Pearl Zhu's Blog, page 1279
November 10, 2016
The New Book “IT Innovation” Introduction Chapter 7 Empower IT as Digital Change Agent
 Digital is about changes. Digital transformation is a journey. Literally transformation is a journey. Literally transformation is to radically change the nature of something. Digital transformation is a radical change of the business via its underlying business processes, invisible business culture or emergent new business model, etc. There are “significant bits and bytes of information” needed when evaluating a new market, new technology or any business growth opportunity. Hence IT should be run as digital change agent to explore such an “art of possible.”
Digital is about changes. Digital transformation is a journey. Literally transformation is a journey. Literally transformation is to radically change the nature of something. Digital transformation is a radical change of the business via its underlying business processes, invisible business culture or emergent new business model, etc. There are “significant bits and bytes of information” needed when evaluating a new market, new technology or any business growth opportunity. Hence IT should be run as digital change agent to explore such an “art of possible.”Running IT as a change engine of the business: Organizations can make major leaps forward in change capability by involving the entire organization in major change efforts that support key business strategies to drive performance improvement. Change Management is all about balancing the main elements impacting changes such as people, strategies, processes, procedures, and IT. IT is not only the superglue, but also an integrator to weave all important change elements seamlessly and make people change, process change, and technology change sustainable. Change is a dance between the top management and the affected parts of the organization. And Change is a dance between the top management and the affected parts of the organization. And Change Management has to maintain and fix any imbalance in those elements by involving the executives in the HR, IT and operations, and take a structural approach, to make sure all of the management is on board and educated well on the change objectives and how to carry them out effectively.
A change agent IT should get deeper understanding the issues facing both internal customers and end customers: Change is not for its own sake, it is IT responsibility to identify opportunities for the business transformation wherever analysis and assessment indicate the potential benefits of transformation efforts, to oversee key business processes and influence organizational cultures, to enable and catalyze the business transformation. The business transformation should not be undertaken lightly because it must align diverse and divergent stakeholders’ interests toward a common goal. IT is in a unique position because it can see the whole organization and should have the program skills to implement transformation successfully.
 Optimizing people/performance management: Either managing IT talent or customer/vendor relationship, people are usually the weakest link, but the most expensive investment in IT and business. While IT is pervasive these days, this will come about as more people begin to interact with and understand IT and what can be provided. From discerning customers, demanding executives to enthusiastic vendors, identify, cultivate and optimize people management capability via following fundamental IT principle. First people - then process - then technology in that order. Optimization is not just about fixing things, but to leveraging trade off to improve business efficiency, flexibility, agility, and risk intelligence.
Optimizing people/performance management: Either managing IT talent or customer/vendor relationship, people are usually the weakest link, but the most expensive investment in IT and business. While IT is pervasive these days, this will come about as more people begin to interact with and understand IT and what can be provided. From discerning customers, demanding executives to enthusiastic vendors, identify, cultivate and optimize people management capability via following fundamental IT principle. First people - then process - then technology in that order. Optimization is not just about fixing things, but to leveraging trade off to improve business efficiency, flexibility, agility, and risk intelligence. Change cannot be just another thing that needs to be accomplished. It has to be woven into the collective mentality, process, action, and communication of the organization. It takes a lot of energy to break bad habits and outdated thought processes such as silo mentality, get out of comfort zone, frame the right problems and solving them effectively. Change is happening at a more rapid pace now, if you make change part of your routine and ongoing business capability, then change becomes easier to deal with and improve strategy execution.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 10, 2016 22:37
November 9, 2016
“Digital Master” Book Monthly Tuning: The Characteristics of Digital Enterprise Nov. 2016
 Digital makes a significant impact on every aspect of the business from people, process to technology, both horizontally and vertically. Digital becomes the very fabric of high performing business, being outside-in and customer-centric is the new mantra for forward-looking and high mature digital organizations today. At the heart of digital, it is people and how to build a customer-centric organization. But how to assess the digital fitness of your organization for such a paradigm shift. The Characteristics of Digital Enterprise Three Portmanteau Hybrid Words to Envision a Digital Organization? Organizations large or small are on the journey to digital transformation, it is not an overnight phenomenon, but a well-planning strategy with the step-wise approach. There are physical buildings and virtual, always-on working environment; there are next innovation practices and “always do things like this” best practices; there’s abundance of information but still the scarcity of insight. It is the hybrid business world full of options. Digital is the age of alternatives, here are three portmanteau hybrid words to convey the management principles in running a digital organization.?
Digital makes a significant impact on every aspect of the business from people, process to technology, both horizontally and vertically. Digital becomes the very fabric of high performing business, being outside-in and customer-centric is the new mantra for forward-looking and high mature digital organizations today. At the heart of digital, it is people and how to build a customer-centric organization. But how to assess the digital fitness of your organization for such a paradigm shift. The Characteristics of Digital Enterprise Three Portmanteau Hybrid Words to Envision a Digital Organization? Organizations large or small are on the journey to digital transformation, it is not an overnight phenomenon, but a well-planning strategy with the step-wise approach. There are physical buildings and virtual, always-on working environment; there are next innovation practices and “always do things like this” best practices; there’s abundance of information but still the scarcity of insight. It is the hybrid business world full of options. Digital is the age of alternatives, here are three portmanteau hybrid words to convey the management principles in running a digital organization.?Three Characteristics of Digital Organizations Organizations large or small are on the journey of digital transformation. Digitalization implies the full-scale changes in the way the business is conducted so that simply adopting a new digital technology may not be sufficient. You have to transform the company's underlying functions, processes, and cultures, and organization as a whole with adjusted digital speed. Otherwise, companies will begin a decline from its previous good performance. More specifically, what are the characteristics of digital organizations, and can you make an objective self-assessment whether your organization is a Digital Master or a laggard?Sharpen Three Business Elements to Get the Organization “Digital Ready” Organizations large and small are on the journey of digital transformation. “Being digital ready” goes beyond just applying the latest digital technology, or renovate IT organization only. It is a holistic effort and multifaceted discipline to touch every aspect of the business. Here are three critical business elements need to be sharpened in order to get the organization “Digital Ready.”?
Three Characteristics of Digital Organizations? Digital organizations are hyper-connected and interdependent, they need to be agile and innovative in order to adapt to the “VUCA” digital new normals. With the fast pace of changes and emerging digital technologies such as “SMAC,” companies large or small are also brainstorming and experimenting the next generation of organizational structure design, to improve employees’ engagement, productivity, as well as creativity across the enterprise ecosystem. So what are the important characteristics of digital organizations from organizational design and business innovation perspective?
 Three Digital Effects to Catalyze Business Maturity: Digital transformation represents the next stage of business maturity which will improve how the enterprise works and interact with its ecosystem, with the customer at the center of its focus. Digital becomes the very fabric of the modern business, being outside-in and customer-centric is the new mantra for forward-looking digital organizations today. So how can businesses amplify positive digital effects and grow into the high-performing Digital Master?
