety of keywords brining natural search traffic to Intel (apx. 3 million universal keywords per month with the navigational query “Intel” accounting for about 6% of our total Natural Search traffic).
Since Keyword Not Provided visibility in analytics is significantly decreased but consider themselves only “slightly irritated” on the Pain and Suffering/Impact scale.
Natural Search should be fully integrated within each component of the Digital Marketing Framework . SEO is not something you do, it’s something you do when everything is done right. It should be a part of your whole digital marketing framework, not something that stands alone in it’s own silo.
Content → publish/promote → measurement → insights
“(Not Provided) has not been the biggest impact for us in the areas of Insights and Measurement.“
Want to glean data post (not provided)? We need to reverse our model; not look at keywords, but look at optimization at the page-level.
How our processes have been impacted and how we’ve adapted
Search helps us better understand out audience. (What are their problems? What are they searching for? What are they trying to solve?) Intel utilizes insights from search to inform multi-channel marketing including content, paid search, social, display, and retail channel support.
For Intel, the search insights process begins with collecting a master keyword landscape. (They use a word cloud process to do this.)
- Google Keyword Planner is their primary source for keyword data.
- Data from the Keyword Planner is augmented with analytics data from Paid and Natural Search, and then that data is categorized into a “monthly search by topic” system to better surface insights and opportunities.
Then…
An opportunity vs. Performance Gap Analysis is performed. Integration of Paid and Natural Search performance data against a categorized keyword/topic backdrop begins to reveal gaps between opportunity and performance.
That said… Keyword-level Natural Search Data is a requirement to produce this view. Since we can’t get this data from Google Analytics anymore we turn to Google AdWords Paid & Organic Reports to get Natural Search keyword data. This tool has some nice features but also some significant drawbacks:
Pros:
- Natural Search keyword impressions/CTR
- Natural Search average ranking by keyword
- Integrated Paid/Natural performance by keyword
- Exportability of large volumes of keywords
Cons:
- Account linking limited to top level GWMT accounts
- No segmentation of data by page
- Limited to Google
- No post-click metrics (conversions, etc.)
Another keyword insight tool option is Google Webmaster Tools
Keyword availability improves with progressive granularity in GWMT accounts. For this reason, Intel has established GWMT accounts for top-level directories and many second level directories totaling more than 250 GWMT accounts that align with different directories.
Looking at Five Keyword Research Data Sources and the Insights They Deliver
This Chart is Helpful!
Part Two: Impact on Measurement
However beautiful the strategy you should occasionally look at the results” Winston Churchill (great quote!)
4 Timeless Measurement Best Practices
- Measure what stakeholders care about
- Identify what’s working
- Find out why
- Do more of what’s working!
Asset-centric reporting:
Several years ago Intel shifted from keyword-centric reporting to asset-centric reporting to better align with stakeholder’s goals.
Their asset-centric reporting style means their measurement plan always begins by defining a narrow site section of interest and then using that narrow site section as the focus of performance reporting.
They do it this way because direct and indirect views of defined page groups of pages give stakeholders a more complete picture of the impact of Natural Search.
Trended Views by Page help them uncover stories to explain performance and guide deeper investigation. Engagement data at the Page Level helps them refine content and optimization in alignment with the interests of searchers.
Aligning GWMT sites to allocated Site Sections provides keyword-level Natural Search visibility data, but we do lose Keyword Engagement and Indirect Views data.
The Takeaway…
Keyword level data by page is available through the GWMT interface and can be used to investigate a specific page (but note that CTR and Average Position data may not be available).
Dimension v. Natural Search Metric v. Impact
Another useful chart!
Using a Tool Like BrightEdge to Integrate Data Platforms
Intel utilizes the BrightEdge Platform to have data from Web Analytics, GWMT and their target keyword ranking data all integrated into a single integrated environment that facilitates analysis.
Final Intel Recommendation…
Minimize paid and suffering brought on by keyword not provided by adopting a page-centric approach to measurement and configuring GWMT in alignment with site sections.
#SMX Liveblog: Capturing the Mobile Paid Lead #23C
#SMX Liveblog: Capturing the Mobile Paid Lead #23C was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Moderator Greg Sterling drops a kernel of new info: if consumers have a negative map experience they’ll make that negative association with the brand. It’s important to make sure your brand’s data is right on maps and mobile.
Winning Mobile
Speaker: Ben Braverman, Head of Growth at URX, @braveben
His presentation centers on capitalizing on the supercomputer in your customer’s pocket. In January, the time U.S. consumers spent in apps officially eclipsed the time spent on the web otherwise. His company drives revenue after the install.
First, get an app.
Build it
Buy it
In-app conversion rate > mobile web
US user time spent in app = 4x time in mobile web
Install strategy
Deeplinks
URLs take you to specific pages on a site, deeplinks do the same for apps
Deeplinks are a big part of the reason that apps are able to take off — a good user experience
If your app is not deeplinked, Google won’t index your app by the end of the year
Home-brew or Open Source frameworks like Turnpike
Google App Indexing
Deeplinks can degrade gracefully
Social media, email marketing, paid marketing
Discovery: A big issue for app developers is getting your app discovered. How users find apps (from most popular way on): App Store search, friends and family, third party sites
App Store SEO:
Experiment with different app categories
Deeplink your app
App title: multi-word name, include keywords
Keyword field (look at the top apps’ keyword field)
Paid user acquisition:
In the early days, buying an app install was unheard of. Now you can price out an app install on hundreds of networks. 2 years ago, being an ad network was prestigious. Now ad networks are commodities that are as valuable as their publisher network. Programatic buying, RTB and exchanges allow you to adjust your bidding strategy. Facebook is the largest mobile app ad network and he expects a Facebook Mobile FBX will be coming soon.
Programatic Buying:
Mobile advertising at scale
Set goals in the most relevant metric (CPI/CPA/CPC/CPM)
How your installs become customers:
An installed user isn’t a customer, they’re an opportunity
Average user has 80 apps
60%+ opened between 1-10 times
Push notifications, paid engagement
Personalized marketing
Mobile-centric app value
He says track everything unless terms of service require you to delete it. There’s some controversy over device ID in the iOS App Store that you’ll want to look into.
Your Mobile Action Plan in 10 Steps
Speaker: Joseph Kerschbaum @joekerschbaum, 3Q Digital account director
He’ll be zooming in on Google AdWords (apologizing to Bing and saying he had to focus in). The steps get harder as he goes through this presentation.
