Craig Murray's Blog, page 14
May 5, 2024
Starmer Smashed in Blackburn
The leadership of genocide enthusiast Keir Starmer – who is still supporting arms sales to Israel and the “Israeli right to self-defence”, who still refuses to acknowledge one single Israeli war crime – cost the Labour Party dear in Blackburn in the local elections.
The result means I am very likely to win the parliamentary seat.
The Blackburn Independent Councillors, who resigned from Labour over Gaza and invited me to stand as their parliamentary candidate, were re-elected and took new seats. They did not gain control of the council only because this was an election for just one third of Blackburn with Darwen’s council seats. The council has annual elections by thirds.
The parliamentary seat is no longer contiguous with the council area, with Darwen now excluded. The result inside my parliamentary seat was an even more convincing win for the Independents.
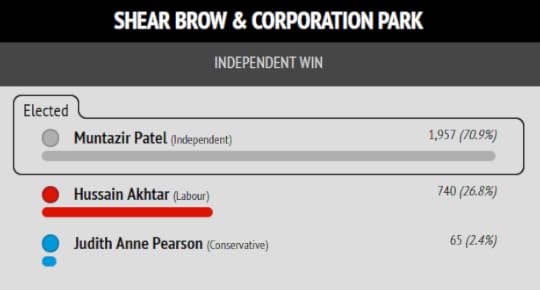
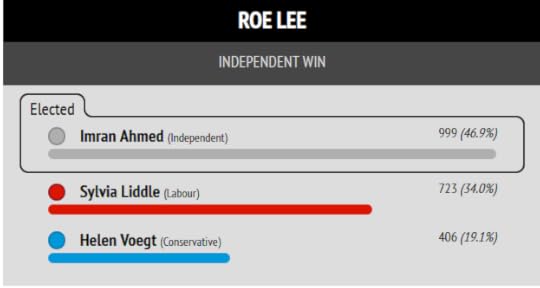
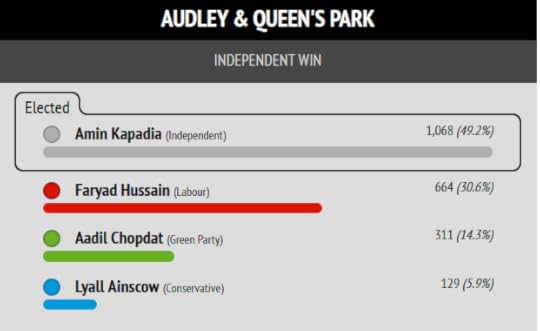
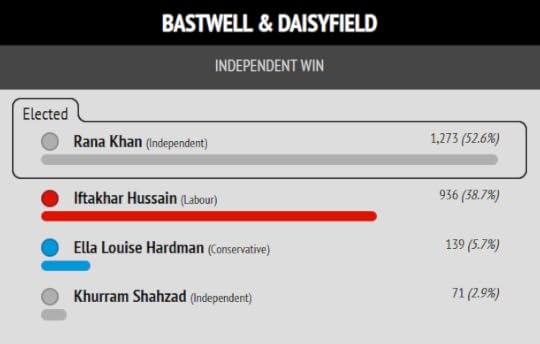
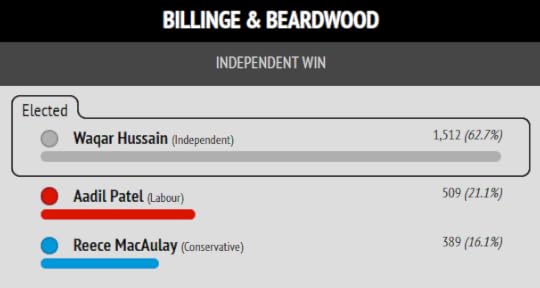
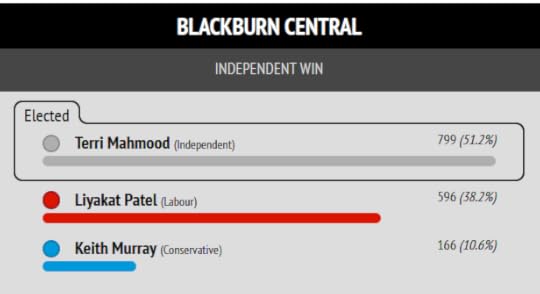
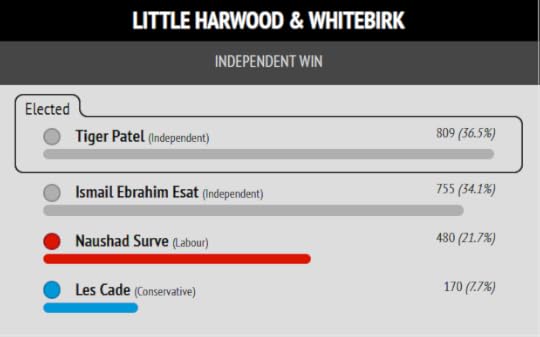
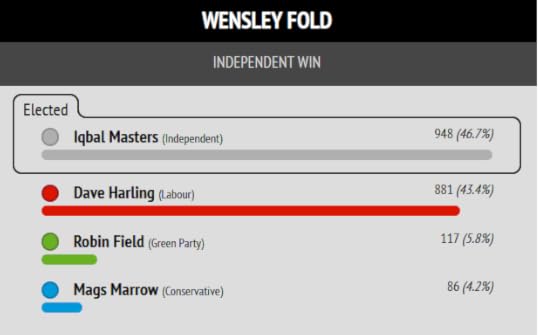
I put Muntazir Patel’s stunning result in Shear Brow and Corporation Park first, because this is where the cover photo of my book “Zionism is Bullshit” was shot.
When I stood against the war criminal Jack Straw in Blackburn in 2005, his Labour/BAE fixer Lord Ahmed Patel ensured I was excluded from the mosques and community events there, so I stood outside in the street on a Friday canvassing. That is the cover shot. Muntazir has now swept the area against Labour.

I am sure we can win. I am going to be very honest. When I accepted the joint offer from the Independent Councillors and the Workers Party of Great Britain to fight the seat, I did not then think we could really win. I accepted on the basis that, if we gave Labour a hard fight in Blackburn, they would be forced to divert resources they could otherwise concentrate on attacking George Galloway in nearby Rochdale.
So my strategy was to help George get re-elected by tying up Labour and by adding to the feeling of a real new working class movement across the North West and elsewhere in England.
I say this without shame.