Three Digital Effects to Catalyze Business Maturity: Digital transformation represents the next stage of business maturity which will improve how the enterprise works and interact with its ecosystem, with the customer at the center of its focus. Digital becomes the very fabric of the modern business, being outside-in and customer-centric is the new mantra for forward-looking digital organizations today. So how can businesses amplify positive digital effects and grow into the high-performing Digital Master?The “Future of CIO” Blog has reached 1.5+million page views with about #3200+ blog posting in 59+ different categories of leadership, management, strategy, digitalization, change/talent, etc. blog posting. The content richness is not for its own sake, but to convey the vision and share the wisdom, to inspire critical thinking and spur healthy debates. Blogging is not about writing, but about thinking and innovating the new ideas; it’s not just about WHAT to say, but about WHY to say, and HOW to say it. It reflects the color and shade of your thought patterns, and it indicates the peaks and curves of your thinking waves. Unlike pure entertainment, quality and professional content takes time for digesting, contemplation and engaging, and therefore, it takes the time to attract the "hungry minds" and the "deep souls." It’s the journey to amplify diverse voices and deepen digital footprints, and it's the way to harness your innovative spirit.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 09, 2016 22:27
Understanding Three Business Effects and Paradoxes for Improving Management Effectiveness
Modern management is both science and art. We should learn from both our own experiences and from others’ lessons, as well the collective wisdom.
 Either at the individual level or organizational level, people experience, grow, fail and learn, from their own experiences or others' failure lessens. There are many interesting effects in the respective field of the study. From a business management perspective, which “effects” should you understand in order to achieve management effectiveness and efficiency? The Abilene Paradox: Like many things in the world, there are both pros and cons in the crowd of wisdom and team decision-making. The team decision works because they bring different perspectives and more information to the table. If there is a hererogenerous group setting, they help balance out the biases that from which we all suffer, or fill the blind spots each one of us perhaps has some. They help generate more of everything (viable alternatives, criteria, etc.), all of which is shown to improve the quality of decisions. However, there are a number of contrary factors at play in a team decision-making. There is the Abilene Paradox that comes into play often in groups. In an Abilene paradox, a group of people collectively decide on a course of action that is counter to the preferences of many of the individuals in the group. It involves a common breakdown of group communication in which each member mistakenly believes that their own preferences are counter to the group's and, therefore, does not raise objections. A common phrase relating to the Abilene paradox is a desire to not "rock the boat." That often turns little defect to the bigger problem or even the serious business failure.
Either at the individual level or organizational level, people experience, grow, fail and learn, from their own experiences or others' failure lessens. There are many interesting effects in the respective field of the study. From a business management perspective, which “effects” should you understand in order to achieve management effectiveness and efficiency? The Abilene Paradox: Like many things in the world, there are both pros and cons in the crowd of wisdom and team decision-making. The team decision works because they bring different perspectives and more information to the table. If there is a hererogenerous group setting, they help balance out the biases that from which we all suffer, or fill the blind spots each one of us perhaps has some. They help generate more of everything (viable alternatives, criteria, etc.), all of which is shown to improve the quality of decisions. However, there are a number of contrary factors at play in a team decision-making. There is the Abilene Paradox that comes into play often in groups. In an Abilene paradox, a group of people collectively decide on a course of action that is counter to the preferences of many of the individuals in the group. It involves a common breakdown of group communication in which each member mistakenly believes that their own preferences are counter to the group's and, therefore, does not raise objections. A common phrase relating to the Abilene paradox is a desire to not "rock the boat." That often turns little defect to the bigger problem or even the serious business failure.
Gestalt Effect: The Gestalt effect is the capability of our brain to generate whole forms, particularly with respect to the visual recognition of global figures instead of just collections of simpler and unrelated elements (points, lines, curves). Gestalt psychology tries to understand the laws of our ability to acquire and maintain meaningful perceptions in an apparently chaotic world. The central principle of Gestalt psychology is that the mind forms a “whole” with self-organizing tendencies. This principle maintains that the human mind considers objects in their entirety before, or in parallel with, the perception of their individual parts; suggesting the whole is other than the sum of its parts. The fundamental "formula" of Gestalt theory could be expressed in this way, "There are whole, the behavior of which is not determined by that of their individual elements, but where the part-processes are themselves determined by the intrinsic nature of the whole. It is the hope of Gestalt theory to determine the nature of such wholes." From a business management perspective, it encourages holistic thinking and understanding the intrinsic interconnectivity between parts and whole, in order to solve problems in a structural way.
 Bystander effect. As social psychologists have long known, people are far more likely to aid a victim in distress or report an apparent emergency if they are alone than if other people are around. One reason: If you’re uncertain what to do, you’re likely to take your cues from other people whenever possible. Some psychologists suggest that simply being aware of this tendency is perhaps the greatest way to break the cycle. From the business management perspective, when faced with a situation that requires action, understanding how the bystander effect might be holding you back and consciously taking steps to overcome it can help.
Bystander effect. As social psychologists have long known, people are far more likely to aid a victim in distress or report an apparent emergency if they are alone than if other people are around. One reason: If you’re uncertain what to do, you’re likely to take your cues from other people whenever possible. Some psychologists suggest that simply being aware of this tendency is perhaps the greatest way to break the cycle. From the business management perspective, when faced with a situation that requires action, understanding how the bystander effect might be holding you back and consciously taking steps to overcome it can help.
Modern management is both science and art. We should learn from both our own experiences and from others’ lessons, as well the collective wisdom. The difference in utility between one’s own experience and the experience of another is nothing more or less than the difference between the credibility of direct observation coupled with one's own interpretation of it, and the credibility of a reported observation coupled with multiple interpretations that arise from multiple examinations of the observation. Not just get puzzled by those effects or paradoxes, but to avoid the pitfalls, learn and grow from them, to improve digital management maturity.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
 Either at the individual level or organizational level, people experience, grow, fail and learn, from their own experiences or others' failure lessens. There are many interesting effects in the respective field of the study. From a business management perspective, which “effects” should you understand in order to achieve management effectiveness and efficiency? The Abilene Paradox: Like many things in the world, there are both pros and cons in the crowd of wisdom and team decision-making. The team decision works because they bring different perspectives and more information to the table. If there is a hererogenerous group setting, they help balance out the biases that from which we all suffer, or fill the blind spots each one of us perhaps has some. They help generate more of everything (viable alternatives, criteria, etc.), all of which is shown to improve the quality of decisions. However, there are a number of contrary factors at play in a team decision-making. There is the Abilene Paradox that comes into play often in groups. In an Abilene paradox, a group of people collectively decide on a course of action that is counter to the preferences of many of the individuals in the group. It involves a common breakdown of group communication in which each member mistakenly believes that their own preferences are counter to the group's and, therefore, does not raise objections. A common phrase relating to the Abilene paradox is a desire to not "rock the boat." That often turns little defect to the bigger problem or even the serious business failure.
Either at the individual level or organizational level, people experience, grow, fail and learn, from their own experiences or others' failure lessens. There are many interesting effects in the respective field of the study. From a business management perspective, which “effects” should you understand in order to achieve management effectiveness and efficiency? The Abilene Paradox: Like many things in the world, there are both pros and cons in the crowd of wisdom and team decision-making. The team decision works because they bring different perspectives and more information to the table. If there is a hererogenerous group setting, they help balance out the biases that from which we all suffer, or fill the blind spots each one of us perhaps has some. They help generate more of everything (viable alternatives, criteria, etc.), all of which is shown to improve the quality of decisions. However, there are a number of contrary factors at play in a team decision-making. There is the Abilene Paradox that comes into play often in groups. In an Abilene paradox, a group of people collectively decide on a course of action that is counter to the preferences of many of the individuals in the group. It involves a common breakdown of group communication in which each member mistakenly believes that their own preferences are counter to the group's and, therefore, does not raise objections. A common phrase relating to the Abilene paradox is a desire to not "rock the boat." That often turns little defect to the bigger problem or even the serious business failure.Gestalt Effect: The Gestalt effect is the capability of our brain to generate whole forms, particularly with respect to the visual recognition of global figures instead of just collections of simpler and unrelated elements (points, lines, curves). Gestalt psychology tries to understand the laws of our ability to acquire and maintain meaningful perceptions in an apparently chaotic world. The central principle of Gestalt psychology is that the mind forms a “whole” with self-organizing tendencies. This principle maintains that the human mind considers objects in their entirety before, or in parallel with, the perception of their individual parts; suggesting the whole is other than the sum of its parts. The fundamental "formula" of Gestalt theory could be expressed in this way, "There are whole, the behavior of which is not determined by that of their individual elements, but where the part-processes are themselves determined by the intrinsic nature of the whole. It is the hope of Gestalt theory to determine the nature of such wholes." From a business management perspective, it encourages holistic thinking and understanding the intrinsic interconnectivity between parts and whole, in order to solve problems in a structural way.
