Bruce Clay's Blog, page 12
June 14, 2016
VIDEO: Dr. Pete Meyers on Major Search Changes and How to Deal
VIDEO: Dr. Pete Meyers on Major Search Changes and How to Deal was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Google’s search engine results page (SERP) never stays the same for too long. Google is constantly experimenting with the look and functionality of the SERP.
At Bruce Clay, Inc., our SEO agency is always paying attention to those changes — and so is renowned marketing scientist Dr. Pete Meyers. He’s the brains behind MozCast, the Google algorithm “weather report” that chronicles changes to the SERP as they happen. He’s also presenting his Guide To The Changing Google SERPs Search Marketing Expo (SMX) Advanced this month.
While Google announces major updates like Panda, Penguin and Hummingbird, it stays silent on the vast majority of its changes. Eric Schmidt, executive chairman of Google’s parent company Alphabet, revealed in congressional testimony that there were 516 changes to the Google algorithm in a single year.
That means it’s up to SEOs and digital marketers to keep their eyes on the SERP to monitor what’s happening day in and day out.
To keep us digital marketers in the know, Meyers joined Bruce Clay, Inc. Senior Technical Writer Paula Allen and I for a candid conversation on the latest changes to the SERP and what it means for SEO.
We talked 2016’s most impactful SERP updates, including:
How SEOs should proceed with the new title and description length
Google’s motivation behind larger text ads
The disappearance of the right-hand column — perhaps entirely
And how standardizing mobile and desktop SERPs could lead to future design changes
Catch up with all the latest SERP news in the above interview with Dr. Pete! It’s an outstanding preview of what’s to come at SMX Advanced. If you’re headed to Seattle for SMX Advanced, you can catch his session at 11 a.m. PDT on June 20.
No SMX Advanced ticket? No problem. I’ll be there liveblogging the conference. Subscribe to the Bruce Clay, Inc. Blog to get all the news coming out of SMX Advanced as it happens … for free!
June 13, 2016
Szetela’s Scoop! Microsoft’s LinkedIn News May Imply More than LinkedIn Ad Integration for Bing Advertisers
Szetela’s Scoop! Microsoft’s LinkedIn News May Imply More than LinkedIn Ad Integration for Bing Advertisers was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Microsoft’s announced acquisition of LinkedIn today has already sent ripples through the advertising industry. Marketers are predicting (or hoping) that the LinkedIn ad platform will be merged with Bing Ads, allowing PPC advertisers to run Bing Ads and LinkedIn ad campaigns from the same dashboard.
I think the acquisition could actually be the cornerstone of an important new Bing Ads strategy: the creation and expansion of a Microsoft Display Network.

Urgent Push for a Microsoft Display Network
Microsoft has never been a major player in display advertising. Currently, Bing Ads advertisers can place text ads on Microsoft’s owned and operated sites (like MSN Money), but that’s just a handful of sites, and targeting options are limited to rudimentary demographics.
Facebook and Google display advertising, on the other hand, account for billions in revenue for those two dominant players. Flexible hypertargeting capabilities have helped advertisers finally reap ROIs that rival those obtainable through search advertising.
Two recent developments underscore Microsoft’s sense of urgency:
First, Google just announced that they’re expanding their display network (already reaching, they say, 90 percent of all internet users) by the addition of Cross-Exchange Buying inventory.
Secondly, Facebook has been quietly building the size of its Facebook Audience Network to include people and sites outside the set of Facebook users. And they recently announced a new feature that will let advertisers target an even bigger audience.
3 Moves for Microsoft to Rival Google & Facebook
Look for Microsoft to muscle its way in and grab a big slice of the display ads pie. I see three big moves by Microsoft ahead:
Step 1 will be the integration of Bing Ads and LinkedIn Advertising.
Step 2 will be the introduction of additional ad sizes and formats for display advertising.
For Step 3, I wouldn’t be surprised if Microsoft grows its display network through other means, like additional acquisitions, or the creation of a publisher program to rival Google’s AdSense.
Long-time Microsoft watchers know that the Redmond giant rarely gets it right the first time, but time and again has “versioned” its way to dominance. Could the Bing Ads we know today be the Windows 3.1 of PPC advertising — and is Microsoft about to go all Windows 95 on us? A Microsoft Display Network would be a big play that would give display advertisers exciting new options for their ad dollars.
Wondering how to improve your search engine marketing campaigns? Request a free PPC audit from David Szetela and the PPC team at BCI.
June 9, 2016
Which Social Media Networks Should Your Business Invest In?
Which Social Media Networks Should Your Business Invest In? was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Are you evaluating the many social media networks and aren’t sure which would return the most benefit for your investment if you were to build an active presence for your business?
With so many choices, kicking off social media marketing can be overwhelming. To help you choose the best fit social networks for your business, we’re shining a light on:
The primary user base of the most popular social networks
What brands are doing to find success marketing on each
Guidelines for determining if your business could be a good match for marketing, branding, community building or customer service on each platform
And any special considerations to be aware of that engagement on the platform may require

These are the six social networks covered here:
Google+
You can jump to each section from the link above.
Criteria for Evaluating a Social Investment
Here are some questions to ask to decide if a social network is right for your business:
Are my target users among this network’s user base?
Does my business’s products or services fit the type of content that is popular on this network?
Can I commit resources to an ongoing campaign to create or publish content that is popular on this network?
What are the ideal actions a user could take from this network that would benefit my business?
Below you’ll find each network’s primary user demographics and the popular content types as well as an example of a brand that has built a loyal and engaged community of followers.
While the examples of brands making each network work for them provides a template of what your business might be able to do, what has worked in the past is certainly not the limit to what could work in the future.
It’s important to note that every successful campaign strategy begins with creative thinking about a business brand and the audience it serves. In other words, your brand story could break the mold and be the next case study of a business doing social right!
Pinterest: Visual Candy Collectors
Popular content: Food, fashion, décor and DIY images that users find around the web
Most followed brands are Perfect Pallet, Real Simple and The Beauty Department
Established in 2010
100 million active users
85 percent of users are female
Pinterest users post images to the platform (usually images they came across while browsing the web, sometimes images or graphics they may have created or published themselves) sorting or categorizing them by theme or subject matter which other users can then follow or browse. Pinterest has become a hub of inspiration for creatively inclined people, 4 out of 5 of whom are women. The industry themes that thrive on Pinterest include:
Wedding and event planning
Home décor
Recipes
Fashion
Crafting and DIY
A Brand’s Pinterest Success
Upscale cosmetic retailer Sephora joined Pinterest in 2012. The brand boasts more than 290,000 followers and 6,500 pins showcasing product lines, tutorials for how to use their products and beauty looks created with their products, in other words, their products at work.