Under the first past the post system, on average less than 100 seats change hands at a UK parliamentary election. That means in only at most 150 seats are there two candidates who might realistically win. In the other 500 seats there is normally only one candidate likely to win, and the six or so other candidates know they are fighting a losing battle.
So out of about 5,000 candidates in a British parliamentary election, only 800 normally are going to win or to come a close second. Others are standing to advance their arguments and to give voters a choice. Of course few candidates ever admit they do not expect to win.
I now do expect to win. We now know that the revolt against Starmer – accelerated by Gaza, but also by his leading the Labour Party so far to the right they are in all crucial policies indistinguishable from the Tories – is very real.
Starmer is the chosen one of the Establishment, and the media are bigging up his mild gains in the local council elections. But in fact Labour achieved only 35% of the vote nationally in England and Wales, which is one of their worst results and below the average result Labour obtained in national local government and general elections under Corbyn.
I shall be one of a number of candidates standing to give voters a genuine choice of more left wing policies at home and an end to perpetual war and support for Zionism abroad. Those candidates will include Jeremy Corbyn, George Galloway, Andrew Feinstein, Peter Ford, Monty Panesar and others. The informal alliance is growing and bonds are being knit. I hope by election day all voters in England will be offered a left wing, anti-war choice for their vote.
The media and political parties are doing their best to hide the desire for such a choice. But at the English local elections 37% of those who voted, did not vote either Labour or Tory. That is huge. The narrative being spun that those who did not bother to vote are actually enthusiastic Labour or Tory supporters and this will change in a general election with a higher turnout, does not stand up to ten seconds’ serious consideration.
I look forward to having the chance to tell a number of very hard truths in the House of Commons, and to help offer real opposition to the Blue and Red conservative parties. But I need now to take very seriously indeed the role of representing, supporting and improving the lives of all the people of Blackburn. I shall therefore shortly be moving to live full time in the constituency.
I have a lot to give, but also a very great deal to learn from Blackburn people. I approach that with determination and humility.
I judge that the public revulsion at the genocide in Gaza has now made it very difficult for the police to continue to hound me over my support for Palestine, and of course mad Suella Braverman is no longer Home Secretary. Two very brief test visits did not see me arrested again, so I shall now return from exile to run for Parliament. It is a risk I need to take.
When I stood in Blackburn in 2005 against Jack Straw, against the Iraq War and the excesses of the “War on Terror”, many scores of readers of this blog turned up in the town to campaign for me.
We will need you all again, now alongside solid and enthusiastic local support – and this time we are going to win!
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post Starmer Smashed in Blackburn appeared first on Craig Murray.
April 28, 2024
The Curious Case of the Freedom Flotilla
The departure of the spectacular “Freedom Flotilla” to Gaza carrying 5,500 tonnes of aid has been postponed (again), because the flag state of the major vessels, Guinea Bissau, has withdrawn their registration.
The key question is why the organisers were proceeding with such an unreliable flag state in the first place?

In the 2010 Freedom Flotilla, the vessel Mavi Marmara was boarded by Israeli troops and ten aid workers were executed in cold blood. Just days before sailing, the Mavi Marmara had changed its flag from Turkey to the Comoros Islands.
On a vessel at sea outside the twelve mile territorial limit of a state (as the Mavi Marmara was when boarded), the law that applies is that of the flag state. Had the vessel still been Turkish flagged, the murderers would have been within Turkish jurisdiction and subject to investigation by Turkey and prosecution in Turkish courts.
I flew to Izmir to investigate the case and I concluded that it was Turkish security services who had obliged the change of flag to the Comoros Islands, thus facilitating the Israeli murderous attack.
Plainly the Mavi Marmara incident should indicate to organisers of aid to Gaza the vital necessity of having a vessel registered to a flag state which would be able to react strongly to an attack by Israel on its ship, and indeed whose flag might deter Israel from such an attack.
So it makes no sense to me that the organisers intended to proceed under the flag of Guinea Bissau.
On 8 April I received a Whatsapp message from organisers asking me to publicise the flotilla. This was my reply.
Hi Irfan and thank you. May I ask what are the flag states of the four vessels?
This is extremely important.
The Mavi Marmara organisers made the literally fatal mistake of allowing the ship to reflag to the Comoros Islands before sailing. Outside the 12 mile territorial sea the vessels are under the law of and entitled to the protection of the flag state
After a holding reply I received
Sorry for the late reply. It is still to be confirmed sir
I reiterated
OK, I am very keen that people understand that it is crucially important.
I have always believed pro Israeli security services influenced the change of flag of the Mavi Marmara.
Any Israeli forces boarding the ships beyond the 12 mile territorial limit are subject to the law of the flag state of the vessel. I should be grateful if you confirm to me the organisers fully understand this.
The reply was simply
Thank you sir
I am therefore entirely perplexed that the organisers went with Guinea Bissau as the flag state rather than a state likely to stand up to Israel and the US. Of course it failed.
Is the problem incompetence, or is it again security service influence?
I should make plain that I absolutely support the aims and the strategy of the Gaza Freedom Flotilla. I have several friends on board, and I believe my good colleague Ann Wright is among the organisers. I am however intensely frustrated.
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
The post The Curious Case of the Freedom Flotilla appeared first on Craig Murray.
April 25, 2024
Worse Than You Can Imagine
Governments cannot take big decisions extremely quickly except in the most extreme of circumstances. There are mechanisms in all states that consider policy decisions, weigh them up, involve the various departments of the state whose activities are affected by that decision, and arrive at a conclusion, though not necessarily a good one.
The decision to stop aid funding to UNRWA was not taken by numerous western states in a single day.
In the UK, several different government ministries had to coordinate. Even within only a single ministry, the FCDO, views would have to be coordinated through written submissions and interdepartmental meetings between the departments dealing with the Middle East, with the United Nations, with the United States, with Europe and then of course between the diplomatic and development wings of the ministry.
That process would include seeking the views of British Ambassadors to Tel Aviv, Doha, Cairo, Riyadh, Istanbul and Washington and to the United Nations in Geneva and in New York.
It is not necessarily a lengthy process but it is not a day’s work, and nor would it need to be. There was no practical impact to making the announcement of cutting UNRWA funding a day sooner or a day later.
Consider that the parallel process had to be completed in the United States, in Canada, in Germany, in Australia and in all the other Western powers that contributed to starvation in Gaza by cutting aid to UNRWA.
All of these countries had to go through their procedures, and it could only be by prior coordination – weeks in advance – between these states that they announced all on the same day the destruction of the life support system for Palestinians, then in absolute need.
And then consider that we now know for certain that the Israelis had produced no evidence whatsoever of UNRWA complicity in Hamas resistance, on which these decisions in all those states were allegedly based.