 Bystander effect. As social psychologists have long known, people are far more likely to aid a victim in distress or report an apparent emergency if they are alone than if other people are around. One reason: If you’re uncertain what to do, you’re likely to take your cues from other people whenever possible. Some psychologists suggest that simply being aware of this tendency is perhaps the greatest way to break the cycle. From the business management perspective, when faced with a situation that requires action, understanding how the bystander effect might be holding you back and consciously taking steps to overcome it can help.
Bystander effect. As social psychologists have long known, people are far more likely to aid a victim in distress or report an apparent emergency if they are alone than if other people are around. One reason: If you’re uncertain what to do, you’re likely to take your cues from other people whenever possible. Some psychologists suggest that simply being aware of this tendency is perhaps the greatest way to break the cycle. From the business management perspective, when faced with a situation that requires action, understanding how the bystander effect might be holding you back and consciously taking steps to overcome it can help.Modern management is both science and art. We should learn from both our own experiences and from others’ lessons, as well the collective wisdom. The difference in utility between one’s own experience and the experience of another is nothing more or less than the difference between the credibility of direct observation coupled with one's own interpretation of it, and the credibility of a reported observation coupled with multiple interpretations that arise from multiple examinations of the observation. Not just get puzzled by those effects or paradoxes, but to avoid the pitfalls, learn and grow from them, to improve digital management maturity.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 09, 2016 22:22
The Business Effects and Paradoxes
 Either at the individual level or organization level, people experience, grow, fail and learn, from their own experiences or other’s failure lessens. There are many interesting effects in the respective field of the study; from a business management perspective, which “effects” should you understand in order to achieve management effectiveness and efficiency? The Abilene Paradox: Like many things in the world, there are both pros and cons in the crowd of wisdom and team decision-making. The team decision works because they bring different perspectives and more information to the table. They help balance out the biases that from which we all suffer, or fill the blind spots each one of them perhaps has some. They help generate more of everything (viable alternatives, criteria, etc.), all of which is shown to improve the quality of decisions. However, there are a number of contrary factors at play in a team decision-making. There is the Abilene Paradox that comes into play often in groups. In an Abilene paradox, a group of people collectively decide on a course of action that is counter to the preferences of many of the individuals in the group. It involves a common breakdown of group communication in which each member mistakenly believes that their own preferences are counter to the group's and, therefore, does not raise objections. A common phrase relating to the Abilene paradox is a desire to not "rock the boat." That often turns little defect to the bigger problem and ultimate cause the serious business failure.
Either at the individual level or organization level, people experience, grow, fail and learn, from their own experiences or other’s failure lessens. There are many interesting effects in the respective field of the study; from a business management perspective, which “effects” should you understand in order to achieve management effectiveness and efficiency? The Abilene Paradox: Like many things in the world, there are both pros and cons in the crowd of wisdom and team decision-making. The team decision works because they bring different perspectives and more information to the table. They help balance out the biases that from which we all suffer, or fill the blind spots each one of them perhaps has some. They help generate more of everything (viable alternatives, criteria, etc.), all of which is shown to improve the quality of decisions. However, there are a number of contrary factors at play in a team decision-making. There is the Abilene Paradox that comes into play often in groups. In an Abilene paradox, a group of people collectively decide on a course of action that is counter to the preferences of many of the individuals in the group. It involves a common breakdown of group communication in which each member mistakenly believes that their own preferences are counter to the group's and, therefore, does not raise objections. A common phrase relating to the Abilene paradox is a desire to not "rock the boat." That often turns little defect to the bigger problem and ultimate cause the serious business failure.Gestalt Effect: The Gestalt effect is the capability of our brain to generate whole forms, particularly with respect to the visual recognition of global figures instead of just collections of simpler and unrelated elements (points, lines, curves). Gestalt psychology tries to understand the laws of our ability to acquire and maintain meaningful perceptions in an apparently chaotic world. The central principle of Gestalt psychology is that the mind forms a “whole” with self-organizing tendencies. This principle maintains that the human mind considers objects in their entirety before, or in parallel with, the perception of their individual parts; suggesting the whole is other than the sum of its parts. The fundamental "formula" of Gestalt theory could be expressed in this way, "There are whole, the behavior of which is not determined by that of their individual elements, but where the part-processes are themselves determined by the intrinsic nature of the whole. It is the hope of Gestalt theory to determine the nature of such wholes." From a business management perspective, it encourages holistic thinking and understanding the intrinsic interconnectivity between parts and whole, in order to solve problems in a structural way.
 Bystander effect. As social psychologists have long known, people are far more likely to aid a victim in distress or report an apparent emergency if they are alone than if other people are around. One reason: If you’re uncertain what to do, you’re likely to take your cues from other people whenever possible.Some psychologists suggest that simply being aware of this tendency is perhaps the greatest way to break the cycle. From the business management perspective, when faced with a situation that requires action, understanding how the bystander effect might be holding you back and consciously taking steps to overcome it can help.
Bystander effect. As social psychologists have long known, people are far more likely to aid a victim in distress or report an apparent emergency if they are alone than if other people are around. One reason: If you’re uncertain what to do, you’re likely to take your cues from other people whenever possible.Some psychologists suggest that simply being aware of this tendency is perhaps the greatest way to break the cycle. From the business management perspective, when faced with a situation that requires action, understanding how the bystander effect might be holding you back and consciously taking steps to overcome it can help.Modern management is both science and art. We should learn from both our own experiences and from others’ lessons as well, the difference in utility between one’s own experience and the experience of another is nothing more or less than the difference between the credibility of direct observation coupled with one's own interpretation of it, and the credibility of a reported observation coupled with multiple interpretations that arise from multiple examinations of the observation. Not just get puzzled by those effects or paradoxes, but to avoid the pitfalls, learn and grow from them, to improve digital management maturity.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 09, 2016 22:22
The New Book “IT Innovation” Book Introduction Chapter 6: Rebuild IT as Digital Capability Multiplier
Running IT as a digital multiplier is really about being strategic, capable, innovative, differentiated, accelerated, and influential.
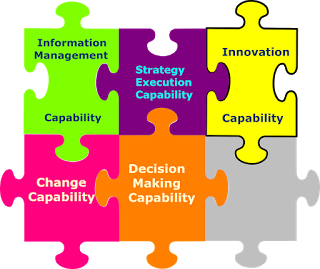 IT touches both hard business processes and soft human behaviors. More often technology is the disruptive force of digital innovation and information is the lifeblood of the organization. IT needs to be a proactive business problem solver because it is in a unique position to gain business insight and customer foresight. The emergent lightweight digital technologies just make innovation easier to do now than in the past, less costly, and easily accessible. Therefore, IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into technical solutions and leveraging necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft to the full set of digital capabilities and the differentiated business competency; it means to run IT as a digital multiplier for the business’s long-term growth and maturity.