Since Sephora began advertising on Pinterest, Pinterest became one of Sephora.com’s top ten sources of referral traffic. Not only is Sephora boosting its reach with Pinterest, but it’s also able to improve its offerings via the data collected through it. Sephora learns about their users and the products they are most interested in, along with other key marketing information, by mining their Pinterest data.
How new content will be used on Pinterest is a consideration of every new campaign. “When we create content for our site or emails, we think of additional ways that we can help the story along on Pinterest,” said Sephora CMO Julie Bornstein. “We use web analytics to look at top pins, test quote layouts from brand founders, and try different product shots — we spend time learning about what works and experiment often to get it right.”
Instagram: Public Diarists
Popular content: Photos by celebrities and brands revealing what goes on behind the scenes and glamorous lifestyles
Most popular brands are Nike, Starbucks and NBA
Launched in October 2010
400 million active users and counting
80 million photos shared per day
Men and women are rather evenly represented among Instagram’s young (18-29) user base
On Instagram, users publish photos and videos (up to 15 seconds) dressed up with filters, user tagging and hashtags. Brands that succeed on Instagram are those with stories to tell, drawing users into the lifestyle the brand is portraying through the vignettes and characters featured in their photo stream.
Here’s a photo from BCI’s Instagram account. That’s BCI’s content and media manager Virginia Nussey, me, and senior technical writer Paula Allen (left to right) showing some behind-the-scenes fun at the office on Flannel Friday.
A photo posted by Bruce Clay, Inc. (@bruceclayinc) on Mar 18, 2016 at 10:11am PDT
A Brand’s Instagram Success
The ice cream purveyor Ben & Jerry’s reached 9.8 million users on Instagram through a paid ad campaign on the network. The campaign consisted of 4 sponsored images of its ice cream disseminated among a target audience of 18- to 35-year-olds in the U.S. over eight days. The end result was greater top-of-mind recall, brand recognition and product demand.
“Since its launch, Instagram has provided us with an amazing platform to connect with our fans and tell our story visually. Ads on Instagram let us reach and engage with more fans about our flavors, fun and values,” said Mike Hayes, digital marketing manager at Ben & Jerry’s.
Google+: Conversationalists Plus Max SEO Benefits
Popular content: Articles on Digital marketing, business and technology – which is no surprise considering the top eight occupations among Google+ users are engineers, developers, designers, software engineers, web developers, writers, software developers and programmers. Google+ is also popular among photographers who use Google+ to showcase their work (and, fittingly, photographer is the ninth most commonly listed occupation on Google+).
Launched in June 2011
300 million active users and counting
68% of users are male
Special note to consider in a business’s evaluation for network investment: There are SEO benefits to Google+ including increased visibility opportunities for a business’s content to be displayed in search results, and a quick way to get content crawled by Google
Brands leading the way on Google+ include:
Topshop
TOMS
H&M
The Financial Times
Cadbury
Mashable
Fitbit
Flixster
Hotel Tonight
Read brand stories and case studies for each of these companies.
A Brand’s Google+ Success
Like many other leading brands on Google+, British chocolatier Cadbury has leveraged Google+ to create conversations via Hangouts On Air.
“The thing that’s most different (on Google+) is Hangouts – you can’t really do it on any other platform. We’ve done three hangouts so far. The first one we created a chocolate version of our Google+ page. Then we did a second with Rebecca Adlington, one of the Olympians we’re sponsoring … We just met up with one of chocolate tasters and had an informal discussion on the basics of chocolate,” said Jerry Daykin, Cadbury’s social media and community manager.
“We spent quite a long time with our first Hangout thinking what will we do, when will we do what, and made it quite complicated in our head. And the reality was it’s as easy as having a conversation with someone face-to-face … My favorite feature about Hangouts On Air is the ability to have this really close connection to a small group of people but do it in a way that lets thousands of people see it.”
LinkedIn: Consultants, Personal Brands and B2B Reach
Popular content: Professional profiles and resumes, business-centric news and articles, and job opportunities
Established in May 2003
400 million members
3 million business pages
Top company pages on LinkedIn include Mashable, HubSpot, NPR, Kellogg and AppleOne
Among LinkedIn’s users are many owners, presidents, founders and C-Suite executives – i.e., people with the ability to make change, hire companies and acquire new talent. If you are a B2B company, LinkedIn provides a golden opportunity to market your company in front of businesses who can hire you.
A Brand’s LinkedIn Success
One such B2B company advertising on LinkedIn is marketing software company HubSpot. HubSpot uses LinkedIn to distribute white papers, drive traffic to their own site, increase high quality leads, and reach targeted professional industries.
“With LinkedIn, we’re able to truly identify our core audience by going a step further and targeting by company, job title, job function and groups,” said Dan Slagen, head of paid search marketing at HubSpot. “This gives us the unique ability to tailor messaging and target the exact audience segment that we need.”
For HubSpot, LinkedIn advertising resulted in a lower cost-per-click rate than with search engine advertising. Slagen said that the CPC averaged at $3, “which is actually a fraction of the cost of paid search advertising … on traditional PPC search engines, we’ve seen average CPC rates that are … as much as three times higher.”
Facebook: Local and National Brands Alike, but Come with a Budget
Popular content: Photos (including selfies), coordination of social plans, posts about what people are doing, likes and shares of content found on the web
Established in July 2004
More than 50 million business pages
1.65 billion active monthly users – with this many users, everyone’s on there, which is how Facebook has been able to grow its ad products that feature a high degree of audience targeting capabilities
Special note to consider in a business’s evaluation for network investment: paid promotion is required for visibility
Facebook has been the dominant platform within the social media sphere for many years. It has the most users, and, speaking to its prominence users’ daily lives, 48 percent of 18-34 year old Facebook users check Facebook when they wake up. But when talking about Facebook as a marketing channel today, the discussion must begin with advertising.
If you’re considering investing in Facebook for your business, you should understand that you will likely need to dedicate an advertising budget for promoting your content on the network, even among your own fans. Without paid promotion, Facebook reportedly shows brand page content to a mere 1 to 2 percent of a page’s followers. In order for a brand page’s posts to show to its fans and followers, reach must be amplified by paid promotion.
Facebook points to the following industries as leaders in Facebook advertising:
Automotive
Consumer goods
Financial services
Gaming
Politics
Retail/ecommerce
Technology
Travel
A Few Brands’ Successes on Facebook
On Facebook, national brands and local retailers alike successfully pay to play with the social networks. Global retailer Michael Kors, for example, was able to use Facebook ads to drive more than one million view to its sneaker videos, increasing brand awareness and sales.
