Jesper Juul's Blog, page 17
August 13, 2014
Are Game Experiments Apolitical? Avant-garde and Magic Realism.
This is my seventh monthly Patch Wednesday post where I discuss a question about video games that I think is unanswered, unexplored, or not posed yet. I will propose my own tentative ideas and invite comments.
The series is called Patch Wednesday to mark the sometimes ragtag and improvised character of video game studies.
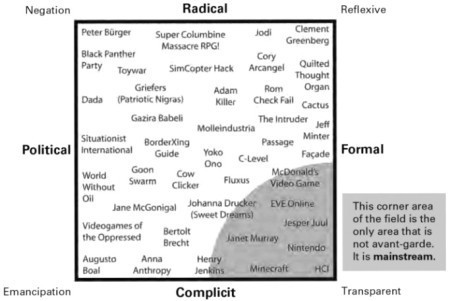
Here is a figure from Brian Schrank’s interesting new book Avant-garde Videogames. In the book, Schrank discusses various types of art-world avant-garde, and examines how they correspond to experimental video games.
Schrank structures the discussion around two axes of radical-complicit and political-formal. (I am personally placed in the bottom-right mainstream formal and complicit quadrant, but that’s OK.) He acknowledges the simplicity of this model and has many nuanced points and observations.
But let me just look at the political-formal axis. It represents video games, and art, such that a video game is either political or it is a formal experiment. Art historians can talk about this question at great length, but it is certainly an idea that was also expressed in 1940′ies denunciations of experimental, formalist, art. In that case, a powerful political entity felt threatened by experimental art and therefore decreed that artists should simply stop experimenting and rather only express established ideas in well-known form. And of course, the well-worn argument about art for art’s sake - that art should be judged on its own terms outside politics – sets up a similar opposition between the political and the formal experiment.
But is this really what we see in video games? Consider any of the high-profile political video game such as Howling Dogs, Dys4ia, Unmanned, September 12th, Cart Life. All of these games are highly experimental in form and political. In fact, it is clear that their political messages are expressed through their experimental form. And it seems the formal-political distinction breaks down in most of the obvious examples of political video games.
Fortunately, there is an alternative view which has much more explanatory power. Here is Salman Rushdie reviewing Gabriel Garcia Márquez’ novel Chronicle of a Death Foretold. Rushdie says that magical realism (where supernatural events naturally happen in seemingly realist settings) is a way of expressing experiences that cannot be expressed through established more forms such as plain naturalism. The formal experiment is necessary in order to express political ideas and overlooked experienced:
El realismo magical, magic realism, at least as practised by Márquez, is a development out of Surrealism that expresses a genuinely ‘Third World’ consciousness. It deals with what Naipaul has called ‘half-made’ societies, in which the impossibly old struggles against the appallingly new, in which public corruptions and private anguishes are somehow more garish and extreme than they ever get in the so-called ‘North’, where centuries of wealth and power have formed thick layers over the surface of what’s really going on. In the works of Márquez, as in the world he describes, impossible things happen constantly, and quite plausibly, out in the open under the midday sun. (Salman Rushdie, Imaginary Homelands)
This, I think, is a more convincing way of seeing the issue. New and experimental literary forms are necessary because they are the only way to express complex and hitherto unexpressed experiences. Political video games are also formal experiments in game design because this is the only way to express new and radical ideas. There is no opposition between the political and the formal experiment. Fortunately, for think how drab the world would be otherwise.
PS. And this is not a criticism of Schrank’s very useful book. It’s just a discussion of a particular view on the relation between formal experiment and political expression.
Are Game Experiments Apolitical? Avant-garde and Magical Realism.
This is my seventh monthly Patch Wednesday post where I discuss a question about video games that I think is unanswered, unexplored, or not posed yet. I will propose my own tentative ideas and invite comments.
The series is called Patch Wednesday to mark the sometimes ragtag and improvised character of video game studies.
Here is a figure from Brian Schrank’s interesting new book Avant-garde Videogames. In the book, Schrank discusses various types of art-world avant-garde, and examines how they correspond to experimental video games.
Schrank structures the discussion around two axes of radical-complicit and political-formal. (I am personally placed in the bottom-right mainstream formal and complicit quadrant, but that’s OK.) He acknowledges the simplicity of this model and has many nuanced points and observations.