IT touches both hard business processes and soft human behaviors. More often technology is the disruptive force of digital innovation and information is the lifeblood of the organization. IT needs to be a proactive business problem solver because it is in a unique position to gain business insight and customer foresight. The emergent lightweight digital technologies just make innovation easier to do now than in the past, less costly, and easily accessible. Therefore, IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into technical solutions and leveraging necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft to the full set of digital capabilities and the differentiated business competency; it means to run IT as a digital multiplier for the business’s long-term growth and maturity.
Digital coherence: Digital strategy execution is a dynamic continuum. How effective the strategy execution is directly dependent on the coherence of its business capabilities. The organization’s competency is based on the set of differentiated and cohesive capacities and how fast and effective to build on. Digital coherence is not just based on “doing more with less,” to focus on efficiency only; but about continuous renewal for the digital transformation. With a maturity attribute like “adoption,” “agility,” “flexibility,” and “measurability,” the digital maturity of the business would be based on the ability to deliver on customer needs or to achieve the desired business outcome. The digital coherence is the decisive factor for the success of strategy implementation and how well they can make the digital transformation, deliver the value to the customers and build a long-term winning position.
Capacity to change: IT leaders should continue ask these tough questions in order to manage an effective digital transformation: Is IT often the force to drive changes, or the obstacle to stifle changes? If radical changes are needed, does the Change Management structure exist internally to deliver on it? When the need for significant change is identified, it’s generally naive to think it will succeed without transformation. At the lower level of maturity, IT reacts to the business changes with slower speed or even turns to be the very obstacle for changes. However, the high mature IT organizations are at an inflection point to lead the organizational level digital transformation. Change is not always equal to innovation, but innovation is change, When the change was often previously discrete, intermittent, and predictable, it is now constant, discontinuous, and unpredictable, so we need to change the way we change. IT needs to become the change agent organization of the business, and a digital multiplier for enforcing changeability.
 Threshold digital competency: IT stands out as a value-added function by managing information effectively and efficiently. The abundance of data and information brings both significant opportunities and enormous risks in businesses today; as organizations can harness the power of information to provide the emergent business trends with a more fact-based vision of where to aim and how to get there. From information management to innovation management, IT must bring to the table innovative solutions that meet customers’ needs, also digitize the touch point of customer experience via innovative services and products. IT has the threshold competency to build an information savvy and high-innovative organization. If IT can do this, it will become a digital multiplier to bring the unique value for the business’s long-term success.
Threshold digital competency: IT stands out as a value-added function by managing information effectively and efficiently. The abundance of data and information brings both significant opportunities and enormous risks in businesses today; as organizations can harness the power of information to provide the emergent business trends with a more fact-based vision of where to aim and how to get there. From information management to innovation management, IT must bring to the table innovative solutions that meet customers’ needs, also digitize the touch point of customer experience via innovative services and products. IT has the threshold competency to build an information savvy and high-innovative organization. If IT can do this, it will become a digital multiplier to bring the unique value for the business’s long-term success.
Digital is the age of differentiation and innovation. If the business is not different, you are a commodity, either for IT or the business as a whole. Assuming the company has a great product, creating meaningful, relevant and compelling differentiation in the mind of customers is the challenge. This is the foundation in which brains are built. Therefore, running IT as a digital multiplier is really about being strategic, capable, innovative, differentiated, accelerated, and influential, always “Keep the end in mind,” to delight customers and catalyze business growth and digital transformation.
"IT Innovation" Amazon Order Link
"IT Innovation" Barner & Noble Order Link
"IT Innovation" iBook Order Link
"IT Innovation" Book Introduction
"IT Innovation" Book Presentation Slideshare
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 1 Introduction -Reinvent IT as an Innovation Hub
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 2 Introduction - Reimagine IT as an Innovative Outlier
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 3 Introduction - Renovate Hybrid IT and a Digital Organization
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 4 Introduction - Fine Tune IT as the "Digital Whole Brain" of the Organization
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 5 Introduction - Accelerate IT at the Fast Lane
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 6 Introduction - Rebuild IT as Digital Capability Multiplier Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
 IT touches both hard business processes and soft human behaviors. More often technology is the disruptive force of digital innovation and information is the lifeblood of the organization. IT needs to be a proactive business problem solver because it is in a unique position to gain business insight and customer foresight. The emergent lightweight digital technologies just make innovation easier to do now than in the past, less costly, and easily accessible. Therefore, IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into technical solutions and leveraging necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft to the full set of digital capabilities and the differentiated business competency; it means to run IT as a digital multiplier for the business’s long-term growth and maturity.
IT touches both hard business processes and soft human behaviors. More often technology is the disruptive force of digital innovation and information is the lifeblood of the organization. IT needs to be a proactive business problem solver because it is in a unique position to gain business insight and customer foresight. The emergent lightweight digital technologies just make innovation easier to do now than in the past, less costly, and easily accessible. Therefore, IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into technical solutions and leveraging necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft to the full set of digital capabilities and the differentiated business competency; it means to run IT as a digital multiplier for the business’s long-term growth and maturity. Digital coherence: Digital strategy execution is a dynamic continuum. How effective the strategy execution is directly dependent on the coherence of its business capabilities. The organization’s competency is based on the set of differentiated and cohesive capacities and how fast and effective to build on. Digital coherence is not just based on “doing more with less,” to focus on efficiency only; but about continuous renewal for the digital transformation. With a maturity attribute like “adoption,” “agility,” “flexibility,” and “measurability,” the digital maturity of the business would be based on the ability to deliver on customer needs or to achieve the desired business outcome. The digital coherence is the decisive factor for the success of strategy implementation and how well they can make the digital transformation, deliver the value to the customers and build a long-term winning position.
Capacity to change: IT leaders should continue ask these tough questions in order to manage an effective digital transformation: Is IT often the force to drive changes, or the obstacle to stifle changes? If radical changes are needed, does the Change Management structure exist internally to deliver on it? When the need for significant change is identified, it’s generally naive to think it will succeed without transformation. At the lower level of maturity, IT reacts to the business changes with slower speed or even turns to be the very obstacle for changes. However, the high mature IT organizations are at an inflection point to lead the organizational level digital transformation. Change is not always equal to innovation, but innovation is change, When the change was often previously discrete, intermittent, and predictable, it is now constant, discontinuous, and unpredictable, so we need to change the way we change. IT needs to become the change agent organization of the business, and a digital multiplier for enforcing changeability.
 Threshold digital competency: IT stands out as a value-added function by managing information effectively and efficiently. The abundance of data and information brings both significant opportunities and enormous risks in businesses today; as organizations can harness the power of information to provide the emergent business trends with a more fact-based vision of where to aim and how to get there. From information management to innovation management, IT must bring to the table innovative solutions that meet customers’ needs, also digitize the touch point of customer experience via innovative services and products. IT has the threshold competency to build an information savvy and high-innovative organization. If IT can do this, it will become a digital multiplier to bring the unique value for the business’s long-term success.