Mobile Ads – Do Them Now
Mobile-optimized text ads and extensions will be given preference on mobile devices.
He recommends 2 mobile ads and 2 desktop ads.
Tip: Avoid truncation. Mobile ads should be shorter. Aim under 60 characters.
The same applies to Sitelinks. You have to tell Google (go in your Ad Extensions) and set mobile optimized Sitelinks.
Tip: Mobile optimized sitelinks are shorter. Aim for 15-17 characters in links.
Mobile Devices Are Actually Phones
Set up call extensions under Ad Extensions.
Charged the same as for a standard click on the ad.
Clickable on devices that allow a user to click and call.
Utilized Google call-forwarding for tracking.
If they last longer than 60 seconds Google registers this as a conversion and that can be reported by Google.
Get Purposeful with Mobile Bid Ads
Determine a mobile bidding strategy
Keep in mind there are modifiers modifying each other all over the place. AdWords is becoming a much more complicated machine
There are so many things influencing each ad. So:
Active Bid Adjustments
Review all bid modifiers. Go under Settings and look for “Active bid adj.” to add. Now you can see location, ad schedule and device. And you can see all bid modifiers listed for that ad and a bid adjustment range.
Improve Mobile & GDN – Don’t Cross the Streams
Mobile + Display = Sadness
In mobile, a consumer’s in a snack mode. For display, consumers are blocking you out. He’s found GDN campaigns on mobile perform terribly.
Instead, craft your structure. Here’s how they do it:
Exclude mobile devices from GDN
Tablets Are Mobile Devices
GDN: Better than mobile isn’t good
Tablets bring down their GDN campaigns overall.
What you can do is go under Display network, go to targeting, go to category options and remove entire categories. You can also remove all apps (adsenseformobileapps.com).
All Your Effort = Fail?
Conversion Optimizer is great but it’s a bit of a mystery.
Use accelerated ad delivery with Conversion Optimizer. He thinks bid adjustments clicked in.
Remember, it’s not just responsive design, it’s responsive experience. People on mobile are on the go, browsing, not ready for a long-term relationship. Optimize for design and content. You want to make sure visitors know what to do on the mobile site. Optimize your web experience for design AND user intent.
Monitor mobile lead quality closely. Not all leads are equal. You need to be able to separate out conversions by device. This can be difficult to implement, but not having this data is crucial. You don’t want a single bucket of all conversions.
Start thinking about cross-device behavior. People are addicted to screens. What to know now:

People start on a phone and end on a larger device. The 10 steps he shared. can be used to support this behavior.
bit.ly/Mobile-Action-Plan includes a spreadsheet for you to track your implementation of these 10 steps.
Mobile Leads and Click-To-Call
Speaker: John Busby @JohnMBusby, SVP Marchex
M-commerce is important. Mobile influenced sales is much bigger than m-commerce. Look at “The Roll of Click to Call on the Path to Purchase” — a paper by Google. Besides Google, consumers search on local and vertical directories. Vertical aggregators are another source of mobile clicks. They buy traffic to harness consumer intent and the experience is a lead form or phone call. Voice search is also an important channel driving mobile leads, despite this not being monetized yet.
What brands and agencies should do about click-to-call:
1. Have a tracking phone number. This isn’t the call extension Google gives you from call extensions — it’s everywhere you put your phone number.
2. Have an IVR (or phone menu). This is important because people make a lot of accidental calls and you want to avoid burdening your call centers with that plus spammers and telemarketers. An IVR also qualifies intent of the caller and provides real-time reporting for optimization.
3. Measure the effectiveness of your mobile landing page.
Simple changes could mean more ROI.
4. Consider “rescuing” calls. It’s unlikely a consumer will leave a voice mail. Work with a call solution to collect lead info and then email that to the business.
5. Measure intent. If you know why consumers are calling you can adjust and improve your ad copy.
#SMX Liveblog: Small Company; Big Results (#22D)
#SMX Liveblog: Small Company; Big Results (#22D) was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
This SMX West 2014 session is framed kind of like a small biz to small biz one on one strategy sesh. The presenters have all worked with (or own) small businesses; they’ve all tried things that work, and they’ve all tried things that don’t work. In these three presentations they share with us their success stories and tips you can apply to your own small business efforts.
First up is Andrew Melchior – VP and founder of Avalaunch Media (@Atraine)
Andrew starts with wise words: You need to think of your small business as a smaller business that can 100% compete with bigger companies. Being small doesn’t mean you are unable to succeed with big business competition.
An example that tickles the crowd…. Fat Baby Friday. He’s telling us about a client he talked with once. He asked them “Whats been your most successful campaign?” and they said… Fat Baby Fridays. (Seriously.) Then he asked about ROI and they said there wasn’t much. (Hrm.) Here’s the point:
Don’t fall into the Viral Trap! You need to do much more with content than just focus on virility.
Start thinking strategically. Lead with content that’s centered around your message.
A Case Study he offers as a learning tool:
Company Profile: Ski Utah. They’re a non-profit; marketing efforts are aimed at promoting Utah’s snow season and the above-par quality of their snow.
What they did:
1) Created an infographic (or “Strategraphic” as Andrew calls it) to visualize their articulated advantage.
2) Followed the graphic up with viral content that is supportive. (For example: The Evolution of Skis.)
Market Your Small Business Better: 6 Tips (Click to tweet)
1) Get Your Internal Communication Tight
Talk to the people you work with in-house to get a collective big-picture idea of what they each need; what each of your in-house people need to accomplish. What assets they have to bring to the table. What assets they need you to bring to the table. Try leading focus groups, give them surveys, hold off-site events to get everyone speaking up.
2) Identify your Best Content
Perform content audits. Understand what is working and what is not. Don’t just blindly create content and then leave it floating around the Internet without any sense of it’s performance or resonance.
3) News Jacking is the shizdizzle (it’s good.)
Find something that happened in the media space and leverage that buzz to create buzzing content for your own brand. For instance, The Oscar selfie picture was a recent news buzz. Avalaunch news jacked this opportunity by taking a Avalaunch team selfie that got picked up and called out as one of the week’s “best news jacks.” Think about what you can do to attach yourself to what’s already happening in the media.
4) Monitor social media now and historically.
What are your consumers telling you about their preferences and needs? What feedback about your product are you hearing? What are people looking for? How can social media help you better fulfill your consumer’s needs?
5) Learn more about your competition.