But let me just look at the political-formal axis. It represents video games, and art, such that a video game is either political or it is a formal experiment. Art historians can talk about this question at great length, but it is certainly an idea that was also expressed in 1940′ies denunciations of experimental, formalist, art. In that case, a powerful political entity felt threatened by experimental art and therefore decreed that artists should simply stop experimenting and rather only express established ideas in well-known form. And of course, the well-worn argument about art for art’s sake - that art should be judged on its own terms outside politics – sets up a similar opposition between the political and the formal experiment.
But is this really what we see in video games? Consider any of the high-profile political video game such as Howling Dogs, Dys4ia, Unmanned, September 12th, Cart Life. All of these games are highly experimental in form and political. In fact, it is clear that their political messages are expressed through their experimental form. And it seems the formal-political distinction breaks down in most of the obvious examples of political video games.
Fortunately, there is an alternative view which has much more explanatory power. Here is Salman Rushdie reviewing Gabriel Garcia Márquez’ novel Chronicle of a Death Foretold. Rushdie says that magical realism (where supernatural events naturally happen in seemingly realist settings) is a way of expressing experiences that cannot be expressed through established more forms such as plain naturalism. The formal experiment is necessary in order to express political ideas and overlooked experienced:
El realismo magical, magic realism, at least as practised by Márquez, is a development out of Surrealism that expresses a genuinely ‘Third World’ consciousness. It deals with what Naipaul has called ‘half-made’ societies, in which the impossibly old struggles against the appallingly new, in which public corruptions and private anguishes are somehow more garish and extreme than they ever get in the so-called ‘North’, where centuries of wealth and power have formed thick layers over the surface of what’s really going on. In the works of Márquez, as in the world he describes, impossible things happen constantly, and quite plausibly, out in the open under the midday sun. (Salman Rushdie, Imaginary Homelands)
This, I think, is a more convincing way of seeing the issue. New and experimental literary forms are necessary because they are the only way to express complex and hitherto unexpressed experiences. Political video games are also formal experiments in game design because this is the only way to express new and radical ideas. There is no opposition between the political and the formal experiment. Fortunately, for think how drab the world would be otherwise.
PS. And this is not a criticism of Schrank’s very useful book. It’s just a discussion of a particular view on the relation between formal experiment and political expression.
August 11, 2014
Game Studies 14/01 is out
Game Studies: The International Journal of Computer Game Research has just published its latest issue (Volume 14, Issue 1, July 2014).
Articles
Game Definitions: A Wittgensteinian Approach
by Jonne Arjoranta
This article looks at how games have been constantly redefined in game studies without reaching an agreement. It is argued that such an agreement is not necessary, and a Wittgensteinian approach to game definitions is preferable. This approach sees the cycle of redefinition as a hermeneutic circle that advances the understanding of games.
The Heuristic Circle of Real-Time Strategy Process: A StarCraft: Brood War Case Study
by Simon Dor
The heuristic circle of real-time strategy process is a summary of key ideas about the cognitive and perceptive processes in StarCraft competitive play. It describes the way strategy in the game relies on the inference of three levels of game states and on the use of three kind of strategic plans at the same time.
Magic Nodes and Proleptic Warfare in the Multiplayer Component of Battlefield 3
by Johan Höglund
This article explores the construction of ludic spaces in the multiplayer map Grand Bazaar in Battlefield 3. It observes that this map constitutes a “magic node” that encircles a ludic space where only certain activities are possible. It concludes that the map Grand Bazaar represents a civilian Middle-Eastern locale as a permanent battleground.
Bioshock: Complex and Alternate Histories
by Ryan Lizardi
This article performs a close reading on the Bioshock series and determines that it encourages a comparative and contemplative look at the historical, cultivated through counterfactual and alternative experiences of accepted histories and reinforced through both ludic and narrative elements.
A Practiced Practice: Speedrunning Through Space With de Certeau and Virilio
by Rainforest Scully-Blaker
Through a discussion of Michel de Certeau and Paul Virilio, this article puts forth a language to discuss speedrunning, the practice of beating a game as fast as possible without cheating, as it relates to games as spatial narratives. A new set of terms for discussing game rules as they relate to speedruns is also applied to the analysis.
Play and Possibility in the Rhetoric of the War on Terror: The Structure of Agency in Halo 2
by Gerald Voorhees
This essay contends that Halo 2 helps attitudinally position players in relation to the War on Terror. It considers a range of possible, potentially-overlapping affective responses to Halo 2, foregrounding both the rhetorical efficacy of digital games and the player’s agency to determine their rhetorical effect.