Threshold digital competency: IT stands out as a value-added function by managing information effectively and efficiently. The abundance of data and information brings both significant opportunities and enormous risks in businesses today; as organizations can harness the power of information to provide the emergent business trends with a more fact-based vision of where to aim and how to get there. From information management to innovation management, IT must bring to the table innovative solutions that meet customers’ needs, also digitize the touch point of customer experience via innovative services and products. IT has the threshold competency to build an information savvy and high-innovative organization. If IT can do this, it will become a digital multiplier to bring the unique value for the business’s long-term success.Digital is the age of differentiation and innovation. If the business is not different, you are a commodity, either for IT or the business as a whole. Assuming the company has a great product, creating meaningful, relevant and compelling differentiation in the mind of customers is the challenge. This is the foundation in which brains are built. Therefore, running IT as a digital multiplier is really about being strategic, capable, innovative, differentiated, accelerated, and influential, always “Keep the end in mind,” to delight customers and catalyze business growth and digital transformation.
"IT Innovation" Amazon Order Link
"IT Innovation" Barner & Noble Order Link
"IT Innovation" iBook Order Link
"IT Innovation" Book Introduction
"IT Innovation" Book Presentation Slideshare
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 1 Introduction -Reinvent IT as an Innovation Hub
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 2 Introduction - Reimagine IT as an Innovative Outlier
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 3 Introduction - Renovate Hybrid IT and a Digital Organization
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 4 Introduction - Fine Tune IT as the "Digital Whole Brain" of the Organization
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 5 Introduction - Accelerate IT at the Fast Lane
"IT Innovation" Book Chapter 6 Introduction - Rebuild IT as Digital Capability Multiplier Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 09, 2016 22:15
The New Book “IT Innovation” Book Introduction Chapter 6: Rebuild IT as Digital Multiplier
 IT touches both hard business processes and soft human behaviors. More often technology is the innovation disruptor and the information is the lifeblood of the organization. IT needs to be a proactive business problem solver because it is in a unique position to gain business insight and customer foresight. The emergent lightweight digital technologies just make innovation easier to do now than in the past, less costly, and easily accessible. Therefore, IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into technical solutions and leveraging necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft to differentiative business competency and running as a digital multiplier for the business’s long-term growth and maturity.
IT touches both hard business processes and soft human behaviors. More often technology is the innovation disruptor and the information is the lifeblood of the organization. IT needs to be a proactive business problem solver because it is in a unique position to gain business insight and customer foresight. The emergent lightweight digital technologies just make innovation easier to do now than in the past, less costly, and easily accessible. Therefore, IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into technical solutions and leveraging necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft to differentiative business competency and running as a digital multiplier for the business’s long-term growth and maturity. Digital coherence: Digital strategy execution is a dynamic continuum. How effective the strategy execution is directly dependent on the coherence of its business capabilities. The organization’s competency is based on the set of differentiated and cohesive capacities and how fast and effective to build on. Digital coherence is not just based on “doing more with less,” to focus on efficiency only; but about continuous renewal for digital transformation. With a maturity attribute like “adoption,” “agility,” “flexibility,” and “measurability.” The digital maturity of the business would be based on the ability to deliver on customer needs or to achieve the desired business outcome. The digital coherence is the decisive factor for the success of strategy implementation and how well they can make the digital transformation, deliver the value to the customers and building a long-term winning position.
Capacity to change: Is IT often the force to drive changes, or the obstacle to stifle changes? If radical changes are needed, does the Change Management structure exist internally to deliver on it? When the need for significant change is identified, it’s generally naive to think it will success without transformation as well. At the lower level of maturity, IT reacts to the business changes with slower speed or even turns to be the very obstacle for changes. However, the high mature IT organizations are at an inflection point to lead the organizational level digital transformation. Change is not always equal to innovation, but innovation is change, When the change was often previously discrete, intermittent, and predictable, it is now constant, discontinuous, and unpredictable, so we need to change the way we change. IT needs to become the change agent organization of the business, and a digital multiplier for enforcing changeability.
 Threshold digital competency: IT stands out as a value-added function by managing information effectively and efficiently. The abundance of data and information brings both significant opportunities and enormous risks in businesses today; as organizations can harness the power of information to provide the emergent business trends with a more fact-based vision of where to aim and how to get there. From information management to innovation management, IT must bring to the table innovative solutions that meet customers’ needs, also digitize the touch point of customer experience via innovative services and products. IT has the threshold competency to build an information savvy and high-innovative organization. If IT can do this, it will become a digital multiplier to bring the unique value for the business’s long-term success.
Threshold digital competency: IT stands out as a value-added function by managing information effectively and efficiently. The abundance of data and information brings both significant opportunities and enormous risks in businesses today; as organizations can harness the power of information to provide the emergent business trends with a more fact-based vision of where to aim and how to get there. From information management to innovation management, IT must bring to the table innovative solutions that meet customers’ needs, also digitize the touch point of customer experience via innovative services and products. IT has the threshold competency to build an information savvy and high-innovative organization. If IT can do this, it will become a digital multiplier to bring the unique value for the business’s long-term success.Digital is the age of differentiation and innovation. If the business is not different, you are a commodity, either for IT or the business as a whole. Assuming the company has a great product, creating meaningful, relevant and compelling differentiation in the mind of customers is the challenge. This is the foundation in which brains are built. Therefore, running IT as a digital multiplier is really about being strategic, capable, innovative, differentiated, accelerated, and influential, always “Keep the end in mind,” to delight customers and catalyze business growth and digital transformation.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 09, 2016 22:15
November 8, 2016
The Monthly Insight of the Board Room: Running a Digital-Ready Boardroom Nov. 2016
 Modern corporate boards play significant roles in guiding businesses toward the right direction and achieve expected business results. Due to the “VUCA” characteristics -Complexity, Uncertainty, Ambiguity and Velocity of the Digital Era, the directorship in any organization must have the agility to adapt to changes, and build abilities to advise, inspire and motivate a group of people toward accomplishing shared visions and goals. .
Modern corporate boards play significant roles in guiding businesses toward the right direction and achieve expected business results. Due to the “VUCA” characteristics -Complexity, Uncertainty, Ambiguity and Velocity of the Digital Era, the directorship in any organization must have the agility to adapt to changes, and build abilities to advise, inspire and motivate a group of people toward accomplishing shared visions and goals. .Running a Digital-Ready Boardroom The Digital Board’s Journey from Good to Great? Due to the complexity, uncertainty, ambiguity and volatility of the digital age, the directorship in any organization must have the ability to inspire, guide, and motivate top management team toward accomplishing shared visions and goal. The level of the board accomplishment may vary but the essential competencies will remain the same, BoDs need to be insightful, influential, strategic, and highly effective, and the board as a whole needs to be able to create the cohesive vision, holistic view, and transform from compliance-centric to performance-driven. This also implies that Boards of the future will need to work much more closely and collaboratively to take the digital journey from good to great.
A Tech-Savvy Board: Forward-looking organizations cross-sector claim they are at information businesses, as IT touches every facet of business today, from strategy to operation; from key processes to competitive capabilities. Based on an industry survey, the majority of BoDs think IT is critical to their companies, and more and more organizations also put IT oversight in their boardroom agenda, does it mean it is the right timing to shape a tech-savvy Board, if so, what shall they focus on?
The Digital Savvy Board with High “Tech IQ”: Although Information Technology nowadays makes significant impacts on almost every aspect of the business, there is still a propensity to try to make the technology changes "go away" or to ignore them. The matter of fact is that the changes sweeping the world are hugely disruptive and there is nowhere to hide. While directors bring many competencies to the table, most do not have access to information about technology driven innovation and its potential related to the businesses they oversee. So how to build the board with high “tech IQ,” to produce a wave of response at board level, improve directorship effectiveness and innovate digital leadership??