I have no doubt at all that the western political elite, paid tools of the zionist machine, are complicit in the genocide of Palestinians and ethnic cleansing of Gaza at a much deeper level than the people have yet understood. The refusal by Starmer and Sunak to contemplate ending arms sales and military support to Israel is not due to inertia or concern for the arms industry. It is that they actively support the destruction of the Palestinians.
The coordinated decision of the western nations to fast track famine by stopping UNRWA funding was announced within an hour, following the ICJ ruling that Gazans were at immediate risk of genocide, and drove from the media headlines the adverse ruling against Israel.
This sent the clearest signal in response that the Western powers would not be stopped from the genocide by international law or institutions.
The Western powers give not a fig for 16,000 massacred Palestinian infants. No evidence of mass graves in hospitals will move them. They knew genocide was happening and continued actively to arm and abet it.
This genocide is the desired goal of the West. No other explanation is remotely plausible.

Western Political Support for this Genocide is No Accident
I have never believed the spin that Biden is trying to restrain Netanyahu, while simultaneously arming and funding Netanyahu and using US forces to fight alongside him.
Biden is making no effort to restrain Netanyahu. Biden fully supports the genocide.
My reading of this was reinforced when I was looking back at the Israeli murders on the Mavi Mamara in 2010, when they killed ten unarmed aid workers attempting a Freedom Flotilla aid delivery to Gaza. Israel’s actions were clearly both murderous and in breach of international law. Joe Biden as Vice President defended Israel staunchly then. It is essential to understand that Genocide Joe has always been Genocide Joe.
Joe Biden took the lead in defending the raid to the U.S. public. In an interview with PBS, he described the raid as “legitimate” and argued that the flotilla organizers could have disembarked elsewhere before transferring the aid to Gaza. “So what’s the big deal here? What’s the big deal of insisting it go straight to Gaza?” Biden asked about the humanitarian mission. “Well, it’s legitimate for Israel to say, ‘I don’t know what’s on that ship. These guys are dropping eight — 3,000 rockets on my people.’”
Biden is not outplayed by Netanyahu. He is actively abetting Netanyahu and shares with him the objective of full Israeli occupation of Gaza after the Palestinian people are killed or expelled into Sinai. He also shares with Netanyahu the aim of a wider regional conflict in which the US and Gulf states ally with Israel against Iran, Syria, Yemen and Hezbollah. This is their joint vision of the Middle East – Greater Israel, and US hegemony operating through the Sunni monarchies.
If you believe all the spin from the White House about Biden trying to restrain Netanyahu, I suggest you look instead at the White House and State Department spokesmen refusing to accept any single instance of Israel atrocity and deferring to Israel on every subgle crime.
I am currently in Pakistan, and I must say it has been a great refreshment to be in a country where everybody understands why ISIS, Al Nusra etc never attacked Israeli interests, and sees precisely what Western governments are doing over Gaza. What is understood by developing nations is thankfully understood by GenZ in the West as well.
The Arab regimes of the Gulf and Jordan are dependent upon Israeli and US security services and surveillance for protection from their own people. The lack of really massive street protest against their own regimes by Arab peoples is a direct testimony to the effectiveness of that vicious repression, particularly when states like Jordan actually fight alongside Israel against Iranian weapons.
The anti-Iranian card is of course the trick both Biden and Netanyahu have left to play. By promoting an escalation with Iran, western politicians were able to default to a position of claiming the case for arming Israeli was proven – and I think were genuinely perplexed to find the public did not buy it.
The political class, across the western world and the Arab world, is utterly divorced from its people over Gaza. We are seeing worldwide repression, as peaceful conferences are stormed by police in Germany, students are beaten by police in American campuses, and in the UK old white people like me suffer the kind of continual harassment long suffered by young Muslim men.
This is not the work of Netanyahu operating as a rogue. It is the result of the machinations of a professional political class across the Western world welded to zionism, with the supremacy of Israel as an article of fundamental belief.
Times are not this dark by accident. They were designed to be this dark.
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post Worse Than You Can Imagine appeared first on Craig Murray.
April 16, 2024
The Farce of Diplomatic Assurances
The United States has now, on the face of it, produced the Diplomatic Note giving the two assurances required by the High Court to allow the extradition of Julian Assange to proceed. The assurance that Julian Assange will be allowed to rely on the First Amendment in his defence is a blatantly weak piece of sophistry.
You can read my analysis on the High Court judgment of Assange’s right to an appeal here.
Let me dispense with the assurance against the death penalty. I am sure it will be accepted by the court. The USA does not need to execute Julian, it can incarcerate him in a tiny concrete tomb for life, under extreme sensory deprivation, as a terrible half living warning to any journalist who might reveal their crimes.
Should that ever become inconvenient, he can be Epsteined or Seth Riched at any moment. Remember this is a government that plotted to kidnap and/or assassinate him, as pled and not denied in court.
The assurance required on First Amendment protection is being misunderstood by almost everybody reporting it, and the US Diplomatic Note seeks to take advantage of the confusion.
The High Court took the view that the First Amendment provides the same protections as Article X of the European Convention on Human Rights, and therefore Assange’s Convention rights will be protected if he is allowed to plead the First Amendment as a defence before a US court. The court did not ask for an assurance that such a plea would succeed. Article X of the ECHR is itself absolutely shot through with authoritarian national security and other exceptions.

The assurance on which the High Court did insist was that such a plea could not be struck down on the grounds of Assange’s nationality. That would contradict the separate ECHR provision against discrimination by nationality. The US Diplomatic Note has failed genuinely to address this point: but it pretends to do so.


The US prosecutor in an affidavit to the UK court had already stated that Assange may be barred from First Amendment protection because he was a foreign national who had acted abroad. Mike Pompeo had also stated this officially. The principle is plainly articulated by the Supreme Court in the case of USAID vs Open Society:

THE CRUCIAL “SEEK TO”
The United States was therefore simply unable to state that Julian Assange will be able to make a First Amendment defence, because the judge, following the Supreme Court precedent, is almost certainly going to disallow it on grounds of nationality.
The Diplomatic Note therefore states that Assange may seek to raise a First Amendment defence without prohibition on grounds of nationality. This means precisely that his lawyers are permitted to say:
“My client wishes to claim the protection of the First Amendment for freedom of speech”
This is “seeking to raise” it.
The judge will immediately reply:
“The First Amendment does not apply to your client as a foreign national acting abroad, as established by the US Supreme Court in USAid vs Open Society”.