Sam’s Chowder House, a locally owned restaurant in San Francisco, attributed a 19 percent increase in guests and revenues to Facebook’s promoted posts. The day after their most successful promoted posts, they experienced 58 percent sales increase and 22 percent guest count increase.
Twitter: Build Awareness Through Fast Feedback
Popular content: Users have 140 characters to broadcast commentary, links and images or converse with other users. The avenues of success on Twitter are broad and varied, with popular accounts ranging from musing celebrities (@ladygaga) to humorous shticks (@shitmydadsays) to businesses providing stellar customer service (@JetBlue) to food trucks tweeting the day’s location (@CurbsideCupcake)
Established in March 2006
310 million active users on Twitter
83 percent of Twitter users access Twitter from a mobile device
Compete.com recently looked at the online habits of 2,000 consumers and found that 38.9 percent of users made online purchases from retailers whose tweets they had seen … compared to only 26.9 percent of users who made online purchases without being exposed to any tweets. A brand that tweets stands to gain a 37 percent increase in online sales.
“Consumers who see Tweets from retailers are people who, for one reason or another, are engaged in conversation about or with that retailer. These people prove to also be much more likely to shop and buy from retailers’ websites … The results demonstrate that more exposure correlates with more retail activity.”
Here’s a photo tweet by @BruceClayInc of me speaking on social media marketing at a recent event in LA. Photos are easy to post to Twitter through the mobile app, and tend to get higher engagement than tweets without images.
Branding on Instagram and Snapchat panel at Media Leaders Growth Summit #dgs16 https://t.co/eQoIi1Sr9H pic.twitter.com/OJIAn8zV92
— Bruce Clay, Inc. (@BruceClayInc) May 6, 2016
A Few Brands’ Successes on Twitter
As with Facebook, brands of all sizes and from all industries are using Twitter. Chicago bakery Whipped Bakeshop used a promoted account to increase followers in Philadelphia and attract new customer. The Barack Obama presidential campaign used promoted trends get keep voters informed in real time and gain record engagement in 2008. The American Red Cross used promoted tweets to drive donations (reaching 100% of its goal) and attract new volunteers.
Next Steps for a Social Media Marketing Strategy
Success in social media marketing is measured by the quality of interactions over the quantity of interaction. No matter how your business’s online social presence develops, it’s critical to determine and track metrics that align with your business goals so you can decide what’s working and what’s not.
As you’re deciding what social network to invest in, determine the metrics you’ll be tracking to measure your efforts. That way, when you’ve launched a campaign to build brand awareness, provide customer service, enhance visibility of your products, and grow loyalty, you’ll be able to tell if your efforts are making progress for your business and adjust your tactics accordingly.
Want Social Media Recommendations Just for Your Business?
If you’re interested in a free 15-minute social media review from me, BCI’s social media editor, and learning more about how we can help you build your online presence, let us know and we’ll be in touch!
June 3, 2016
What Is Google PageRank, How Is It Earned & Does It Matter in 2016?
What Is Google PageRank, How Is It Earned & Does It Matter in 2016? was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Editor’s note: This article was updated in June 2016 to reflect the latest SEO understanding of Google PageRank.
When a user enters a search query, the search engine’s number one goal is to return results that are high-quality, relevant and able to best give them what they want. One of the 200+ factors Google takes into consideration to determine which webpages best fit the bill is PageRank.
What Is PageRank?
PageRank (PR) is a calculation, famously invented by Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin, which evaluates the quality and quantity of links to a webpage to determine a relative score of that page’s importance and authority on a 0 to 10 scale.
 The handful of PageRank 10 domains, including USA.gov, Twitter.com and Adobe Reader Download, have the highest volume of inbound links of any sites on the web.
The handful of PageRank 10 domains, including USA.gov, Twitter.com and Adobe Reader Download, have the highest volume of inbound links of any sites on the web.
The top sites set the bar, so to speak, and the 10-point scale plummets exponentially down from there.
PageRank 5 websites have a good number of inbound links, PR 3 and PR 4 sites have a fair amount, and brand new websites without any inbound links pointing to them start at PageRank 0.
NOTE: You may be curious what your site’s or your competitor’s PR score is. But Google no longer reveals the PageRank score for websites. It used to display at the top of web browsers right in the Google Toolbar, but no more. And PR data is no longer available to developers, either. Even though it’s now hidden from public view, however, PageRank remains an important ingredient in Google’s secret ranking algorithms.
Since Google wants to return page one results that are high quality, relevant, and trustworthy, it may return webpages with better PageRank scores higher up in the SERPs, although PageRank is only one of many ranking factors taken into consideration.
Since PageRank is only one factor in the Google ranking algorithm, it’s important to remember that a high PageRank does not guarantee high rankings — but it can significantly help.
What Is “Link Juice” and What Are PageRank “Points”?
When Site A links to your webpage, Google sees this as Site A endorsing, or casting a vote for, your page. Google takes into consideration all of these link votes (i.e., the website’s link profile) to draw conclusions about the relevance and significance of individual webpages and your website as a whole. This is the basic concept behind PageRank.
When a website links to your site, or when you link internally from one of your pages to another, the link passes PageRank points. This passing of PageRank points is also commonly called “link juice” or “link equity” transfer.
The amount of link juice passed depends on two things: the number of PageRank points of the webpage housing the link, and the total number of links on the webpage that are passing PageRank. It’s worth noting here that while Google will give every website a public-facing PageRank score that is between 1 and 10, the “points” each page accumulates from the link juice passed by high-value inbound links can — and do — significantly surpass ten. For instance, webpages on the most powerful and significant websites can pass link juice points in the hundreds or thousands. To keep the rating system concise Google uses a lot of math (ask in the comments if you want to hear about it) to correlate very large (and very small) PageRank values with a neat and clean 0 to 10 rating scale.
How Link Juice Is Passed
Think of it this way: Every webpage has a limited amount of link juice it can pass, and the top of that limit is the total PageRank points that page has accrued. So, a webpage with 20 accrued PageRank points cannot pass more than 20 points of link juice per page.
If a page with 20 PageRank points links to one other page, that one link will transfer the full amount of link juice to that one other webpage. But if a page with 20 PageRank points links to five webpages (internal or external), each link will transfer only one-fifth of the link juice.