Sign up for their newsletters. Read their content. Learn from the things they are doing well, and from those they are doing really, really badly.
6) Repurpose Content!
Squeeze every last drop of goodness out of your content. Transform content you already have — content that is already winning — into new content by simply reworking the content without reinventing the wheel. For instance, consider turning your blog content into a:
- slide deck/presentation
- video
- podcast
- white paper
- image (or slideshow)
- infographic
Find what the hits are and then go out with it again and again.
______________________________________
The next presenters are Don Willis (Founder of Storage West; launched first website in 1999; @Sunergon) and his business partner Fionn Downhill (@Fionnd).
Don and Fionn’s presentation takes us through a small business website restructuring. He starts by setting us up with a house metaphor; the point being, it’s important to have a strong foundation if you want to have a stable house that will last over the years through thick and thin.
For Don, a key part of building this solid foundation is attending conferences and consistently making efforts to ensure you are pushing your business in a forward motion.
“When I would attend conferences I would always think: Whats one thing I can learn here, and implement right when I get back?”
To start the story he tells us about the metaphorical jalopy house that was his first website. With his original site build he had a lot of ideas that were piece-milled together to make a hodge-podge website that ranked well, but was… kind of a mess. To get things in order Don decided to focus on team building, or, as he put it, “bringing in an expert from afar.” (His business partner Fionn who is Irish.) With an investment made in his team, he shifted his focus to re-working his approach.
Some notable changes they were sure to implement as a part of their site restructuring:
- Improved navigation
- Added testimonials and videos
- Tried to really personalize the website presentations – put a video with a real person by the call CTA
- Changed from hard-coded HTML to an easy to use (and update) WordPress website
- Made website mobile-friendly
Fionn emphasizes the importance of 301 remapping when you are going through a website redesign.
The results? Conversion within the first two months doubled. Total they implemented 703 301-redirects and, as a result, they saw no SERP ranking loss.
With their new, functioning, optimized website in place their next steps:
- Content projects
- Local SEO in place
- Social media launched
- Blog current and updates
________________________________________________
The third presentation is all about small business PPC case studies. These are really hard to relay via liveblog. If you are interested in hearing about the small business PPC case studies that Angela Needham (Senior search specialist at Nina Hale) presented today, please comment on this post below or reach out to Angela directly via Twitter (@ARaeNeedham).
#SMX Liveblog: Long-Term SEO: How to Win for Years, Not Days (#21A)
#SMX Liveblog: Long-Term SEO: How to Win for Years, Not Days (#21A) was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Up first is Rhea Drysdale (CEO Outspoken Media; @Rhea).
What Makes a Great Website?
The single greatest factor in the success or failure of a website is YOU. It’s up to you to manage that website; everything from the consultants you work with an the strategies you implement.
She highly recommends the book Good to Great by Jim Collins.
It’s about handling the implementation and being disciplined, she says. It’s about understanding your values, the values of the industry, and where SEO is going as an industry.
SEO is not dead! It’s growing and maturing. And Rhea thinks this is very exciting.
As an SEO, it’s so important to work yourself into your internal systems and to gain trust with your company.
Your decisions affect brand, and the success of that brand.
Human behavior forces algorithm updates!
Humans write the algorithm, and when we – humans; SEOs; Internet trolls – make bad choices that produce crap quality, that’s when the algorithm changes and causes a spike in another direction.
Invest in Strategy Not Tactics
Understand how to market your business and communicate the risks.
Highlighted areas represent risk areas:
In Rhea world, I don’t like being told I cant write press releases. I think that’s crap” understand that these tactics are ultimately tacticts that are not going away; it’s all about being smart and knowing how to use them.
These days it’s all about being a brand. What does that mean? It means embodying the characteristics of a great brand:
ModCloth Be the Buyer Example. This campaign is a win because they’ve crafted an interactive system that encourages consumers not to show up one time to buy a dress, but to come back day after day to be a part of that brand and engage:
The key is to: Know what to create; look at feedback from social channels; capitalize on opportunity
Crowdsource (Let your customer tell you what to create); Curate; Create.
ModCloth knows their audience; they identified an audience problem; and created content about that problem, to serve that problem. (That’s what smart SEOs — and smart markets — do.)
Also remember: A diverse product offering naturally building natural links.
A second example: Complex
Identifies their consumers as “Ready to buy, collect, and obsess.” To respond to their consumer’s needs, they built out a multi-media platform with multiple domains and made a sizeable investment in video. As a result they saw a jump to 90 million monthly unique visitors across brands, and are still showing a steady climb. Their win: Producing their own content and investing in video.
A third example: Search Engine Journal.
Rhea suggests we not zone out here… she didn’t bring this up because SEJ is the event sponsor; she’s bringing them up because they are truly industry innovators.
They are experts who offer explanatory journalism, a type of journalism that informs marketers how to take action. Their goal is to provide value to you, the reader. As a result, they are ranking well for head terms like “Hummingbird” (458 backlinks; 266 referring domains). They succeed because they focus on really understanding their audience and what the audience needs.
______________________________
 Up next is Mark Munroe (Director and SEO at Trulia; @MarkMunroe). He’s in the real estate space with a large organic footprint. Wants everyone to own SEO success! … and to own the problems.
Up next is Mark Munroe (Director and SEO at Trulia; @MarkMunroe). He’s in the real estate space with a large organic footprint. Wants everyone to own SEO success! … and to own the problems.
Going to be talking about SEO from an in-house perspective, with an emphasis on reputation building and ways to embed SEO intelligence throughout an organization.
Part One: How to embed SEO intelligence throughout an organization
What Do We Mean By “Long-lasting SEO”?
All successful SEO initiatives (outside of branded SEO) tend to level off. Our challenge as SEOs is to keep that growth growing.
3 Steps We Need to Take To Become Better In-House SEOs
1) You need to work closely with internal teams, and you need to get those teams working closely with each other. It’s essential to break down the silos between QA, UX, HR, Engineering, Marketing, etc. When everyone works together with targets in mind the improvement can be staggering.
2) Over-communicate at every step. Offer guides; don’t just say “make the title this;” explain why the title should be that. Every SEO question should be followed with an explanation.
3) Keep in mind Google’s intent when making recommendations. Whenever making a decision on an SEO strategy or tactics, consider Google’s intent. If your strategy matches the intent of Google’s algorithm, you are moving in the right direction.