 A Progressive Board -Setting the Top Leadership Tone to Drive Digital Transformation: At today’s “VUCA” digital dynamic, organizations face both unprecedented opportunities to grow and hyper-competition or great risks to survive. Therefore, the corporate board plays a more significant role in overseeing business strategy, setting principles and policies, and making the judgment on and assurance of corporate action within a framework of practical knowledge. The digital fitting BoD is about mental toughness, progressive perspective, and in-depth business understanding in order to set the right digital leadership tone and lead change effortlessly. Leadership is all about future and progression, so how to build a progressive board to catalyze digital transformation?
A Progressive Board -Setting the Top Leadership Tone to Drive Digital Transformation: At today’s “VUCA” digital dynamic, organizations face both unprecedented opportunities to grow and hyper-competition or great risks to survive. Therefore, the corporate board plays a more significant role in overseeing business strategy, setting principles and policies, and making the judgment on and assurance of corporate action within a framework of practical knowledge. The digital fitting BoD is about mental toughness, progressive perspective, and in-depth business understanding in order to set the right digital leadership tone and lead change effortlessly. Leadership is all about future and progression, so how to build a progressive board to catalyze digital transformation?Twenty-Three Themes of Digital Boardrooms: The contemporary corporate boards play important roles in strategy advising, governance oversight, leadership exemplification, culture tuning, and talent management influence. BoDs also have to shift from the industrial mentalities to the digital styles. A professional digital board is not only about filling with cool-headed, high-professional and high-intelligent BoDs, but also about tuning the structured process to digitize itself, optimize decision-making capacity, inspire innovation, and improve the board's overall effectiveness, agility, and maturity.
The “Future of CIO” Blog has reached 1.5 million page views with 3100+ blog posting in 59+ different categories of leadership, management, strategy, digitalization, change/talent, etc. The content richness is not for its own sake, but to convey the vision and share the wisdom. Blogging is not about writing, but about thinking; it’s not just about WHAT to say, but about WHY to say, and HOW to say it. It reflects the color and shade of your thought patterns, and it indicates the peaks and curves of your thinking waves. Unlike pure entertainment, quality and professional content takes time for digesting, contemplation and engaging, and therefore, it takes time to attract the "hungry minds" and the "deep souls." It’s the journey to amplify your voice, deepen your digital footprints, and match your way for human progression.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 08, 2016 22:44
Bridging Gaps in Talent “Performance Management”
 The core of "Performance Management" is to creating goals that are aligned with organizational strategic objectives, and to provide reflective feedback to the person who can make continuous improvement. However, in many organizations, traditional performance management has many negative aspects: reactive, not proactive; past-focused, not future oriented; administrative, not strategic; process-driven, not people centric. How to bridge the gaps and improve the performance of “Performance Management”?
The core of "Performance Management" is to creating goals that are aligned with organizational strategic objectives, and to provide reflective feedback to the person who can make continuous improvement. However, in many organizations, traditional performance management has many negative aspects: reactive, not proactive; past-focused, not future oriented; administrative, not strategic; process-driven, not people centric. How to bridge the gaps and improve the performance of “Performance Management”? Bridging the gaps between the past performance and future performance: Performance Management has always been followed by the word "system" or "process.” First, you need to consider why you need to do performance management. Strategically, Performance Management should focus on managing future performance and unleashing talent potential. However, in many traditional organizations, performance management becomes an annual routine to focus mainly on the past performance treat people as human resource. Move the purpose of performance reviews away from "evaluating" the past, and to improving success in the future; from treating people as human resource as a “fixed asset” to think people as human capital to invest in. When you lead a business or an organization, you really need to be passionate about what you are trying to achieve for the customer and long term prosperity of your organization. You then need to be able to convey this passion to your people and show passion for both the customer and your people. Digital leaders need to be talent master, they guide, they coach, they teach, they set expectations, they motivate, they develop, and they find ways to ensure that the team members can align their personal goals with the business goal, and perform at their best for the future.
From subjectivity to objectivity: No evaluations or employee reviews are absolutely objective. Subjectivity abounds so you need to stop pretending that your ways of evaluating employee performance are objective. What is important is setting agreed upon goals and objectives, establishing key indicators, and then working with the employee so there is a common understanding of goals and agreement on how to measure them. It means a negotiated and interactive approach with well-designed work processes and systems, collaborative colleagues, insightful leadership, and great communication. Traditional Performance management does not work well, simply because, for most employees, their results or outcomes are dependent on other people and other factors.
Shift from an administrative performance management process to an interactive talent development scenario: Performance development is to focus on positive, rather than negative aspects. Many talent management experts dislike the term Performance Management because traditionally it is a logistic and an administrative process to do routine works such as annual performance review, with much negative implication. In many organizations, employees need creative leadership, interpersonal relationship, managerial support, resources, appropriate environment, clear goals, job-tailored training, motivation, manuals, job aids, ergonomically designed workplace, tools, performance evaluation and feedback, culture, appropriate rules and regulations, and policies. If they are not present, the manager has to implement so that he/she can get maximum performance from the employees. Therefore, talent development management needs to be integrated with performance management, and shift from reactively annual performance reviewing to proactively guiding, advising and motivation. It also indicates the manager has a job to deliver in the business as well to provide support and development to their team, so the senior management team has a role in this process too and ultimately the company ethos needs to be real, to shift from an administrative performance management process to an interactive talent development scenario. Performance communication and enhancement are to manage employees in a more proactive way to enforce their performance, rather than reactively reviewing. Performance communication is an ongoing communication about expectations, feedback and growth through the year. Mapping the employee’s performance to the overall business performance: One should first consider the desired outcome of the performance management process and scenario. Yes, it is indeed a review of the employee's performance, but the terminology currently used is too narrow and specific. The desired outcome is to assess the employee's contribution and ability to fulfill tasks and objectives in line with the organizational goals and vision both qualitatively and quantitatively. Do they meet the desired standard or are there gaps, what is required to fill these gaps? Business has to create metrics in order to measure the RIGHT things right. Not only measuring productivity but also innovation. No only measuring "Doing Performance" but also evaluating "Thinking Performance." Not only assessing what's been done but also HOW's it been done. Without measurement, you have no idea if people are improving. You should have both metrics and an understanding of human nature and needs. That's all about bringing your cumulative best talents and efforts to bear on business challenges, and to achieve performance maximization.