Book Reviews
Sound in a Participatory Culture
by Kristine Jørgensen
Playing with Sound. A Theory of Interaction with Sound and Music in Video Games. (2013) by Karen Collins. Cambridge. Mass.: MIT Press. ISBN: 9780262312288 .
by Hanna Wirman
Play Redux: The Form of Computer Games. (2010) by David Myers. University of Michigan Press. ISBN: 978-0472050925
July 9, 2014
What are the unanswered questions?
My monthly Patch Wednesday series is on holiday this July.
To think about over the summer: What are the unanswered questions in video game studies? What are the questions that we have not answered as well as we imagine?
June 13, 2014
Introducción al tiempo de juego (Introduction to Game Time)
Mike Morell has kindly made a Spanish translation of my Introduction to Game Time paper.
It is “Introducción al tiempo de juego / Tiempo para jugar“.
June 11, 2014
The Impostor Syndrome in Video Games
This is my sixth monthly Patch Wednesday post where I discuss a question about video games that I think is unanswered, unexplored, or not posed yet. I will propose my own tentative ideas and invite comments.
The series is called Patch Wednesday to mark the sometimes ragtag and improvised character of video game studies.
You pick up a video game, and everything about it is just right, the fiction, the subtle variations on existing game designs, the controls. The game is a perfect match to what you think of as your very own and somewhat sophisticated taste. But something refuses to click. You are not feeling it.
This happens to me at regular intervals. For example, I think I value tight, replayable, logical, small playfield and spatial games, but I do not enjoy Threes at all. Something must be wrong with the game.
In 2010, Jason Mittell wrote a thoughtful essay on disliking Mad Men. He describes how everything seems to be stacked in favor of the show being able to win over Jason:
Mad Men is lodged squarely within my habitus: along with other cable series from channels like HBO, Showtime and FX, it’s part of the wave of “quality television” serial dramas that has raised the medium’s cultural value in the 2000s (as Lynne Joyrich discusses in this volume), and served as the object of much of my own scholarly research and personal fandom over the decade (see Mittell 2006). The show is steeped in cultural references that resonate with my own background as a media scholar, flattering my otherwise esoteric knowledge of U.S. advertising and media history. Nearly every television scholar and critic with whom I interact loves the show.
He then analyzes particular traits of the show that he finds off-putting such as the unpleasantly sexist male characters, low emphasis on empathy.
Elsewhere, Oliver Sacks and Vilayanur S. Ramachandran talk about the Capgras Delusion, where a patient is convinced that all their relatives and loved ones, even dogs, have been replaced by impostors who, the patient admits, look and act like the relative, but at the same time certainly is not that person.
Capgras syndrome is often related to brain injury, and a common interpretation is that while the patient was able to recognize faces as usual, they were unable to experience the emotional arousal that we usually experience in relation to familiar faces. Hence the experience that a person is an impostor – he or she looks like the real relative, but does not feel like the relative. The patient is not feeling it, and the relative appears alien for that very reason.
The impostor syndrome in video games
Video games: and this provides a different description of the impostor syndrome in video games (and television). We often approach a video game or some other work that ticks off all the boxes on our personal lists. We may even be invested in the aesthetic criteria on our personal list. And yet, we do not feel what we think we should be feeling. We rationally recognize the game, but our emotions fail to follow suit.
We may then send ourselves hunting for explanations, showing that the game we are playing will in some way fail to satisfy our criteria for what a good game is. This is not to discount Mittell’s discussion of Mad Men, but to point out that we often want our articulated tastes to be able to capture what we subjectively and emotionally enjoy. Whenever we feel that a particular work is an impostor, this is an incentive to find flaws in the work (the flaws may actually be there but the impetus comes from a mismatch between articulated taste and emotional response).
There are then two impostor syndromes here:
When we think of a game (or other work) as an impostor that only on the surface pretends to be a genuinely important work.
That we may feel like impostors ourselves. In this case, we are closer to the common meaning of “impostor syndrome” in that we may think that we are only pretending to understand what makes a game, TV show, or art work truly valuable. Yet we failed to have the genuine emotional response what we are supposed to have as true connoisseurs. We may feel that we are frauds, hoping not to be found out.