That is consistent with the actual operative phrase in the US Diplomatic Note: “A decision as to the applicability of the First Amendment is entirely within the purview of the US Courts”.
On 20 May there will be a hearing to determine whether this non-assurance is adequate to protect Julian Assange from discrimination on grounds of nationality and permit the extradition to proceed.
Now being a reasonable person, you doubtless are thinking that it is impossible that such a flimsy confection of legal sleight of hand could ever be accepted. But if so, dear reader, you have no idea of the corruption of the stool pigeons disguised as British judges.
Who would think that they could have ruled that the UK/US Treaty has legal force to extradite Julian Assange, but that Article IV of the Treaty forbidding political offence strangely does not have legal force?
Who would have thought that they could have ruled that the US government spying on his attorney/client legal conferences and seizing his legal papers did not invalidate the proceedings?
Who would have thought they could have ruled that the US government plot to kidnap or murder him is irrelevant, because if he is extradited the US government will have no further need to kidnap or murder him?
I could go on. I shall be very surprised if the High Court judges following the 20 May hearing do not rule that the right to ask not to be discriminated against on grounds of nationality (and be denied) is sufficient protection against discrimination by nationality.
They really are that shameless.
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post The Farce of Diplomatic Assurances appeared first on Craig Murray.
April 15, 2024
I Stand in Blackburn
I shall be standing for election to Parliament as the member for Blackburn. This unexpected turn of events requires an honest declaration.
1) I am standing because of the Genocide in Gaza.
2) I am standing because of the appalling pro-Genocide stance of the Labour Party and Keir Starmer’s continued support of arms exports to Israel.
3) I am standing because the Blackburn Independent Councillors and the Workers’ Party invited me to.
The political class, including both the Labour and Tory parties, has continued to offer wholehearted support for Israel. The Tories are a lost cause, irrelevant in Blackburn and I will not waste words upon them. The Labour Party is led by Keir Starmer, a man who has declared himself an unqualified zionist, is a member of Labour Friends of Israel, who refused to oppose Israel’s blockade of food and water to Gaza, refuses to acknowledge any war crimes committed by Israel, let alone the ongoing genocide, and strongly supports the continued sale of arms to Israel.
40% of Labour’s shadow cabinet, at least, are financed by the zionist lobby.
Starmer has also expelled more Jews from the Labour Party than every previous Labour leader combined – under the excuse of “anti-semitism”, but in reality because they are Jews who honestly oppose the murderous ethnic cleansing of Palestinians and the schemes of the apartheid state of Israel.
The people of Blackburn, like all voters in the UK, deserve the chance to vote for a candidate who actually opposes the genocide. The Independent Councillors in Blackburn, who have resigned from the Labour Party over the issue, have chosen me to be that candidate. I have accepted.
Following George Galloway’s victory in nearby Rochdale under the banner of the Workers’ Party, I have also accepted the support of that party. I expect to fight the seat as a party candidate.
While Gaza motivated me to stand, it is by a long way not the only issue on which the voters of Blackburn deserve an alternative choice.
The Labour Party has abandoned working people. Last weekend Keir Starmer said Labour would increase defence spending to 2.5% of GDP – a 25% increase. Yet the Labour Party has stated it will be bound by Tory fiscal rules and austerity, and there is no money for education or health and other public services.
The Labour Party has stated it will be harsher than the Tories on welfare payments and on immigration controls. Wes Streeting is itching to privatise the Health Service – and he and his frontbench colleagues are sponsored to do so. Plans to renationalise water and other public utilities have been abandoned. Starmer’s party is a Tory Party.
There is a vast disparity in wealth in society which is growing incredibly fast. The 1,000 wealthiest people in the UK are now worth an average of £750 million each, a figure which has doubled in under a decade. Yet we have millions of children living below the poverty line.
This does not happen by accident, nor is it a factor of a free market. It is the product of a system of law and regulation designed to produce this unnatural outcome. It can only be countered by fundamental reform of laws around the formation and ownership of capital. For that reason, I am happy to ally with the Workers’ Party, which recognises this truth.
The people of Blackburn deserve the opportunity to vote for fundamental social and economic change.
I am standing as part of a wider movement in England which is seeking to challenge the two-party conservative duopoly. This alliance is coming together and will embrace Independent candidates and candidates from other small parties. Informal organisation is developing. I expect the Workers’ Party to have a slate of hundreds of candidates, while Andrew Feinstein spoke alongside me in Blackburn on Saturday and will be challenging Keir Starmer directly in the election. Jeremy Corbyn will romp back into parliament in Islington North.
In Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland the nationalist parties have been much better on the Gaza genocide, reflecting the experience of those peoples of ethnic cleansing and occupation. They are also notably more socialist than Labour. I need to explain to you, and particularly to my many Scottish readers, why I am not standing in Scotland.
Firstly, it is important to make clear my support for Scottish Independence is undiminished (which I sincerely believe would be good for the people of England too, including Blackburn, in allowing a modern country to emerge from the trappings of Imperial decay).
Secondly, I talked it over with Alex Salmond before I accepted to stand in Blackburn. I have not left the Alba Party. Alex and I mutually agreed that at this election it would be better for me not to stand for Alba in Scotland, as that would give the unionist press an opportunity to continue to muck-rake over the lawfare to which we had been subjected.
Thirdly, George Galloway has declared that he no longer will participate in the Independence debate in Scotland.
I have also seen it reported that the Workers’ Party will not stand candidates in Scotland. That will need to be worked through, but at the minimum I expect we can reach an agreement they will not stand anywhere against the Alba Party, which would render my own position impossible. As Alba is only planning to stand in up to 16 constituencies this should not be difficult. Working relationships between the two parties in the Commons are amicable, and all of this will be resolved in the next few weeks.
Finally, I would say that the events of the last 48 hours have confirmed my decision. Israel’s murderous destruction of Iran’s Damascus consulate, crashing the Vienna Convention, was condemned by neither Labour nor Tories. George Galloway is the only MP to have even mentioned it in the House of Commons, one clear indication of why I am not just content but proud to stand besides George. Iran’s demonstration attack in response – which killed nobody – appears to have restored the shaken confidence in the entire political class in proclaiming their zionist credentials. They hope we have all now forgotten the genocide.
We shall prove them wrong.
From mid-May I shall be relocating my home to Blackburn. Three short visits to the UK seem to have confirmed there is no longer any current intention by the state to arrest me for my support for the Palestinians’ legal right to armed resistance as an occupied people.