 Performance Management is more as planning than tools: Performance Management is not a bunch of paperwork, but a combination of actions leading to a constantly improving product. Performance Management uses performance evaluation as the main tool, it will not be of much value. But when it is more on work or performance planning, then better results will follow. Performance Management gets "stuck" when the people in charge get "stuck." A manager is involved with his/her people and is there to teach, advise, listen, correct, reward, motivate, and discipline, things change for the better. This is Performance Management. Managers are leaders/trainers/teachers, and it is their job to prepare their people, not only for their current job but for their next job as well. Evaluation is water down the bridge even if this is supposed to be used for development or as a lesson for future work unless the work will be exactly the same. But if performance management is done at the initial stage where managers review work approaches to accomplish goals and sustained throughout the work as it is being done, then there will be better chances for success. This is why regular discussions during the course of accomplishing a goal are helpful. The words "development, enhancement, coaching," imply a better mindset for performance management
Performance Management is more as planning than tools: Performance Management is not a bunch of paperwork, but a combination of actions leading to a constantly improving product. Performance Management uses performance evaluation as the main tool, it will not be of much value. But when it is more on work or performance planning, then better results will follow. Performance Management gets "stuck" when the people in charge get "stuck." A manager is involved with his/her people and is there to teach, advise, listen, correct, reward, motivate, and discipline, things change for the better. This is Performance Management. Managers are leaders/trainers/teachers, and it is their job to prepare their people, not only for their current job but for their next job as well. Evaluation is water down the bridge even if this is supposed to be used for development or as a lesson for future work unless the work will be exactly the same. But if performance management is done at the initial stage where managers review work approaches to accomplish goals and sustained throughout the work as it is being done, then there will be better chances for success. This is why regular discussions during the course of accomplishing a goal are helpful. The words "development, enhancement, coaching," imply a better mindset for performance managementPerformance management is not a silo management practice to monitor or measure the quantitative delivery of an employee; but a holistic people management discipline to involve development, enablement, and enhancement, to well align with talent management, culture management, and strategy management, to treat people not just the cost or resource, but the human asset and capital to invest in, not just for bringing short-term result, but for driving business’s long-term prosperity. Until and unless there is a mutual agreement between both management and staff as to a vested and balanced approach to the goals and vision of the organization, the performance management process will most likely remain an adversarial relationship. Simply input, buy-in and ownership are the keys to advancing the mutual goals of the organization.
Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 08, 2016 22:42
The New Book “IT Innovation” Introduction Chapter 5 Accelerate IT on the Fast Lane
 With increasing speed of changes and continuous digital disruption, IT has to adapt to changes in faster and proactive ways; and more often, IT has to drive changes and plays a pivotal role in the digital transformation, focus on the fastest speed available, because that is where the main threat to competitiveness. It is about running IT as a business enabler to catalyze growth and improve organizational agility.
With increasing speed of changes and continuous digital disruption, IT has to adapt to changes in faster and proactive ways; and more often, IT has to drive changes and plays a pivotal role in the digital transformation, focus on the fastest speed available, because that is where the main threat to competitiveness. It is about running IT as a business enabler to catalyze growth and improve organizational agility.High-response to changes: Running IT on the fast lane means to speed up the organizational vehicle. Due to the unique position to oversee business processes, IT plays an important role in building up a high-performing digital organization which can succeed in combining two distinct but interconnected elements: strategic responsiveness and organizational flexibility, with the combination of an innovative culture that promotes responsiveness throughout the company. IT has to not only improve its own speed, but also overall organizational agility. The type of speed issues such as IT slows to change comes from gaps created between IT and the rest of company. To mind the gap, CIOs need to work closely with the business partners, take business problems, find solutions for them, increase value propositions, simplify operations and be better partners with the rest of the organizations.
Streamline information flow across functional boundaries: Information and technology catalyze today’s digital businesses. Information brings about business ideas and insight; business ideas generate lots of information. It is so critical to streamline information flow across functional boundaries, because fundamentally, information management is to make sure that the right information is in the right place at the right time and shared to the right persons. This information is open to interpretation accordance to the level of knowledge one has. IT as a business enabler and catalyzer should achieve such business objectives, gain a pervasive appreciation throughout the enterprise, particularly executive-level management.
 Setting priorities to solve the problems and accelerate digital transformation: More and more organizations are at the strategic inflection point of the digital transformation. It is the broader and longer journey with many leaps and jumps, bumps and curves, perils and pitfalls on the way. It implies the full-scale changes in the way the business is conducted, such as mindset, talent, skills, processes, technologies. IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into a technology solution, also, leverage necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft, to orchestrate a digital symphony. IT is an enabler and catalyzer for the busieness to reach the era of radical digital.
Setting priorities to solve the problems and accelerate digital transformation: More and more organizations are at the strategic inflection point of the digital transformation. It is the broader and longer journey with many leaps and jumps, bumps and curves, perils and pitfalls on the way. It implies the full-scale changes in the way the business is conducted, such as mindset, talent, skills, processes, technologies. IT plays an important role in interpreting business issues into a technology solution, also, leverage necessary resources to solve them. And more broadly, IT can weave all necessary business elements, either hard or soft, to orchestrate a digital symphony. IT is an enabler and catalyzer for the busieness to reach the era of radical digital. IT is an accelerator for speeding up the business. IT’s about applying information and technology to enhance productivity, efficiency, agility, and maturity; uncover customer insights, predict business trends, catalyze innovations, create new business models. IT can run with full speed without too many distractions and misunderstanding. It is a continuous journey to adapting to today’s fast-changing and dynamic digital ecosystem.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 08, 2016 22:38
November 7, 2016
The CIO’s Digital Agenda: Close the Talent Gaps in IT Digital Transformation Nov. 2016
The talent gap is the reality, not a fiction, this is particularly true for IT talent management.
 With the increasing speed of changes, many organizations are inundated with tactical tasks and daily operational duties, they don’t spend enough time on scrutinizing the long term strategy and identify disastrous gaps or blind spots in order to make a smooth business transformation. Indeed, there are both huge gaps and fatal blind spots in strategy formulation and execution. So how to bridge them in order to accelerate IT digital transformation. Close the Talent Gaps in IT Digital Transformation IT Skills Gap? According to industry surveys, IT skills gap is a significant challenge facing IT leaders today, what are exactly the skills gaps and what are the resulting symptoms? For example, business have job openings, but cannot find people with the right skill set; or the talent people they current have do not have the right competencies to adapt to the changes; or their business partners do not understand IT. Sometimes, the gaps people usually pick are not root causes, they are symptoms of specific best practices not being used. So what are the organizational best practices/ways that have been deployed to close the gap?
With the increasing speed of changes, many organizations are inundated with tactical tasks and daily operational duties, they don’t spend enough time on scrutinizing the long term strategy and identify disastrous gaps or blind spots in order to make a smooth business transformation. Indeed, there are both huge gaps and fatal blind spots in strategy formulation and execution. So how to bridge them in order to accelerate IT digital transformation. Close the Talent Gaps in IT Digital Transformation IT Skills Gap? According to industry surveys, IT skills gap is a significant challenge facing IT leaders today, what are exactly the skills gaps and what are the resulting symptoms? For example, business have job openings, but cannot find people with the right skill set; or the talent people they current have do not have the right competencies to adapt to the changes; or their business partners do not understand IT. Sometimes, the gaps people usually pick are not root causes, they are symptoms of specific best practices not being used. So what are the organizational best practices/ways that have been deployed to close the gap?
How to Close the Gaps in IT Talent Management People are always the most invaluable asset to any organization, and having the right person in the right position at the right time is always one of the biggest challenges facing any business. This is particularly true for IT, due to the changing nature of technology and abundance of information. Some fresh mindsets, new skills, or integral digital capabilities are needed every day because we live in a time of rapidly changing digital dynamic. However, people are often the weakest link in strategy execution as well, so how to identify and close the gaps in IT talent management more specifically?Is IT skills Gap Fact or Fiction? There’s always a debate regarding IT talent supply and demand, does IT skills gap really exist? Or is it due to any management issues such as misunderstanding or miscommunication upon talent value chain? What is the root cause and how to solve the problem?
Digital Talent Gap Minding in Running a Digital Fit IT? Human capital is always the most valuable asset in any business, especially now the rate of change is accelerated, and knowledge life cycle is significantly shortened. The talent gap is the reality, not a fiction, this is particularly true for IT talent management due to the exponential growth of information and change nature of technology. More specifically, which approach should IT take to fill the mindset/capability/skill gaps and also innovate talent management to capture the emergent digital trends, ride above the learning curve, and build an alternative digital talent pipeline?