For Threes, I have been arguing for myself that I dislike Threes because I dislike the introduction of new tiles in the playfield, but is that really it? It is likely that we can never fully account for even our own tastes. We will continue to experience impostors.
May 28, 2014
New paper: High-tech Low-tech Authenticity: The Creation of Independent Style at the Independent Games Festival.
I have posted a new paper, High-tech Low-tech Authenticity: The Creation of Independent Style at the Independent Games Festival.
In which I study the history of visual style in Independent Games. I look particularly at the Grand Prize winners of the Independent Games Festival (IGF) from 2000-2014. I argue that what I call Independent Style is a “representation of a representation”, using contemporary technology to emulate earlier, simpler types of representation. Examples include pixel style graphics, games made with crayons, paper, paint etc…
Interestingly, the 2000-2004 winners do not look like the style we would associate with Independent Games today. Consider Tread Marks, winner at the first IGF.
Year
Name
Screenshot
Visual style
Theme / gameplay
2000
Tread Marks

3d
Tank battle
It is then from 2005 (with Gish) and on that the Independent Style we have come to know begins to dominate the IGF. In the paper I argue that this coincides with an increased focus on non-physical distribution as well as self-publishing.
I also claim that this Independent Style (which is the style by which we recognize independent games) is meant to signal that a small-budget production is small-budget by choice and that small-budget development has a particular authenticity and honesty.
And I also discuss the Arts and Crafts movement, texture settings in Unity, locavore food, Jeff Koons and fake wood.
All comments are welcome!
The paper was presented at the recent Foundations of Digital Games conference.
http://www.jesperjuul.net/text/independentstyle/
May 14, 2014
Patch Wednesday #5: What do Games Mean? An Interpretation Matrix
This is my fifth Patch Wednesday post where I discuss a question about video games that I think is unanswered, unexplored, or not posed yet. I will propose my own tentative ideas and invite comments.
The series is called Patch Wednesday to mark the sometimes ragtag and improvised character of video game studies.
What do games mean? There is a lot of good work on meaning and values in games, of course, but I think there is a very simple question that has not been fully addressed. (When I talk about “mean” here, it is primarily in the sense of a game making a normative statement about what is good/bad.)
If something is present in a game, is that a statement to the effect that what happens in the game is good and ought to be present in regular life?
Certainly, negative media commentary about video games tends to follow a very simple form, assuming that if something happens in a game (say, war), this is a ringing endorsement of war in general. In table form, it would look like this:
This is good
Event
War
That is obviously too simple. A pro-war game will say that war is good, but an anti-war game will say that war is bad. That the endorsement view is too simple doesn’t let video games of the hook, it just means that there is more to the discussion, as there are at least two different interpretations of similar game events. The classic example is Monopoly, where the game structure was originally designed to criticize land ownership (in The Landlord’s Game), but in Monopoly this is usually interpreted as an endorsement of land ownership and capitalism. In matrix form:
This is good
This is bad
Event
Hoarding property
Hoarding property
But there is an additional possibility. If we think of sci-fi games or any game which does not claim to represent the world as it currently is, the game can also be making statements about possible futures (say, the fight between humans and machines). It follows that a game can either say something about the current state of the world, or about a possible future (or the past). Consider the example of whether money buys political influence, and consider a game in which this is the case. This could then be taken in four different ways: Saying that 1) this is already the case (and it is bad), 2) this is already the case (and it is good), 3) this is not yet the case (and it would be bad), 4) this is not yet the case (and it would be good). (Remember that some people do believe that this is good.) This is the basic interpretation matrix:
This is good
This is bad
How it is
Money buys political influence
Money buys political influence
How it could be
Money buys political influence
Money buys political influence
The very hard question, then, is how we interpret a particular game such as Grand Theft Auto V. I may have sometimes been too keen on making the “it’s more complicated than that”-argument and leaving it at that. So let’s go on.