Google applies a decay value to every pass, so the actual numbers will be a little less than our diagram shows below. But to explain the PageRank concept simply, the formula is PR points divided by number of on-page links, or in this case, 20 divided by five:
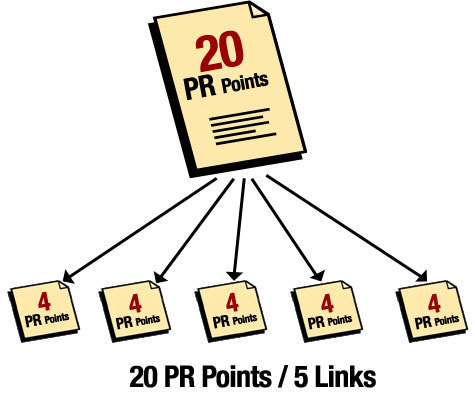
Visualize it: This diagram shows what it looks like when a webpage with 20 PageRank points links out to five other webpages that, accordingly, each receive approximately four PageRank points.
What if you want to link to several resources to aid user experience, but you have a strategic reason to withhold passing PageRank to those pages?
You can tell Google not to pass PageRank by amending some links with a rel=”nofollow” attribute. A nofollowed link is not crawled by the search engines, and no PageRank or anchor text signals are transferred.
However, Google still sees nofollowed links as part of the total number of links on the page. The PageRank value available to pass through the remaining, followed links is thus reduced.
So for example, if you have a PageRank 18 webpage with 100 PR points that has four links on a page, and three of those links have rel=”nofollow” tags, the one link that doesn’t have rel=”nofollow” will probably pass only one-fourth, or 25 points, of link juice. (Find out when nofollow is essential below.)
Transferring PageRank/Link Juice with Internal Linking
You can help Google see pages of your website as subject matter authorities by linking to your own important pages from related articles.
For instance, if you have an article called “How To Do Keyword Research,” you can help reinforce to Google the relevance of this page for the subject/phrase “keyword research” by linking from an article reviewing a keyword research tool to your How To Do Keyword Research article. This linking strategy is part of effective siloing, which helps clarify your main website themes.
When Nofollow Is Essential
Adding rel=”nofollow” to a link may not conserve PageRank, as SEOs once used it to sculpt the flow of PR value through a site (aka “link sculpting”). Still, nofollow is essential for certain types of links:
Paid links and ads
Links that would dilute your subject relevance
Links to untrustworthy pages
Paid-for links and ads on your site MUST have a nofollow attribute (see Google’s policy on nofollow). If you have paid links that are left followed, the search engines might suspect you are trying to manipulate search results and slap your site with a ranking penalty. Google’s Penguin algorithm eats manipulative paid links for lunch, so stay off the menu by adding nofollow attributes where applicable.
Nofollow is also essential on links to off-topic pages, whether they’re internal or external to your site. You want to prevent search engines from misunderstanding what your pages are about. Linking relevant pages together reinforces your topic relevance; to preserve your silos, strategic use of the nofollow attribute can be applied when linking off-topic pages together.
A third case Google gives for using nofollow is for untrustworthy sites. Of course, you wouldn’t want to pass PageRank to a sketchy site.
A word of caution: Now that you understand basically how PageRank works, we don’t want to give you the wrong idea. It’s not true that the more links you have, the better off you are.
In today’s world, QUALITY is more important than quantity. Google penalties have caused many website owners to not only stop link building, but start link pruning instead. Poor quality links (i.e., links from spammy or off-topic sites) are like poison and can kill your search engine rankings. Only links from quality sites, and pages that are relevant to your website, will appear natural and not be subject to penalty. So never try to buy or solicit links — earn them naturally or not at all.
Want to know more? Learn more about link pruning, the action you take when links from low quality pages are giving Google the wrong idea about your website.
May 26, 2016
Why the Coming Google AdWords Changes Are Mobile Advertising Game-changers
Why the Coming Google AdWords Changes Are Mobile Advertising Game-changers was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Bigger text ads that get clicked more often
Ability to fine-tune your bidding by device type
Map ads that draw in mobile searchers near your store
New technology that better ties ad clicks to in-store visits
Ability to create similar audiences for search ad targeting
That and more is what’s coming to Google AdWords advertisers following announcements this past Tuesday. For our PPC SEM services clients and others, we’ll walk through the exciting opportunities coming out of Google Performance Summit.
We followed up this article with an on-air discussion of AdWords’ new game-changers:
“Mobile-First” Means Greater Reach
This week at the Google Performance Summit keynote we were introduced to a “completely re-imagined and rebuilt” AdWords system for a “mobile-first world.”
Both the AdWords advertising platform and Google Analytics are getting major redesigns to help search advertisers better meet mobile consumers’ needs. Advertisers are getting some new opportunities to interact with people specifically in those “micromoments” when a person wants to know something, do something, or buy something.
The bottom line is this: Marketers will have new ways to be present at critical points when an ad can perfectly answer a searcher’s intent and context.
Bigger Text Ads to Get More Clicks
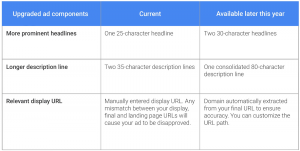
Text ads longer: Recent formatting changes in the Google search engine results page (SERP) paved the way for what Google announced as “the biggest update to the ad creative” in many years.
(Quick review: Ads stopped appearing in the right-hand column, and the main search results column increased from 512 pixels to around 600 pixels wide.)
Now AdWords text ads can have much longer headlines — up to two lines of 30 characters each — and descriptions can hold up to 80 characters with the new formatting on both desktop and mobile SERPs.
Here’s a comparison of existing text ads and the new expanded text ads:
—> Dramatic change here. With 50 percent more room for ad text overall, text ads can do a better job of delivering compelling messages highlighting features and benefits. PPC managers should take a look at expanding their current ad copy. Use additional words to give more info and more specifically engage target personas, which will increase CTRs (click-through rates). Google claims that testing has shown a 20 percent increase in CTR — that’s huuuuge!
Fine-Tuned Device-Type Bidding for Optimized CPA
Bid modifiers for ALL devices: Our prayers have been answered! Advertisers will be able to set individual bid adjustments for each device type. For instance, if your tablet ads are exhibiting poor performance, you can adjust the bid downward while leaving your other device bids the same, all within a single AdWords campaign.
—> This new bidding flexibility deserves the big applause it got at the AdWords Summit. Fine-tuning for optimal CPA can finally be accomplished via bid adjustments on every device. Better ROI!
New Ads in Google Maps to Drive Foot Traffic
Google Maps receives 1.5 billion destination searches per month. Using location extensions, advertisers can be found by nearby searchers by including a new promotional message within a local map result. For example, when someone searches in Google Maps for electronics stores, Best Buy could feature “10% off phone accessories” in local map results.