4) Link building is still incredibly important to SEO
- Set aggressive link goals across each organization
- Get executive buy in
- Perform periodic reviews (twice quarterly works) and adjust based on what’s working and what’s not.
Remember: As a site and a brand grows it becomes increasingly hard to move the needle. Tremendous amount of work is required to continue sustained growth.
Your whole site is an SEO disaster just waiting to happen! Be proactive!
That’s just how it is. Rises and falls happen. These (in this here slide chart) are all issues that could happen….

Some potential SEO disasters that come with the territory…
How to be proactive? Training, training, training! Train your in-house SEO team and any of your in-house touch points (remember we want to break down silos). Here are some training recommendations:
Pay attention to where the Spider is crawling:
- Where is the spider spending its time? On a large site with a billion possible pages, this can be a concern.
- Even if a site is well indexed key pages may get stale in Google’s cache because too much spider crawl time is being spent on low-value pages.
- Beware of search result modifiers containing potentially nearly infinite combinations.
Pay attention to Crawler Capacity
- Always over-engineer your crawler capacity
- If possible have dedicated servers for crawlers vs. users
- If possible have separate servers for Bing vs. Google
Be Sure to make calculated optimization changes and then be prepared to talk about those changes in the light of unforeseen traffic drops.
Don’t be unprepared when the CEO asks you about a drop in traffic.
Part Two: Reputation Building Techniques
The evolution of reputation building techniques:
Content marketing is really where it’s going right now.
Building an earned reputation versus a faux reputation
It’s important that your brand is building a genuine, earned reputation that is based on realized value proposition. Your reputation should arise naturally and not be manipulative. If you are trying to build your reputation by any non-organic means, this is faux reputation and it will hurt you.
Link building is no problem if your reputation is earned; if your links are earned. You want to get links without every having to ask for links.
Should I ask for links?
Sure! As long as the recommendation is genuine. If you honestly have a piece of valuable content that will honestly add value to the site you are reaching out to, it is a-ok to ask a site to link to your blog post. It’s natural , it’s not manipulative and it makes sense.
What about anchor text manipulation?
Don’t optimize for big-dollar keywords; focus on brand. If you’re pitching an article to a website to get a link, don’t recommend anchor text; let them choose whatever is appropriate.
_____________________________
 Closing today is Eric Enge (CEO Stone Temple Consulting; @StoneTemple)
Closing today is Eric Enge (CEO Stone Temple Consulting; @StoneTemple)
First off Eric jumps right in with a strings vs. things conversation. He tells us (as we probably know by now, so this may be review for some of you) that search engine used to be all about strings; they would return your content if they crawled your page and found strings of words and attributes that made your page appear to be a more relevant result for X search query. Now — in 2014 — with a things-base search engine; it’s all about context and how one consumer search can influence the next. It’s not just plug and play SEO anymore.
And then we have wearable devices and embeds…
The point? We’re not necessarily in a stable landscape. The times are changing. We need to have a forward-facing point of view.
People want to have a trust relationship with the people they buy from. From Sam’s corner store to buying on the Internet this trust relationship has eroded a little bit.
In the future consumers will always check your reputation and “trustability” before buying from you.
10 one-liners that can help frame your SEO strategy (Click to Tweet)
1) Be an expert or go home. It’s hard to build trust with random writers creating content on your behalf.
2) Peruse extreme differentiation. Think of Seth Godin’s purple cow. Regular old run of the mill content just isn’t going to cut it. Bring something new to the conversation. Highly differentiated content is the goal.
3) Links are the result, not the goal. Instead, focus on reputation and brand as your top priorites. If you make these factors your guiding light you will end up with organic links that make an impact.
4) You can’t vote for yourself! Building your reputation is about setting up the circumstance so that other people choose to endorse you and vote for you.
5) The true value of press releases is to generate interest from media. (Seriously. They’re not content marketing and they’re not for link building.)
6) Strong social media presences are like a built in PR channel.
7) Pursue relationships with influencers. They are the accelerators in the process. Their word is worth quite a lot so they can help you build trust and reputation quickly. These are the signals the search engines want to find anyway; the real life signals.
8) Don’t just focus on influencers! Give back to the larger community and interact with a lot of other people in it. Make yourself be seen as open and available (and actually be open and available).
9) If you’re ever arguing about whether a link is a good link, the conversation is already over. It’s not a good link. If it’s a good link ther shouldn’t be any questions.
10) The company you keep defines you. Even if you can’t get into the New York Time, start smaller; go for the Boston Globe or The San Francisco Chronicle and work your way up the ladder.
#SMX Liveblog: App Store Optimization & SEO for Mobile Apps #22C
#SMX Liveblog: App Store Optimization & SEO for Mobile Apps #22C was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
If you have a mobile app, this panel covers opportunities to reach new users through mobile app SEO and App Store optimization.
The What, The Why, The How
Speaker: Ian Sefferman, CEO MobileDevHQ
Over the last 10 years he’s worked on organic marketing in various settings, including email marketing and SEO for apps. The MobileDevHQ is an App Store optimization product.
What
App Store Optimization (ASO) is different than SEO because app stores are different. ASO also includes: Top Charts, icons, screenshots, ratings, reviews, etc. Like SEO, the best ASO is a full, well-rounded marketing strategy.
Why
Apps are eating mobile. The percentage of time spent on mobile apps while on mobile: 80%
“For the average app, search actually makes up the vast majority of installs.” —Google Play. 50% of daily active users (DAUs) search for apps weekly. There are 6 million unique phrases searched monthly in Google Play App Store. These figures were shared at the last Google I/O conference.
Does ASO work?
Here’s an example of a game app that optimized their title, keyword and screenshots.
In this non-game example, simply focusing on more targeted keywords and moving away from head terms saw 4x more downloads.
Components of ASO
On-Metadata ASO – keywords
Off-Metadata ASO – ratings and reviews
On-Metadata: Keywords
Relevance – what sort of results are returned?
Volume – how frequently is it searched for on the App Store?
Difficulty – how much competition and how entrenched are the top 5 or 10 results?
On-Metadata: Title
Including a keyword in the title helps your rank for both iOS and Google Play.
Off-Metadata: Reviews
Text in reviews is being counted (lightly) in rankings, they have found.
Off-Metadata: Links
Links to your app will effect Google Play apps but not iOS.
Off-Metadata: Social
He expects that Twitter may come into play soon. He believes that Google+ signals affect Google Play store rankings today.