The enjoyment of bad things
The problem with GTA V probably is that while it on some level can be seen as making social commentary about violence, race, gender, and politics, arguably placing it in the how it is / this is bad square (given that all characters are anti-heroes), it just does that in an uncomfortably leery, consistent and celebratory fashion. So the interpretation matrix is rather like this, where the game at least part of the time seems to be signaling the right thing, but that it is hard not to feel that there is a voice in the game screaming “AWESOME!” at the in-game violence, sexism and racism. Matrix:
This is good
This is bad
How it is
GTA V world
GTA V world
(“IT’S ALSO AWESOME!“)
How it could be
GTA V world
GTA V world
This doesn’t quite end it though. In reception studies (say Janet Staiger’s Perverse Spectators) one discussion concerns what we can call interpretation-by-proxy. I.e. “I am a good person with all the right morals, critical faculties and so on, but the actual audience for this movie/game/book obviously lacks these qualities and will be brainwashed and interpret things very differently. And I will make judgments based on my prejudices about that naive audience “.
What we can say about GTA V is that a suspicious amount of energy and care has gone into making a particular game world with events that we would at any time say we are against, but which are also meant to be enjoyable (in a broad sense) when we play the game. Of course, this is a criticism to be leveled at any kind of art or discussion about unpleasant subjects – that they end up aestheticizing what they are supposed to be against. (See also the PPPS below.)
So how can we tell if there is such an “AWESOME!” model player of GTA V, and that it isn’t just us being prejudiced about a game audience in the same way that academics have traditionally been prejudiced about the television, romance novel, game audiences? The short answer is that we cannot simply assume that we are personally superior to the imagined audience of a given game/movie/novel.
In the end, then, I think the problem with GTA V is that it seem to show too much love for its own present/dystopian world. And this is what makes us skeptic about the meaning of the game; about what value the game is assigning to its content.
This is what the interpretation matrix is for: by looking at the meaning of a game as an interpretation matrix, we can to take a step back and think more broadly about possible, and sometimes conflicting, meanings.
***********
PS. I don’t think I have seen these interpretation matrices before, but it seems like an obvious idea, so I may be wrong.
PPS. In A Year with Swollen Appendices, Brian Eno describes the impossible futures-game, where participants have to describe futures that can never take place. One example is people with different astrological signs waging war against each other. This is the “how it could not possibly be”-variation, which is quite rare.
PPPS. Susan Feagin talks about (“The Pleasures of Tragedy“) that we may enjoy tragedy for the fact that it makes us feel good about our own moral standing, “We find ourselves to be the kind of people who respond negatively to villainy, treachery, and injustice. This discovery, or reminder, is something which, quite justly, yields satisfaction.” We probably associate this with the too keen and PR-minded celebrity who is into good causes, but of course it could also be that we are like that ourselves. In matrix form:
This is good
This is bad
How it is
Violence
Violence
(“This belief makes me a good person!”)
How it could be
Violence
Violence
April 9, 2014
Patch Wednesday #4: Where did Threes come from? A History Example
This is my fourth Patch Wednesday post where I discuss a question about video games that I think is unanswered, unexplored, or simply not posed yet. I will propose my own tentative ideas, and invite comments.
The header sounds a bit like Ash Wednesday, so we can reaffirm our faith in the idea of examining video games, but Patch Wednesday to mark the sometimes ragtag and improvised character of video game studies.

Where did Threes come from? The currently massively popular puzzle game Threes is seen as the victim of a large number of clones, particularly 2048. To prove their point, the developers have posted a long article explaining their design process.
At the same time, though 2048 is in many ways similar to Threes, some people also whisper that they think 2048 is the better game, because it is simpler (always doubling 2, 4, 8 rather than the 1+2=3 merging of Threes). It certainly is more intuitive to a programming mind.
Life is not fair, of course, and it seems a shame that someone can borrow from the game that someone else developed and through a minor change reap the seeds of the iterative design process of someone else. But you cannot copyright game ideas, only their expression.

Regardless, where does Threes come from? As a headline, the game contains two particular and rare mechanics: merging (the combination of objects to form higher-level objects) and slide-to-combine (pushing the entire screen to one side at a time, combining objects that are pushed into each other).
1) Merging
The merging mechanic does at this time seem to be inspired by Triple Town, where merging is reminiscent of match-three games. Yet where regular match-three matches lead to clearing the objects matched, Triple Town matches always creates a new higher-level object.
But where does this merging mechanic come from? Dan Cook, triple town developer stated that it was inspired by the idea of sets in card games as well as by crafting systems.
Quick research and the twittersphere proposed a few sources for merging:
 The king in Checkers – but this is not what I meant, since the stacking of two pieces is just a convenient way to signal a special piece, rather than an element of the gameplay. So merging is to be understood in a gameplay-sense.