I am going to need help – leafleting, canvassing, manning offices and the many myriad tasks of an election campaign. I am also (I am sorry) going yet again to call on readers of this blog to fund the campaign. I am buoyed by the solid start we have in support across all communities in Blackburn. There will be no shortage of space for volunteers to sleep. So start to look in your diaries. We are going to give Starmer a roasting, we are going to take on the zionist monopoly of power, and it is going to be great fun!
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post I Stand in Blackburn appeared first on Craig Murray.
Free at Last
I have today the permission of the surgeon to use my right hand for typing for the first time in over three weeks, provided I am careful not to extend the arm. On Saturday I put my arm in a sleeve and managed to remove my sling while making a speech in Blackburn, which I hope to bring you shortly (it was filmed by Consortium News but there is a job to do on sound synchronisation). The ligaments in my shoulder need another three weeks to heal and may require an operation, but my spirits are lifted enormously by being able to use the hand, even though it hurts.
I am going today to write an article on my decision to stand in Blackburn.
Huge thanks for your patience and messages of support, especially those who kindly subscribe.
Craig
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post Free at Last appeared first on Craig Murray.
April 1, 2024
An Urgent Message About Gaza
I can’t type much with my left hand but I wanted to get this out there. It then took me ten hours to upload with a maximum speed here of 0.5mbps. Still more breaking news now. May do a follow-up tomorrow.
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post An Urgent Message About Gaza appeared first on Craig Murray.
March 29, 2024
The Assange Hearing Permission Appeal Judgment: Mad and Bad.
The latest judgment by the High Court in the Assange case achieved completely the objectives of the UK and US states. Above all, Julian remains in the hell which is Belmarsh maximum security prison. He is now safely there alone and incommunicado, from the authorities’ point of view, for at least several more months.
Importantly, the United States has managed to keep him detained without securing his actual appearance in Washington. It is crucial to grasp that the CIA, who are very much controlling the process, do not actually want him to appear there until after their attempt to secure the re-election of Genocide Joe. No matter what your opinion of Donald Trump, there is no doubt the CIA conspired against him during his entire Presidency, beginning with the fake Russiagate scandal and ending with their cover-up of the Hunter Biden laptop story. They do not want Trump back.
Biden is politically in deep trouble. Biden’s lifelong political support for Israel has been unwavering to the point of fanaticism. In the process he has collected millions of dollars from the Zionist lobby. That always seemed a source of political strength in the United States, not of weakness.
The current genocide in Gaza has changed all those calculations. The sheer evil and viciousness of the Israeli state, the open and undisguised enthusiasm for racist massacre, has achieved the seemingly impossible task of turning much American public opinion against Israel.
That is particularly true among key elements of the Democratic base. Young people and ethnic minorities have been shocked that the party they have supported is backing and supplying genocide. The mainstream media have lost control of the narrative, when the truth is so widely available on mobile phones, to the point that the MSM have actually been forced to change course and occasionally tell truths about Israel. That also was unthinkable a few months ago.
Precisely the same groups who are outraged by Biden’s support for genocide are going to be alienated by the attack on a journalist and publisher for revealing true facts about war crimes. Assange is not currently a major public issue in the United States, because he is not currently in the United States. Were he to arrive there in chains, the media coverage would be massive and the issue unavoidable in the presidential election campaign.
The extradition proceeding has therefore had to be managed in such a way as to keep Assange locked in a living hell the whole time, without actually achieving the extradition until after the presidential election in November. As the years of hearings have rolled by this has become increasingly difficult for the British state to finesse on behalf of their American masters.
In this respect, and only in this respect, Dame Victoria Sharp and Lord Justice Johnson have done brilliantly in their judgment.
Senior British judges do not have to be told what to do. They are closely integrated into a small political establishment that is socially interlinked, defined by membership of institutions, and highly subject to groupthink.
Dame Victoria Sharp’s brother Richard arranged an £800,000 personal loan for then Prime Minister Boris Johnson, and subsequently became chairman of the BBC despite a complete lack of relevant experience. Lord Justice Johnson as a lawyer represented the intelligence services and the Ministry of Defence.
They did not have to be told what to do in this case explicitly, although it was very plain that they entered the two-day hearing process knowing nothing except a briefing they had been given that the crux of the case was the revelation of names of US informants in the Wikileaks material.
The potential danger of an appeal, the granting of which would achieve the United States’ objective of putting the actual extradition back beyond the election date, was that it would allow the airing in public of a great catalogue of war crimes and other illegal activity which had been exposed by Wikileaks.
Sharp and Johnson have obviated this danger by adjourning the decision with the possibility of granting an appeal, but only on extremely limited grounds. Those grounds would explicitly gag the defence from ever mentioning again in court inconvenient facts, such as United States war crimes including murder, torture and extraordinary rendition, as well as the plans by the United States to kidnap or assassinate Julian Assange.
All of those things are precluded by this judgment from ever being raised again in the extradition hearings. The politically damaging aspect of the case in terms of the Manning revelations and CIA behaviour has been cauterised in the UK.
There has been some confusion because the judgment stated that three grounds of possible appeal were open. But in fact this was really only two. The judgment states that freedom of expression under article 10 of the European Convention is adequately covered by the First Amendment protections of the US Constitution. Therefore this point can only be argued by the defence against extradition if the First Amendment will not be applied in the case.
The second ground of appeal which they stated may be allowed was discrimination by nationality, in that the prosecution has stated that as a foreign citizen who committed the alleged acts whilst outside of the United States, Julian may not have the protection of the First Amendment or indeed of any of the rights enshrined in the US Constitution.
So the first two grounds are in fact identical. Sharp and Johnson ruled that both would fall if an assurance were received from the government of the United States that Julian would not be denied a First Amendment defence on grounds of nationality.
The other ground on which an appeal may be allowed to go forward is the lack of an assurance from the United States that, following additional charges, Julian may not become subject to the death penalty.
I shall go on to analyse what happens now and the chances of success on any of these allowed appeal points, but I wish first to revisit the points which have not been allowed and which are now barred from ever being raised in these proceedings again.
The most spectacular argument in the judgment, and one which I trust will become notorious in British legal history, refers to the application to bring in new evidence regarding the US authorities’ illegal spying on Julian and plotting to kidnap or assassinate him.
There are any number of things in this case over five years which are so perverse that they have to be witnessed to be believed, but none has risen to this height and it would be a struggle for anybody to come up with anything in British legal history more brazen than this.
Judge Johnson and Judge Sharp accept that there is evidence to the required standard that the US authorities did plot to kidnap and consider assassinating Julian Assange, but they reason at para. 210 that, as extradition is now going to be granted, there is no longer any need for the United States to kidnap or assassinate Julian Assange: and therefore the argument falls.