There’s a cultural difference between iOS and Google Play.
iOS: media world (there’s a title and a rating). Google: constant iterative refinement, big data, graphs, come from the web, use and know how to use many signals. He believes this will put Google on top in the long run.
Videos are your friend. Videos are integrated into Google Play App Store. They tell the story of the app which is powerful when you only have a few screenshots to tell the story otherwise.
Google App Indexing: Android users search the web will be able to open apps from links in browser.
Should Your App Go Global? How to Evaluate the Opportunity and Leverage It
Speaker: Jennifer Wong, Director of Product Marketing at HasOffers and MobileAppTracking, @Jenerationy
Why go global?
What to consider
The three levels to win in the global market
Why Go Global?
There are more apps created outside the U.S. than within the U.S. today. Angry Birds is developed by a company in Finland. Cut the Rope in Russia. SwiftKey in the U.K. If you’re an app developer in a small company that doesn’t have English as your local language, then you have to take care to think about who the geo market is for your app.
8 out of 10 of the largest mobile app markets don’t speak English primarily.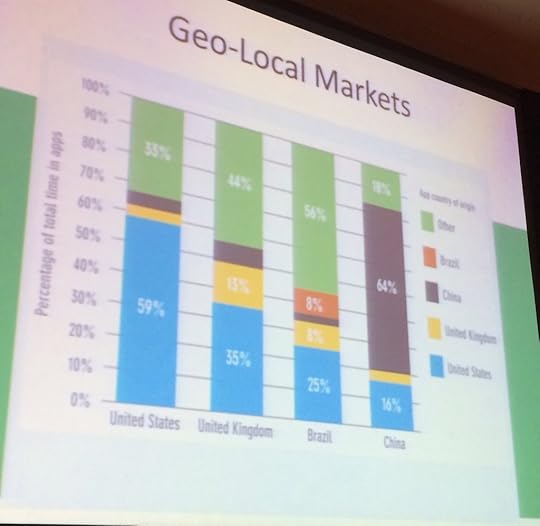
What to Consider
View the app map – the world as it breaks down into mobile adoption
The category of the app – the population using game apps on iOS, for example
Top Charts – you can see the types of content most popular by region
3 Levels to Win
1. Localize your App Store listing: title of the app, developer name, description, content on the listing page. Closely monitor downloads for the associated languages and countries with that region.
2. Localize the content of the app. Translate the in-app language to the language of the region, working with a translation company or an expert in the language, not just pouring the text into Google Translate.
3. Invest in the location with a local team. Highlight your local optimized app in your marketing material. To fully support this audience, develop a local time to localize your company website, your social media promotion, your customer service support and your user acquisition strategy.
The Opportunity for SEO for Mobile Apps
Speaker:Justin Briggs, @justinrbriggs, oversees organic marketing at Getty Images
Mobile hasn’t cannibalized desktop search overall. There are limitations in the App Store. There’s limited editorial shelf space and very little exposure. An editorial, categorized approach to the web is not going to work long term. Top Charts are influenced by spend/paid traffic. The search in App Store is very basic – title, descriptions, keywords. It takes a few minutes so what’s the next step? Paid advertising. This shows the diminishing returns of ASO. The competitive advantage of ASO is reducing as more apps leverage keyword targeting. This will stay true until app search becomes more innovative as will probably be ushered in by Google.
In a period of 2.5 months there was a sizeable shift:
App devs weren’t doing basic ASO and then they were
And the results from that ASO became less effective as more people employed them.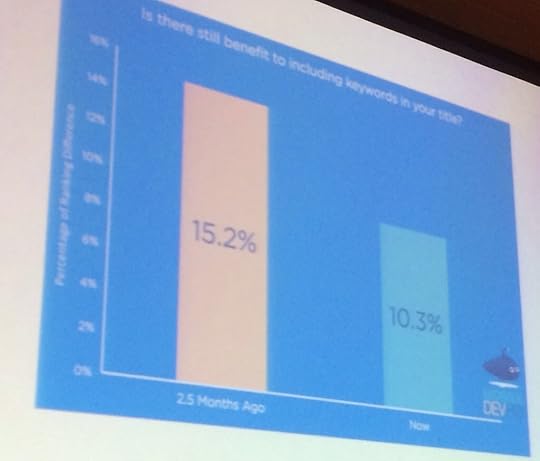
Opportunity: leveraging web search to drive traffic to the App Store. Web and mobile app channels don’t work in isolation from each other. Marketing in one channel drives results in another.
3 Organic Web Search Opportunities
landing page on your website
your App Store page
your social media pages
Most apps lack a dedicated landing page. He saw a doubling of revenue for an app YOY by making this change. Be careful of 12-month averages reported by app optimization tools; look at seasonailty and trending of terms that may be hidden in the raw data.
Rankings shift from downloads (spend) to links (content and outreach). SEO fundamentals include: PR, events, game reviews, blogger outreach and contests. This kind of basic promo work can allow you to dominate markets.
March 11, 2014
#SMX Liveblog: Google Search Chief Amit Singhal’s Keynote Conversation
#SMX Liveblog: Google Search Chief Amit Singhal’s Keynote Conversation was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
TL;DR version: At Google, it’s all about the user experience.
Before things really get started, Matt Cutts runs onto the stage after Danny Sullivan and Amit Singhal sit down. Matt says he wants a group selfie.

SMX Power Selfie: Google’s Amit Singhal and Matt Cutts with Search Engine Land’s Danny Sullivan
Ride that selfie train, my friends!
Now to the business we’re here for. Amit Singhal is “the one who knows how Google ranks things,” Danny Sullivan, Search Engine Land editor-in-chief, says as he introduces our feature keynote speaker. Amit’s resume reads Senior Vice President and Google Fellow, Google, Inc.
Hummingbird has been a complete rewrite of our system. The last time we did a complete rewrite was shortly after 2000. In the last decade, numerous new technologies have been built, including Knowledge Graph. And people are speaking queries naturally. To serve the future you have to change things. One thing that’s changed is that people are going to type 2-word queries. The mobile revolution has forced us to rethink a search system that is awesome, like Google has always sought to be.
Natural language, longer queries, how close various words are in order to signal a concept — these are things Google has been working on.
Whenever you build a technology, take ideas you have (such as Google Now) and try them with the existing technology. When you try a few times you realize the technology that exists isn’t going to solve the problem so you start from the ground up with a new foundation. Your previous foundation may have allowed you to add one more layer, but not more than that, so you start with a new foundation.