Promoted pins can show a logo and a special promotion or other ad message to a nearby person who’s looking at a map. For example, someone walking while searching might see a Starbucks offer pinned along the route. The opportunity here is huge for driving foot traffic to brick-and-mortar establishments. Google says that 30 percent of mobile searches are related to location, and location-related mobile searches are growing 50 percent faster than other types of mobile searches.
—> The ability to highlight a physical location on Google Maps is a game-changer. As an advertising platform, Maps can help local businesses get noticed by people who are nearby and drive in-store visits.
Mobile Responsive Display Ads Will Always Look Good and Require Less Work by Advertisers
Google-designed display ads: The new AdWords will do the work for you of building display ads. As the advertiser, you’ll need to provide only a headline, description, image and link; the system will then automatically design a responsive ad that appears differently for each platform throughout the Google Display Network (GDN). Google promises that such ads will be “beautiful and easy to click/swipe.”
—> Responsive mobile ads are the future. Letting Google auto-design ads may not suit every advertiser, especially if branding is a priority. The layout modification to fit each different platform will be convenient. The wording and image creation, where the real skill comes in, remain the advertiser’s job. But the production values of Google’s auto-generated ads are surprisingly high, and perfectly well-suited to constructing similar ads while testing ad messaging.
Reaching more GDN customers: Google shared a rather astonishing statistic: Advertisers on the GDN, which now numbers two million publisher sites, can reach a whopping 90 percent of all internet users.
Not to sit on their laurels, Google announced that the GDN reach will exceed that 90 percent by allowing advertisers to spread ads to “cross-exchange inventory.”
—> They weren’t specific about which ad exchanges or sites would start displaying GDN ads, but more sites = more conversions per GDN campaign — great for remarketing efforts!
New Tech to Tie Online Ads to In-store Activity
Google studies found that three-fourths of local mobile searchers who clicked an ad visited a store within a day, and 28 percent of those visits resulted in a purchase. It’s clear that AdWords is accountable for an increasing amount of in-store activity.
Beacon signals: Beacon signals will improve existing location data and track store visits better, letting advertisers measure the impact of online ads on in-store activity to build a local strategy. According to Larry Kim, Google will simply look at phone location history to tell whether the person who searched and clicked on your ad ended up walking into the store.
—> Tying online ad clicks to purchases in a physical store has so far been difficult, but increasingly this is how people shop. Beacons will help track a local advertising strategy.
Similar Audiences and Remarketing to Extend Your Targeted Ad Audience
Savvy advertisers know that GDN remarketing campaigns, whereby ads are shown to previous site visitors, are essential to maximizing traffic and conversion volume. An under-utilized variant that’s been around for a while, Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSAs), helps boost the performance of search campaigns. And Google has announced a new feature that will make RLSAs even more powerful …
Similar Audiences for Search: Reaching searchers who have similar interests as those who’ve already visited your site allows you to expand into bigger “similar audiences.” Google said this new feature will automatically create a similar audience for each remarketing and Customer Match list. These additional lists can be used to target RLSAs.
Demographics for Search Ads: Another format that’s currently in beta is DFSAs, which allow advertisers to target search ads using Google-inferred demographics data like age and gender.
—> Applying similar lists and demographic targeting to search campaigns will certainly boost traffic and conversion volume. Keep an eye on CPAs, though — these new audiences might convert at a lower rate than “non-RLSA” campaigns.
While We Wait …
Google is filling advertiser arsenals with some powerful new tools to be rolled out in coming months. At BCI we’ll be using them to boost our clients’ conversion volumes and profitability.
Why these changes now? We’re in the AI age of course! Google’s artificial intelligence-based technology, which uses machine learning, is making sense of the search giant’s vast amount of user data. From this, we advertisers are getting ground-breaking opportunities.
These changes will be rolling out through the year. Talk to us today to get your Google AdWords account in shape for when these hyper-targeted, mobile-first opportunities unfold for your business.
May 19, 2016
What a Career in CRO Looks Like #ConvCon
What a Career in CRO Looks Like #ConvCon was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Tim Ash, the Conversion Conference chair, has assembled a panel of CROs from a range of backgrounds to show us what a career in CRO might look like.
Chris Mercer runs an interactive agency SeriouslySimpleMarketing
Krista Seiden works in-house at Google
Alex Harris is a CRO consultant
What are the skills a CRO needs to work with you or be you?
Alex: Being a CRO consultant requires thick skin to get clients, getting results and keeping cash flow. You learn a lot. The ability to manage projects, manage PNL, and to find contractors to accomplish that. What’s specific to CRO consultant? To streamline your time to get the best results possible. Thinking about the clients and customers to get the best results possible. Much higher pressure on results.
What do you look at in a CRO as an employee?
Chris: It comes down to a UI systems person. There are CROs that are backend and CROs that are client facing. The back end CROs are very process focused, and comfortable with a system managing you. The front-end is a data-driven sales person, like a sales engineer. You have to constantly sell clients on waiting to call the test, and other coddling. A sales person who is data driven is pretty rare. It’s equivalent of finding a developer who understands marketing. If you’re that person, write your own ticket.
Krista: Someone who’s really going to dive into the analytics and find golden nuggets.
What’s the most effective way to become a contributor as an entry-level CRO?
Alex: Make mistakes early. Have mentors around you that can help you learn. Be in an organization that has some risk tolerance.
Chris: They hire people as marketing manager assistants and give a foundation for how to explain starting from the data. It’s important to soak in the data at first and then coming up that will be ingrained.
Krista: If you’re just starting out in CRO because it’s becoming part of your job, there’s a good chance that your organization doesn’t have a full-time dedicated CRO person. When she started a new job, she had to be the enthusiastic advocate for doing CRO.
Tim: If you’re not passionate about it, if you don’t really want to help visitors to your website have a less painful experience, you shouldn’t be in CRO.
How do you manage CROs?
Krista: Teams that she’s worked with can struggle to find the meaningful tests. Things she challenges CROs to do is dive into the data and ask the hard questions.
Chris: It’s about building a system that manages them and they have a hand in that so the management gets buy in. Testing velocity is a metric that can be objectively tested and gives the CRO a system to manage themselves.
Krista: An initiative to have 100 tests in the quarter caused a lot of poor quality tests going out.
Tim: What gets measured gets done. People will adjust to the penalty-reward system you put in front of them. An award to the highest test velocity doesn’t account for business outcomes. The focus should be on the quality and not the quantity of the test. More experienced manager will focus on managing systems and processes, not people.
