The Significance of Homo floresiensis (Our Hobbit-Like Human Ancestor)
Despite the immense progress science has made, the evolution of human beings is still a topic full of surprises and mysteries. Humans evolved from being animals of no significance to becoming the unchallenged masters of the planet, something no other species had managed to do before us.
Our enigmatic past is a matter that inspires both unbridled curiosity and unexplained fear.
How did humans evolve to dominate the planet? Was there something special about us?
What secrets we may uncover when we go digging our past? Could it turn out that we were just a bunch of lucky apes and there was nothing special about us?
Though finding evidence of any new species of ancient humans is a matter of great importance, none created as much drama as the discovery of Homo floresiensis.
When was the Homo floresiensis Fossil Discovered?On October 28, 2004, a startling announcement shocked the world.
The remains of a tiny little humanlike creature known as Homo floresiensis had been found in a cave called Liang Bua on the island of Flores in Indonesia.
 Liang Bua Cave in Flores, Indonesia
Liang Bua Cave in Flores, IndonesiaThis discovery was a joint Indonesian-Australian effort. The team consisted of Australian archaeologist Michael Morwood, his anthropological colleague Peter Brown and an Indonesian colleague Thomas Sutkina.
According to the jaw-dropping paper submitted by Morwood and his team, they announced the discovery of the tiny bones of a human-like creature that lived in the late Pleistocene period. This period is generally seen as the end of the ice-age.
Within the gigantic cave’s deep sediments, the team found a scattering of animal bones, primitive stone tools and an almost complete skeleton of what looked like a shrunken human. This skeleton was named Liang Bua 1 (or LB1).
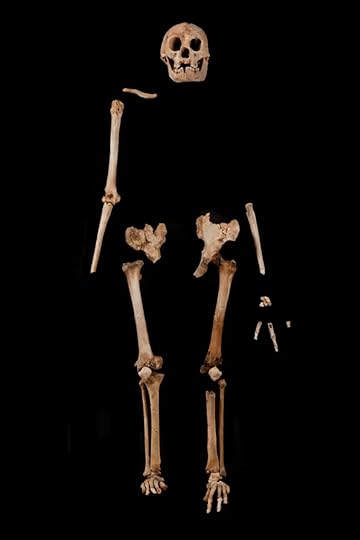 Homo Floresiensis Skeleton
Homo Floresiensis SkeletonSince 2004 happened to be the age of the popular fantasy series the Lord of the Rings, LB1 became famous with the nickname Hobbit.
The one almost complete skull that was found was extremely small in size. It had housed a brain about the size of a chimpanzee’s. Peter Brown’s analysis suggested that these were the remains of a previously unknown human species.
Dating these specimens led to even more bizarre conclusions. These little people may have inhabited the island of Flores as recently as 18,000 years ago. This is long after the generally agreed timeline of modern humans remaining as the only dominant human species left to rule the planet. In other words, the little people turned out to be our contemporaries.
During their time, this tiny species would have contented with stegodons, ferocious rat-like animals and giant Komodo dragons that resided on the island of Flores. And all of this without having a brain as large as modern humans.
The discovery of Homo floresiensis challenged our very core ideas about human evolution.
The Controversy about Homo floresiensisNeedless to say, the explosive discovery led to a storm of controversy in the scientific community.
Within a matter of months after the publication, the bones of LB1 were taken away from the original discoverers by Teuku Jacob, who was a leading figure in the Indonesian Anthropological Science and had a lot of political influence.
Soon, a new study was published that completely refuted the claim by the original researchers. According to this new study, the LB1 does not belong to a new species, but is a diseased form of modern human available to be seen elsewhere on the island of Flores.
However, despite the seeming obviousness of the new study, the controversy surrounding Homo floresiensis did not die down. In fact, over the years, more research on the topic has revealed some surprising conclusions and answered some important questions.
Did Homo floresiensis Have Microcephaly?During the initial years of the discovery, there were many deniers for the new-species theory.
The common theme of the deniers was that LB1 was an ordinary modern human, probably afflicted with microcephaly.
Microcephaly is a rare human condition in which the brain is underdeveloped. The cranial capacity of modern humans varies from 1200 to 1700 cubic centimetres. A microcephalic person’s brain is typically less than 700 cubic centimetres with a few cases even going below 400. Most of the people afflicted with this situation also have a small stature.