Danny asks whether Google looks at “Obama” and understands that’s a person. Amit says that’s indeed what Google understands, as communicated in the motto “things not strings.” Strings scientifically hit a limit as to how much you can work with them. In this more sophisticated system, they can look at “Bush” and understand if it’s Sr. or Jr.
Danny asks about links and if it still functions as a primary ranking signal. Links, Amit says, are clearly an important signal that shows the importance of popular content. But at the end of the day they look at a holistic view of the type of content a site has.
Double checking, Danny asks if social signals are still not being used for ranking. Amit confirms that’s correct and that social signals are unreliable as currently available. As they become available they’ll test them and could add them. Google+ is different because the data available is reliable, and thus users may see a great impact based on Google+ social signals when they’re searching logged in. This comes from the fact that Google believes that it serves the user based on their needs and psychology.
Beyond social and links are there other signals you would use to determine if a page is relevant, Danny asks? Amit goes back to the perspective of the user — what would the user find useful. Things you think are useful are the same things the Google engineers think of. Danny brings up authorship of content being something he could see as a signal and Amit says possibly it could.
May 2012 was the launch of Knowledge Graph. Danny asks how has that gone. Amit says it’s awesome. How far is the Earth from the sun? Yes, Google could deliver formulas and statistics, but what about the straight answer?! Giving straight answers when the circumstance calls for it, users love that experience. Google views Knowledge Graph as their “understanding of the world.” Danny asks if there will be a day when Google delivers all results as answers. Amit says that the web is a Swiss army knife and you’re used to using all the tools. You’re comfortable with the knives and scissors. But sometimes you need a corkscrew. Knowledge Graph is a tool that you can use on the go, especially in the mobile world. When you add Knowledge Graph to your Swiss army knife, you use your knife more often and it becomes more useful and you carry it with you more. They don’t only use the one new tool more, they use all the tools available to them more.
How is search handled as a product within Google? Search is unlike some products like Android or YouTube because it crosses boundaries. Amit is a strong believer in the fact that beautiful products are built when separate areas collide. Ocean reefs see the most diversity of underwater life because they’re the clashing of worlds. Natural language processing, Knowledge Graph, and the next emergent area, these are all going to collide for the best search, and there’s no reason to try to define the boundaries of search because of that.
In the world of technology, you don’t know what comes next. Timelines are so compressed. If you don’t focus on products users love you will get passed by. Technology will come from directions you can’t predict. Make sure you’re doing right by your users.
Over time, Google searches have been moving toward secure servers and losing reporting of keyword referral data. When it comes to webmasters, there’s lots of info available to you on webmaster console and you can improve your user’s experience with this data. Google users have said that having secure searches are important to them in today’s world. Amit is hinting at an announcement, some coming solution to stay tuned for, presumably that addresses advertisers’ needs for data and searchers’ need for security.
What should marketers focus on in the future? The world is changing. The last few years has been about the mobile search revolution. The power of devices is tremendous. Users are living in a world where they have all these devices all the time. Even in a remote village in India you can reach the World Wide Web. Technology and knowledge is an equalizer and that’s an awesome time to live in. Devices will get smaller. And they’ll reach another 5 billion users. Marketers should think of how they’ll reach those next 5 billion users on devices with limited technologies but vast power.
What’s been awesome? The progress that’s been made in natural language understanding.
Do Larry or Sergey ever come into your office and say let’s do this? And do you jump or? Amit says that one nice thing about working at Google is everyone is a user.
Who’s the best Star Trek captain? Amit’s not getting in the middle of this. Danny says it’s Janeway. The crowd groans and Amit says that’s why he didn’t answer! Danny gives Amit a gift of a tricorder and a series of funky noises wrap up the convo. 
#SMX Liveblog: Twitter For Business (#14C)
#SMX Liveblog: Twitter For Business (#14C) was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
It wasn’t that long ago that Twitter first debuted in 2007 at SXSW. And, in fact, it wasn’t that long ago that we didn’t even consider ourselves “social media marketers”—we were search marketers.
![IMG_1946[2]](https://i.gr-assets.com/images/S/compressed.photo.goodreads.com/hostedimages/1414769983i/11689700._SX540_.jpg) If you only take one thing from this session, this should be it: Twitter is about human communication. Any brand that has an audience that they want to connect with can excel on Twitter. It’s all about finding the community; using the tools they’re using; engaging your community with content that adds value.
If you only take one thing from this session, this should be it: Twitter is about human communication. Any brand that has an audience that they want to connect with can excel on Twitter. It’s all about finding the community; using the tools they’re using; engaging your community with content that adds value.
Ready for more? Here’s Ric Dragon’s nitty gritty Twitter for Business run down:
A quick intro to Twitter:
• When to use a handle? If your name is really, really long.
• Twitter posts have 5 basic elements: display name; hashtags; @mentions; shortened URL; via or by at the end of the tweet.
• RT = rewteet. What does MT mean? Modified Tweet! (Start using it tweet modifiers!)
• If you’re using an @mention, make sure you are including a period (or other character) before the @mention if you want that tweet to go into your public newsfeed (and not just to you and the person you are @mentioning)
• Consider the words you use in your bio; all of these words (including hashtags and @pages) are searchable
• Consider your background image. Ric uses Geico as an example of a company that is doing a great job. It doesn’t take too much and it makes a big impact to have a designed background image.
• Your user icon: As a brand, think about trying to humanize yourself with your profile image. Don’t try to include too much information. Make sure your profile image is clear.
What makes the language in a tweet great?
Make your tweets engaging! It’s like any other venue for content marketing. You have to write something enticing that will make your audience want to click through.
Here are some examples that excel:
When you’re retweeting, try adding a bit of personality to your retweets. Make people want to follow you.
Some Twitter for Business Best Practices
1) Write more @ tweets!
Communicate directly with people. Make an effort to reach out and talk directly with your community more. It’s not all about getting people to look at you; it’s all about you/your brand/your business engaging with the community.
2) Don’t automate tweets.
Yes, you can schedule tweets, but don’t automate them. Automation = content is going right from one platform to another (IE: right from your blog to your Twitter; or right from Facebook to Twitter). Imagine: What if your automation makes your account tweet something about Miley Cyrus when a catastrophic hurricane has just hit a neighboring state? Automation can inadvertently put your brand in awkward, unforeseen PR-disaster situations if you’re not careful.
3) Add value in what you tweet!