Alex: He’s turned designers into CROs, analysts into CROs, and he challenges them to take a decision to its next step — owning the test, presenting to the client, and getting mentorship and guidance from Alex along the way. Young talent tends to play it safe and he pushes people to try new things. Encourage risk-taking as a manger.
What’s the biggest challenge you face if you’re a full-time CRO?
Alex: Time management. Start with where you’re going to make the most money and then work back from there. It’s about prioritization.
Chris: It’s hard to grow the agency. As we grow the company, some structure has to be left behind so someone can come in and take their place as others move up. Asking questions like how do you know what you know? It’s frameworks, checklists – extracting their knowledge and formulating it.
Where should CRO ideally live in a company, or to whom does it report?
Alex: An early startup he was in didn’t know where CRO went in the organization. Ultimately they built an acquisition team that held CRO.
Tim: You could put it under analytics, under product development, under IT … these are difficult.
Krista: She’s seen it under product, under research. In large companies, she’s seen it best effective aligned with analytics under marketing.
Chris: The Make More Money department.
Tim: At SiteTuners they make organizations more mature on CRO. Customer experience, measurement, tools and technology, process and culture, and skills and structure. At the advanced model, it’s reporting to the very top of marketing, the CMO. Not part of the team that touches the web experience. The most dynamic companies have a team reporting to the CMO, and every other part of the company ask them to break, re-break, fix and then give it back. Not part of the team that touches the web experience.
Krista: She thinks that Tim’s point about not having CRO as part of the team that touches the web experience keeps the team from being invested.
Tim: The problem at the website experience level is that you’re invested in incremental tinkering improvements rather than at the strategic level.
Advice for pricing your services?
Alex: Move to a retainer model. Get the customer the best results possible in a month time. Start small and then every client you get, raise your price.
Chris: If you want to grow and add to your staff, you need to charge more than you think you need to. Add some skin in the game clause – as I increase your revenue, dear client, then I can earn from that as bonus based on performance. This is good for small businesses where you’re dealing with the principles.
Tim: This doesn’t work for big businesses because the contract negotiations get caught up on that clause and you lose time when you could be getting more work.
Alex: You can also start with packages of tests, like one to three tests to get started.
Tim: Goes into retainer after some consultation analysis. Then they have two packages, the high gas package and the minimum required for results.
Effective CRO for Particular Roles
Tim is going to name off job roles and the panel will share their biggest challenge to being an effective CRO.
Copywriter
Alex: Be persuasive using data – be direct response focused.
Krista: Not being too tied to a perfect message crafted in your head but tie back to what the data tells you.
Chris: There are more research-driven copywriters.
User Experience Engineer
Krista: mindset for beautiful design will be their biggest hurdle
Chris: understanding purpose-driven design will be their biggest hurdle
Psychologist
Chris: Over-complicating will be the weakness. It goes back to Mona Patel’s BS excuse persona of the Scaffolder. (Read the liveblog coverage of Patel’s keynote).
Alex: When you’re defining the user journey you focus on understanding the psych for user personas, but may overlook the design aspect.
Mathematician or Statistician
Alex: You may look at the numbers but how do you understand it holistically, melding the qualitative and quantitative. And they may not have the business knowledge to understand how an optimization will affect the business.
Krista: She sat on the core team for the Optimize 360 product. A statistician on the team was very vocal about how the test reports would look and the data provided to the user. But she doesn’t think the user needs to see too many details. They wanted to pair it down to the key reports.
Tim: Sometimes the numbers lie. Running a test where environmental factors can skew the data. What’s missing is the context of the numbers — the business context.
Subscribe to the blog to get all the news coming out of Conversion Conference 2016!
How to Conduct Solid, Data-Driven Conversion Research #ConvCon
How to Conduct Solid, Data-Driven Conversion Research #ConvCon was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
“If I had an hour to save the world, I’d spend 55 minutes identifying the problem and 5 minutes implementing the solution.” — Albert Einstein
You’re tuned in to Conversion Conference 2016 and a presentation by Michael Aagaard of Unbounce. He loves that quote by Einstein because it relates to CRO. The story he’s going to tell today is about how we can change our mindset to just straight testing and broadening it to understanding the problem.
He starts us off viewing a landing page with lead capture form. Being a conversion optimizer, he wanted to optimize the page. He removed three of the fields on what he’d call a monster form. The result was 14% lower conversions. Ouch! So next he went looking at where the drop off occurs on the form. He found which form fields had low interaction and high drop-off and addressed them by rearranging the order of the fields (putting ones that were a low commitment higher up) and tweaked label copy.
This time they got 19% increase in conversions.
The question: why didn’t he do the research right away and why did who jump to best practices?
It’s very difficult to understand a problem that you don’t understand. Vice versa, it’s easy to solve a problem when you understand it.
He asked other conversion optimizers what keeps them from doing conversion research:
Time
Client/Company Buy-in
Budget
Not knowing where to start
Split testing is not an excuse to skip your homework.
6 Things You Can Do Right Away
… to conduct better research, better hypotheses, get better results.
1. Manual step-drop analysis with Google Analytics.
Same with ecommerce.
There’s a custom report in GA that he wrote and we might be able to get it later.
2. Run feedback polls on critical pages.
There’s a conflict in CROs.
Get more data
Don’t bother users
For everyday ninja analysis, feedback polls are cool, unobtrusive, and you just ask one questions. But you can do them wrong. A question like “did you find what you were looking for today” and then a scale of 1 to 10 is bad. Start with the question “what were you looking for” and then “did you find it.” What does it mean if 50% of people choose 4? That data is useless.
His tip is to lower the perceived time investment of filling out the poll with clever formatting.
The person will click on “yes” or “no” and then the form will change to let them type in the reason why.
3. Conduct interviews with sales and support.
These are the questions to ask them:
What are the top three questions from potential customers?
How do you answer when you get these questions?
Are there any particular aspects of ______ that people don’t understand?
What aspects of ______ do people like the most/least?
Did I miss anything important? Got something to add?
4. Perform 5-second tests.
Here’s the tool: http://fivesecondtest.com/. You give a user a screenshot to view for five seconds and then ask, “What do you think this page was about?” He showed users an Unbounce page with an employee of theirs on the page. Yes, we think people on pages is good for conversions. But when they showed that page to five-second testers, no one knew what the page was about, and some even said they were distracted by the image.
5. Calculate your sample size and test duration.
Before you can call a test trustworthy, you need statistical significance. There’s a very fascinating set of calculations he does. Look for a simple size and test duration calculator. Unbounce.com has one A/B Test Duration & Sample Size Calculator.
6. Formulate a data-driven test hypothesis.
You need to know some things before you can make a hypothesis:
Why do we think we need to make a change?
What is it that we want to change?