The king in Checkers – but this is not what I meant, since the stacking of two pieces is just a convenient way to signal a special piece, rather than an element of the gameplay. So merging is to be understood in a gameplay-sense.Combining stones in Mancala – again, I had to realize that this was not what I meant, and had to narrow down the concept of merging: merging should be unidirectional, as in the player being unable to take apart the merged object.
Dan Cook’s suggestion of sets in card game was also not what I meant by merging, since sets are (generally) immediately removed from a game.
A similar objection applies to the suggestion that melds in Gin Rummy are a type of merging, since melds do not become separate entities.
Aaron Isaksen reminded be that he had shown me his chip-merging his Chip Chain game (2012).
A promising candidate for a first merging-game is Money Puzzle Exchanger (1997) where you can combine yen coins into higher denominations.
Dan Cook also suggested that the powerups in Bejeweled 2 (2004) are actually a type of merging. We may not think of it as merging because the default response to a match (three) is for the tiles to disappear. On the other hand, high-level match-three playing is quite similar to Triple Town in the requirement for planning the location of the generated powerups.
A non-puzzle example is the Archon in StarCraft (1998), created from two high templars.
And crafting, of course, but is it the same, or is it too much about managing inventory items and too little about what’s on the screen? If it is the same, then we may have to dive into the history of D&D (Jon Peterson’s Playing at the World would be a place to start.)
(Winner) But then I was pointed to the 1996 Mouja, which also features merging of coins. As far as I can tell this is the first puzzle game to use merging, but on the other hand this also seems unlikely, given how simple a mechanic merging is.
For analog games, Cassino (ca. 1797) is a candidate, given the focus on building cards stacks that act as one card.
I am sure I have missed something here (let me know). Until I came upon Cassino (which I played as a child), I was entertaining the theory that merging is simpler to do in digital form, and therefore was rare in analog games, but this theory is probably wrong.
2) Slide to combine
(Winner) T![DBTPlay07[1]](https://i.gr-assets.com/images/S/compressed.photo.goodreads.com/hostedimages/1397272568i/9257275.jpg) his was easy: I immediately recognized the slide to combine control of Denki Blocks (2001). In Denki Blocks, objects don’t merge to occupy a shared space, but rather become stuck to each other.
his was easy: I immediately recognized the slide to combine control of Denki Blocks (2001). In Denki Blocks, objects don’t merge to occupy a shared space, but rather become stuck to each other.
Is there an earlier one?
What we’ve learned
The “first game to x” is not be as simple as it sounds. In this case, the concept of merging had to be defined more clearly before I could start tracing it. Slide to combine only had one obvious candidate.
Finding the “first” is very hard, since you can never prove your argument, only hope not to be disproved.
Note that the Threes developers have (as far as I know) not mentioned any of the games I have cited as sources for merging and sliding. I think some of this is due to a particular mechanic simply being “in the air”, and some of it may be parallel invention. In many cases, we will never know.
Games are made out of bits of other games, people!
Thanks
To Eric Zimmerman, Frank Lantz, Dan Cook, Alexandre Houdent, Aaron Isaksen, Bruce Boyden, Mikkel Faurholm, Clay Branch, Matthijs Holter.
March 24, 2014
ToDiGRA Special Issue, Nordic DIGRA 2012
Transactions of the Digital Games Research Association has published Vol 1, No 2 (2014). This is a special Issue, with selected articles from Nordic DIGRA 2012.
Introduction: Exploring Nordic Game Research
HTML PDF
Raine Koskimaa, Frans Mäyrä, Jaakko Suominen
Digital Materialities and Family Practices: The Gendered, Practical, Aesthetical and Technological Domestication of Play
HTML PDF
Jessica Enevold
Player Types: A Meta-synthesis
HTML PDF
Juho Hamari, Janne Tuunanen
Player-reported Impediments to Game-based Learning
HTML PDF
J. Tuomas Harviainen, Timo Lainema, Eeli Saarinen
A Practical Guide to Using Digital Games as an Experiment Stimulus
HTML PDF
Simon Järvelä, Inger Ekman, J. Matias Kivikangas, Niklas Ravaja
Should I stay or should I go? A Study of Pickup Groups in Left 4 Dead 2
HTML PDF
Jonas Linderoth, Staffan Björk, Camilla Olsson
In Defence of a Magic Circle: The Social, Mental and Cultural Boundaries of Play
HTML PDF
Jaakko Stenros