A story should have a narrative arc over time, and so should your tweets. Does your business have an event coming up? Creating a narrative arc around that event. Build up to it; offer sneak peeks; make the event your high point; and then keep the narrative going even after the event.
4) Leave room for retweets.
When possible craft your Twitter messages in a way that allows for the added “RT” without chopping off the end of your post (especially if the end of your post is the URL).
Twitter Lists
1) Use Twitter lists to connect with influencers
2) Consider the story that your list of lists is telling
3) Subscribe to lists that include you
Some Twitter Tools
Communi.it
Allows you to see if someone has followed you and you haven’t followed them back. Also allows you to see your top content influencers; your followers who are very active and often interact with your content (these people are your brand advocates!). It’s a good way to identify your brand advocates (and to help you reach out to them).
Twiangulate
This tool can take two or more other profiles (as designated by you) and see who the two profiles have in common. It’s a great tool that can help you discover people to engage with; people that would be a great addition to your community.
TweetUp
Definition: A group of friends on Twitter that are planning to meet up. Also a request by a user to meet with friends via Twitter.
This is the idea behind a TweetUp: TweetUps are comprised of a bunch of people who want to meet up and communicate with each other via Twitter but they don’t want to have to include everyone’s handle every time (in every tweet), so they all start using a hashtag to communicate. And, thus, a TweetUp is born! This creates a great community experience, and also an excellent shared history for all the users.
TwitterChats
Twitter chats are great places to meet people with common interests, and a great way for a brand to start building community with their community.
TwitterChat Lists
Search for this; this is a list of TwitterChats that are active
TwitterChat Etiquette
- Stay on topic (don’t ask questions that are off topic. Don’t start side conversations.)
- Number your answers. (A1 after Q1; A2 after Q2; etc.)
- Don’t self-promote (unless the moderator asks you [everyone] to introduce themselves at the beginning of the session, or if it’s at the end of the session and you have a relevant link to share)
- RT with attribution
- If late, don’t ask “whats the topic” (just read the stream! Catch yourself up)
- Say thank you (that’s just nice.)
Looking to make sales from Twitter? Do This…
The key is truly to connect with individuals and participate in real conversations. To become a real part of real communities with real people.
As a Twitter sales person you need to be asking yourself:
Can I help 5 people out per day?
Can I join 3 (or however many) TwitterChats per week
Can I host a meet-up?
Can I take time each day to engage with community for X hours?
Think in terms of a virtuous cycle of activity you can do:
Engage → Reciprocate → Nurture connections → Create Content

Should a brand follow back? Ric advocates for reciprocal followbacks
Take time to stop, analyze what you’ve been doing, and consider whether you can do better. Can you write better tweets? Can you engage more with the community? Can you personalize your @responses to people?
Should I have two Twitter profiles? One for me, and one for me as X-brand advocate?
Ric doesn’t advocate for two reasons:
1) Nine out of 10 times one of these accounts is going to get dropped off; you’re going to just give up on one of them.
2) Social media is all about being human. People want to know that Jon the Dell worker is also into Fishing. They want to see Jon as a human. Only positivity can come from showing your personality next to your professional tweets.
What if my brand is somber, or boring? Can we still use Twitter?
Yes! Using Twitter is all about connecting human to human. Sure silliness is a part of that connection, but it isn’t the sole reason people are on Twitter. As an example, if your business is a team of Divorce court attorneys (a rather somber profession) you don’t have to tweet doom and gloom; this “how can I serve my community? What do my clients (and potential clients) need?” Consider hosting something like a #DivorceChat TwitterChat so that people [your potential consumers] can get together and ask each other – and you! – questions.
Some Community Manager Considerations
- Don’t try to control the conversation; enable the conversation.
- Consider ways you, as the community manager, can help humanize the brand. One logistic that helps is ending your tweets with a human signature (for instance ^CA). You can also put the handle of the person that is managing the page in the brand’s Twitter bio. Mayb
e even use the community manager’s photo as the Twitter page user icon (of course, branded. Make sure the manager is wearing a shirt; or watermarked with a logo; or something else creative that allows you to clearly convey to your users “this is the X brand channel, and this is the human who is running this channel. Talk to them!”)
#SMX Liveblog: Paid Social Media Opportunities Including Facebook for Business #13C
#SMX Liveblog: Paid Social Media Opportunities Including Facebook for Business #13C was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
SMX West’s Social Media Marketing Boot Camp continues on the topic of paid social — advertising and amplification, a critical tool in the social media marketing toolbox. Social media is a pay to play space for brands today, especially on Facebook where the News Feed algorithm can make it difficult for brand pages’ content to display even to followers without a money-backed boost. Presenter Lisa Buyer, author of “Social PR Secrets,” is this session’s boot camp instructor.
Public relations and social advertising — we’re all trying to gain more visibility in the News Feed and it’s very competitive to get seen there. The lines between earned, paid and owned media are blurring.
Content is what matters — take your content and then amplify it so it gets in front of more people. Visuals are going to be an important part of any social media strategies.
Social advertising is expected to hit $11 billion in revenues by 2017.
Social ads work better on mobile than traditional.
U.S. social mobile ad revenues approached $600 million in 2012, and are expected to grow to $2.2 billion by 2017.
Start with goals of brand building (vs. direct response). Balance your expectations and figure out what you’re trying to achieve.
Why does paid social work?
Microtargeting
Personalization: Message can be controlled for the target audience
Network: Each network offers different voice, audience, results, size
Distribution
Exposure: It’s an organic type of exposure that’s using paid to reach more
Real time: Capitalize on current events and trends
Speed: Jump into something immediately
Lead generation: It’s possible on social but start by building the brand’s community
Conversion: This has to be last on the list — and your expectations have to be realistic
Mobile reach
Viral aspect
Facebook for Business
This is the biggest network with the most opportunity. Flip side: it has the most opportunity to fail. It’s become harder and harder to reach your fans organically in the Facebook News Feed. Organic reach is down and it’s becoming a necessity to use ad options.
Watch the video on YouTube called “Facebook Fraud?” Then keep in mind that video addresses Facebook advertising from 2012 and a lot of ad types and features that didn’t exist before now give advertisers options.

All the listed options here did not exist in 2012.
Facebook won’t work if:
You treat it like PPC
Are you stuck in 2012?