What impact do we expect to see?
How will we measure this impact?
When do we expect to see results?
Here’s a mad-libs style hypothesis exercise you can fill out for your hypothesis:
Because ________, we expect that ________ will cause ________. We’ll measure this using ________. We expect to see reliable results in ________.
It’s all about seeing through the eyes of your users. Data driven empathy is what it’s about. He gives credit to Andy Crestodina, sitting behind me, for that phrase.
The reasons that you have to do conversion research:
Time
Client/company buy-in
Budget
Don’t know where to start
Final Thought
Be like Einstein: prioritize understanding the problem before you start your testing. Always be aware of bias and be critical of data (you can make it say whatever you want if you torture it enough). Also, split testing is only a tool.
Subscribe to the blog to get all the news coming out of Conversion Conference 2016!
Essential Analytics to Turbo-Charge Your CRO #ConvCon
Essential Analytics to Turbo-Charge Your CRO #ConvCon was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Krista Seiden is an analytics advocate at Google. She’s spent lots of years as a practitioner of analytics and optimization at Google, the Apollo Group and Adobe. She’s also co-chair of the San Francisco chapter of the Digital Analytics Association.
Here’s her agenda:
How Analysis Drives CRO
5 Tips for Accelerating CRO via Analytics
Bonus Tip: Rapid Optimization Plan
The Future of Testing, Adapting and Personalizing

How Analysis Drives Optimization
What is optimization? Conversion rate optimization is the ongoing, data-driven process of continually discovering what works for your consumer.
#CRO is the ongoing, data-driven process of discovering what works for your consumer. @KristaSeiden
Click To Tweet
Testing or analysis? Whether testing or analysis is appropriate depends on the question you’re asking or the hypothesis you have. You can use analytics to justify the test you want to run.

Conversion rate optimization requires analytics and testing.
Why don’t people convert? There are many factors that can contribute to low conversion rate:
User experience
Site content and personalization
Actionable web analytics
Development resources
Next, she’ll give five tips for accelerating CRO via analytics.
Tip #1: Implement Ways to Track CRO
Email testing: Use campaign tagging to distinguish variations. Use campaign tracking to tag calls to action (CTAs) on buttons and links from email to test different headlines or email copy.
Ad testing: Use the utm_content slot to denote the ad variation. She usually describes the special offer — it’ll add a lot of light to your analysis later on.
Social media testing: Tag each post with unique campaign parameters to ensure you can track back to find out which individual post and channel are driving the highest conversions.
Use the dataLayer to collect test IDs. If you’re using a tag management system, you’ll have a data layer.
Tip #2: Set Up Analytics Goals to Track CRO Success
In analytics, you can set goals and create a funnel for that goal.

Example of a three-step CRO funnel
In this slide, we see that it’s a three-page sign-up flow. She actually has set goals for each of those steps (micro conversions) leading to the user completing the final goal, signing up (macro conversion).
Tip #3: Your Site Can Tell You What’s Important
Site Search will tell you what topics people are looking for on your site. Take that information and use it to determine your roadmap for different posts you’re going to write.
Heat maps can pinpoint areas to optimize. The Crazyegg confetti report of where and when people click even lets you sort by time to click. How long does it take a visitor to click what you want? Are they clicking on what you want, or are they distracted by something else on the page?
Tip #4: Use Key Google Analytics Reports
The Devices report (in Google Analytics) lets you look at where conversions came from. Do you need to spend more time optimizing the mobile experience?
Browser reports and the Browser Version report tell you if your performance varies based on browser types and versions.
The Site Search report lets you create a custom report and see when people search for something and also convert. Then you can create more content about that topic.
Fallout Funnel is her favorite report. You can zoom in on the flow and see where the drop offs are happening in the funnel.
A few other report ideas:
Look for high traffic, high bounce rate landing pages and segment these to find out if performance varies by demographic, browser, device or other factors (such as location).
Use custom funnels to identify user drop off through your path to conversion.
Tip #5: Qualitative Surveys as CRO Tie-breakers
Add to quantitative testing and analysis with qualitative feedback. The combination is powerful. You can ask how satisfied they are with multiple choices of satisfaction levels and ask what the main reason they visited today was. You can also ask who they are, and that gives you another lens to analyze the data against.
Bonus Tip: Analytics to the Rescue with a Rapid Optimization Plan
She explains that over two years, they ran a lot of tests before launching a site redesign: 453 unique variations, 159 unique tests, 25 locales and 4 different product lines. The result was 50+ key learnings.
What they tested:
CTAs
Headlines (see variants in slide below)
Images
Grids for pricing
Demos

CRO testing involving 5 headline variations
“If we see a 5 percent increase in sign-ups, then we’ll launch the new site,” she says. They didn’t reach the 5 percent mark; the sign-ups were flat. So she dove into analytics. She saw that they might want to change the button color to the old style. They changed the color of the icons. They also found a video that was a blank part of the page if the user scrolled too quickly. They addressed these three items and tested again, and this time they did see the 5 percent increase they were looking for — test validated.
Read Krista’s article for more details: Rapid Optimization Plan Blog Post
The Future of Analytics, CRO and Testing
It’s easier to have an engaging conversation in the offline world. Online it’s more difficult, but we have analytics to slice and dice our traffic. Even still, we serve people the same web experience even though we know they are different and have preferences.
Google Optimize 360 customizes your site by customer.

Personalization is the big bonus of Optimize 360. You can use the audience segments built in GA to target experiences to different customers on the web. If you’re a travel brand, you can segment your customers by different levels of spend. You can target people on the site and give them a different experience.
Next, she explains how Google Optimize 360 makes enterprise-level testing and personalization simple. It’s because they designed it to integrate (“best-in-class”) with the Google Analytics 360 Suite and other Google products:
Simple to use from start to finish
With powerful testing and personalization capabilities that support sophisticated needs
Enabling users to act on all their data seamlessly.
Because this is the scenario we all want to get to:

Subscribe to the blog to get all the news coming out of Conversion Conference 2016!
Engineering Persuasion, Emotion and Trust for Higher Conversions #ConvCon
Engineering Persuasion, Emotion and Trust for Higher Conversions #ConvCon was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
You’re tuned in to the morning keynote of the 2016 Conversion Conference. Dr. Eric Schaffer, HFI Laboratories, is a psychologist and human experience engineer will talk to us about the complex science behind UX.
How can we tell a computer program is going to convert? A user experience engineer thinks about conversion in the model of a mouse and a piece of cheese. Between the two is an electrical grid. The levers you pull are: you can increase the size of the cheese and decrease the shock of the electricity. If you’re giving away free Jaguars, your emails can suck.