How to Fill Skills Gaps via Proper Trainings? We live in a time of rapidly changing technology and business dynamic, the growth minds, the new skills, or digital capabilities are needed every day. From talent management perspective, more specifically, how do you identify skill gap issues (some are real, some are “artificial,”) and how to fill competency gaps via proper training?
 How to Mind Gaps and Measure Human Capital Effectively? People are always the most invaluable asset to the organization but often turn to be the weakest link in strategy execution. Unlike the other tangible value of business assets which are more easily measured in a quantitative way. The true value of people, especially today’s high professional knowledge workforces include many tangible and intangible factors because people are not just the cost or the resource to be managed, but the capital to be invested in and their potential if unleashed can bring the quantum leap in the business growth. So what are the premium approach and methodology to measure human asset and capital? What KPIs would you recommend to determine the value an employee adds to their department and ultimately to their organization, and how would you implement it?
How to Mind Gaps and Measure Human Capital Effectively? People are always the most invaluable asset to the organization but often turn to be the weakest link in strategy execution. Unlike the other tangible value of business assets which are more easily measured in a quantitative way. The true value of people, especially today’s high professional knowledge workforces include many tangible and intangible factors because people are not just the cost or the resource to be managed, but the capital to be invested in and their potential if unleashed can bring the quantum leap in the business growth. So what are the premium approach and methodology to measure human asset and capital? What KPIs would you recommend to determine the value an employee adds to their department and ultimately to their organization, and how would you implement it?
The “Future of CIO” Blog has reached 1.5+million page views with about #3200+ blog posting in 59+ different categories of leadership, management, strategy, digitalization, change/talent, etc. blog posting. The content richness is not for its own sake, but to convey the vision and share the wisdom, to inspire critical thinking and spur healthy debates. Blogging is not about writing, but about thinking and innovating the new ideas; it’s not just about WHAT to say, but about WHY to say, and HOW to say it. It reflects the color and shade of your thought patterns, and it indicates the peaks and curves of your thinking waves. Unlike pure entertainment, quality and professional content takes time for digesting, contemplation and engaging, and therefore, it takes the time to attract the "hungry minds" and the "deep souls." It’s the journey to amplify diverse voices and deepen digital footprints, and it's the way to harness your innovative spirit.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
 With the increasing speed of changes, many organizations are inundated with tactical tasks and daily operational duties, they don’t spend enough time on scrutinizing the long term strategy and identify disastrous gaps or blind spots in order to make a smooth business transformation. Indeed, there are both huge gaps and fatal blind spots in strategy formulation and execution. So how to bridge them in order to accelerate IT digital transformation. Close the Talent Gaps in IT Digital Transformation IT Skills Gap? According to industry surveys, IT skills gap is a significant challenge facing IT leaders today, what are exactly the skills gaps and what are the resulting symptoms? For example, business have job openings, but cannot find people with the right skill set; or the talent people they current have do not have the right competencies to adapt to the changes; or their business partners do not understand IT. Sometimes, the gaps people usually pick are not root causes, they are symptoms of specific best practices not being used. So what are the organizational best practices/ways that have been deployed to close the gap?
With the increasing speed of changes, many organizations are inundated with tactical tasks and daily operational duties, they don’t spend enough time on scrutinizing the long term strategy and identify disastrous gaps or blind spots in order to make a smooth business transformation. Indeed, there are both huge gaps and fatal blind spots in strategy formulation and execution. So how to bridge them in order to accelerate IT digital transformation. Close the Talent Gaps in IT Digital Transformation IT Skills Gap? According to industry surveys, IT skills gap is a significant challenge facing IT leaders today, what are exactly the skills gaps and what are the resulting symptoms? For example, business have job openings, but cannot find people with the right skill set; or the talent people they current have do not have the right competencies to adapt to the changes; or their business partners do not understand IT. Sometimes, the gaps people usually pick are not root causes, they are symptoms of specific best practices not being used. So what are the organizational best practices/ways that have been deployed to close the gap?How to Close the Gaps in IT Talent Management People are always the most invaluable asset to any organization, and having the right person in the right position at the right time is always one of the biggest challenges facing any business. This is particularly true for IT, due to the changing nature of technology and abundance of information. Some fresh mindsets, new skills, or integral digital capabilities are needed every day because we live in a time of rapidly changing digital dynamic. However, people are often the weakest link in strategy execution as well, so how to identify and close the gaps in IT talent management more specifically?Is IT skills Gap Fact or Fiction? There’s always a debate regarding IT talent supply and demand, does IT skills gap really exist? Or is it due to any management issues such as misunderstanding or miscommunication upon talent value chain? What is the root cause and how to solve the problem?
Digital Talent Gap Minding in Running a Digital Fit IT? Human capital is always the most valuable asset in any business, especially now the rate of change is accelerated, and knowledge life cycle is significantly shortened. The talent gap is the reality, not a fiction, this is particularly true for IT talent management due to the exponential growth of information and change nature of technology. More specifically, which approach should IT take to fill the mindset/capability/skill gaps and also innovate talent management to capture the emergent digital trends, ride above the learning curve, and build an alternative digital talent pipeline?
How to Fill Skills Gaps via Proper Trainings? We live in a time of rapidly changing technology and business dynamic, the growth minds, the new skills, or digital capabilities are needed every day. From talent management perspective, more specifically, how do you identify skill gap issues (some are real, some are “artificial,”) and how to fill competency gaps via proper training?
 How to Mind Gaps and Measure Human Capital Effectively? People are always the most invaluable asset to the organization but often turn to be the weakest link in strategy execution. Unlike the other tangible value of business assets which are more easily measured in a quantitative way. The true value of people, especially today’s high professional knowledge workforces include many tangible and intangible factors because people are not just the cost or the resource to be managed, but the capital to be invested in and their potential if unleashed can bring the quantum leap in the business growth. So what are the premium approach and methodology to measure human asset and capital? What KPIs would you recommend to determine the value an employee adds to their department and ultimately to their organization, and how would you implement it?
How to Mind Gaps and Measure Human Capital Effectively? People are always the most invaluable asset to the organization but often turn to be the weakest link in strategy execution. Unlike the other tangible value of business assets which are more easily measured in a quantitative way. The true value of people, especially today’s high professional knowledge workforces include many tangible and intangible factors because people are not just the cost or the resource to be managed, but the capital to be invested in and their potential if unleashed can bring the quantum leap in the business growth. So what are the premium approach and methodology to measure human asset and capital? What KPIs would you recommend to determine the value an employee adds to their department and ultimately to their organization, and how would you implement it?The “Future of CIO” Blog has reached 1.5+million page views with about #3200+ blog posting in 59+ different categories of leadership, management, strategy, digitalization, change/talent, etc. blog posting. The content richness is not for its own sake, but to convey the vision and share the wisdom, to inspire critical thinking and spur healthy debates. Blogging is not about writing, but about thinking and innovating the new ideas; it’s not just about WHAT to say, but about WHY to say, and HOW to say it. It reflects the color and shade of your thought patterns, and it indicates the peaks and curves of your thinking waves. Unlike pure entertainment, quality and professional content takes time for digesting, contemplation and engaging, and therefore, it takes the time to attract the "hungry minds" and the "deep souls." It’s the journey to amplify diverse voices and deepen digital footprints, and it's the way to harness your innovative spirit.Follow us at: @Pearl_Zhu
Published on November 07, 2016 22:55