It does not seem to occur to them that a willingness to consider extrajudicial violent action against Julian Assange amounts to a degree of persecution which obviously reflects on his chances of a fair trial and treatment in the United States. It is simply astonishing, but the evidence of the US plot to destroy Julian Assange, including evidence from the ongoing criminal investigation in Spain into the private security company involved, will never again be allowed to be mentioned in Julian’s case against extradition.
Similarly, we are at the end of the line for arguing that the treaty under which Julian is being extradited forbids extradition for political offences. The judgment confirms boldly that treaty obligations entered into by the United Kingdom are not binding in domestic law and confer no individual rights.
Of over 150 extradition treaties entered into by the United Kingdom, all but two ban extradition for political offences. The judgment is absolutely clear that those clauses are redundant in every single one of those treaties.
Every dictatorship on Earth can now come after political dissidents in the UK and they will not have the protection of those clauses against political extradition in the treaties. That is absolutely plain on the face of this ruling.
The judgment also specifically rejects the idea that the UK court has to consider rights under the European Convention of Human Rights in considering an extradition application. They state that in the United States—as in other Category 2 countries in terms of the Extradition Act 2003—those rights can be presumed to be protected at trial by the legislation of the country seeking extradition.
That argument abdicating responsibility for application of the ECHR is one that is not likely to be accepted if this case ever gets to Strasbourg (but see below on the possibility of that happening).
By refusing to hear the freedom of expression argument, the court is ruling out listening to the war crimes exposed by the material published and hearing that the publication of state level crime is protected speech. That entire argument is now blocked off in future hearings and there will be no more mention of US war crimes.
The judges accept—hook, line and sinker—the tendentious argument that Julian is not being charged with the publication of all of the material but only with those documents within the material which reveal the name of US informants and sources. As I reported at the time, this was plainly the one “fact” with which the judges had been briefed before the hearing.
That it is a legitimate exercise to remove entirely from consideration the context of the totality of what was revealed in terms of state crimes, and to cherry pick a tiny portion of the release, is by no means clear; but their approach is in any event fatally flawed by a complete non sequitur:

At para. 45 they argue that none of the material revealing criminal behaviour by the United States is being charged, only material which reveals names. Their argument depends upon an assumption that the material revealing names of informants or sources does not also reveal any criminal behaviour by the United States. That assumption is completely and demonstrably false.
Let us now turn to the grounds on which a right to appeal is provisionally allowed, but may be cancelled in the event of sufficient diplomatic assurances being received from the United States.
To start with the death penalty, which has understandably drawn the most headlines: it astonishes me, as this argument has been in play now for several months, that the United States has not provided the simple assurance against imposition of the death penalty which is absolutely bog standard in many extradition proceedings.
There is no controversy about it, and it is really quick and easy to do. It is a template: you just fill in the details and whiz off the diplomatic note. It takes 5 minutes.
I do not believe the Biden administration is failing to provide the assurance against the death penalty because they wish to execute Julian Assange. They do not need to execute him. They can entomb him in a tiny concrete cell, living a totally solitary existence in a living hell. Arguably, he is of more value alive that way as a terrible warning to other journalists, rather than an executed martyr.
I view the failure so far to produce a guarantee against the death penalty as the clearest evidence that the Biden administration is trying simply to kick this back past the election. By not providing the assurance, already they have achieved a delay of another few weeks which they have been given to provide the assurance, and then further time until the hearing on 20 May to discuss whether assurances produced have been adequate. Not giving the death penalty assurance is simply a stalling tactic, and I am sure they will go right up to the deadline given by the court and then provide it.
The second assurance requested by the court is actually much more interesting. They have requested an assurance that Julian Assange will be able to plead a First Amendment defence on freedom of expression and will not be prevented from doing so on the grounds of his Australian nationality.
The problem which the United States faces is that it is the federal judge who will decide whether or not Julian is entitled to plead that his freedom of speech is protected by the First Amendment. Neither the Department of Justice nor the State Department can bind the judge by an assurance.
The problem was flagged up by the US prosecutor in this case who stated that it is open to the prosecution to argue that a foreign national, operating abroad as Julian did, does not have First Amendment rights. It is extremely important to understand why this was said.
The prisoners in Guantanamo Bay are deemed not to have any constitutional rights, despite being under the power of the US authorities, because they were non-US citizens acting abroad.
A key US Supreme Court judgment in the case of USAID versus Open Society stated unequivocally that non-US citizens acting abroad do not have First Amendment protection. At first sight that decision appears to have little relevance. It concerns foreign charities in receipt of US aid funds which, as a condition of aid, they must oppose sex work. They attempted to claim this was in breach of First Amendment rights but the Supreme Court ruled that, as foreigners acting abroad, they did not have any such rights.
While that may appear of limited relevance, referring to NGOs not individuals, there is a paragraph in the Open Society judgment which states as a rationale that were First Amendment rights to be granted to those NGOs they would also have to be granted to foreigners with whom the US military and intelligence services were in contact – i.e. the Guantanamo problem.
This paragraph of the Supreme Court ruling appears inescapable in the Assange case:

Julian was a foreign national operating abroad when the Wikileaks material was published. So I do not see how the United States can simply give an assurance on this point, and indeed it seems to me very likely that Julian would indeed be denied First Amendment rights at trial in the United States.
The sensible solution would of course be that as a non-US citizen publishing material outside the United States, Julian should not be subject to US jurisdiction at all. But that will not be adopted.
So I anticipate the United States will produce an assurance which tries to fudge this. They will probably give an assurance that the prosecutor will not attempt to argue that Julian has no First Amendment rights. But that cannot prevent the judge from ruling that he does not, especially as there is a Supreme Court judgement to rely on.
In May when we come to the hearing on the permitted points of appeal, it is vital to understand that there will be two parts to the argument. The first part will be to consider whether the assurances received by diplomatic note from the United States are sufficient for the grounds of appeal to fall completely.
However if it is decided that the assurances from the United States are insufficient, that does not automatically mean that the appeal succeeds. It just means that the appeal is heard. The court will then decide whether the death penalty or nationality discrimination points are strong enough to stop the extradition.
The absence of the death penalty assurance should end the extradition process. But the hearing would see the prosecution argue that it is not necessary, as there are no capital charges currently and none are likely to be added. The judges could go with this, given the undisguised bias towards the United States throughout.
The state will again kick in with its iron resolve to crush Julian. I don’t think that the United States will be able, for the reasons I have given, to provide assurances on the nationality and First Amendment rights, but I think the court will nonetheless order extradition.