The cranial capacity of LB1 was found to be around 400 cubic centimetres and its stature was about 1 metre.
But did this indicate LB1 was simply a modern human suffering from microcephaly?
The ones backing this explanation have made some points to prove their theory:
The Rampasasa people, who tend to be short in height, live in Flores today, not too far from the Liang Bua cave.Some of the Rampasasa people also have receding chins.LB1 has a very asymmetrical skull as would be expected in a person with a pathological condition.Typically, in smaller species brains are relatively larger in proportion. If the Homo floresiensis was really a dwarf descendant of a larger human species, its brain size would be much bigger. Based on this, they concluded that LB1 was a microcephalic specimen.However, with more findings, the theory that Homo floresiensis suffered from microcephaly has been refuted.
Firstly, the claimed asymmetry of the skull of LB1 turned out to be due to damage to the skull during post mortem.
Second, the Rampasasa people used as a model for explaining the LB1 are definitely short, but none has been found to be as short as LB1 was.
Also, further analysis revealed that the brain of LB1 was very much like a tiny, but normal human brain. This was quite different from the series of microcephalic brains studied by a team of scientists.
While these points were already significant, the last nail in the coffin of the pathological theory came about when more specimens were discovered from Liang Bua.
More parts of LB1 were discovered in 2005 along with the remains of seven other individuals. All of these specimens were also diminutive in size. In fact, they were found to be even smaller than LB1.
Some of the other specimens were found from the lower deposits, going back to levels dated between 74,000 and 95,000 years ago. It turned out that Homo floresiensis had inhabited the cave over a period of more than 60,000 years ago. It is hardly credible that during such a vast period of time, the remains of only 9 microcephalic people and no one else ended up in the Liang Bua cave.
Was Homo floresiensis an Example of Island Dwarfism?Another theory about Homo floresiensis proposes that they are an example of Island Dwarfism (also known as insular dwarfism).
Insular dwarfism is the process and condition of large animalsevolving to a reduced body size when their population is restricted to a small environment such as an island.
Hominins were present on the East Indonesian island of Flores as early as 880,000 years. At this time, Homo erectus was thought to be the only hominin species in East Asia. Therefore, it was naturally assumed that Homo floresiensis was the result of insular dwarfing of an ancestral Homo erectus population.
However, over the years, a more logical alternative hypothesis has been suggested by Morwood. Based on detailed analysis of the skeletal remains of Homo floresiensis, it has been suggested that several morphological traits indicate that they may be descendants of a pre-erectus hominin species in Asia. These traits include the mandible morphology, limb proportions, wrist and foot morphology and also, the brain size.
If you don’t know, morphology is the study of the structure of plants and animals to derive conclusions.
The study suggests that Homo floresiensis separated from the mainstream hominin line before the evolution of Homo erectus in Africa. The ancestor of Homo floresiensis arrived on Flores with both a small body and a small brain. Even if this ancestor arrived on Flores around 900,000 years ago, there would be sufficient time for it to evolve its own unique traits, even if it were somewhat larger in size originally.
There is direct evidence that the island-based Stegodon reduced in size from the larger-bodied Stegodons during this period.
 Homo floresiensis battling Stegodons and Komodo Dragons
Homo floresiensis battling Stegodons and Komodo DragonsOf course, the specific nature of the Homo floresiensis ancestor awaits future fossil discovery. Studies suggest that its closest affinities may lie with older African species such as the Homo habilis.
Impact of Homo floresiensis on human evolutionThe discovery of Homo floresiensis has radically challenged our pre-conceived notions about the evolution of human species.
If Homo floresiensis is a surviving representative of early Homo, it questions the traditional Out of Africa 1 model for the first colonization of Eurasia by an early form of Homo erectus. If the affinities of Homo floresiensis are with pre-erectus hominins, the logical conclusion is that earlier and more primitive hominids had succeeded in leaving Africa much before than previously estimated.
The discovery of Homo floresiensis demonstrates that we are naive to believe we have discovered the full picture of human evolution. In fact, we may be on the threshold to a major transformation in our understanding of human evolution.
The post The Significance of Homo floresiensis (Our Hobbit-Like Human Ancestor) first appeared on Saurabh Dashora.