Conversions and short-term unrealistic goals
Your ad manager is inexperienced
You’re not testing
You have low-quality followers
Your content quality and quantity is off
Why Facebook Ads Work
Custom targeting
Remarketing
Conversion tracking
Branding
High-quality traffic
Facebook Ads and Devices: She says that right-hand side ads generally perform the poorest.
Engage with image ads. Drive awareness and engagement of your message with an image.
Share messages with video ads.
Social to store with Offer Ads. Drive people to your store with ads.
Simple text-only Status Ads. This doesn’t often get as much engagement or awareness as ads including some kind of visual.
Website Ads (Blog Content Ads) drive clicks to your website.
Social to Mobile App Ads promote mobile apps.
Logout Ads are an option for a slick presentation.
 Try to avoid the tempting shortcuts that Facebook presents to you (like “Boost Post”). They’re very pricey and you can do better with the power editor.
Try to avoid the tempting shortcuts that Facebook presents to you (like “Boost Post”). They’re very pricey and you can do better with the power editor.
Ad language to avoid includes foul language, drugs and alcohol. There’s a pretty stringent morality overview and Facebook will disapprove your ads.
Dark posts are unpublished posts on your Page but you select/target who sees it by paying for specific audiences.
As a traditional marketing tool you can workplace targeting of the media with an ad with news about your brand.
Custom Audiences let you build relationships. Advertisers find their existing audiences among people who are on Facebook. 6x return on ad spend when you create a custom audience from email addresses or phone numbers.
Lookalike Audiences are a sales dream. Lets you draw up your ideal customer and Facebook finds more people like that.
Website to News Feed Retargeting using Facebook Exchange (FBX)
1. Website visitor looks at a product on your site
2. Same user sees that product as an ad on Facebook.
Facebook Ads Manager
Managing spend, custom reports
See if you’re meeting your objectives
KPIs:
Facebook Insights
Referring Traffic
Google Analytics Social Reporting
Simply Measured
Twitter: The Real-Time Network
Faster way to reach a wider, engaged audience.
Why use Twitter Ads?
Twitter is still the best real-time news network
You can build audience and reach
You can get better exposure than organic
Lead generation option
Media relations — journos and editors are checking out who your brand is on Twitter
Twitter Ads Overview:
Promoted Accounts: A way to reach more followers if you’re trying to build your following target by geo or interest; only pay when someone follows you
Promoted Trends
Promoted Tweets: Possible use when you want people to see some piece of news or announcement; regular tweets with bonus of reaching current and potential followers you target; these tweets show up in Twitter Search
Analytics
Pro tips for writing promoted tweets: Start organically; avoid optimizing direct response tweets with hashtags, mentions or images. Include a call to action. Include a relevant, compelling offer.
Types of targeting: usernames, similar usernames, keywords in tweets, geo, news headlines
Twitter Cards for images, photos and lead gen are an advanced Twitter ad option — don’t jump into it if you’re new but know it exists.
Best Practices for Twitter Paid
Images are awesome and get 2x engagement but cost more
Create a goal ahead of time
Leave enough characters for retweets
Monitor
LinkedIn: The Business Side of Social
Explore if you’re in the professional arena and B2B. Lead gen and brand awareness are good reasons to use LinkedIn social ads.
Ad formats: Text and Image ads (video ads or text only ads) and Sponsored Updates
Targeting: Geo, industry, groups, job title
Setup is pretty easy to figure out yourself. You’re looking at setting up your audience, message, budget and schedule.
Pro tips for creating and writing LinkedIn ads:
1. Must have a LinkedIn account.
2. Define your ideal customer.
3. Be sure to have a good landing page.
4. Keep testing and optimizing. Check out other LinkedIn ads.
5. Remember the image will be a thumbnail.
Measure results. Test headlines and ad variations.
CPCs start at around $2 and run up to $4 or $5 per click.
Up and Comers of Social Advertising
Pinterest Promoted Pins
Instagram paid ads: Sponsored labels
Google+ Post Ads, similar to Facebook to hep you amplify content to News Feed
4 Metrics that Rock:
Conversation rate (i.e., comments per post)
Amplification rate (retweets/shares per post)
We’ll have to wait until Lisa chimes in or puts her slides online before this list is updated complete.




















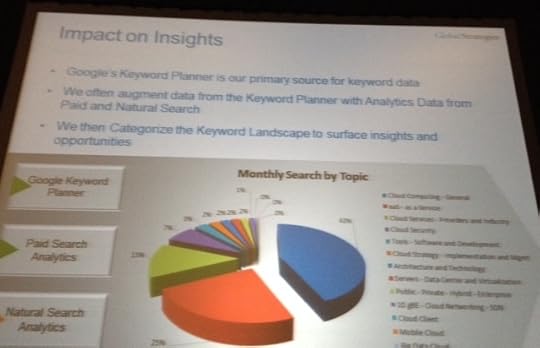
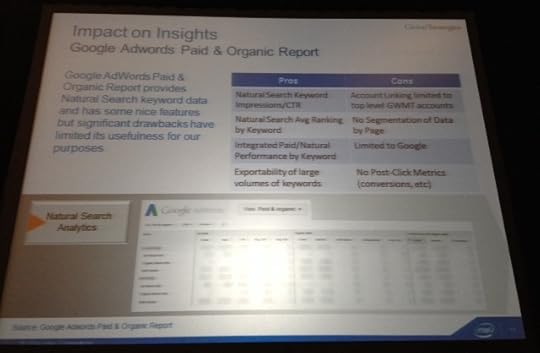








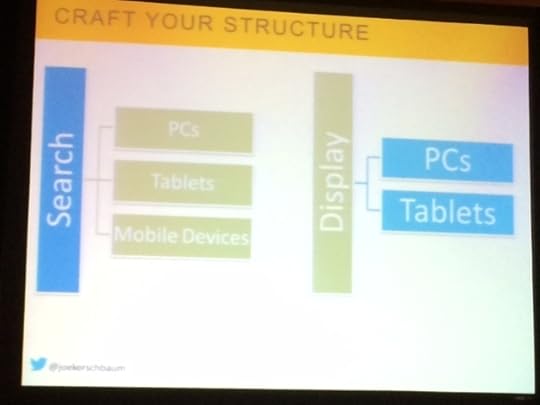


















![IMG_1944[1]](https://i.gr-assets.com/images/S/compressed.photo.goodreads.com/hostedimages/1414769983i/11689701._SX540_.jpg)