The United States will argue that it is a free country with a fair trial system and independent judges and that Julian will be allowed to make the argument in court that he should have First Amendment rights. The UK court should accept that the US judge will come to a fair decision which protects all human rights considerations. They will say that it is perfectly reasonable and normal for states to treat citizens and foreign nationals abroad in different ways in different contexts, including consular protection.
A justice system which is capable of ruling that a person should be handed over to his attempted kidnapper, because then the kidnapper does not have to kidnap him, and ruling that the clauses of the very treaty under which somebody is being extradited do not apply, is capable of accepting that the ability to argue in court for a First Amendment defence is sufficient, even if that defence is likely to be denied.
There is, however, plenty of meat in those questions that would allow another adjourned hearing, another long delay for a judgment and plenty of leeway to get past the November election for Genocide Joe.
The British establishment continues to move inexorably towards ordering Julian’s extradition at the time of its choosing. Once extradition is ordered, Julian in theory has an opportunity to appeal to the European Court of Human Rights.
The European Court of Human Rights can delay the extradition until it hears the case by a section 39 order. But there are two flaws: firstly the extradition may be carried out immediately upon the court judgement before a section 39 order can be obtained, which would take at least 48 hours. Secondly the Rwanda Safety Act has provision, though specifically in the Rwanda context, for the government to ignore section 39 orders from the ECHR.
It cannot be ruled out that the British government would simply extradite Julian even in the face of an ECHR hearing. That would be popular with the Conservative base and, given Starmer’s extremely extensive and dubious role in the Assange saga while Director of Public Prosecutions, I certainly do not put it past him either. It is worth noting that there have been several occasions in recent years when the Home Office has deported people despite British court orders putting a stay on the deportation. There has never been any consequence other than a verbal rap on the knuckles for the Secretary of State from the court.
So the struggle goes on. It is a fight for freedom of speech, it is a fight for freedom of the press, and above all it is a fight for the right of you and me to know the crimes that our governments commit, in our name and with our money.
I am ever more struck by the fact that in fighting for Julian I am fighting exactly the same power structures and adversaries who are behind the genocide in Gaza.
I need to close with an appeal. Please do not stop reading. You will recall that I recently addressed the UN Human Rights Committee on Julian’s case and in doing so had the opportunity to state a few hard truths about the war crimes of the United States.
https://www.craigmurray.org.uk/wp/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/video.mp4My opportunity to do so was organised by the Swiss NGO Justice For All International, who submitted a shadow report (open link and click on red icon) by their lawyers to the UN 7 year Periodic Review of the UK’s human rights record. Justice For All also carried out a great deal of lobbying activity in connection with this to get me onto that stage and into meetings with key officials.
I had agreed a fee to pay Justice For All for this legal and lobbying activity, in the expectation that it would be met from the substantial funds held by the bodies comprising the US/European institutions of Julian Assange campaign.
Unfortunately the Assange campaign has refused to meet the bill and I have been left holding it.
I have been told that I failed to follow correct procedures to apply for the spending. I am frankly in shock and a form of grief, because I thought we were friends working for a common cause, in my own case for free. I am reminded of the brilliant perception of Eric Hoffer: “Every great cause begins as a movement and becomes a business”.
I am left with this bill I cannot pay for the work at the UN. Justice For All could not have been nicer about the situation, but if you could contribute to this Justice For All crowdfunder, I should be very grateful.
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post The Assange Hearing Permission Appeal Judgment: Mad and Bad. appeared first on Craig Murray.
March 28, 2024
Injured
My run of bad luck with health continues. A week ago I fell, dislocated my shoulder and damaged my knee. I am very strapped up and won’t have the use of my right arm and hand for a minimum of another week. Am working on a post by auto dictation but it’s not easy.
The post Injured appeared first on Craig Murray.
March 20, 2024
Scotland’s Hate Speech Act and Abuse of Process
On 1 April Scotland’s notorious Hate Crime Act comes into force. I have explained before why it is so noxious. It has been condemned by every civil liberties body you can think of. Police Scotland have made matters still worse by telling their officers that the measure of whether a Hate Crime has been committed should be whether the person reporting it feels offended or threatened, and that the officer should make no objective judgment as to whether that is reasonable from the facts of the case.
But I want to concentrate on one very specific aspect of this legislation. It will apply to social media, and indeed it is highly probable that a very significant proportion of the “Hate Speech” will be found on social media.
It is a well establsihed principle in Scots law that anything published on the internet, which can be read in Scotland, is deemed to be published in Scotland. The act of publication is not deemed to be the person actually publishing the item, let us say in Tahiti. The act of publication is deemed to be the reader opening the item on their device in Scotland.
(To emphasise the total illogic of this approach, while it is the person opening it which constitutes the act of publication, it is not the person who opened it who is deemed to have published it but the original creator/publisher. To emphasise the state’s dishonest thinking still more, if however what is being opened is not, say, libel or hate speech but rather illegal pornography, then it is in that case the person who opened it who is deemed to have published it).
So a person in Tahiti who publishes a tweet which is opened by and offends somebody in Scotland because it offends a protected characteristic, had committed a crime in Scotland, even though they never left their home in Tahiti and may never have been anywhere near Scotland.
I know this sounds completely crazy, but I do assure you it is absolutely true. As kindly confirmed here by the Dean of Faculty.
Craig is absolutely correct here. If it’s published online and read in Scotland then – in law – it is published in Scotland.
— Roddy Dunlop KC (@RoddyQC) March 15, 2024
This means, beyond a doubt, that hundreds of thousands, and possibly millions, of new crimes will be committed in Scotland every year from 1 April. Committed in Scotland by people who were, at the time, all over the world.
If you think that is bad, let me tell you it gets infinitely worse. In addition to holding that Scots courts have jurisdiction over anything published on the internet anywhere in the world, because if it can be read here it is published in Scotland, Scottish judges have also invented the doctrine of “continuing publication”.
As it is the act by the reader of opening the matter online which constitutes publication, every time it is opened by someone in Scotland from the internet that constitutes a new publication. So any “hate speech” that has been online for ten years constitutes a new offence if you read it in Scotland now. “Hate speech” as defined in the Act, anywhere on the Internet, no wonder when or where it was published, is going to be a new crime in Scotland if someone opens it or reads it after 1 April.
What I have said is simply true. It is irrefutable. There may sometimes be argument over who committed the crime – for example, it may sometimes be the author or sometimes the publisher who is guilty, (though on social media they are in most instances deemed the same person). But that a crime has been committed in Scotland is not in doubt.
So how will Police Scotland and the Crown Office cope?
Through selective prosecution. With literally millions of available criminal offences being committed annually, the authorities have fantastic latitude to choose who and who not to pursue.