“UX design is focused on decreasing the shock.” -@EricSchaffer
Click To Tweet
We have tools to let us see where the eye moves on a page to maximize the visual links, or visual access. People scan complex areas, saturated colors and dark areas. Having a person in an ad looking at the product or text makes the viewer look at that text or product.
Removing the complexity from forms is one way to reduce shock. But what else can we do?
Engineering Performance and Persuasion
Think about PET. PET = persuasion, emotion and trust. In other words, PET is persuasion engineering.
When do we have hope?
The power of relatively is something a PET engineer uses to reduce shock and increase usability.
Compare these two slides. It might look like shipping costs a lot so the user abandons. Add another big number (money saved) and that shipping cost isn’t a detractor. We’re suckers for the scarcity principle.
Look at the most persuasive sites. Amazon, Facebook and YouTube. They aren’t “pretty” but they have value and persuade in other ways.
PET Flow Strategy
We want to get direction through evidence-based design. We need user data. We do surveys using scales to get feedback. Unfortunately this is unreliable.
Scarcity and divestiture influence people. Divestiture version is the difference between what we say we’d pay for something we didn’t get versus what we’d sell a ticket for that we believe is rare. In a research study, our typical response to “did you like it” isn’t useful.
Galvanic skin response can test and find when a person is tense, but you can’t tell why they’re tense. In eye-tracking studies, you can tell where people are looking and when pupils dilate, but you can’t tell why their pupils dilate. You can study facial expression and even when parts of the brain light up – but you can’t tell why. This is not useful for design.
A/B testing and big data will tell us which version is working. There is some information you can never get to. So there’s a psychology methodology of doing deep interviews to understand the emotional motivations behind decision making.
Fear, sex, survival and progeny — these are our basic underlying motivators. We can research users and decompose these drives, blocks and feelings. Schaffer mentions there was a study on youth that found young customers like having money. Why run that study?! Anyone could have told you that! But take a look at the findings:
You can test ads against the prediction model. You can see before you go to market how the ad will be received. This is the core of omnichannel strategy — the biggest design challenge UX companies have today. The challenge we have to overcome is getting everyone and everything to fit together — because when you silo departments, they come out with strange ideas.
Unintended Consequences of Giving Away Things for Free
Giving away stuff isn’t a great strategy. It has unintended consequences. Here’s a story. There’s an old man who lives in a neighborhood that’s getting run down and kids are making noise by his home. He goes to the kids and asks them to make noise by his house and he’ll give them a dollar. They do and he does. The next day is the same. Then the next day the kids come to his house and say we’re ready to make noise! And he says he can only afford to give them $.10 and they say they’re never going to make noise by his house again.
Subscribe to the blog to get all the news coming out of Conversion Conference 2016!
Optimized Employee Experience has Direct Effect on UX #ConvCon Keynote
Optimized Employee Experience has Direct Effect on UX #ConvCon Keynote was originally published on BruceClay.com, home of expert search engine optimization tips.
Mona Patel is the author of “Reframe: Shift the Way You Work, Innovate, and Think.” When she arrived here at Conversion Conference she was struck by the attendees, finding it amazing how much time we spend working to understand our customers. She has a background in design and UX so optimizing the user experience and meeting customers’ needs is what she thinks about.
But Patel wonders if we ever take that lens and point it inward. She wants to enable businesses so that employees feel optimized and fulfilled. Why? Employees are a big part of customer service. The way employees interact with your customers are going to affect your customer experience.
In 2009 she started her own company of one. She had clients and then she got pregnant. She decided to hire people to take care of her clients while she was on maternity leave. She wanted to design a hiring process that would match the customer experience she wanted. Patel started thinking about how to create a platform where she took talented people and made sure they were optimized to bring their best work to the marketplace.
This brought her to thinking about EX – employee experience. Where would you rank how optimized you feel at work? If you’re an entrepreneur or company of one, where would someone you hire rank their optimization of employee experience? Where would you rank your work experience? If you’re not a 10, write down the reasons your work is not optimized – areas where you could see improving.
If you wrote some things down, there’s good news. These are probably excuses. We can fix excuses. She’ll cover the excuses here. The fixes are in her book.
The BS Excuse Personas
She tells a story of a visit she made to a CEO. When she arrived she was pointed to the fourth floor. Turns out that was the gym and she actually is made to take a physical test before she could see the CEO. Does a test like this work? Who knows! Is there any data to support it?
Persona #1: The Brat
A brat is a person who judges an idea before they have data. They don’t listen to the data or the facts. They already know. We see this come up as “this is never going to work.” It comes up in design and in the workplace. This is one of the most common excuse personas we see in the design world.
Persona #2: The Bullied
A bullied persona is the one who thinks they’re a victim. They aren’t going to do anything because someone’s holding them down.
Persona #3: The Bottlenecker
The bottlenecker requires that all ideas go through them before they’re implemented. He or she will stick themselves into a process where they don’t need to be. A bottlenecker likes to be busy, but because they’re so busy, they don’t take action on plans to improve.
Persona #4: The Scaffolder
The scaffolder is the persona who builds up an idea so big that they make an excuse that something can’t be done. A larger topic — baby boomers or the economy — might be the excuse for something in the way of actually making changes.
Persona #5: The Square
The square loves the lines in the box to explain why they can’t come up with better ideas and can’t make changes. In design work we might hear that the technology doesn’t support it or there are regulations. Their excuses are actual facts that might exist but which really shouldn’t have anything to do with making changes. Look at your business from a design lens; that forces you to start from a blank slate and create.
Persona #6: The Sheep
The sheep has a herd mentality. This person has to do what everyone else is doing. They think things like, “I’m not happy at my job but no one else is either, and it won’t be better anywhere else.” If you feel like this, you might be right — but you’re not going to feel like a 10 on your satisfaction rating scale. You need to stop worrying about being right.
Persona #7: The Blamer
The blamer is going to say “It’s not me. It’s you.” It’s always something else. The blaming prevents you from having to solve the problem.
Persona #8: The Blamer
The slacker is the passenger in the car. They’re definitely not driving. And you may want to ask yourself if it’s preventing you from being happy.
Stop the Excuses
Do you relate to any of these personas? Do you work with anyone who manifests some of these traits? Stop the excuses. What’s holding you back?
Think about what you need to do to move your numbers up and get to the ten on the job satisfaction scale. Don’t let the BS excuses keep you down. If you start thinking “yeah but” then think about it – you’re bringing up excuses again.
Touché, Mona.
Subscribe to the blog to get all the news coming out of Conversion Conference 2016!