In theory of course all crime should be pursued equally. In practice that will be impossible. Scotland will have put itself into this impossible situation by the combination of two terrible bits of law. Scotland’s legal doctrine on internet publication is appalling and Scotland’s new Hate Crime and Public Order Act is appalling. The combination of the two is almost indescribably bad.
Scotland’s internet doctrine that the entire internet is published in Scotland if you read it here, is a claim of universal jurisdiction over the internet. It should be derided into vanishing.
But the internet posed a dilemma for the courts. EIther they had to accept a massive increase in freedom of speech, or claim jurisdiction over the entire internet. How do you enforce an injunction if somebody can simply publish the information from their home in Tahiti and you cannot touch them? Needless to say, the stupid and arrogant judges of Scotland went for the universal jurisdiction path and not the freedom path (to be plain, so have the courts in England and Wales).
There is however a real problem here. Outside the UK, Scottish judges can only get their hands on our “criminal” from Tahiti if they happen to come here, or by extradition. But extradition depends on the principle of dual criminality – the act has to be a criminal offence in the country being extradited both to and from. As there are few countries in the world willing to jail you for telling a story that starts “An Englishman, Scotsman and Irishman went into a pub”, extradition will be difficult in most cases.
It will, incidentally, certainly be an imprisonable offence in Scotland from 1 April to tell a joke beginning “An Englishman, a Scotsman and an Irishman went into a pub”. The police just need someone to complain.
But this opens a very interesting question with England and Wales. Plainly there is an enormous amount of online social interaction between Scots and people in England and Wales. The Scottish courts do not need to extradite people from England and Wales, the police just truss them up and deliver them. But is England really going to accept that a woman sitting at home in Leicester, who made a bad taste joke online whilst in Leicester that is perfectly legal in England, can be sent to Scotland and imprisoned?
Did anybody actually think that through in passing this Act through the Scottish Parliament?

The Hate Crime Act makes it a criminal offence to insult somebody. You can go to jail for seven years for insulting somebody. That does not have to be your own insult. It includes by “displaying, publishing, distributing” “giving, sending, showing, playing” or “making the material available”. It includes giving someone an album that contains offensive lyrics, or acting in a performance that contains offensive lines. It really does.

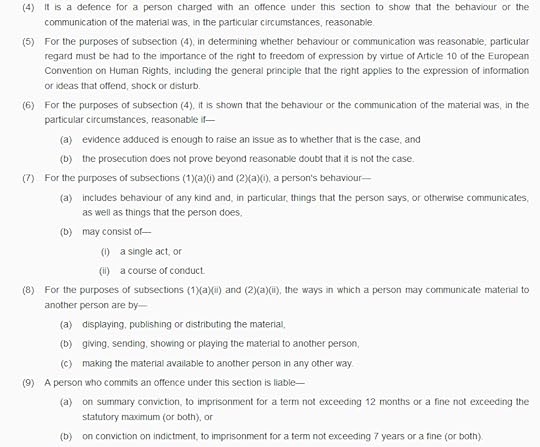
The most basic notion of liberty has been discarded.
To make plain the culture wars motivation, three of the six protected characteristics are sexual orientation, transgender identity and variations in sex characteristics. I genuinely do not know what the last one means. It does not mean being male or female. Strangely enough it will still be perfectly legal to insult women or men.
Rather worryingly, much of the opposition to the bill comes from people who want to make more things illegal, rather than give the state less arbitrary power to bang up huge numbers of people.
The truth is that this appalling legislation was always a part of Nicola Sturgeon’s grand scheme to destroy the Scottish Independence movement from within through culture wars. Everybody sentient in Scotland knows that the entire intention is a massive abuse of process. Of the millions of people who could be prosecuted for online content read in Scotland, the intention is selectively to attack those who are gender critical.
Now I am in fact not gender critical myself. I still find the intolerance puzzling. But I absolutely defend the right of those who are convinced that trans people are a threat to womens’ rights to state their position, free from the legal harrassment that is about to be unleashed upon them.
What we are seeing is terrible repressive legislation, amplified by a terrible legal doctrine, leading to massive power by the state over individuals. We are going to see monumental abuse of process. The state will take completely arbitrary decisions on selective prosecution according to a state political agenda, and will refuse to prosecute millions of other “crimes” under the same Act. This is fascism.
In the short term, I have no doubt that the Israeli lobby will be generating thousands of complaints of alleged anti-semitism aimed at those criticising Israel for its genocide. There is an extremely high correlation between Scottish unionism and zionism which doubtless will be in play.
The situation contradicts, at the very least, article 1, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 and 17 of the European Convention on Human Rights. A nightmare is coming.
————————————————
Forgive me for pointing out that my ability to provide this coverage is entirely dependent on your kind voluntary subscriptions which keep this blog going. This post is free for anybody to reproduce or republish, including in translation. You are still very welcome to read without subscribing.
Unlike our adversaries including the Integrity Initiative, the 77th Brigade, Bellingcat, the Atlantic Council and hundreds of other warmongering propaganda operations, this blog has no source of state, corporate or institutional finance whatsoever. It runs entirely on voluntary subscriptions from its readers – many of whom do not necessarily agree with every article, but welcome the alternative voice, insider information and debate.
Subscriptions to keep this blog going are gratefully received.
Choose subscription amount from dropdown box:
Recurring Donations3 Pounds : £3.00 GBP – monthly5 Pounds : £5.00 GBP – monthly10 Pounds : £10.00 GBP – monthly15 Pounds : £15.00 GBP – monthly20 Pounds : £20.00 GBP – monthly30 Pounds : £30.00 GBP – monthly50 Pounds : £50.00 GBP – monthly70 Pounds : £70.00 GBP – monthly100 Pounds : £100.00 GBP – monthly

PayPal address for one-off donations: craigmurray1710@btinternet.com
Alternatively by bank transfer or standing order:
Account name
MURRAY CJ
Account number 3 2 1 5 0 9 6 2
Sort code 6 0 – 4 0 – 0 5
IBAN GB98NWBK60400532150962
BIC NWBKGB2L
Bank address Natwest, PO Box 414, 38 Strand, London, WC2H 5JB
Bitcoin: bc1q3sdm60rshynxtvfnkhhqjn83vk3e3nyw78cjx9
Ethereum/ERC-20: 0x764a6054783e86C321Cb8208442477d24834861a
The post Scotland’s Hate Speech Act and Abuse of Process appeared first on Craig Murray.
Craig Murray's Blog
- Craig Murray's profile
- 39 followers



